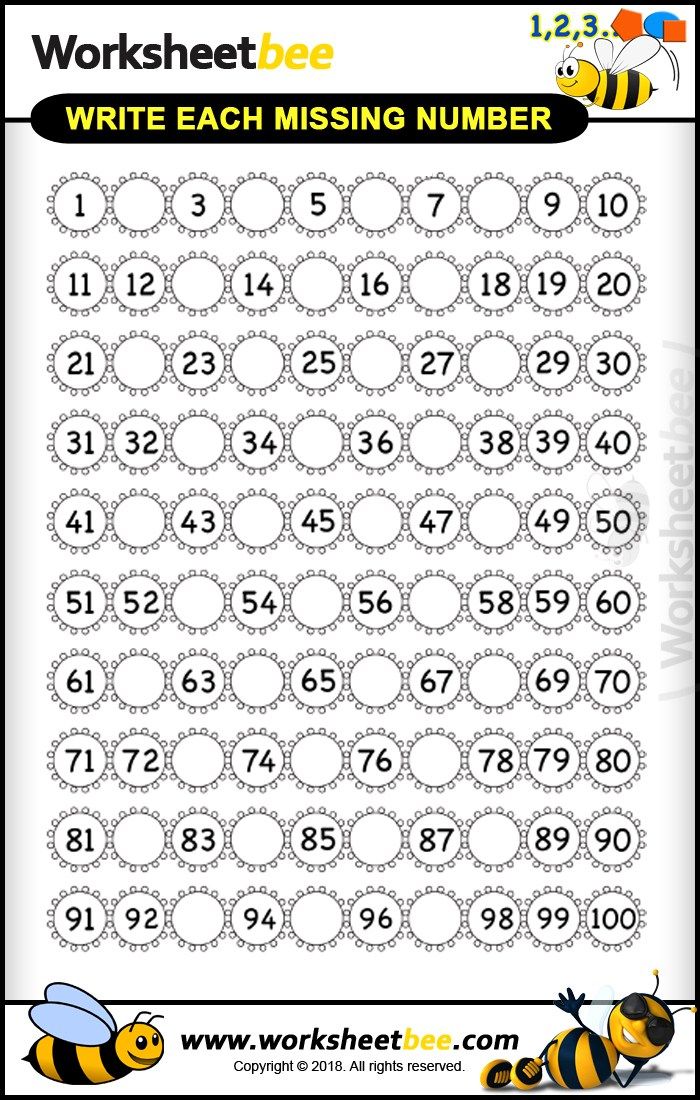
Children learn alphabet
6 Ways To Help Your Child Master Letters
Is your child showing an interest in learning the alphabet? Are you unsure of the best approach to help them master letters? If so, you’ve come to the right place.
We have plenty of tips up our sleeves to help you teach your child the letters of the alphabet and, more importantly, have fun doing it!
Keep reading to learn why gaining an understanding of the alphabet is important in early development; plus, discover our favorite ways to practice this new skill.
The Importance Of Learning The Alphabet
Seeing letters in their written form can be confusing for young learners. Plus, aside from learning the letter names, you also want your child to connect the sound of each letter to its written form, as this is crucial for learning the alphabet in its entirety.
Knowing the sounds associated with each letter in the alphabet helps children build a solid foundation for a variety of tasks — from reading activities to writing activities —and helps develop confident learners.
Children are often eager to learn the alphabet — after all, it’s a developmental rite of passage. For some children, this will come naturally. But, for others, it might not be as straightforward.
Children who are developing their working memory, or those who have weaknesses in their working memory, can find tasks such as learning the alphabet frustrating. While this might be disheartening to see, don’t worry! There are ways to overcome it.
Start working on the alphabet with your child early, around age two or three. If they seem uncomfortable rather than interested or they back off, it’s best not to rush them.
If this is the case, try sticking to simple activities — such as singing alphabet songs, reading alphabet books, and having magnetic letters available to play with — and hold off on more complex activities until they’re ready.
The key to making learning the alphabet a fun activity is to keep things playful and engaging! With that in mind, take a look below at our six favorite ways to help your child learn the alphabet.
6 Ways To Encourage Learning The Alphabet
1) Read Alphabet Books
Reading alphabet books with your child is a great way to expose them to the uppercase and lowercase versions of each letter of the alphabet. The more opportunities your young learner has to identify letters, the better!
Look for alphabet books that have bright, colorful pictures with the letters printed in a large, bold font to make it as simple as possible for your child to memorize.
Having each letter singled out and associated with a particular picture (for example, a picture of an apple for the letter “A”) helps children focus on one letter at a time.
Try reading alphabet books together at bedtime while you snuggle to help your child associate reading and learning with positive feelings. By starting your child’s reading journey in a positive way, you’re setting them up for success.
2) Learn The Letters Of Important Names
Since your child has known their name for some time now, it makes sense that one of the first written words they should learn is their name.
You can start by teaching your child the individual letters in their name. As they become more familiar with the written version of their name and they’re able to match the sounds to the letters, try adding the names of loved ones into the mix.
Family members like Mom, Dad, Grandma, Grandpa, siblings, and pets are a great place to start!
3) Choose A Letter Of The Day
As we mentioned earlier, the thought of memorizing 52 letters that each have an uppercase and lowercase version can feel very overwhelming — not only for your child but also for you.
It can be helpful to pick a “letter of the day” to focus your learner’s attention on. Try focusing first on letters with names similar to their sounds.
For example, the letter “B” and its sound are connected, whereas a letter like “H” is more difficult to grasp because it’s not pronounced the same or similarly to its name.
Once you’ve chosen your letter, see how many times you can spot it as you go about your day. Draw your child’s attention to street signs, words on food packaging, and phrases that come up in their favorite books or television shows.
Draw your child’s attention to street signs, words on food packaging, and phrases that come up in their favorite books or television shows.
Anytime you can incorporate learning the alphabet in a fun way and make a game of it, take advantage of the opportunity.
4) Play With Magnetic Letters
Magnetic letters are a great tool to incorporate into your daily routine when helping your child learn the alphabet.
Simply having a set of magnetic letters on your refrigerator is a good start, as your child will see them regularly. Plus, you can easily have your child practice reciting some of the letters throughout the day whenever you’re in the kitchen making a meal or snack.
For example, if you’re cutting up an apple for your child, you might ask them, “Apple starts with the letter ‘A.’ Can you find an ‘A’ on the refrigerator?”
Another engaging way to incorporate magnetic letters into learning is by hiding them in places your child might not expect and discussing the letter sound when they find it.
Try sneaking a letter into the cutlery drawer, onto their seat at the dinner table, next to their toothbrush — anywhere that they’re likely to come across it. When they notice it, make it a fun game by saying, “How did that sneaky letter ‘B’ get in there?”
Once your child is more familiar with particular letters, you might like to ask them what the letter is, rather than telling them. Try a phrase like, “Wow, that letter must be following you! Which letter is that?”
By repeating simple games like this, you can help your child recognize letters and remember their corresponding sounds.
5) Sing Alphabet Songs
In addition to the classic ABC song, there are many songs available on the HOMER Learn & Grow App as well as YouTube and Spotify that can help your child with learning the alphabet.
If your young learner has a favorite educational television show, try searching for songs featured on the show that incorporate learning letters and letter sounds.
If you can’t find the perfect one, make up your own! You and your child will have a great time using silly rhymes and funny sounds to write an alphabet song. And if they’re involved in the process, it’s going to be a project they’re proud of and can’t wait to show off.
You could even come up with a dance to accompany your new song! This is a great chance to get creative with your child and enjoy some fun movement together as well.
6) Incorporate Your Child’s Favorite Toys
What child doesn’t love playing with their toys? Whether it’s trucks or dolls, incorporating your child’s favorite toys into their learning journey is a clever way to help them understand the alphabet.
For this game, you can use your magnetic letters or create your own by writing each letter on a small piece of paper.
If your child has a collection of toy trucks that they love, stick a letter onto the tray of each truck. As your child plays, you can ask them to move the “B truck” or the “C truck” from one place to another. This is great for practicing letter recognition.
This is great for practicing letter recognition.
You could also incorporate letter sounds into this activity by asking your child to drive the truck with the letter that makes a “buh” or “kuh” sound (for the letters “B” and “C” respectively).
If your child has a set of dolls they play with often, there’s no doubt they each have special names. Try sticking the first letter of each doll’s name onto the toy to help your child recognize and memorize the letters and letter sounds associated with each one.
This is also a good time to introduce the idea of using initials to recognize what belongs to us, as you would with a backpack for school.
Have Fun Learning The Alphabet With HOMER!
Learning the alphabet doesn’t have to be overwhelming or boring! With our fun activities listed here, from using songs and dances to incorporating your child’s favorite toys, you can both enjoy this part of the learning process together.
Remember to keep it up by practicing these activities throughout the day — repetition is a fantastic learning tool to help your child master letters.
To build on your young learner’s alphabet skills, our Explore Letters Kit is the perfect addition to your daily activities. Watch your child’s confidence grow as they develop their literacy skills through play on ABC Island!
Author
5 Ways to Teach the Alphabet
Disclosure: This post contains affiliate links to Amazon. See my disclosure for details.
Teaching the alphabet is foundational for reading and writing. Around the age of 2, children begin showing interest in learning alphabet letters. While some kids learn letters very quickly, others need more repetition and time to learn letters. Today I’m going to share with you some of my favorite ways to teach the alphabet to little ones.
Here’s what a preschooler should know before kindergarten:
- Recite/sing the alphabet
- Identify uppercase letters
- Identify lowercase letters
- Match uppercase letters to lowercase letters
- Identify the sounds each letter makes
- Traces letters
- Write some alphabet letters
Here are my five favorite ways to teach the alphabet to children.
1. Read Alphabet Books
Read all sorts of alphabet books to your children, even starting as babies. The repetition will really help your child learn the alphabet at a young age. When my oldest was born, I was surprised at how many alphabet books we had been given as gifts. We loved reading all of them because they were different from each other. I found that around 18 months both my kids really started enjoyed reading alphabet books. Here are a few of our alphabet books:
Here are some of our favorite alphabet books.
The Three Bears ABCChicka Chicka Boom Boom (Board Book)Eating the AlphabetThe Farm Alphabet BookG is for GoatHarold’s ABC (Purple Crayon Book)I Stink! (Kate and Jim Mcmullan)Bad KittyThe Letters Are Lost!AlphaOops!: The Day Z Went FirstZ Is for Moose (Booklist Editor’s Choice. Books for Youth (Awards))Q Is for Duck: An Alphabet Guessing GameABC T-RexWork: An Occupational ABC
2. Sandpaper Letters
Using sandpaper letters is a great way to introduce letters to children. My favorite ones are Didax Sandpaper Tracing Letters or School Supply Tactile Letters Kit. This is a perfect pre-writing activity because children use their finger to trace the sandpaper letters. I love that the cards tell the child where to start and which direction to go.
My favorite ones are Didax Sandpaper Tracing Letters or School Supply Tactile Letters Kit. This is a perfect pre-writing activity because children use their finger to trace the sandpaper letters. I love that the cards tell the child where to start and which direction to go.
Sandpaper letters are part of the Montessori approach to learning how to read. These letters provide a tactile and visual way to help children learn the alphabet. In the Montessori method, you teach letters to a child in the 3-period lesson.
1st period is introducing the letter (“this is” period). Show your child the letters. Have them trace the sandpaper letters. The best way to teach children alphabet letters is by telling them their phonetic sound. So each time they trace the letter, say the phonetic sound.
2nd period is association (“show me” stage). Ask your child to follow simple directions with the letters. For example, please pick up the /m/ and set it by the window. Continue to do this with each letter several times to reinforce this. If it is too difficult, return to the first period.
Continue to do this with each letter several times to reinforce this. If it is too difficult, return to the first period.
3rd period is recall (“what is this?” period). Only go to this period when they’ve mastered the other two periods. Put a letter in front of the child and say “Can you trace this and tell me what it is?” Continue with the other letters in the same way.
When you use these sandpaper letters, you are teaching them 3 things: the shape of letters, the feel of its shape and how its written, and how you pronounce its sound.
3. Alphabet Puzzles
I think teaching letters with alphabet puzzles are an amazing tool for teaching the alphabet. This is my favorite puzzle, from Melissa and Doug. It’s a beautiful wooden puzzle with neat pictures. This is a great way to practice vocabulary and verbal skills, too.
4. Sensory Activities
While some kids learn letters very quickly, others need more repetition and time to learn letters. I’ve always said that children learn best when they have many multisensory experiences with letters.
I’ve always said that children learn best when they have many multisensory experiences with letters.
I love to incorporate sensory play into learning alphabet letters. When children have meaningful activities with repeated exposure, they start to pick up on letter names. One way is this alphabet ice excavation activity.
You could also make a colorful sensory bin!
Or practice writing letters in the sand, like this sensory writing tray.
5. Alphabet Printables
I have quite a few alphabet printables on my blog, but here is a set that is easy and fun for preschoolers. You will need Do a Dot Markers or dot stickers to fill in the circles.
I love pulling printables out for a quick and easy activity. I’m always advocating for hands-on learning, but sometimes it’s nice to do a few paper activities. Using Do a Dot markers or dot stickers is great for hand-eye coordination and fine motor skills.
If you’d like to download this printable, just click the button below.
How to learn the alphabet with a child. Learning letters together
Letters are all around us. Signs, announcements, books and magazines - all this the child sees from a very young age. But it doesn’t immediately become clear that these “squiggles” are not just incomprehensible meaningless icons, but a way to convey information in the form of text. Therefore, with the study of the alphabet, a completely new world opens up for the baby, in which letters are folded into syllables, and syllables into words that can be read and later written. In our article, we will tell you when to start learning the alphabet, how to make the process interesting for a child, and what methods are best for children of different ages. nine0003
Why learn the alphabet?
It seems that the answer to this question is quite obvious - that the child can read. However, it's worth digging a little deeper. Often, parents do not fully realize what caused their desire for the child to quickly master the letters. If the kid is already 5-6 years old, and the first grade is just around the corner, then the desire to learn the basics so that further study is easier, understandable and logical. Or maybe your child is only three years old, but you want him to show off his knowledge at a family evening? Or do all the acquaintances vying with each other say that their children have not only learned the alphabet, but also read freely? Give yourself an honest answer to these questions, and consider whether it is necessary to postpone training until a more appropriate moment. nine0003
Often, parents do not fully realize what caused their desire for the child to quickly master the letters. If the kid is already 5-6 years old, and the first grade is just around the corner, then the desire to learn the basics so that further study is easier, understandable and logical. Or maybe your child is only three years old, but you want him to show off his knowledge at a family evening? Or do all the acquaintances vying with each other say that their children have not only learned the alphabet, but also read freely? Give yourself an honest answer to these questions, and consider whether it is necessary to postpone training until a more appropriate moment. nine0003
The most important thing is whether your child is ready. Curiosity, interest in new things, the ability to memorize previously unknown information are all signs that you can start learning the alphabet. But you should always remember that there is no point in teaching against the child’s desire, all classes should be held in an unobtrusive playful way. Questions “how to read?”, “What kind of letter?” Are pouring in on you, the baby is interested in not only pictures in books, but also captions to them, or are you going to school soon? Well, then feel free to start your acquaintance with the alphabet. nine0003
Questions “how to read?”, “What kind of letter?” Are pouring in on you, the baby is interested in not only pictures in books, but also captions to them, or are you going to school soon? Well, then feel free to start your acquaintance with the alphabet. nine0003
Basic tips for learning the alphabet with a child
The alphabet is not just a certain sequence of letters. This is the foundation from which the child's learning to read begins. Therefore, it is important to understand that simply learning the alphabet as a rhyme or a counting rhyme is possible, but practically useless if there is no practical application of the information received. If you do not start trying to teach your child to read immediately, but after a long break, there is a high probability that your baby will simply forget the letters by this point, and you will have to start all over again. nine0003
There are a few general rules to follow when you start learning the alphabet with children:
1.
 Learn the sounds, not the letters
Learn the sounds, not the letters It's easy for us adults to figure out what the name of the letter is and what sound it is means may not match. For a small child, on the contrary, such a concept may be too complicated. Do not confuse the baby, he will eventually learn that the letters are called “be”, “el” or even “and short”, better demonstrate what sounds are indicated by the corresponding signs - “b”, “l”, “y”, give examples of words with these sounds. In this way, the child, with less effort, will be able to understand how syllables are read, and later whole words. nine0003
2. Do not learn the alphabet in order
Remembering a clear sequence is, of course, useful for the development of a child's memory, but it does not make it obvious to him what he actually learned and why. If, however, the alphabet is disassembled gradually, according to a clear and logical system, without overloading the child's perception excessively, there will be much more benefit, since knowledge will not be superficial, but based on a deeper understanding of the structure of the language.
3. Do not mix vowels and consonants
Learning letters mixed up is no less a mistake than memorizing the alphabet strictly in order. Vowels and consonants must be studied separately, otherwise the child will be completely confused. Always remember that things that seem clear and simple to us, small children learn for the first time, so even the main sign by which sounds are divided (vowel-consonant) is not immediately comprehended. The situation when the studied letters do not have any common feature is confusing and slows down the assimilation of the material.
4. Vowels first
There are only 10 vowels in the Russian alphabet, so the child will have to remember a little at first. In addition, vowels require only a long “singing” and slight changes in the articulation of the lips, neither the tongue nor the teeth need to be connected, so it will be easier for the baby to understand how the written sign correlates with the sound being pronounced. When all the vowels are firmly learned, it will be possible to add consonants.
5. Don't force learning
Of course, you really want your child to learn all the letters and start reading as soon as possible, but you still shouldn't rush. Learn one or two letters, repeat what you have learned more often, do not move on to a new one without waiting for the consolidation of what has already been studied. Start with very simple and clear things. Show the young student the letter "A", tell how it is pronounced, what it looks like, what words begin with it. Fold it together with the baby from sticks, draw or mold it from plasticine - tactile sensations will help the child better remember the image of the letter and associate it with sound. Apply theory to practice, for example, ask while walking to look for the letter "A" on signs, in advertisements, and so on. Only when the child has learned the letter and the corresponding sound, proceed to the next, all the same one at a time, methodically and slowly. nine0003
Age-appropriate alphabet learning
3-4 years old
If you think your child is ready to learn letters at 3 years old, here are some tips and tricks to help you get great results.
First of all, in no case do not force or coerce the child into classes, they should take place exclusively at the request of the child, in a fun way, and end as soon as you see signs of fatigue and weakening of concentration. The optimal lesson time for a three-year-old is 5-7 minutes. nine0003
Do not set a goal to learn the entire alphabet in a short time, it is at best pointless, and in some cases it can even be harmful - up to a certain point the child's brain may simply not be ready for this or that knowledge. Do not try to outwit nature, at three years old your task is more to interest, captivate the child, show him the basics.
Do not overload your child with a lot of information - let your “lessons” take place no more than twice a week, and take the rest of the time to consolidate and repeat the studied material. At the same time, the regularity of classes is very important, conducting them from time to time is not the best idea, the child will get confused and forget what you went through with him. nine0003
nine0003
Start with vowels. Move on to consonants only when you are sure that the child has firmly learned all 10 vowels and brought the skill to automatism. Vowels are best taught in pairs: A - Z, O - E, U - Yu, E - E, S - I. So it will be easier for the baby to remember. Later, this will also help with the assimilation of the principle of hardness-softness of consonants.
Use books with bright, large pictures. Closer to the age of four, the child will also be interested in blocks with letters, coloring books and stickers, posters with and without voice acting; but be careful with the posters - remember that we need to learn the sounds, not the names of the letters, so look for posters that pronounce exactly the sounds. Magnetic letters will also help - they can be placed on a magnetic board or simply on the refrigerator. You can learn rhymes and songs with the mention of the sounds that you are studying, play with letters cut out of paper. nine0003
Let the child represent the letter in different ways - by drawing, modeling with plasticine, folding with sticks or drawing lines in the sand or grits. Such activities are also useful for fine motor skills, and this is a very important skill for the baby, which affects, among other things, the development of speech.
Such activities are also useful for fine motor skills, and this is a very important skill for the baby, which affects, among other things, the development of speech.
There are more consonants in the Russian language, so it will take a longer time to study them, and if you consider that most consonants have both hard and soft variants, the task becomes even more complicated. But with the right approach, there should not be any particular difficulties. If the child has already mastered all the vowels and understands the difference between, for example, “A” and “I”, then it will not be difficult for him with your help to figure out how “ma” and “me” differ. You can make a table where such pairs of syllables will be shown clearly. The main thing is to always clearly pronounce the sound yourself and achieve the same pronunciation in the child. Correct articulation is the key to both good diction and correct reading in the future. nine0003
5-6 years old
For all our commitment to early development, many experts agree that the optimal age for learning the alphabet is 5-6 years old. The child will soon go to school, which means that his brain is already quite ready to memorize all the letters and gradually learn to read. At this age, it is especially important that your preschooler speaks clearly and correctly, so pay maximum attention to his speech, whether all sounds are pronounced without problems, whether some of them need to be corrected independently or with the help of a speech therapist. nine0003
The child will soon go to school, which means that his brain is already quite ready to memorize all the letters and gradually learn to read. At this age, it is especially important that your preschooler speaks clearly and correctly, so pay maximum attention to his speech, whether all sounds are pronounced without problems, whether some of them need to be corrected independently or with the help of a speech therapist. nine0003
If at three years the emphasis is on the play component of classes, then by the age of 5-6 it can be slightly shifted towards the child's consciousness. Tell us about how great it will be to read books yourself, how knowledge of the alphabet will come in handy at school. Keep the elements of the game, use the same methods that are suitable for four-year-olds, but increase the lesson time, introduce more printed materials. You will need special recipes for preschoolers, books and manuals with creative tasks, various sets of cards. nine0003
Introduce your child to syllables. Use single letter flashcards to show how a syllable is built - for example, say that a consonant and a vowel run or are attracted to each other and demonstrate their convergence by saying the syllable at the same time. Later, use cards with a ready-made printed or hand-drawn syllable in the lessons. Do not forget about the regularity of classes and the constant repetition of the material covered.
Use single letter flashcards to show how a syllable is built - for example, say that a consonant and a vowel run or are attracted to each other and demonstrate their convergence by saying the syllable at the same time. Later, use cards with a ready-made printed or hand-drawn syllable in the lessons. Do not forget about the regularity of classes and the constant repetition of the material covered.
Primer learning
By the age of six, a good primer will be clear and easy to learn. For example, the “Primer” by N. Zhukova is considered one of the best, although for younger children it may seem boring - it focuses on learning without providing entertainment materials. But in this primer much attention is paid to speech therapy moments. nine0003
“My primer: a book for teaching preschoolers to read” N.V. Nishchevoi - a manual also with a speech therapy bias, but the author adheres to his own methodology for studying letters and sounds. The path from simple sounds to complex ones will help the child develop both reading skills and good articulation.
In order for a child to develop a love for reading from a very early age, VV Shakirova's Journey to the Sound Book is a good choice. There is more entertainment material here that will interest and captivate the child. In addition, Shakirova paid a lot of attention to the development of motivation, and this will definitely come in handy in the future, in the process of further study. nine0003
Games for learning the alphabet
In this section, we will give examples of games that will make learning more interesting and at the same time more effective. Entertaining elements will not only diversify classes, but also provide a fairly wide field for applying the acquired knowledge in practice.
"Find the letter" . On a sheet of paper, arrange different letters in a random order. Let them be bright and large. You name the letter, and the child must find it and show it. A mobile version of this game is to hang sheets with large letters around the room, let the child find and tear off the desired sheet. nine0003
nine0003
Memo . Prepare a set of cards, each letter must be represented in duplicate to get a certain number of pairs. Cards are laid out in several rows face down. Have the child turn over one card and name the sound that the letter on it represents. Then you need to find a pair for her by opening other cards. It didn’t work the first time - the cards are turned back face down and you have to look again. A pair was found - the player takes both cards for himself, and so on until the moment when all the cards run out. nine0003
“What letter does it begin with?” . Arrange several animals in a row - these can be drawings on paper, cards or small toys. Select the letters with which their names begin, and give them mixed to the child. The task is to correlate which letter refers to whom, and put it next to the desired animal.
Collect the letter . Draw a letter the size of the entire sheet of paper. Cut into several parts, let the kid assemble the resulting puzzle and name which letter is depicted on it.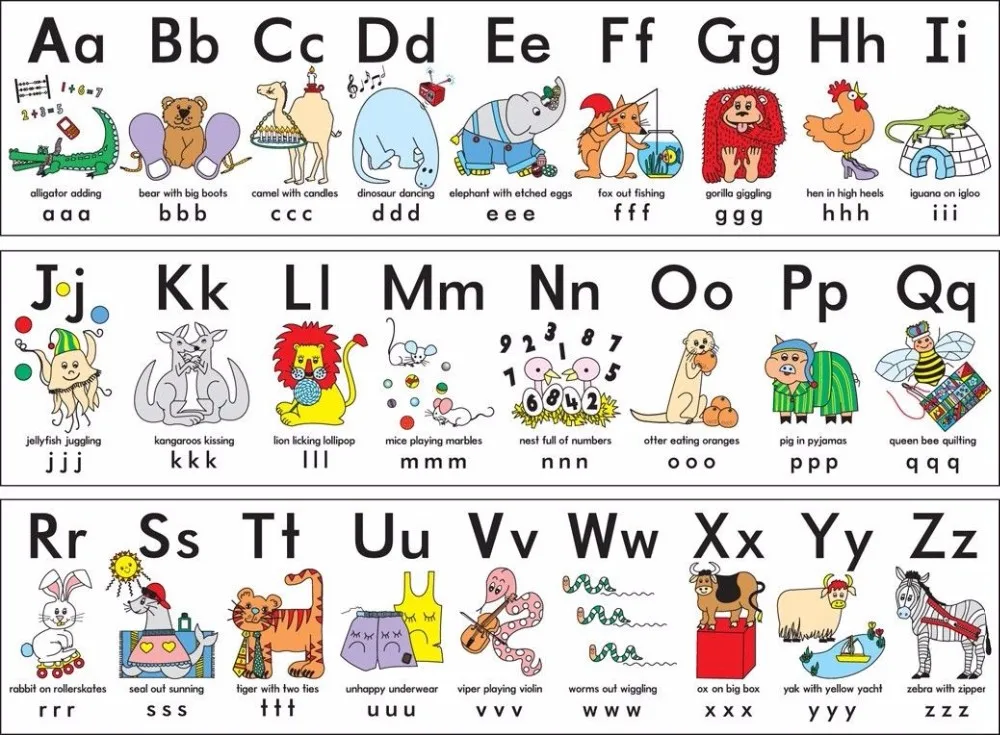 nine0003
nine0003
Dice game . Surely you have cubes with letters, and if not, they are easy to make yourself out of paper. You roll a die and see which letter comes up on top. The child needs to remember an animal (or even an object!), The name of which begins with this letter and show it, for example, if the letter “B” fell out, then you can depict a crow - wave your hands like wings and croak.
Edible Letters . The alphabet is not only useful, but also delicious! Your child will have even more fun learning if he can not only name the letter, but also eat it. You can buy ready-made cookies in the form of letters, or bake them yourself, so the baby will even be more interesting, especially if you decorate the finished cookies together. You can also cut out letters from fruits and vegetables. nine0003
No matter how your activities progress, be patient with your child, don't demand too much from him or scold him if something doesn't work out. If you follow the basic principles and recommendations, creatively approach the lessons and give the baby positive emotions, your child will definitely learn the alphabet easily and with pleasure.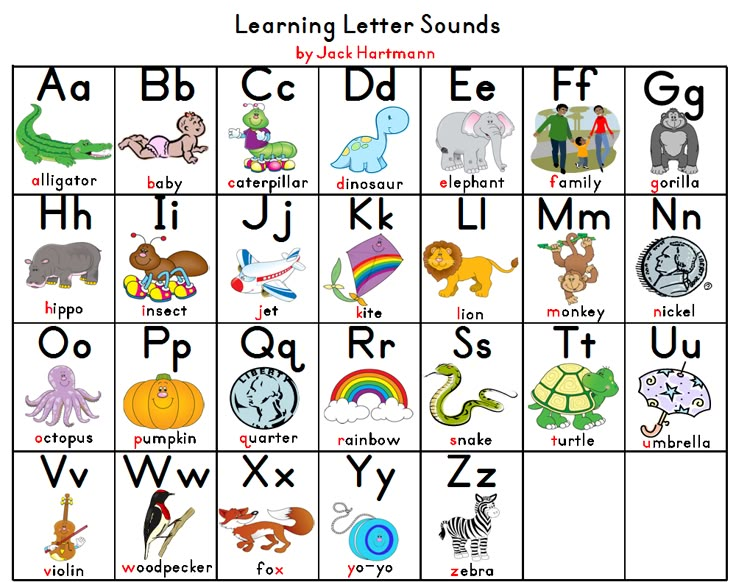
Learning the alphabet: methods, exercises and games for children
The alphabet is the foundation of reading. Therefore, before you start reading and writing, teach your children the letters. nine0003
Children can start learning to read at an early age. Parents and teachers need to teach their child how to pronounce sounds correctly in their native language. These are important prerequisites for learning letters and learning to read successfully. The educational process of preschool children is based on visual, acoustic and tactile exercises. The use of various channels of perception in the educational process increases its effectiveness and stimulates long-term memorization of letters.
Learning the alphabet: introducing the child to the alphabet. nine0005
To master reading, a child must learn and recognize not only the graphic form of letters, but also be able to match them with their corresponding sounds. This means that the child must be able to write letters and pronounce them. When the child learns to correctly pronounce all the sounds in his native language and distinguish letters by visual form, go directly to reading. As a rule, at the age of 5-6 years, most children no longer experience difficulties in this.
When the child learns to correctly pronounce all the sounds in his native language and distinguish letters by visual form, go directly to reading. As a rule, at the age of 5-6 years, most children no longer experience difficulties in this.
See also: Reading and bilingualism. Bilingualism in children
From the age of 5 to 6, children begin to understand that there is a lot of information encoded in language using letters. Thus, they are interested in learning to read by then, as they are naturally curious.
Of course, babies can learn and memorize individual letters quite early. However, their interest, mostly spontaneous, is directed to individual words and letters. Here it is important to gently motivate the child by encouraging him to learn through games and a comfortable environment. However, too much pressure can lead to stress, causing little ones to lose any motivation to learn letters. nine0003
Alphabet learning games
The first rule of learning the alphabet: learn the letters one by one!
Don't forget, each letter is made up of visually similar elements.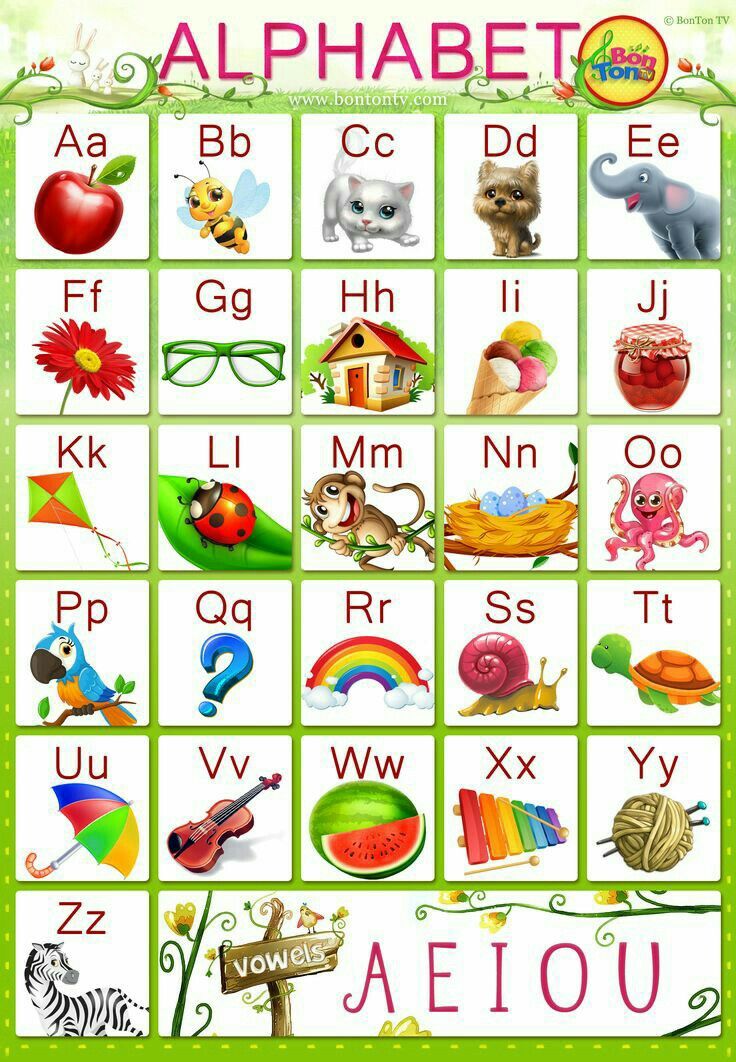 If you try to teach a child several letters at a time, he may become confused. Learn the letters one by one. One lesson - one letter.
If you try to teach a child several letters at a time, he may become confused. Learn the letters one by one. One lesson - one letter.
Second rule of learning the alphabet: take your time!
Give your child enough time for each letter. Plan 1-2 lessons for each new letter. Organize the lesson in a form that is interesting for the child with the help of games. nine0003
Tactile method: from studying letters to reading
The child sees something abstract in a letter. Chains of associations will help in learning letters. Associating each letter with something specific or familiar helps the child fix it in his memory.
1. Make a letter out of plasticine
Memorize what a letter looks like and develop fine motor skills.
We will need: plasticine (should be elastic), modeling board and a disposable plastic knife. nine0003
Together with your child, roll out 8 approximately identical sausages from plasticine. 2 - divide in half, 2 - divide into 3 parts. From the remaining 4, make rings by blinding their edges and cut 2 of them in half, creating semicircles. Thus, you should get a set of elements to compose any letters of the alphabet. Show the child a couple of examples and ask them to repeat, collecting previously passed letters.
2 - divide in half, 2 - divide into 3 parts. From the remaining 4, make rings by blinding their edges and cut 2 of them in half, creating semicircles. Thus, you should get a set of elements to compose any letters of the alphabet. Show the child a couple of examples and ask them to repeat, collecting previously passed letters.
2. Magic wands
Let's memorize letters, learn how to make letters from sticks, learn how to transform letters. nine0003
We need: a set of counting sticks. If not, you can replace with matches or toothpicks.
The easiest way is to lay out letters from sticks according to a pattern or without a pattern (according to the idea). When the child learns to lay out all the letters, you can complicate the task by laying out objects familiar to the child from them, and then ask them to change them, for example, make a figure resembling a door out of sticks, and then ask the child to remove 2 sticks to make the letter P.
3.
 Tactile letters
Tactile letters Memorize letters and develop fine motor skills
We will need: sandpaper, velvet paper, scissors.
Cut out letters from sandpaper or velvet paper. The child will have to close his eyes to identify the letter by touch.
4. Draw a letter on the semolina
Memorize letters, develop fine motor skills
We will need: a bright dish tray, semolina
Pour sand or semolina in a thin layer on the tray. Set an example for your child, show how to write letters on the croup with a finger or a stick. Ask him to write next to the letter, the same as you wrote, to write a letter more or less than yours, to add an unfinished letter, or to erase the extra detail of the "wrong" letter. Children will like this game, just shake the tray a little, and the mistake or inaccuracy made disappears! nine0003
5. Mirror letter
Memorize letters and train attention
We will need: cardboard, pencil and scissors
Prepare identical cards cards, 2 pieces for each letter. Write 1 letter on each card. Write the letters in mirror image and correctly. Lay out cards with the same letter in front of the child and offer to choose the correct one.
Write 1 letter on each card. Write the letters in mirror image and correctly. Lay out cards with the same letter in front of the child and offer to choose the correct one.
6. Memory test game
Train memory
We will need: scissors, cardboard and a pencil
The game "Memory Test" will challenge even older children. Write each capital letter on one card and lowercase letter on the other card. Turn over all the cards and place them on the table. Ask your child to match uppercase and lowercase letters. You can complicate and add a dictionary element. Have the children match the letter of the alphabet with the picture that starts with that letter.
7. Bean bag
Memory training
We will need: a bag of beans or other loose material, a tablecloth or a large piece of paper.
If you want to warm up a bit while you study the letters, play a game of Beanbag. Write the alphabet randomly on a large piece of paper.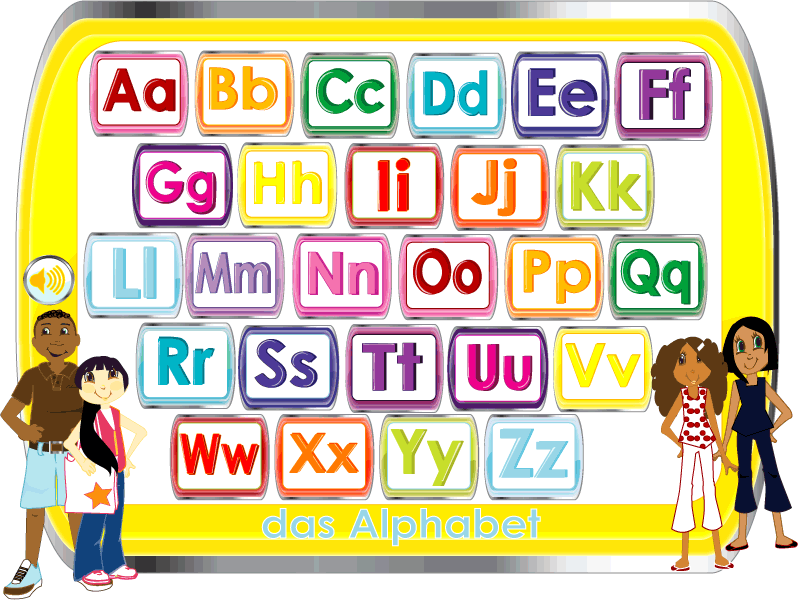 Give the children a bean bag and ask them to put it on paper. The child must name a word that begins with the letter on which the bag fell. If a student is stuck, help him.
Give the children a bean bag and ask them to put it on paper. The child must name a word that begins with the letter on which the bag fell. If a student is stuck, help him.
Ask the child to check the chosen letter with letters from the alphabet. Be sure to ask the name of the letter. The exercise will help children learn to distinguish visually similar letters and avoid mistakes when writing them in the future. nine0003
Drawing, coloring, cutting letters out of paper and gluing them together develop fine motor skills in children. Self-made flash cards with letters facilitate memory and associative thinking, creating the basis for tactile games. You can make postcards alone or with your child. Letters can be cut out of paper of various textures and pasted onto cards made of cardboard or paper. Then you can ask the child to pick up letters from 2-3 cards with their eyes closed.
Literacy begins with learning the letters of the alphabet. Combine different perceptual styles.