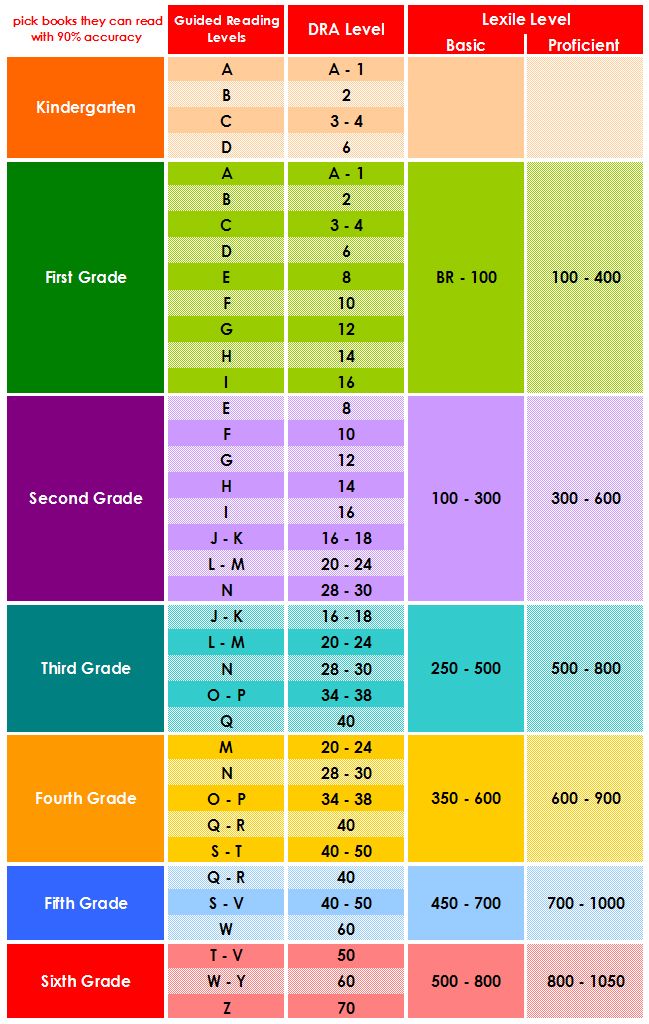
Dra guided reading level
Leveling Chart | Scholastic Guided Reading Program for the Classroom
Use the grid below to shop by Guided Reading, Developmental Reading Assessment (DRA), and Lexile® Levels. This chart includes Lexile level recommendations and may also be used as a general leveling guide.
Click on links to shop the Teacher Store!
| Grade | Scholastic Guided Reading Level | DRA Level | Lexile® Levels |
|---|
| Grade | Scholastic Guided Reading Level | DRA Level | Lexile® Levels | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kindergarten |
| Beginning Reader | |||||||||||||||||||
| 1 |
|
| 190L-530L | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2 |
|
| 420L-650L | ||||||||||||||||||
| 3 |
|
| 520L-820L | ||||||||||||||||||
| 4 |
|
| 740L-940L | ||||||||||||||||||
| 5 |
|
| 830L-1010L | ||||||||||||||||||
| 6 |
|
| 925L–1070L |
Back to Top
How to Determine the Reading Level of a Book
This content contains affiliate links. When you buy through these links, we may earn an affiliate commission.
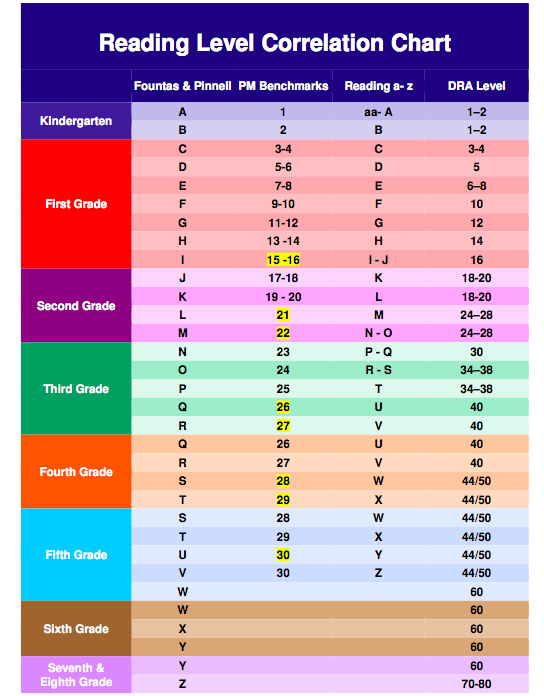
Fountas and Pinnell, Lexile Level, Primer, Pre-primer, Beginning Reader are all terms you may have heard if you have a young reader in your house. Seriously, what does it all mean? Is there actually a way how to determine the reading level of a book? If your child can read The Cat in Hat, which is a level J in Guided Reading, can she independently tackle Diary of a Worm, which has a Lexile Level of 510L or is she ready for Keena Ford and the Second Grade Mix-Up, even though that one has a DRA of 30?
Through this post, I am going to attempt to elucidate and explain reading levels. So scroll through to find the system that your child’s teacher uses or pour yourself a large cup of coffee and sift through all of the various ways educators, librarians, and book publishers level and categorize books for young readers.
Reading Levels Are Like Starbucks Sizes
I admit, I don’t visit Starbucks unless I have a gift card.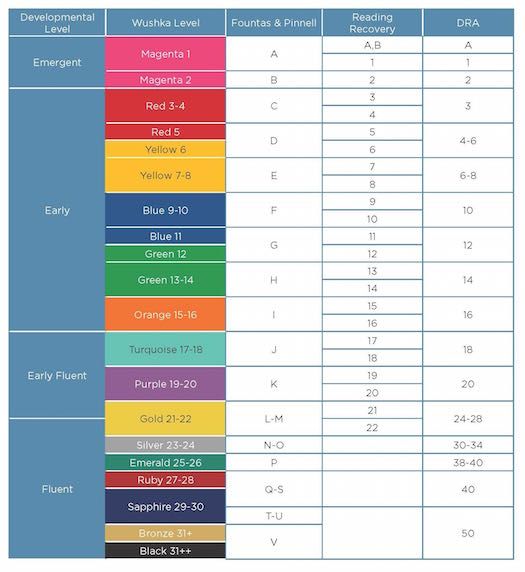 I am also that person who goes to Starbucks and still tries to order a large iced tea. The barista calmly asks if I would like a venti or a trenta and then explains that I need to choose between Passion Tango, Matcha Green, or Guava White Tea. Then comes the question of sweetened, unsweetened, or added lemonade.
I am also that person who goes to Starbucks and still tries to order a large iced tea. The barista calmly asks if I would like a venti or a trenta and then explains that I need to choose between Passion Tango, Matcha Green, or Guava White Tea. Then comes the question of sweetened, unsweetened, or added lemonade.
For the young reader, finding a book that can be read independently can be as tricky as remembering all of the variables in a Starbucks order. Little readers who are not familiar with reading levels or taught to find a “good fit book” often go for books that are too easy and boring, too difficult and frustrating, or, like my kindergarten son, books that have too many unreadable Star Wars planet names like Kashyyyk. If a child knows her reading level, she can find books that contain sight words she knows, plot lines that are not too advanced, and vocabulary that is manageable.
Explain the Levels, Please
There are many different ways that books are leveled. Here are the three most popular methods for how to determine the reading level of a book.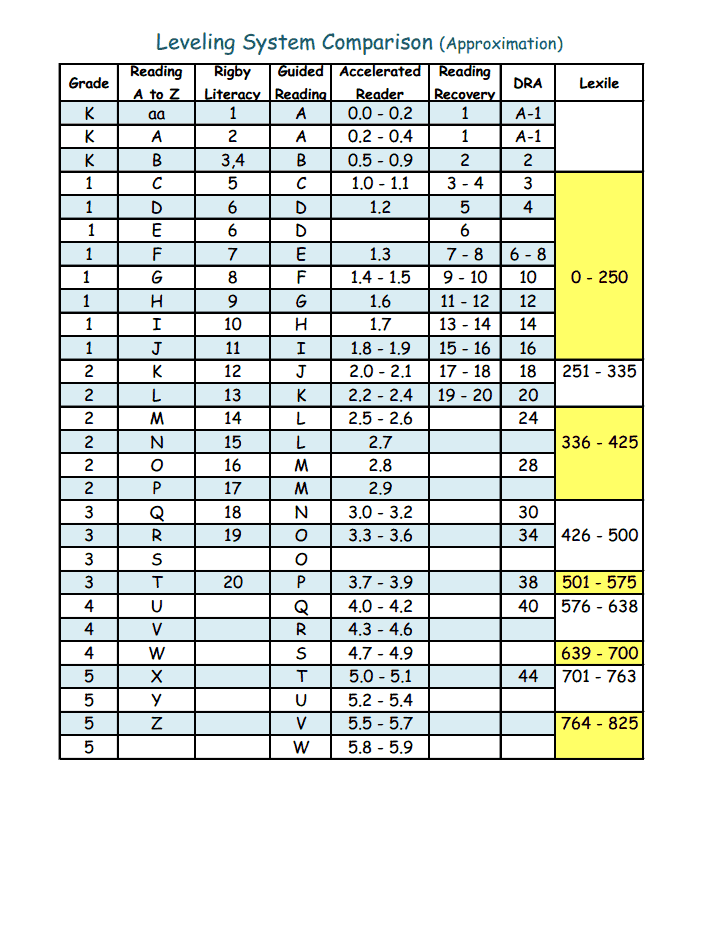
Developmental
Children become readers by moving through different developmental reading stages. These stages range from the emergent pre-reader to the expert fluent reader. Typically, the emergent pre-reader is between six months and six years of age, while the expert fluent reader is 16 years and older. The developmental categories are broader categories than many of the other leveling systems.
Letter Levels
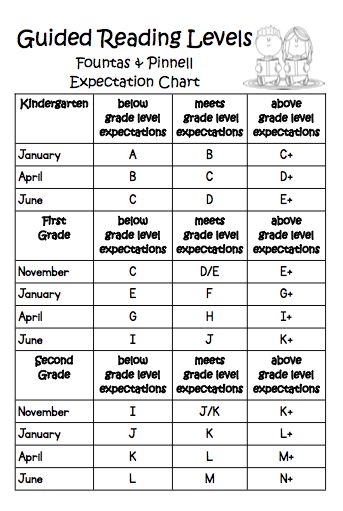
When I taught first and second grade, I found letter levels to be the most kid friendly way to organize a classroom library. If your child’s school levels books using Fountas and Pinnell, Reading A-Z, Scholastic Books, or Guided Reading Levels, then books will be leveled using a letter system. While it would be nice, these leveling systems do not always correlate. A book that is a Reading A-Z Level P, is not always a Level P using the Guided Reading Levels.
Number Levels
Books can be leveled through such systems as Lexile Numbers, The Direct Reading Assessment (DRA), and Reading Recovery.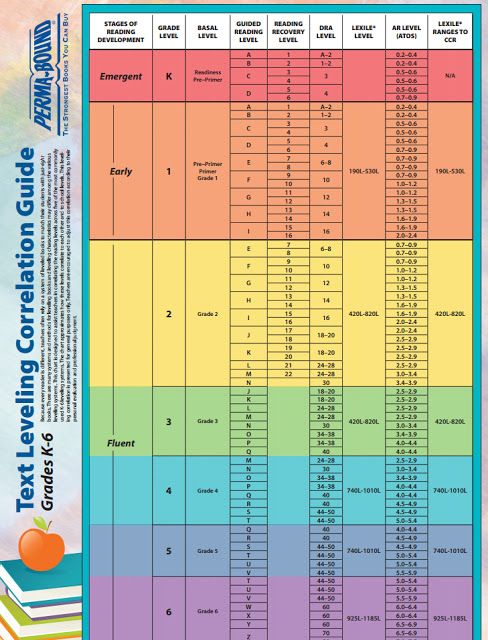 These systems measure texts by complexity and a reader’s skill level and then assign a number.
These systems measure texts by complexity and a reader’s skill level and then assign a number.
I Have My Child’s Reading Level, Now What?
Throughout the school year, your child’s teacher will probably perform reading inventories or assessments with your child. These will determine your child’s reading level.
If you homeschool or your child’s school does not use leveled reading, then use a simple test called the “five finger test” to roughly determine your child’s reading level. Have your child choose a book and open to the second page. Ask your little one to read the text out loud. If your child struggles with independently reading five or more words on that page, the book is too difficult and is not a good fit. You should also ask some comprehension questions to make sure that your young reader understands what she is reading. When a book passes the five finger test, use one of the links below to determine that book’s reading level.
Once you have the reading level, take a look at these five helpful websites, apps, and charts that will help you and your child find or level the perfect book:
- Book Wizard : Type in the title of a book to retrieve the Guided Reading Level and grade level.
- Lexile Find-a-Book :Visit this site to find the Lexile Number for a specific book or to generate a list of books with a particular Lexile Number.
- Reading A-Z Level Correlation Chart : This is the best conversion chart out there for reading levels.
- Reading Levels Explained : Check out this very clean and user friendly site if you are still feeling overwhelmed by all of the reading level systems.
- Literacy Leveler app : Download this app and then use it to scan a book’s ISBN to see its Lexile, DRA, and GRL.
Levels Should be Helpful, Not Stressful
Reading levels should not feel restrictive. They should be used as helpful tools and not as a draconian system that kills the love of reading. Encourage your child to read books on her level, but don’t be upset if she chooses to reread an old favorite or picks up a nonfiction book that has some advanced vocabulary. Imagine how horrible it would be if adults had to always adhere to a reading level.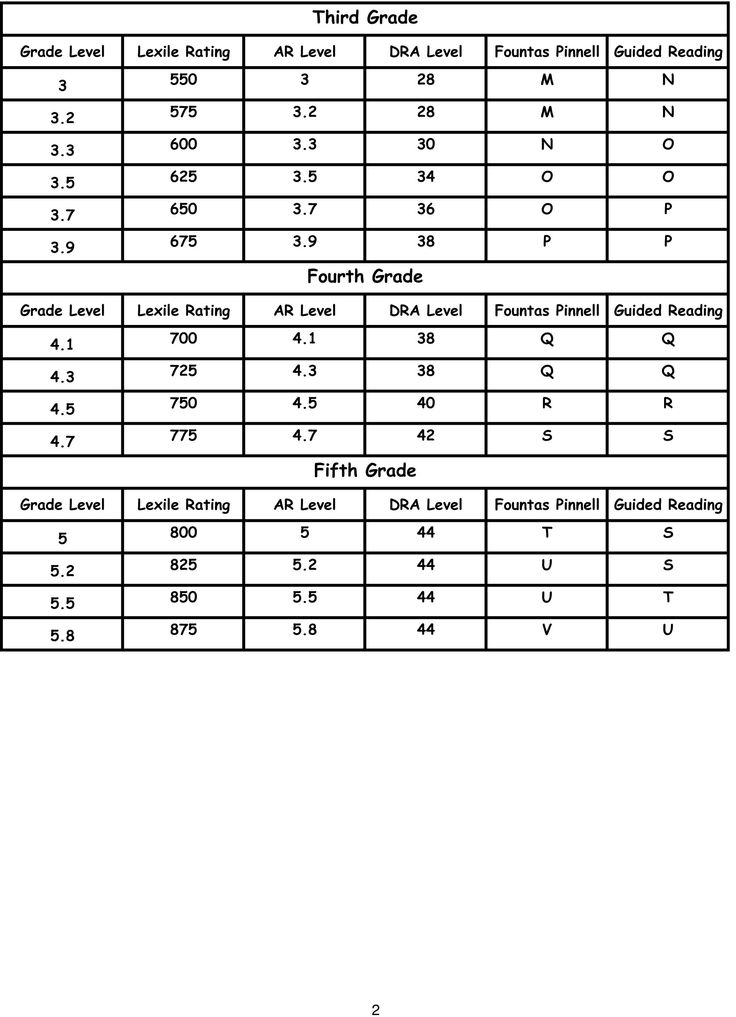 I am well aware of the fact that some of my beach reads are probably a fourth grade reading level, with a Guided Reading Level of Q, 820L, and DRA of 40. I may not always be challenged as a reader, but it is still fun to sip my trenta Passion Tango unsweetened iced tea and enjoy a book simply for the fun of reading.
I am well aware of the fact that some of my beach reads are probably a fourth grade reading level, with a Guided Reading Level of Q, 820L, and DRA of 40. I may not always be challenged as a reader, but it is still fun to sip my trenta Passion Tango unsweetened iced tea and enjoy a book simply for the fun of reading.
Need some books to practice leveling? Help yourself to 50 Must-Read Books for Beginning Readers, 20 Must-Read Books for First Graders and Second Graders, The Best Chapter Books for Kids: Engaging with Words, and 70 Must-Read Books for 3rd Graders.
Lock management in transaction
The mechanism for managing data locks in a transaction allows locking mutable data not by means of the database management system used, but by means of the platform. This data lock management is performed not in terms of DBMS data, but in terms of the subject area. Thanks to this, locks are applied “more precisely” and the parallelism of the work of users increases.
1C:Enterprise 8 configuration can work in one of three modes of lock management in a transaction: nine0003
- automatic;
- managed - standard mode for new configurations;
- automatic and controlled.
The automatic data lock management mode uses the repeatable read and serializable transaction isolation levels provided by the database management system. These transaction isolation levels ensure consistent and consistent reading of data, and no additional lock management is required from the developer. nine0003
Managed mode allows you to increase the parallelism of the work of users in the client-server mode of operation by using a lower level of database transaction isolation (Read Committed). When writing data in a transaction, 1C:Enterprise language objects automatically lock the required data. The developer needs to manage data locks in cases where business logic requires a consistent and consistent reading of data in a transaction.
Automatic and managed mode allows you to use the ability to manage locks in a transaction only for some configuration objects. This mode can be used to optimize the concurrency of user work with individual application objects (for example, with several of the most intensively used documents) or to gradually transfer large configurations to the mode of managing locks in a transaction.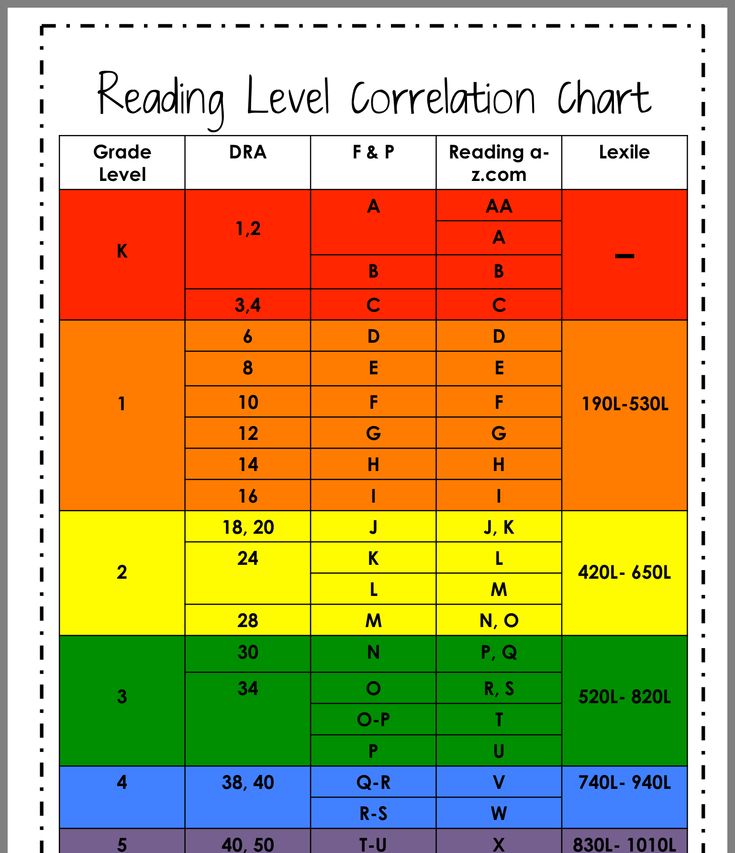 nine0003
nine0003
In summary, the differences between working in the automatic blocking mode and in the managed blocking mode are shown in the following table:
Most often, the need to manage data locks in a transaction arises in the process of posting documents, when you need to read and then write changed data to the same tables. For example, if balance control is performed when posting a document.
Especially for this, the record sets of accumulation registers and accounting registers have the LockForChange property.
If you need to control the balances, and then record movements in the same register, then this property must be set for the recordset of this register in the Movements property.
The effect of this property is the same as if the developer had independently set (written in the code) the necessary 1C:Enterprise 8 managed locks. The platform will set the required managed lock automatically when writing this set of records.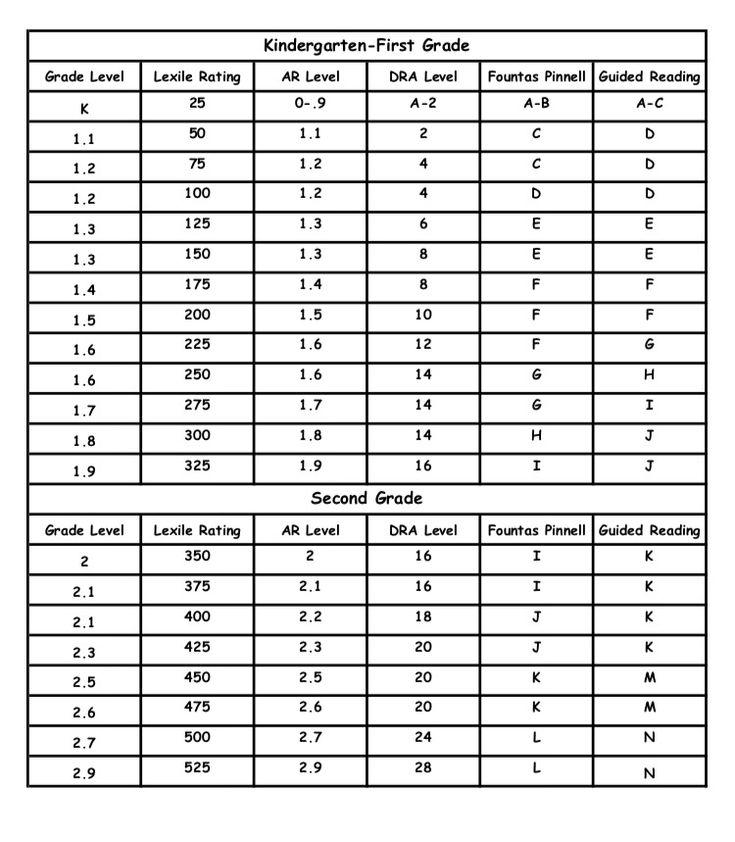 As a result, other managed transactions using a similar lock will not be able to start reading this register until the current transaction ends. nine0003
As a result, other managed transactions using a similar lock will not be able to start reading this register until the current transaction ends. nine0003
Below is an example of "manual" control of data locks when reading the data of the accumulation register Accounting for Items in the processing of posting the Invoice document. In this example, managed locks are created and set completely using the 1C:Enterprise language only.
SmartE is a new series of entry-level industrial switches from EtherWAN. STAT#3/21
Author: Sergey Vorobyov
nine0044 This article provides a brief overview of EtherWAN's new line of SmartE managed industrial Ethernet switches, which offer a low price point and a balanced feature set to meet many basic needs.
The article was published in the journal MODERN AUTOMATION TECHNOLOGIES №3/2021
Over the past 10 years, industrial Ethernet switches have become a separate class of devices capable of solving a wide range of tasks for building reliable, fault-tolerant and multi-service data transmission networks.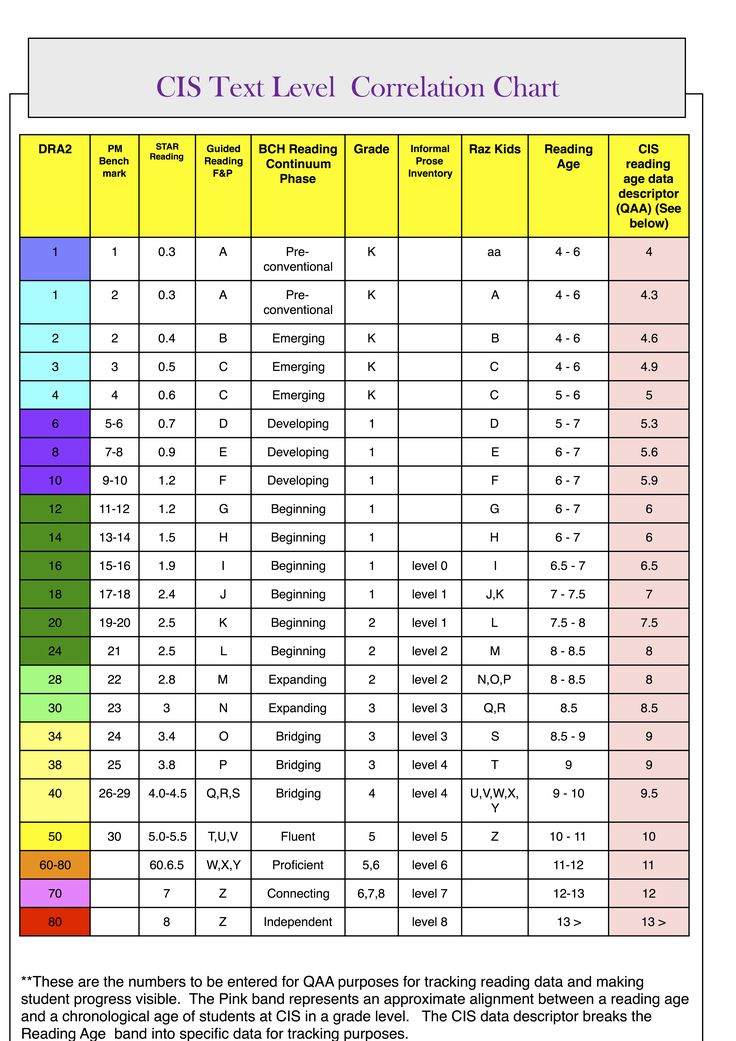 Every year, the industrial switch market is becoming more and more cumbersome, new players, new equipment appear, and manufacturers are constantly adding new functionality. nine0048
Every year, the industrial switch market is becoming more and more cumbersome, new players, new equipment appear, and manufacturers are constantly adding new functionality. nine0048
As a result, a modern industrial switch is a complex device equipped with a large set of functions. Indeed, if we take a closer look at the functionality of an industrial managed Ethernet switch in the middle price segment, then you can find a very large number of features in it: support for several redundancy protocols, security, work with multicast traffic, etc.
However, when solving problems of building an industrial network, such examples of application are very rare when most of the functions are in demand. And this is due to many factors, ranging from the scope of application to the tasks that need to be solved. nine0003
Speaking of switches, you should always pay attention to the functionality, which very often determines the final price of the device. You have to pay for functionality, but it is not always needed and in full demand.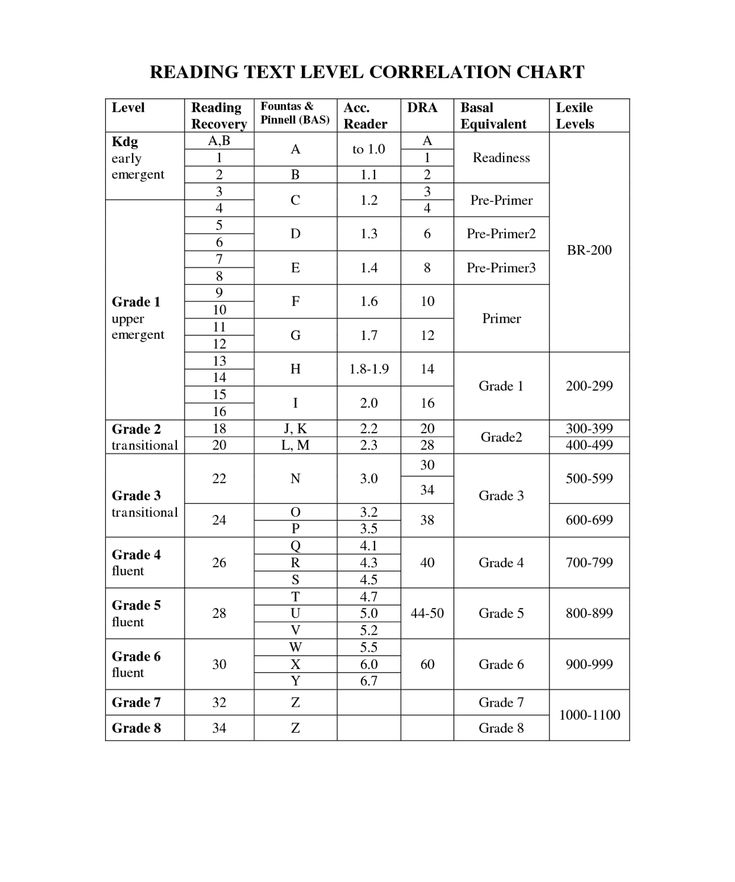
Now in the arsenal of many manufacturers of industrial network equipment, you can find several types of industrial switches with different functions:
- unmanaged switches;
- managed switches with L2 feature set; nine0008
- managed switches with L3 feature set.
Each type of switches is aimed at solving its own range of tasks and differs significantly in price, capabilities and, of course, functions. Now a modern industrial Ethernet network is a complex and competent combination of all three types of switches. As a rule, only in this case it is possible to build a reliable, balanced, functional and, most importantly, cost-effective system.
However, over the past 3–4 years, many tasks have appeared where an even more specific solution is needed, for example, building a network where the functionality of unmanaged switches is insufficient, and the functionality of managed L2 switches is very redundant. A typical task is to provide network redundancy and its segmentation into VLANs (Virtual Local Area Network - virtual local computer network).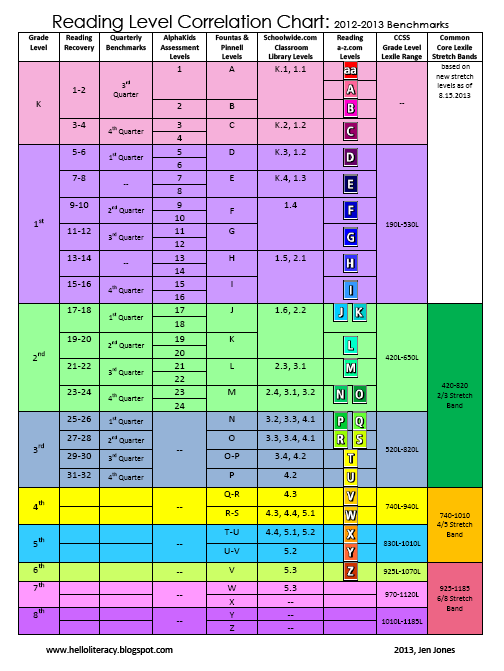
It will not be possible to solve it without a managed switch. And the price of a full-fledged managed L2 switch differs several times from that of an unmanaged one. nine0003
As a result, the price of the final solution increases significantly. In terms of budget savings, this fact forces designers and integrators to use more economical commercial segment equipment that is not designed for solving industrial problems.
As a result, it is possible to provide functionality and even the price may turn out to be acceptable, but an industrial network built on commercial switches will most likely not meet the requirements for reliability and fault tolerance. In this regard, manufacturers of industrial network equipment offer customers more and more niche solutions. nine0003
Using the example of the Taiwanese manufacturer EtherWAN, whose equipment is in the middle price segment, it can be shown that the class of industrial network switches is growing and is currently represented by the following types (Fig.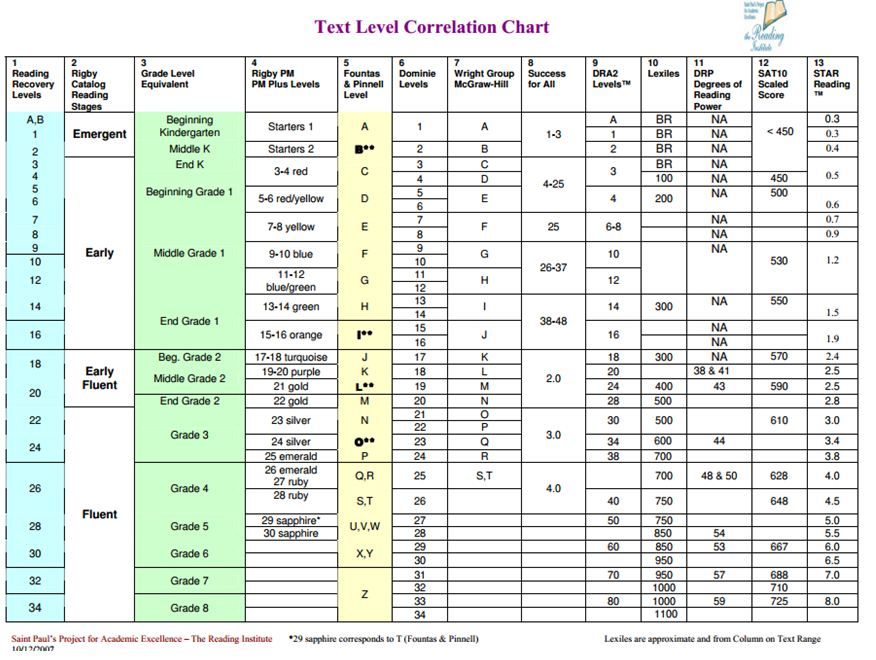 1):
1):
- unmanaged switches;
- managed switches with a basic set of L2 functions;
- managed switches with full L2 functionality;
- managed switches with a basic set of L3 functions; nine0008
- managed switches with full L3 functionality.
Fig. 1. EtherWAN Industrial Ethernet Switch Portfolio
And if managed switches with a basic set of L3 functions, the so-called Lite L3, are the lot of fairly large networks, then managed switches with a basic set of L2 functions are equipment that can be used to solve a huge number of tasks where high-performance capabilities are not required, but high reliability of the equipment is required. In 2021, EtherWAN introduced a new series of managed switches with a basic L2 feature set, called SmartE. nine0003
About EtherWAN
EtherWAN is an industrial network equipment manufacturer headquartered and manufactured in Taiwan. It was founded in 1996, and today you can find a lot of devices in the portfolio [1].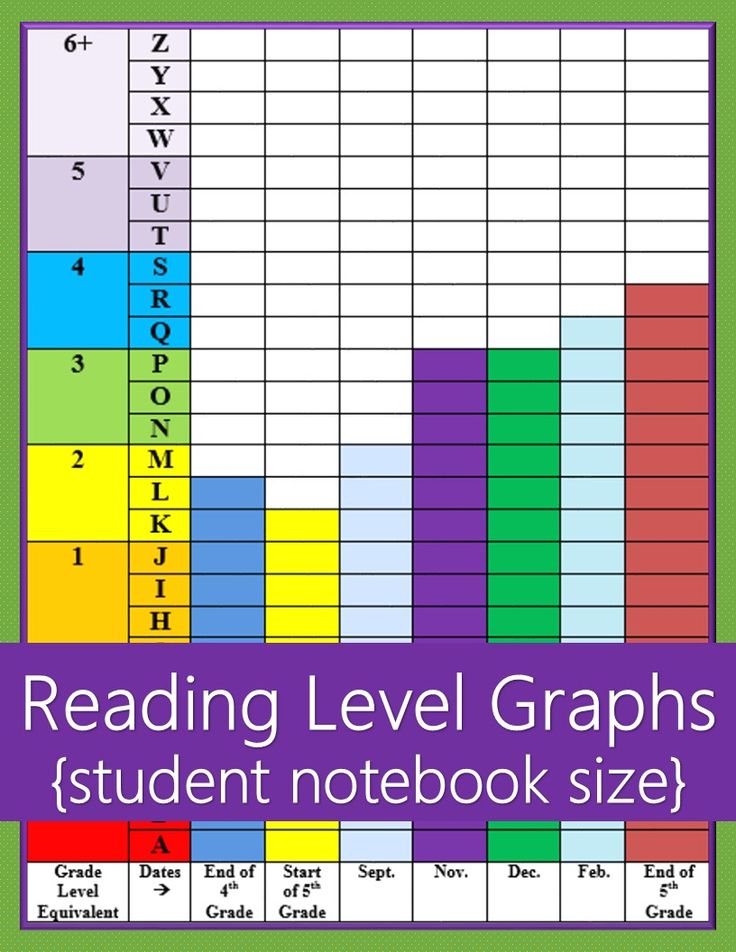
The company's products are successfully used in such vertical markets as energy, oil and gas industry, urban infrastructure, etc.
SmartE Series
Series SmartE (Fig. 2) is a very interesting addition to the existing portfolio [2], as it is designed taking into account industrial requirements, but at the same time it has a fairly low and affordable price.
Fig. 2. EtherWAN's New SmartE Switch Series
At the moment, the portfolio of the series includes 9 devices (Table 1) with various port configurations, which allows you to make a choice for a specific task. nine0048
Table 1. Nomenclature of SmartE Series Switches
As in any line, there are switches with Fast Ethernet speed and options with gigabit Uplink ports, which are implemented using SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable - the standard for modular transceivers).
Separately, it is worth noting the simultaneous support of SFP modules with different speeds, that is, gigabit versions of SmartE switches can work with Fast and Gigabit Ethernet SFP modules (Fig. 3). nine0048
3). nine0048
Fig. 3. Appearance and design of the SmartE switch
Switch frame
Switches of the new series are made in a standard industrial design for EtherWAN equipment (Fig. 3). Naturally, this is a rugged metal case with an IP30 degree of protection and fully conductive cooling. The switches are designed for mounting on a DIN rail. The kit comes with everything you need for installation. Also, the switch is equipped with a duplicate power supply input and has protection against polarity reversal and overcurrent. Input voltage range 12…57 VDC. There is a voltage comparator at the input, and when voltage is applied to both inputs, it automatically selects a higher value and makes this input the main one. When the voltage fails at one of the inputs or when its level drops below 12 V, the switch automatically switches to the second channel and closes the control relay. This function allows you to monitor the state of the power supply network of switches and promptly signal abnormal operation.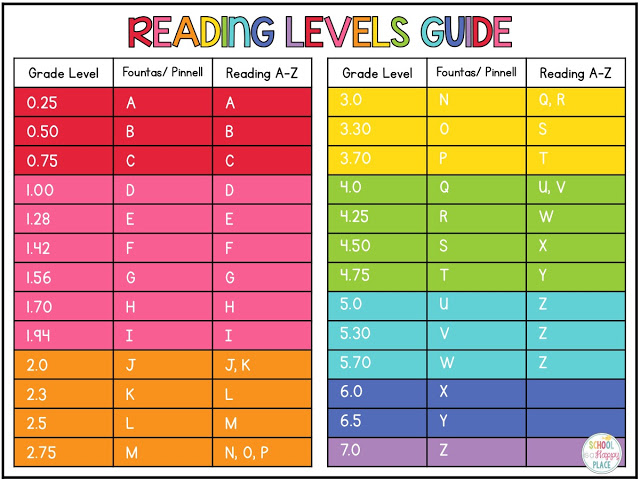 nine0003
nine0003
Operating modes
The presence of several modes of operation is also one of the "chips" of the new series. Using the select button, you can start the switch in one of four modes (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4. Selecting the operation mode of the SmartE series switch
- Restore factory default settings
This mode is required to reset the device. Since the switches are not equipped with a console cable, this mode can make it much easier to solve problems if you accidentally set the wrong function. In this mode, all saved configuration and IP parameters are reset. nine0008 - Fixed IP operation
This mode is quite useful when you need to get emergency access to the switch without changing its configuration. In fact, when operating in this mode, the switch is available at 192.168.0.254. At the same time, the DHCP server is launched on the switch, which allows you to assign the IP address of the PC that is connected to the switch.
- Reset switch IP configuration
The mode allows you to reset the IP address of the switch to the standard 192.168.254/24. - Unmanaged switch operation
This mode is probably self-explanatory: at the output, the switch operates in unmanaged mode.
To select the operating mode after the boot phase of the switch, as soon as the LEDs of all ports turn off, you must press and hold the mode button for more than 10 seconds (step 1). The four Port 1 and Port 2 LEDs will blink, indicating that the switch is ready for mode selection. Step 2 - Select the desired mode: Briefly press the mode button. Step 3 - exit selection mode: press and hold the mode button for more than 5 seconds. nine0003
SmartE switch functions
EtherWAN has developed a new hardware platform for the new SmartE series, the performance of which is enough to solve many problems. Conceptually, this is still a non-blocking architecture operating in the “Store and Forward” mode. But taking into account the focus of the line on a small budget, the manufacturer has identified a pool of the most popular functions that are used in small industrial networks, and equipped the switches with them. The set of supported protocols, of course, turned out to be not as rich as in the flagship lines, but it includes all the main options that are usually used to solve small local problems. But taking into account the reduction in the number of functions, their list turned out to be quite impressive. Even the name indicates that the switch is smart - “Smart” and, therefore, is capable of solving a wide variety of tasks. The switch supports VLAN (up to 32), data link aggregation, port mirroring, QoS functionality, SNMP protocol, as well as LLDP, SNTP, RMON, can work with multicast traffic (IGMP-snooping - network management protocol multicast, which organizes multiple devices into groups), filter MAC addresses, etc. At the same time, the switch supports very interesting redundancy functionality, which distinguishes this series from competitors.
But taking into account the focus of the line on a small budget, the manufacturer has identified a pool of the most popular functions that are used in small industrial networks, and equipped the switches with them. The set of supported protocols, of course, turned out to be not as rich as in the flagship lines, but it includes all the main options that are usually used to solve small local problems. But taking into account the reduction in the number of functions, their list turned out to be quite impressive. Even the name indicates that the switch is smart - “Smart” and, therefore, is capable of solving a wide variety of tasks. The switch supports VLAN (up to 32), data link aggregation, port mirroring, QoS functionality, SNMP protocol, as well as LLDP, SNTP, RMON, can work with multicast traffic (IGMP-snooping - network management protocol multicast, which organizes multiple devices into groups), filter MAC addresses, etc. At the same time, the switch supports very interesting redundancy functionality, which distinguishes this series from competitors.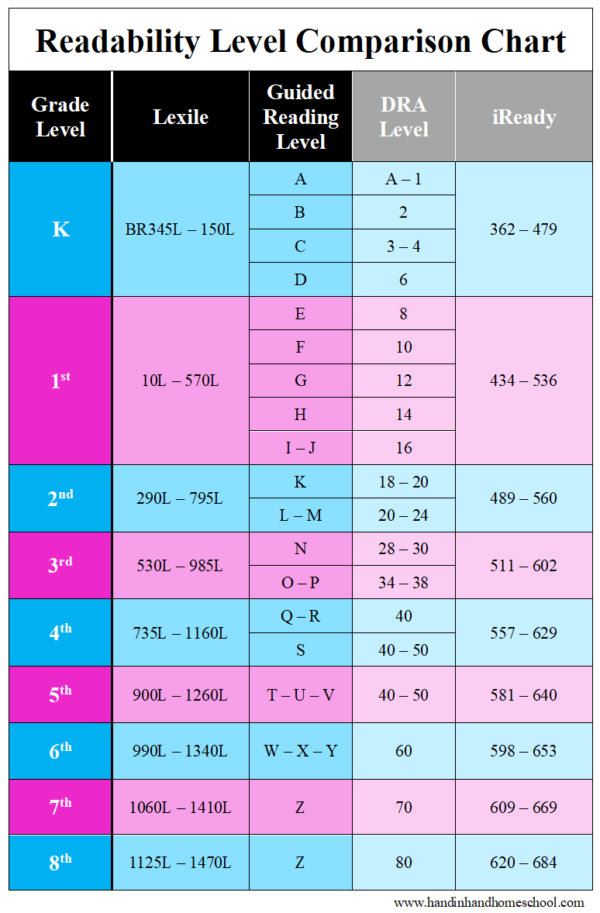 Consider the redundancy of an industrial network in more detail. nine0003
Consider the redundancy of an industrial network in more detail. nine0003
Industrial redundancy with SmartE switches
If you look at the technical description of the switches of the new series, you can see support for RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol, IEEE 802.1w), this is not surprising, as a rule, this protocol is supported by many industrial managed switches. However, the EtherWAN manufacturer, focusing on the current market realities, decided to supplement this functionality.
We all know that ring redundancy topologies are the most popular these days, and you can often see RSTP in these rings. RSTP for the ring is not the best solution, since with standard settings it is recommended to use up to 15 devices in the ring, while the recovery time can be up to 10 seconds. In fact, RSTP is not optimized for ring topologies. nine0003
When developing a new series, the manufacturer took into account the fact that 15 devices are not always enough for modern realities, even for small tasks, and a recovery time of 10 seconds is also not the best indicator.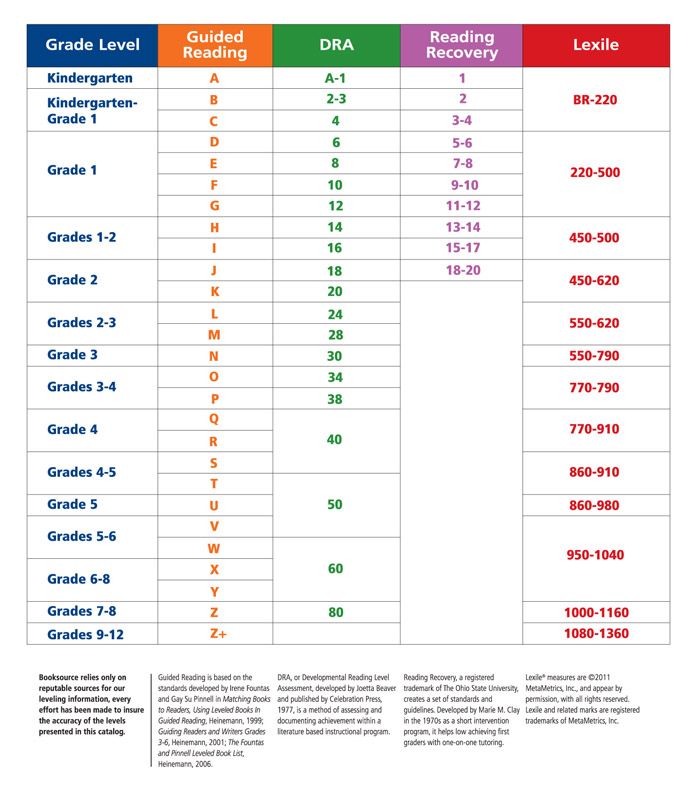 The manufacturer slightly optimized the RSTP protocol, and the new series has support for two interesting options.
The manufacturer slightly optimized the RSTP protocol, and the new series has support for two interesting options.
Large Tree Support ( LTS ) - the name of this function can be translated as "large tree support". With this option, it is possible to build redundant ring topologies of a larger network diameter. In other words, you can increase the ring size of LTS-enabled switches up to 57 devices. The disadvantage of this feature is that it is proprietary and can only work with switches of the new SmartE series. nine0003
Fast Ring Detection ( FRD ) - this function adds speed to the process of switching to a backup path, significantly speeding up switching to it in case of an error. When operating, a switch with FRD enabled assigns an ID to each ring. This identifier is sent to each switch in the corresponding ring. One switch can simultaneously belong to several different rings, for example, you can combine the RSTP protocol with the LTS and RTS options enabled and the regular RSTP protocol (Fig.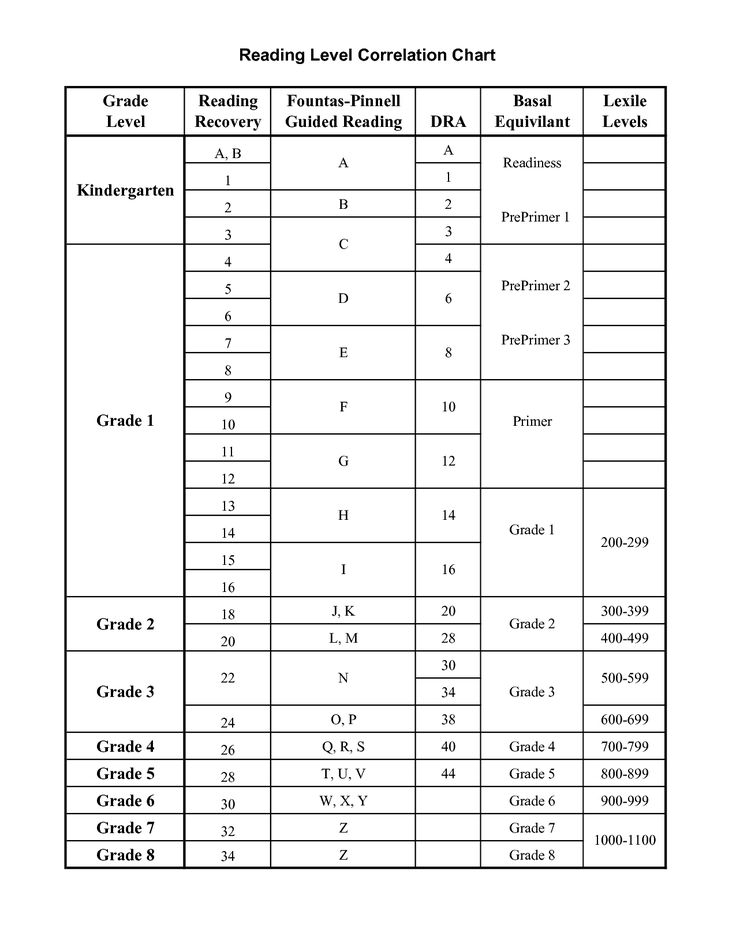 5). nine0048
5). nine0048
Fig. 5. Possible redundant topologies using SmartE switches
This allows you to use and combine equipment from different manufacturers with RSTP support.
Separately, it is worth noting the recovery time: with the FRD option enabled, it will not exceed 500 ms. This value is acceptable for most general industrial tasks.
As a result, with the LTS and RTS options enabled, you can create more flexible redundant topologies of industrial networks, combine equipment from different manufacturers, while the recovery time remains at a very decent level. nine0003
SmartE application example at a public transport station
An example of the successful use of SmartE series switches is shown in Fig. 6.
Fig. 6. Application example of SmartE series switches (Ethernet network of public transport station)
SmartE switches were used to implement a multi-service data transmission network for a large station, or, as it is now also called, a public transport hub.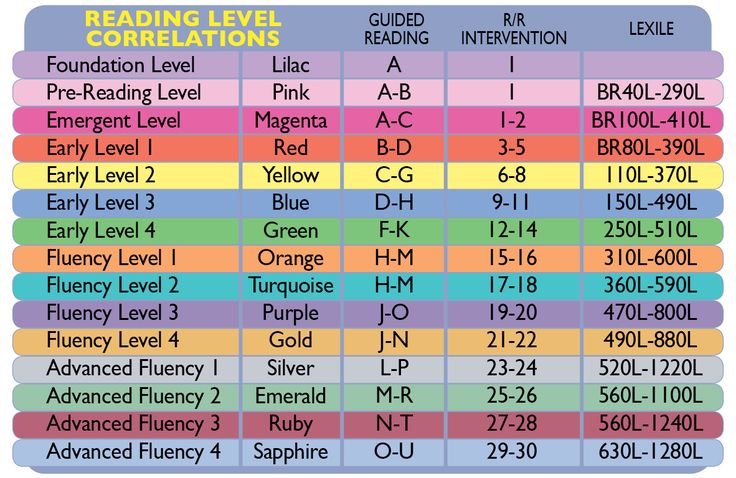 When implementing a network of such an object, it is necessary to ensure fault-tolerant and reliable operation of all the main elements of the station: terminals, turnstiles, control points, etc. However, the tasks that are set before the functionality of the equipment are not extremely high: there is no need to support multiple redundancy protocols, there is no need for precise time synchronization, support for highly specialized industrial protocols, etc. But at the same time, just everything you need is present in the SmartE line, from redundancy to segmentation and QoS functionality. Nevertheless, the design of the switches is industrial and, most importantly, the price remains at a low level. nine0003
When implementing a network of such an object, it is necessary to ensure fault-tolerant and reliable operation of all the main elements of the station: terminals, turnstiles, control points, etc. However, the tasks that are set before the functionality of the equipment are not extremely high: there is no need to support multiple redundancy protocols, there is no need for precise time synchronization, support for highly specialized industrial protocols, etc. But at the same time, just everything you need is present in the SmartE line, from redundancy to segmentation and QoS functionality. Nevertheless, the design of the switches is industrial and, most importantly, the price remains at a low level. nine0003
Conclusion
The market for industrial managed switches has changed over the past 3-4 years. This is due to the fact that many tasks have appeared where a simple budget solution with basic functionality is needed, for example, when a simple inexpensive budget switch with basic features (VLAN, redundancy, QoS, etc.