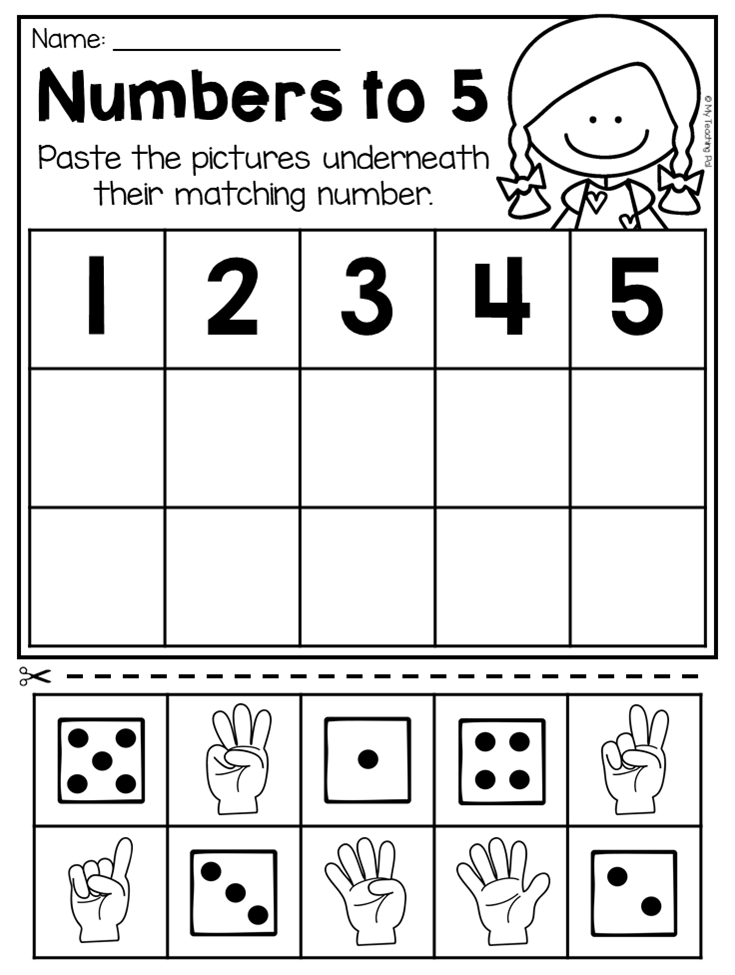
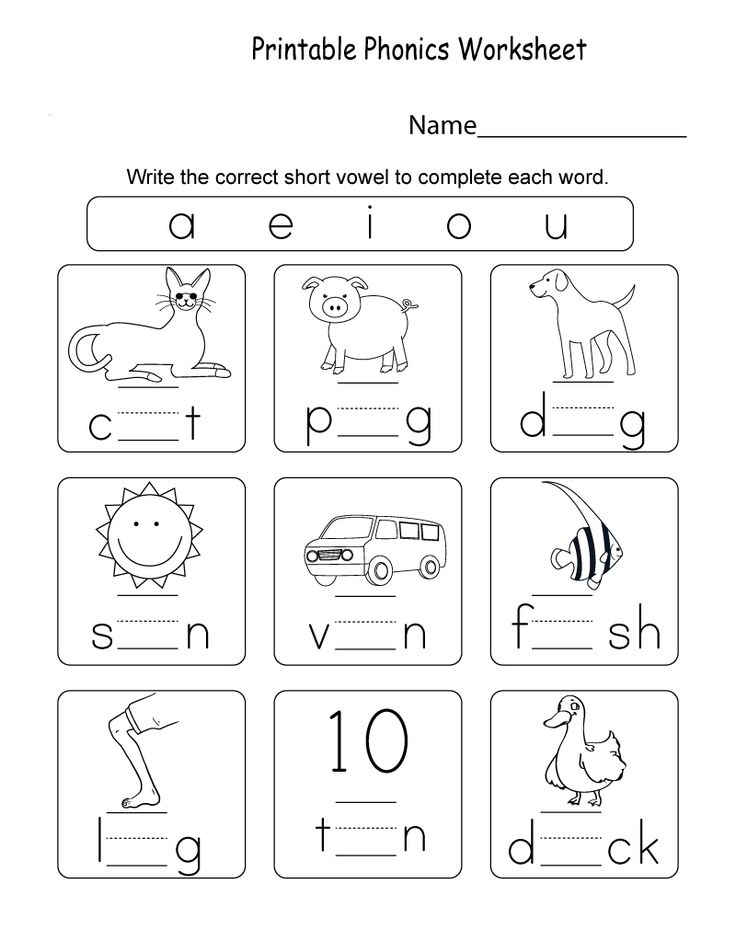
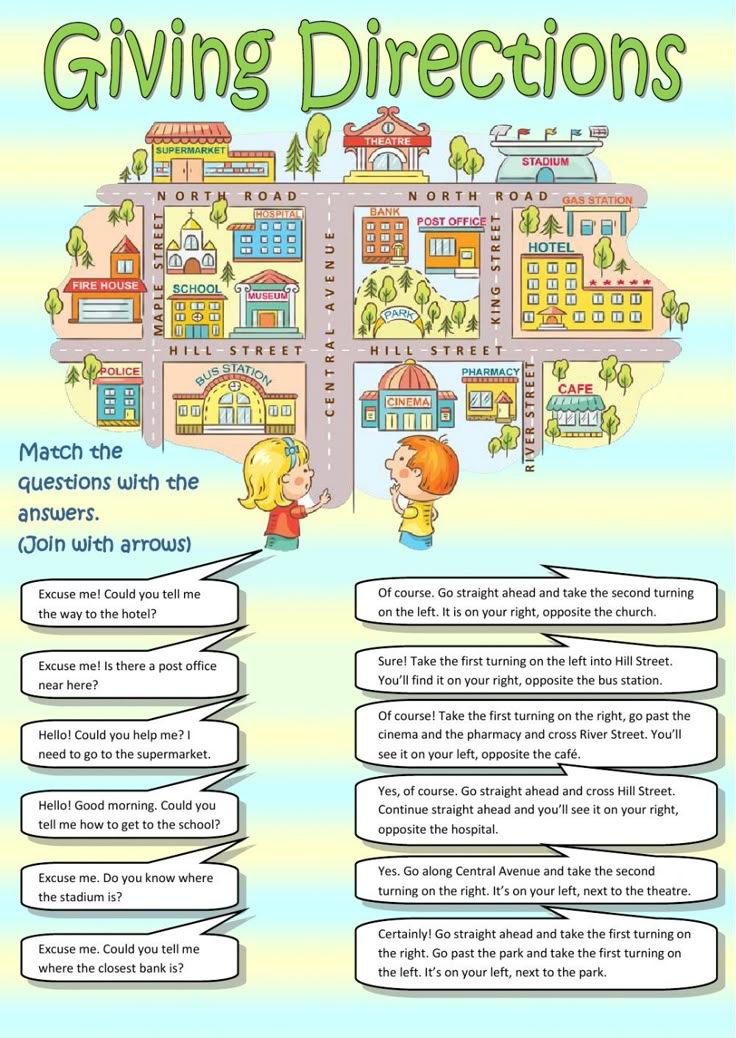
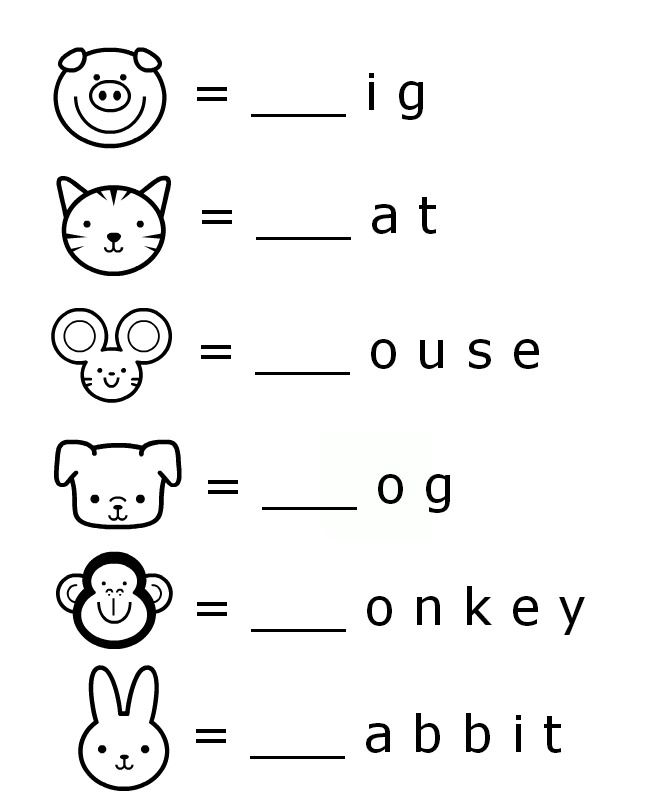Following directions definition
Following Instructions - Kid Sense Child Development
What is following instructions?
Following instructions is a part of everyday life. It is the child’s ability to act on requests by others. Following instructions requires the child to attend to detail in spoken language, to sequence the information in the appropriate steps and to seek clarification if they have trouble remembering or recalling the information. At home, parents ask their children to do things around the house (e.g. “Put the cup on the table”) and at school teachers ask their students to follow commands within the classroom (e.g. “Go to your bag and get your lunch”) and within academic tasks (e.g. “Copy the spelling words on the board, then put each of them into a sentence”). When children engage with their peers, they often give each other instructions in play (e.g. “Can you put the doll in the bed?” or “Let’s make the train go to the station, then get all the people”).
Why is the ability to following instructions important?
It is important for children to be able to follow instructions so that they can function effectively across different environments (e. g. home, kindergarten/school, when at the park or visiting a friend’s house). If a child struggles with following instructions this impacts on their ability to reach the desired ‘purpose’ or ‘outcome’ and thus complete tasks effectively.
What are the building blocks necessary to develop following instructions?
- Hearing
- Receptive (understanding) language: Comprehension of language, especially concepts and vocabulary.
- Attention and concentration: Sustained effort, doing activities without distraction and being able to hold that effort long enough to get the task done.
- Working memory: The ability to temporarily retain and manipulate information involved in language comprehension, reasoning, and learning new information and to update this information as change occurs.
- 1 – 2 years of age: Can follow simple 1 step instructions (e.g. “Give the cup to mum”).
- 2 – 3 years of age: Can follow 2 part commands (e.g. “Go to your room and get your jacket”).
- 3 – 4 years of age: Can follow 3 part instructions (e.g. “Point to the cat, dog and monkey”).
How can you can tell if my child has problems with following instructions?
If a child has difficulties with following instructions they might:
- Need instructions to be presented in a short and simple manner.
- Struggle with following longer instructions and commands need to be repeated.
- Fail to follow instructions accurately and often misinterprets information.
- Appears to be distracted or non-compliant.
- Look at you blankly when you give them an instruction.
- Avoid carrying out instructions by talking about something else to distract the person.
- Look to peers to work out what they need to do.
What other problems can occur when a child has difficulties with following instructions?
When a child has following instruction difficulties, they might also have difficulties with:
- Behaviour: The actions of a person, usually in relation to their environment (e.
 g. a child may refuse to listen to instructions and/or engage in another activity of their choosing).
g. a child may refuse to listen to instructions and/or engage in another activity of their choosing). - Completing academic work (e.g. the child may misinterpret or fail to comprehend verbal or written instructions for classroom activities and are therefore unable to complete work and fail to meet the task requirements).
- Planning and sequencing: The sequential multi-step task/activity performance to achieve a well-defined result.
What can be done to improve following instructions?
- Eye contact: Get the child’s visual attention before giving them an instruction.
- Single instructions: Give your child only one instruction at a time.
- Simple language: Keep language simple and direct.
- Break verbal instructions into parts: Instead of “Go and get your lunchbox and your hat and go outside”, say “Get your lunchbox.
 ” When the child has followed that instruction, say “Now get your hat” then “OK, now you can go outside”.
” When the child has followed that instruction, say “Now get your hat” then “OK, now you can go outside”. - Repeat: Get your child to repeat the instruction to ensure that they have understood what they need to do (e.g. “Go and get your bag then sit at the table. What do I want you to do?’).
- ‘First/Then’: Use this concept to help the child know what order they need to complete the command (e.g. “First get your jacket, then put on your shoes”).
- Clarify: Encourage the child to ask for clarification if they forget part of the instruction or have trouble understanding what they need to do. Encourage them to ask for the command to be repeated or clarified (e.g. “Can you say that again please?”).
- Visual aids (e.g. pictures, gestures, body language and facial expression) can be used to assist the child’s comprehension and recall of the instruction.
- Visual cues can often be very useful to help the child to follow longer instructions as it provides them with something to refer back to if they are having difficulty remembering what they need to do.
 It also highlights the order in which they need to complete the instruction.
It also highlights the order in which they need to complete the instruction.
What activities can help improve following instructions?
- Simon Says: Gradually increase the length of the command when playing this game (e.g. “Simon Says pat your head”; “Simon says first pat your head, then touch your nose”).
- Robot game: Blindfold the ‘Robot’ (listener) so the child must listen very carefully to instructions to find something (e.g. go 3 steps forward, then 1 step to the right). This can be reversed so that the child has to give someone else the instructions.
- Drawing games: Describe a picture that the child cannot see and they must try and draw a similar picture from your verbal instructions. Compare the two pictures at the end. Use previously drawn background scenes (e.g. street scene, park scene, shelves of a cupboard, rooms in a house). Take turns giving instructions about where to draw or stick on pictures of objects or people (e.
 g. ‘put the plate on the second shelf’).
g. ‘put the plate on the second shelf’).
Why should I seek therapy if I notice difficulties with following instructions in my child?
Therapeutic intervention to help a child with following instruction difficulties is important to:
- Help a child to follow instructions within the educational setting (e.g. classroom instructions, academic task requirements).
- Help a child to follow commands within social situations (e.g. playing games with peers, engaging effectively with individuals during out-of-school activities such as playing sport).
- Help a child to understand and complete routine and unfamiliar tasks appropriately around the house or at school.
If left untreated what can difficulties with following instruction lead to?
When children have difficulties with following instructions, they might also have difficulties with:
- Understanding instructions during social interactions with peers and unfamiliar adults.

- Comprehending commands within academic tasks in higher levels of education.
- Following instructions in the workplace, which impacts on task efficiency.
What type of therapy is recommended for difficulties following instructions?
If your child has difficulties following instructions, it is recommended they consult a Speech Therapist.
If there are multiple areas of concern (i.e. beyond just following instructions) both Occupational Therapy and Speech Therapy may well be recommended to address the functional areas of concern. This is the benefit of choosing Kid Sense which provides both Occupational Therapy and Speech Therapy.
follow directions definition | English definition dictionary
vb
1 to go or come after in the same direction
he followed his friend home
2 tr to accompany; attend
she followed her sister everywhere
3 to come after as a logical or natural consequence
4 tr to keep to the course or track of
she followed the towpath
5 tr to act in accordance with; obey
to follow instructions
6 tr to accept the ideas or beliefs of (a previous authority, etc. )
)
he followed Donne in most of his teachings
7 to understand (an explanation, argument, etc.)
the lesson was difficult to follow
8 to watch closely or continuously
she followed his progress carefully
9 tr to have a keen interest in
to follow athletics
10 tr to help in the cause of or accept the leadership of
the men who followed Napoleon
11 tr
Rare to earn a living at or in
to follow the Navy
12 ♦ follow suit (Cards)
a to play a card of the same suit as the card played immediately before it
b to do the same as someone else
n
13 (Billiards, etc.)
a a forward spin imparted to a cue ball causing it to roll after the object ball
b a shot made in this way, (See also)
→
follow-on →
follow out →
follow through →
follow up
(Old English folgian; related to Old Frisian folgia, Old Saxon folgon, Old High German folgen)
♦
followable adj
follow-my-leader
n a game in which the players must repeat the actions of the leader, (U. S., Canadian, and Irish name)
follow-the-leader
S., Canadian, and Irish name)
follow-the-leader
follow-on (Cricket)
n
1 an immediate second innings forced on a team scoring a prescribed number of runs fewer than its opponents in the first innings
vb
♦
follow on
2 intr, adv (of a team) to play a follow-on
follow out
vb tr, adv to implement (an idea or action) to a conclusion
follow through
vb adv
1 (Sport) to complete (a stroke or shot) by continuing the movement to the end of its arc
2 tr to pursue (an aim) to a conclusion
n
♦
follow-through
3 (Sport)
a the act of following through
b the part of the stroke after the ball has been hit
4 the completion of a procedure, esp. after a first action
after a first action
follow up
vb tr, adv
1 to pursue or investigate (a person, evidence, etc.) closely
2 to continue (action) after a beginning, esp. to increase its effect
n
♦
follow-up
a something done to reinforce an initial action
b (as modifier)
a follow-up letter
4 (Med) a routine examination of a patient at various intervals after medical or surgical treatment
What is Marketing Mix: Models - Definition
Marketing Mix is the concept of promoting a company and products on the market using different marketing models. The classic version of this model is called 4P and consists of the following areas: product (Product), price (Price), place (Place), promotion (Promotion).
In this video, In-scale founder Nikita Zhestkov talked about what 4P and 5P marketing is.
Purpose of the marketing mix
The marketing mix helps to improve the efficiency of the company and meet the needs of the target audience. For effective promotion in the market, it is important to develop a strategy and create a detailed marketing plan for solving the tasks. Let's see what goals can be achieved with the help of the marketing mix.
For effective promotion in the market, it is important to develop a strategy and create a detailed marketing plan for solving the tasks. Let's see what goals can be achieved with the help of the marketing mix.
- Sales increase. With the help of marketing mix tools, brands build new distribution channels, develop loyalty programs, and increase awareness. Sales growth increases the company's profits and strengthens its position in the market.
- Increasing customer satisfaction. With the help of the marketing mix, companies satisfy the needs and desires of the target audience. This increases customer loyalty and also improves retention and LTV.
- Building a positive image of the company. With the help of ATL and BTL advertising, social proof, event marketing and other tools, companies increase brand awareness, win the favor of the target audience and strengthen the reputation.
- Business process optimization.
 Quality process management helps to track performance, control the speed and quality of work, improve marketing strategy.
Quality process management helps to track performance, control the speed and quality of work, improve marketing strategy.
Regardless of what results a company wants to achieve and which marketing mix model it chooses, success depends largely on setting clear goals. Therefore, it is best to use the SMART system. Then the goals will be specific (Specific), measurable (Measurable), achievable (Attainable), relevant (Relevant). Read on to learn more about the classic marketing mix model.
Elements of the marketing mix 4P
The marketing mix model was described in an article by Nel Borden in 1964. He brought together all the marketing tools needed to promote the company's product. Later, Jerome McCarthy took Borden's marketing mix and converted it into a 4P model. A world-famous marketer Philip Kotler made a great contribution to its popularization. See what elements the 4P model consists of.
- Product This is where the marketing mix begins.
 In order to interest the target audience and satisfy its needs, the company thinks over the properties of products, assortment, creates a corporate identity and much more.
In order to interest the target audience and satisfy its needs, the company thinks over the properties of products, assortment, creates a corporate identity and much more. - Price (price). The cost of a product or service is determined based on the average market price, demand, cost of goods and desired profit. The company investigates the pricing of competitors, sets the retail price, and also thinks over the system of discounts.
- Place (place of sale). In this direction, they determine the distribution channels, type of distribution, ways of placing goods at points of sale, think over logistics and solve other problems that affect the availability of products to the target audience.
- Promotion (promotion). To increase brand awareness and tell potential customers about a product, companies use many different tools. They develop media planning, connect event and direct marketing, think over ways to stimulate sales, and much more.
 The marketing budget is also set at this stage.
The marketing budget is also set at this stage.
Depending on the niche and the specifics of the company, brands complement the 4P model to suit their needs. Therefore, there are other variations of this marketing mix, which you will learn about in the next section.
Marketing Mix Models
- 5P
- 7Р
- SIVA
High competition and constant changes in the market led to the expansion of the 4P model and the search for new areas of marketing planning. Check out some of them.
5P
This marketing mix includes the 4P model plus the additional People element, relationship marketing. This direction involves the development of mechanisms for interaction between the subjects of market relations, the selection and training of personnel, the creation of methods for working with opinion leaders, the launch of loyalty programs, and much more. Model 5P is ideal for service companies: hotels, restaurants, beauty salons and so on.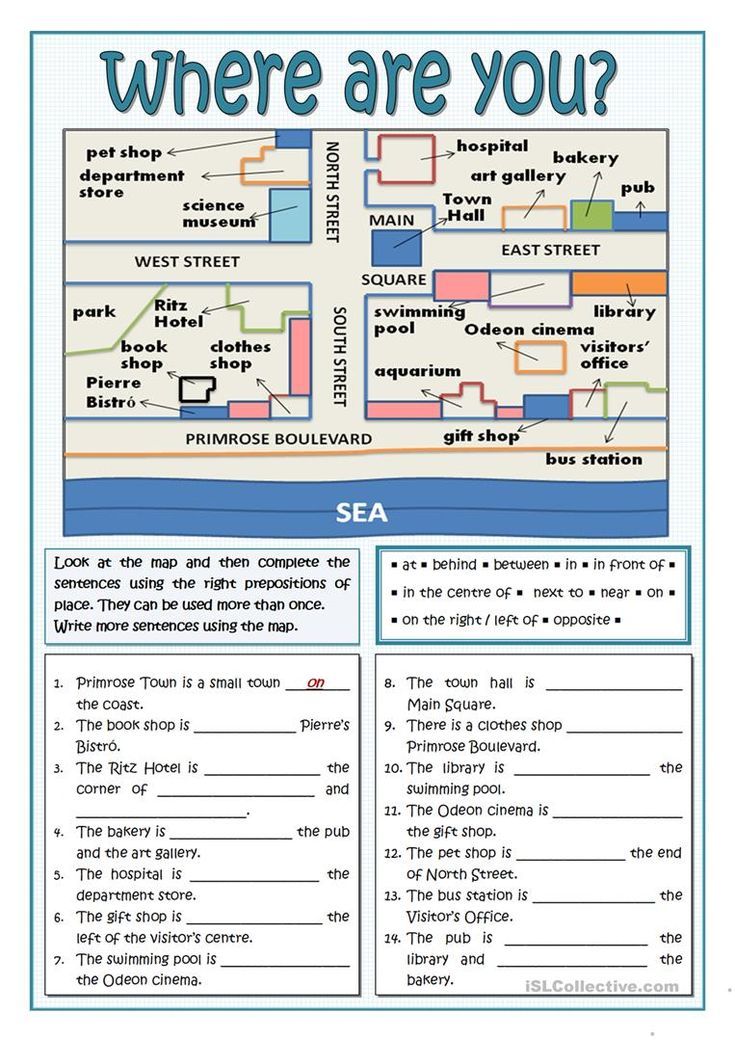
7P
Model 7P is an even more advanced version of 4P. It is complemented by the following elements: People, Process (service delivery process) and Physical evidence (physical environment). Let's take a closer look at the last two.
- Process . It implies the development and honing of customer interaction processes. This direction helps to increase customer loyalty and increase the competitiveness of the company. So the well-coordinated work of McDonald’s employees helped to achieve a high speed of service, for which many people love this network.
- Physical evidence . This direction involves creating a favorable atmosphere around the consumer, as it influences his purchase decision and loyalty. The right physical environment helps build a positive brand image and highlight the main benefits of the product.
SIVA
The SIVA model is an alternative to the 4P that was introduced in 2005. The focus of this marketing mix is redirected from the product to the solution to the customer's problem. Let's take a closer look at each of the elements of the SIVA model.
The focus of this marketing mix is redirected from the product to the solution to the customer's problem. Let's take a closer look at each of the elements of the SIVA model.
- Solution. This direction is aimed at finding the most suitable solution to meet the needs of customers.
- Information. Companies find out whether the target audience is familiar with the product, whether they have enough information, what they lack to make a purchase decision, what channels to use for communication, and so on.
- Value. In this direction, companies determine the value of products for customers. They analyze the competitive environment, examine analogues on the market, and calculate the added value.
- Access. This direction involves the creation of points of sale convenient for consumers. Companies strive to provide customers with access to products and services in a convenient place and at a convenient time for them.

There are a number of other marketing mix models. For example 4C, 4A, 5P+1S and others. The choice of a marketing strategy model depends on the scope of the company, the level of competition, goals and other factors. The main thing when choosing a marketing mix is to rely on the convenience of work. The model should systematize and simplify business processes.
Resources:
- On this site you will read the history of the 4Ps and also learn about advanced models of the marketing mix.
- In this article, you will get acquainted with the basic models of the marketing mix.
- Find examples of marketing mix here.
- Read about the concept of the marketing mix on the website of the Marketer's Notes.
- And in this article you will learn how to develop a marketing mix for your company.
Updated: 09/29/2022
Learn to distinguish the directions of painting in fifteen minutes? Easily!
There are countless trends in art. Most of them give rise to more and more new branches, which are difficult to understand, but nevertheless, over time, some styles are honed, acquire clear boundaries, take root deeply and become classics. It is about them that we will talk today.
Most of them give rise to more and more new branches, which are difficult to understand, but nevertheless, over time, some styles are honed, acquire clear boundaries, take root deeply and become classics. It is about them that we will talk today.
Vyacheslav Tishin, director of the federal art sales platform Art-most.com, noted: “The average art buyer is not a collector or a professional expert in painting, so he can get confused in numerous styles and genres. On our website, for the convenience of the buyer, we have tried to highlight the most voluminous and common areas: abstractionism, avant-gardism, impressionism, constructivism, conceptualism, modernism, naive art, pop art, realism, symbolism, surrealism and expressionism.»
How to determine the style of a work? What features are characteristic of a particular direction of style? Which artists are prominent representatives of the aforementioned trends? Let's try to figure it out!
Avant-gardism is a movement with many “faces”, it is a whole branch that combines Fauvism, Cubism, Futurism, Expressionism, Abstractionism, Surrealism, Actionism, Pop Art and Conceptual Art. The main features of avant-gardism can be called the following:
The main features of avant-gardism can be called the following:
- a certain duality is inherent in the flow, for example, rationalism and irrationality
- new forms, techniques and means not previously used in the art world
- denial or recognition of traditions, established foundations in painting
- experiments with shapes, colors and shades
Kazimir Malevich, Mikhail Larionov, Natalia Goncharova are some of the most famous avant-garde artists. A prominent representative of the avant-garde trend at Art-most.com is Alexey Klintsov, Vladimir Terekhin, Nikola Zverev.
Alexey Klintsov
Kazimir Malevich
Vladimir Terekhin "Faces"
Nikola Zverev "Swings"
Expressionism - a trend that arose in Western European art at the beginning of the 20th century as a response to the revolutionary movements of the First World War. Expressionists are characterized by mysticism and pessimism, and the subjectivity of the creative act and the emotional effect are above all.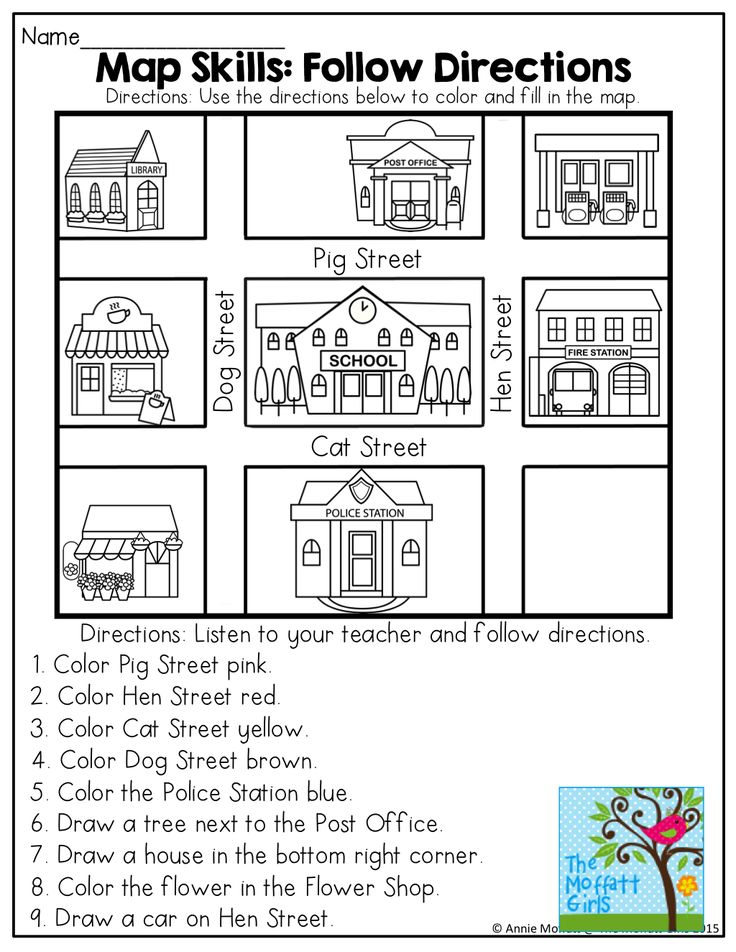 It can be noted that many works are characterized by motifs of torment, pain, suffering, screaming.
It can be noted that many works are characterized by motifs of torment, pain, suffering, screaming.
The works of such famous masters as Edvard Munch, Vincent van Gogh and James Ensor most clearly represent this trend. Art-most.com invites you to get acquainted with the following expressionist artists: Marco Grassi, Alexander Otroshko, Frol Vesely.
Marco Grassi
Alexander Otroshko
Frol Vesely
Edvard Munch
Abstractionism is a direction of art that least of all resembles reality in the depiction of forms. The goal is to achieve harmony, create certain color combinations and geometric shapes in order to evoke various associations in the observer.
The main representatives of abstract art were: Wassily Kandinsky, Pablo Picasso. On Art-most.com, the direction of abstract art is represented by Alexander Radtke, Nikolai Kulebakin, Rustam Salikhov and many others.
Alexander Radtke
Nikolai Kulebakin
Rustam Salikhov
Wassily Kandinsky
Impressionism is a trend in European painting that originated in France in the middle of the 19th century.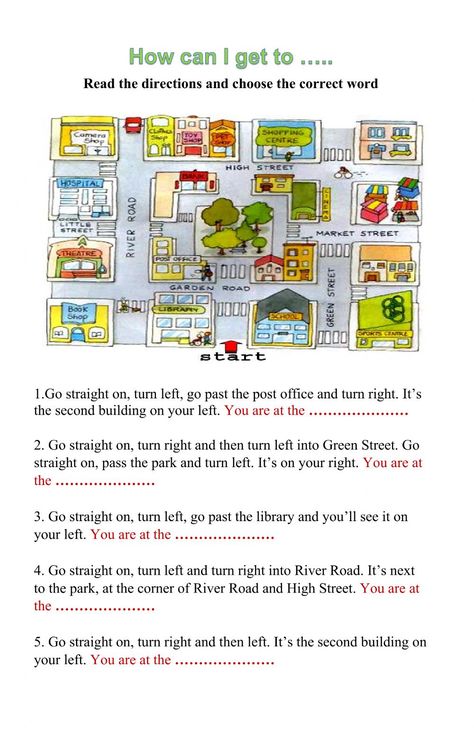 Impressionist paintings do not carry social criticism, do not touch upon social problems such as hunger, illness, death, presenting only the positive aspects of life. Impressionists avoid any details in the drawing and try to capture the general impression of what the eye sees at a particular moment. Colors and textures play an important role. Main features:
Impressionist paintings do not carry social criticism, do not touch upon social problems such as hunger, illness, death, presenting only the positive aspects of life. Impressionists avoid any details in the drawing and try to capture the general impression of what the eye sees at a particular moment. Colors and textures play an important role. Main features:
- barely visible, fine strokes
- lighting change
- open composition
- simple general purpose
The most famous artists of this style of painting: Pierre Renoir, Edgar Degas, Claude Monet, and others. On Art-most.com you can buy works in the style of impressionism by such artists as Bato Dugarzhapov, Dmitry Mantrov, Svetlana Kruglova, Yuri Novikov, and others
Svetlana Kruglova
Claude Monet
Bato Dugarzhapov "Spring motive"
Dmitry Mantrov "At a mountain lake"
Yuri Novikov "Still life with a bronze clock"
Surrealism. Once Salvador Dali said: “Surrealism is me!”, And that says it all. This direction arose in France in the middle of the 20th century. It is distinguished by the use of allusions and paradoxical combinations of forms. Surrealism is a collage of real and subconscious, fantastic images.
Once Salvador Dali said: “Surrealism is me!”, And that says it all. This direction arose in France in the middle of the 20th century. It is distinguished by the use of allusions and paradoxical combinations of forms. Surrealism is a collage of real and subconscious, fantastic images.
The most famous surrealists: Salvador Dali, Rene Magritte. Lev Karnaukhov, Andrey Karablin, Nikolay Dyachenko, Igor Bragin and others present a number of works in a surrealistic style on Art-most.com
Lev Karnaukhov
Andrey Karablin
Nikolai Dyachenko
Salvador Dali
Igor Bragin Big House from One Pear
Pop art gained popularity in the United States in the 1950s. Artists of this trend reproduce typical items of modern life (household items, packaging of goods, fragments of interiors, car parts, etc.), popular printed images of stars, newspaper clippings.
The most famous pop artists: Jasper Johns, Robert Rauschenberg and Andy Warhol. Pop Art on Art-most.com is represented by the following artists: Igor Sever, Irina Chernavina, Andrey Kolosov, etc.
Pop Art on Art-most.com is represented by the following artists: Igor Sever, Irina Chernavina, Andrey Kolosov, etc.
Igor Sever
Irina Chernavina
Andrey Kolosov
Andy Warhol
Conceptualism - intellectual creativity 9001 in the majority ironic - arose initially as a counterbalance to commercial art. Conceptualism is the triumph of ideas over emotions, these are paintings created for intellectual perception.
The most famous artists of this trend: Joseph Kossuth (main theorist), Douglas Huebler, Robert Barry. Representatives of the conceptual direction at Art-most.com are Oksana Stogova, Igor Sever, Alexei Bandura, Ksenia Krestova and others. "No. 8"
Constructivism is a trend that emerged in the USSR in the 1920s. XX century. Proponents of constructivism strive to show the simplicity and emphasized utilitarianism of new objective forms. This style is characterized by rigor, geometrism, conciseness of forms and solidity of appearance. Constructivism is simple, flat, symbolic colors, image transmission without volume and perspective.
Constructivism is simple, flat, symbolic colors, image transmission without volume and perspective.
The main representatives of constructivism were: Alexander Rodchenko, Lyubov Popova, Vladimir Tatlin, Kazimir Malevich, and others. A prominent representative of the constructive trend on Art-most.com is Boris Klevogin.
Boris Klevogin
Alexander Rodchenko
Modernism is the general name for art movements of the late 19th and 20th centuries: cubism, Dadaism, surrealism, modernism, futurism, expressionism, abstract art, functionalism, neo-impressionism, post-impressionism, etc. Otherwise, modernism is sometimes called "another art". His goal is to create unique paintings that are not like others. The main feature of the works is a special vision of the world by the author. Modernists often experiment with form, and are also prone to abstraction, often accompanied by outrageousness and a certain challenge to established canons.
Henry Matisse and Pablo Picasso are considered to be one of its brightest representatives. Art-most.com invites you to get acquainted with the following modernist artists: Ildar Gilmanov, Viktor Golovy, Yulia Bobrova.
Art-most.com invites you to get acquainted with the following modernist artists: Ildar Gilmanov, Viktor Golovy, Yulia Bobrova.
Ildar Gilmanov
Victor Golovy "Red and Black"
Yulia Bobrova
Henry Matisse
Naive Art children's style. Naive art has the following characteristics:
- background plain or with a few shades
- missing perspective
- the main motif occupies most of the canvas, consists of simple and clear lines
- figures of animals and people are flat, not three-dimensional
- sweeping and often repeated rhythm gives the image a dynamic character
Such well-known masters as Henri Rousseau, Niko Pirosmani, Lyubov Maikova will most clearly present this direction. Art-most.com invites you to get acquainted with the following artists working in the naive style: Mary Ogembo, Niko Kerkeladze, Alfrid Shaimardanov and others.
Mary Ogembo
Niko Kerkeladze
Alfrid Shaimardanov
Henri Rousseau
Realism is a movement in art characterized by depicting social, psychological and other phenomena as close to reality as possible. The term "realism" literally means "real", "real".
The term "realism" literally means "real", "real".
The most famous realists: Ilya Repin, Ivan Shishkin, Vasily Polenov, Vasily Surikov, Isaac Levitan. On Art-most.com, realism is represented by Yuri Lezhnikov, Vasily Larionov, Yuri Filippov, Ilgiz Nasibullin and many others.
Yuri Lezhnikov
Yuri Filippov
Vasily Larionov The Volga near Bakhilova Polyana
Ilgiz Nasibullin Still Life with Apples
Symbolism .G. Symbolists are distinguished by their experimental nature, the desire for innovation, the use of symbolism, understatement, allusions, mystery and mystery, cosmopolitanism and a wide range of influences.
Symbolist artists: Aubrey Beardsley, Mikhail Vrubel. Anna Osipova, Vitaly Skobeev, Alexander Sulimov, Anna Tarasenko and others present a number of works in the style of symbolism at Art-most.com
Vitaly Skobeev
Alexander Sulimov "The Secret"
Anna Osipova "Springs inspired by the breath"
Anna Tarasenko “Himalayan Embrace”
There are, of course, many more trends in painting.