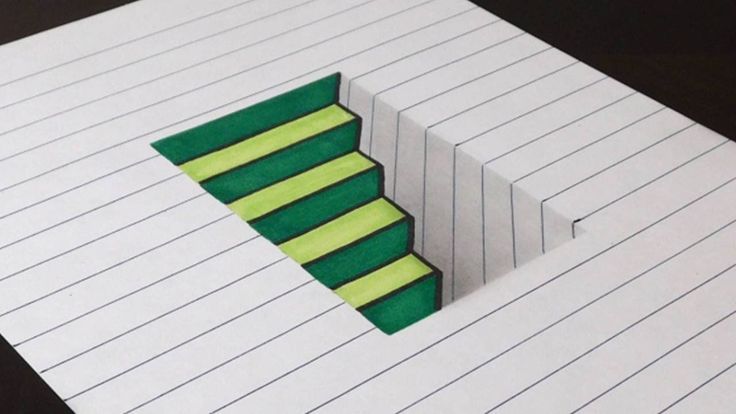
Fun optical illusions for kids
Optical Illusions For Kids - All Free and Cool! | Fractus Learning | Brain Illusions | Optical Illusion Pictures | Optical Illusionz | Optical Illusion Images
Skip to content
ByBryan Bigari Last Updated:
Optical illusions are fun ways to improve kids’ cognitive abilities. An optical illusion image stimulates problem–solving skills and visual memory recall because the child will want to figure out how it works.
Optical illusions are caused when the brain interprets the object that the eyes see differently. The rods and cones are the optic receptors in the eyes. What the eyes see is transformed into the brain as electric impulses which the brain interprets. The brain tries to make sense of what the eyes see. Optical illusions present something unusual to the brain.
Illusions aren’t hallucinations. An optical illusion is seeing an object differently, whereas a hallucination is viewing an object that isn’t there.
The three types of optical illusions are literal, cognitive, and physiological. A literal illusion is seeing an image as something different than the image or images displayed. Although the images exist, what you see is based on your perception. A cognitive illusion is how the brain interprets something new that wasn’t explained. It reveals how the mind relates one object to another and what it’s subconsciously thinking. With a physiological illusion, the brain is confused by what the eye sees with light, color, size, movement, and dimension. The brain rectifies its confusion and then interprets what the eye saw, which isn’t physiologically possible.
The first known optical illusion created was about 2500 years ago on the island of Lesbos in Greece. The coin shows the two animals facing each other forms a wolf face facing forward.
Confetti Illusion
How many different colored circles do you see?
Answer
The circles are all the same color.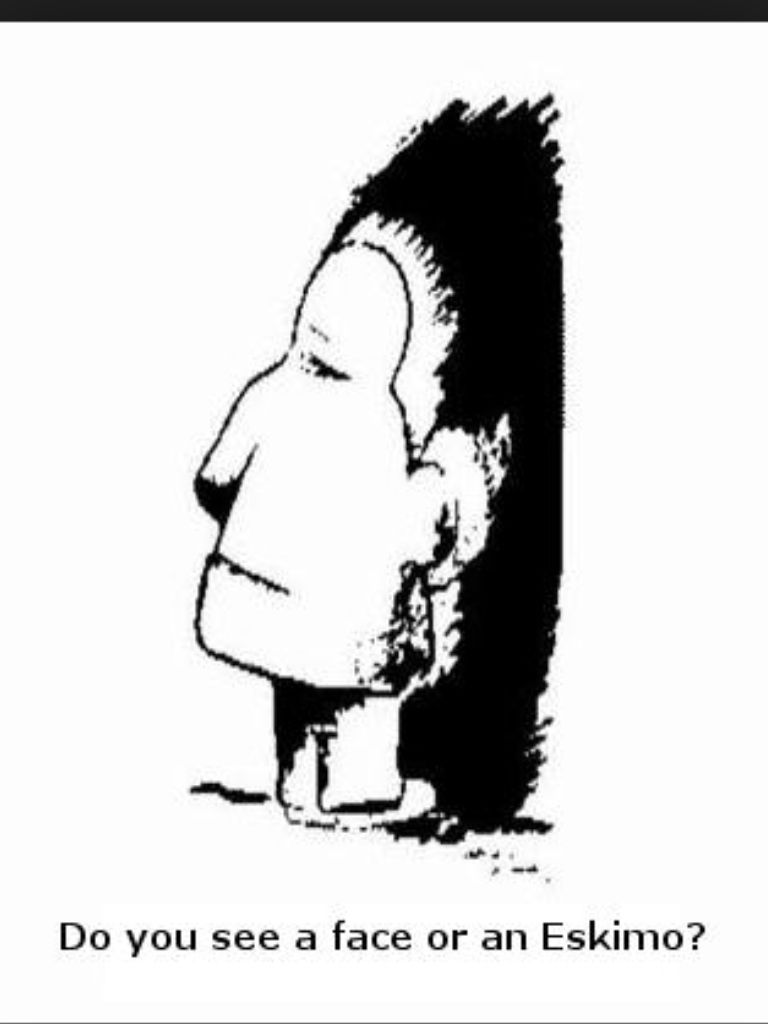 In July 2018, Dr. Novick, University of Texas professor, shared the Confetti illusion on Twitter. The optical illusion is an example of a Munker illusion where surrounding horizontal stripes in different colors influence the color perception of objects.
In July 2018, Dr. Novick, University of Texas professor, shared the Confetti illusion on Twitter. The optical illusion is an example of a Munker illusion where surrounding horizontal stripes in different colors influence the color perception of objects.
Image Source
Hermann Grid Optical Illusion
Take a look at this illustration. How many black dots do you see?
Answer
No, this isn’t an animated GIF. There are no black dots. There are only black blocks and white space. The high contrast presents the eyes the illusion of grey or black dots at the intersections. Focus on the dot, and you’ll see the dots are white.
Animal Optical Illusion
Take a look at this sketch. How many animals do you see?
Answer
Two: a rabbit is looking to the right, and the duck is looking to the left. The duck’s beak is the rabbit’s ears.
The illusion appeared for the first time in a German magazine in 1892.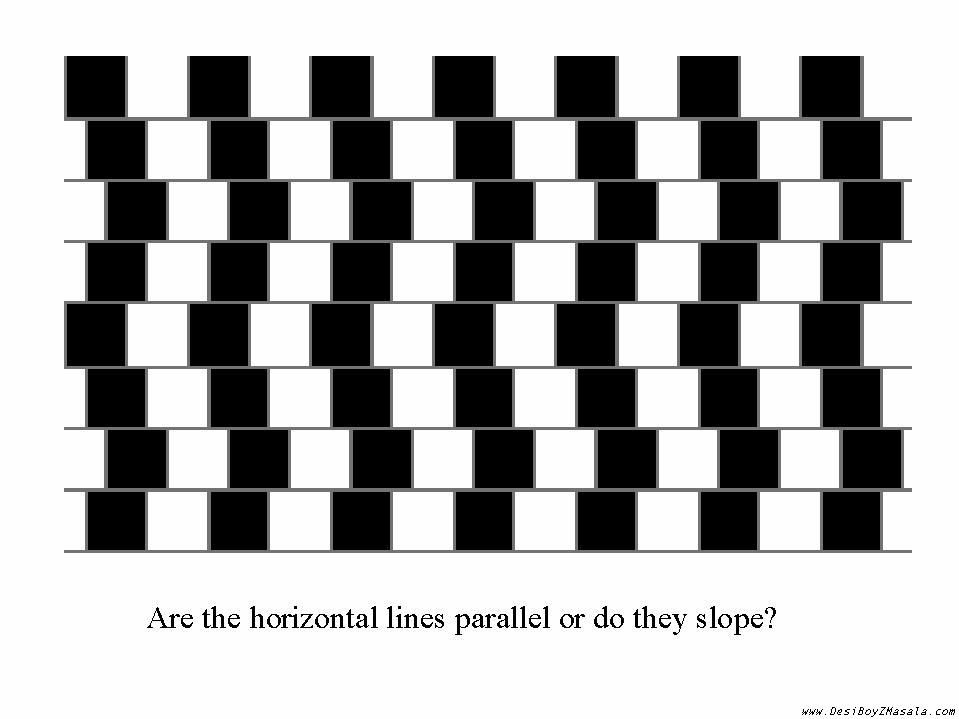 According to American psychologist Joseph Jastrow, the quicker you switch between the two animals, the more creative you are.
According to American psychologist Joseph Jastrow, the quicker you switch between the two animals, the more creative you are.
Elephant Leg Illusion
How many legs does this unusual elephant have?
Answer
It is a literal optical illusion. The brain perceives two different images in one. The artist drew one leg with a foot, four legs without feet and four feet without legs.
Kanizsa Triangle Optical Illusion
What patterns do you see? Do you see triangles? Discs?
Answer
Most people see a white triangle facing upwards and the outline of a black triangle downwards with three black discs. The symmetrical image is three black discs missing a triangular part and three pairs of lines. There is no large white triangle in the middle of the page – though I’m sure you see one!
Italian psychologist Gaetano Kanizsa described the illusion. It explains the law of closure where objects grouped seem to be part of a whole.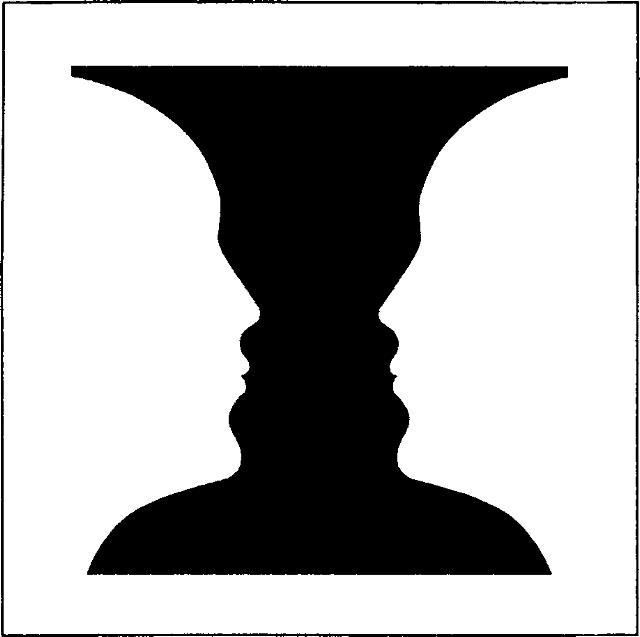 The brain ignores the gaps and perceives the contour lines as a whole.
The brain ignores the gaps and perceives the contour lines as a whole.
Color Gradient Optical Illusion
Which side of the inner rectangle is the darkest?
Answer
The bar is the same color. The optical illusion is lightness perception. The eyes perceive colors differently depending on the color in the background or foreground.
Muller-Lyer Optical Illusion
Observe the two lines with arrowheads on each end. Which line is the longest?
Answer
The lines are the same length. For most people, the line with the fins facing outward seems longer than the line with the spines facing inward. The illusion was created by a German psychologist F.C. Muller Lyar in 1889. Opinions differ on how the perceptual illusion works, whether it has to do with depth, size, or length
Wife or Mother-in-Law Illusion
Who do you see, the wife or the mother-in-law?
Answer
The mother-in-law’s nose is the wife’s jawline. The wife’s necklace is the mother-in-law’s mouth.
The wife’s necklace is the mother-in-law’s mouth.
British cartoonist William Ely Hill created this brainteaser in 1915. It’s almost impossible to see the wife and the mother-in-law’s faces at the same time. According to Australian researchers, people tend to see the faces of people of similar ages. Therefore, younger people see the wife and older people see the face of the mother-in-law.
If you can’t see the mother-in-law, focus on the wife’s right ear. If you can’t see the wife, focus on the mother-in-laws left eyelash.
Image Source
Impossible Trident Illusion
How many prongs are in the fork?
Answer
The impossible fork, also known as blivet, shows an object that can’t exist. At the one end, there are two rectangular prongs, and at the other end, it looks like three cylindrical prongs. It was discovered in 1964 when D. H. Shuster noticed an “ambiguous figure of a new kind” in the advertising section of an aviation journal.
Twelve Black Dots Illusion
How many dots do you see at the same time?
Answer
Most people can’t see all 12 dots simultaneously. The dots in the middle of their vision stay constant. Peripheral vision isn’t as clear. The brain guesses that the continuous pattern of white lines on a grey background continues peripherally and misses the black dots at certain intersections.
Although posted on Twitter and Facebook, the variation of the Hermann Grid was first published in 2000 in a scientific journal SAGE.
Pink or Grey Sneaker Illusion
What color is the sneaker?
Answer
The shoe is pink and white but many people see it as grey. The brain decides a color by considering the colors surrounding the object. Most people probably see the shoe as grey and teal because the brain takes into consideration the colors of the hand holding the shoe. Those who brains see a blue background depicts that the shoe is pink and white.
Zöllner Optical Illusion
Observe the diagonal lines in the image. Are the lines parallel?
Answer
German astrophysicist Johann K. F. Zöllner discovered this effect in 1760. The parallel diagonal lines intersect with short horizontal and vertical bars. It creates an image where the parallel lines seem to join and separate from each other. Scholars aren’t sure why this happens. It could be the way the brain adjusts angles, or it may be how it perceives depth. The illusion disappears when the colors in the image have equal values of red and green.
Lilac Chaser Illusion
Stare at the plus sign in the middle of the image for twenty seconds or so. What do you see happening in the circles around the +?
Answer
While staring at the + focal point, it seems as if the lilac dots move in a circle that changes to a space moving around the circle of lilac dots. After about 10-20 seconds a green dot appears that runs around the ring.
Vision expert Jeremy Hinton created the lilac disc in 2005. Apparent movement is when a person sees something in one spot and then in another place, and the brain perceives it as a movement. The green color is the afterimage. When a person stares at a color for a while and looks away, they may see the same color, which is the positive afterimage. Alternatively, they see the negative afterimage, which is the opposing color of the image.
Poggendorff optical Illusion
Observe the three lines on image. Which line does the black line connect to?
Answer
Although it seems as if the black line links with the blue line, it matches the red line. The image is distorted by the brain‘s perception of diagonal lines interacting with horizontal and vertical edges.
In 1860, German physicist Poggendorff received a letter from Johann Zöllner describing the illusion created by the fabric design. Poggendorff noticed the misalignment of the diagonal lines in the fabric design. The illusion is caused when a thin diagonal line is placed behind wider stripes at an angle.
The illusion is caused when a thin diagonal line is placed behind wider stripes at an angle.
Two Women Illusion
What do you notice about the women in the picture? Which one is shorter than the other?
Answer
The women are the same size – although they seem to be different sizes. The room appears square but distorts into a trapezoidal shape. The woman at the left is standing closer than the woman to the right, but it seems visually as if they are in the same depth of field. Hence, the one looks taller than the other.
Image Source
Ponzo Optical Illusion
Which yellow horizontal line is the longest?
Answer
The two yellow lines are the same length. The upper line seems longer because of the parallel lines converging in the distance. The perspective hypothesis explains the illusion. In three dimensions an object in the distance needs to be larger to appear the same size as a closer object.
Ebbinghaus Optical Illusion
Which of the two orange discs is smaller – the left one or the right one?
Answer
The orange discs are the same size. The illusion was discovered by German psychologist Hermann Ebbinghaus but was popularized in 1901 when published in a textbook by Edward Titchener. It is a size contrast illusion. The surrounding blue disc sizes influence the perception of the orange disc sizes.
Image Source
Hering Optical Illusion
Which way do the vertical lines bend?
Answer
The lines are straight. It seems as if the lines are bending outward due to the false impression of depth created by the radial background. German physiologist Ewald Hering discovered this geometric optical illusion in 1861.
Moon Illusion
Is the moon bigger when seen at the horizon than in the sky?
Answer
It seems as if the moon is more prominent, surrounded by scenery than high in the sky. The reason why the moon seems bigger closer to the horizon is due to depth perception. The trees, building, and surrounding images are the depth cues. In the sky, there aren’t any depth cues to relate to the moon. The color of the moon, atmospheric perspective, and visual factors influence how the moon’s size is perceived.
The reason why the moon seems bigger closer to the horizon is due to depth perception. The trees, building, and surrounding images are the depth cues. In the sky, there aren’t any depth cues to relate to the moon. The color of the moon, atmospheric perspective, and visual factors influence how the moon’s size is perceived.
Stroop Effect Illusion
Which is faster to read the words or ignoring the words but reading the color of each word?
Answer
It’s faster to read the text. J. Ridley Stroop discovered this marvel in 1930. When reading the color instead of the word, the brain receives conflicting messages. The Speed of Processing theory explains the interference because the text reads faster than words. According to the Selective Attention Theory, naming the color requires more attention than reading the text.
Strawberry Illusion
What color are the strawberries?
Answer
The strawberries aren’t red. There are no red pixels in the image; only cyan pixels. Japanese Psychology professor Akiyoshi Kitaoka published the picture on Twitter. The National Eye Institute explains that the brain ‘corrects’ the color when it perceives it in a different color.
There are no red pixels in the image; only cyan pixels. Japanese Psychology professor Akiyoshi Kitaoka published the picture on Twitter. The National Eye Institute explains that the brain ‘corrects’ the color when it perceives it in a different color.
Troxler’s Fading Circle Illusion
What happens to the circle when you stare at the dot in center of the ring for about 20 seconds?
Answer
The circle fades and disappears. In 1804, Swiss physician and philosopher Ignaz Troxler used the illusion to demonstrate how efficient the brain functions. The brain filters out unimportant and non-threatening information to focus on what’s important. When staring at the dot, the brain doesn’t receive any new information, and the circle fades into the white background as the brain disposes of unimportant data.
Image Source
Checkerboard Cylinder Shadow Optical Illusion
Take a look at the checkerboard pattern. What color is square A? Square B?
What color is square A? Square B?
Answer
The two checker squares A and B are the same color. The illusion is created by the way the brain interprets contrasts and shadow. The brain perceives a light source from the right that casts a shadow on the board. Therefore, square A seems darker than square B, but both are light grey. The checker shadow illusion was published in 1995 by MIT professor of Vision Science, Edwards Adelson.
Question-Answer Optical Illusion
What word(s) do you see in the painting?
Answer
Question and Answer are the two words. John Langdon’s painting is an example of an intentional perceptional illusion. It is a type of steganography where words are hidden in larger scenes. A person tends to perceive the larger picture and often misses the smaller details.
Image Source
Coffer Optical Illusion
How many circles do you see? How many rectangles?
Answer
There are 16 circles. Vision scientist Anthony Norcia form The Infant Laboratory at Smith-Kettlewell was one of the ten finalists in 2016 Best Illusion of the Year Contest with the Coffer Illusion. The brain identifies grouped objects to form edges and contours. Segmentation cues contradict the interpretation of a series of rectangular coffers with closed boundaries. The horizontal lines can represent a circle or the intersection of rectangles.
Vision scientist Anthony Norcia form The Infant Laboratory at Smith-Kettlewell was one of the ten finalists in 2016 Best Illusion of the Year Contest with the Coffer Illusion. The brain identifies grouped objects to form edges and contours. Segmentation cues contradict the interpretation of a series of rectangular coffers with closed boundaries. The horizontal lines can represent a circle or the intersection of rectangles.
Image Source
Bryan Bigari
Bryan Bigari is the current editor of Fractus Learning. As a father of three, Bryan has a passion for helping kids to both excel in school and have fun with friends and parents. He has worked on education issues at the state and federal level, and is looking forward to sharing his first hand education and toy knowledge with you.
Optical Illusions | Optics for Kids
This website uses cookies to deliver some of our products and services as well as for analytics and to provide you a more personalized experience. Visit our Cookie Notice to learn more.
Visit our Cookie Notice to learn more.
By continuing to use this site, you agree to our use of cookies. We’ve also updated our Privacy Notice. Visit our Privacy Policy to see what’s new.
What is an Optical Illusion?
Optical Illusions can use color, light and patterns to create images that can be deceptive or misleading to our brains. The information gathered by the eye is processed by the brain, creating a perception that in reality, does not match the true image. Perception refers to the interpretation of what we take in through our eyes. Optical illusions occur because our brain is trying to interpret what we see and make sense of the world around us. Optical illusions simply trick our brains into seeing things which may or may not be real.
Try out some of these illusions and discover just how tricky it can be for your brain to accurately interpret the images from your eyes. Click on any of the images below to begin your exploration of optical illusions.
Moiré
Are the pinwheels moving?
Answer: No, the wheels are not turning. The Moiré effect can produce interesting and beautiful geometric patterns.
Light Bulb
Stare closely at this light bulb for 25 seconds. Then immediately stare at a white wall or sheet of paper. What do you see?
Answer: You should see a glowing light bulb!
Elephant Legs
How many legs do I have?
Answer: Four
Teach
In this illusion you can see the word Teach and its reflection. Can you read the reflection too? What does it say?
Answer: Learn
The Animal
How many animals do you see in the image?
Answer: Look closely, you should be able to see a rabbit and a duck.
The Box and the Sphere
Keep your eyes on the dot. Is it in the front or in the back of the cube?
Ask a friend and see if they agree!
Color Blind
What number do you see in the circle?
Answer: You should be able to see the number 26, but people with various degrees of color blindess may only see the 2 or the 6.
Color Illusion
How many colors are present in the image?
Answer: One shade of green and one shade of red! <br /> <br /> It may look as if the two arms of the "X" use different shades of red, but in face the whole "X" only uses a single shade of red. Likewise, only one shade of green is present throughout the image.
Gradients
Which side of inset bar is darker?
Answer: They are both the same shade!
Hermann Grid Illusion
Count all the black dots you can see
Answer: There are no black dots.<br /> <br /> If you focus directly on each dot, you'll see that all of them are white.
Horizontal Lines
Are the horizontal lines sloping or straight?
Answer: All of the lines are straight.<br />
<br />
The black and white blocks are not aligned and thus fool your brain into thinking that the lines are sloping.
Kanizsa Triangle
How many triangles are present in the image?
Answer: There are no triangles.<br /> <br /> In reality there are only 3 V shapes and 3 shapes that look like Pac-Men.
Muller-Lyer Illusion
Take a very close look at the 2 vertical lines. Do you think one line is longer than the other?
Answer: They are the same size! Hard to believe; get out your ruler to measure the lines and see for yourself!
My Wife and My Mother-in-Law
How many figures can you see in the image below?
Answer: If you look closely, you can see both a young and an elderly woman.<br /> <br /> The picture, My Wife and My Mother-in-Law, is a good example of two images existing in one, and was published in 1915 by the cartoonist W.E. Hill.
Snakes
Are the circles moving in the image?
Answer: Look closely, they aren't moving.
Zollner Illusion
Do you think these lines are parallel?
Answer: They are parallel!
Refraction Illusion
Are both arrows pointing the same direction on the paper behind the glass?
Yes! This illusion demonstrations <a href="~/what-is-optics/refraction/">refraction</a>, the bending of light.
😮 30 Cool Optical Illusions: Brain Explosion | Interesting facts
We are used to taking the world around us for granted, so we do not notice how our brain deceives its own masters. The imperfection of our binocular vision, unconscious false judgments, psychological stereotypes and other distortions of world perception serve as a pretext for the emergence of optical illusions. There are a lot of them, but we tried to collect for you the most interesting, crazy and incredible of them.
Top Stunning Optical Illusions
Impossible Figures
At one time this genre of graphics was so widespread that it even got its own name - impossibilism.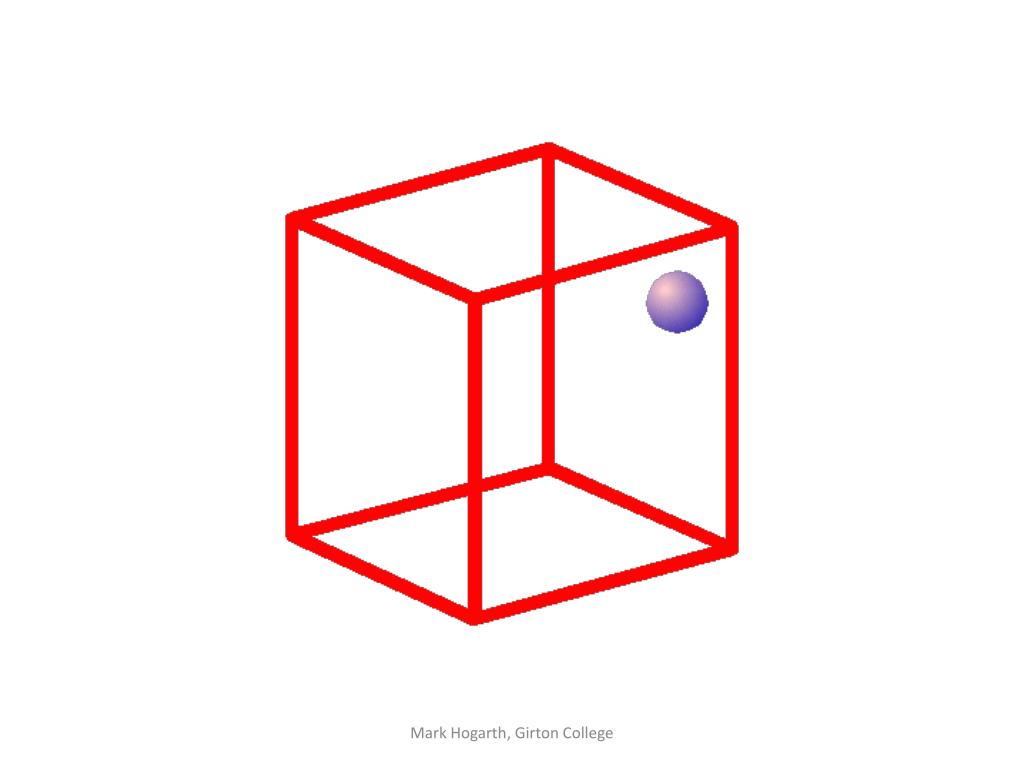 Each of these figures seems quite real on paper, but simply cannot exist in the physical world.
Each of these figures seems quite real on paper, but simply cannot exist in the physical world.
Impossible Trident
Classic Impossible Trident
Classic blevet is perhaps the brightest representative of optical drawings from the "impossible figures" category. No matter how hard you try, you will not be able to determine where the middle prong originates.
Another striking example is the impossible Penrose triangle.
Impossible triangle
It is also in the form of the so-called "endless staircase".
Infinite Penrose Stairs
And Roger Shepard's "impossible elephant".
Shepard's Impossible Elephant
Ames' Room
Adelbert Ames Jr. has been interested in optical illusions since early childhood. After becoming an ophthalmologist, he did not stop his research on depth perception, which resulted in the famous Ames Room.
Ames Room Optical Illusion
How the Ames Room works
In a nutshell, the effect of the Ames Room can be expressed as follows: it seems that two people, a dwarf and a giant, are standing in the left and right corners of its back wall. Of course, this is an optical trick, and in fact these people are of quite ordinary height. In reality, the room has an elongated trapezoidal shape, but because of the false perspective, it seems to us rectangular. The left corner is farther away from the visitors' view than the right corner, and therefore the person standing there seems so small.
The principle of the Ames room
Illusions of movement
This category of optical tricks is of the greatest interest to psychologists. Most of them are based on the subtleties of color combinations, the brightness of objects and their repetition. All these tricks mislead our peripheral vision, as a result of which the perception mechanism goes astray, the retina captures the image intermittently, spasmodically, and the brain activates the areas of the cortex responsible for detecting movement.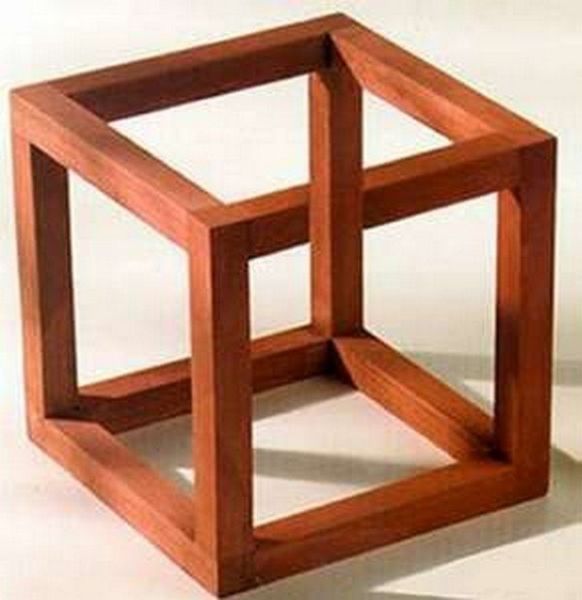
Floating star
It's hard to believe that this picture is not an animated gif-format, but an ordinary optical illusion. The drawing was created by Japanese artist Kaya Nao in 2012. A pronounced illusion of movement is achieved due to the opposite direction of the patterns in the center and along the edges.
"Floating Star" Kaya Nao
There are quite a few such illusions of movement, that is, static images that seem to move. For example, the famous spinning circle.
A spinning circle
Or yellow arrows on a pink background: when you look closely, they seem to sway back and forth.
Moving hands
Warning, this image may cause eye pain or dizziness in people with weak vestibular apparatus.
Rays from the center
Honestly, this is a regular picture, not a gif! Psychedelic spirals seem to drag somewhere into the universe full of oddities and wonders.
Striped spirals
Flipped illusions
The most numerous and fun genre of drawings-illusions is based on changing the direction of looking at a graphic object. The simplest upside-down drawings just need to be rotated 180 or 90 degrees.
Nurse or old woman
Two classic flip-flop illusions: nurse/old woman and beauty/ugly.
Beauty or ugly
A more artistic picture with a twist - when rotated 90 degrees, the frog turns into a horse.
Horse or frog
Other "double illusions" are more subtle.
Girl / old woman
One of the most popular dual images was published in 1915 in the cartoon magazine Puck. The caption to the drawing read: "My wife and mother-in-law."
The most famous optical illusions: the old woman and vase profiles
Old people / Mexicans
An elderly couple or Mexicans singing to the guitar? Most see old people first, and only then do their eyebrows turn into a sombrero, and their eyes into faces.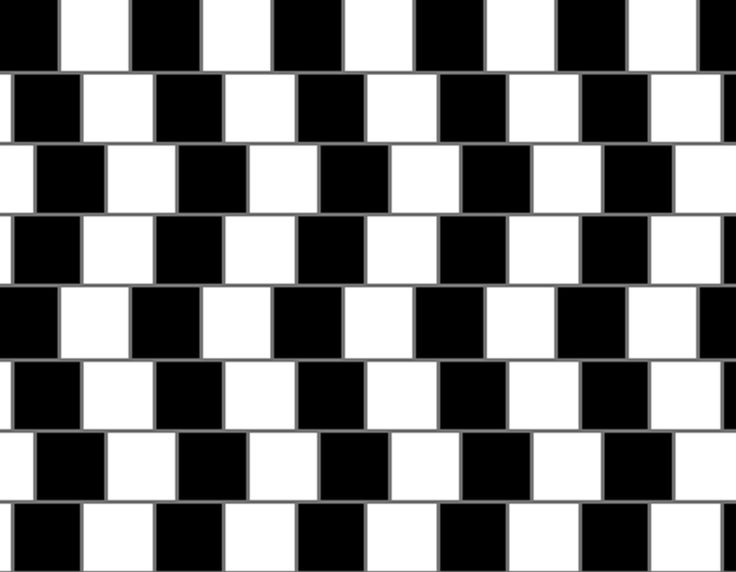 The authorship belongs to the Mexican artist Octavio Ocampo, who created many pictures-illusions of a similar nature.
The authorship belongs to the Mexican artist Octavio Ocampo, who created many pictures-illusions of a similar nature.
Old men/Mexicans Octavio Ocampo
Lovers/dolphins
Surprisingly, the interpretation of this psychological illusion depends on the person's age. As a rule, children see dolphins frolicking in the water - their brain, not yet familiar with sexual relationships and their symbols, simply does not isolate two lovers in this composition. Older people, on the contrary, first see a couple, and only then dolphins.
Dolphins or lovers - another interesting optical illusion
The list of such dual pictures is endless:
The well-known Eskimo Indian
In the picture above, most people first see the face of the Indian, and only then look to the left and distinguish the silhouette in a fur coat. The image below is usually interpreted by everyone as a black cat, and only then does a mouse appear in its contours.
Cat or mouse?
A very simple upside-down picture - you can easily make something similar with your own hands.
Snow White or Sherlock Holmes?
Illusions of color and contrast
Alas, the human eye is imperfect, and in our assessments of what we see (without noticing it) we often rely on the color environment and the brightness of the background of the object. This leads to very interesting optical illusions.
Gray squares
Optical illusions of colors are one of the most popular types of optical illusion. Yes, yes, squares A and B are painted in the same color.
Squares A and B are actually the same color
This trick is possible due to the way our brains work. A shadow without sharp borders falls on square B. Thanks to the darker "environment" and smooth shadow gradient, it seems to be much lighter than square A.
And here is the proof
Green Spiral
There are only three colors in this photo: pink, orange and green.
The blue color here is just an optical illusion
Don't believe me? Here's what happens when you replace pink and orange with black.
Without a distracting background, you can see that the spiral is completely green
Is the dress white and gold or blue and black?
However, illusions based on the perception of color are not uncommon. Take, for example, the white and gold or black and blue dress that conquered the Internet in 2015. What color was this mysterious dress, and why did different people perceive it differently?
The explanation of the dress phenomenon is very simple: as in the case of gray squares, it all depends on the imperfect chromatic adaptation of our organs of vision. As you know, the human retina consists of two types of receptors: rods and cones. Rods capture light better, while cones capture color. Each person has a different ratio of cones and rods, so the definition of the color and shape of an object is slightly different depending on the dominance of one or another type of receptor.
Rods capture light better, while cones capture color. Each person has a different ratio of cones and rods, so the definition of the color and shape of an object is slightly different depending on the dominance of one or another type of receptor.
Those who saw the white and gold dress noticed the brightly lit background and decided that the dress was in shadow, which means that the white color should be darker than usual. If the dress seemed blue-black to you, then your eye first of all paid attention to the main color of the dress, which in this photo really has a blue tint. Then your brain judged that the golden hue was black, brightened due to the rays of the sun directed at the dress and the poor quality of the photo.
Mysterious white and gold or black and blue dress
The actual dress was blue with black lace.
The dress turned out to be blue and black
And here is another photo that baffled millions of users who could not decide if it was a wall in front of them or a lake.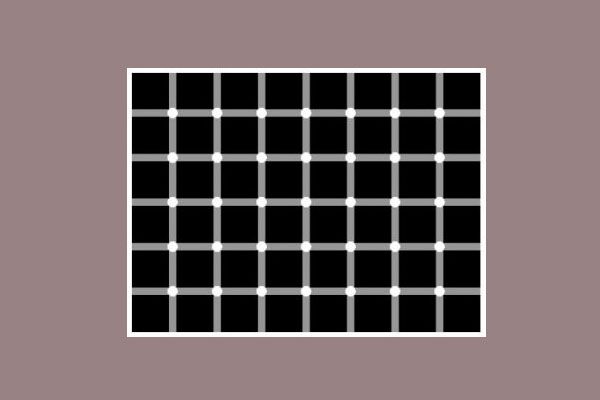
Wall or lake? (correct answer is a wall)
Disappearing circles
Optical illusions on the video
Ballerina
This crazy optical illusion is misleading: it is difficult to determine which leg of the figure is the supporting one and, as a result, to understand in which direction the ballerina is spinning. Even if you succeeded, while watching the video, the supporting leg can “change” and the girl seems to start to rotate in the other direction.
The most popular optical illusion "Ballerina"
If you could easily fix the direction of the ballerina's movement, this indicates a rational, practical mindset. If the ballerina rotates in different directions, this means that you have a stormy, not always consistent imagination. Contrary to popular belief, this does not affect the dominance of the right or left hemisphere.
Monster Faces
If you look at the cross in the center for a long time, then peripheral vision will frighteningly distort the faces of celebrities.
Monster Face Illusion
Optical Illusions in Design
Illusions of the eye can be a spectacular tool for those who want to spice up their home. Very often, “impossible figures” are used in design.
It seemed that the impossible triangle was doomed to remain only an illusion on paper. But no, the design studio from Valencia has immortalized it in the form of a spectacular minimalist vase.
Impossible triangle vase
Bookshelf inspired by the impossible trident. Designed by Norwegian designer Bjorn Blikstad.
Blikstad's "impossible" bookshelf
Here's a bookcase inspired by one of the most famous optical illusions, Johann Zöllner's parallel lines. All shelves are parallel to each other - otherwise what would be the use of such a cabinet - but even for those who have long acquired such a rack, it is difficult to get rid of the impression of slanted lines.
Inclined shelving
The creators of the Zellner rug were inspired by the same example.
Curvature of lines - optical illusion
Of interest to fans of unusual things is a chair designed by Chris Duffy. It seems that it relies solely on the front legs. But if you dare to sit on it, you will realize that the shadow cast by the chair is its main support.
Chair on two legs
parallel lines become non-parallel)
Illusions that have become popular on the Web (and how they work)
really. Optical illusions are known to play a cruel joke on our perception, easily deceiving our senses, means of perception and analysis, and ultimately us.
Magic? Accident? System bug? Do you want to learn new interesting illusions, solve them and understand how they work? Well, we are ready to show our readers such unusual examples. And although the mechanisms of work and influence of these illusions are different, they all have one thing in common - they are extremely interesting and charming!
1.
 An optical illusion containing 25 hidden animals
An optical illusion containing 25 hidden animals
There are about 25 animals hidden in this image, and the task of the illusionist, set before the audience, is to identify them in 2 minutes. If you succeed at this, you will be in the top 0.1% of players who can!
The portrait was made in the style of the 16th century Italian painter Giuseppe Arcimboldo.
Hint: you can find an elephant, a horse, a tiger, a fox, a kangaroo, and also a bear in the picture.
A sloth, a grasshopper and a peacock are also hiding somewhere in the image.
Players with good attention to detail can even find a turtle, a rabbit, and a gorilla.
See also
12 optical illusions
2. Which wardrobe is bigger? They are the same!
Hammonds Furniture
Hammond Furniture's painting shows how easy it is to fool viewers who are looking at two-dimensional images.
The illusion that two wardrobes are completely different sizes when placed next to each other.
However, both cabinets are exactly the same size (yes, we are surprised too)!
It's our brain that wants to see a 2D image in 3D, which makes us think that the cabinets are different sizes. The illusion was first described by Roger Shepard in 1990, when he demonstrated the differences between simple geometric properties and their perception.
This image shows two identical parallelograms (in this case the top of the cabinets) that appear to be different sizes.
Since we live in a 3D world, we naturally adapt to 2D images in our own 3D interpretation, which occurs in this optical illusion.
The purple top cabinet on the left looks narrow and thin due to its vertical position.
3. An optical illusion that will determine whether you are an introvert or an extrovert
A new optical illusion can say a lot about you.
For example, a picture can tell if you are an extrovert or an introvert. Just look at it!
Just look at it!
The picture shows a turquoise circle with a face and two birds forming a luxurious mustache on a black background.
You have to look at the image for a short amount of time (a second or two is enough) to notice what you saw first.
In one case, you can first see the round face of the moon, and in the other two birds creating a "whisker".
If you see the face of the blue moon first, it means you are an introvert, according to Jagran Josh, an Indian educational web portal.
It also means that you are a sensitive, kind person who avoids conflict and has an amazing intuition to stay away from difficult problems.
It also means that you learn from your mistakes if problems do arise, and you draw the right conclusions!
And if you catch a glimpse of birds first, it shows that you are a welcoming and cheerful extrovert.
This means that you enjoy life to the fullest, are carefree, cheerful, spiritual and playful.
It also means that you can be friendly to other people, open and pleasant in communication.
See also
10 optical illusions that were recognized as the best in 2019: video0007
Getty Images / iStockphoto
Optical illusions can sometimes be confusing.
Thus, netizens were absolutely discouraged by the playing card, as many only recently noticed its obvious feature.
While most people have been using decks of cards for their intended purpose for years, many social media fans have been stunned by the design of one of them.
The space between the diamonds on the “eight of diamonds” resembles the number “8” itself.
By the way, it's interesting that this card is the only one in the deck with such a secret function. So the next time you hold cards, you can surprise your friends with a sudden discovery!
5. The hidden symbol in an optical illusion can reveal your worst character traits
A new optical illusion can reveal a lot about you as a person.
In the image, what you see first may reveal one of your worst personality traits.
Visual personality tests take only a few seconds and are thought to give you an idea of your various characteristics.
In this illusion, viewers must see four things - a woman, a river, a bridge, and a boat.
The first thing you look at says a lot about one of your narcissistic traits.
Narcissists have a distorted self-image, need constant admiration, and often lack empathy.
So what do you see first?
Woman
If you saw a woman first, your worst character trait is focus on appearance .
It doesn't mean you're conceited or judging others by how they look, but that's what you do when you're feeling stressed.
In addition, you have a tendency to assert yourself by comparing your appearance with others.
Also, you can't help but look at your own appearance, as well as at the appearance of others, when you feel insecure.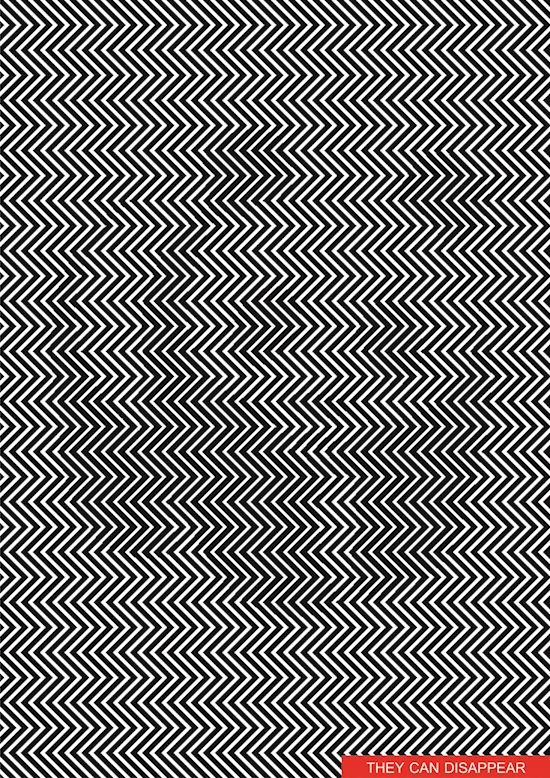
River
According to Your Tango, if you see a river first, your worst personality trait is focus on one's social status .
You think that the quality of your relationships with other people is the most important thing in the world.
But it can be difficult for you to shift your focus from your own career aspirations to the people you love.
This means that people's social status can mean much more to you than how they treat you or other people.
Bridge
Spotted the bridge first? This means that your worst character trait is lack of empathy .
Lack of empathy does not mean you are cold or incapable of feeling.
But being aware of another person's feelings is not always your prerogative.
Boat
If you saw a boat when you first looked at the illusion, then your worst character trait may be self-importance .
You may be a wonderful person, but you don't need to make life difficult by assuming you have all the skills to do any job in the world.
Sometimes it's important to put your ego aside and rely on the skills of others.
See also
20 optical illusions that show the imperfection of our brain and eyes
6. Optical illusion shows 10 hidden persons - and not many people can find them all
Painting Valley 9000 9000 caused a real headache on the Internet - as many people try to solve it, but only 1% of them manage to distinguish all the contours of male and female heads in the picture.
Many viewers can see only a part of the faces hidden in the branches and in the drawing of the tree. But in fact, in the image, there are 10 of them…
The illusion known as the Tree of National Leaders is said to include the faces of Margaret Thatcher and Mikhail Gorbachev.
Others claim the drawing dates from 1880 and was created for Harper's Illustrated...
So, how many faces can you find?
7. Optical illusion with color changing circles
Lenstore
A moving illusion in which the blue circle appears to change color.
But the truth is that the color of the circle doesn't really change at all.
This optical illusion of color saturation shows how easily we can be fooled when trying to distinguish colors.
This illusion works directly with our brain, which determines the color of the circle when compared to other colors and the background of the environment.
An illusion can confuse viewers, but it also proves how static images can really deceive us.
Sujata Paul, Head of Professional Services at Lenstore, explained why these illusions deceive people.
Optician said:
"We have cells in the retina, some of which are called cones, they determine the color, and others are called rods, which determine the brightness.
"
It is they who transmit information by means of signals through the optic nerve to the brain, where it then tries to figure out what we see, according to the signals it receives.
"Certain exposure to brightness, patterns and colors can affect perception, and that's what happens when we see this optical illusion of color saturation."
8. Cat and Dog Optical Illusion - What You See First Will Tell You a Lot two favorite animals.
And what you see first will not only show if you like cats or dogs, but also give an idea of your personality.
The colorful design features one dog, a two-tone long-eared spaniel and two cats side by side.
So if you see puppy first, then, as psychologists say, people who prefer dogs are more likely to be loyal and friendly.
They are also playful, easy to talk to and often just outgoing. They love to communicate with loved ones and enjoy communication.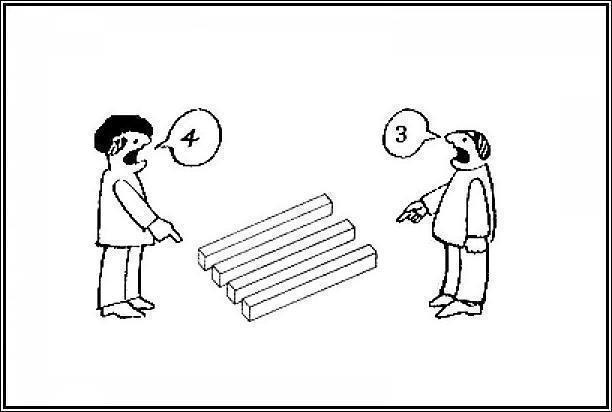 Such people are more likely to be productive in their relationships and very loving. It is said that they can get lonely if they don't have company, but they tend to look on the bright side of things.
Such people are more likely to be productive in their relationships and very loving. It is said that they can get lonely if they don't have company, but they tend to look on the bright side of things.
Meanwhile, those who have noticed a cat will have other character traits.
First of all, they say that people who prefer cats are more purposeful and motivated.
They are more likely to enjoy their own company (when alone), be introverted or independent.
See also
10 classic and modern illusions that were widely discussed by Internet users
9. A confusing optical illusion: does a square have straight or curved lines?
Gala Spins
Here is another illusion confusing the Internet. It includes squares in the puzzle that are not clear whether they have straight or curved lines.
In a survey, 77% of British adults said the square had straight lines, not curved. .. So what do you see?
.. So what do you see?
Optometrist Bhavin Shahom explains:
“Our visual system does not process peripheral vision in the same way as central vision. Peripheral vision uses fast processing, where accuracy is not as important as speed."
Expert added:
“There is also some post-image processing that takes place at the periphery of the retina to increase contrast. This means that the perception can be changed to make the details stand out more.”
10. Disappearing Chip Optical Illusion
Rainbow Riches Casino
Optical illusions can confuse many people.
And now a new version of the classic illusion has been created, and we think that it can quite confuse itself!
It was inspired by the Troxler effect, also known as the Troxler phenomenon.
If you look at a certain point, even for a short period of time, everything that is outside this point will begin to disappear, and this will significantly change the person's perception of what is really there.