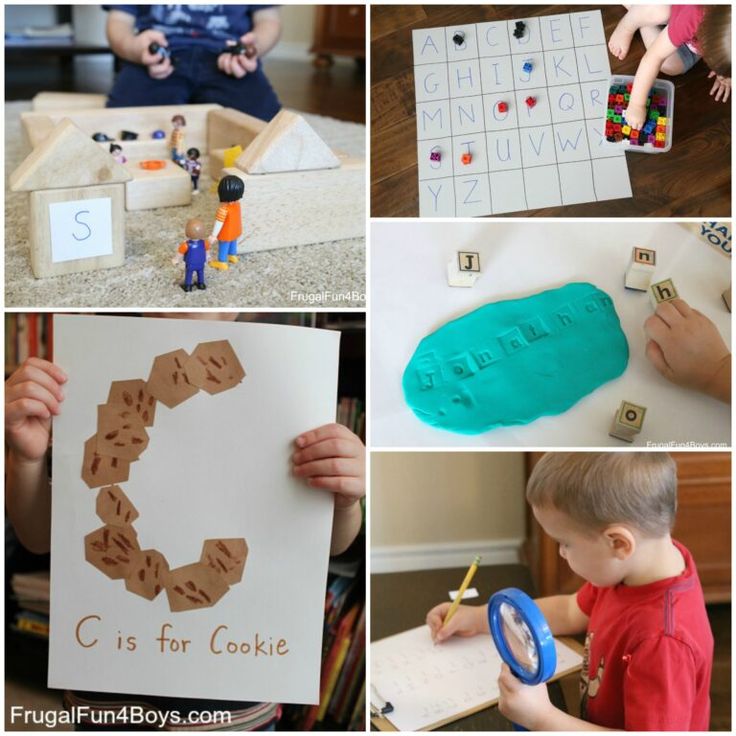
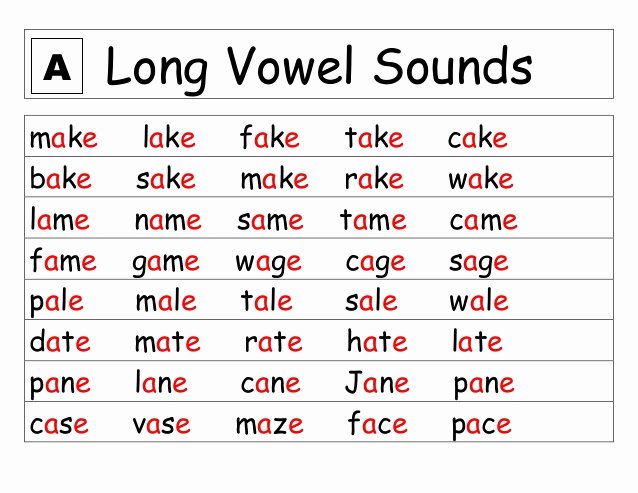
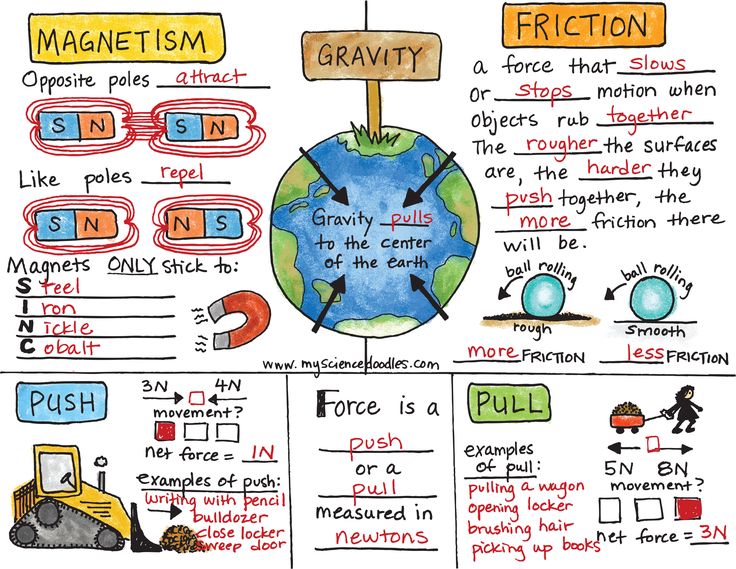
Hands on math activities for preschoolers
Hands-On Math Activities for Preschoolers
Disclosure: This post contains affiliate links to Amazon. See my disclosure policy for details.
Math is so fun to teach to preschoolers because there are a lot of daily activities that incorporate math. Preschoolers don’t need worksheets for math…they should learn through play and hands-on activities.
1. Patterns with Bears
Counting Bears are a great math manipulative to use with preschoolers. You can sort, count, or use them with patterns.
I created some pattern cards to help with this. The first page is an AB pattern, meaning two colors alternate in the pattern. The second page is an ABC pattern, meaning three are three colors in the pattern. For this activity, your preschooler will set the colored bear on top of the matching color to create a pattern. On the ABC pattern cards, the last circle is left empty. That is for your child to tell you what color it should be.
You can get the color patterns printable at the bottom of this post.
Math Skill: Patterns and Relationships
You can find more pattern activities here.
2. Sorting Colors with Bears
Sorting is a skill preschoolers should work on a lot. One way to sort is by color. We do this with our counting bears and a sorting mat.
You can get the sorting mat printable at the bottom of this post.
You can even use colored tape and pom poms to practice sorting! Add in some tweezers for some extra fine motor practice.
We also love counting mats! These are great for learning to count and working on one-to-one correspondence.
Math Skill: Patterns and Relationships
3. Money Muncher
A fun way to work on sorting is with the Money Muncher! It’s also a great activity for fine motor skills. To see all the fun details, click here.
Math Skill: Patterns and Relationships
4. Sorting Jelly Beans
Anytime we work with candy, my kids love it! You can sort M&Ms or jelly beans or whatever! To see how we did this with jelly beans, click here.
You can get the jelly bean sorting printable at the bottom of this post.
One more idea for sorting is by using toy animals. Have them sort by different characteristics, such as land animals and sea animals.
Math Skill: Patterns and Relationships
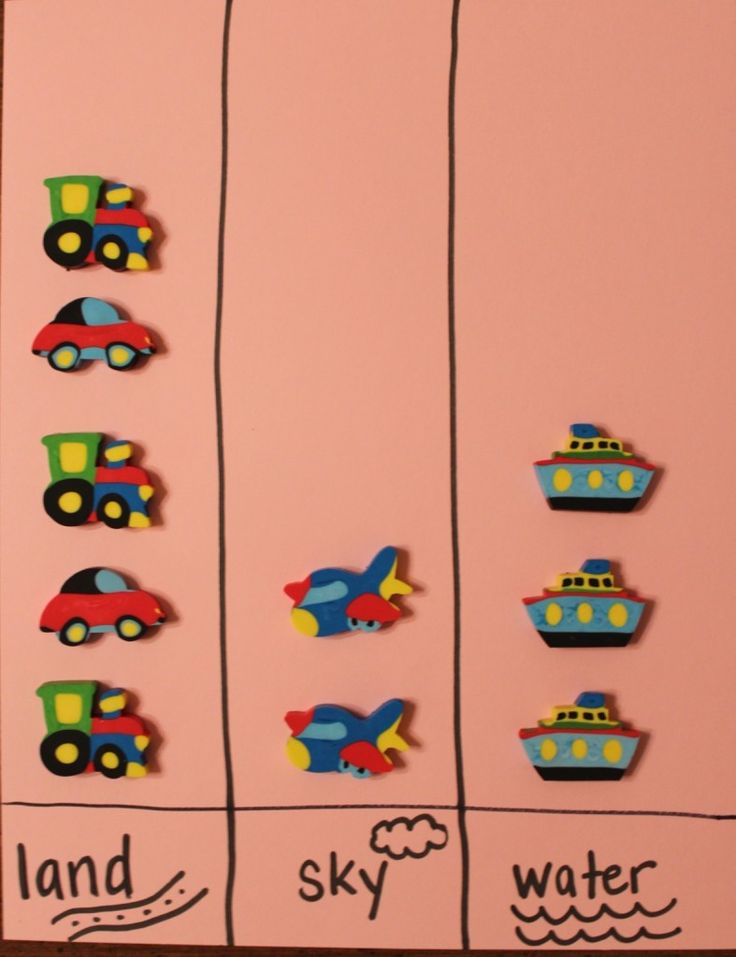
5. Graphing
Graphing is always good to introduce to preschoolers. It doesn’t have to be complex, but you can do a simple activity like graphing the types of transportation on a bar graph and use small pictures or toys (or I used erasers from The Dollar Tree).
Make graphing hands-on using apples! Even young preschoolers can begin learning about graphing with this activity.
Check out this free gumball graphing activity right here.
Math Skill: Patterns and Relationships
6. Shape Wheel
This is a fun activity for learning shapes! Just print this shape wheel and draw the same colored shapes onto clothespins. Have your child match the clothespin to the shape on the wheel. This is great for working on fine motor skills!
Have your child match the clothespin to the shape on the wheel. This is great for working on fine motor skills!
You can get the shape wheel printable at the bottom of this post.
Math Skill: Geometry
7. Shape Sorter
An easy way to practice shapes is with a Shape Sorter! I bought these shapes at Michaels Craft Store many years ago, but these 3D geometric shapes would be a good option if you’re interested in creating a Shape Sorter. Check out this post for details on how to make this easy math activity.
Math Skill: Geometry
8. Noodle Shape Cards
A neat sensory activity and a fun way to learn shapes are with noodles! See the post here to download the free shape cards.
Math Skill: Geometry
9. Foam Sticks
Learn shapes in the tub with these foam sticks! You can see how we did this here.
Another fun way to practice shapes is with the cookie shapes matching activity!
And my favorite way to teach about shapes is with my shape rhymes!
10. Dice Game
Dice Game
This is a really fun game! I took this Melissa & Doug wooden toy and put white circle stickers on the top of the pegs. I wrote numbers 1-6 and had 2 stars. I had my son roll the dice and whatever number it landed on, he would pound with a toy hammer. If the number he rolled was already down, he hit the star. Not only was this fun for him, but he was able to “subitize”, which simply means to recognize numbers instantly without counting the dots.
Math Skill: Number Concepts
11. Star Number Cards
Practice counting and recognizing numbers with star number cards. This one is great for working on one-to-one correspondence and fine motor skills.
You can get the star number printable cards at the bottom of this post.
Math Skill: Number Concepts
12. Ladybug Math
We made these adorable ladybugs and they were a hit! Not only were they fun to play with, but we did a lot of counting and sorting with them. Read all about it here.
Read all about it here.
Math Skill: Number Concepts
13. Balloons
Learn the order of numbers with this really fun game involving balloons! Check out the details here.
Math Skill: Number Concepts
14. Estimating with Water
We learned about estimation with a dropper with some fun, hands-on water activities.
Math Skill: Measurement
15. Pouring and Comparing
We practiced pouring skills with rice into these beakers. Then I had my son line them up from biggest to smallest. Using comparative words like big/small or empty/full help teach preschoolers about simple concepts of measurement. This is simple and you could elaborate on this activity.
One more easy way to practice measurement is with Unifix cubes. Place different lengths of tape on the floor or poster board. Then have your child use Unifix cubes to measure the lines. This is a simple way to practice counting, measuring, and comparing lengths.
This is a simple way to practice counting, measuring, and comparing lengths.
Math Skill: Measurement
Lastly, check out this really easy and fun way to practice counting!
If you’re looking for digital math activities, make sure to check out my counting activities using Google Slides.
If you’d like to download the 5 free printables I shared in this blog post, just click on the button below!
Preschool Math Activities that are Super Fun!
If you are looking for preschool math activities then you're in luck! I gathered my favorite hands-on math activities and math center ideas for preschool and I am sharing them here!
Math skills are so important and finding playful and engaging ways to teach those skills to preschoolers is crucial. Whether you teach math to a classroom full of preschoolers or homeschool one or two at home, it's important to use hands-on math experiences.
This is a list of the best preschool math activities that I could find! I hope they will be super helpful to you.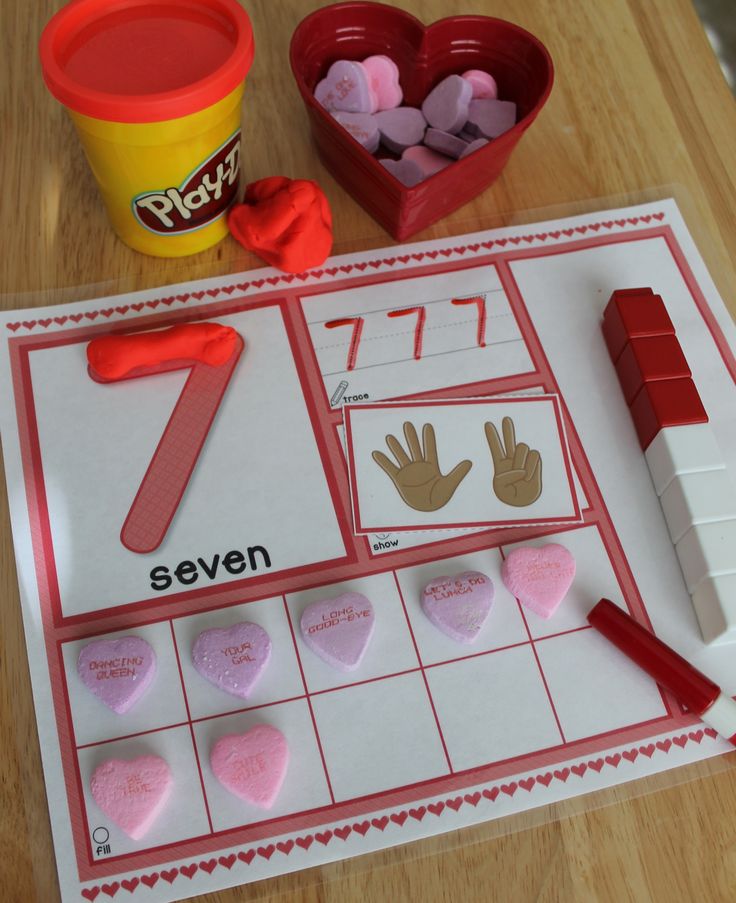
Hands-On Preschool Math Activities
1. Roll and Dot the Number is a quick preschool math game that will teach kids to identify numbers and count while learning one to one correspondence! It is one of our favorite preschool math activities!
2. This Build and Measure Block Center is such a neat way for kids to explore measurement!
3. These Counting Bears Number Strips are a hands-on way for toddlers and preschoolers to learn numbers, counting and even colors.
4. These Tree Play Dough Numbers Mats are a great way to work on a number of math skills including counting to 10!
5. Work on color recognition and sorting with these Button Sorting Cups.
6. This Simple Fine Motor Counting Math Tray is super easy to set up and provides excellent fine motor practice too.
7. Grab your craft sticks and make these Colors and Patterns craft sticks for your math center!
8. Teaching Symmetry to Preschoolers with LEGO DUPLO is perfect for teaching symmetry to preschoolers and young kids.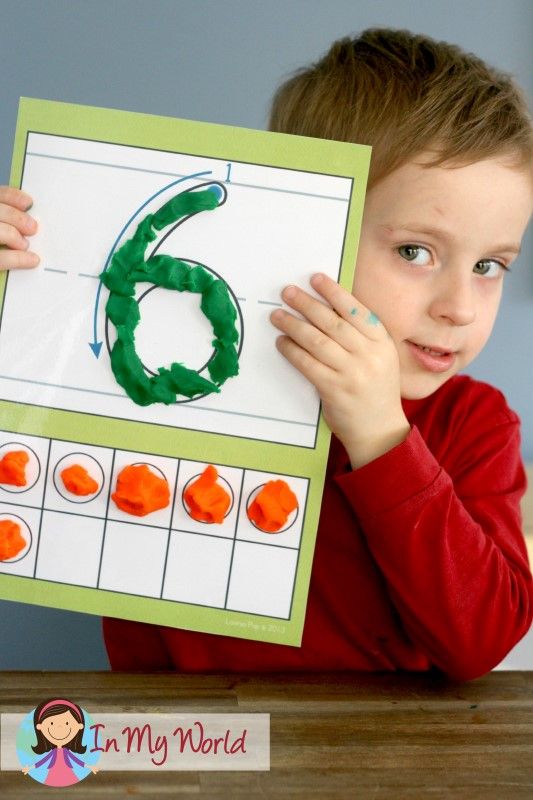
9. Your kids will have a blast learning to count with Bugs in a Jar!
Preschool Math Activities that are Fun and Engaging!
10. These DIY Tactile Counting Sticks are very easy to make and are perfect for kids who are learning to count.
11. Measuring with Bear Counters is an excellent way to introduce preschoolers to measurement!
12. I love this Play Dough Geometry activity! All you need is play dough and craft sticks!
13. This Pattern Making activity only requires a few common supplies. It's a hands-on way to introduce young preschoolers to patterns.
14. Number learning is really fun with this Car Parking Numbers Game!
15. Your kids will love learning about shapes with this Preschool Shape Scavenger Hunt!
16. This Number Pocket Game is a hands-on way for young preschoolers to learn numbers.
17. This Car Color Sort math activity is a great way for kids to practice sorting while playing with cars.
18. This Smack the Number Counting Game is fun way to practice number recognition and one to one correspondence.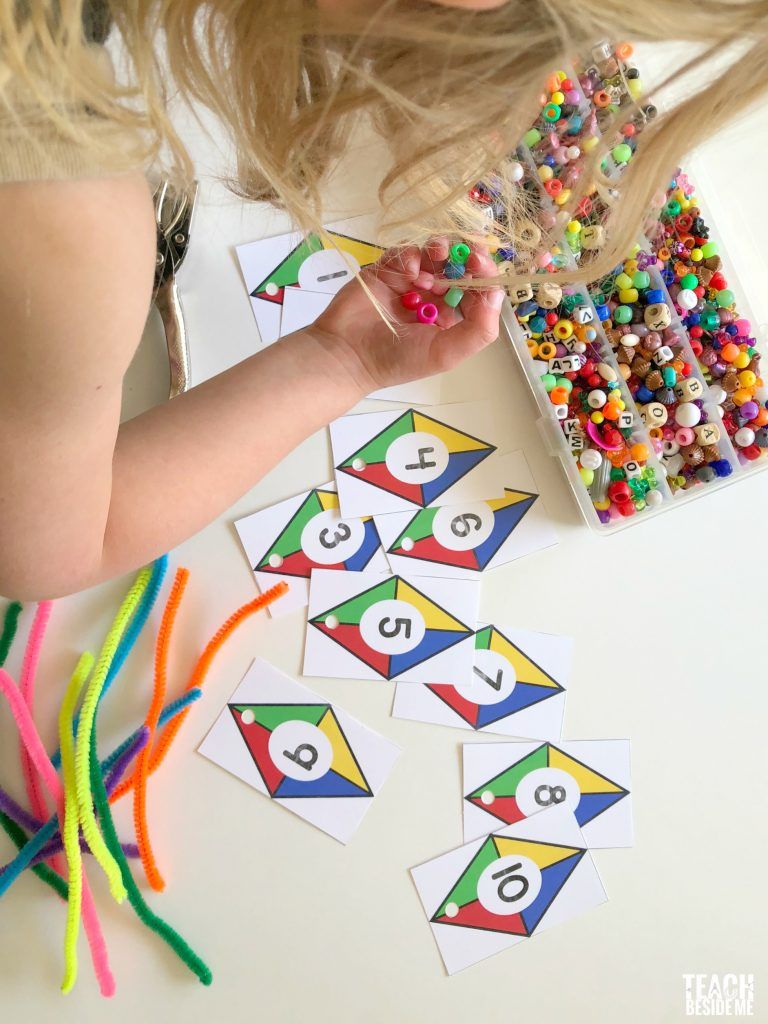 This was one of our favorite preschool math activities when my son was younger.
This was one of our favorite preschool math activities when my son was younger.
Math Activities for Preschool Math Centers
19. Make counting practice a game with this Race to Fill the Cup activity! This is a must-do when it comes to preschool math activities!
20. Finding shapes with I Spy Shape Glasses is a totally cool idea!
21. Counting and Measuring with LEGO is a fun way to work on counting, ordering and measuring numbers!
22. Take the learning outdoor with this super cool Pool Noodle Abacus!
23. This Button Counting Activity is a hands-on way for preschoolers to learn numbers and practice counting!
24. Work on fine motor skills and counting in this neat Counting beads on pipe cleaners activity!
25. Use clothespins to reinforce fine motor skills, colors and match numbers in this Hickory Dickory Dock Matching Clothespins activity!
26. This Printable Number Puzzle is a great way to work on a variety of ways to represent numbers.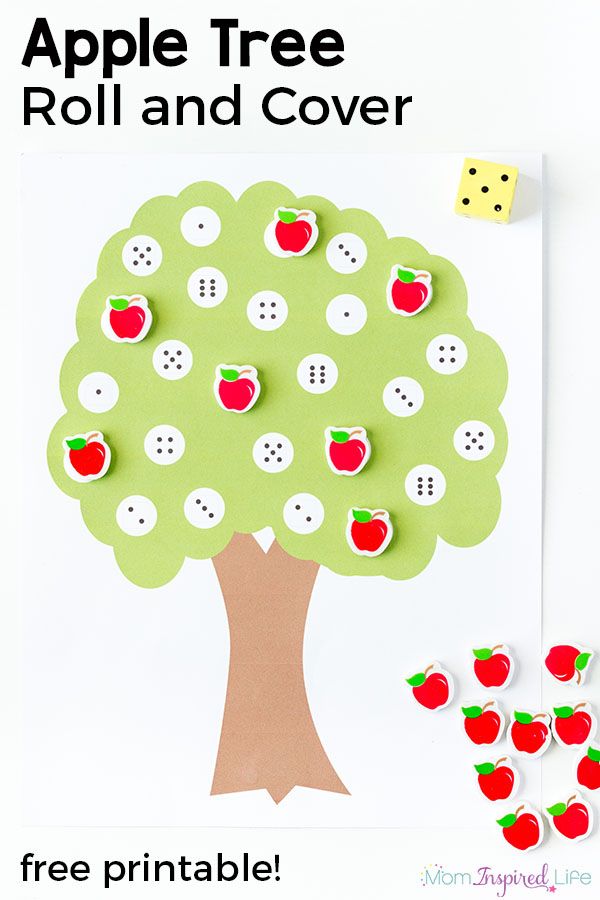
27. This Play Dough Math Invitation is open-ended and will keep preschoolers busy while learning a variety of math skills.
Even More Hands-On Math Activities for Preschoolers
28. These fun Farm Animal Rainbow Counters activity helps preschoolers learn to count and compare more or less!
29. Your kids will work on direction following, ordinal numbers and important vocabulary in this Matching Paths activity!
30. Your kids will have fun counting with this Ladybug Counting Busy Bag!
31. Counting Nature is a great way to work on counting and explore nature!
32. Your kids will have a ton of fun with Play Dough Addition.
33. Exploring Symmetry with Art is an awesome idea!
34. Use a Numbered Nature Tray to encourage number skill work while exploring nature!
35. This Play Dough Color Match Learning Activity is a fun way for kids to learn colors, matching, and sorting!
36. Your kids will love these 3 Counting Bear Activities for the Balance Scale!
37. This Counting Math Game for Kids is great for practicing one-to-one correspondence!
This Counting Math Game for Kids is great for practicing one-to-one correspondence!
38. LEGO and Math combine in these LEGO Pattern Cards. A great activity to work on hands-on pattern building!
39. Counting Blocks While Building Towers is a fun way to learn with numbers!
40. These printable shapes are so inviting and are jam-packed with learning! You definitely have to add this to your list of preschool math activities to try with the kids!
Check out all of our other preschool math activities!
And because I LOVE combining literacy and math, here are 60 fantastic Math Picture Books for Preschool. Swap these in and out of your math center all year-long!
I hope this list will help you plan preschool math activities for the year ahead. I am really excited to do so many fun and engaging math activities with my kids this year!
I would love for you to share your favorite math activities for preschoolers in the comments!
PRACTICAL CLASSES ON THE FORMATION OF ELEMENTARY MATHEMATICAL REPRESENTATIONS IN A PRESCHOOL
To effectively conduct self-study according to the curriculum, students are given homework to learn a certain topic and solve the corresponding tasks.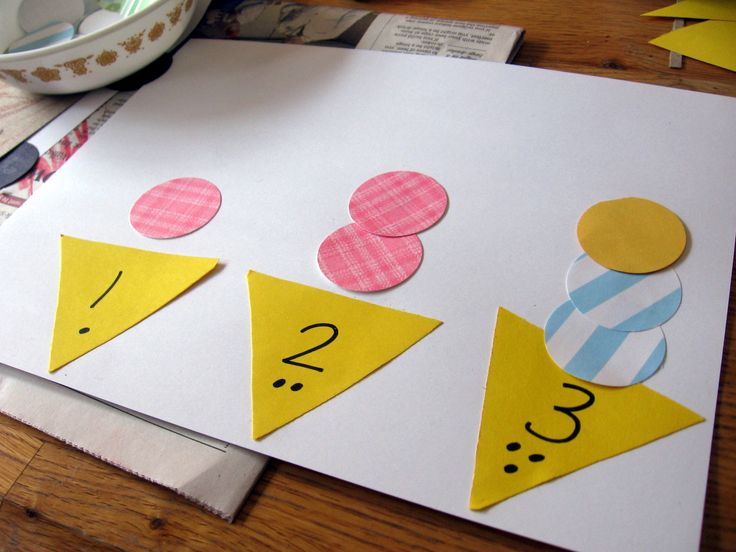 To this end, students briefly outline the topic, do sums and tests in notebooks and give to the teacher.
To this end, students briefly outline the topic, do sums and tests in notebooks and give to the teacher.
Keywords: Independent work, credit, credit system of education, teacher, students, independent work of students, and independent work of a student with the guidance of a teacher.
Information about the author:
Barotzoda Kamoliddin Ashur – Candidate of Pedagogical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of General Biology and Teaching Methods Biology of the Tajik State Pedagogical University named after Sadriddin Aini, Tel.: (+992) 934050446.
About the author:
2 Ashur – Candidate pedagogical sciences Associate Professor of the Department of General Biology and Teaching Methodology Biologists of the Tajik State Pedagogical University named after Sadriddin Aini, tel.: (+992) 934050446.
UDC. 51 (075) BBK. 74.262 B. 91
Practical classes on the formation of elementary mathematical representations in the preschool
Burkhanov K. T.
T.
Hajand State G. Gafurov
V. Currently, the staff of a preschool educational organization is working on the problem of "Improving the pedagogical process in preserving and strengthening the physical and mental health of children, the worldview and social and personal development of preschoolers." One of the main tasks solved by teachers is the development of logical thinking of preschoolers in mathematics classes through the use of didactic games with logical and mathematical content.
The formation of elementary mathematical concepts (FEMP) in preschool children in modern conditions is an important part of intellectual and personal development. In accordance with the program, a preschool educational organization is the first stage of education, so the kindergarten performs an important function of preparing children for school. The success of further education of the child depends on how well and timely it will be prepared.
Teaching mathematics to preschool children is unthinkable without the use of didactic games. Their use helps the most profound assimilation of the material, the child becomes an active participant in cognitive activity.
Their use helps the most profound assimilation of the material, the child becomes an active participant in cognitive activity.
On the way to the formation of the methodology for the development of mathematical concepts in preschool children, its basis as a scientific discipline was oral folk art: various fairy tales, counting rhymes, proverbs, sayings, riddles, jokes. At the first stage of the development of the methodology, special attention was paid to the content and methods of teaching preschoolers arithmetic and the development of ideas about dimensions, measures of measurement, time and space. Ya.A. Komensky, I.G. Pestalozzi, KDUshinsky, L.N. Tolstoy and others expressed certain suggestions about the content and methods of teaching children, mainly in the family. Methods for developing ideas about number and form in children were reflected and further developed in the systems of sensory education of the German teacher F. Frebel, the Italian teacher M Montessori and others. In these classical systems of sensory education, the issues of familiarizing children with geometric shapes and sizes were specifically considered; learning to count, measure, draw up rows of objects by size, weight.
In these classical systems of sensory education, the issues of familiarizing children with geometric shapes and sizes were specifically considered; learning to count, measure, draw up rows of objects by size, weight.
So, the leading teachers of the 20th century, Russian and foreign, recognized the role and necessity of primary mathematical knowledge in the development and upbringing of children before school, singled out arithmetic as a means of mental development and strongly recommended that children be taught it as early as possible, from about three years[1, p. 5].
In the 1920s A fundamentally new system of public preschool education was created. During these years, E.I. Tikheeva, L.V. Glagoleva, F.N. Bleher developed teaching aids, programs, games and didactic materials that promote the mathematical development of preschoolers.
In the 1950s and 1960s A.M. Leushina dealt with the development of quantitative representations in preschoolers. The essence of the method was as follows: the assimilation by the child of mathematical representations
is carried out in the process of life and various activities. She developed the foundations of a didactic system for the formation of elementary mathematical representations, creating a program, the content of which was the methods and techniques of working with children from 3 to 6 years old.
She developed the foundations of a didactic system for the formation of elementary mathematical representations, creating a program, the content of which was the methods and techniques of working with children from 3 to 6 years old.
The current state of the theory and technology of the development of mathematical concepts in preschool children developed in 80-90-ies of XX century. and to this day, under the influence of the development of ideas for teaching children mathematics, as well as the reorganization of the entire education system.
It is necessary that the process of forming elementary mathematical concepts in children be associated with all aspects of the educational work of a preschool organization and is aimed at solving the problems of mental education and mathematical development of preschool children. Preschoolers use their knowledge and skills in various types of activities: labor, productive, playful, cognitive research, when it is necessary to count, recalculate, count or measure the required number of objects and materials. So, for example, during classes on creating an appliqué, children are convinced that the number of objects does not depend on their location (when decorating malitsa with Nenets ornaments - chumaks, their number remains unchanged regardless of how they are pasted: one after another, on a certain distance or nearby).
So, for example, during classes on creating an appliqué, children are convinced that the number of objects does not depend on their location (when decorating malitsa with Nenets ornaments - chumaks, their number remains unchanged regardless of how they are pasted: one after another, on a certain distance or nearby).
At the lessons of drawing, modeling, appliqué and designing, preschoolers consolidate their ideas about geometric shapes and bodies, about the shape, size of objects, their spatial arrangement, and quantity.
In cognitive research activities, ideas about time periods are improved, preschoolers get acquainted with methods for measuring the length, weight and volume of objects.
In physical education classes, children often encounter quantitative and ordinal counting when building, performing physical exercises, and during outdoor games.
N.A. Vinogradova noted that due to the age characteristics of preschool children, for the purpose of their education, didactic games, board-printed games, games with objects (plot-didactic and dramatization games), verbal and game techniques, didactic material.
There is no, and cannot be, full mental development without play. The game is a huge bright window through which a life-giving stream of ideas and concepts flows into the spiritual world of the child. The game is a spark that kindles the flame of inquisitiveness and curiosity (V.A. Sukhomlinsky).
Today, and even more so tomorrow, mathematics will be necessary for a huge number of people of various professions. Mathematics has great opportunities for the development of children's thinking, in the process of their learning from a very early age.
Mathematics has a unique educational effect. “She puts the mind in order”, i.e. in the best way forms the methods of mental activity and the qualities of the mind, but not only. Its study contributes to the development of memory, speech, imagination, emotions; forms perseverance, patience, creative potential of the individual. A mathematician plans his activities better, predicts the situation, expresses his thoughts more consistently and more accurately, and is better able to justify his position.
The main purpose of doing mathematics is to give the child a sense of self-confidence, based on the fact that the world is ordered and therefore comprehensible, and therefore predictable for a person.
It must be remembered that mathematics is one of the most difficult subjects, but the inclusion of didactic games and exercises allows you to change the types of activities in the classroom more often, and this creates conditions for increasing the emotional attitude to the content of the educational material, ensures its accessibility and awareness.
Teaching mathematics to preschool children is unthinkable without the use of entertaining games, tasks, and entertainment. At the same time, the role of simple entertaining mathematical material is determined taking into account the age capabilities of children and the tasks of comprehensive development and education: to activate mental activity, to interest in mathematical material, to captivate and entertain children, to develop the mind, to expand, deepen mathematical representations, to consolidate the acquired knowledge and skills, to exercise applying them in other activities, new environment.
Using didactic games to form ideas, get acquainted with new information. In this case, an indispensable condition is the use of a system of games and exercises.
Children are very active in perceiving tasks-jokes, puzzles, logical exercises. They are persistently looking for a course of action that leads to a result. In the case when an entertaining task is available to a child, he develops a positive emotional attitude towards it, which stimulates mental activity. The child is interested in the ultimate goal: to add, find the desired figure, transform, which captivates him.
Of all the variety of entertaining mathematical material in preschool age, didactic games are most widely used.
Their main purpose is to provide children with exercise in distinguishing, highlighting, naming sets - objects of numbers, geometric shapes, directions, etc. In didactic games, there is
the opportunity to form new knowledge, introduce children to ways of action. Each of the games solves a specific problem of improving the mathematical (quantitative, spatial, temporal) representations of children.
Each of the games solves a specific problem of improving the mathematical (quantitative, spatial, temporal) representations of children.
Didactic games are included in the content of classes as one of the means of implementing program tasks. The place of the didactic game in the structure of the lesson on the formation of elementary mathematical representations is determined by the age of the children, the purpose, purpose, content of the lesson. It can be used as a training task, an exercise aimed at performing a specific task of forming representations.
Didactic games and game exercises of mathematical content are the most famous and frequently used types of entertaining mathematical material in the modern practice of preschool education. In the process of teaching preschoolers mathematics, the game is directly included in the lesson, being a means of forming new knowledge, expanding, clarifying, and consolidating the educational material.
At preschool age, play is essential in the life of a small child. The need for play in children persists and occupies a significant place in the first years of their schooling. In games there is no real conditioning by circumstances, space, time. Children are creators of the present and the future. This is the charm of the game.
The need for play in children persists and occupies a significant place in the first years of their schooling. In games there is no real conditioning by circumstances, space, time. Children are creators of the present and the future. This is the charm of the game.
Consider other types of entertaining material, such as math games. These are games in which mathematical constructions, relationships, patterns are modeled. To find an answer (solution), as a rule, a preliminary analysis of the conditions, rules, content of the game or task is necessary. In the course of the solution, the use of mathematical methods and inferences is required [5, p. 10-12].
"Chain of examples" games
Purpose. To train children in the ability to perform arithmetic operations.
Game progress. Two groups of participants sit on chairs - one against the other. One child takes the ball, calls a simple arithmetic example: 3 + 2 - and throws the ball to someone from another group.The one to whom the ball is thrown gives an answer and throws the ball to a player from the first group. The one who catches the ball continues the example in which it is necessary to perform an action with the number that is the answer in the first example.The participant in the game who gave the wrong answer or example, out of the game, the group of kids with the most players left wins.0003
The one who catches the ball continues the example in which it is necessary to perform an action with the number that is the answer in the first example.The participant in the game who gave the wrong answer or example, out of the game, the group of kids with the most players left wins.0003
Note. The game is offered for individual work with children aged 6-7 who have successfully mastered the program material for the development of elementary mathematical concepts.
Guess the number games
Purpose. Strengthen the ability of children to compare numbers.
Game progress. On the instructions of the leader, the child must quickly name the number (numbers) less than 8, but more than 6; more than 5, but less than 9, etc. The child who fulfilled the conditions of the game receives a flag. When children are divided into 2 groups, the one who answered incorrectly is eliminated from the game.
Both games are simple in content and task: their participants must perform arithmetic operations or name the required number based on knowledge of the sequence of numbers and the relationships between them. Amusement, interest provide game actions (throwing the ball), game goal setting, rules, methods of stimulating mental activity.
Amusement, interest provide game actions (throwing the ball), game goal setting, rules, methods of stimulating mental activity.
A variety of mathematical games and tasks are logical games, tasks, exercises. They are aimed at training thinking when performing logical operations and actions: “Find the missing figure”, “What is the difference?”, “Mill”, “Fox and geese”, “Four by four”, and other games “Growing a tree”, “Miracle bag", "Computing machine" suggest a strict logic of actions.
"Only one property" games
To play, you need to make a special set of geometric shapes. It includes four figures (circle, square, triangle and rectangle) of four colors, such as red, blue, yellow and white, small size. The same set includes the same number of the listed figures of the indicated colors, but larger in size. Thus, for the game (per participant) you need 16 small geometric shapes of four types and four colors and the same number of large ones.
Purpose. To consolidate knowledge of the properties of geometric shapes, to develop the ability to quickly select the desired figure, describe it.
Game progress. Two playing children have a full set of figures. One (the one who starts the game) puts any piece on the table. The second player must place a piece next to it that differs from it in only one way. So, if the first player puts a large yellow triangle on the table, then the second one puts a large yellow square or a large blue triangle, etc. A move is considered incorrect if the second player puts a figure that does not differ from the first or differs from it by more than one sign. In this case, the piece is taken from the player. The one who is first left without pieces loses. (Options are possible.)
The game is built like dominoes. In the course of the game, a quick orientation of the players in the color, shape, size of the pieces is required, hence the impact on the development of logic, the validity of thinking and actions.
Entertaining material includes various didactic games, as well as exercises that are attractive in form and content. They are aimed at the development of logical thinking, spatial representations in children of different ages, provide an opportunity to exercise children in counting and calculations.
Number series games
(for older preschool children)
Purpose. To consolidate knowledge of the sequence of numbers in the natural series.
Game progress. Two children sitting at the same table lay out cards with numbers from 1 to 10 face down in front of them. At the same time, each of the children is given a certain number of cards with numbers (for example, up to 13). Some of the digits appear twice in the set. Each player in turn takes a card with a number, opens it and puts it in front of him. Then the first player opens another card. If the number indicated on it is less than the number of the previously opened card, the child puts the card to the left of the first, if more, to the right. If he takes a card with a number already revealed to him, then he returns it to its place, and the right to move is transferred to a neighbor. The first person to lay out their row wins.
We can conditionally distinguish 2 more large groups of games and exercises. The first includes all mathematical problems, games of ingenuity.
The first includes all mathematical problems, games of ingenuity.
Say the number games
Purpose. Exercise children in the ability to make oral calculations.
Game progress. An adult or older child says: “I can guess the number that you have in mind. Think of a number, add 6 to it, subtract 2 from the sum, then subtract the conceived number, add 1 to the result. You got the number 5.
In this simple task of ingenuity, the intended number can be any number, but to solve it you need to be able to calculate verbally.
Solving problems of the second group does not require special mathematical training, only resourcefulness and ingenuity are needed [6, 20-25].
Kindergarten plays an important role in preparing children for school. The success of his further education largely depends on how well and timely the child is prepared for school.
One of the main subjects at school is mathematics. Mathematics has a unique developmental effect.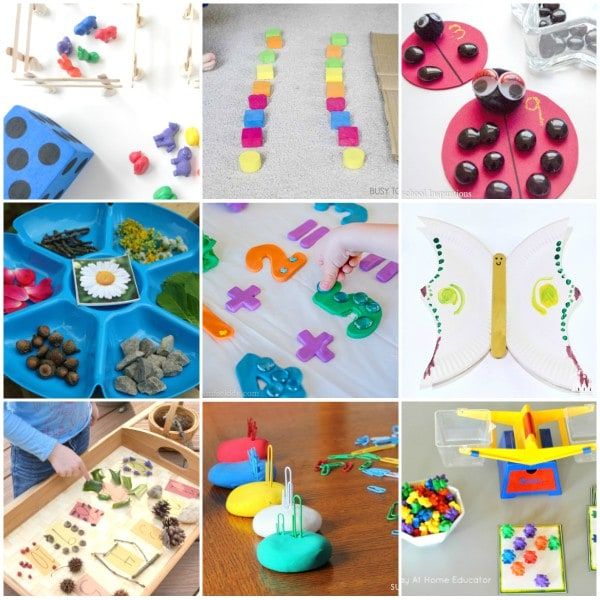 Its study contributes to the development of memory, speech, imagination, emotions; forms perseverance, patience, creative potential of the individual. The main purpose of doing mathematics is to give the child a sense of self-confidence, based on the fact that the world is ordered and therefore comprehensible, and therefore predictable for a person.
Its study contributes to the development of memory, speech, imagination, emotions; forms perseverance, patience, creative potential of the individual. The main purpose of doing mathematics is to give the child a sense of self-confidence, based on the fact that the world is ordered and therefore comprehensible, and therefore predictable for a person.
Teaching mathematics to preschool children is unthinkable without the use of didactic games. Their use well helps the perception of the material and therefore the child takes an active part in the cognitive process.
LITERATURE
1. Beloshisgaya A.V. Formation and development of mathematical abilities of preschoolers: questions of theory and practice: -M.: 2003.-400s.
2. Bondarenko A.K., Matusik A.I. Education of children in the game. Handbook for the kindergarten teacher. - M.: Enlightenment, 1983.-300s.
3. Burkhanov K.T., Shukrulloeva M.A. Formation of representations of game and entertaining tasks in elementary mathematics for preschoolers. - Khujand - 2013.-36 p.
- Khujand - 2013.-36 p.
4. Veraksa NE, Komarova T.S., Vasil'eva M.A. From birth to school. Approximate basic educational program of preschool education. Publisher: Mosaic-sintez, 2015.-383s.
5. Kovalenko V. Didactic games in mathematics lessons.-M.: 1990.-148p.
6. Mikhailova Z.A. Game entertaining tasks for preschoolers. M.: Enlightenment, 1990.- 120s.
PRACTICAL EXERCISES FOR THE FORMATION OF ELEMENTARY MATHEMATICAL REPRESENTATIONS IN A PRESCHOOL
Didactic game requires perseverance, a serious attitude, the use of the thought process. Play is a natural way for a child to develop. Only in the game, the child joyfully and easily, like a flower under the sun, reveals his creative abilities, masters new skills and knowledge, develops dexterity, observation, imagination, memory, learns to think, analyze, overcome difficulties, while absorbing invaluable communication experience.
Didactic games justify in solving the problems of individual work with children in their free time. Systematic work with children improves general mental abilities:
Systematic work with children improves general mental abilities:
logic of thought, reasoning and action, ingenuity and ingenuity, spatial representations.
Key words: team, preschool education, institutions, formation, mathematics, goal, tasks, didactics, game, logic, methodology.
PRACTICAL LESSONS FOR THE FORMATION OF ELEMENTARY MATHEMATICAL REPRESENTATIONS AT PRESCHOOL INSTITUTIONS
Didactic games require perseverance, a serious attitude, the use of the thought process. The game is a natural way of developing a child. Only in the game the childjoyfully and easily, like a flower under the sun, reveals his creative abilities, develops new skills and knowledge, develops dexterity, observation, imagination, memory, learns to think, analyze, overcome difficulties, while absorbing invaluable communication experience .
Didactic games are justified in solving the problems of individual work with children in their free time. Systematic work with children improves general mental abilities: the logic of thought, reasoning and action, ingenuity and quick wit, spatial representations.
Keywords: collective, preschool education, institutions, formation, mathematics, goal, tasks, didactics, game, logic, methodology.
Information about the author:
Burkhanov Kurbonboy Tursunrajbovich – candidate of pedagogical sciences, associate professor of the department of natural mathematics, aesthetic education and its teaching, Khujand State University named after Academician B.Gafurov (Republic of Tajikistan, Khujand), Tel. mob. (+992) 918909172. E-mail: [email protected] 9IK Gift of Mussadoi Tadsiloti Miyunai Umomu
Palavonov AM
Donishkadairifi Maorifi Ba Nomi A. Tsomiyani Academy Tahriloti Tocycyston
Fayratov M.H. Tocyziston Ba Nomi Yaki Chuza Mukhimi Tali vakti muayyan dar sinfkhona va yo hamchun mashguliyati berun az sinfy guzaronida meshavad.Maksadi asosii dars musallah namudani honandagon bO donishi amika mustahkam wa mahoratu malaka meboshad. kasb, doshtani layokatu mahorati dastras kardani donish ba digaron, tashkil karda tavonistani mukhiti oromi teacher-talimi dar sinf va berun az on ba shumor meravad. Dar dars yak yo az in ziyod honandagon ishtirok mekunand. (Onhoro, toliba, talaba va yo donishchu ham menomand), ki bo onkho omuzgor az in yo on fan dars meguyad.
Dar dars yak yo az in ziyod honandagon ishtirok mekunand. (Onhoro, toliba, talaba va yo donishchu ham menomand), ki bo onkho omuzgor az in yo on fan dars meguyad.
Asosguzori nizomi darsi sinfy olimi Czech Ya. A. Kamensky meboshad, ki u tarzi guzaronidani mashguliyatkhoro dar sistemai sinfy asosnok namud, darsro chunin ta’rif dodaast: “Dars in kismi mantikan tom yakluhti talimu tarbiya mahdumuronida buda, dar yak vakti . [11, p. eight].
Nizomi sinfii muvofiki dars mashguliyatkho 45 daksha davom mekunad va on az lahzakhoi mahsus iborat ast. Bayni mashguliyatkho tanaffusho muayyan gardidaast. Khdmin shakli talimii guruhiro nizomi sinfii dars nomidaand, ki he saikal yofta, then zamoni mo omada rasidaast va baroi salt tahsil khar ruza vakt miracle gardidaast.
Olimon darsro muchizavu sanat nomidand, chunki kudaki khurdsol dar natichai azhudkuniy mavodi darskho dar davomi solkhoi tahsil ba kamol merasad va komilan digargun shuda, shahsiyatash tashakkul meyobad. Makhz az khamin sabab, chomea va ahli maorif ba dars chun shakli asosii tashkilia kori talim talabothoi zerinro peshnikhod namudaast:
Khdr dars muvofiki sokhti hud - ogaz guzorishi maksad, sharhi ezoh, mustahdamkuny, chambastu suporishi vazifai honagy pasi kham guzorad;
Darsi tarihi khalki tojik boyad ba talabothoi usulkhoi ilmiyu metodi chavobgu boshad va hususiyathoi psychology honanda ba hisob girift shavad;
Dar darskhoi tarihi halki tojik az dastovardhoi peshkadami omuzgoron istifoda burda shavad;
Entertaining mathematics for preschoolers | Systematics
for preschoolers
We solve interesting problems and puzzles, get ready for school
from 450 ₽
/ lesson
Start of the season. Recording in progress
Recording in progress
Sign up for a club
Trial class
When
All year
Season start
Enrollment in progress
Duration
45 minutes
Format
• Mini groups of 3-5 people
• Online classes with a teacher
• Once a week on schedule
When
All year round
Season start
Recruitment in progress
Duration
45 minutes
Format
• Mini groups of 3-5 people
• Online classes with a teacher
• Once a week according to the schedule
What does the circle give
Interest
to mathematics
Let's show that mathematics is not boring, but interesting. We ignite even the humanities with mathematics.
Overcoming fear
before mathematics
Remove the fear of complex problems. The child understands that he is able to solve even what he does not know.
Decision skill
non-standard tasks
Solving puzzles and non-standard tasks develops logic and imagination.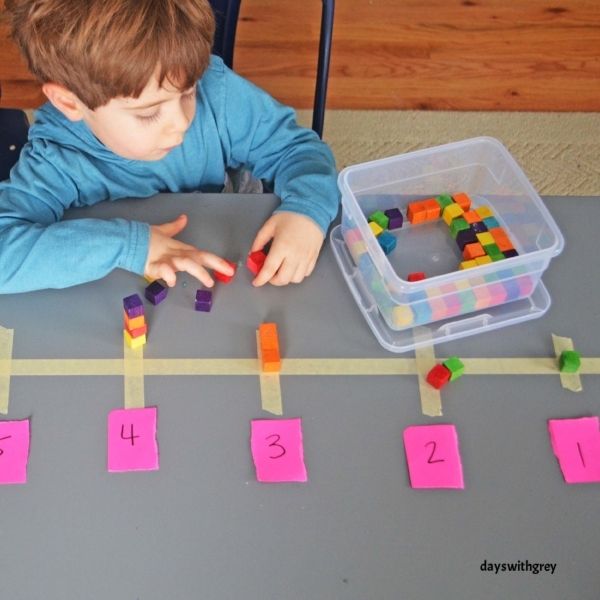
Readiness for school
Confidence and knowledge of the basics will make it easy and interesting to study mathematics at school.
Interesting problems
Interesting explanation
Good atmosphere
I can do it
Interest in mathematics in your child
students who have been crammed at the university but still outperform their professors. Worst of all solve these simple problems are Nobel and philosophical laureates.0003
Vladimir Arnold
Academician, in the preface to his collection of Olympiad problems
How the classes are held
1
We open access to the materials 6 hours before class
If you wish, tasks can be downloaded and printed
2
Demonstrate tasks on the screen
Turn the Zoom screen into a whiteboard using a graphics tablet
3
Discussing a topic in dialogue mode
We direct the thought, but let the children walk and figure it out themselves
4
We explain the principle of the solution using an example
We take a typical problem and analyze the solution together
5
We solve problems from simple to complex
Please show the train of thought on the screen or write an answer in the chat
6
We pay enough attention to everyone
Let everyone speak in turn, if something is not clear, we explain it personally
We open access to materials 6 hours before class
If you wish, you can download and print assignments
Demonstrate tasks on the screen
Turn the Zoom screen into a blackboard using a graphics tablet
We discuss the topic in a dialogue mode
We direct the thought, but let the children go and figure it out themselves
We explain the principle of the solution using an example
We take a typical problem and analyze the solution together
We solve problems from simple to complex
Please show the train of thought on the screen or write a reply to the chat
We pay enough attention to everyone
Let everyone speak in turn, if something is not clear, we explain it personally
Thoughtful
program
We solve interesting problems and play, master the basic concepts
The teacher will help you get comfortable
A good atmosphere, an interested teacher and a group will help you get comfortable and get involved in the process with interest
The main thing is interest
If a child can solve problems and has a knowledge of the basic principles, everything will be fine at school!
Smart
program
We solve interesting problems and play, mastering basic concepts
The teacher will help you get comfortable
A good atmosphere, an interested teacher and a group will help you get comfortable and get involved in the process with interest
The main thing is interest
If the child succeeds in solving problems and eating knowledge of the basic principles, everything will be fine at school!
Our classes are held in a relaxed atmosphere, and teachers know how to interest students.
This is how we solve the problems for combinatorics
Program for preschool children
32
Lessons
32
Lessons
Why is it worth studying online
Bore for the main
Child for the main
child, and does not spend strength on strength on strength on road, so classes are more productive.
Maintain
concentration
Online classes last 60 minutes - enough to keep your attention.
We support
the general mood
If the child is tired and starts to play around, turn off the sound so that it does not distract the other children.
Saving the strength of
children for the chief
The child is learning, not wasting energy on the road, so classes are more productive.
Keeping concentration
Online classes last 60 minutes — enough to keep your attention.
We support
general mood
If the child is tired and starts to play around, turn off the sound so that it does not distract other children.
We work online
We have been teaching online for more than five years. We know the intricacies of this format and teach it to all teachers.
Teachers of the online circle
The circle is led by teachers with extensive experience in Olympiad and entertaining mathematics
More than 5 years of experience
Martynova Olga Alekseevna
Education UNN them. Lobachevsky, Faculty of Radiophysics; additional education teacher
Places of teaching I have been working with children since 2017: teaching robotics at the Nizhny Novgorod Robbo Club, mathematics olympiads at the Nizhny Novgorod branch of the Creative Laboratory 2 × 2, in summer and winter camps of the MMMF school
Experience over 5 years
Ekaterina Aristova
Education Tula State Pedagogical University named after L.N. Tolstoy
Places of teaching CO 25 with in-depth study of individual subjects, Tula
MBOU secondary school 4 Donskoy, the world of Severozadonsk, Donskoy
MBOU CO 51, Tula Primary school teacher
Online - school number 1, St. Petersburg - Primary school teacher.
Petersburg - Primary school teacher.
Places of teaching Participation in holding city events in mathematics. Conducts classes with younger students in mathematics, both individual and in small groups, classes in technical creativity
Recruitment in progress
Schedule
You can study once a week. Only groups that are open for recording are shown in the schedule.
Monday:
11:00
- 11:45
Friday:
18:15
- 19:00
Saturday:
12:20
- 13:05
Subscription fee
Subscription allows you to visit any circles and intensive courses of Systematics
One subscription is enough for brothers and sisters
4 lessons
2240 ₽
3200 ₽
560 ₽ per lesson
Enroll
8 lessons
4200 ₽
6000 ₽
525 ₽ per lesson
Enroll
16 lessons
7840 ₽
11200 ₽
490 ₽ per lesson
Enroll
32 lessons
16640 ₽
20800 ₽
520 ₽ per lesson
Enroll
Buy a subscription
You can use one subscription for different online clubs
read reviews →
We issue a certificate
At the end of the course each student receives a personal certificate - it will be available via the link on our website. You can also print the certificate yourself.
You can also print the certificate yourself.
What you will need for classes
Paper (better to have a notebook for our classes)
Pencil and eraser (preferably)
Pen
Laptop or tablet
Students about us
Click on the name to see the courses completed by the student
Anna Poguntke
Deutschland, Baldham
Involved
2 years 3 months
The classes are interesting and meet the interests of the child, as the desire was expressed to study twice a week. I really like the teacher Yana, Vasily, who replaced the teacher, was also positively noted.
read morecollapse
Yana Malysheva
Russia, Moscow and the Moscow region
3 years 10 months
Daughters really like to study online, the groups are small, the teacher Mikhail explains very intelligibly and calmly, none of the guys stay away from the discussion.
read fullcollapse
I liked the classes very much, they are interesting, the time flies by quickly
read morecollapse
Maria Galieva
Russia, Moscow
Involved
4 years 4 months
Many thanks to the organizers for their attentiveness and responsiveness. Maria has been participating in the Systematics program for the third year and has learned a lot during this time
read morecollapse
about the Mathematics Olympiad
Anna Revkova
Russia, Moscow
Involved
2 years 1 month
Good afternoon! My daughter really likes classes with Mikhail and Yana. The tasks are interesting, non-standard, but not abstruse. I also like the approach of teachers - they always know when to let them think for themselves, and when to bring them to a decision. At first it was difficult, because it was unusual to think outside the box)) but now Anya is not afraid of new tasks, she doesn’t get upset if something doesn’t work out and, of course, she is very inspired by her own victories. In general, our expectations were met by 100%. And most importantly, the child's self-motivation has grown and faith in his own strength has strengthened. I also like the large selection of times and days of the week for classes. I can only say a big thank you for the opportunity to participate in Systematics classes!
I also like the approach of teachers - they always know when to let them think for themselves, and when to bring them to a decision. At first it was difficult, because it was unusual to think outside the box)) but now Anya is not afraid of new tasks, she doesn’t get upset if something doesn’t work out and, of course, she is very inspired by her own victories. In general, our expectations were met by 100%. And most importantly, the child's self-motivation has grown and faith in his own strength has strengthened. I also like the large selection of times and days of the week for classes. I can only say a big thank you for the opportunity to participate in Systematics classes!
read fullcollapse
It seems to us that zoom resources are well used, it is possible to send answers before the discussion and resolve issues in private with the teacher. The selection of the group by complexity seems to us successful. Many tasks of a difficult level that are not solved instantly, but are also diluted with entertaining short tasks - a good balance. An additional plus from live classes with a teacher is the versatility of thinking of other participants. Contact with the teacher is optimal: the role of the teacher is not central, the children themselves speak a lot, the teacher directs. Passing the material for the lesson is sufficient.
An additional plus from live classes with a teacher is the versatility of thinking of other participants. Contact with the teacher is optimal: the role of the teacher is not central, the children themselves speak a lot, the teacher directs. Passing the material for the lesson is sufficient.
read fullcollapse
Lev Filimonov
Russia, Obninsk
Studying
2 years 8 months
Leo is happy to rush to every lesson, Svetlana (teacher) leads the class at the pace of the children, finds her own approach for everyone and manages to cheer everyone up - we, parents, like it. Special thanks to the team - a very attentive attitude to the students, we changed the group and the teacher with the administrator helped us choose the best option.
read fullcollapse
I like the teacher, Xenia. Lively communicates with children, tries to get a dialogue with children. Involves them in activities. I liked that during the lesson the children were in dialogue with the teacher, and not in a monologue.
read fullcollapse
Answering frequently asked questions
Other math classes
Recorded course
Two tasks for a week from 9 to 99 years old
Video with theory, practical tasks, checking by the teacher, video with analysis of tasks
Calling
Recorded course
Olympiad mathematics course for grades 2
Olympiad mathematics course for grades 2
Video with theory, practical tasks, checking by the teacher, video with analysis of tasks
Enrollment in progress
Recorded course
Two tasks for a week from 9 to 99 years old
Two tasks for a week from 9 to 99 years old
Video with theory, practical tasks, checking by the teacher, video with analysis of tasks
Calling
Recorded course
Olympiad mathematics course for grade 1
Olympiad mathematics course for grade 1
Practical tasks, teacher check, video with task analysis
Enrollment in progress
Show all
Recording in progress
TRIZ and the History of Civilizations
Course on the development of thinking using TRIZ tools. For those who like to think and are fond of history.
For those who like to think and are fond of history.
10 modules
November 14-26
TRIZ-intensive "History of Ancient India"
November 14-26
History of Ancient India
Development of thinking using TRIZ tools based on stories from the history of civilizations
4 lessons
Recording in progress
TRIZ intensive "Mesopotamia and Persia"
October 17-29
Module 2. History of Mesopotamia and Persia
Development of thinking using TRIZ tools based on plots from the history of civilizations
4 lessons
Recording in progress
TRIZ – Intensive "History of Ancient Greece"
August 15 - 26
Module 3. History of Ancient Greece
Development of thinking using TRIZ tools based on stories from the history of civilizations
4 lessons
Recording in progress
TRIZ and History of Civilizations
TRIZ and History of Civilizations
Course on the development of thinking using TRIZ tools.