Homeschool reading level assessment
Homeschool Reading Placement & Assessment Online— Let's Go Learn
Skip to contentHomeschool Reading Placement & Assessment OnlineJohn Williams2021-11-17T01:10:34+00:00
Find your child’s grade level for every reading skillOur placement test and assessments analyze mastery of grade-level reading objectives and identify
learning gaps.
For 20+ years, Let’s Go Learn has helped homeschool parents teach their children.
- Our research-based reading scope and sequence offers depth and breadth.
- Our adaptive placement test analyzes mastery by topic and grade-level equivalency.
- Our reports identify learning gaps by topic and grade level.
- Our online instruction uses placement data to assign lessons that close learning gaps.
Go to our Store…
In addition to reading placement, our online platform significantly supports your child’s reading growth and achievement.
- Uses our research-based scope and system for each grade level
- Adapts up and down to a child’s mastery regardless of child’s grade
- Offers child a game-like experience as they answer test items
- Provides parents or home teachers with easy-to-read reporting
- Identifies reading learning gaps
- Includes skills-based quizzes and subtopic tests to monitor academic growth
- Provides optional online learning that addresses specific learning gaps
Go to our Store…
Let’s Go Learn provides homeschool parents with the tools they need to make instructional decisions.
We know the purpose of placement is to advance your child’s learning, so we have designed accurate and easy-to-read reading placement reports. These are available immediately after your child completes the test. For example, the Summary of Scores Report describes a high-level view of your child’s performance.
- A legend at the top describes score ranges for each reading domain for every grade level.
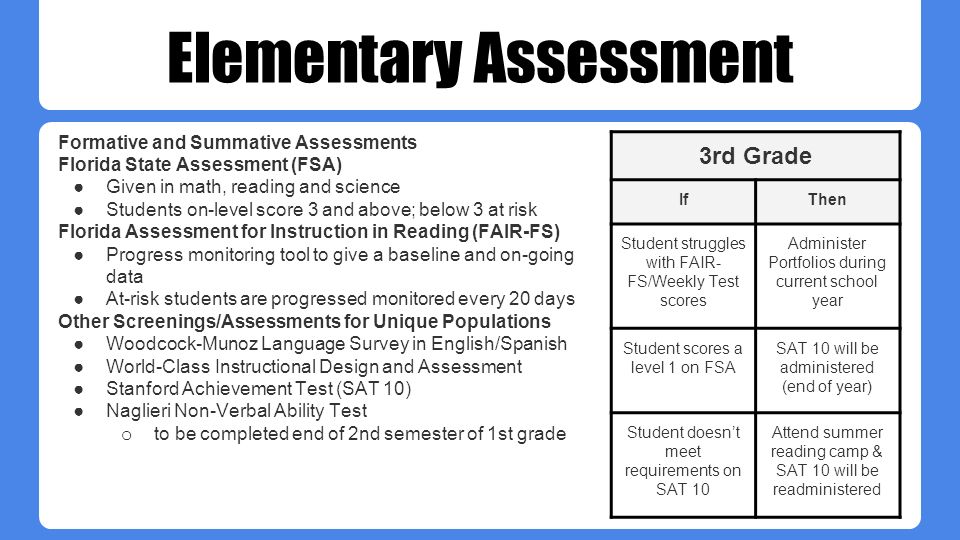
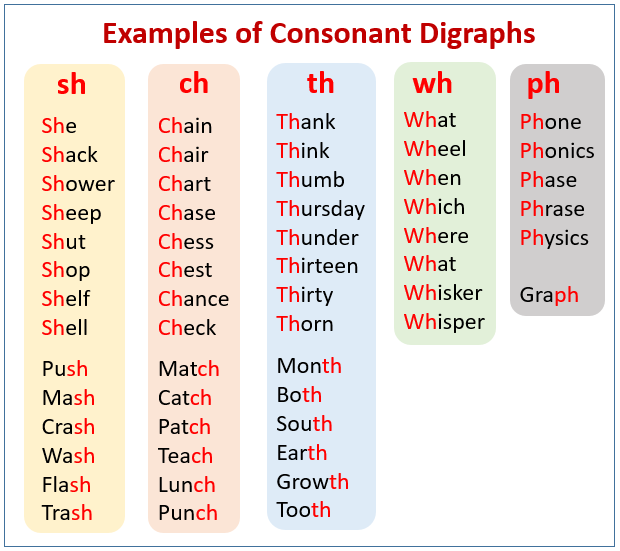
- Reading content is divided into seven skills: high-frequency words, phonemic awareness, phonics, fluency, spelling, vocabulary development, and reading comprehension.
- Your child’s raw score and grade level are shown for each skill.
- An overall summary of your child’s reading grade level is included in the report.
- Below the legend, skills (called sections) are displayed and an instructional goal for each skill is shown.
- Every skill either has a raw score and corresponding grade level or is shown as NT (Not Tested).
- As a parent, you can now present instruction at the level your child needs in order to grow reading skills, regardless of their age or grade. It doesn’t matter if your child is below, at, or above grade level, you have all the information you need to make decisions.
Go to our Store…
Reading Diagnostic Assessments
DORA
The Diagnostic Online Reading Assessment is a K-12 web-based assessment that diagnostically evaluates students’ reading abilities.
Measures eight essential subskills of reading
Reveals a student’s unique reading profile across multiple areas
Aligned to Common Core, TEKS, and other state standards
Engaging interactive technology features a combination of audio, text, and multimedia images
DORA Dyslexia Screener
DORA DS provides a valid and reliable means to screen all students quickly online and accurately for dyslexia, as required by many states.
Measures five
essential skills 100% online – Product sheet
Checks for mouse or touch-screen dexterity bias when students are screened
Provides instant results for teachers and administrators
Integrated into the greater LGL platform for a total solution: screener to full diagnostics
DORA Phonemic Awareness
DORA PA provides a thorough assessment of oral phonemic awareness skills.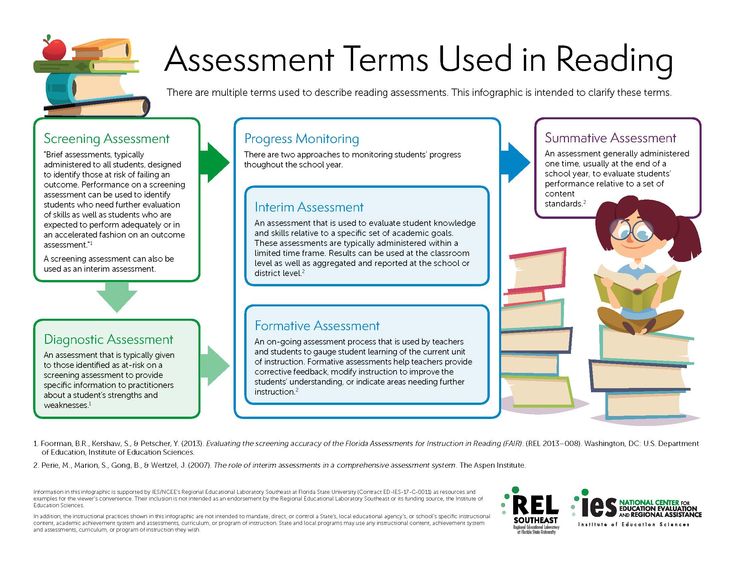
Measures nine essential phonemic awareness skills
View the specific phonemic awareness categories tested
Evaluates non-readers or struggling readers with audio and picture-only items
Automates oral one-on-one phonemic awareness diagnostics
DORA Spanish/EDELL
Evaluación Diagnostica Español de Lectura en Línea is a diagnostic assessment of student Spanish reading abilities.
Measures seven essential subskills of Spanish reading
Reveals a student’s unique reading profile automatically
Instant diagnostic and prescriptive individual student reporting
Ideal for K-12 English Language Learners and adult ESL programs
Common Questions
How does our placement test identify gaps caused by learning loss or unfinished learning?
Our test treats students separate from their grade level. This means that if a 6th grade student takes it, the items will not be limited to 5th to 6th grade, as in many benchmark tests and screeners. The test will find each student's gaps across a K-12 grade range. Optional online instruction driven by student scores is available in LGL Reading Edge.
The test will find each student's gaps across a K-12 grade range. Optional online instruction driven by student scores is available in LGL Reading Edge.
How does our placement test measure student progress?
Our placement test is made up of seven sub-tests, which can be given in parts. Individual parts such as phonics, phonemic awareness, vocabulary, and comprehension can be given. Alternatively, you can give even smaller quizzes in specific areas such as short vowels, beginning sounds, or 5th-grade comprehension.
Is our placement appropriate for children who have IEPs?
Yes, our placement can identify a student's present levels very precisely--a key tool in writing accurate IEPs and setting appropriate goals.
How are phonics tested?
When testing phonics, our test finds the student's instructional point in the phonics linear sequence of skills, starting with beginning sounds and ending with multi-syllabic words.
How does our test deal with the assessment of decoding skills?
It breaks decoding into multiple sub-tests. Students successful in decoding need to be able to use skills in sight words or high-frequency words, phonics, phonemic awareness, and even spelling. All of these areas are tested to give parents the most insight into a child's diverse set of skills and strategies when encountering unknown words.
Students successful in decoding need to be able to use skills in sight words or high-frequency words, phonics, phonemic awareness, and even spelling. All of these areas are tested to give parents the most insight into a child's diverse set of skills and strategies when encountering unknown words.
How does our test evaluate phonics abilities in children who have very strong word knowledge already?
This is a great question. Especially with older students, word recognition skills may be very high. Our test assesses each phonics principle or skill in a sequential scope and sequence in a set of 10 questions. Within each set, half of the target words are nonsense words. By using this strategy, we can determine whether children actually understand each phonics principle. A breakout of types of errors is also provided. As you would guess, for older children who have not quite mastered phonics, it is often the case that 100% of their errors are with the non-words.
How does DORA compare to other types of assessments, such as iReady, STAR, or MAP-ELA?
This is a very broad question. DORA is essentially a multiple-measure diagnostic assessment, designed to explain why a student is struggling or doing well, rather than simply to measure summative assessment outcomes. So if DORA says a student is at grade level 1.17 in phonics, you also know that the student is working on short vowels. Scores are tied to specific skills and concepts, unlike in other assessments that focus on providing data for school administrators, who mainly want data for accountability purposes. The best way to evaluate and compare is to look at sample reports from each of these assessments. One other item that separates DORA from other assessments is that DORA is a series of tests.
DORA is essentially a multiple-measure diagnostic assessment, designed to explain why a student is struggling or doing well, rather than simply to measure summative assessment outcomes. So if DORA says a student is at grade level 1.17 in phonics, you also know that the student is working on short vowels. Scores are tied to specific skills and concepts, unlike in other assessments that focus on providing data for school administrators, who mainly want data for accountability purposes. The best way to evaluate and compare is to look at sample reports from each of these assessments. One other item that separates DORA from other assessments is that DORA is a series of tests.
Does our placement test measure phonological awareness?
Phonological awareness is a broad skill that includes manipulating and identifying oral language – parts such as words, syllables, and onsets and rimes. Phonemic awareness refers to the ability to focus on and manipulate individual sounds in spoken words. We measure in three ways. One measure that is included in our test is a phonological awareness screener. We also have a stand-alone test that measures both phonemic awareness and phonological awareness. In addition, we have a Dyslexia Screener that includes a phonological awareness screener.
We measure in three ways. One measure that is included in our test is a phonological awareness screener. We also have a stand-alone test that measures both phonemic awareness and phonological awareness. In addition, we have a Dyslexia Screener that includes a phonological awareness screener.
Discover LGL ELA Instruction
Page load linkGo to Top
How To Determine Your Child’s Reading Level And Choose The Best Books
When you sit down to read a book, you want to enjoy the story in front of you. The same is true for your child. That’s why uncovering your child’s reading level is an important step in fostering their love of words from a young age!
Consider the different factors that allow kids to enjoy the books they read. For example, does it tie into their interests, and is it slated as an appropriate option for their level? By answering these questions, you can make sure they’re reading books that are just right for them!
If your child is in school, you’re probably no stranger to jargon like “reading level. ” But what exactly does Lexile Framework, Guided Reading Levels (GRL), or Developmental Reading Assessment (DRA) actually mean?
” But what exactly does Lexile Framework, Guided Reading Levels (GRL), or Developmental Reading Assessment (DRA) actually mean?
Additionally, if your child is just starting to read on their own (or already reading independently) and is learning from home, how can you figure out what reading level is right for them? If any of these thoughts have crossed your mind, you’ve come to the right place.
We’re here to answer your questions so you and your child can sit down and enjoy a good book together!
What Is A Reading Level?
A reading level is simply a measure of your child’s ability to read text. It reflects how well your little one can read independently. Importantly, reading levels help you choose books that are a good match for your child while still presenting a challenge.
Keep in mind these levels are meant to be helpful, not stressful. They don’t limit your child, but, rather, help them blossom into a fluent, excited reader.
When your child reads books that are appropriate for their current reading level, it boosts their confidence so they can truly enjoy reading! Also, knowing what level your child is at allows you to work with them to improve their skills.
That being said, it’s important to remember that children are unique and develop differently. Comparing your child to their peers isn’t necessarily the best approach when trying to assess their reading ability.
Why Is Determining Reading Level Important?
It’s helpful to determine your child’s reading level so you can find books that are appropriate for them to read on their own: not too difficult but challenging enough to encourage growth.
Reading level classification is a convenient tool you can use when searching online or at the library. And when you provide books that are on your child’s level, you create excitement and build their confidence, which can lead to a lifetime love of learning and reading!
If you’re looking for ways to help your little one read at the best level for them, Our new app HOMER Learn & Grow has a Stories section that gives age-appropriate story recommendations!
This is a great resource that takes your child’s specific interests and recommends stories just for them. What’s more, your child can choose to read along or read on their own.
What’s more, your child can choose to read along or read on their own.
How Is Your Child’s Reading Level Measured?
Your child’s reading level is usually measured at their school in first or second grade, and we’ll show you how that’s done. Here’s a tip: since your child’s teacher knows their reading level, consider asking the teacher (or the school librarian) for books your child can read at home.
Don’t worry if your child isn’t in school yet or if they’re homeschooled. We’ll show you how you can measure their reading level at home, too!
Before we dive in, it’s important to note that we think of books for kids at three levels: independent reading, instructional reading, and frustrating to read.
As the names indicate, independent reading books are ones a child can read with ease and without support from an adult.
Instructional ones are the books just above independent that teachers might use to stretch a child’s reading as they offer support while the child makes that next step.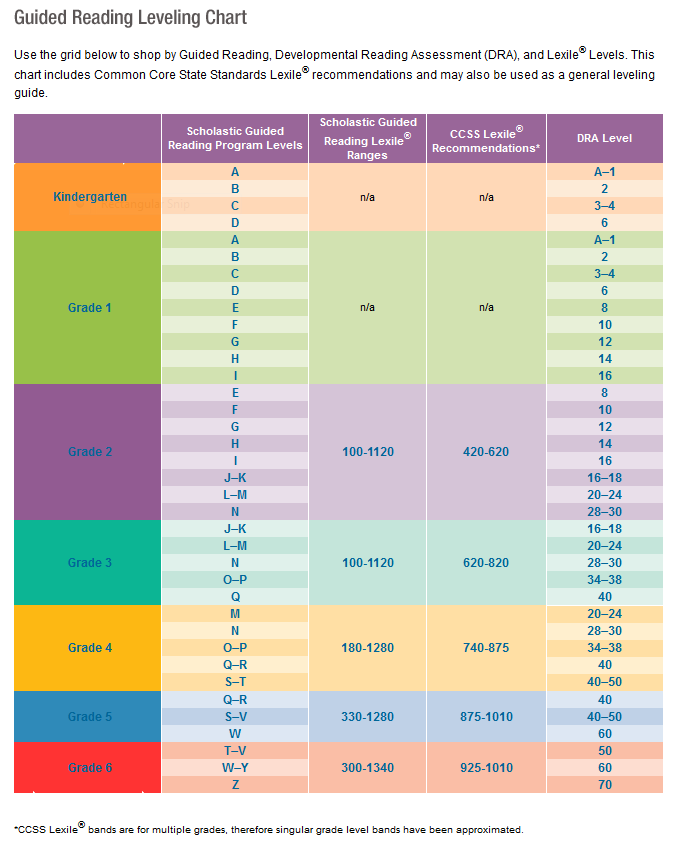 Finally, frustrating books are too hard for a child to read even with adult guidance.
Finally, frustrating books are too hard for a child to read even with adult guidance.
Now that you have an idea of how to think of the different books your child might encounter, let’s talk about the tools used for determining or describing reading levels.
Lexile Framework For Reading
Lexile Framework For Reading is an educational tool that ranks books by order of their difficulty using a scale called a Lexile. Usually, your child’s teacher will determine their Lexile reading level and then choose books that have a matching score.
The Lexile score, or measure, describes your child’s reading ability and matches them with books and other reading materials. This measure ranges anywhere from 0L to 2000L.
Kids are encouraged to read within their Lexile “range” — 50L above to 100L below their actual level. For instance, if your little one is reading with a Lexile measure of 500L, they would read books ranging anywhere from 400L to 550L.
Using standardized assessments, schools will often measure a child’s reading level several times a year to help them select books that are appropriate for independent reading.
Guided Reading Levels (GRL)
GRL is a guided reading system used in some schools.
To determine reading levels using GRL, children sit one-on-one with their teacher and read from a book that’s considered standard for their grade level — a “benchmark” book. GRL books range from A to Z with A being the easiest.
While reading these books, the teacher will take notes on any missed words and ask comprehension questions, such as, “When did the story take place?” or, “What was the problem in the story?”.
Through guided instruction, the teacher will gradually move children into more difficult books.
Developmental Reading Assessment (DRA)
DRA is a standardized reading test given by teachers or reading specialists. As with GRL, children sit individually with the test administrator and read a book.
Several factors are taken into consideration to determine reading level, including:
- Reading comprehension
- Phonemic awareness
- Fluency
DRA books are labeled with an A for the easiest books and then move into a numerical grading system. The levels range from 1 to 80 with 1-3 representing a kindergarten reading level and 80 representing an eighth-grade reading level.
The levels range from 1 to 80 with 1-3 representing a kindergarten reading level and 80 representing an eighth-grade reading level.
Once a child has a DRA or a GRL level, a teacher or parent can search for the reading level of any particular book and can usually discover either the Lexile, DRA, or GRL of that particular text. Here’s a chart for your reference.
At-Home Reading Levels
If you’re looking for a way to find out your child’s reading level without using any of the methods listed above, you might try the five-finger rule.
For the five-finger rule, choose a book and flip to any page. If your child seems to have trouble reading more than five words on the page, it’s a good indicator that the book is too advanced for them.
To be sure, though, you can have your child try another page, especially if they seem eager to read a particular book.
This can be a helpful strategy, but it’s OK to let your child try a book and see how the reading goes. If a book is too hard, most kids will figure that out — and there is nothing wrong with reading books that are too easy!
If a book is too hard, most kids will figure that out — and there is nothing wrong with reading books that are too easy!
Sometimes a child may be interested in a book that’s a little too hard for them. If this happens, we encourage you to read aloud to your child. You can also read together by alternating pages, paragraphs, or sentences.
It’s important not to completely avoid books that may be a little above your child’s reading level.
Even if your child struggles a bit to read them without assistance, these books can still be beneficial in helping build their vocabulary, improve comprehension, and increase general knowledge — not to mention, encourage their love of reading!
When your emerging reader seems overwhelmed by one book, you can always give the five-finger rule a try with other books until you find the right match. And if your child is particularly interested in a topic, you can always read the book to them and stop on words you know they can read.
Also remember that when a child is really enjoying a book and highly motivated to read it, they will read at a higher level than if the material is not as interesting to them.
Tip: Most libraries and bookstores have books arranged by reading level so you can easily choose the best one for your emerging reader!
Feel free to ask librarians and knowledgeable staff at bookstores to offer suggestions. You could even say something like, “My child happily read a Clifford book; can you suggest others at the same level?”
How To Help Your Child Become A Stronger Reader
As we mentioned earlier, you can easily determine your child’s reading level at home so that you can help them choose books that are just right! We suggest incorporating some of the tips below to help your child become a stronger reader.
Start With Clues
- Is your child using “sounding out” techniques to figure out unknown words?
- When your child reads, are they getting tripped up by sight words — common words that are hard to sound out?
- Is your child using pictures to help them understand what is written on the page?
- Is your child using context clues to figure out what word makes sense to come next as they read sentences?
Check Vocabulary
- Play games with your child to see what words they know.
 For example, say a sentence and point out one word in the sentence. Then ask them if they can come up with a different word (synonym).
For example, say a sentence and point out one word in the sentence. Then ask them if they can come up with a different word (synonym). - Play synonym games to see what words your child knows. For example, challenge yourselves to think of 10 or more ways to describe speaking (shout, whisper, mumble).
While you’re talking with your child, describe something specific from your day. Make sure to use interesting adjectives, and don’t hold back from using sophisticated vocabulary when talking with your child.
You can help your child’s vocabulary grow through day-to-day conversations and activities!
Ask Comprehension Questions
Understanding what they read is an important part of your child’s reading journey.
- To check for reading comprehension, we suggest pausing every other page to talk about what you’ve just read. Make this a natural reaction to the story, like you’re thinking aloud about the story or characters, so that it doesn’t feel like a test.
- Consider encouraging your child to act out and retell the story (for younger children).
- Try discussing themes/lessons with your child (for older children). Remember: this isn’t a test, but a conversation between book lovers!
Talk To Your Child
When most people implement strategies to help their children improve their reading skills, they often forget about the importance of verbal communication. It’s essential to talk to your child frequently in short and simple sentences.
This includes singing songs, telling them wonderful stories, reciting fun nursery rhymes, and describing the world around them. All of this exposes children to lots of different words. It also helps them learn that language is a powerful tool for communication.
Discover Your Child’s Favorite Books
- Children often choose books that are a little below their actual reading level. At home, this is a good thing. It keeps reading fun and exciting!
- We recommend choosing books that interest your child — with a certain character or activity they like — so they’re curious and excited about reading.
Reading books your child enjoys together can encourage their love of reading. And letting them read those same books to you can boost their confidence over time.
Together, these two activities increase your child’s fluency and reading enjoyment!
Create A Reading Corner
Establishing a reading corner in your house can benefit your child. The setup doesn’t need to be elaborate. This can be a simple, quiet, private area where your child can confidently read independently or with you.
It’s also great for the spot to be well-lit and filled with lots of books your child enjoys reading.
Is Reading The Same Book Over And Over OK?
Just like you might pick up an old favorite book to read, your child may do the same, and that’s OK! At least you know they’re enjoying a good book and the process of reading!
Rereading books can have many benefits for a child, including:
It allows children to get more from the text. Have you ever developed a deeper understanding of a story after rereading it? That’s because the more you engage with a story, the more you can take away from it.
You can pick up on new information, establish connections between yourself and some of the characters, and even improve your understanding of the overall story.
Similarly, allowing your child to read their favorite books for the second, third, fourth (or more) time will enable them to get more from the story.
It also allows for bonding. Did you know that rereading books can help bring your family closer together?
Many of us remember a couple of books that our family read together regularly. This can be a holiday book or a favorite story. Rereading is a great way to get the whole family involved, as everyone can take turns reading and connecting on the same story.
What’s more, reading familiar books can actually help develop a young reader’s fluency. It allows them to learn the words and helps them become familiar with narrative structure or storylines (i.e. beginning, middle, and end), which builds reading comprehension later on.
So feel free to let your child choose the same book over and over!
FAQs About Reading Levels
What Reading Level Should My Child Be In Each Grade?
It’s challenging to answer this question because each child is different and will naturally develop at their own pace. For example, just because your child’s friend has started reading fluently doesn’t mean your child will be able to do that yet.
While no parent wants their own child to be a little behind compared to their peers, putting too much pressure on them to “catch up” might actually have an adverse effect. In fact, they might feel overwhelmed by the pressure and develop a negative attitude toward reading.
It’s also important to note that there’s no direct link between a certain Lexile measure and a specific grade level. When using any of the reading level measures we mentioned, remember that they are an estimate of a child’s performance and shouldn’t be interpreted literally.
Also, if you’re really concerned about your young learner’s development, you can always address those concerns with their teacher or another professional. They can offer tips and advice on how to best work with your child.
Finally, remember to be patient and positive no matter what. With lots of time and effort, your child will develop a lifetime love of reading!
Who Can Help Me Choose Books That Match My Child’s Reading Level?
The best place to start is to consult your child’s teacher. They will have the expertise to guide you in buying the right books for your child.
It’s also possible for you to look up most books online and find their reading levels. Furthermore, for beginner readers, there are publishers who label books in stages with age and/or grade suggestions attached.
If you’re homeschooling, you can also reach out to your local librarian or bookstores. As people who spend each day surrounded by books, they often have knowledge on this topic and may be able to recommend a few relevant books in your child’s reading level.
What If My Child Is Reading At A Lower Level?
The last thing a parent wants to hear is that their child’s reading level isn’t on par with their peers. But what can you do if, from the assessment used at your child’s school, you find out that your young learner is reading below the average grade level?
Firstly, it’s important not to panic. As mentioned earlier, kids develop reading skills at different stages of their development. Some children might be early readers, while others may take time to get there.
The most effective way to help your child improve their reading level is by continuing to encourage reading at home. While reading, remember to discuss the content to ensure comprehension.
Reading For Fun
From assessments to the five-finger rule, determining reading levels varies across the board. No matter which method you choose, remember these measurements are meant to be helpful and encouraging, not stressful and limiting.
Keep this in mind when assessing your young learner. You don’t want your child to sense any stress about their abilities, as this might overwhelm them and have an adverse effect on how they view reading.
While reading is an essential early learning (and lifelong) skill, you want your child to LOVE reading and not only view it as a test of their intelligence.
At the end of the day, the way reading makes your child feel is more important than their reading level. Each child learns in a way that’s special and unique to them.
The HOMER Road To Reading
The road to discovering how to read can be a fun ride, but sometimes it’s bumpy. This is why we’re more than a learning program. We’re your learning partner.
If you’re looking for a resource to help develop your child’s love of reading and learning, consider taking a look at the HOMER Learn & Grow app. It’s full of stories curated based on your child’s interests!
When your child develops a love for reading, they’ll move up to the next level before you can say “Developmental Reading Assessment”!
Author
Reading technique for grades 1-4
Reading is one of the basic skills for every child. Being able to read is important not only for the lessons of literature and the Russian language, but also for all other sciences. It will be difficult for a student to learn material in mathematics, English or the world around him if he does not know how to quickly familiarize himself with the text and understand what he read. It is reading that opens the door to the world of knowledge. Mastering cognitive texts or works of art, children learn to communicate, learn about the surrounding reality, and broaden their horizons. Cognitive abilities are also honed - memory, attention. Therefore, reading is considered the basis of success in further education.
But how do you know if a child reads well for his age or not? This can be done by checking the reading technique. Many parents do not quite understand the format and meaning of this test, believing that the determining criterion is speed, that is, the number of words read per minute. In fact, the test is focused on assessing not only the pace of reading, but also other skills. Let's try to deal with the requirements prescribed for reading technique in the Federal Standards.
Reading technique: basic criteria
How fast should you read? Is everything okay with a child with technology? Perhaps his skills do not meet some standards? These questions always concern responsible parents. And I must say that there is nothing wrong with this excitement, because involvement in the process of teaching children is in many ways the key to future success. But is it really worth worrying about reading speed?
To answer this question, it is necessary to understand in detail what exactly is assessed when testing reading technique. According to the requirements of the Federal State Educational Standard, the following are assessed:
- reading speed - the number of characters that a child is able to read in one minute;
- way of reading - reading words syllable by syllable or whole, smoothly;
- correctness - the absence of errors and hesitations made by the child when reading;
- awareness - the ability to understand the meaning and idea of what is read;
- expressiveness - the ability to correctly place stresses, observe intonation and maintain pauses when reading.
Analyzing the listed criteria, we can say that the test of reading technique is based on the assessment of two components: semantic and technical. At the same time, the technical side - tempo, expressiveness, correctness - is subordinated to the semantic, that is, the ability to understand the content of the text.
Reading technique: what is really important?
Reading is the most important type of speech activity, based on the ability to perceive and assimilate information. Unlike drawings, diagrams and video sequences, it activates the imagination. Scientists have proven that when reading poetry, other areas of the brain are involved than when mastering prose. This fact is explained by the different structure of phrases and phrases used in prose and poetry. Therefore, the ability to read can be considered as a tool for self-development. But this is not a basic skill, but acquired in the learning process. And here it is important not to force things, but to focus on the abilities and capabilities of the child.
It must be understood that reading technique is just one of the criteria, and it is not necessary to focus only on it. Especially parents whose children are not yet in school. Don't just chase the pace. At this stage, it is more important to broaden your horizons, get acquainted with different topics, memorize new words. And the best way to achieve this is to read a lot, daily, but not to put speed at the forefront.
As far as schoolchildren are concerned, two parameters essentially matter here: technique and meaningfulness of reading. Technique is usually called the ability to distinguish letters, transform them into sounds, compose syllables and words. Meaningfulness is a deeper concept. It is based on understanding the meaning and content of the text.
It would be erroneous to require a child to make sense of what they read until they have developed the skill of technical letter recognition. All the efforts of the crumbs, who are just learning to read, are aimed at memorizing and recognizing letters, syllables, words. In order to understand the essence of what is written in the text, he no longer has any intellectual strength or time. Therefore, primary education teachers first focus on technology, and only when it is brought to automatism, they begin to form a meaningful approach to reading.
Reading speed standards for elementary school
Reading speed standards adopted for elementary school students:
- Grade 1: 1st semester - 20-25 words per minute, 2nd semester - 30-40 words;
- Grade 2: I half-year - 40-50 words; II half-year - 50-60 words;
- Grade 3: I half-year - 60-70 words; II half-year - 70-80 words per minute;
- Grade 4: 1st half year – 80-90 words per minute; end of the school year - 100-120 words.
In classes and schools for gifted children, the rate of reading may be higher. So, in the first grade, such children read more than 60 words per minute, in the second - 90-95, in the third - 95-105 words per minute. The pace when reading to yourself should be 20-50 words faster than when reading aloud.
Other test parameters
And a few more parameters that you should pay attention to:
- Grade 1 - the student can read a significant part of the text by syllables.
- Grade 2 - higher requirements are imposed on reading technique: only complex words can be read by syllables, it is important to observe pauses and correctly place stresses.
- Grade 3 - reading must be conscious and expressive, with observance of intonation. In order to correctly assess the skills of the child, retelling is practiced.
- Grade 4 - the student should be able to analyze what he has read and express his personal opinion.
Focusing on the standard, we can draw some conclusions about the effectiveness of training. But even if the child cannot read the number of words prescribed in the standards, you should not worry too much about it. After all, these are just average standards developed on the basis of general data. Each student has their own level and pace of development. Checking the technique is rather information for the teacher and parents. After analyzing the results, you can understand in which aspects of training you need to show more diligence.
Testing your reading skills yourself
You can organize a reading test at home, but don't turn it into an exam. Some children are quite sensitive to any tests, and in stressful situations they cannot always demonstrate everything they are capable of. Come up with a game format or check the technique discreetly. If the child himself wants to know what success he has achieved, then no problems will arise.
Action sequence:
- Arm yourself with a watch with a second hand. To check, you can use a stopwatch on your smartphone, but it’s better to refuse an hourglass, since a child who has never seen such a thing will be distracted by them.
- Prepare a text and show it to the child.
- Ask to read the text aloud.
- The time should be recorded from the start of reading.
- If you notice that a child has made a mistake, do not stop him, but simply make a note for yourself.
- Rate the result. To get the most objective picture of the student's skills, you should conduct a control check and compare the results.
If you see that the child is not concentrated enough, he is in a bad mood or is not feeling well, check the reading technique on another day.
Correctly evaluate the result
Count the number of words read. Points to pay attention to when counting:
- conjunctions, particles, prepositions consisting of one or two letters are counted as one word;
- when wrapping, the word is counted not as one, but as two;
- words with a hyphen are counted differently: if there are three or more letters on both sides of the hyphen, then the word is counted as two, less than three letters - as one word.
Not only speed is important, but other criteria as well. Be sure to evaluate the correctness of the text you read. All mistakes made should be sorted out with the child. If you notice that there are a lot of hesitations, corrections, changes in endings and whole words, you should consult with the teacher. Perhaps professional correction of reading skills is needed.
It is also important to understand how well the child understood the meaning of the text. It is not necessary to ask the student to retell what they have read. It is enough that he describes the content in a few words. Ask him to identify the main idea. If there are problems with this, then you can resort to retelling.
Pay attention to expressiveness. The student should try to observe intonation, pause in accordance with punctuation marks. Unfortunately, not all children are able to read a passage with an expression. Tell the child in which places you need to increase the pace and emotionality, which words need to be emphasized.
Requirements for texts used to test reading skills
When choosing a text, adhere to the following recommendations:
- It should be a text unfamiliar to the child, but not too complex, age appropriate.
- Pay attention to the structure of sentences: they should be short, without dialogues and a lot of punctuation marks.
- It is better to choose text without pictures.
- Font size is also important - it should be large enough.
- Text must not be split into two pages.
Of course, you shouldn't check your reading technique using the instructions for household appliances or a manual for housewives. The best option is short stories about nature, animals, seasons.
Tips for Improving Reading Technique
If your test results don't meet the standards, don't get upset. But what really needs to be done is to put more diligence and not be lazy to practice. You can seek help from specialists or deal with the child on your own. But just remember that you need to do at least 15 minutes every day.
There are many exercises to improve reading technique:
- reading the same text several times in a row with a gradual increase in pace;
- "buzzing reading" - daily five minutes of reading in a low voice;
- "gibberish writing" - the use of texts in which some of the letters are written upside down;
- "word search" - an exercise to search for a specific word in the text;
- exercise with syllabic tables.
This is just a part of the exercises to improve your reading technique. There are also recommendations for working on literacy, expressiveness, understanding the meaning of what is read:
- if there are problems with diction, you should focus on tongue twisters;
- in order for the child to better understand the meaning of what he read, ask him to retell texts more often, make plans, draw illustrations for any passage;
- Poems are most suitable for improving the expressiveness of reading. Only you need to recite them not quietly and calmly, but loudly and emotionally.
It is believed that the speed of reading should be comparable to conversational speech. This opinion is shared by both distinguished teachers and young innovative teachers. On average, 120-150 words per minute - it was to this pace that the human articulatory apparatus adapted over several centuries of evolution. Of course, such indicators are applicable for middle and high school students, but this does not mean that they should not be strived for. After all, all the basic skills laid down in the primary grades will definitely come in handy in the future. The ability to read an average of 120 words will allow you to quickly master the material and cope with tasks. Naturally, provided that this is a conscious reading with an understanding of the meaning. Therefore, you need to work on the technique and pace of reading constantly.
Grade and Quarter Standards
Reading is a key skill that opens the gate to the land of knowledge. Thanks to this skill, children learn about the phenomena and events of the world around them, get acquainted with the characters and actions of people, meet new problems and ideas. This skill helps them to broaden their horizons and ideas about the world, develops critical thinking and trains cognitive abilities - attention, imagination, memory. Reading is the foundation for further successful learning.
To understand how well a child develops this skill, it helps to check the reading technique. Reading technique is a multifactorial test that characterizes the development of a skill from different angles. In reading technique, the following are evaluated:
- reading speed,
- reading method,
- reading awareness,
- correct reading,
- expressiveness of reading.
A difficult reading skill consists of both a technical and a semantic component and is aimed at achieving the main goal - understanding and assimilation of the information read.
Reading technique parameters
Let's consider all the components of reading technique in more detail.
- Reading speed - the number of words read in a certain period of time. Often, parents focus on the formation of fluent reading, while the child makes many mistakes, does not understand and does not remember what he read. It is not necessary to force only speed, slower conscious reading and a gradual increase in tempo are better than fast mechanical reading with errors and inaccuracies.
- Reading method — syllabic reading or reading the whole word, smoothly. With the development of the skill, the child has a gradual transition from syllabic reading to smooth reading in whole words.
- The correctness of reading is characterized by the absence of errors and hesitation. Inattention, problems of diction lead to inaccurate reading, indistinct articulation and, as a result, to a distortion of meaning. Pay attention to the correct reading - this will be the key to competent writing.
- Reading awareness involves reading comprehension, awareness of the idea and meaning of the text, and in the future - this is the ability to catch the subtext, humor, irony, the attitude of the author. Interfering with reading comprehension can be low reading speed, distorted reproduction - guessing words, changing the shape of words, not reading endings.
- Reading expressiveness - the use of pauses, finding the right intonation, the correct placement of stress.
The expressiveness of reading is inextricably linked with awareness. When understanding what is read, it is easier for the child to observe the necessary pauses, select the correct intonation and place logical stresses.
Reading speed standards for primary school
GEF standards determine the desired reading speed for a child at a certain point in learning, help to understand whether the development of a skill is successful or whether additional attention is required. Standards - indicative values; it is important to take into account the individual psychophysiological characteristics of each child and evaluate the growth of his personal indicators.
Grade 1 reading speed standards
Reading speed standards in grade 2
Reading speed standards in grade 3
Reading speeds in grade 4,
Reading speed, to which it is necessary schools, is reading at the speed of conversational speech, 110-120 words per minute. The human articulatory apparatus has adapted to this speed over time. And most importantly, the reading should be conscious, correct, expressive.
Other parameters of reading technique
Grade 1
At the end of the first half of the year. Reading is smooth syllabic, conscious and correct, with a clear pronunciation of syllables and words.
At the end of the second half of the year. Reading is conscious, correct, simple words are read as a word. Words with a complex syllabic structure can be read syllable by syllable.
Grade 2
At the end of the first half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. Compliance with logical stresses. Compound words can be read syllable by syllable.
At the end of the second half of the year. Reading meaningful, correct, in whole words. With observance of logical stresses, pauses and intonations. Syllabic reading is undesirable.
Grade 3
At the end of the first half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, with the help of which the child expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is being read.
At the end of the second half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the child expresses understanding of the meaning of what is being read.
4th grade
At the end of the first half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With the help of observed pauses and intonations, the child not only expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is being read, but is able to express his attitude to what he has read.
At the end of the second half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the child expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is read, and his attitude to the content of what is read.
How can I test my child's reading skills on my own?
Have your child see how well they read already. Children usually love to know how many centimeters they have grown, and they may also be interested in knowing their progress in reading. Warn about the upcoming test and ask the child to read quickly.
The control of reading technique in sensitive children who, due to their temperament, can hardly tolerate various tests, can be carried out imperceptibly or in the form of a game. Do not create unnecessary excitement around the upcoming test, do not arrange a test in the form of an exam. If the child is worried, stutters, transfer control to another time.
Verification process:
- Prepare a clock with a second hand or use the stopwatch on your phone, and choose the appropriate text.
- Ask the child to take a seat.
- Show him the text and ask him to read it aloud.
- Track the time from the moment your child starts reading.
Not all children are able to immediately start reading on command, which leads to inaccurate results.
- Usually, one minute is noted for checking, but some experts recommend taking 2 minutes for monitoring, since not all children are equally quickly included in the work. Divide the result obtained in 2 minutes in half.
- When reading, do not correct or interrupt. It is better to discuss the mistakes made after the child has finished reading.
- Assess the speed, correctness, awareness and expressiveness of reading.
- Retest and compare results. Reading technique may differ depending on the child's fatigue, health status and mood.
Which text is suitable for verification?
For this purpose, both fiction and popular science texts, appropriate for the age of the child, are suitable. The text should be unfamiliar, but understandable to the child, have educational and educational value. The texts of V. Bianchi, L. Tolstoy, N. Nosov, B. Zhitkov, K. Ushinsky, V. Dragunsky are suitable. The text for verification can be found in special manuals or in a textbook on the Russian language and literature.
You should find the text that is located on the spread of the book so that the child does not have to waste time turning pages. Choose text without an abundance of punctuation marks and distracting illustrations. It is not desirable that the passage contains common complex sentences and dialogues. The font must be large enough and legible. The text should not have a technical focus and contain terms incomprehensible to the child.
Test score
Speed score
Count how many words the child read in one minute. When counting words, pay attention:
- prepositions, conjunctions, particles of 1-2 letters are counted as one word;
- when wrapping, a word counts as 2 words;
- if the word is written with a hyphen, look at how many letters are on both sides of the hyphen: if there are more than three, we count it as 2 words, for example, “long-long”, if less than three, for example, “somehow”, - as one .
Compare your score with the recommended range and your child's previous performance.
Comprehension score
Determine how well the child understood what they read. If the student reads slowly and has read only a couple of sentences, let him read the passage to the end. Ask your child a few questions about the text. Ask what or who he read about. Ask the child to identify the main idea of what they read and retell the text.
For a deeper check of the meaning of the reading and learning, use special teaching kits.
Correctness assessment
Pay attention to whether the child reads what is written correctly, whether he pronounces words clearly, whether there are hesitations and corrections, whether he alters words, whether he changes endings, whether he places stresses correctly. Discuss the mistakes with the student.
Evaluation of expressiveness
To assess the expressiveness of reading, the child is offered a familiar text. Listen to whether the child observes pauses and other punctuation marks, whether he changes intonation, whether he highlights the main idea.
Improving reading technique
Poor results in reading technique are not a reason to be upset, but only a signal that additional efforts need to be made to improve the skill. You can work with the child on your own or contact a specialist who will analyze the weak points and select the appropriate exercises. Conduct additional activities with the child in the mode of "sparing reading" without pressure. It is more important to observe the regularity and frequency of classes: 10-20 minutes daily.
How can you motivate your child to read:
- Reward your efforts with stickers, stars.
- Mark progress visually - create a success board so your child can visually see their progress
- Conduct activities in the form of a game, such as "going to the library" or "reading to your favorite toys.
"
- Choose books and texts that are interesting for your child.
- Let the child read to the pets, they are grateful and accepting listeners. Reading to them, the child is not afraid to make a mistake, he relaxes and overcomes the fear of failure.
- Have a reading competition between peers and siblings.
To improve the speed of reading will help:
- Reading by syllabic tables.
- Multiple reading. Read the same text several times, increasing the pace. From the second time the child will be able to read faster.
- "Tug". An adult leads a finger along the line, setting the pace. The child tries to read at a given pace.
- Tops and roots. The child reads the words, covering the upper or lower half of the letters with a ruler.
- Reading in a book turned upside down.
- Lightning. Alternating reading at a comfortable pace with reading at the highest possible speed for 20 seconds on the command "Lightning!".
- "Sprint". Reading speed competition between classmates.
- Work on expanding the field of view according to Schulte tables.
- Reading with a window to eliminate "regression" - recurrent eye movements that lead to repeated reading.
For correct reading:
- Work on clear diction, do articulatory gymnastics.
- Read tongue twisters and tongue twisters.
- Invite the child to correct the deformed sentences: "The weather is good on the street."
- "Imaginary word". When reading, the wrong word is pronounced, the child must correct it.
Reading comprehension
- “Reading in a wave”. First, the child reads aloud, then retells what he read.
- Drawing up a plan for reading.
- The student reads to himself at a comfortable pace, tells what he understood and felt, what he thought about
- Discuss unfamiliar words and expressions.
- Invite the child to draw a picture of the passage they read.