Learning shapes activity
25 Creative Activities and Ideas For Learning Shapes
Learning shapes is one of the earliest concepts we teach kids. This readies them for geometry in the years ahead, but it’s also an important skill for learning how to write and draw. We’ve rounded up our favorite activities for learning shapes, both 2-D and 3-D. They all work well in the classroom or at home.
1. Start with an anchor chart
Colorful anchor charts like these are terrific reference tools for kids learning shapes. Have kids help you come up with examples for each one.
Learn more: A Spoonful of Learning/Kindergarten Kindergarten
2. Sort items by shape
Collect items from around the classroom or house, then sort them by their shapes. This is a fun way for kids to realize that the world around them is full of circles, squares, triangles, and more.
Learn more: Busy Toddler/Shape-Sorting
3. Snack on some shapes
Everyone loves a learning activity you can eat! Some food items are already the perfect shape; for others, you’ll have to get a little creative.
ADVERTISEMENT
Learn more: Chieu Anh Urban
4. Print with shape blocks
Grab your shape blocks and some washable paint, then stamp shapes to form a design or picture.
Learn more: Pocket of Preschool
5. Go on a shape hunt
These “magnifying glasses” make an adventure of learning shapes! Tip: Laminate them for long-term use.
Learn more: Nurture Store UK
6. Hop along a shape maze
Use sidewalk chalk to lay out a shape maze on the playground or driveway. Choose a shape and hop from one to the next, or call out a different shape for every jump!
Learn more: Creative Family Fun
7. Assemble a truck from shapes
Cut out a variety of shapes (excellent scissors skills practice!), then assemble a series of trucks and other vehicles.
Learn more: Little Family Fun
8.
 Stretch out shapes on geoboards
Stretch out shapes on geoboards
Teachers and kids love geoboards, and they’re a great tool for learning shapes. Give students example cards to follow, or ask them to figure out the method on their own.
Learn more: Mrs. Jones’ Creation Station
9. Drive on shaped roads
Use these free printable road mats to work on shapes. Bonus: Make your own road shapes from sentence strips!
Learn more: PK Preschool Mom
10. Find shapes in nature
Take your shape hunt outside and look for circles, rectangles, and more in nature. For another fun activity, gather items and use them to make shapes too.
Learn more: Nurture Store UK
11. Put together craft stick shapes
Add Velcro dots to the ends of wood craft sticks for quick and easy math toys. Write the names of each shape on the sticks for a self-correcting center activity.
Learn more: Surviving a Teacher’s Salary
12.
 Blow 3-D shape bubbles
Blow 3-D shape bubblesThis is a STEM activity that’s sure to fascinate everyone. Make 3-D shapes from straws and pipe cleaners, then dip them in a bubble solution to create tensile bubbles. So cool!
Learn more: Babble Dabble Do
13. Prep a shape pizza
Cover a paper plate “pizza” with lots of shape toppings, then count the number of each. Simple, but lots of fun and very effective.
Learn more: Mrs. Thompson’s Treasures
14. Construct shapes from toothpicks and Play-Doh
This is an excellent STEM challenge: how many shapes can you make using toothpicks and Play-Doh? Marshmallows work well for this activity too.
Learn more: Childhood 101
15. Outline shapes with stickers
Kids adore stickers, so they’ll enjoy filling in the outlines of the shapes they’re learning. They won’t realize it, but this gives them fine motor skills practice too!
Learn more: Busy Toddler/Sticker Shapes
16.
 Lace shapes
Lace shapesLacing cards have long been a classic, but we really like this version that uses drinking straws. Just cut them into pieces and glue them along the edges of the cards.
Learn more: Planning Playtime
17. Make shapes with LEGO bricks
LEGO math is always a winner! This activity also makes a good STEM challenge. Can your students figure out how to make a circle from straight-sided blocks?
Learn more: Pocket of Preschool
18. Categorize shapes by their attributes
Work on geometry terms like “sides” and “vertices” when you sort shapes using these attributes. Start by placing shapes into paper bags and asking students questions like, “The shape in this bag has 4 sides. What could it be?”
Learn more: Susan Jones Teaching
19. Count and graph shapes
These free printable worksheets challenge kids to identify shapes, then count and graph them. Lots of math skills, all in one!
Learn more: Playdough to Plato
20.
 Create a shape monster
Create a shape monsterAdd arms, legs, and faces to create cheery (or scary) shape monsters! These make for a fun classroom display.
Learn more: Fantastic Fun and Learning
21. Sift through rice for shapes
Sure, kids can identify their shapes by sight, but what about by touch? Bury blocks in a bowl of rice or sand, then have kids dig them out and guess the shape without seeing them first.
Learn more: Fun With Mama
22. Craft an ice cream cone
Ice cream cones are made up of several shapes. Encourage kids to see how many different ways they can make a sphere of “ice cream.”
Learn more: Extremely Good Parenting
23. Ask “What does the shape say?”
If you don’t mind the risk of getting that song stuck in your kids’ heads, this is such a neat way to combine writing and math.
Learn more: Around the Kampfire
24. Piece together shape puzzles
Use wood craft sticks to make simple puzzles for kids who are learning their shapes. These are inexpensive enough that you can make full sets for each of your students.
These are inexpensive enough that you can make full sets for each of your students.
Learn more: Toddler at Play
25. Feed a shape monster
Turn paper bags into shape-eating monsters, then let kids fill their hungry bellies!
Learn more: Teach Pre-K
From teaching shapes to long division and everything in between, these are the 25 Must-Have Elementary Classroom Math Supplies You Can Count On.
Plus, 22 Active Math Games and Activities For Kids Who Love to Move.
27 Amazing Activities for Learning Shapes
Learning shapes is an early and important teaching concept. This is a terrific way to introduce children to problem-solving skills and pattern recognition. The learning of shapes prepares students for future math courses such as geometry. Check out these 27 amazing ideas for learning shapes!
1. Box of Chocolates
Create your very own box of chocolates with a variety of shapes.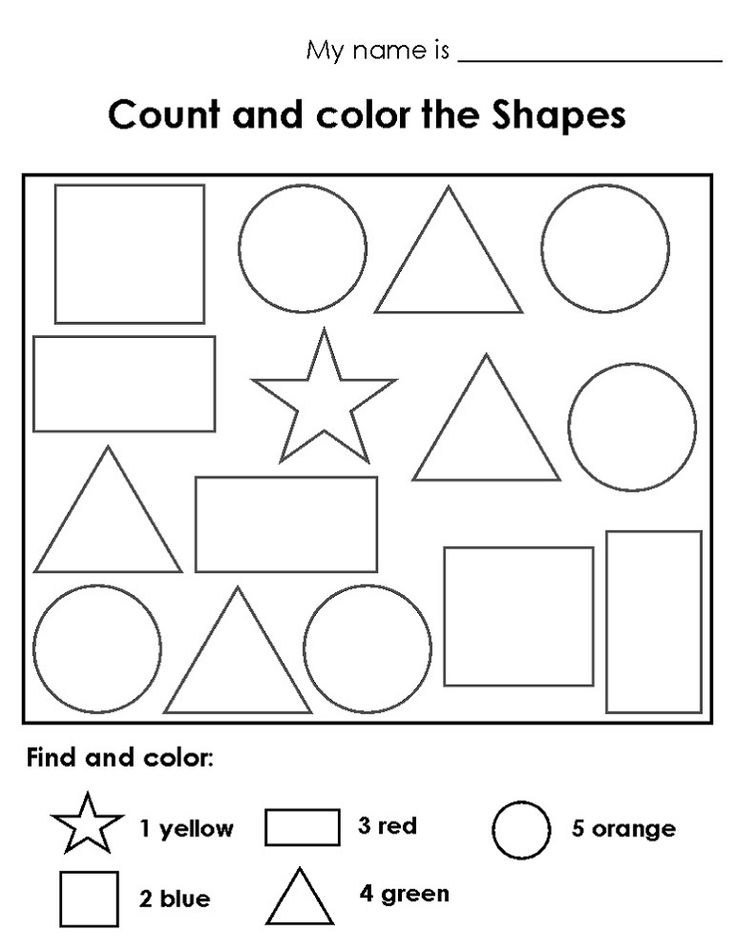 Use a stencil to cut shapes from foam board. Draw basic shapes inside a heart drawing to represent a box of Valentine’s chocolates. Students will match the foam shapes to the drawings. This is a super activity for Valentine’s Day!
Use a stencil to cut shapes from foam board. Draw basic shapes inside a heart drawing to represent a box of Valentine’s chocolates. Students will match the foam shapes to the drawings. This is a super activity for Valentine’s Day!
Learn more: Active Littles
2. Shape Bingo
Shape Bingo is a great idea for 3D shape practice! This fun activity is free and can be used in the classroom with the entire group or for classroom learning centers.
Learn more: 123 Homeschool 4 Me
3. Beanbag Shape Hop and Toss
For this engaging activity, use painter's tape to create outlines of shapes on the floor. Have your children hop from shape to shape. You can have them say the name of the shape once they hop into it. They can also throw beanbags into the shapes for more fun.
Learn more: Learn Play Imagine
4. Edible Shapes: Tic-Tac-Toe Cookies
Kids will absolutely love this shape activity. They will get to help make chocolate chip cookies shaped like X's and O's. Once they finish playing a few rounds of tic-tac-toe, they will have the opportunity to eat the delicious cookies!
They will get to help make chocolate chip cookies shaped like X's and O's. Once they finish playing a few rounds of tic-tac-toe, they will have the opportunity to eat the delicious cookies!
Learn more: The Realistic Mama
5. Shapes Sorting Suncatcher
This is a favorite shape sorter for 2 to 3-year-old children. You will need contact paper, scrapbook paper, and felt or foam shape pieces. You can make or own or purchase them.
Learn more: Happy to Shelf
6. Snowman Shape Matching
Children love building snowmen, so they will have a blast with this free snowman-themed activity! Kids will learn about shapes as they match each snowman's head to its same shaped body.
Learn more: Tot Schooling
7. Shape Art
Cut out several shapes and create a piece of art as a classroom example. Next, give each student a stack of the same shapes and have them create the same masterpiece.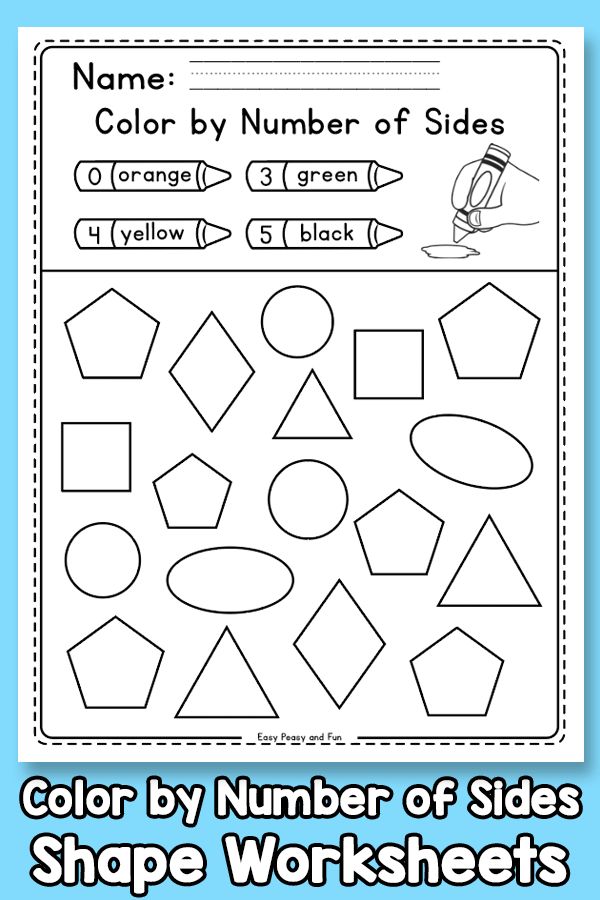 When students have completed their artwork, you will have a fun classroom display!
When students have completed their artwork, you will have a fun classroom display!
Learn more: Raising the Spenglers
8. Marshmallow Geometry
Marshmallow geometry is an engaging and fun activity for teaching children shapes. They will learn the names of 2D shapes as well as their characteristics. All you need is pretzel sticks, miniature marshmallows, markers, and card stock or construction paper.
Learn more: Playdough to Plato
9. 2D Shape Poems
Children love these shape poems! These poems are free and allow students to be introduced to a variety of key shapes. Leave these displayed in your classroom for students to see on a daily basis.
Learn more: Miss Kindergarten
10. Clip Shapes
These free shape printables are a fun activity for shape identification for preschoolers and toddlers. They will learn to be successful at shape-matching while they strengthen their fine motor skills.
Learn more: Modern Preschool
11. Ice Tray Shape Sorting
Purchase wooden circles, a plastic ice tray, and shape stickers or colored paper cut in shapes. If you use colored paper, you will also need glue to attach the shapes to the wooden circles. Children will place the wooden circles in the correct spot on the tray.
Learn more: Mess for Less
12. Shape Monsters Craft
The shapes monsters craft is so much fun for kids! They will learn about shapes and colors as they create their very own monsters. The only supplies you need are construction paper, glue, and scissors.
Learn more: Live Well Play Together
13. Circle Collage
Teach children about the circle shape. You will need colored paper, scissors, and glue to complete this activity. Have the child cut out a large circle and many small circles. The child will then glue the smaller circles on the larger circle.
Learn more: Family Education
14. 20 Fun Shape Books
Using stories about shapes is a terrific way to teach kids all about shapes! They can learn about shape names with these books. This resource will help you find the perfect shape book to use with your child today!
Learn more: 123 Homeschool 4 Me
15. Basic Shapes Workbook
Using shape workbooks is a wonderful way to teach your children all about shapes. This workbook is created for preschoolers and offers shape guides, tracing, patterns, matching, activities, and much more. Buy yours today!
Learn more: Libro World
16. DIY Shape Puzzle
This simple shape puzzle is a DIY activity that is so easy to make. Your little one will enjoy playing with it over and over again as they learn all about basic shapes and their characteristics.
Learn more: Laughing Kids Learn
17. Preschool Shape Scavenger Hunt
Preschoolers will love this shape activity, and it is so easy and inexpensive to create. Just draw some shapes on pieces of paper and have your child find real-life objects to match the shapes.
Just draw some shapes on pieces of paper and have your child find real-life objects to match the shapes.
Learn more: Frugal Fun 4 Boys
18. Learn Shapes with Sticks
You and your child can venture out in nature and have your child pick up a few small sticks to create simple craft stick shapes. They will have a blast in nature as well as create these basic shapes.
Learn more: Toddler in Action
19. Shape Sensory Bottles
The little learners will have lots of sensory shape fun with this activity! These sensory bottles are super easy to make, and little ones can twist, flip, or shake the bottles to find the basic shapes. These bottles are perfect for center time or quiet time!
Learn more: Pocket of Preschool
20. Shape Clouds
Little ones will enjoy making clouds out of shapes. This activity is simple to create; all you need is a shape printable, glue, and cotton balls. Let your little one create clouds of different shapes and have a blast doing so.
Let your little one create clouds of different shapes and have a blast doing so.
Learn more: Planning Playtime
21. Spaghetti Noodle Shapes
This free resource provides 10 shapes printables that will help your child strengthen motor skills while learning all about shapes. Your child will use cooked spaghetti noodles to outline the shapes. They will have a tremendous amount of fun completing this activity!
Learn more: Schooltime Snippets
22. Bubble Wrap Painting - Learning Shapes
Kids will love this bubble wrap painting activity, and they will learn about shapes. They will have a blast popping the bubbles and painting different shape patterns. Your child will also develop fine motor skills as well as improve hand and eye coordination.
Learn more: Learning 4 Kids
23. Sticky Shape Rainbow Activity
Purchase a large tub of foam sticker shapes, so your child can create a shape rainbow. Draw the outline of a rainbow and put one shape of each color in a certain place on the rainbow outline and then allow your child to fill in the rest.
Draw the outline of a rainbow and put one shape of each color in a certain place on the rainbow outline and then allow your child to fill in the rest.
Learn more: Fun Learning for Kids
24. Magazine Shape Hunt and Sort
Are you searching for an engaging activity that will increase your child's fine motor skills and hand-eye coordination? If so, this is the perfect activity. It will also teach your child about shapes and encourage the use of critical thinking skills.
Learn more: Fun Learning for Kids
25. Preschool Pipe Cleaner Shapes Activity
This video will explain the preschool pipe cleaner shapes activity. This fabulous activity is perfect for 2-4-year-old children. It increases fine motor skills as well as hand-eye coordination. Your child will also learn about shapes, colors, and counting.
Learn more: Zaneta The Work At Home Mama
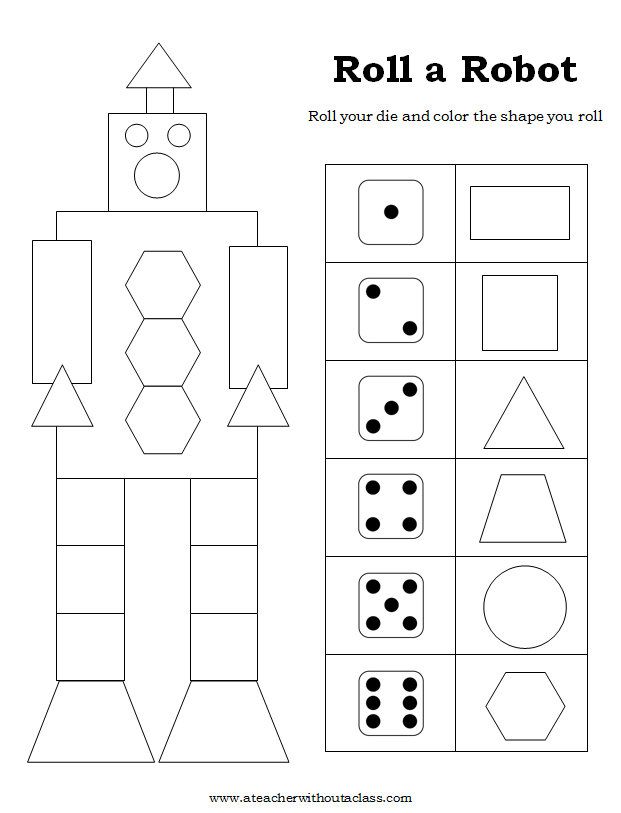
26. Build a Robot
Your child will learn about shapes while creating a cool robot! This engaging activity also develops cognitive skills and fine motor skills. Cut out the shapes and glue the robot together.
Cut out the shapes and glue the robot together.
Learn more: Fun House Toys
27. Magic Disappearing Shapes
Draw a variety of basic shapes on a coffee filter. Name a shape and have your child drip water over the correct shape. The shape will disappear, and you can move to the next shape. This activity is also terrific for fine motor practice!
Learn more: Gift of Curiosity
Program "From sound to letter. Formation of sound analytical and synthetic activity of preschoolers as a prerequisite for literacy training" (Elena Kolesnikova)
I will wait
The price on the site may differ from the price in the chain stores. The appearance of the book may differ from the image on site.
Out of stock
The price on the site may differ from the price in the chain stores. The appearance of the book may differ from the image on site.
Partial educational program “Echo to the letter.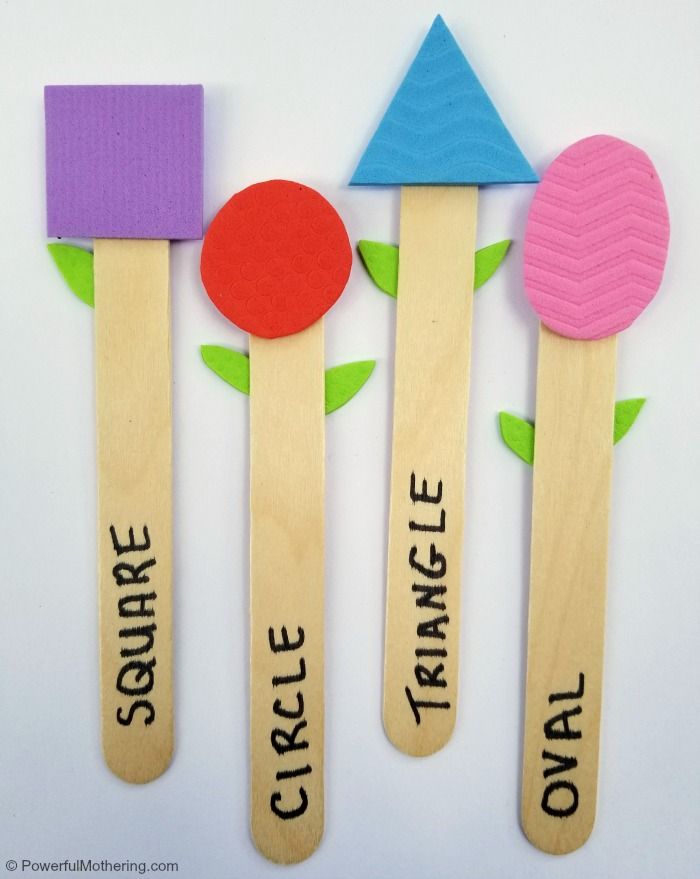 The formation of analytical and synthetic activity as a prerequisite for teaching literacy” is the result of the author’s many years of experience working with preschool children (more than 25 years). . .It defines the content, volume, conditions for implementation and the planned results of the development of the program “From sound to letter. Formation of sound analytical and synthetic activity as a prerequisite for teaching children 2-7 years old to read and write (educational area "Speech development"). . .The program is accompanied by an educational and methodological kit for children aged 2-7 years (24 manuals), which includes didactic manuals for both adults and children. Availability of teaching materials is one of the conditions for the effective implementation of the Program (FGOSDO). . .Recommended to all participants in the educational process - children, teachers, parents. .
The formation of analytical and synthetic activity as a prerequisite for teaching literacy” is the result of the author’s many years of experience working with preschool children (more than 25 years). . .It defines the content, volume, conditions for implementation and the planned results of the development of the program “From sound to letter. Formation of sound analytical and synthetic activity as a prerequisite for teaching children 2-7 years old to read and write (educational area "Speech development"). . .The program is accompanied by an educational and methodological kit for children aged 2-7 years (24 manuals), which includes didactic manuals for both adults and children. Availability of teaching materials is one of the conditions for the effective implementation of the Program (FGOSDO). . .Recommended to all participants in the educational process - children, teachers, parents. .
Description
Characteristics
Partial educational program “Echo to the letter. The formation of analytical and synthetic activity as a prerequisite for teaching literacy” is the result of the author’s many years of experience working with preschool children (more than 25 years). . .It defines the content, volume, conditions for implementation and the planned results of the development of the program “From sound to letter. Formation of sound analytical and synthetic activity as a prerequisite for teaching children 2-7 years old to read and write (educational area "Speech development"). . .The program is accompanied by an educational and methodological kit for children aged 2-7 years (24 manuals), which includes didactic manuals for both adults and children. Availability of teaching materials is one of the conditions for the effective implementation of the Program (FGOSDO). . .Recommended to all participants in the educational process - children, teachers, parents. .
The formation of analytical and synthetic activity as a prerequisite for teaching literacy” is the result of the author’s many years of experience working with preschool children (more than 25 years). . .It defines the content, volume, conditions for implementation and the planned results of the development of the program “From sound to letter. Formation of sound analytical and synthetic activity as a prerequisite for teaching children 2-7 years old to read and write (educational area "Speech development"). . .The program is accompanied by an educational and methodological kit for children aged 2-7 years (24 manuals), which includes didactic manuals for both adults and children. Availability of teaching materials is one of the conditions for the effective implementation of the Program (FGOSDO). . .Recommended to all participants in the educational process - children, teachers, parents. .
BINOM. Knowledge Lab
There are no reviews for this product yet
Be the first to share your opinion
How to get bonuses for reviewing this product
1
Make an order in the online store
2
Write a detailed review of 300 characters only for what you bought
3
Wait for the review to be posted.
If he is among the top ten, you will receive 30 Favorite Shopper Card bonuses. Can write unlimited number of reviews for different purchases - we will add bonuses for each one published in top ten.
Bonus Rules
If he is among the top ten, you will receive 30 Favorite Shopper Card bonuses. Can write unlimited number of reviews for different purchases - we will add bonuses for each one published in top ten.
Bonus Rules
The book "The program "From sound to letter. Formation of sound analytical and synthetic activity of preschoolers as a prerequisite for learning to read and write"" is available in the online store "Chitay-gorod" at an attractive price. If you are in Moscow, St. Petersburg, Nizhny Novgorod, Kazan, Yekaterinburg, Rostov-on-Don or any another region of Russia, you can place an order for a book Elena Kolesnikova "The program" From sound to letter. Formation of sound analytical and synthetic activity of preschoolers as a prerequisite for literacy training "" and choose a convenient way to receive it: pickup, delivery by courier or sending mail. To make buying books even more pleasant for you, we regularly hold promotions and contests.
Formation of sound analytical and synthetic activity of preschoolers as a prerequisite for literacy training "" and choose a convenient way to receive it: pickup, delivery by courier or sending mail. To make buying books even more pleasant for you, we regularly hold promotions and contests.
Formation of professional and creative activity of students in the process of teaching the composition of Palekh miniature painting
One of the types of traditional miniature tempera painting on papier-mache lacquer products (boxes, caskets, plates) is Palekh miniature painting, which arose in 1923 in the village of Palekh Ivanovo region. Palekh art of miniature painting is based on the traditions of Palekh icon painting, ancient Russian painting and folk art, as well as much of world art. The birth of a new art in Palekh was a natural result of the development of centuries-old traditions in new historical conditions.
Initially, the art of Palekh has two distinct beginnings: tradition and innovation.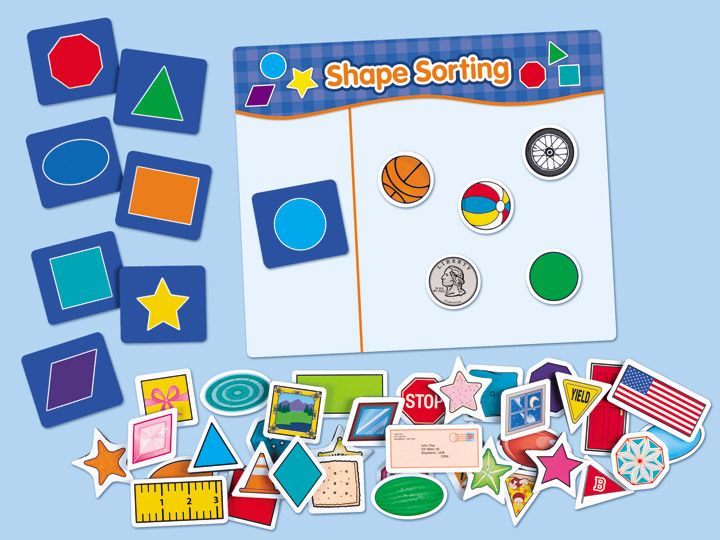 On the one hand, the general pictorial style of Palekh arose on the basis of traditional Orthodox culture, on the basis of a high culture of icon painting, on the other hand, it received great support from the Soviet authorities, as "art born of the revolution." As A. V. Bakushinsky notes, “the new content, the new structure of images, new materials and techniques have made profound changes in the forms of traditional art” [2, p. 250].
On the one hand, the general pictorial style of Palekh arose on the basis of traditional Orthodox culture, on the basis of a high culture of icon painting, on the other hand, it received great support from the Soviet authorities, as "art born of the revolution." As A. V. Bakushinsky notes, “the new content, the new structure of images, new materials and techniques have made profound changes in the forms of traditional art” [2, p. 250].
At present, Palekh miniature is an integral part of domestic traditional arts and crafts. The formed style of Palekh miniature art is characterized by the poetic nature of the means of expression - the “melodiousness” of the image, based on its great rhythm; ornamentality, giving great importance to the beauty of silhouettes; decorative; elongation, elegance of proportions; special calligraphy, expressed in the virtuosity of such a pictorial tool as a line; flatness, a special construction of space, which unfolds not in depth, but upwards; wholeness; a penchant for improvisation; subtle color relationships.
Almost all researchers of the art of Palekh miniature painting share the view of traditions as a living, developing structure and warn against the “use”, “application” of traditions, which is fraught with external stylization, mannerisms, imitation, degeneration into a “pseudo-Russian style”. Thus, traditions in folk art can be mastered, developed, you can refer to them, but you need to understand that each Palekh artist must find his own style, different from everyone else, as I. I. Golikov, I. I. Zubkov found their style, N. M. Zinoviev and others.
With the organization in 1930 of a vocational school in Palekh, reorganized in 1934 into an art college, professional education in the field of Palekh traditional lacquer miniature painting begins. In 1936, the technical school was renamed the Palekh Art School. M. Gorky. This educational institution of secondary vocational education functions to this day.
The professional culture of the future master artist is formed on the condition that he is included in the spiritual space of the Palekh traditional culture, through training at the Palekh Art School. M. Gorky, and then - independent professional creative activity. Therefore, the main goal of preparing students is the purposeful formation of professional and creative activity. Education at the school for the future master becomes direct communication with the professional environment that forms his professional culture - the culture of the artist Palekh.
M. Gorky, and then - independent professional creative activity. Therefore, the main goal of preparing students is the purposeful formation of professional and creative activity. Education at the school for the future master becomes direct communication with the professional environment that forms his professional culture - the culture of the artist Palekh.
The formation of the personality of a young artist is influenced by theoretical and special academic disciplines studied at an art school. But a special place in the preparation of the artist-master of Palekh miniature painting is given to composition, as an academic discipline that is most conducive to the development of imaginative thinking and creative abilities.
Composition is the foundation of any work, summarizing life observations, subordinating them to the creative goals of the artist. To convincingly solve an artistic image is the main thing in compositional work.
Back in 1933, A. V. Bakushinsky noted that “. .. Palekh should think about some serious restructuring of his language, his form, decisively overcome the conservatism and passivity of his tradition, not breaking with it, but using all its values, rebuilding from within… The future of Palekh and any art that arises from similar conditions and traditions depends on this or that decision…” [2, p. 280].
.. Palekh should think about some serious restructuring of his language, his form, decisively overcome the conservatism and passivity of his tradition, not breaking with it, but using all its values, rebuilding from within… The future of Palekh and any art that arises from similar conditions and traditions depends on this or that decision…” [2, p. 280].
M. A. Ilyin believed that the creative artistic life of Palekh, the creation of prerequisites for a new creative impulse for its further development, are associated with experimental work: “... works should ideally be new in spirit and appearance, creatively processing the ever-renewing decorative principles and techniques of Russian art. And then we will be able to talk about Palekh as a living, developing artistic center, in which the principles of “wonderful patterning” will find fundamentally new incarnations, consonant with our time” [4, p. 107].
In 1972, he wrote: “... decorativeness must be sought in the reality around us, as the old masters of Palekh searched and found it according to their worldview. Today's worldview of the Paleshans is different, and it is necessary to reflect it in a different way... All these new techniques should be based on a composition that does not copy the composition of icons and fresco scenes of the 17th century, but on their own new composition, found in the process of working on new artistic tasks" [4, With. 106].
Today's worldview of the Paleshans is different, and it is necessary to reflect it in a different way... All these new techniques should be based on a composition that does not copy the composition of icons and fresco scenes of the 17th century, but on their own new composition, found in the process of working on new artistic tasks" [4, With. 106].
In the field of traditional applied art, it is necessary to note such important criteria of professional culture as fundamental knowledge of the technique of performance, technology and skills in the practical application of the high style of traditional painting, the assimilation of the spiritual potential inherent in this unique national art, designed to form the worldview of a person of traditional culture as a translator of values this culture.
There are two levels of abilities: reproductive and creative. These levels are interconnected. At the reproductive level of development of abilities, a high ability to assimilate knowledge, master activities and carry them out according to the proposed model is revealed. At the creative level of development of abilities, a person creates a new, original. No creative activity is possible without reproductive activity. Thus, in order to form the creative activity of the future artist-master of Palekh lacquer miniature painting, it is first necessary to master the craft.
At the creative level of development of abilities, a person creates a new, original. No creative activity is possible without reproductive activity. Thus, in order to form the creative activity of the future artist-master of Palekh lacquer miniature painting, it is first necessary to master the craft.
In the Soviet period, the People's Artist of the USSR Nikolai Mikhailovich Zinoviev did a great job of studying and systematizing the traditions of Palekh art. He developed a methodology for teaching the skill of Palekh painting. N. M. Zinoviev wrote two books: The Art of Palekh and Stylistic Traditions of Palekh Art.
There are no teaching aids directly on composition in Palekh traditional painting today.
As a result of practical pedagogical observation, it was revealed that modern students of the Palekh Art School, brought up on the perception of realistic painting, have difficulties with the specific construction of space inherent in Palekh miniature painting, based on spherical and reverse perspective. Also, difficulties cause the need to monitor the beauty and clarity of the silhouette, the “live” line, the plasticity of the image, the fear of a blank slate, the inability to think figuratively and a number of other problems. In the process of long-term assimilation of the complex artistic language of traditional Palekh art, students often lose a keen interest in creative activity.
Also, difficulties cause the need to monitor the beauty and clarity of the silhouette, the “live” line, the plasticity of the image, the fear of a blank slate, the inability to think figuratively and a number of other problems. In the process of long-term assimilation of the complex artistic language of traditional Palekh art, students often lose a keen interest in creative activity.
Thus, the question arises of how to increase students' motivation for creative activity.
Creativity is always stimulated by a new task that requires search, tension, restructuring of existing stereotypes. This is a kind of “feeding” of creative energy. Creative skills are formed on non-standard material, which gives a “shake-up” to the psyche of the performer. Thus, the creative activity of students can be increased by performing special short-term warm-up exercises in the classroom.
When including short-term exercises aimed at the professional and creative activation of students, it is important to take into account the specifics of Palekh art when including short-term exercises in the academic discipline "Composition".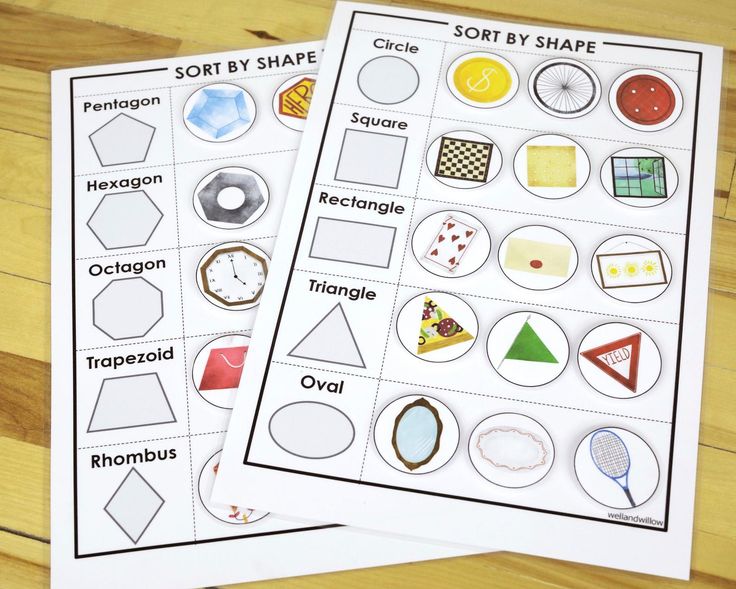 At the same time, the warm-up should be carried out in the form of a game, creating an atmosphere of spontaneity and freedom. After completing the exercise, you should conduct a general review of the work with a discussion of the advantages and disadvantages of each of them.
At the same time, the warm-up should be carried out in the form of a game, creating an atmosphere of spontaneity and freedom. After completing the exercise, you should conduct a general review of the work with a discussion of the advantages and disadvantages of each of them.
Artistic talent has two main components: the personality of the creator and his abilities. Proceeding from this, the development of a creative personality should occur in two directions.
The first direction is the formation of special character traits: the desire for creative novelty; desire for self-expression; originality and speed of thinking; courage and resourcefulness; desire to go in creativity in their own way. The second direction is the improvement of cognitive mental processes: attention; sensations; perception; thinking; memory [5, p. 200].
It is known that creative activity is built on the basis of human cognitive abilities that can be developed.
1. Attention is a mental state that is characterized by the complete concentration of all mental and physical forces on the action being performed. Any complex activity, and primarily creative, is impossible without a well-developed control of one's attention.
Any complex activity, and primarily creative, is impossible without a well-developed control of one's attention.
Attention does not belong to the sphere of cognitive mental processes, but it is the most important condition, without which the full-fledged work of these processes (and, accordingly, the effectiveness of activity) is impossible.
Voluntary attention can be developed with the help of an exercise in which students must reproduce a sample drawing from memory. Also, the ability to concentrate attention is facilitated by the performance of a brush drawing without prior preparation with a pencil, when the student is forced to mentally keep the existing image entirely in his mind, while accurately working with a brush, without the possibility of corrections.
2. Sensations are a cognitive mental process in which individual properties of objects are reflected in their direct impact on the sense organs.
There are visual, auditory, olfactory, gustatory and kinesthetic sensations. There are also spatial sensations.
There are also spatial sensations.
For the profession of an artist, visual and spatial types of sensations are essential. Thus, artists learn to distinguish a significant number of shades of color. Also in professional artistic activity, so-called sensory syntheses appear, based on the close interaction of various types of sensations.
For the development of synthetic syntheses, we have developed the following exercise: perform two color monotypes, based on the sensory perception of two pieces of music with different emotional coloring.
3. Perception. If sensations are a reflection of the individual properties of an object, then perception is a reflection of all the properties of an object. Perceptions, like sensations, are divided into visual, auditory, gustatory, tactile, and olfactory. For the development of perception in a learning situation, purposeful observation is organized, during which there is a comprehension and interpretation (explanation) of what a person observes. Observation goes from the external properties of objects, sensually perceived and emotionally experienced, to the knowledge of the internal connections and patterns of the phenomenon.
Observation goes from the external properties of objects, sensually perceived and emotionally experienced, to the knowledge of the internal connections and patterns of the phenomenon.
Exercise: analytical analysis of works of fine art. Comparative analysis of techniques, means of depicting easel art and traditional art of Palekh.
In the process of developing artistic perception, students gain an understanding of the expressive means of a work of art, which leads to a more adequate, complete, deep perception of it.
4. Memory - "a storehouse of life experience and professional skills."
The development of visual memory is based on the exact fixation of what was previously seen. A distinctive feature of the development of artistic memory is the principle of artistic selection based on plastic vision. The accumulation of visual impressions not only strengthens observation, has a fruitful effect on the conscious attitude to drawing, but also makes it possible to emerge from the depths of memory once seen, which is extremely important when working on a composition.
5. Thinking is a cognitive mental process by which reality is reflected in a generalized and indirect form. Thinking reveals such connections and relations in an object that are inaccessible to sensory perception.
The artist conveys his thoughts in the form of an artistic image.
In artistic creativity, the solution of problem situations is connected with finding the greatest expressiveness and originality of the image created by the artist.
For the development of thinking, independent work of thought and problem situations are necessary. A creative person is characterized by divergent thinking, which consists in finding many solutions to the same problem. Exercise: find different solutions to the same topic. The search is carried out in the form of creating 10 fore-sketches in a short time.
6. Imagination is a mental process that consists in creating new images and ideas based on their elements obtained earlier in a person's previous experience.
Imagination is the highest stage in the development of all higher mental functions. In it, to solve a practical problem, sensations and perceptions, thinking and memory, emotions and will are brought together. Therefore, in the processes of artistic creativity, imagination plays a paramount role.
In it, to solve a practical problem, sensations and perceptions, thinking and memory, emotions and will are brought together. Therefore, in the processes of artistic creativity, imagination plays a paramount role.
Exercise: to see and complete the specific images in the previously created color monotypes. On the basis of these works, make a graphic brush drawing of the composition.
The basis of the creative process of creating a work is the emergence of a plastic motif, the artist's ability to think in visible images. The embodiment in a specific image of the stock of existing knowledge and ideas that express a certain content is the most essential feature of this process.
In addition, in order to translate an idea into a sketch, to find a convincing plastic figurative expression for it, it is necessary to have a developed spatial representation, fluency in drawing, and a powerful force of artistic imagination.
In today's difficult conditions, the goal of the Palekh Art School is to train not a master performer, but a creative person with a highly developed artistic taste, a highly professional artist.