Verbs for 5th graders
Verb Unit 5th Grade - DEVINE
To begin the year we will do a mini unit/review on verbs. 1. Action verbs 2. Present tense 3 Past tense 4. Linking verbs 5 Helping verbs 6. Irregular verbs (See the link below called: VerbsBeginning for copies of the worksheets used) We will review with the Kahoot links below. At the end of this review week students will take a quiz. A little later in the review we will study verbs more in depth with the English Text book. See the lessons outlined below. A copy of the text book pages are also linked for easy access at home. We will end the year with another review and regular practice with daily language review. +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ Goals: Identify the subject and predicate in a sentences Identify the verb or verb phrase in the predicate Memorize 23 Helping Verbs:
Kahoot: Verb Practice #1 Verb practice #2 Introduction to action verbs Action Verbs Select the verb in the sentence Verb phrases Helping verbs Verb review-Winn Dixie Action Verbs #1 - Shows what the subject does or did Jill pitches the ball. Direct Objects #2 - a noun or pronoun in the predicate that received the action of the verb. Main Verbs and Helping Verbs #3 - The main verb shows the action. The helping verb works with the main verb. Linking Verbs #4 A linking verb links the subject of a sentence with a word or words in the predicate. Anna is a lifeguard. Anna is the subject. "Is" is the linking verb. What is Anna.....a lifeguard. Common linking verbs: am, is, are, was, were, will be, look, feel, taste, smell, seem, appear Present Tense #5- A verb that tells what its subject is doing right now is the present tense. Rules for forming present tense: Most verbs - add s gets, plays Verbs ending is s, ch, sh, x and Z - add es passes, punches, pushes, mixes, fizzes Verbs ending with a consonant and y- change the y to i and add es. Past Tense #6 - A verb that shows what has already happened is past tense. Rules for forming past tense: Most verbs add -ed played, reached Verbs ending with e - add d believed, hoped Verbs ending with a consonant and y - change the y to i and add - ed studied, hurried Verbs ending with a single vowel and a consonant - double the final consonant and add -ed stopped, planned Future Tense #7 - A verb that tells what is going to happen is in the future tense. To form the future tense of a very, use the helping verb will or shall with the main verb. Subject-Verb Agreement #8 - A present tense verb and its subject must agree in number. Agreement with be and have #9 Subject Form of be Form of have I am, was have, had You are, were have, had He, she it is, was has, had We are, were have, had You are, were have, had They are, were have, had Contractions with not #10 don't didn't isn't can't Regular and Irregular Verbs #11 bring brought come came go went make made run ran More Irregular Verbs #12 Verb Phrases with have #13 could have could've would have would've should have should've must have must've Teach, Learn: Let, Leave #14 Sit, Set; Can, May #15 sit - to rest set- to place or put can- to be able may - to be allowed |
List of Verbs for Kids
List of Verbs for Kids - Verb Online GamesA verb is a word that conveys ACTION, OCCURRENCE, or STATE OF BEING. Verbs are needed to form complete sentences or questions. In a sentence, a verb works as the main component of the predicate, the part of a sentence that indicates what the subject (person or thing) is or does. The three main types of verbs are action verbs, helping verbs, and linking verbs. Unlike most of the other parts of speech, verbs change their form. Pair our lists of verbs for kids with our fun verb online games for engaging practice!
Verbs are needed to form complete sentences or questions. In a sentence, a verb works as the main component of the predicate, the part of a sentence that indicates what the subject (person or thing) is or does. The three main types of verbs are action verbs, helping verbs, and linking verbs. Unlike most of the other parts of speech, verbs change their form. Pair our lists of verbs for kids with our fun verb online games for engaging practice!
1
Verbs Sample List
Click 'Continue' to play with this list or enter your own
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
2
Choose
an Activity
3
Play and Learn
Play the game using your words
Everything on Verbs | |
|---|---|
| Verbs Tenses | show when the action in the sentence takes place |
| Irregular Verbs | are verbs that do not follow the rules for changing tenses |
| Action Verbs | describe something that a person, animal, thing, or force of nature can do |
| Linking Verbs | do not describe an action, but tell about the state or condition of subjects |
| Helping Verbs | are a set of two or three consonant letters that when pronounced, retain their sound |
Verbs Tenses
A verb tense shows when the action in the sentence takes place. In English, there are a total of 12 verb tenses, as well as conditional tenses that indicate when an action may or may not happen.
In English, there are a total of 12 verb tenses, as well as conditional tenses that indicate when an action may or may not happen.
The three main tenses on lists of verbs for kids are:
- Past – an action has already happened
- Present – an action is currently happening
- Future – an action will happen at a later time
Verbs are conjugated to communicate details, such as person, number, gender, tense or mood. The following table shows the verb “walk” conjugated to the three main verb forms with the subject being “I”.
Verb Tenses List | |
|---|---|
| Past | Yesterday, I walked to the park. |
| Present | I walk to the park. |
| Future | Next week, I will walk to the park. |
A verb like “walk” is a regular verb because it follows set rules when conjugated (adding -ed to indicate past tense, for example). Irregular verbs, however, are verbs that do not follow the rules for changing tense. For instance,the verb “sing” is an irregular verb. It does not follow the rule for past tense verbs as “sanged,” but rather as the irregular conjugation “sang.”
Irregular verbs, however, are verbs that do not follow the rules for changing tense. For instance,the verb “sing” is an irregular verb. It does not follow the rule for past tense verbs as “sanged,” but rather as the irregular conjugation “sang.”
Irregular Verbs List | |
|---|---|
| Verb | Past Tense |
| break | broke |
| buy | bought |
| do | did |
| drive | drove |
| eat | ate |
| feel | felt |
| find | found |
| grow | grew |
| have | had |
| ring | rang |
Types of Verbs
Not all verbs serve the same function. Verbs fall into three basic categories: action, linking, and helping.
Action Verbs
Action verbs describe something that a person, animal, thing, or force of nature can do. Verbs like run or jump are examples of action verbs.
Verbs like run or jump are examples of action verbs.
Action Verbs Lists | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| K-2 Verbs | 3-5 Verbs | 6-8 Verbs | 9-12 Verbs |
| eat | climb | compose | negotiate |
| run | grasp | emphasize | fluctuate |
| jump | borrow | interrupt | modify |
| drink | laugh | persuade | extinguish |
| walk | paint | investigate | thrive |
| chop | observe | erupt | eavesdrop |
| sing | rescue | adjust | acquire |
| act | search | vibrate | abolish |
| kick | travel | pursue | confiscate |
| mix | celebrate | verify | plunder |
Linking Verbs
Linking verbs do not describe an action, but tell about the state or condition of subjects. They link the subject with either a noun that renames it or an adjective that describes it. For example, the word “am” in the sentence “I am tall” describes the subject. There are some action verbs that function as linking verbs, such as grow. In the sentence “He grows tired,” the verb describes the subject rather than an action, so it works as a linking verb. Below are a list of other linking verbs.
They link the subject with either a noun that renames it or an adjective that describes it. For example, the word “am” in the sentence “I am tall” describes the subject. There are some action verbs that function as linking verbs, such as grow. In the sentence “He grows tired,” the verb describes the subject rather than an action, so it works as a linking verb. Below are a list of other linking verbs.
Linking Verbs List | |
|---|---|
| Forms of be | be, am, is, are, was, were, been, being |
| Other linking verbs | appear, become, feel, grow, look, seem, remain, smell, sound, stay, taste, turn |
Helping Verbs
Helping verbs do not express action, and they cannot stand alone in a sentence without another verb present. They are part of verb phrases that “help” the main verb. Helping verbs define the tense (past, present, future) or change the meaning of the main verb.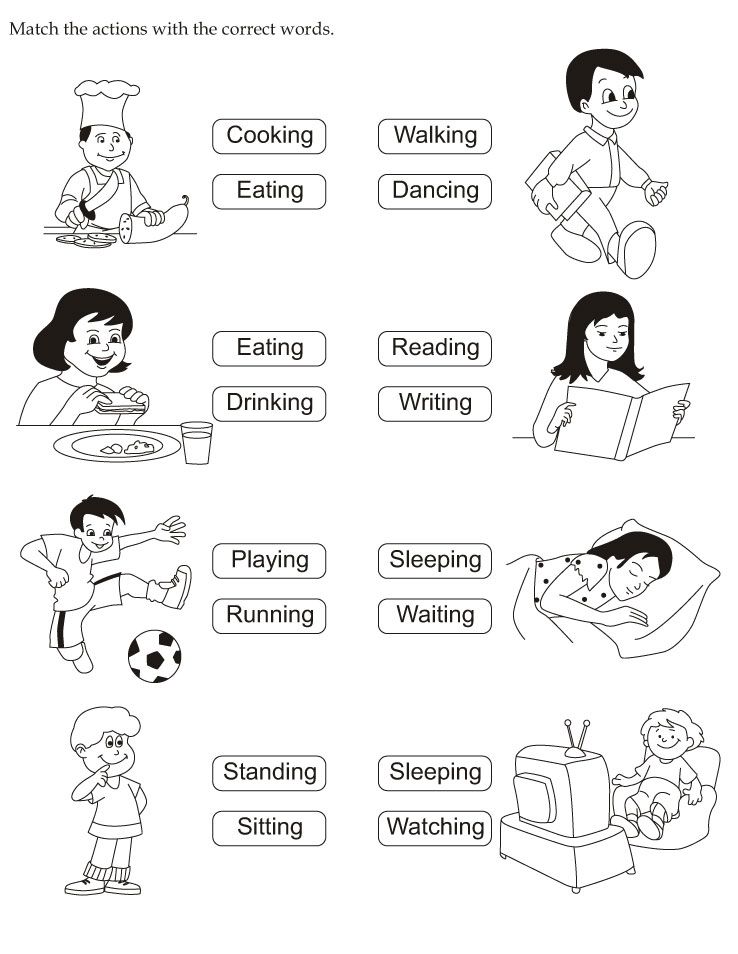 The verb “will” functions as a linking verb in the sentence “He will eat” because it helps the main verb “eat” and indicated a future tense. Some common helping verbs:
The verb “will” functions as a linking verb in the sentence “He will eat” because it helps the main verb “eat” and indicated a future tense. Some common helping verbs:
Helping Verbs List | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| will | must | must | had |
| had | do | shall | may |
| was | am | did | did |
| have | were | is | does |
| should | has | been | are |
| being | could | might | having |
The following table shows 50 common English verbs conjugated in the past, present, and future tense using the subject “I.” These are commonly found on lists of verbs for kids.
Common English Verb Lists | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Verb (base form, infinitive) | Past Tense | Present Tense | Future Tense |
| to ask | asked | ask | will ask |
| to be | was | am | will be |
| to become | became | become | will become |
| to bring | brought | bring | will bring |
| to build | built | build | will build |
| to buy | bought | buy | will buy |
| to call | called | call | will call |
| to change | changed | change | will change |
| to come | came | come | will come |
| to cut | cut | cut | will cut |
| to do | did | do | will do |
| to draw | drew | draw | will draw |
| to eat | ate | eat | will eat |
| to fall | fell | fall | will fall |
| to feel | felt | feel | will feel |
| to find | found | find | will find |
| to get | got | get | will get |
| to give | gave | give | will give |
| to go | went | go | will go |
| to have | had | have | will have |
| to hear | heard | hear | will hear |
| to help | helped | help | will help |
| to hope | hoped | hope | will hope |
| to keep | kept | keep | will keep |
| to know | knew | know | will know |
| to learn | learned | learn | will learn |
| to let | let | let | will let |
| to live | lived | live | will live |
| to make | made | make | will make |
| to move | moved | move | will move |
| to need | needed | need | will need |
| to play | played | play | will play |
| to put | put | put | will put |
| to read | read | read | will read |
| to run | ran | run | will run |
| to say | said | say | will say |
| to sell | sold | sell | will sell |
| to show | showed | show | will show |
| to stop | stopped | stop | will stop |
| to take | took | take | will take |
| to talk | talked | talk | will talk |
| to tell | told | tell | will tell |
| to think | thought | think | will think |
| to try | tried | try | will try |
| to turn | turned | turn | will turn |
| to use | used | use | will use |
| to walk | walked | walk | will walk |
| to want | wanted | want | will want |
| to work | worked | work | will work |
| to write | wrote | write | will write |
Share:
English Irregular Verbs - Translation Table, List of Forms (Grade 5)
4. 2
2
Average Grade: 4.2
Total Grades: 367.
4.2
Total Grades: 4.2
9002 Total Grades: 4.2 900Irregular verbs of the English language are exceptions against the background of the analytical type of grammar, where the conjugation of verbs occurs by adding auxiliary words. These parts of speech during the transition from the present to the past can be completely transformed or remain unchanged. nine0003
Brief description
In English, verbs are divided into 2 groups according to the type of creation Past Simple (Simple Past) and Past Participle (past participles). The correct ones add -ed to the stem. The wrong ones undergo a number of transformations during the formation of the second, third form:
It is impossible to accurately answer the question: “How many irregular verbs are there in English?” According to one of the authoritative dictionaries, the full list of such words has about 470. For successful learning, you need to learn 100-150 of the main most common ones.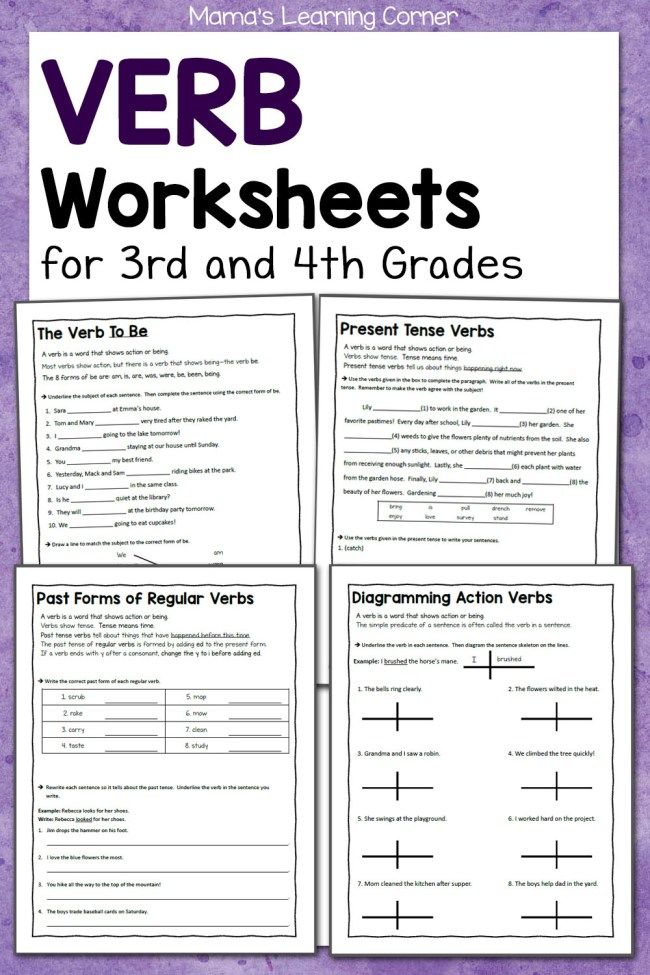 nine0003
nine0003
Table of Irregular English Verbs
The three forms of the verbs of this group are usually presented in the form of a table with transcription. Such a scheme with a translation is easy to print or use for online classes. For students of grade 5 and subsequent steps, a small list of irregular verbs is sufficient, the use of which is more common.
| Primary | Transcription | Translation | Past Simple | Transcription | Past Participle | Transcription |
| be | [bi:] | be | was/were | [wɔz]/[wз:] | been | [bi:n] |
| become | nine0030 [bɪ ‘kʌm]becomes | became | [bɪ ‘keɪm] | become | [bɪ ‘kʌm] | |
| begin | [bɪ ‘gɪn] | start | began | [bɪ ‘gæn] | started | [bɪ ‘gʌn] |
| bite | [baɪt] | bite | bit | [bɪt] | bitten | [‘bɪtn] |
| break | nine0030 [breɪk]break | broke | [brook] | broken | [‘broukən] | |
| bring | [brɪŋ] | bring | brought | [brɔ:t] | brought | [brɔ:t] |
| build | [bɪld] | build | built | [bɪlt] | built | [bɪlt] |
| buy | [baɪ] | buy | bought | [bɔ:t] | bought | [bɔ:t] |
| catch | [kætʃ] | catch | caught | [kɔ:t] | caught | [kɔ:t] |
| choose | [tʃu:z] | choose | chose | [tʃouz] | chosen | [‘tʃouzən] |
| come | [kʌm] | come | came | [keɪm] | come | [kʌm] |
| cost | [kɒst] | cost | cost | [kɒst] | cost | [kɒst] |
| cut | [kʌt] | cut | cut | [kʌt] | cut | [kʌt] |
| dig | [dɪg] | dig | dug | [dʌg] | nine0030 dug[dʌg] | |
| to | [du:] | do | did | [dɪd] | done | [dʌn] |
| draw | [drɔ:] | draw | drew | [dru:] | drawn | [drɔ:n] |
| drink | [drɪŋk] | drink | drank | [dræŋk] | drunk | [drʌŋk] | nine0072
| dream | [dri:m] | dream, dream | dream | [dremt] | dream | [dremt] |
| drive | [draɪv] | drive a car | drove | [drouv] | driven | [‘drɪvən] |
| eat | [i:t] | yes | at | [et] | eaten | [‘i:tn] |
| fall | [fɔ:l] | fall | fell | [fel] | fallen | [‘fɔ:lən] |
| feed | [fi:d] | feed | fed | [fed] | fed | [fed] |
| feel | [fi:l] | feel | felt | [felt] | felt | [felt] |
| fight | [faɪt] | fight | fought | [fɔ:t] | fought | [fɔ:t] |
| find | [faɪnd] | find | found | [faʊnd] | found | [faʊnd] |
| fit | [fit] | fit (fit) | fit | [fit] | fit | [fit] |
| fly | [flaɪ] | fly | flew | [flu:] | flown | [flu:] |
| forget | [fə ‘get] | forget | forgot | [fə ‘gɒt] | forgotten | [fə ‘gɒtn] |
| forgive | [fə ‘gɪv] | forgive | forgave | [fə ‘geɪv] | forgiven | [fə ‘gɪvən] |
| freeze | [fri:z] | nine0030 freezefrost | [frouz] | frozen | [‘frouzən] | |
| get | [get] | receive | got | [gɒt] | got | [gɒt] |
| give | [gɪv] | give | gave | [geɪv] | given | ['gɪvən] |
| go | [gou] | go | went | [went] | gone | [gɒn] |
| grow | [grou] | grow | grew | [gru:] | grown | [groun] |
| have | [hæv] | have | had | [hæd] | had | [hæd] |
| hear | [hɪər] | hear | heard | [hɜ:d] | heard | [hɜ:d] |
| hide | [haɪd] | hide | hid | [hɪd] | hidden | [‘hɪdn] |
| hit | [hɪt] | hit | hit | [hɪt] | hit | [hɪt] |
| hold | [hould] | keep | held | [held] | held | [held] |
| hurt | [hɜ:rt] | hurt | hurt | [hɜ:t] | hurt | [hɜ:t] |
| keep | [ki:p] | store | kept | [kept] | kept | [kept] |
| know | [now] | know | knew | [nu:] | known | [noun] |
| lay | [leɪ] | put | laid | [leɪd] | laid | [leɪd] |
| learn | [lɜ:rn] | recognize | learned | [lɜ:nt] | learned | [lɜ:nt] |
| leave | [li:v] | leave | left | [left] | left | [left] |
| let | [let] | allow | let | [let] | let | [let] |
| lie | [laɪ] | lie down | lay | [leɪ] | lay | [leɪn] |
| lose | [lu:z] | lose | lost | [lɒst] | lost | [lɒst] |
| make | [meɪk] | do | made | [meɪd] | nine0030 made[meɪd] | |
| mean | [mi:n] | mean | meant | [ment] | meant | [ment] |
| meet | [mi:t] | meet | met | [met] | met | [met] |
| mistake | [mis'teik] | err | mistook | [mis'tuk] | mistaken | [mis'teik(e)n] |
| pay | [peɪ] | pay | paid | [peɪd] | paid | [peɪd] |
| put | [pʊt] | put | put | [pʊt] | put | [pʊt] |
| read | [ri:d] | read | read | [red] | read | [red] |
| ride | [rad] | ride | rode | [roud] | ridden | [‘rɪdn] |
| ring | [rɪŋ] | ring | range | [ræŋ] | rung | [rʌŋ] |
| run | [rʌn] | run | ran | [ræn] | run | [rʌn] |
| say | [seɪ] | say | said | [sed] | said | [sed] |
| see | [si:] | see | saw | [sɔ:] | seen | [si:n] |
| sell | [sel] | sell | sold | [sould] | sold | [sould] |
| send | [send] | send | sent | [sent] | sent | [sent] |
| show | [ʃou] | show | showed | [ʃoud] | shown | [ʃoun] |
| sing | [sɪŋ] | sing | sang | [sæŋ] | sun | [sʌŋ] |
| sit | [sɪt] | sit | sat | [sæt] | sat | [sæt] |
| sleep | [sli:p] | sleep | slept | [slept] | slept | [slept] |
| smell | [smel] | smell | smelt | [smelt] | smelt | [smelt] |
| speak | [spi:k] | talk | spoke | [spouk] | spoken | [‘spoukən] |
| spend | [spend] | spend, spend | spent | [spent] | spent | [spent] |
| stand | [stænd] | stand | stood | [stʊd] | stood | [stʊd] |
| swim | [swɪm] | swim | swam | [swæm] | swum | nine0030 [swʌm]|
| take | [teɪk] | take | took | [tʊk] | taken | [‘teɪkən] |
| teach | [ti:tʃ] | teach someone | taught | [tɔ:t] | taught | [tɔ:t] |
| tell | [tel] | tell | told | [tould] | told | [tould] |
| think | [θɪŋk] | think | thought | [θɔ:t] | thought | [θɔ:t] |
| throw | [θrou] | throw | threw | [θru:] | thrown | [θroun] |
| understand | [ʌndər ‘stænd] | understand | understood | [ʌndər ‘stʊd] | understood | nine0030 [ʌndər ‘stʊd]|
| wake | [weɪk] | wake up | woke | [wouk] | woken | [‘woukən] |
| wear | [weər] | wear clothes | wore | [wɔ:] | worn | [wɔ:n] |
| win | [wɪn] | win, win | won | [wʌn] | won | [wʌn] |
| write | [raɪt] | write | wrote | [route] | written | [‘rɪtn] |
Despite the large number of such exceptions, many of them form Past Simple and Past Participle according to the same pattern. This makes it much easier to remember.
This makes it much easier to remember.
What have we learned?
The list of irregular verbs in English includes words that do not form the past tense according to the rule. There are about 470 such verbs, but it is enough for students at school to learn the basic 100-150. nine0003
10/10
Nasigat Magomedova
9/10
Estimation of Article
4.2
Average rating: 4.2
A total of evaluations: 367.
9 9000A What kind of VASH?
Table of irregular verbs for grade 5, TMC "Rainbow English" | Methodological development in English (Grade 5) on the topic:
Posted on 06.12.2017 - 0:28 - Boichenko Anna Yurievna
Table of irregular verbs in Grade 5, Unit 1-2. nine1453
Hear
HeARD
Hear, listen to
on the topic: Methodological development, presentations and notes
Table of incorrect verbs
Verings of English.

 tries, empties
tries, empties