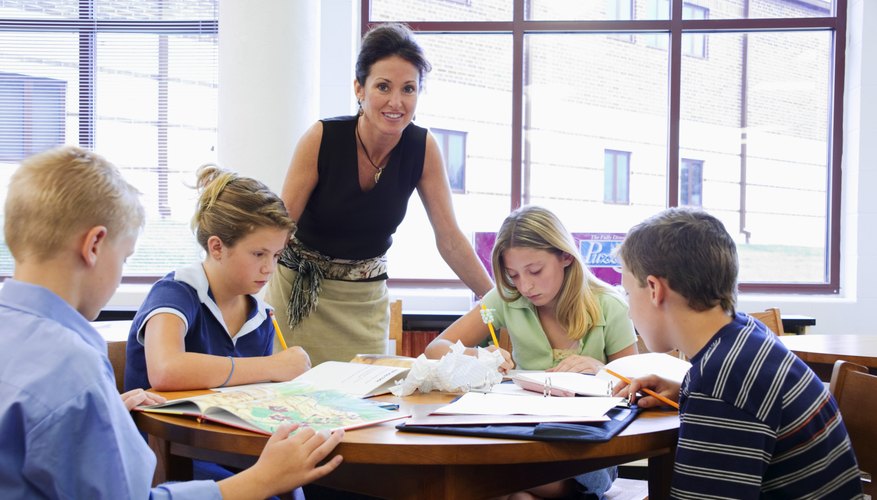
What 5th graders should know in math
The 4 Major Math Concepts Your Kids Learn in Grades 5-6
There can be quite a jump in math knowledge from fifth grade to sixth grade, and I like to think of it as crossing a bridge. The more we can connect the bridge, the better our children will feel about themselves in middle school. Fifth grade is a culmination of all that students have learned at the elementary level, while sixth grade can be seen as the starting point for middle school. And no matter how your child’s middle school works, there is a distinct connection between these grades. The more comfortable children are with these concepts by the end of sixth grade, the more they’ll be equipt for middle school.
Here are four of the major math concepts your child will cover in fifth and sixth grade:
1. Number System. In fifth grade, students focus on adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing whole numbers, fractions, and decimals. Your kid will become fluent with computing these types of numbers and understanding the relationship between them. Students should also be able to use these numbers in real-world scenarios. In sixth grade, kids continue their understanding of these numbers, and are also introduced to negative numbers. They will begin to identify rational numbers and integers on a number line as well as compare them. Using models will greatly improve your child’s understanding of these concepts.
Encourage your child to:
- Recognize and calculate using fractions and decimals in the real world. For example, have your child figure out the discount from a sale; the amount of tax while shopping; find the tip of a bill, or explain sports stats.
- Use fraction bars to compute (adding, subtracting, multiplying, or dividing).
Image courtesy: LearnZillion
- Find examples of positive and negative numbers in the real world (temperature, distance, sea-level, etc.) and use models to help understand the relationship between them.
Image courtesy: The positive impact of Math
2. Ratios. Students will use their knowledge of fractions and decimals in fifth grade to reason ratio and rate problems in sixth grade. Kids will need to connect their understanding of multiplication and division with real-world problems using ratios. They will use models (diagrams, table, double number lines, etc.) to help them make these connections and solve unit rate problems. Students will also learn about percents and how they match up with fractions and decimals.
Ratios. Students will use their knowledge of fractions and decimals in fifth grade to reason ratio and rate problems in sixth grade. Kids will need to connect their understanding of multiplication and division with real-world problems using ratios. They will use models (diagrams, table, double number lines, etc.) to help them make these connections and solve unit rate problems. Students will also learn about percents and how they match up with fractions and decimals.
Encourage your child to:
- Find examples of ratios in the real world. For example, “The ratio of wings to beaks in the birdhouse at the zoo was 2:1, because for every 2 wings there was 1 beak.”
- Use models to help understand ratio and rate problems:
Image courtesy: Mr. Pratt's 6th Grade Class
Image courtesy: nzmaths.
- Create real-world problems using ratio understanding. For example, “This recipe has a ratio of 3 cups of flour to 4 cups of sugar, so there is 3/4 cup of flour for each cup of sugar.
 ”
”
3. Expressions & Equations. Students start to distinguish the difference between an expression and an equation. They use variables to represent an unknown number in both expressions and equations. Fifth and sixth graders follow the appropriate order of operations to solve problems, including parentheses and exponents. Your children are beginning to read, interpret, and write expressions and equations, as well as solving one-variable equations.
Encourage your child to:
- Distinguish between an expression and an equation, and understand the meaning of the equal sign:
Expression: 4y + 2
Equation: 4y + 2 = 14
- Solve problems using the acronym of PEMDAS:
Image courtesy: coolmath.com
- Read and write expression with ease: Subtract n from 8" as 8 - n.
- Create and solve real-world problems using variables. For example, "
It costs $100 to rent the skating rink plus $5 per person.
 Write an expression to find the cost for any number (n) of people. What is the cost for 25 people? Answer: 100 + 5n; so for 25 people = 100 + 5(25) = 225."
Write an expression to find the cost for any number (n) of people. What is the cost for 25 people? Answer: 100 + 5n; so for 25 people = 100 + 5(25) = 225."
4. Geometry: Students continue classifying figures into categories based on their properties. Your child will learn to find the area of triangles and some quadrilaterals. They will learn to calculate the volume of 3-D figures using whole numbers and fractional edges. Students begin to use represent real-world problems by graphing points on the coordinate plane.
Encourage your child to:
- Understand the difference between finding area of a 2-D figure versus finding the volume of a 3-D figure. Point out different objects and ask if your kid would find the area or volume of that figure. For example, "Would you find the area oro volume of that backyard?" Or, "Would you find the area of volume of that swimming pool?"
- Use appropriate vocabulary when describing different polygons and geometric properties.
 For example, "What are parallel lines?" Answer: "Two lines on a plane that never meet. They are always the same distance apart."
For example, "What are parallel lines?" Answer: "Two lines on a plane that never meet. They are always the same distance apart." - Use their third grade learning on understanding how to find the area of a rectangle or to find the read of a triangle:
Image courtesy: The University of Georgia Department of Math Education
- Develop an understanding of the coordinate plane and begin to plot points using real-world scenarios (using graph paper). For example, “On a map, the library is located at (-2, 2), the city hall building is located at (0,2), and the high school is located at (0,0). Represent the locations as points on a coordinate grid with a unit of 1 mile.”
Don't worry if these concepts feel a little intimidating at first. Remember, you haven't been taking yearly math classes that build on each other like your children have. (At first, it may even feel like your chidren understand it better than you do!)
But that's the point of our "Major Math Concepts" blog series. We want you endowed with understanding these math concepts as well. You may get a jump start on your kids' learning, you may keep pace with them, but either will help you connect more with your child on what is often a challenging subject.
We want you endowed with understanding these math concepts as well. You may get a jump start on your kids' learning, you may keep pace with them, but either will help you connect more with your child on what is often a challenging subject.
Have any questions about these concepts or any other questions on your child’s math? Submit them to Jennifer here so she can consider answering in an upcoming blog. Or share them with us on the Scholastic Parents Facebook Page.
Featured photo credit: © Oktay Ortakcioglu/iStockphoto
Math Skills Your Child Will Learn in Fifth Grade
- Math Tips
- 5th
In fifth grade math, your child will extend understanding of decimals and fractions, as well as exploring numerical expressions, volume, and graphs. That’s a lot to cover! Help your child succeed in fifth grade math by learning more about what he’ll be doing.
Over the year, your child will:
1. Solve numerical expressions
Your child has had lots of experience solving problems using the four operations. Now your child will develop this understanding even further by learning how to use parentheses in numerical expressions and evaluate expressions with them. Your child will learn about order of operations and will solve the parts of expressions in parentheses first.
Help your child practice his knowledge of order of operations by giving him longer expressions to evaluate, both with and without parentheses. Give your child the same expression but with different placements of parentheses. Talk with your child about how the parentheses affected the expression.
2. Work with decimals
In fifth grade, students learn to read, write, and compare decimals to thousandths. They also practice adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing decimals to the hundredths, which can be tricky!
Support your child by talking about different strategies to use.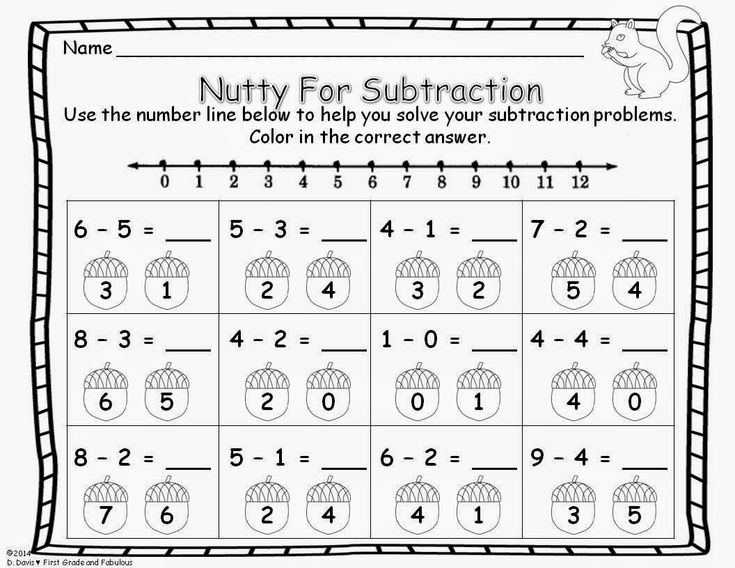 Have your child use drawings or models to try to visualize the decimal problems he’s solving. For example, draw a 10x10 grid and have your child see each square as a hundredth. Use the grid to help visualize decimals when solving problems.
Have your child use drawings or models to try to visualize the decimal problems he’s solving. For example, draw a 10x10 grid and have your child see each square as a hundredth. Use the grid to help visualize decimals when solving problems.
3. Add and subtract fractions with unlike denominators
In fourth grade, students learned to compare fractions with unlike numerators or denominators. Now they will extend this understanding by learning how to add and subtract fractions with unlike denominators by finding common denominators.
Give your child real-world addition and subtraction tasks to complete. For example, when cooking you can have your child calculate ⅓ cup of flour + ½ cup of flour. Help your child relate common denominators to their knowledge of multiplication by thinking about common multiples. (Check out our fractions page to brush up on your fractions knowledge!)
4. Multiply and divide fractions
The fraction work doesn’t stop with addition and subtraction! Fifth graders are ready to multiply fractions by whole numbers or fractions. They will also divide unit fractions (fractions where the numerator is 1) by whole numbers and whole numbers by unit fractions.
They will also divide unit fractions (fractions where the numerator is 1) by whole numbers and whole numbers by unit fractions.
These concepts can be tricky, so instead of explaining them to your child, have your child explain them to you. The opportunity to be the teacher can help your child develop stronger understanding, and gives you the chance to see how well it’s all sinking in.
5. Measure volume
Fourth graders have had practice measuring lengths and weights. But they will be introduced to a new type of measurement this year: volume. Students will learn to measure volumes by counting unit cubes, using cubic cm, cubic in, and cubic ft. They will learn the formula for computing the volume of cubes and rectangular prisms (volume = length x width x height)
Have your child notice the volume of drinks that your family consumes. Talk about how different size containers, like 2 liter and 1 liter bottles, hold different amounts of liquids.
6. Graph points on the coordinate plane
In fifth grade, students will learn how a coordinate system has an x-axis and y-axis and how points can be given by their coordinates (x,y).
Have your child draw a coordinate plane using graphic paper and practice having your child locate certain points. Games like Battleship can also be a great way to practice the idea of coordinates. If you don't have the board game, here's how you can play Battleship using just pen and paper!
Throughout your child’s fifth grade experience, find opportunities to check in and hear what he is learning. Fifth grade math can get complex, so take it as an opportunity to brush up on your skills too!
Found this useful? Check out our grade by grade math guides from Kindergarten to 5th grade
Written by Lily Jones, Lily loves all things learning. She has been a kindergarten & first grade teacher, instructional coach, curriculum developer, and teacher trainer. She loves to look at the world with curiosity and inspire people of all ages to love learning. She lives in California with her husband, two kids, and a little dog.
She has been a kindergarten & first grade teacher, instructional coach, curriculum developer, and teacher trainer. She loves to look at the world with curiosity and inspire people of all ages to love learning. She lives in California with her husband, two kids, and a little dog.
About Komodo – Komodo is a fun and effective way to boost K-5 math skills. Designed for 5 to 11-year-olds to use in the home, Komodo uses a little and often approach to learning math (15 minutes, three to five times per week) that fits into the busy family routine. Komodo helps users develop fluency and confidence in math – without keeping them at the screen for long.
Find out more about Komodo and how it helps thousands of children each year do better at maths – you can even try Komodo for free.
Back to School - 5 Tips to Help you Ease Back into the Routine
Here are some steps you can take to ease children back from full vacation mode so that the first week of school doesn't knock you sideways.
Mindset - The Path to Mastery
People who have a growth mindset believe that they always have the potential to learn and improve. They are more motivated to persevere with difficult tasks, to take risks and to learn from failure.
| No. | Lesson topic | Lesson type | Level requirements preparation | Control type, meters | Elements additional content | Homework | Date | ||||||
| M | Ft | ||||||||||||
1. Natural numbers and scales. (16 hours) Natural numbers and scales. (16 hours) | |||||||||||||
| 1 | Designation of natural numbers. | KU | Know: the concept of number and digits, definition of natural numbers, classes, digits, a million, a billion. Be able to: read and write multiple digits. | FO, IK.
| P.1 No. 18 (a, b), 23 (a, b), | ||||||||
| 2 | Designation of natural numbers. | KU | FO, MD | P.1 No. 23 (c, d, e), 24 (a, b, c). | |||||||||
| 3 | Designation of natural numbers. | UPZU | SR | P.1 No. 24 (d, e, f), 25.30 (a). | |||||||||
| 4 | Cut. Cut length. Triangle. | UONM | Know: the concept of a segment, the concept of a triangle, the concept of the length of a segment. Be able to: draw a line, draw a triangle, measure segment length, compare segments, find sides and vertices of triangles polygons. | MD,UO | Histor. help (p21) help (p21) | P.2 No. 64(1,2,3),65. | |||||||
| 5 | Cut. Cut length. Triangle. | KU | MD | P.2 No. 64(2,4,6),66 | |||||||||
| 6 | Cut. Cut length. Triangle. | KU | UO, SR | P.2,3 No. 68 (a, b), 60. | |||||||||
| 7 | Plane. Straight. Ray. | UONM | Know: concept plane, straight line, beam, additional beams. Be able to: find and name a line on a drawing, build it by two points; draw rays, find them on drawing, name. | FROM, UO. | P.2,3 No. 68 (c, d), 99. | ||||||||
| 8 | Flat. Straight. Ray. | KU | UO, MD | P.3 No. 100,102,106(a,b). | |||||||||
| 9 | Scales and coordinates. | UONM | Know: scale concept, scale division, coordinate beam. Be able to: define a single segment on the scale. Build coordinate ray, find coordinates of points and build points according to given coordinates. | SR | P.4 No. 106 (c, d), 136 (1) | ||||||||
| 10 | Scales and coordinates. | UZIM | US | P.4 No. 136 (3.4), 138, | |||||||||
| 11 | Scales and coordinates. | UPZU | FO | P4 No. 139,144 (a, b). 139,144 (a, b). | |||||||||
| 12 | Less or more. | KU | Know: concept comparisons, digits of numbers. Be able to: compare natural numbers with the same number of digits, with different number of digits. | UO, MD | Histor. reference "Measures of mass" page41) | P.5 No. 144 (c), 168 (a, b). | |||||||
| 13 | Less or more. | UOSZ | SR | P. 5 No. 168 (c, d), 169 (c) 5 No. 168 (c, d), 169 (c) | |||||||||
| 14 | Less or more. | US | P.5 No. 169 (a, b), 172 (a) | ||||||||||
| 15 | Test work No. 1 on the topic: "Natural numbers and scales." | UKKZU | Be able to: generalize and systematize knowledge on the topics covered and use them in solving problems and problems. | KR | |||||||||
| 16 | Analysis of control work. | UKZ | Work on error. | ||||||||||
| 2. Addition and subtraction natural numbers. (20 hours). | |||||||||||||
| 17 | Addition of natural numbers and its properties. | KU | Know: name components and the result of the addition action, addition properties. Be able to: add multi-digit numbers, apply addition properties when calculating. | MD | Histor. reference(p32) | P. 6 No. 239,240 (a, b). 6 No. 239,240 (a, b). | |||||||
| 18 | Addition of natural numbers and its properties. | UPZU | SR | P.6 No. 231 (a, b), 240 (c, d). | |||||||||
| 19 | Addition of natural numbers and its properties. | UOSZ | MD | P.6 No. 231 (c, d), 240 (e, f). | |||||||||
| 20 | Subtraction. | KU | Know: name components and the result of the subtraction action, subtraction properties. Be able to: subtract multi-digit numbers, apply properties subtraction in calculations. | FO, FROM | Histor. help (p65) | P.7 No. 289,290 (a, b). | |||||||
| 21 | Subtraction. | KU | MD | P.7 No. 290 (c, d), 291. | |||||||||
| 22 | Subtraction. | UPZU | UO | P.7 No. 292,293. | |||||||||
| 23 | Numeric and alphabetic expressions. | UONM | Know: definitions numeric and alphabetic expressions. Be able to: compose expressions, read them and find the value of a numeric expression; explain letter values, write the solution of the problem in the form numeric or literal expression. | US | P.8 No. 328 (a, b), 330 (a, b). | ||||||||
| 24 | Numeric and alphabetic expressions. | UPZU | MD | P.8 No. 330 (c, d), 331 (c, d). | |||||||||
| 25 | Numeric and alphabetic expressions.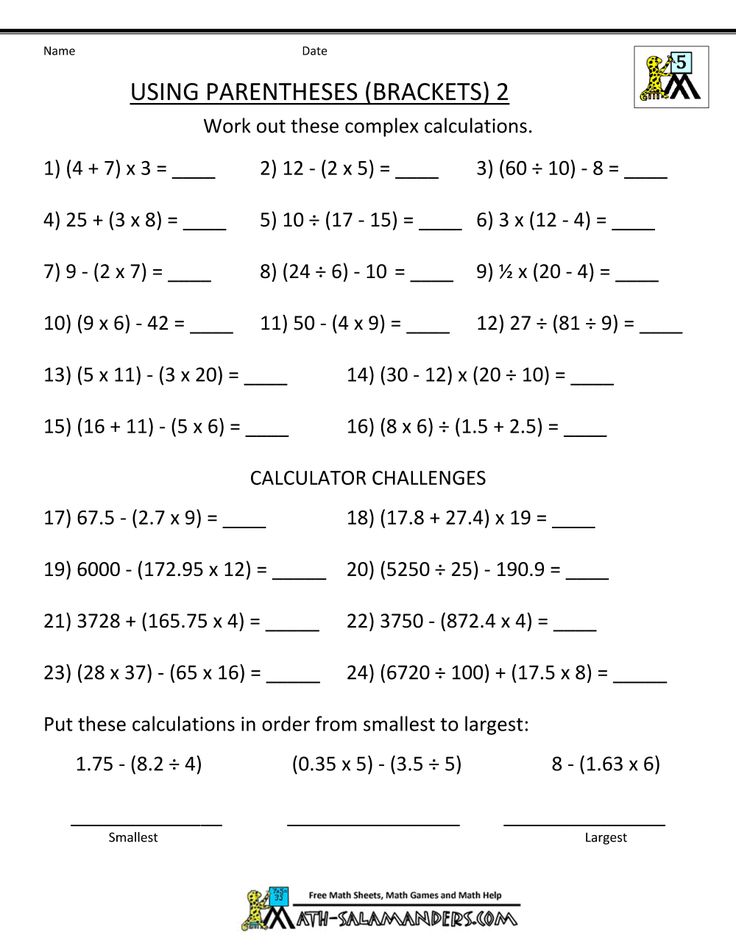 | KU | SR | Clause 8 No. 333,334,336(a 1 ,b 1 | |||||||||
| 26 | Alphabetic notation of properties addition and subtraction. | UONM | Know: properties addition and subtraction. Be able to: write properties of addition and subtraction using letters, use them to simplify calculations and literal expressions. | MT | P.9 No. 364 (a, b), 365 (a 1 ). | ||||||||
| 27 | Alphabetic notation of properties addition and subtraction. | KU | FO | P.9 No. 364 (c, d), 365 (b 1 ). | |||||||||
| 28 | Alphabetic notation of properties addition and subtraction. | KU | SR | P.9 No. 365 (a 2 , b 2 ),367. | |||||||||
| 29 | Test No. 2 on the topic: "Addition and subtraction of natural numbers." | UKKZU | Be able to: generalize and systematize knowledge on the topics covered and use them when solving.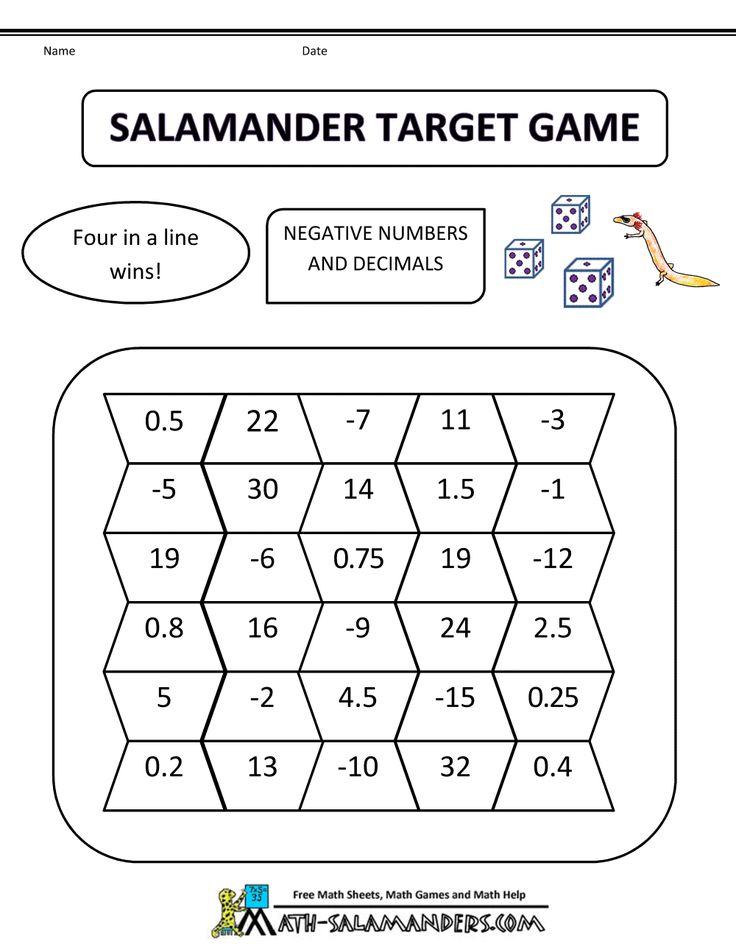 | KR | |||||||||
| 30 | Analysis of control work. | UKZ | Working over error. | ||||||||||
| 31 | Equation. | UONM | Know : definition equations, the concept of the root of the equation. Be able to: find components when adding and subtracting, solve problems using equations. | MD | P. 10 No. 392(1),393(a 1 ),395(a,b) 10 No. 392(1),393(a 1 ),395(a,b) | ||||||||
| 32 | Equation. | KU | T | P.10 No. 393 (b 1 ), 395 (b, d, f), 396 (a), 397 (a). | |||||||||
| 33 | Equation. | UPZU | SR | D / material, str. 34-35, Var B-1. | |||||||||
| 34 | Equation. | UOSZ | MD | ||||||||||
| 35 | Test work No. 3 on the topic: "Equations". 3 on the topic: "Equations". | UKKZU | Be able to: generalize and systematize knowledge on the topics covered and use them in your decision. | KR | |||||||||
| 36 | Analysis of control work. | UKZ | Work on error. | ||||||||||
| 3. Multiplication and division natural numbers 22 hours. | |||||||||||||
| 37 | Multiplication of natural numbers and its properties. | KU | Know : name components and the result of the multiplication operation, multiplication properties. Be able to: multiply multi-digit numbers, represent the number in the form products, apply the properties of multiplication when calculations. | UO, MD | P.11 No. 450 (a), 451 (a, c), 455 (a, b, c, d). | ||||||||
| 38 | Multiplication of natural numbers and its properties. | KU | SR | P.11 No. 450 (b), 451 (b, d). | |||||||||
| 39 | Multiplication of natural numbers and its properties. | UPZU | US | P.11 No. 462 (a, b). | |||||||||
Mathematics grade 5 lesson topics
Getting ready for school
In mathematics in the 5th grade, the topics of the lessons will be devoted to addition and subtraction, multiplication, division of natural numbers. Then they move on to the study of fractional numbers with an emphasis on decimal fractions. Consider addition, multiplication, rounding, comparison, division, subtraction of decimal fractions.
In addition, time is allocated for the basics of areas and volumes, the use of tools and scales for measuring weights, distances, volumes. This stage is of great value for the use of mathematics in everyday life, so it must be approached with particular care.
Natural numbers
Let's start the program with the study of natural numbers. So it will be easier for the assimilation of the subsequent material:
- Positional and non-positional number system. Decimal, hexadecimal, octal number system.
- The concept of numbers and numbers. Origin of numbers. We will learn about how they were recorded by different peoples of the world.
- Point, line, ray and line. This stage is the foundation for all geometry.
- Segment, its comparison and finding out the length.
- Various units of mass, distance, volume.
- Plane, infinity, shapes, angle, triangle, broken line.
- Measuring instruments and scales. Hour, minute and second hands.
- Matching natural numbers, various equal signs.
Subtraction and addition of natural numbers
In the next two stages, the basic methods and laws of mathematics are studied, so they should be treated carefully.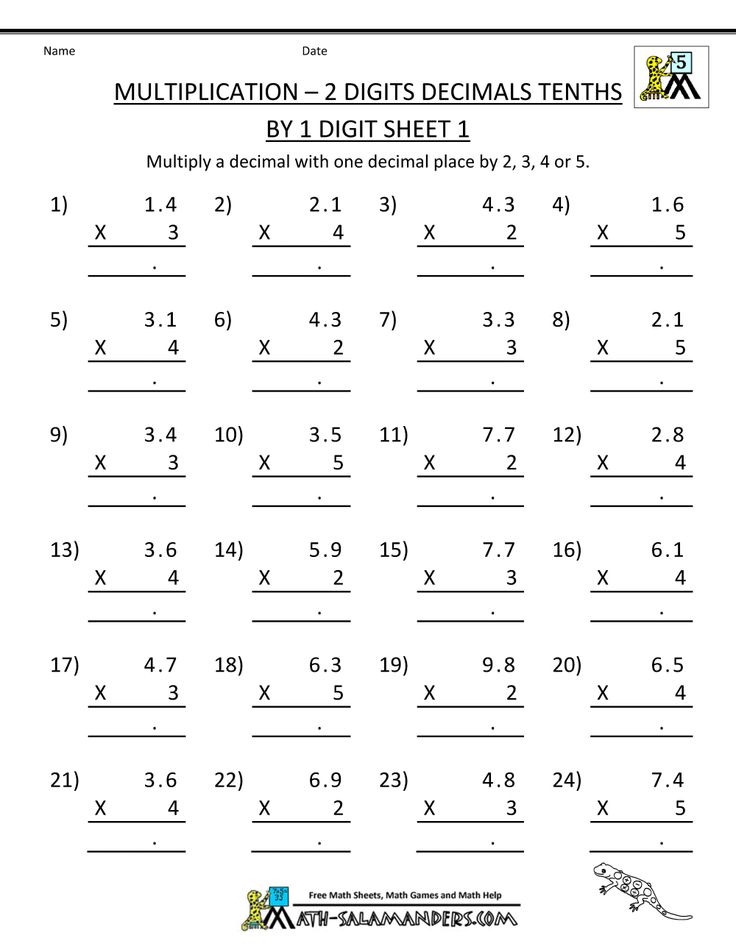 An important topic of math lessons for grade 5 is what can be done with natural numbers. Take up the study of additions and calculations:
An important topic of math lessons for grade 5 is what can be done with natural numbers. Take up the study of additions and calculations:
- Addition of natural numbers
- Commutative and associative law
- Subtraction of natural numbers
- Alphabetic and numeric expressions and their characteristics
Division and multiplication of natural numbers
Finish with multiplication and division:
- Multiplication and its characteristics
- Division, features and characteristics of
- Division with and without remainder
- Mathematical notation. Language architecture and mathematical linguistics
- Expression simplification - find its value in one or more variables
- Sequence of actions for solving equations. Why are parentheses needed? Equality of addition and subtraction, as well as division and multiplication. Prerogative of division and multiplication over operations such as addition and subtraction
- Power of a number.
 The sequence of mathematical operations with it. Square and cube
The sequence of mathematical operations with it. Square and cube - Solution of motion equations
Volumes and areas
This knowledge is the foundation for modeling technology, as well as other things and phenomena. Study on the example of rectangles and parallelepipeds:
- Formulas. Definition, theorem, identity, experimental formula
- Square. Units. The ratio of square millimeters, centimeters, meters
- Finding the area of a rectangle
- Square
- Ancient Methods for Measuring Areas
- Cuboid faces, corners, planes
- Surface area search
- Understanding and finding volume
- Volume measuring systems
- Volume of cube and cuboid
- Circle and circle. Arc, radius, diameter
Fractional numbers
Fractions is the most difficult topic this year, so you need to take it apart slowly and carefully. In mathematics for grade 5, the topics of the lessons include the study of various types of fractions:
- Simple fractions and their construction, characteristics
- Why fractional notation is required
- Proper and improper fractions
- Comparison and definition of common fractions
- Subtraction and addition of fractions with identical and different denominators
- Part and whole search
- Improper fractions and their classification
- Mixed numbers
- Arithmetic with mixed numbers
Decimal fractions, their subtraction and addition
Next, you need to learn how to use fractions in mathematical calculations.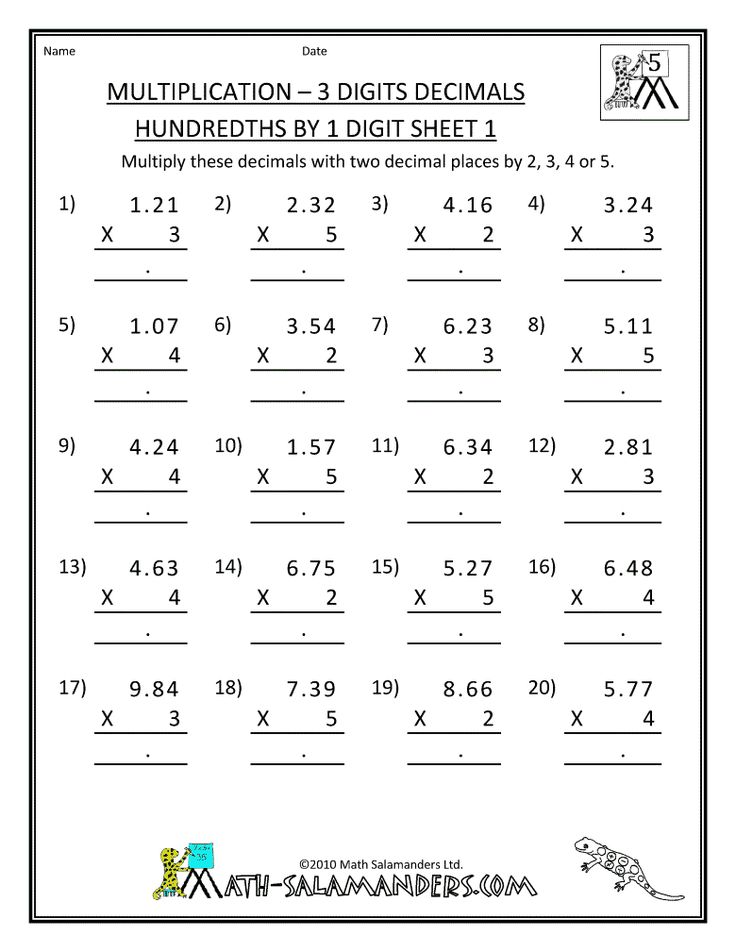 And first - subtraction and addition:
And first - subtraction and addition:
- Decimals, definition and characteristics
- Their depiction and reading
- Comparison rules
- Mapping on coordinate system
- Subtraction and addition in columns
- Rounding up and down
Decimals, division and multiplication
Finish the study of decimal fractions by analyzing their division and multiplication:
- Division and multiplication by 10, 100, 0.1, 0.01. Shifting a comma when there are no digits
- Division and multiplication of decimals
- Arithmetic mean
Calculation and measurement tools
This group of lessons will introduce you to mathematics as a world culture, as well as its importance for scientific and technological progress. Next come the various math tools:
- Full, extended, straight, acute, obtuse angle
- Degrees. Protractor and its application. Setting corners
- Bisector and median
- Interest.