What reading level should my 2nd grader be at
What Reading Level Should a Second Grader Be At? – Making English Fun
Both learning to read and reading to learn are an essential developmental skill and assessment tool at all levels of education from second grader to university level. Reading levels are an integral educational tool to not just assess progress of students but also give information to help teachers, parents and educators plan to improve students reading levels.
A second grader reading level will range between 6 to 20 on RR and Pm Reading levels. There will be outlying numbers depending on the situation of individual students. Reading levels allow teachers to choose appropriate reading materials to effectively develop students reading and comprehension skills.
This what reading level should a second grader be at article will also cover the following information:
- What are reading levels and how they can be used to help your 2nd graders to improve their reading skills.
- What you can do to support your students, 2nd grade and others, to progress.
- Reading skills and concepts that students will learn in second grade.
- Links to our 2nd grade reading resources ( and other resources)
If you are looking for worksheets for grade 2 we have a large collection here in the article below.
What Is a Reading Level?
There are multiple different programs and tools to assess students reading levels. The majority of these reading level assessments all share common indicators. They assess the comprehension, pronunciation, decoding and fluency ability of a student of English while they are reading a short leveled text.
Second graders are highly unlikely to be reading at a seventh grader level and it would not be useful or effective to have them reading the same materials. At this stage, in second grade, there is still more emphasis on reading skills and the actual mechanics of reading.
Reading comprehension is included in 2nd grader lessons but it is introduced as their hard reading skills become more developed. It is impossible for them to understand something they cant actually read!
Scholastic, have detailed information on the different reading level assessments and programs which, as highlighted above, all have commonalities. They do of course have difference as well, with some like Lexile concentrating on word count or difficultly of words and others like the PM benchmark looking at simplicity of both words and sentence construction.
Different schools, regions and educational systems will use different reading assessment tools, but the chart below offers a handy comparison to help both teachers and parents when it comes to choosing reading materials.
The different systems can be confusing at first and when choosing what reading levels books to choose for 2nd grade classrooms it is definitely of use to spend some time with both your reading resources and the chart
to make sure they fit the reading level of your students.
We use this chart in all our reading level articles.
Many Guided reading publishers have developed their own systems as well.
- Scholastic Guided Level Reading Program
- CCSS Lexile Recommendations
- DRA Level
- PM Benchmark
For both ease and continuity, ( as we have used this Reading level assesment tool in our other reading level articles) we will use the DRA reading level today.
What is the DRA Reading Levels Assessment.The DRA ( Developmental Reading Assessment) is a reading skill assessment tool that aims to evaluate students reading levels to enable teachers and parents to assess students reading skills including fluency, comprehension and phonics. They aim to discover the independent and instructional reading level of students.
What is an Instructional Reading Level?
Instructional Reading level is the reading level directly below independent. Students should be able to comprehend and decode upwards of 80% of the text at an instructional level. This level can vary between students and also between subjects as students have interest and motivators that differ.
This level can vary between students and also between subjects as students have interest and motivators that differ.
What is an Independent Reading Level?
An independent reading level is a level of reading ability that allows students to read texts without assistance from teachers or parents. When reading this level of text students will be able to decode over 90% of words and answer increasingly complex comprehension questions independently.
What is a Frustration Reading Level?
Frustration level reading can be defined as text that are to complex for a students current reading level. Texts at this level will not help progress students to higher levels, conversely attempting to read at this level will demotivate students and hinder their development of reading skills.
In 2nd grade, as well as other grades, classrooms and homes teachers and parents should aim at using an instructional reading level.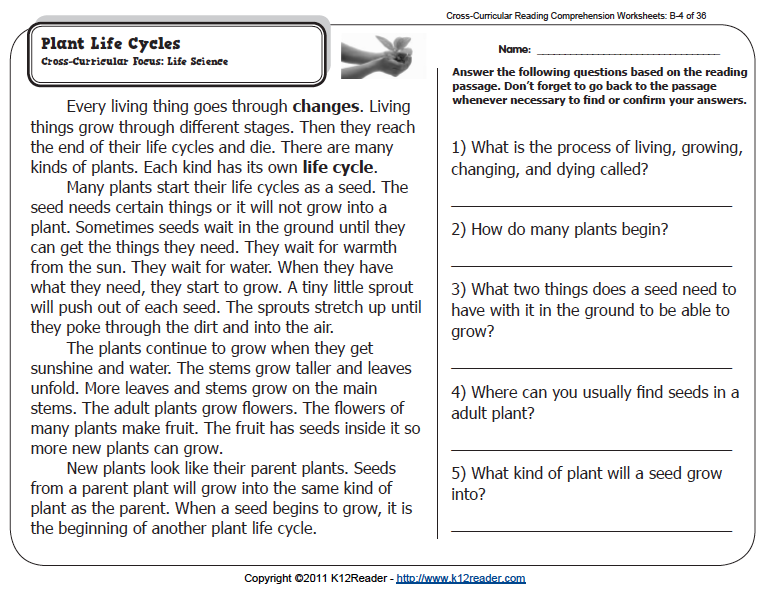 This enables students to comprehend and therefore engage with texts with minimal assistance, and gives them the motivation to see they are doing well, but still have the support and guidance of teachers and parents.
This enables students to comprehend and therefore engage with texts with minimal assistance, and gives them the motivation to see they are doing well, but still have the support and guidance of teachers and parents.
Guided reading, for which we have many articles and resources, is an excellent way of introducing text at this levels to small groups of 2nd graders. In fact is it more beneficial to introduce guided reading at this stage as students have matured and are becoming more independent. Check out the links to know more. We have an article here on what age you can start teaching guided reading.
What 2nd Graders Learn Throughout the Year.
As we mentioned above a second grader can be reading from about reading level 6 to level 20. However please don’t worry if your students or children are below this, or be to confident if they are above this.
As time progresses so will your students reading levels. Just aim to to the best job you can, and provide them with appropriate leveled 2nd grade materials and the time to cover them.
Just aim to to the best job you can, and provide them with appropriate leveled 2nd grade materials and the time to cover them.
The next section covers what skills they will learn to help them improve their reading levels through out the second grade.
Note: Children develop at very different speeds, and different learning environments will impact. If English is a second language, or if there are other demands on students or parents time will all play a part. Be assured that in the vast majority of cases, with a little planning, all students progress and develop their reading skills.
What Reading Skills They Will Learn in Second Grade
Although we mentioned in our What level should a first grader be at article, that an essential part of learning and reading in first grade is comprehension, this is not just a face value statement. In First grade there is a focus on shared reading or story telling which is undertaken in whole class or larger groups. This asks students to read together more than in small groups.
This asks students to read together more than in small groups.
They have to retell stories and predict outcomes and books will be fairly formulaic story books with similar phonic and sentence structures. In Second grade, as mentioned above, emphasis can be moved on to guided reading sessions.
According to Reading Rockets, a second grader will be focusing on the following English and reading skills. We have put this information in a table to provide resources for FREE download to help you as well.
Vowels and long vowels will be introduced in greater detail in second grade including Silent E, and some alternative spellings like diphthongs and vowel digraphs. The teaching of these will help students increase their decoding skills and improve their vocabulary.
Punctuation is another essential part of the second grade year. Exclamation points, question marks, periods might be introduced in some grade one classrooms, but will certainly make an appearance in second grade classrooms.
Semicolons and colons might be introduced in more advanced lessons or towards the end of the year. you can find some punctuation worksheets here and on the link in the table above.
Reading and writing skills such and conjunctions, pronouns will be built on and by now capitalization will have been covered so revising that may be necessary if you notice your children or students forgetting or not using this. We have some worksheets here and in the table above if you need. Pronouns are likely to be expanded on as well.
Amazon.com
Phonics Flash Cards - Learn to Read in 20 Phonic Stages - Digraphs CVC Blends...
$17.99
BUY NOW
Amazon.com
Learning Resources Sight Word Swat a Sight Words Game - 114 Pieces, Ages 5+...
$17.99
BUY NOW
Amazon.com
Sight Words Level 2 Bingo Game
$13. 99
99
BUY NOW
Sentences and constructing sentence will become more important in second grade. Reading materials will include more complex versions and teachers and parents can use reading levels to gain appropriate levels of text for their students and children. We have some on the site for free, and in addition we also have sentence making and sentence scramble worksheets as well (link)
However some of the best ways to engage 2nd graders is through online games. By this time they will have become aware of tablets and phones being help in parents and siblings hands. We have articles on some of the best online games, and have a page that has all the ones we make as well. These are free to play and very popular and certainly add motivation to your lessons!
What Can Teachers Do to Improve Reading Levels at 2nd Grade.
Teachers can develop a love of reading in classrooms and encourage students to take control of their own learning as well.
- Have a selection of levelled suitable for 2nd graders covering fiction and NON fiction texts.
- Make sure there is a mix of text types and text subjects.
- Try to have a corner in the classroom for quiet reading.
- Mix up ways of presenting resources, online games, worksheets readers etc.
- Read stories and continue doing story time, many children don’t get chance to experience this enough.
- Display reading strategies and phonics strategies on walls for students to reference. ( also put in their day books or on desks)
- Run Guided reading lessons. ( you can get information on this here)
What Language Will Books at Grade Two Reading Levels Contain?
During students second grade year, Language contained in reading resources will move from three to four letter words and start to include fairly familiar longer words and two or three syllable words. Common words will be used like days of the week, hobbies, weather and more o help increase vocabulary.
Parents.com suggests asking your child questions about books, stories, and sentences that they’re reading. This allows them to process information as they are reading and to move from just learning words to attaching meaning to them. Our reading materials include 3 to 5 questions to help with this. These can be asked verbally or they can complete them as a worksheet post reading.
This is taken from our Reading for first grade article but applies across all grades.
- Break down every word into individual letters. If there’s a combination (sh, th, ough), separate it into its own chunk. This starts to introduce syllables to students.
- Focus on words that they already know how to say. If they’re familiar with the word, they’ll be able to use contextual clues to figure out how to read it.
- Don’t study for too long. Short 15-minute study sessions hold their interest long enough to prevent reading from becoming a boring chore.
 Little and often is better.
Little and often is better. - Use the resources from school and online to supplement these skills. you can access using the following links the 1000s of reading resources on our site for free and premium downloads.
How Can Parents Help Their Second Grader Develop a Love for Reading?
Parents, especially at first and second grade, play a vital role in helping your child become interested in reading. Story telling, appropriate reading resources and books in the house will all help. However we have a list below to help you gather some ideas as well.
Here’s a list of ways that you can help your second grader develop a love for reading:
- Find reading material that they’re interested in. For example, if they love animals or nature , choose those books over anything else. Also allow them to choose as well. It’s not the concept that matters; It’s the words found throughout the reading that makes a big difference.
 We have some leveled reading material aimed at young learners here. However sites like Starfall offer online stories that may help as well.
We have some leveled reading material aimed at young learners here. However sites like Starfall offer online stories that may help as well. - Offer incentives for their reading. Although the aim is to have them choose to read for fun all things start slowly and build momentum. If you can associate reading with enjoyment and reward (extrinsic in the first place) then they will start to enjoy reading and learning for its own merits.
- Picture books can keep your child’s interest . If you stop reading after 15 to 20 minutes, they’ll be begging to jump back into the material. Its great bonding time as well
- Use alternative texts, screen magazines etc. Children can be introduced to different text types to show there are reading opportunities everywhere.
- Ask what your children are covering in school. If you ask their teachers they will be happy to share and offer advice on how to help your second grader progress as well as they can.

- Take a look at using online games to diversify how you introduce learning and reading.
Children are always seeking out new opportunities to learn. Parents can simply guide them to make sure there is a little structure to their learning. Using their interests to guide their reading means they are learning about topics they like and improving their reading. As they progress so with their reading levels.
Finally
We have covered the average reading levels for second graders in native classrooms, of course there will be some difference in ESL or other classrooms. They key takeaway from all of this is that children will progress at their own speed. you can help them on their reading journey but you shouldn’t force them
Reading should be a joy not a chore.
Here’s a quick recap of the post:
- Second graders typically fall between a 6 to 20 reading level.
- Focus on reading for fun, decoding skills, and comprehension.

- Follow their interests, it helps motivate them to read
- Use additional resources and activities to engage and inspire them
if you are looking for other grades reading levels then we have these in the table below.
Other Grades Average Reading Levels.
We have a selection of articles on reading level expectations for different grades below.
Sources
- Scholastic – Learn About Leveled Reading
- Reading A to Z – Levelled Books
- Amazon Second Grade Reading.
Hi I’m Marc. A teacher of over 15 years, English, General Studies and Outdoor Education. Thought it was about time to sharing both what I have learnt during that time and the resources I have put together. On this site we aim to teach the theory and share our thoughts, but also go that one step further and give you access to the hard resources you need for your class or for you children
Making English Fun!
I have been a teacher of English for over 15 years, in that time i made hundreds and thousands of resources and learnt so much i think its worth sharing. Hopefully to help teachers and parents around the world.
Hopefully to help teachers and parents around the world.
2nd Grade / Fountas and Pinnell Reading Level Chart
-
Reading Levels
Grade Levels
A
K
B
K
1
C
K
1
D
1
E
1
F
1
G
1
H
1
2
I
1
2
J
2
K
2
L
2
3
M
2
3
N
3
O
3
4
P
3
4
Q
4
R
4
S
4
5
T
5
U
5
V
5
W
5
Reading technique.
 Norms 1-4 class.
Norms 1-4 class. Since many parents stubbornly refuse to understand what is the point of testing reading technique in elementary school (grades 1-4), I give up and publish reading norms. At the same time, I ask you to carefully read not only the quantitative norm of words per minute, but also my explanations both in the table and below it.
Reading Speed Standards Grade 1-4
→ Number of words may vary slightly depending on curriculum. Increased rates are given in parentheses.
→ Grade 1: no mark given, student “passed” or “failed”. In the first half of the year, the reading technique may not be carried out.
| Grade | at the end of the first half of the year | at the end of the second half of the year |
| 1 class | at least 10 - 15 (20 - 25) wpm | 2 -> less than 15 (25) wpm by 3 -> 15-19 (25-34) words by 4 -> 20-24 (35-40) words by 5 -> from 25 (41) words |
| 2 cl. | by 2 -> less than 25 (40) words per minute by 3 -> 25-29 (40-48) words by 4 -> 30-34 (49-54) words by 5 -> from 35 ( 55) words | 2 -> less than 40 (50) words per minute 3 -> 40-44 (50-58) words 4 words -> 45-49(59-64) words by 5 -> from 50 (65) words |
| 3 cl. | by 2 -> less than 40 (55) words per minute by 3 -> 40-49 (55-64) words by 4 -> 50-59 (65-69) words by 5 -> from 60 (70) ) words | by 2 -> less than 65 (70) words per minute by 3 -> 65-69 (70-79) words by 4 -> 70-74 (80-84) words by 5 -> from 75 (85) ) words |
| 4 class | by 2 -> less than 65 (85) words per minute by 3 -> 65-74 (85-99) words by 4 -> 75-84 (100-114) words by 5 -> from 85 (115) ) words | by 2 -> less than 70 (100) words per minute by 3 -> 70-88 (100-115) words by 4 -> 89-94 (116-124) words by 5 -> from 95 (125) words |
Other reading parameters 1-4 class
| Grade | at the end of the first half of the year | at the end of the second half of the year |
| 1 class | Conscious, correct reading, simple words are read as a word. Words with a complex syllabic structure can be read syllable by syllable. Words with a complex syllabic structure can be read syllable by syllable. | |
| 2 cl. | Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. Compliance with logical stresses. Words of a complex syllabic structure can be read syllable by syllable. | Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of logical stresses, pauses and intonations. Syllabic reading is undesirable. |
| 3 cl. | Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the student expresses understanding of the meaning of what is being read. | Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the student expresses understanding of the meaning of what is being read. |
| 4 cl. | Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the student expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is read, and his attitude to the content of what is read. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the student expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is read, and his attitude to the content of what is read. | Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the student expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is read, and his attitude to the content of what is read. |
Criteria when setting an assessment for reading technique:
- Reading by syllables or word completely,
- Availability of errors when reading,
- number of words per minute,
- expression,
- awareness.
can be clicked to enlarge
As you can see, the number of words read is not decisive.
That is, parents need to understand that such a concept as reading speed is only one of the criteria for determining the level of reading technology . way of reading is checked : the child reads by syllables or the word is read by him smoothly, in its entirety. It is mandatory to check reading comprehension , in other words, whether the student understands what he has read or not. To do this, after reading, a question can be asked about the text, most often “What did you just read about?” and requires a simple answer (a detailed retelling is not needed 😉)
way of reading is checked : the child reads by syllables or the word is read by him smoothly, in its entirety. It is mandatory to check reading comprehension , in other words, whether the student understands what he has read or not. To do this, after reading, a question can be asked about the text, most often “What did you just read about?” and requires a simple answer (a detailed retelling is not needed 😉)
The expressiveness of reading, the presence of errors and / or stammers are also taken into account. Sometimes there is a return to re-reading the previous word, this indicates a lack of awareness and is considered a mistake.
It should also be taken into account that the standards for the speed (rate) of reading may differ depending on the educational institution, the requirements for a student of a gymnasium will be higher, for a student of a correctional class - lower.
The frequency of checking reading technique in elementary school is usually 2 times a year: the end of the first half of the year and the end of the second half of the year. However, in some schools the reading level is checked at the end of each quarter or trimester.
However, in some schools the reading level is checked at the end of each quarter or trimester.
And again! I warn, I exhort - and all the same, the "lion's" part of the students and parents steps on the rake, from which I try to warn.
Understand, memorize, write down and repeat:
No need to speed read! That is, only five words per minute is not good, of course. Some reading speed is needed.
BUT: she, speed, appears as if by itself. The task of the child is simply to read without errors, without stammering or straying, not to swallow the endings and try to observe intonation.
Of course, we are guided by word standards. And yet, do not set the child to "run ahead of the locomotive." Repeat to him a hundred times: you just read and that's it. All!
If you have been reading every day for a year, if your child does not become discouraged when he sees the text, he will pass the reading technique.
The number of words read is not decisive.
Well… I warned you. Conclusions are up to you, dear parents!
English Language Grade 2 | How to learn English from another class
June 6, 2022
June 7 read
Statistical change:
- Grammar topics
- Basic phrases and vocabulary in class 2
- It’s better to master the form of learning
- What is a classmate to blame for before the end of fate?
- Visnovok
Hey guys! If you have read the previous article about the first class students, then you already know what to talk about, but if not, then we can discuss why it is better to start learning English language in another class. Let's analyze the main words that virazi, yakі enter the school program, z'yasuєmo, like the form of learning is better to zastosuvat that one can know a friend of a class to the beginning of the beginning of rock.
As your child learns language from the first class, the cob of new school rock will pass smoothly. Aje learning starts from the alphabet and the rules for reading in English language.
Aje learning starts from the alphabet and the rules for reading in English language.
Even if you only start to know English, then literally in a month you will discover the alphabet and basic reading skills. Also, before the cob of the initial fate, there was a trace of respect based on the English language.
The program of another class is composed of grammatical and lexical material. We chose the main concepts:
Grammar topics
- The word “buti” is the form of the word “to be” in the present hour.
- "have got" structure.
- Associated borrowers, associated officers.
- Numbers and serial numbers. Rahunok up to 100.
- Rules for the adoption of a plurality of names.
- Receivers of the mission.
- Rules for choosing the marked and unmarked articles.
- Modal German "can".
- Present Simple Hour.
- Nutritional words, special nutrition in the present simple hour.
- Custom borrowers "this/these", "that/those".
- Special requests for the current extended hour.
- Present continuous hour.
Basic phrases and virazi in class 2
- Acquaintance
Hello! Goodbye!
What's your name? – My name is…
How are you? – I'm fine, thank you.
How old are you? – I'm seven.
I'm a boy/girl.
This is my friend.
- Colori
It's yellow / green / blue / red / orange / pink / black / brown / gray / white / purple.
My favorite color is (blue).
What color is it?
- Motherland
This is my family.
This is my mum / mother / dad / father / brother / sister / grandmother / grandfather.
I have got a (mother).
- School
I have got a book / pen / pencil / rubber / ruler / bag / pencil case.
This is my (pen).
My (pen) is (blue).
- My dim
This is my home.
This is my room / house.
M y (room) is big / small.
M y (chair) is (brown).
What's this? – It’s a house / chair / table / radio / bed / kitchen / bedroom / living-room / bathroom / window / door / floor.
I have got a bed / table / chair / TV / shelf.
Where is (the chair)? - It's on / in / under / next to (the table).
- Toys
What have you got? - I've got a ball / doll / plane / car. I haven't got drums / a guitar / soldier / ballerina.
He / She's got a train / boat / teddy bear. He hasn't got a bike / kite / puppet.
This is my (car). It is (red) and (small).
Where is the (ball)? - It's under / on / in the (table).
- Vminnya
I can run / jump / play / climb / swim / eat / drink / dance / sing.
I can't fly.
Can you jump? – Yes, I can. / No, I can't.
- Body parts
I have got eyes / ears / a nose / a mouth / legs / hands / dark hair / blond hair.
I have got (brown) eyes and (long) (dark) hair. My nose is small.
- Creatures
I have got a cat / dog / parrot / rabbit / mouse / hamster / tortoise.
This is a monkey / elephant / crocodile / bird / duck / chimps / frog / horse.
My favorite animal is (a cat).
This is my (cat).
It is (big) and (black).
It has got (a nose).
It can (run).
- Cutter
What's your favorite food? – My favorite food is pizza / cake / biscuits / fish / chips.
I like apples / bananas / bread / juice / milk / eggs / cheese / chocolate / tea.
I don't like ice-cream / chicken / hot dogs.
- Weather that pori roku
What's the weather like? – It is sunny / cloudy / rainy / snowy / windy / hot / cold.
I like summer / autumn / winter / spring.
- Odyag
I'm wearing a hat / jacket / coat / T-shirt / skirt.
He/she is wearing jeans / socks / boots / shorts / shoes.
How to learn the form better zastosovuvati
At the first stages of training, you will have both individual lessons with a tutor, and group lessons with other children. Mustache to lie in the temperament of the child and її іndivіdualnyh idiosyncrasies.
Mustache to lie in the temperament of the child and її іndivіdualnyh idiosyncrasies.
Employment at school, as it seems, does not convey an individual approach to skin training and the pace of training, also, as the success of a child is deprived of the best, or if not enrolled in a school program, then we recommend an English course for Skyway. By stretching the course, your child will be able to recognize a lot of new words, learn grammatical constructions and learn, speak, speak.
Read also
English clock like people
How to learn English language from the 2nd class independently?
- Try to learn the English child at home. If your little one loves to read books, read books in English at once overnight. Cultivate the family tradition.
- Color comics is also a great way to speak language. For those little ones, come up with comics about other characters, for those who are older, come up with original comics based on English grammar.

- Listen to love songs English in the car on the way to school, it will be better, because you will be at once from a child to sing along.
- Learn tea in English . To sit down at the table lyalok and plush bears, explain to children, what is a five-o-clock, tell about the traditions of England, the queen. Prompt to speak English, like the help of the royal family.
- Walking to the store , tell the kids to call everything you put in the cat in English.
- New Year's Eve, propagate for hope write a sheet not only to Didov Frost, but to his American relative, Santa Claus . English, obviously.
What is a classmate to blame for before the end of fate?
Until the end of another fate, the child is obliged to master the following skills:
- Write the letters , know the order in the alphabet.

- Write words from the topics covered.
- Keep your speech simple for a clear or complete speech with the necessary words.
- Read short texts , which are composed of simple words, after listening to them in front of the recording.
- Understand the basic understanding simple explanations, prompted by familiar words, based on pictures.
- Take part in simple dialogues , learn to greet and say goodbye, to ask for information about yourself, and also to keep simple rozmov on the same topics: "Motherland", "School", "Working Day", "My Dim"
Read also
Tvіr My trip English translation
Visnovok
Learn at once from a child the format of learning English language, practice my yakomoha more often and do not forget about homework!
Let's hope, our list of grammatical and lexical topics will help your child in learning, and you know what to pay respect to.