Alphabet and letter sounds
Learn Pronunciation with Speak Method
The Sounds of the Alphabet: Learn Pronunciation with Speak Method| English Online with Speak Method |
|
| Online Classes | Pronunciation Facts | R, Th, T and other sounds | 500 Words Practice |
| Local Classes | Business Communication | TOEFL Prep | ESL Stories |
| Contact us | Vowel
Sounds |
Grammar and Idioms | For Young People |
With
this alphabet chart, understand how to say
the names of the letters and read about all the sounds of each letter
from the alphabet. These are the basic phonetic sounds for American English. To learn important sounds using free videos
online, go to Pronunciation in
English: 500 Words.
|
Letter |
Sound of Letter Name |
All sounds of letter |
Examples |
|
A, a |
ā-ee (long a to long e, also spell "ay") |
, ā, ah, ā-uh, uh |
cat, late, all, and, around |
|
B, b |
Bee |
buh |
bike |
|
C, c |
See |
kuh, suh |
cake, city |
|
D, d |
Dee |
duh |
did |
|
E, e |
Ee |
eh, ee, silent |
bed, free, late |
|
F, f |
Ef |
fuh |
fed |
|
G, g |
Jee |
guh, juh |
glad, large |
|
H, h |
ā-ch |
huh, silent |
hotel, what |
|
I, i |
ah-ee |
ah-ee, ĭ |
light, sit |
|
J, j |
Jay |
juh |
jump |
|
K, k |
Kay |
kuh |
kite |
|
L, l |
El |
luh, ul |
lot, full |
|
M, m |
Em |
muh |
mother |
|
N, n |
En |
nuh |
nest |
|
O, o |
ō (oh) |
ah, ō, uh, oo, ů |
hot, slow, computer, fool, good |
|
P, p |
Pee |
puh |
put |
|
Q, q |
Kyoo (kyū) |
kwuh |
quick |
|
R, r |
Ah-r |
ruh, ur |
race, stir |
|
S, s |
Es |
suh, zuh |
stick, is |
|
T, t |
Tee |
tuh, duh, N, silent, stopped tuh |
table, better, mountain, interview, hot |
|
U, u |
Yoo (yū) |
uh, yoo, oo, ů |
up, use, flute, full |
|
V, v |
Vee |
vuh |
very |
|
W, w |
Dubōyoo |
wuh, silent |
well, slow |
|
X, x |
Eks |
ks, zuh |
box, xylophone |
|
Y, y |
Wah-ee |
yuh, ee, ah-ee (i), ĭ |
yes, happy, try, cylinder |
|
Z, z |
Zee |
zuh |
zebra |
|
|
|
|
|
pronunciation English
pronunciation Learn More Sound American: Change Your Speech The 500 Common English Words What is a Vowel? English Free Online |
Speakmethod. com: English
Pronunciation, Seattle, WA
com: English
Pronunciation, Seattle, WA
English online with Speak Method
Try These 10 Fun Phonics Activities to Teach Letter Sounds to Children
What is phonics?
Phonics is the relationship between letters and sounds as well as the understanding of how those sounds connect to form words.
For instance, the /c/ sound, the short /a/ sound, and the /t/ sound blend together to form the word cat.
What does the research say about teaching phonics?
Research indicates the importance of teaching children phonics as a preliminary step for learning to read.
Research also suggests that systematic instruction which incorporates wordplay (manipulating letters/sounds in words to change the word), writing words, and using manipulatives such as magnetic letters to create words are all effective strategies for teaching phonics.
Additionally, research demonstrates the benefits of applying a multi-sensory approach to phonics instruction.
A multi-sensory approach incorporates sight, sound, touch, and movement into instruction. This helps address a variety of learning modalities, enabling students to better absorb the information.
Ten Fun Research-Based Phonics Activities to Teacher Letter-Sounds
1. Play the game “I Spy.”
In the game “I spy” you pick something that you see and don’t tell the child what it is. The child has to guess what you see.
Here is how you can use “I Spy” to teach letter sounds (phonics):
Let’s say you see a book in the room: You can say: I spy something that starts with the letter B or I spy something that ends with the letter K.
After your child guesses what “you spy” have them tell you the sound the letter makes. If your child cannot guess what “you spy” or does not know the letter sound, provide them with assistance.
You can also do the same thing using letter sounds. For example, if you see a book, you can say “I spy something that starts with (make the sound for b)” or “I spy something that ends with (make the sound for k).
After your child finds the object, have them tell you what the first letter (or last letter) of the object is. Take turns with your child. First you spy, then they spy, or vice versa.
2. Put letters on flashcards for a fun activity.
Put one letter on each card as shown below (create upper case and lower case cards):
Here is a sample activity:
Pick three to four-letter words and scramble them up. For example, if the word is pig, put the letters out-of-order (e.g., ipg) on the table in front of your child.
Put the letters one to two feet in front of your child so she has room to work. Next, give them a sheet of paper with three (or four) spaces for letters on it, like so _ _ _.
Then tell them the word or show a picture of the word and give the instruction (e.g., “I want you to make the word pig on the lines below, using the letters above).
If you have Magnetic Letters, you can use these as well. You can also encourage your child to write the letters in with a pen or pencil.
You can do word families to help your child understand that many words are spelled the same way, with only the first letter different. So after pig, try big, wig, and rig.
Rhyming practice is another helpful strategy when teaching kids about letter sounds.
3. Play letter-sound Go Fish.
Make doubles of flash cards. Each player gets five cards and the rest of the cards go in a pile in the center of the table.
Player 1 calls out a letter-sound and asks if player 2 has a match.
If they don’t have a match, tell them to “go fish” which means to choose from the pile. See more detailed rules for how to play Go Fish here.
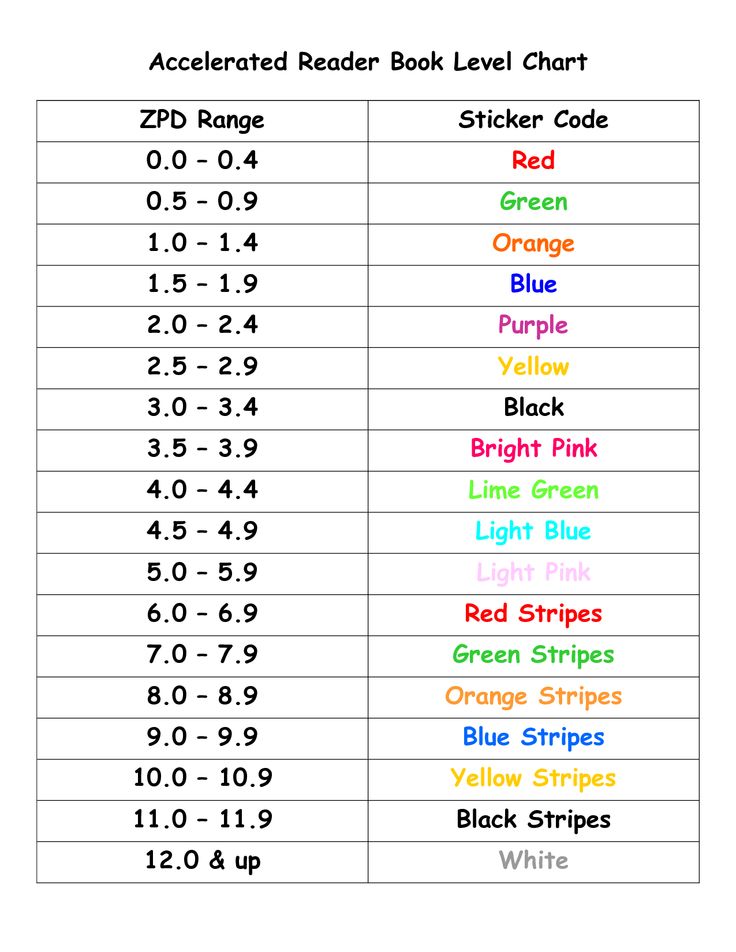
4. Make your own phonics Bingo game.
Draw a grid or make one on the computer like the one below. (You can also print out a large version of the one below here). You can find more blank grids here).
While the grid above has 25 boxes, you can play phonics Bingo with 9 or 16 boxes also.
Here are four options for getting pictures into the boxes:
Option 1 – Draw something simple in each box.
Examples of simple drawings for each letter of the alphabet include an apple, a banana, a comb, a door, an egg, a feather, a girl, a hat, an ice-cube, a jar, a kite, a light bulb, a mitten, a nose, an orange, a pan, a queen, a ring, a spoon, a table, an umbrella, a vase, a worm, a xylophone (that one might not be so easy to draw), and a zipper.
Use colors to make it look fun.
Option 2 – Get images from Google Images, print them, cut them out and glue them in the boxes.
Option 3 – Go to Google Images, copy each image by hitting “control c’ or by right-clicking on the image and selecting copy, then paste each picture into each grid box by right-clicking in the grid and clicking paste or by hitting “control v.”
Option 4 – Find and print out ready-made Bingo grids by doing a search for Kids Bingo Grids
You can play the Bingo game four ways:
1 – Call out a letter sound. If your child has a picture on her Bingo card that starts with that letter sound, have her put a coin, checker piece, or small piece of paper over the picture (you can cut index cards into small pieces.
If your child has a picture on her Bingo card that starts with that letter sound, have her put a coin, checker piece, or small piece of paper over the picture (you can cut index cards into small pieces.
This will work better than regular paper because the pieces will be heavier and stay on the Bingo card better).
2 – Call out a letter. If your child has a picture on her Bingo card that starts with that letter, have her cover the picture.
3 – Call out a letter sound. If your child has a picture that ends with that letter sound, have her cover the picture.
4 – Call out a letter. If your child has a picture that ends with that letter, have her cover the picture.
When your child fills up a row, up, down, or diagonally, she gets Bingo (she wins).
5. Make flashcards with a picture on one side and the letter the picture starts with (or ends with) on the other side
You can draw the pictures yourself or make flashcards using pictures from Google Images.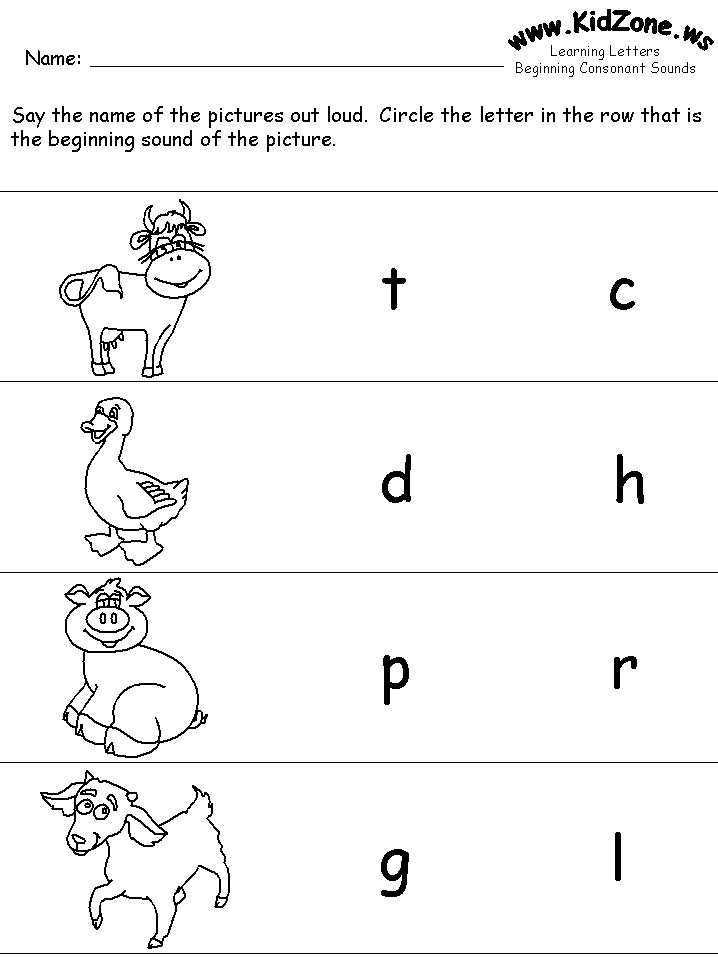
To make a flashcard from Google Images, go to the Image, copy it, “right-click” on it and click copy or hit “control c.” Then go to a word document and paste (right-click and click paste or “hit control v.”).
Then print out the pages, cut out the picture, and write the corresponding letter on the back.
If you know how to insert tables, you can put several pictures on the page in table boxes, print the page, cut out all the pictures, and put the letters on the back. Here is an example:
Show your child a picture and ask them to tell you the letter (or letter sound) it starts with (or ends with). If they are correct, let them know and show them the back of the card. If they are not correct, give them two more tries.
If they do not get the letter or sound, show them the back of the card and tell them the letter and sound (then enunciate the sound as you say the word), have them say the letter/sound back to you twice and shuffle the card back in the pile. Repeat.
6. For children who have a lot of energy, turn a phonics lesson into a movement activity.
Tape four letters onto the wall as shown in the image below:
Call out a letter sound and tell your child to run to the letter that makes that sound, touch it and run back. Spice it up. Here are some examples:
-Hop to the letter that makes the sound
-Skip to the letter that makes the sound
-Tip Toe to the letter that makes the sound
7. For another movement activity, put tape on the floor, with a letter on each piece of tape.
Tell your child to start with their feet on a certain letter (e.g., start on letter A), then tell them to jump to different letters, using the letter sounds.
For example, “Jump to the letter that makes the sound (insert letter sound).”
See an example below:
As your child becomes more independent with his letter sounds, you can make the letters spell actual words. For the word cat, have three pieces of tape, C, A, T.
Tell your child to start at the C, then jump to the next letter in Cat, and then the last letter.
To make it more challenging, have your child spell the word backwards, by starting with the last letter and jumping in order until they get to the first letter.
Mix up the game with upper and lower case letters. The example above has three letters, but you can use as many pieces of tape and letters as you want.
Start out with a few and add more if your child is making good progress.
8. Make a worksheet, using words and pictures with your child’s favorite characters, foods, animals, etc.
You can draw the worksheets by hand or use tables in Microsoft Word. For a three-letter word, make a table with five columns and one row.
Put the picture of the word in the first box of the table (you can draw in the pictures or copy and paste them from Google Images). Put the letters in the other boxes, but leave one letter out. Have your child fill in the missing letter.
Here is an example of the worksheet:
Click here to print out your own version of this sheet.
For children who may have trouble solving this worksheet, try providing them with a letter bank to see if that helps.
See an example of a worksheet with a letter bank below.
Click here to print out your own version of a phonics worksheet with a letter bank.
9. Have your child paste letters on paper as you call out the sounds.
You can use the letter flashcards you made, like in number 2.
You can use this activity to teach your child how to spell words. Draw lines or boxes on the paper so your child knows where to paste the letters.
You can give your child the exact number of letters in the word, or throw in some extra letters to make it more challenging.
Call out the first sound in the word, have your child pick the correct letter, and paste it on the first line.
Then have them do the next sound, and so on, until the word is complete.
Supervise the activity, providing assistance as needed.
When your child is done, hang up their work to show them that you are proud of their effort.
You can also use this idea to teach a child how to spell their name, such as the sample in the image below.
10. Sing the alphabet sound song.
The tune is similar to the traditional alphabet song.
Here is a great example by Kidstv123. You can make up your own version as well.
What else can you do to help your child learn letter sounds?
If your child is significantly struggling with learning letter sounds or acquiring other academic skills, despite consistent practice and guidance, talk to your child’s school and/or doctor.
They can refer you to the appropriate professionals to determine what might interfere with your child’s progress and if additional strategies could help.
Additional Information About Teaching Phonics to Children
Keep in mind that the activities in this article are recommendations. Please do not try to pressure a child into participating in any of these activities.
This can lead to your child feeling frustrated, and possibly shying away from phonics (letter-sound) practice.
Remember to always stay calm when working with a child or student, even if you think they should be getting something that they are not getting.
If you get frustrated with them, they may start to feel anxious, angry, inferior, stupid, etc. which will lead to a less productive learning session.
Keep practice sessions short (2 to 10 minutes for younger children or children who get easily frustrated and 10 to 15 minutes for older children or children who can work for longer periods without frustration), unless the child is eager to keep going.
For suggestions on ways to encourage children to complete tasks or assignments they do not want to do, read the following articles:
- 3 Ways to Use Timers to Encourage Homework and Chore Completion
- How to Use Schedules to Improve Children’s Behavior
Video Presentation
Education and Behavior – Keeping Us on the Same Page for Children.
Rachel Wise
Rachel Wise is the author and founder of Education and Behavior. Rachel created Education and Behavior in 2014 for adults to have an easy way to access research-based information to support children in the areas of learning, behavior, and social-emotional development. As a survivor of abuse, neglect, and bullying, Rachel slipped through the cracks of her school and community. Education and Behavior hopes to play a role in preventing that from happening to other children. Rachel is also the author of Building Confidence and Improving Behavior in Children: A Guide for Parents and Teachers.
“Children do best when there is consistency within and across settings (i.e., home, school, community). Education and Behavior allows us to maintain that consistency. ”
”
www.educationandbehavior.com
Alphabet / Sounds and Letters / Russian language guide for elementary school
- Main
- Handbooks
- Primary school Russian language guide
- Sounds and letters
- Alphabet
Alphabet - these are all the letters of the Russian language, arranged in a certain order. Each letter has its place and its name.
There are 33 letters in the Russian alphabet . Of these, 10 vowels ( a, e, ё, i, o, y, s, e, yu, i ) and 21 consonant d, k, l, m, n, p, r, s, t, f, x, c, h, w, u ).
b and b the signs do not refer to vowels or consonants, b is used to indicate the softness of a consonant, and b is used to separate.
Letters of the Russian alphabet:
Capital alphabet of the Russian language:
Share with your friends on social networks:
We advise you to look:
Vowel sounds and letters denoting them
Consonant sounds and letters denoting them
Syllable
Stress
Phonetic analysis
Sounds and letters 7 The rule is found in the following exercises:
1st class
Page 54, Kanakina, Goretsky, Textbook nine0017
Page 30, Kanakina, Goretsky, Workbook
Exercise 92, Klimanov, Makeeva, Textbook
Page 46, Klimanov, Workbook
Exercise 57, Polyakova, Textbook
Exercise 58, Polyakova, Textbook nine0017
exercise 60, Polyakova, Textbook
Exercise 62, Polyakova, Textbook
Exercise 1, Churakova, Textbook
Exercise 4, Ivanov, Evdokimova, Kuznetsova, Textbook
2nd class
Exercise 6, Kanakina, Goretsky, Textbook, part 1 nine0017
Exercise 163, Kanakina, Goretsky, Textbook, part 1
Exercise 178, Kanakina, Goretsky, Textbook, part 1
Exercise 75, Kanakina, Workbook, part 1
Exercise 45, Klimanov, Babushkina, Textbook, part 1 nine0017
Exercise 62, Klimanov, Babushkina, Textbook, part 1
exercise 30, Polyakova, Textbook, part 1
Exercise 91, Polyakova, Textbook, part 1
Exercise 145, Buneev, Buneeva, Pronina, Textbook
Exercise 147, Buneev, Buneeva, Pronina, Textbook nine0017
3rd grade
Exercise 234, Kanakina, Goretsky, Textbook, part 1
Exercise 86, Kanakina, Workbook, part 1
Exercise 138, Kanakina, Workbook, part 1
Exercise 148, Kanakina, Workbook, part 1 nine0017
Exercise 157, Kanakina, Workbook, part 1
Exercise 32, Klimanova, Babushkina, Workbook, part 1
Exercise 79, Klimanova, Babushkina, Workbook, part 1
Exercise 161, Polyakova, Textbook, part 1 nine0017
exercise 30, Buneev, Buneeva, Pronina, Textbook, part 1
4th class
Exercise 61, Kanakina, Goretsky, Textbook, part 1
Exercise 63, Kanakina, Goretsky, Textbook, part 1
Exercise 98, Kanakina, Goretsky, Textbook, part 1 nine0017
Exercise 14, Buneev, Buneeva, Pronina, Textbook, part 1
5th grade
Exercise 296, Ladyzhenskaya, Baranov, Trostentsova, Grigoryan, Kulibaba, Textbook, part 1
Exercise 298, Ladyzhenskaya, Baranov, Trostentsova, Grigoryan, Kulibaba, Textbook, part 1
Exercise 491, Ladyzhenskaya, Baranov, Trostentsova, Grigoryan, Kulibaba, Textbook, part 2
Exercise 17, Razumovskaya, Lvova, Kapinos, Textbook
Exercise 25, Alexandrova, Rybchenkova, Glazkov, Lisitsin, Textbook, part 1
Exercise 26, Alexandrova, Rybchenkova, Glazkov, Lisitsin, Textbook, part 1 nine0017
Exercise 27, Alexandrova, Rybchenkova, Glazkov, Lisitsin, Textbook, part 1
Exercise 28, Alexandrova, Rybchenkova, Glazkov, Lisitsin, Textbook, part 1
Exercise 29, Alexandrova, Rybchenkova, Glazkov, Lisitsin, Textbook, part 1
Exercise Review § 10 pp.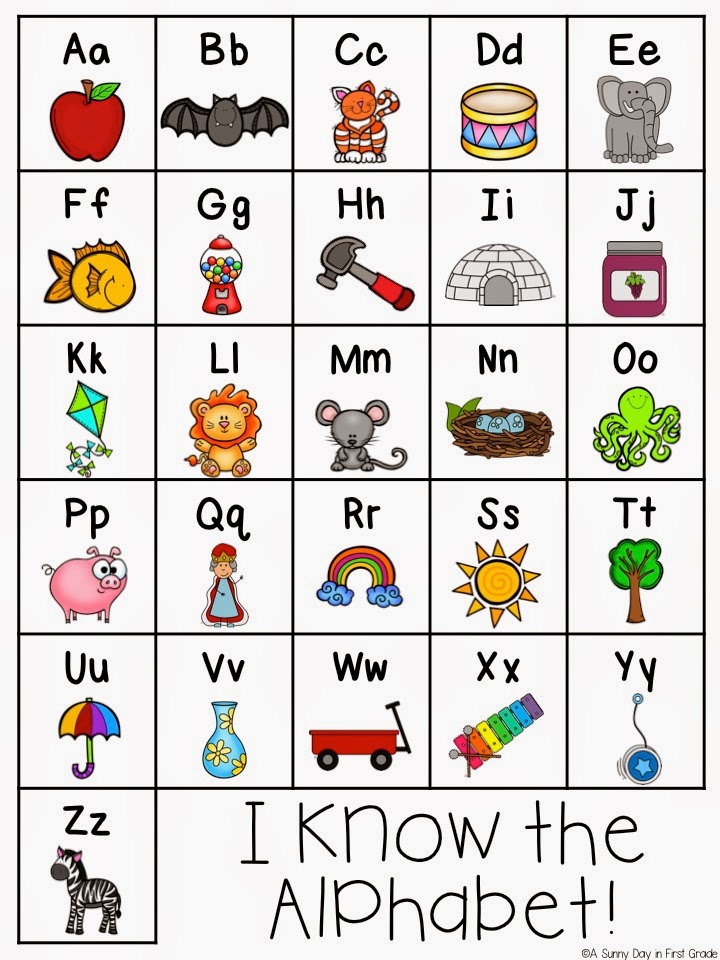 38-39, Alexandrova, Rybchenkova, Glazkov, Lisitsin, Textbook, part 1
38-39, Alexandrova, Rybchenkova, Glazkov, Lisitsin, Textbook, part 1
Grade 8
Exercise 368, Razumovskaya, Lvova, Kapinos, Textbook
letters and sounds in Russian (with audio)
4Mar 03/21/2022What letters and sounds are there in Russian? Which letters represent which sounds? What is the difference between soft and hard consonants? When is a consonant hard and when is it soft? Why do we need soft (b) and hard signs (b)? nine0016
Want to find answers to all these questions? Then read on!
Below you will find an interactive Russian alphabet with audio. For each letter [in square brackets], the sounds that it can stand for are indicated, as well as examples of words with this letter.
And here, for sure, you will immediately have two questions:
№1 Why do some letters have two sounds?
This is a feature of the Russian language. Some letters can represent two different sounds: a hard and a soft consonant. To clearly demonstrate this principle, I specially selected two examples for such letters: one with a hard consonant, and the other with a soft consonant. nine0017
Some letters can represent two different sounds: a hard and a soft consonant. To clearly demonstrate this principle, I specially selected two examples for such letters: one with a hard consonant, and the other with a soft consonant. nine0017
№2 Why are no sounds shown for "ь" and "ъ"?
These are soft and hard marks. By themselves, they do not represent any sounds. They show us how to read the previous consonant: a consonant before a hard sign will be hard, and a consonant before a soft sign will be soft.
Also, sometimes we need to separate a consonant from a vowel, and for this we will write one of these signs between them. This is how we distinguish, for example, the words “seed” [s′ém′ʌ] and “family” [s′im′jʌ́]. nine0017
Now, when you listen to the audio, pay attention to these pronunciation features.
But how do you know when a consonant is hard and when soft?
Very easy! You need to look at the next letter.
- Before with a hard sign (Kommersant) , before other consonants and before the vowels A , O , U E, s consonant - hard .
- Before soft sign (b) and in front of the vowels I , ё , U , , and 9022
Ref: consonant w , w , c 90 016 -
See? This [th]-component makes the consonant soft!
Finally, let's move from theory to practice! Try to read these words. Do you understand them?
Pineapple, vase, banana, guitar, rocket, moon, mom, dad, hello, music, matryoshka, hat, lamp, movie, coffee, tea, lemon, chair, Saturday, dollar, ruble, Italy, America, Spain .