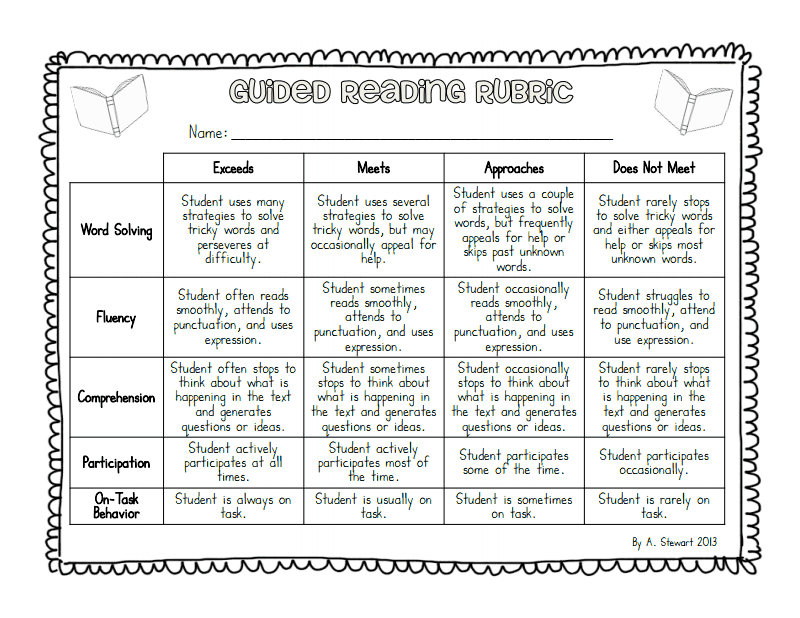
Assessing students reading level
Assessing a Student's Level | Reading A-Z
Digital
Running Records
on Raz-Plus
With our online running record tool, Raz-Plus or Raz-Kids members can:
- Assign a Benchmark Book from Levels aa-J
- Assign a Benchmark Passage from Levels aa-Z2
- Listen to students' recordings from reading aloud a book or passage.
- Score all student recordings using an online running-record tool.
- Listen to students' recordings of retellings.
- Score retellings using an online rubric.
- See quiz questions missed and a report on which comprehension skills to support or re-teach with each student.
- Reward students' progress through awarding stars to spend in the RAZ Rocket.
- Track your students' progress over time.
Reading A-Z provides a three-part assessment process to help you place students in instructionally appropriate level texts.
- Find out at which level to start a student.
- Determine when a student is ready to move to the next level.
Part 1: Students read Benchmark Passages or Benchmark Books (Levels aa-J), and you capture their reading behavior on Running Records.
Part 2: Students retell the text, and you use Retelling Rubrics to score their comprehension.
Part 3: Students take an oral or written Comprehension Quick Check Quiz, and each question's answer tells what skill it assessed to help you identify comprehension skills for additional practice.
Part 1: Start with Benchmark Passages & Running Records or Benchmark Books & Running Records (Levels aa-J). Select a passage or book that best approximates a student's reading level. Use the running records that accompany each passage or book to score a student's reading behavior. (Initially you may have to take more than one running record to determine a student's instructional level.
 ) To assess a student's instructional level in Spanish, use printable versions of the Spanish Benchmark Passages, or
Pasajes estándar.
) To assess a student's instructional level in Spanish, use printable versions of the Spanish Benchmark Passages, or
Pasajes estándar. Review About Running Records to learn about the details of taking, marking and scoring a running record.
Parts 2 & 3: Retelling Rubrics and Comprehension Quick Check Quizzes provide details about a student's understanding and comprehension of the Benchmark Passage or Book.
- Retelling Rubrics provide details that identify strengths and weaknesses students might have comprehending fiction or nonfiction texts; including analysis of text structures.
- Benchmark Passages and Benchmark Books (Levels aa-J) have multiple-choice Comprehension Quick Check Quizzes and answer keys. Use the skill tags on the answer key to see comprehension strengths and opportunities for additional instruction.
The three-part process establishes a baseline of your students' levels. Assign leveled books from Reading A-Z's extensive collection for small group practice at students' instructional levels.
 Allow students to choose books below their instructional levels for independent practice.
Allow students to choose books below their instructional levels for independent practice.How Do I Monitor Students' Reading Progress?
Use Benchmark Books or Benchmark Passages and their associated resources for progress monitoring as students' reading at their instructional levels improves.
Assessment Schedule
| Developmental Level | Reading Level | Schedule |
|---|---|---|
| Beginning readers | Levels aa-C | every 2 to 4 weeks |
| Developing readers | Levels D-J | every 4 to 6 weeks |
| Effective readers | Levels K-P | every 6 to 8 weeks |
| Automatic readers | Levels Q-Z | every 8 to 10 weeks |
Students who are not progressing at the expected rate should be assessed even more frequently than the Assessment Schedule suggests.
The scores your students achieve on running records, retellings, and comprehension quizzes give you valuable information about their reading behavior and comprehension. Use it to inform your instruction in addition to placing students and monitoring their progress.
Use the chart below along with the other information you learn from the three-part assessment process to determine if students are ready to move up a level.
Scores
| Running Record | Quick Check Comprehension Quiz | Action |
|---|---|---|
| 95% + | 100% | Advance Student a Level |
| 95% + | 80% | Instruct at this Level |
| 95% + | Lower a Level, Assess Again | |
| 90-94% | 80-100% | Instruct at this Level |
| 90-94% | Lower a Level, Assess Again | |
| N/A | Lower a Level, Assess Again |
For Raz-Plus members, results from the printable running records can be entered to display in a student's Reading Rate report in your Kids A-Z management hub.
 That way, you have not only the digital running records and assessment information, but also the results from printable running records—all in one place.
That way, you have not only the digital running records and assessment information, but also the results from printable running records—all in one place.
How Do I Match Learning A-Z Levels to Other Leveling Systems?
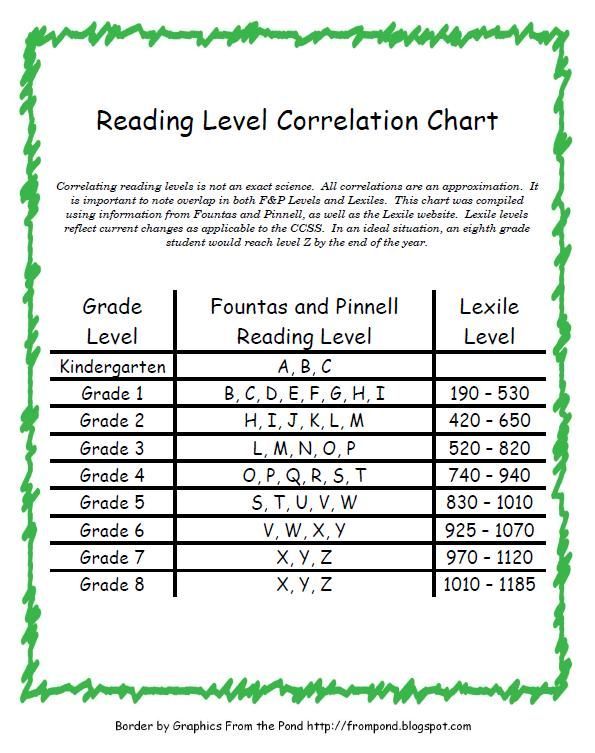
For your convenience, Learning A-Z correlates its levels to other leveling systems. If you've already placed students in levels according to another system, please reference the Level Correlation Chart to determine how another system's levels best match Learning A-Z's levels.
The correlations are not official levels assigned by the other leveling systems, but rather an approximate correlation based on a comparison of attributes in books assigned official levels by both the other leveling system and Learning A-Z.
Assessing A Students' Level
1 Students record themselves reading aloud Benchmark Passages or Benchmark Books (Levels aa-J) and send recordings to your In Basket, which you access through your Kids A-Z management hub. You score their reading behavior on online running records.
You score their reading behavior on online running records.
2 Students record a retelling of the text and send it to your In Basket, and you use online rubrics for fiction or nonfiction texts to score their comprehension.
3 Students take a Comprehension Quick Check Quiz, and our software scores it. Skill Reports help you identify comprehension skills for additional practice.
Save valuable instructional time and assess every student's reading performance with online running records. Each student sends recordings to your In Basket in a three-part assessment process that provides you with a more complete picture of your students' reading abilities and monitors their progress.
- Place students at the appropriate reading level to start.
- Determine students' readiness to advance to the next level after they complete assignments.

- Monitor student reading progress over time.
Part 1
Preview the Benchmark Passages & Running Records or Benchmark Books & Running Records (Levels aa-J) collections before assigning. (Initially you may have to take more than one running record to determine a student's instructional level.)
Assign a Benchmark Passage or Benchmark Book (Levels aa-J) by clicking on the Assign button and selecting students.
Review About Running Records to learn about the details of scoring an online running record.
Parts 2 & 3
Retelling Rubrics and Comprehension Quick Check Quizzes automatically follow the recording of the passage or book and provide details about a student's understanding and comprehension.
Retelling recordings provide details that identify strengths and weaknesses students might have comprehending fiction or nonfiction texts; including analysis of text structures. Listen to recordings and score rubrics for either fiction or nonfiction text.
Listen to recordings and score rubrics for either fiction or nonfiction text.
- Students are prompted to tell you about the story or text in as much detail as he or she can remember.
- Rubrics provide specific details expected from every student so teachers can judge each retelling with the same rigor.
Multiple-choice quizzes provide students with feedback when completed on how well they scored.
- You can preview and review each quiz question and answer in addition to seeing a student's score and skills missed.
- Use the Skill Reports in your Kids A-Z management hub to see comprehension strengths and opportunities for additional instruction for your whole class or look at individual student reports to individualize instruction.
The three-part process establishes a baseline of your students' levels. Assign leveled books from Reading A-Z's extensive collection for small group practice at students' instructional levels. Allow students to choose books below their instructional levels for independent practice.
Allow students to choose books below their instructional levels for independent practice.
How Do I Monitor Students' Reading Progress?
Use Benchmark Passages or Benchmark Books (Levels aa-J) and their associated resources for progress monitoring as students' reading at their instructional levels improves and/or as they complete self-paced assignments. Use Assessment Reports for a whole-class view. Review student profile pages to see individual reading rate and level progress reports so you can further monitor the progress of individual students.
Assessment Schedule
| Developmental Level | Reading Level | Schedule |
|---|---|---|
| Beginning readers | Levels aa-C | every 2 to 4 weeks |
| Developing readers | Levels D-J | every 4 to 6 weeks |
| Effective readers | Levels K-P | every 6 to 8 weeks |
| Automatic readers | Levels Q-Z | every 8 to 10 weeks |
Note Students who are not progressing at the expected rate should be assessed even more frequently than the Assessment Schedule suggests.
Use the chart below along with the information in Assessment Reports to determine if students are ready to move up a level.
Scorecard formulas are automatically calculated based on recording length and errors you have marked using our online rubrics or forms. See Assessment Reports to review a list of calculated scores for your class. See About Running Records to learn more about taking, marking, and scoring a running record.
Scores
| Running Record Accuracy Rate | Quick Check Comprehension Quiz | Action |
|---|---|---|
| 95% + | 100% | Advance Student a Level |
| 95% + | 80% | Instruct at this Level |
| 95% + | Lower a Level, Assess Again | |
| 90-94% | 80-100% | Instruct at this Level |
| 90-94% | Lower a Level, Assess Again | |
| N/A | Lower a Level, Assess Again |
For Raz-Plus members, results from the printable running records can be entered to display in a student's Reading Rate report in your Kids A-Z management hub. That way, you have not only the digital running records and assessment information, but also the results from printable running records—all in one place.
That way, you have not only the digital running records and assessment information, but also the results from printable running records—all in one place.
How Do I Match Learning A-Z Levels to Other Leveling Systems?
For your convenience, Learning A-Z correlated its levels to other leveling systems. If you've already placed students in levels according to another system, please reference the Level Correlation Chart to determine how another system's levels best match Learning A-Z's levels.
The correlations are not official levels assigned by the other leveling systems, but rather an approximate correlation based on a comparison of attributes in books assigned official levels by both the other leveling system and Learning A-Z.
standards for grades and quarters
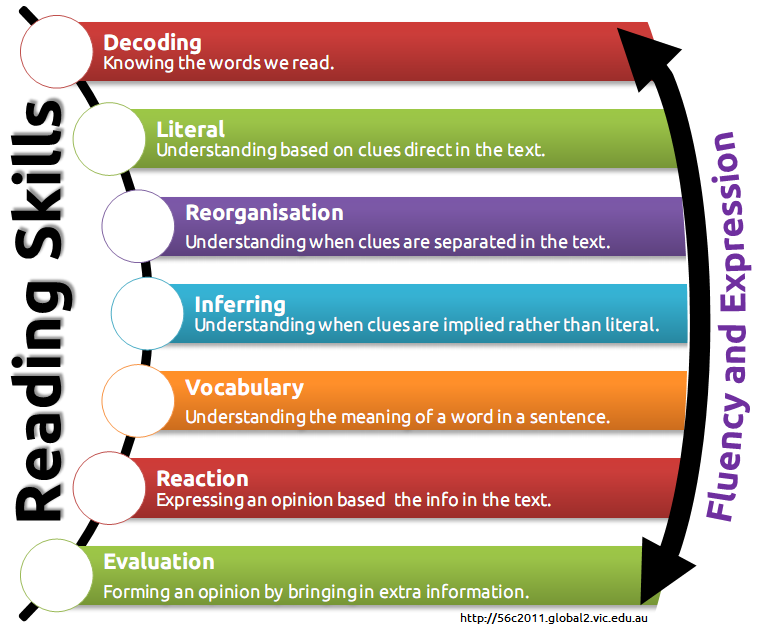
Reading is a key skill that opens the gate to the land of knowledge for a child. Thanks to this skill, children learn about the phenomena and events of the world around them, get acquainted with the characters and actions of people, meet new problems and ideas. This skill helps them to broaden their horizons and ideas about the world, develops critical thinking and trains cognitive abilities - attention, imagination, memory. Reading is the foundation for further successful learning.
This skill helps them to broaden their horizons and ideas about the world, develops critical thinking and trains cognitive abilities - attention, imagination, memory. Reading is the foundation for further successful learning.
To understand how well a child develops this skill, it helps to check the reading technique. Reading technique is a multifactorial test that characterizes the development of a skill from different angles. In the technique of reading are evaluated:
- reading speed,
- reading method,
- reading awareness,
- correct reading,
- expressiveness of reading.
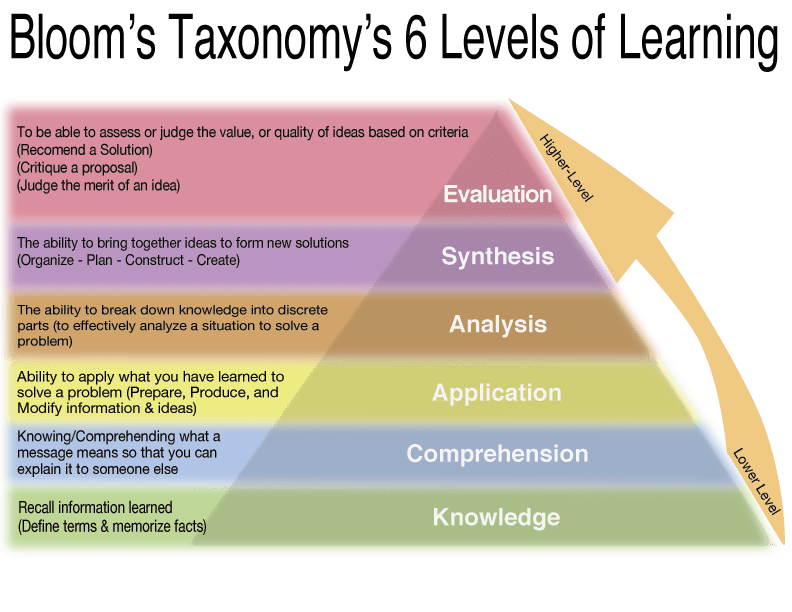
A difficult reading skill consists of both a technical and a semantic component and is aimed at achieving the main goal - understanding and assimilation of the information read.
Reading technique parameters
Let's consider all the components of reading technique in more detail.
- Reading speed - the number of words read in a certain period of time.
 Often, parents focus on the formation of fluent reading, while the child makes many mistakes, does not understand and does not remember what he read. It is not necessary to force only speed, slower conscious reading and a gradual increase in tempo are better than fast mechanical reading with errors and inaccuracies.
Often, parents focus on the formation of fluent reading, while the child makes many mistakes, does not understand and does not remember what he read. It is not necessary to force only speed, slower conscious reading and a gradual increase in tempo are better than fast mechanical reading with errors and inaccuracies. - Way of reading — syllabic reading or reading the whole word, smoothly. With the development of the skill, the child has a gradual transition from syllabic reading to smooth reading in whole words.
- The correct reading of is characterized by the absence of errors and hesitation. Inattention, problems of diction lead to inaccurate reading, indistinct articulation and, as a result, to a distortion of meaning. Pay attention to the correct reading - this will be the key to competent writing.
- Reading awareness involves reading comprehension, awareness of the idea and meaning of the text, and in the future - this is the ability to catch the subtext, humor, irony, the attitude of the author.
 Interfering with reading comprehension can be low reading speed, distorted reproduction - guessing words, changing the shape of words, not reading endings.
Interfering with reading comprehension can be low reading speed, distorted reproduction - guessing words, changing the shape of words, not reading endings. - Reading expressiveness - the use of pauses, finding the right intonation, the correct placement of stresses. The expressiveness of reading is inextricably linked with awareness. When understanding what is read, it is easier for the child to observe the necessary pauses, select the correct intonation and place logical stresses.
Reading speed standards for elementary school
GEF standards determine the desired reading speed for a child by a certain point in learning, help to understand whether the development of a skill is successful or whether additional attention is required. Standards - indicative values; it is important to take into account the individual psychophysiological characteristics of each child and evaluate the growth of his personal indicators.
Grade 1 reading speed standards
Reading speed standards in grade 2
Reading speed standards in grade 3
Reading velocity
Reading speed, to which it is necessary schools, is reading at the speed of conversational speech, 110-120 words per minute.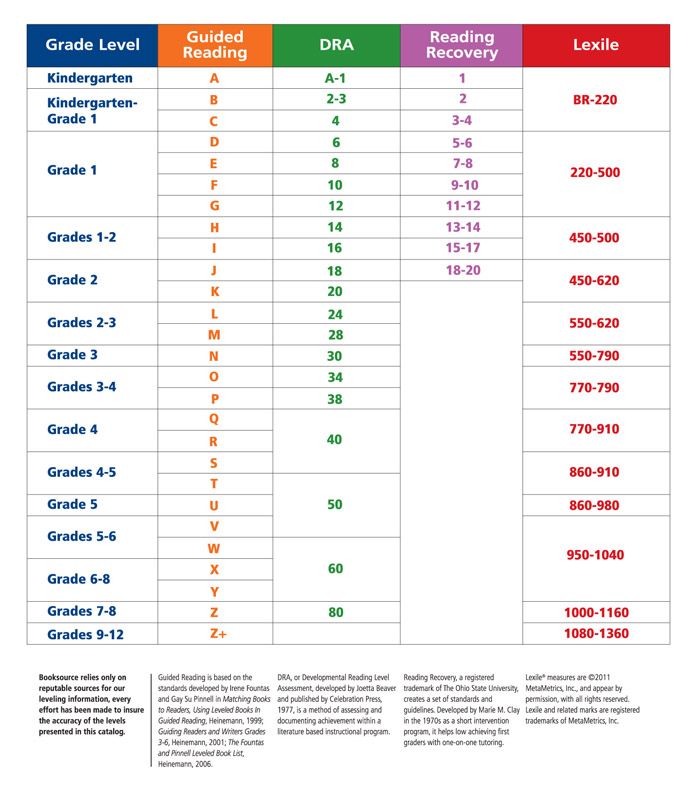 The human articulatory apparatus has adapted to this speed over time. And most importantly, the reading should be conscious, correct, expressive.
The human articulatory apparatus has adapted to this speed over time. And most importantly, the reading should be conscious, correct, expressive.
Other parameters of reading technique
Grade 1
At the end of the first half of the year. Reading is smooth syllabic, conscious and correct, with a clear pronunciation of syllables and words.
At the end of the second half of the year. Reading is conscious, correct, simple words are read as a word. Words with a complex syllabic structure can be read syllable by syllable.
Grade 2
At the end of the first half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. Compliance with logical stresses. Compound words can be read syllable by syllable.
At the end of the second half of the year. Reading meaningful, correct, in whole words. With observance of logical stresses, pauses and intonations. Syllabic reading is undesirable.
Grade 3
At the end of the first half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, with the help of which the child expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is being read.
At the end of the second half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the child expresses understanding of the meaning of what is being read.
4th grade
At the end of the first half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With the help of observed pauses and intonations, the child not only expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is being read, but is able to express his attitude to what he has read.
At the end of the second half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the child expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is read, and his attitude to the content of what is read.
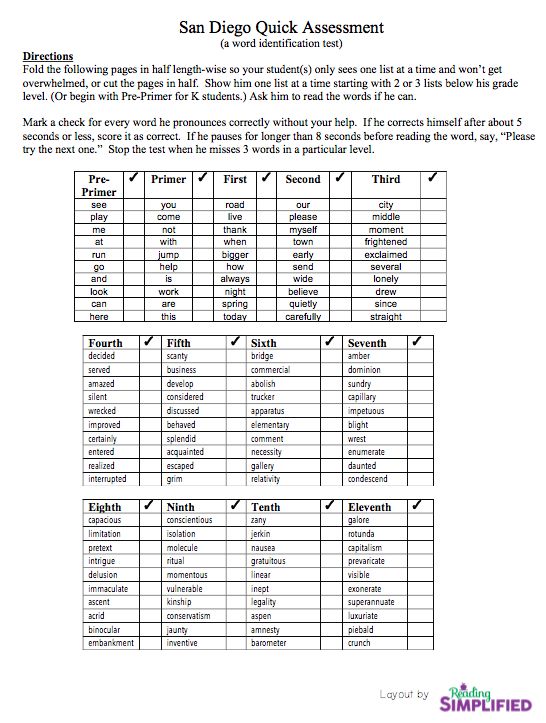
How can I test my child's reading skills on my own?
Have your child see how well they read already. Children usually love to know how many centimeters they have grown, and they may also be interested in knowing their progress in reading. Warn about the upcoming test and ask the child to read quickly.
The control of reading technique in sensitive children who, due to their temperament, can hardly tolerate various tests, can be carried out imperceptibly or in the form of a game. Do not create unnecessary excitement around the upcoming test, do not arrange a test in the form of an exam. If the child is worried, stutters, transfer control to another time.
Verification process:
- Prepare a clock with a second hand or use the stopwatch on your phone, and choose the appropriate text.
- Ask the child to take a seat.
- Show him the text and ask him to read it aloud.
- Track the time from the moment your child starts reading.
 Not all children are able to immediately start reading on command, which leads to inaccurate results.
Not all children are able to immediately start reading on command, which leads to inaccurate results. - Usually, one minute is noted for checking, but some experts recommend taking 2 minutes for monitoring, since not all children are equally quickly included in the work. Divide the result obtained in 2 minutes in half.
- Do not correct or interrupt while reading. It is better to discuss the mistakes made after the child has finished reading.
- Assess the speed, correctness, awareness and expressiveness of reading.
- Retest and compare results. Reading technique may differ depending on the child's fatigue, health status and mood.
Which text is suitable for verification?
Both fiction and non-fiction texts appropriate for the child's age are suitable for this purpose. The text should be unfamiliar, but understandable to the child, have educational and educational value. The texts of V. Bianchi, L. Tolstoy, N. Nosov, B. Zhitkov, K.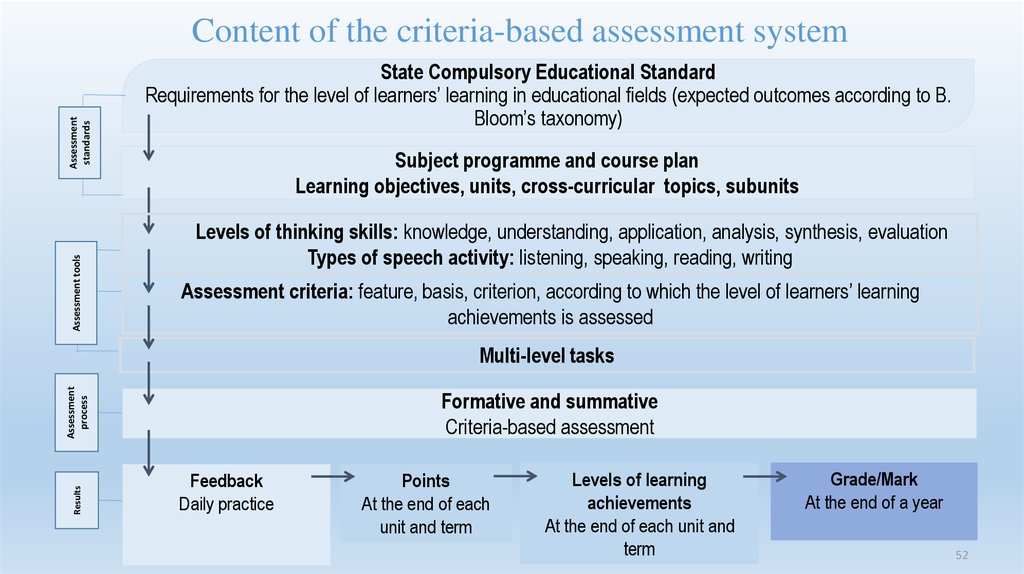 Ushinsky, V. Dragunsky are suitable. The text for verification can be found in special manuals or in a textbook on the Russian language and literature.
Ushinsky, V. Dragunsky are suitable. The text for verification can be found in special manuals or in a textbook on the Russian language and literature.
You should find the text that is located on the spread of the book so that the child does not have to waste time turning pages. Choose text without an abundance of punctuation marks and distracting illustrations. It is not desirable that the passage contains common complex sentences and dialogues. The font must be large enough and legible. The text should not have a technical focus and contain terms incomprehensible to the child.
Test score
Speed score
Count how many words the child read in one minute. When counting words, pay attention:
- prepositions, conjunctions, particles of 1-2 letters are counted as one word;
- when wrapping, the word is counted as 2 words;
- if the word is written with a hyphen, look at how many letters are on both sides of the hyphen: if there are more than three, we count it as 2 words, for example, "long, long", if less than three, for example, "somehow", - as one .
Compare your score with the recommended range and your child's previous performance.
Comprehension score
Determine how well the child understood what they read. If the student reads slowly and has read only a couple of sentences, let him read the passage to the end. Ask your child a few questions about the text. Ask what or who he read about. Ask the child to identify the main idea of what they read and retell the text.
For a deeper check of the meaning of the reading and learning, use special teaching kits.
Correctness assessment
Pay attention to whether the child reads what is written correctly, whether he pronounces words clearly, whether there are hesitations and corrections, whether he alters words, whether he changes endings, whether he places stresses correctly. Discuss the mistakes with the student.
Evaluation of expressiveness
To assess the expressiveness of reading, the child is offered a familiar text. Listen to whether the child observes pauses and other punctuation marks, whether he changes intonation, whether he highlights the main idea.
Listen to whether the child observes pauses and other punctuation marks, whether he changes intonation, whether he highlights the main idea.
Improving reading technique
Poor results in reading technique are not a reason to be upset, but only a signal that additional efforts need to be made to improve the skill. You can work with the child on your own or contact a specialist who will analyze the weak points and select the appropriate exercises. Conduct additional activities with the child in the mode of "sparing reading" without pressure. It is more important to observe the regularity and frequency of classes: 10-20 minutes daily.
How can you motivate your child to read:
- Reward your efforts with stickers, stars.
- Mark progress visually - create a success board so your child can visually see their progress
- Conduct activities in the form of a game, such as "going to the library" or "reading to your favorite toys.
 "
" - Choose books and texts that are interesting for your child.
- Let the child read to pets, they are grateful and accepting listeners. Reading to them, the child is not afraid to make a mistake, he relaxes and overcomes the fear of failure.
- Have a reading competition between peers and siblings.
To improve the speed of reading will help:
- Reading by syllabic tables.
- Multiple reading. Read the same text several times, increasing the pace. From the second time the child will be able to read faster.
- "Tug". An adult leads a finger along the line, setting the pace. The child tries to read at a given pace.
- Tops and roots. The child reads the words, covering the upper or lower half of the letters with a ruler.
- Reading in a book turned upside down.
- Lightning. Alternating reading at a comfortable pace with reading at the highest possible speed for 20 seconds on the command "Lightning!".

- "Sprint". Reading speed competition between classmates.
- Work on expanding the field of view according to Schulte tables.
- Reading with a window to eliminate "regression" - recurrent eye movements that lead to repeated reading.
For correct reading:
- Work on clear diction, do articulation exercises.
- Read tongue twisters and tongue twisters.
- Invite the child to correct the deformed sentences: "The weather is good on the street."
- "Imaginary word". When reading, the wrong word is pronounced, the child must correct it.
Reading comprehension
- Wave Reading. First, the child reads aloud, then retells what he read.
- Drawing up a plan for reading.
- The student reads to himself at a comfortable pace, tells what he understood and felt, what he thought about
- Discuss unfamiliar words and expressions.
- Invite the child to draw a picture of the passage they read.
- Ask them to tell you what they liked about the text, what they remember.
For expressive reading
- Role-playing, staging.
- Put on a "radio show".
- Expressive recitation of poems.
- Voice flexibility training. The ability to speak quieter-louder, higher-lower.
- Conducting reading indicating the tone or strength of the voice.
- Live Picture. One reads, the other reacts with facial expressions.
Improving reading skills in elementary school is very important. It is fluent and meaningful reading that activates the processes of thinking, attention, memory and is the basis for a child's successful learning in the future. This detailed instruction on reading technique control will help you track and improve your child's skill development.
Russian language for students in grades 1-4
We develop thinking skills, prepare for the Olympiads and improve the results of the Russian language in an interactive format
learn more
International studies of the quality of education are held by international organizations: International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement (IEA), Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD).
International Comparative Research allows you to identify and compare the status and changes in education systems in different countries and evaluate the effectiveness of strategic decisions in the field of education.
The comparison is not made speculatively based on the study of various sources of literature, not on the basis of a comparison of the results of prestigious international Olympiads for the elite, but on the basis of the results of studies conducted on representative samples of students from different countries using the same toolkit, which is created taking into account international priorities in education.
Russia has been participating in international studies since 1990.
- PISA: Program for International Student Assessment. The purpose of the study is to assess the ability of students to use the knowledge and experience acquired at school for a wide range of life tasks in various areas of human activity, communication and social relations.
- TIMSS: Third International Mathematics and Science Study. The main purpose of the study is to compare the quality of mathematics and science education in primary and secondary schools
- PIRLS: Progress in International Reading Literacy Study. The study is conducted to compare the level and quality of reading and understanding of the text by primary school students around the world, as well as to identify and interpret differences in national education systems in order to improve the process of learning to read.
- ICILS: International Computer and Information Literacy Study. The purpose of the study is to assess the preparedness of students for study, work and life in the information age, to study the levels of computer and information literacy of 8th grade students in the participating countries, to analyze the identified differences, to promote education in this area at the national and international levels.
- ICCS: International Civic and Citizenship Education Study. The study provides information on the conceptual understanding and competencies in the field of civic education, on the predispositions and attitudes towards it among young people.
International comparative studies have been actively developed in our country and, along with the state final certification, all-Russian verification works and national studies of the quality of education form the Unified System for Assessing the Quality of Education (ESOKO) in the Russian Federation.
For more information about international comparative studies, please visit the website of the Federal Institute for Educational Quality Assessment
Preparing for PISA-2022: mathematical literacy
April 4, 2022 in the Chelyabinsk region will begin an international study of the quality of education PISA. Mathematical literacy, which was the focus of the study in 2003 and 2012, will be the object of special attention in the next cycle of the study.
Preparing for PISA-2022: components of functional literacy
From April 4 to May 15, students from the Chelyabinsk region will take part in the international study of the quality of education PISA.
Functional literacy in the international PISA study
In the spring of 2022, students from seven schools in the Chelyabinsk region will take part in the main phase of the PISA study.
Chelyabinsk region will take part in the international study of the quality of education PISA
From April 4 to May 20, 2022, students of educational institutions of the Chelyabinsk region will take part in the main stage of the PISA study.
Students of the Chelyabinsk region will take part in the PISA study
From October 11 to November 5, 2021, students of educational institutions of the Chelyabinsk region will take part in the all-Russian assessment according to the PISA model.
Pupils of the 4th grade of the region will take part in an international study of the quality of education
In April 2021, fourth-graders from the Chelyabinsk region will participate in the international study of reading quality and text comprehension (PIRLS-2021).
Russia improved its performance in the TIMSS international study of education quality, entering the top six
Russia maintained and strengthened its positions in all areas of the TIMSS international comparative study of education quality, confidently entering the top six world leaders
Rosobrnadzor summed up the first results of studies regions of the Russian Federation in 2019-2020 according to the PISA model
The Federal Service for Supervision in Education and Science, during a press conference held on November 27, summed up the first results of studies of the quality of education in the regions of Russia according to the PISA model, held in 2019-2020.











