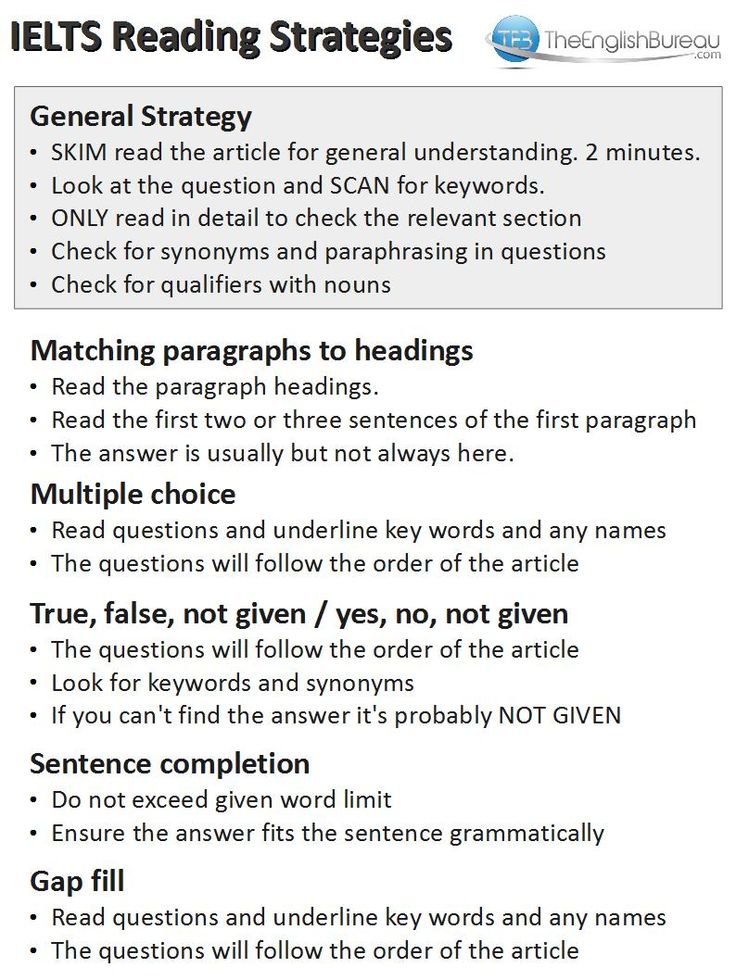
Best reading strategies
Strategies for Reading Comprehension :: Read Naturally, Inc.
Comprehension: The Goal of Reading
Comprehension, or extracting meaning from what you read, is the ultimate goal of reading. Experienced readers take this for granted and may not appreciate the reading comprehension skills required. The process of comprehension is both interactive and strategic. Rather than passively reading text, readers must analyze it, internalize it and make it their own.
In order to read with comprehension, developing readers must be able to read with some proficiency and then receive explicit instruction in reading comprehension strategies (Tierney, 1982).
Strategies for reading comprehension in Read Naturally programs
General Strategies for Reading Comprehension
The process of comprehending text begins before children can read, when someone reads a picture book to them. They listen to the words, see the pictures in the book, and may start to associate the words on the page with the words they are hearing and the ideas they represent.
In order to learn comprehension strategies, students need modeling, practice, and feedback. The key comprehension strategies are described below.
Using Prior Knowledge/Previewing
When students preview text, they tap into what they already know that will help them to understand the text they are about to read. This provides a framework for any new information they read.
Predicting
When students make predictions about the text they are about to read, it sets up expectations based on their prior knowledge about similar topics. As they read, they may mentally revise their prediction as they gain more information.
Identifying the Main Idea and Summarization
Identifying the main idea and summarizing requires that students determine what is important and then put it in their own words. Implicit in this process is trying to understand the author’s purpose in writing the text.
Questioning
Asking and answering questions about text is another strategy that helps students focus on the meaning of text. Teachers can help by modeling both the process of asking good questions and strategies for finding the answers in the text.
Teachers can help by modeling both the process of asking good questions and strategies for finding the answers in the text.
Making Inferences
In order to make inferences about something that is not explicitly stated in the text, students must learn to draw on prior knowledge and recognize clues in the text itself.
Visualizing
Studies have shown that students who visualize while reading have better recall than those who do not (Pressley, 1977). Readers can take advantage of illustrations that are embedded in the text or create their own mental images or drawings when reading text without illustrations.
Strategies for Reading Comprehension: Narrative Text
Narrative text tells a story, either a true story or a fictional story. There are a number of strategies that will help students understand narrative text.
Story Maps
Teachers can have students diagram the story grammar of the text to raise their awareness of the elements the author uses to construct the story.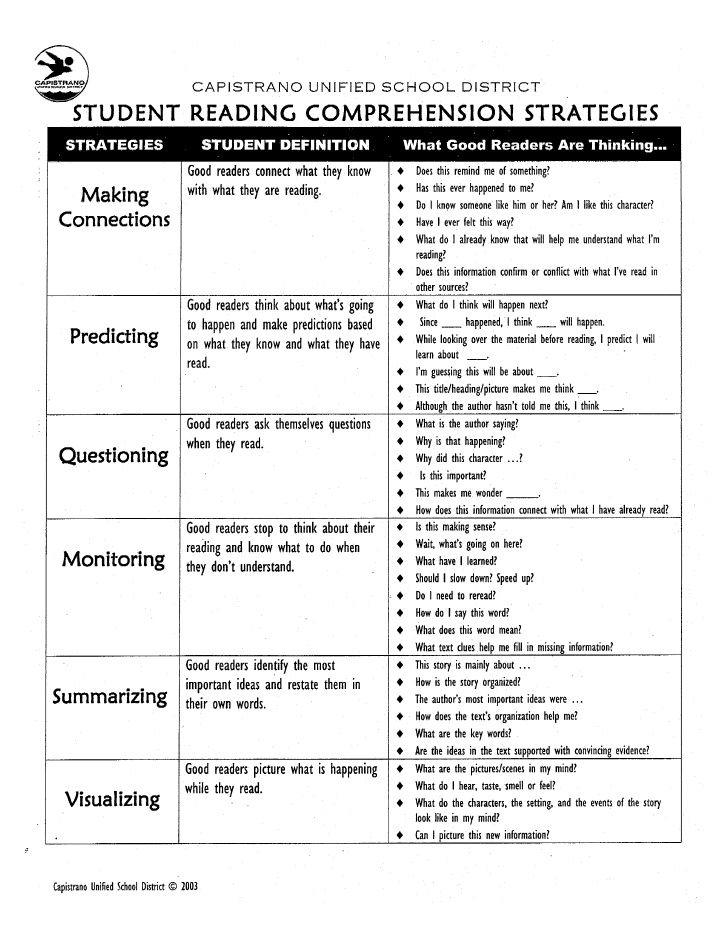 Story grammar includes:
Story grammar includes:
- Setting: When and where the story takes place (which can change over the course of the story).
- Characters: The people or animals in the story, including the protagonist (main character), whose motivations and actions drive the story.
- Plot: The story line, which typically includes one or more problems or conflicts that the protagonist must address and ultimately resolve.
- Theme: The overriding lesson or main idea that the author wants readers to glean from the story. It could be explicitly stated as in Aesop’s Fables or inferred by the reader (more common).
Printable story map (blank)
Retelling
Asking students to retell a story in their own words forces them to analyze the content to determine what is important. Teachers can encourage students to go beyond literally recounting the story to drawing their own conclusions about it.
Prediction
Teachers can ask readers to make a prediction about a story based on the title and any other clues that are available, such as illustrations. Teachers can later ask students to find text that supports or contradicts their predictions.
Teachers can later ask students to find text that supports or contradicts their predictions.
Answering Comprehension Questions
Asking students different types of questions requires that they find the answers in different ways, for example, by finding literal answers in the text itself or by drawing on prior knowledge and then inferring answers based on clues in the text.
Strategies for Reading Comprehension: Expository Text
Expository text explains facts and concepts in order to inform, persuade, or explain.
The Structure of Expository Text
Expository text is typically structured with visual cues such as headings and subheadings that provide clear cues as to the structure of the information. The first sentence in a paragraph is also typically a topic sentence that clearly states what the paragraph is about.
Expository text also often uses one of five common text structures as an organizing principle:
- Cause and effect
- Problem and solution
- Compare and contrast
- Description
- Time order (sequence of events, actions, or steps)
Teaching these structures can help students recognize relationships between ideas and the overall intent of the text.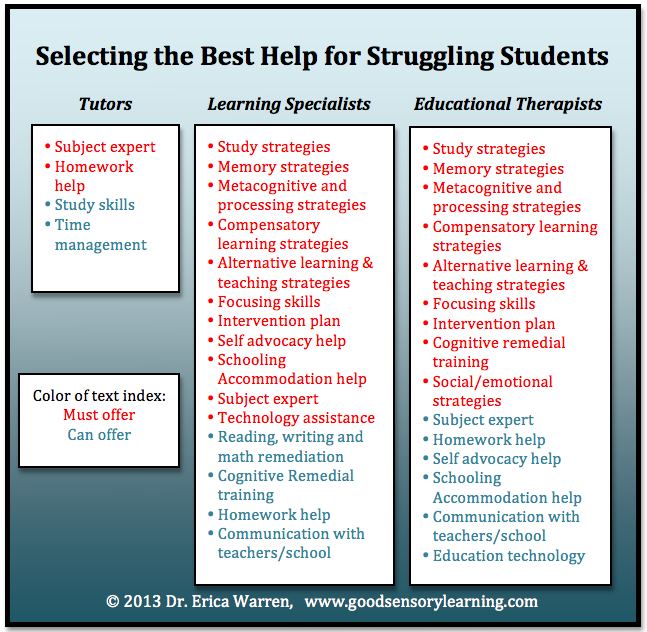
Main Idea/Summarization
A summary briefly captures the main idea of the text and the key details that support the main idea. Students must understand the text in order to write a good summary that is more than a repetition of the text itself.
K-W-L
There are three steps in the K-W-L process (Ogle, 1986):
- What I Know: Before students read the text, ask them as a group to identify what they already know about the topic. Students write this list in the “K” column of their K-W-L forms.
- What I Want to Know: Ask students to write questions about what they want to learn from reading the text in the “W” column of their K-W-L forms. For example, students may wonder if some of the “facts” offered in the “K” column are true.
- What I Learned: As they read the text, students should look for answers to the questions listed in the “W” column and write their answers in the “L” column along with anything else they learn.

After all of the students have read the text, the teacher leads a discussion of the questions and answers.
Printable K-W-L chart (blank)
Graphic Organizers
Graphic organizers provide visual representations of the concepts in expository text. Representing ideas and relationships graphically can help students understand and remember them. Examples of graphic organizers are:
Tree diagrams that represent categories and hierarchies
Tables that compare and contrast data
Time-driven diagrams that represent the order of events
Flowcharts that represent the steps of a process
Teaching students how to develop and construct graphic organizers will require some modeling, guidance, and feedback. Teachers should demonstrate the process with examples first before students practice doing it on their own with teacher guidance and eventually work independently.
Strategies for Reading Comprehension in Read Naturally Programs
Several Read Naturally programs include strategies that support comprehension:
| Read Naturally Intervention Program | Strategies for Reading Comprehension | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prediction Step | Retelling Step | Quiz / Comprehension Questions | Graphic Organizers | |
| Read Naturally Live:
| ✔ | ✔ |
| |
| Read Naturally Encore:
| ✔ | ✔ |
| |
| Read Naturally GATE:
| ✔ | ✔ |
| |
| One Minute Reader Live:
|
| |||
| One Minute Reader Books/CDs:
|
| |||
| Take Aim at Vocabulary: A print-based program with audio CDs that teaches carefully selected target words and strategies for independently learning unknown words. Students work mostly independently or in teacher-led small groups of up to six students.
|
| ✔ | ||
Bibliography
Honig, B. , L. Diamond, and L. Gutlohn. (2013). Teaching reading sourcebook, 2nd ed. Novato, CA: Arena Press.
, L. Diamond, and L. Gutlohn. (2013). Teaching reading sourcebook, 2nd ed. Novato, CA: Arena Press.
Ogle, D. M. (1986). K-W-L: A teaching model that develops active reading of expository text. The Reading Teacher 38(6), pp. 564–570.
Pressley, M. (1977). Imagery and children’s learning: Putting the picture in developmental perspective. Review of Educational Research 47, pp. 586–622.
Tierney, R. J. (1982). Essential considerations for developing basic reading comprehension skills. School Psychology Review 11(3), pp. 299–305.
10 Best Reading Strategies for Students
Reading is one of the essential skills students need to learn to succeed in school and college. However, not all students are good readers, and that is where reading strategies kick in, and even among those who are, there are different types of good readers.
Teachers have to be concerned with the unique learning styles of students. Learning styles can be visual, auditory, and tactile. However, cognitive styles can also be verbal or non-verbal and sequential or global. These various learning styles play an essential role in helping teachers decide how to teach each student best to learn and comprehend lessons.
However, cognitive styles can also be verbal or non-verbal and sequential or global. These various learning styles play an essential role in helping teachers decide how to teach each student best to learn and comprehend lessons.
If you are trying to get your students to be better readers, use some reading strategies when teaching reading to your students.
10 Effective
Reading Strategies to Enhance your Students’ Cognitive AbilitiesRelated Reading: Strategies for Implementing Scaffold Learning in the Classroom
1. Read with Expression
The first strategy to implement is teaching your students to use their voices when reading. If they read a sentence with an exclamation point at the end, they should read it in an excited voice. If they read a sentence with a question mark at the end, they should use an interrogative voice. This takes very little instruction and practice, but it helps your students understand what they are reading better by engaging in the text. This can drastically improve their comprehension skills and help them build fluency skills.
This can drastically improve their comprehension skills and help them build fluency skills.
2. Set a Purpose for Reading Strategies
Setting a purpose for reading is another effective strategy for teaching reading comprehension. When students are assigned a novel or short story to read, have them write out their purpose beforehand.
3. Schema
One of the most effective strategies for teaching reading is called Schema. This strategy asks students to connect what they already know with new concepts presented within the text. The idea is that when you can associate further information with what you already know, you will learn it faster and retain it longer.
For example, if you know how to drive a car and are told that your car has four cylinders under the hood, you will understand that these objects allow your engine to work correctly because you already understand how an engine works. This can help you learn more quickly than someone who knows nothing about cars or engines.
4. Teaching Students to Read a Text
This is very important because it helps them develop their reading and writing skills to read better when they are older. It also helps them learn how to spell things correctly, which will help them in school and tests later on in life.
5. Make Reading Fun
One of the most important strategies is to make reading fun. You can do this by playing games, doing crafts, and getting the children involved in other activities that include reading. This is especially helpful if you have an older child struggling with reading. They will be more likely to participate in activities that involve reading when they are having fun at the same time.
Preparing for Reading with Pre-Reading Activities:
- Read the title, subtitle, and table of contents.
- Read any questions that come before the text.
- Look over headings and pictures or illustrations.
- Skim the reader to get an idea of the general topic or theme.
Related Reading: Best Tips for Creating a Healthy Student-Centered Learning Environment
1. Questions & Doubts
Have students stop periodically during their reading and write down questions about characters or events in the story or text. Ask them questions to help activate prior knowledge and engage their critical thinking.
2. Connect & Predict
Have students connect what they already know and the topic of the story or book they will be reading. Ask them to predict what might happen in the story or text based on the title, illustrations, or cover. Ask them if they think characters will change as the story progresses.
3. Reading Aloud
Model fluent reading by reading aloud a part of the text for your students. This is important for English learners and all readers since it demonstrates how fluent readers sound when they read.
Enhance your students’ reading skills with fun games, courses & worksheets on SplashLearn. Sign up to access the teacher dashboard & assign fun activities!
Sign up to access the teacher dashboard & assign fun activities!
Teachers, sign up & use for free!
4. Conducting Discussions
Reading and discussion are linked, as one enhances the other. When we discuss a text we’ve read, we better understand it, see new things in it that we hadn’t noticed, gain insights into the writing process, and hear different perspectives on what it is saying.
Discussions are a way to assess the students’ understanding and help them understand texts more completely.
The Benefits of Using
Reading StrategiesReading strategies as a mental process helps the reader efficiently comprehend text. In other words, they’re the tools readers use to understand what’s written on a page. These strategies can be taught directly to students and are critical for literacy development.
There are several benefits to using reading strategies before, during, and after reading:
- Understanding how text is organized can help kids understand what they read.
 A reading strategy like previewing can give an overview of the text organization before reading and using this information. In contrast, reading can help you read a passage in detail or skim it.
A reading strategy like previewing can give an overview of the text organization before reading and using this information. In contrast, reading can help you read a passage in detail or skim it.
- Reading strategies can help monitor comprehension by checking what kids understand during and after reading. Asking questions during reading enables them to check to understand. Summarizing and retelling helps review understanding after reading.
- There are several ways to retrieve information from memory that can enhance comprehension. For example, retrieving data from the text is easier if kids use some mnemonic device to create a link between the new information and familiar information already stored in your long-term memory.
- Reading strategies can help students access information that is not explicitly stated. They help readers infer meaning, make conclusions and generalize information. Reading strategies are beneficial for texts that have complex ideas and vocabulary.
 Students can use them to develop comprehension skills and become better readers.
Students can use them to develop comprehension skills and become better readers.
The Opportunities that Come Along Using
Reading StrategiesRelated Reading: Ways to Implement Restorative Practices in the Classroom
Reading strategies are actions that a reader takes to help construct meaning from text. The term reading comprehension refers to the understanding of what is read.
Early childhood education programs provide the opportunity to learn to read. It has been shown that early intervention can significantly improve a child’s success in reading.
The opportunities available when one uses reading strategies are endless. Reading strategies provide a way for readers to make sense of the text. This can be difficult for some students who have not been taught specific strategies to help them grasp the meaning of what they are reading.
There are simple, easy-to-use strategies to help you become a successful reader. Reading strategies can give kids a roadmap to become better readers. Your students will be more involved in the books they read, which will keep them interested in what they are reading.
Reading strategies can give kids a roadmap to become better readers. Your students will be more involved in the books they read, which will keep them interested in what they are reading.
Bottom Line
Boy in libraryReading is one of the biggest and most important subjects in any school or university curriculum. Students are encouraged to read as much as they can, but many people still find it hard to read a book, and some even find reading boring. However, reading is one of the critical factors to succeed in academia because good readers are also good writers.
Reading strategies help students understand what they read in terms that are easy for them to understand. They also help students find new ways to make reading more fun and more accessible to comprehend what they just read. Any educator can use SplashLearn to teach reading and language arts skills.
What are the three main types of reading strategies?
The three different types of reading strategies are skimming, scanning, and in-depth reading.
What are reading strategies?
Reading strategies is the broad term used to describe the planned and explicit actions that can help readers translate print to meaning.
Why are reading strategies important for readers?
Reading strategies are solely used to boost comprehension of the text. Reading strategies are essential to teaching students how good readers think.
How can reading strategies be improved?
By implementing reading strategies and changing how students read, teachers can improve their reading comprehension and make reading more accessible and enjoyable.
Effective strategies for working with text in the classroom at school
The ultimate goal of teaching Russian is practical literacy and language competence. The basis of the content of literature as an academic subject is reading and textual study of works of art.
Work with the text as the main didactic unit allows schoolchildren to combine the activities of developing practical skills of literate writing and speech development. nine0004
nine0004
Every teacher dreams that all students come to the lesson prepared: they have completely read this or that work or paragraph. And not just read, but understood the meaning of the text read. During the final certification, the graduate must also understand the meaning of the read text. Whether it is a task to the text or the text itself.
Teachers working in grades 9 and 11 know that most mistakes are made due to misunderstanding of what is read, as well as when reading the assignment itself. nine0007
Teaching a child to read “correctly”, “effectively”, “productively” is an important task for a teacher. That is why the technology of productive reading (PRT), developed by Professor N. Svetlovskaya, acquires a leading role and contributes to the achievement of the results that are mentioned in the new standards.
The technology is universal and can be used in lessons of any cycle.
It is aimed at the formation of all universal educational activities: cognitive, communicative, regulatory, personal.
The technology of productive reading differs sharply from the traditional technology of transferring ready-made knowledge to a student. The teacher organizes the children's research work in such a way that they themselves "think" about solving the key problem of the lesson and can themselves explain how to act in new conditions. The teacher becomes a partner, a mentor, an observer.
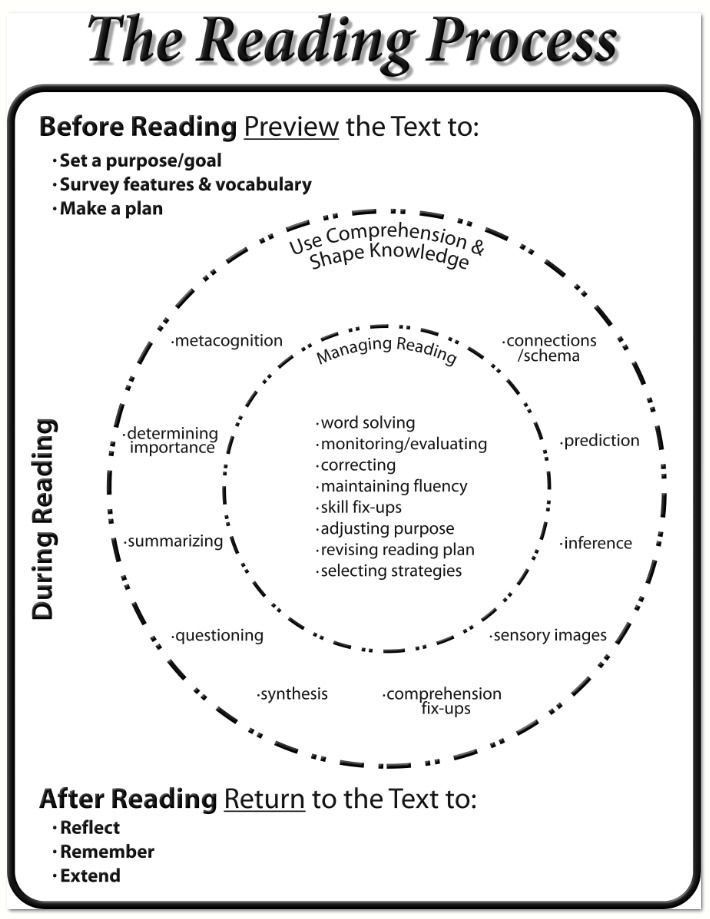
The developed technology includes three stages of working with text, a three-stage process. nine0033
The goal of is the development of anticipation (the ability to guess, predict the content of the text). Task - to develop motivation for reading the text
1. Strategy "Forecast by headline".
Task: think about what can be discussed in the story of K.G. Paustovsky "Warm bread", in the work of P.P. Bazhov "Mistress of the Copper Mountain", etc.
– Try to predict the content by the first line of the story…Remember the name of the story…. Does the content of the story match the title? nine0007
Does the content of the story match the title? nine0007
Give examples of such discrepancies.
Associative bush (circle, row). Today we will read and discuss the topic… What associations do you have about the stated topic?
2. Strategy "Brainstorm" ("Basket of ideas").
Task: answer the questions before reading the text (fairy tales "Warm bread") - What do you know about K. G. Paustovsky? What do you think the story will be about? Who can be the main character? What event in the story can be described. nine0007
3. Strategy "Image of the text".
Task: check your assumptions. Based on the words taken from the text, try to make a short plot story. The title of the story is given.
4. Strategy "Battery of questions".
Task: make up questions to the text according to the title, according to the illustrations.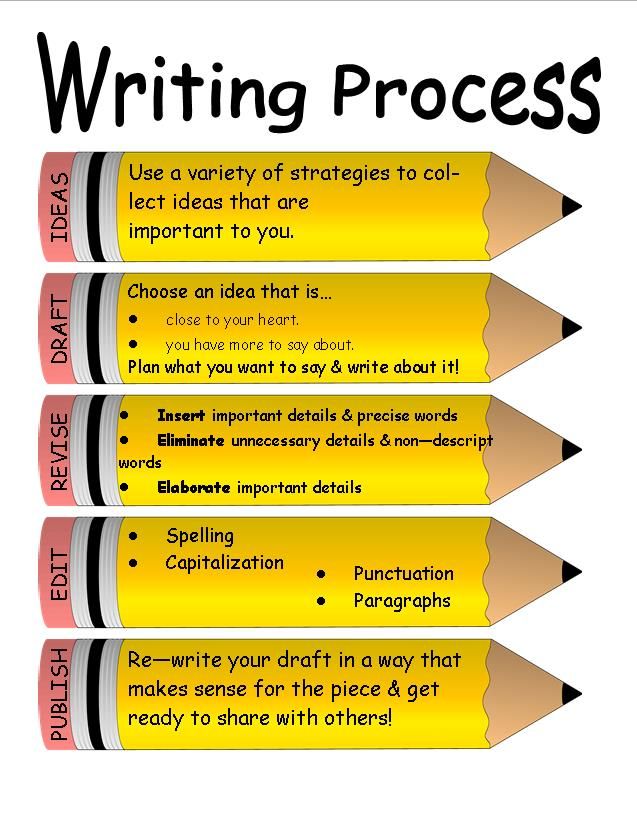
5. Glossary strategy.
Task: look at the list of words and mark those that can be related to the text. When you finish reading the text, go back to these words and look at their meaning and the use of words used in the text. nine0007
6. "Competing with the writer" strategy.
Task: try to predict the content of the book by looking at the illustrations. One student offers his version, the rest complete it.
7. Strategy "True and False Statements".
8. Strategy I know, I want to know, I found out.
Stage 2 - stage of text activity.
The purpose of is to understand the text and create its reader's interpretation, summarizing part of the read text, asking questions of a general nature, making assumptions about the further development of the plot and the role of characters in the composition of the text, etc. ). nine0007
). nine0007
The main task of is to ensure the full perception of the text. The main strategies at the stage of text activity are dialogue with the author, commented reading.
1. Strategy "Reading in a circle". The text is read in turn (each "circle member" reads a paragraph). After this, a stop follows: everyone asks questions to the read passage. If the question cannot be answered (it does not correspond to the text), then the question is considered incorrect. * All correct questions can be recorded. nine0007
2. Silent reading with questions strategy.
3. Strategy “Reading to yourself with notes. (Insert)" . Marginal notes: + - knew; - - new; ? - interesting; V is unclear. Others are possible: B - question; O - answer; Z - I know; N - new; And - interesting; X - I want to know; C - ask; U to clarify.
4. Strategy "Reading with stops". Reading the text with stops, during which tasks are given in the form of questions: some are aimed at checking understanding, others - at predicting the content of the next passage. nine0007
nine0007
5. "Pose a problem - offer a solution" strategy. Remember what problems the heroes of the work face (the problem is formulated and written down in an oval). Next, the children can name several problems, students are divided into groups and offer all kinds of solutions to problems.
6. Strategy "Creating a question plan". The student carries out a semantic grouping of the text, highlights the strong points, divides the text into semantic parts and titles each part with a key question……. nine0007
Stage 3 – stage of post-text (post-text) activity.
The purpose of is to correct the reader's interpretation in accordance with the author's meaning.
The main task of is to provide in-depth perception and understanding of the text, to raise a question to the text as a whole, followed by a conversation, the result of which should be an understanding of the author's meaning. Re-addressing the title, illustrations, performing creative tasks.
2. Question tree strategy Crown – what? where? when? Barrel - why? How? Could you? Roots - how to relate the text to life? With current events? What is the author trying to show?
3. Strategy "Bloom's Cube" (Benjamin Bloom is a famous American teacher, author of many pedagogical strategies = technician).
The beginnings of the questions are written on the faces of the cube: “Why?”, “Explain”, “Name”, “Suggest”, “Think up”, “Share”. The teacher or student rolls the die. nine0007
It is necessary to formulate a question to the educational material on the side on which the cube fell.
The “Name” question is aimed at the level of reproduction, i.e. at the simple reproduction of knowledge.
Question "Why" - the student in this case must find cause-and-effect relationships, describe the processes occurring with a certain object or phenomenon.
“Explain ” question – student uses concepts and principles in new situations. nine0007
All of the above strategies provide for serious work with the text, its deep analysis and understanding, the organization of independent cognitive activity of students on educational material. socially moral experience and makes you think, knowing the world around you.
Technology Advantage:
1. Applicable in the lessons of any cycle and at any level of education.
2. Focused on personal development.
3. Develops the ability to predict the results of reading.
4. Promotes understanding of the text in the lesson.
Articles on the topic
- RAFT technique in Russian language and literature classes
- TRIZ pedagogy techniques in speech development lessons in elementary school
- 4 methods of quick reading of educational and scientific literature
- How to analyze literary texts using the Russian National Corpus
- 5 exercises to develop creative thinking
- Important to know: amazing brain rules that improve learning
"Meaningful reading strategies" research paper
SLIDE
We meet very often with various phrases. What is their meaning? They can be read in different ways.
What is their meaning? They can be read in different ways.
Learning is impossible not to learn! nine0007
Execution cannot be pardoned!
- Read the phrases.
- Why do opinions differ?
- What depends on the punctuation mark?
- Everyone has their own meaning. Everyone will read this phrase in your own way.
There are readers, there are readers. Readers read and carry, as in a briefcase. While inside - the walls are thick, but how did you pull it out - portfolio is empty. Readers absorb and absorb like a sponge. How it was absorbed - the weight has increased, but how it is squeezed out - it is required to fill. Reading from reading is excellent. And you say: what to read? Not what, but how. Although that is also important! nine0007
SLIDE 2
Pedagogical research topic Semantic reading strategies: step by step.
today there is a decrease in interest in reading. Understanding the role of reading, I see the main mission is to arouse in their students an interest in reading and return to the rank active readers, not only high school students, but also their parents.
I was struck data of the Federal Press Agency:
1. The share of Russians has increased not at all reading or reading from time to time. In 2005 79% of Russian residents read at least one book a year, in 2012 - 63%. And most disturbing, share of systematically reading youth decreased from 48% in 2005 to 28% in 2012.
2. Family reading lessons have gone into oblivion: in In 1970, 80% of families regularly read to children, today - only 7%.
I see it as a big social risk, because reading is the most important way of mastering vital information, without it it is impossible to develop a personality with the whole complex of spiritual, intellectual and emotional traits. nine0007
Therefore significant place I give to work on raising the prestige of reading as a cultural values, intensifying this process.
Teaching children literate semantic reading systematically at all without exceptions in the classroom and in the process of extracurricular activities.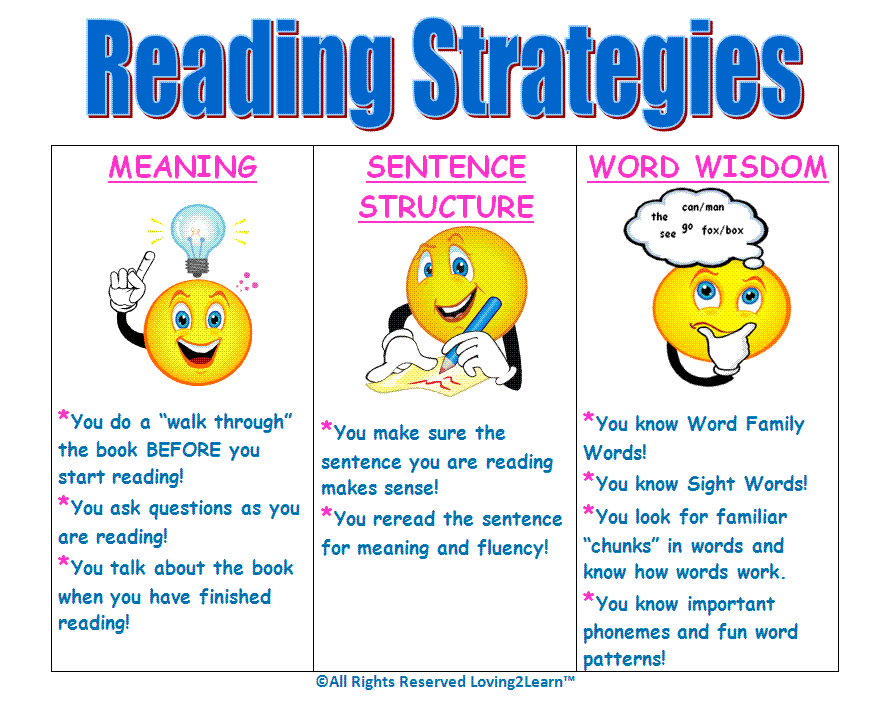 Today it is one of targets of GEF IEO.
Today it is one of targets of GEF IEO.
After all, strong and conscious reading skills are largely promote the acceptance and development of a social role by younger students students, the development of motives for educational activities and the formation of personal the meaning of the teaching. nine0007
Analysis of the new educational standard led me to the idea of the need to use in my pedagogical practice of innovative methods and techniques that allow you to create conditions for the development of students' cognitive activity on the basis of semantic reading, striving for independence, for self-education and self-realization, which is the main priority of modern education.
Therefore, planning my professional activities, I set myself next target :
SLIDE 3
- creation of conditions for the development and socialization of the individual, in the process of mastering learning spiritual, intellectual and emotional qualities through teaching meaningful reading strategies.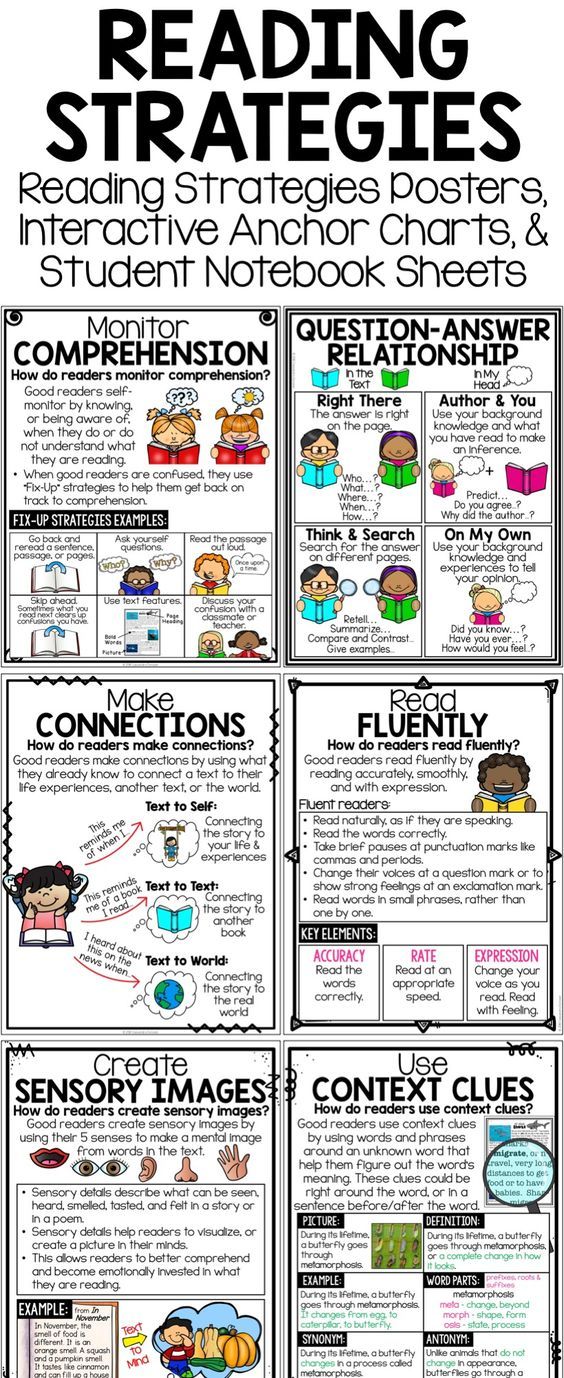
Determined for yourself the solution of the following tasks :
SLIDE 4
1. Spend diagnosing the formation of aspects of semantic reading; nine0007
2. implement in the practice of their work, innovative methods and techniques of semantic reading;
3. Form author's bank of methods and techniques for teaching semantic reading strategies.
4. Create a model for the phased implementation of semantic reading strategies "Step by step".
SLIDE 5
Hypothesis: if students master the strategies of semantic reading, then their level meta-subject training will increase, and educationally important qualities are improved. nine0007
Analyzing the process semantic reading, I used the experience gained in research various types of activities based on the concept of activity system genesis (V.D. Shadrikov, A.V. Karpov, N.V. Nizhegorodtseva, etc.).
Special interest I was provoked by the ideas of Zinaida Ivanovna Klychnikova. According to her, the process of reading does not end only with the understanding of the text, but continues with the acceptance from the outside reading some decision leading to the improvement of his personality.
According to her, the process of reading does not end only with the understanding of the text, but continues with the acceptance from the outside reading some decision leading to the improvement of his personality.
According to Federal Educational Standard of Primary General Education (Chapter 1 p. 8) one of the main results of education is the formation of UUD. Semantic reading is a factor in the formation of UUD, because. programs for various subjects are based on the ability to process information, and one of meta-subject results of mastering the OOP, LEO becomes the ability to work with various sources of information.
As a result theoretical analysis of literature, methodological materials, normative documents, I highlighted educational and important qualities that ensure readiness elementary school students to learning semantic reading. nine0007
SLIDE 6 HS?
Component the composition of semantic reading is presented in the table:
| No. | Functional semantic reading unit | Educational and important quality (UVK) | Method study UVK |
| 1 | B personal-motivational highlighted | - school motivation
- interest in reading | - "Definition motives of teaching” M.R. Ginzburg - "Attitude towards reading" ??? |
| 2 | Representation on the content of activities and methods of its implementation is presented by such UVK, like … nine0332 | - speech development
- understanding the meaning of the text (topic, title, questions to the text) | - "Listen and tell" O. - |
| 3 | B information included | -logical thinking
- arbitrariness attention - arbitrary memory | - "The fourth extra" N.P. Lokalova - "House" N.I. Gutkina - "10 words”, “10 pictures” by A.R. Luria |
First work phase (diagnostic) was directed to carrying out diagnostics of educationally important qualities of the structure of semantic reading. Results diagnostic test :
B September 2009, with the help of a psychologist, students of grade 2 A underwent the following group diagnostics and individual examinations. nine0007
SLIDE 7, 8, 9, 10, 11
Analyzing the results of the diagnostics, I found that positive motivation for school had 95% of the guys. Diagnostics of cognitive processes showed that thinking is quite well developed in 71.5%, attention in 66.5%, better developed auditory memory in 76.8%, visual memory in 71.5% of students. 57% of my children have very low level of speech development. 57% of children still read daily, among of parents 68% read the press, and 11% read fiction, only 23% read to their children, and even fewer (17%) discuss what they have read with their children. nine0007
Diagnostics of cognitive processes showed that thinking is quite well developed in 71.5%, attention in 66.5%, better developed auditory memory in 76.8%, visual memory in 71.5% of students. 57% of my children have very low level of speech development. 57% of children still read daily, among of parents 68% read the press, and 11% read fiction, only 23% read to their children, and even fewer (17%) discuss what they have read with their children. nine0007
On Based on the analysis, a bank of methods was formed, which helped in the work on identified problem.
While working on the text, I identified 3 main strategies:
SLIDE 12 + + +
1. Search information and reading comprehension;
2. Conversion and interpretation of information;
3. Grade information.
| Search information and reading comprehension | Conversion and interpretation of information | Grade information |
| 1. 2. Interactive games 3. Forecast content 4. Text with gaps 5. Yes-no 6. Morphological piggy bank 7. Wheel of knowledge 8. Fishbone 9. Creating word paintings, filmstrips, screenplays | 1. Parallel texts 2. I know - I want to know - Learned 3. Mosaic 4. Double (triple) diary 5. Reader's diary - portfolio 6. 6 thinking hats 7. (role, audience, form, theme) RAFT 8. Reading with notes 9. Plus, minus, interesting 10. Create a portrait
|
1. Interactive games 2. Word associations 3. Decision tree 4. Creative tasks 5. Interview 6. Family Reading Lessons 7. Reader's conferences |
For me identified a group of the most effective techniques.
Information search already at the 1st stage it becomes more productive with the active use of the technique fishbone ,
+ + + GS (on fish skeleton slide) SLIDE 13, 14
which through key concepts expresses the essence of the problem posed in the lesson. Children act according to the algorithm: I read - I search - I understand, while expressing their understanding through model creation. This is the model the children created at the lesson of the world around them. study of the theme "Desert". This technique is rational and in the implementation of all the strategies I outlined and at all stages of learning . ++
Using reception "Morphological box " +
students create interactive information piggy banks on various subjects. Today at in our arsenal of piggy banks of geometric shapes, parts of speech, members of a sentence, wintering birds of the city of Raychikhinsk, trees of the Amur region, created in the programs Powerpoint, Word, Paint. The piggy bank created by the children is cross-cutting, they are supplemented, expanded, are corrected. nine0007
The piggy bank created by the children is cross-cutting, they are supplemented, expanded, are corrected. nine0007
On at all stages of teaching semantic reading strategies the most relevant were interactive and didactic games. +++++ Exactly they provide positive impact on the development of cognitive interests, attitude towards teaching. Coloring with folklore motifs such games as "Carousel", “Translator”, “Artist”, I was able to get the support of my initiatives, saw the support of children and together were able to appreciate each other.
Teaching reading with purpose transformation and interpretation of information, based on existing knowledge and experience.
In order for the text to be assimilated and interpret successfully, where analysis is required of not one text, but several, I I use case studies.
Double (triple) diary + GS, home
allowed help children connect the content of the text with their personal experience. From one sides are written fragments of text that made a special impression, caused the guys some memories, associations with episodes from their own life. On the other hand, they comment: what thoughts did the quote evoke? What kind thoughts come up? I stepped a little further. The guys and I created a triple a diary. The third column - questions to ... the author of the text, teacher, parents, friend friend. nine0007
From one sides are written fragments of text that made a special impression, caused the guys some memories, associations with episodes from their own life. On the other hand, they comment: what thoughts did the quote evoke? What kind thoughts come up? I stepped a little further. The guys and I created a triple a diary. The third column - questions to ... the author of the text, teacher, parents, friend friend. nine0007
Next step this work was the creation of
"Reader's Diary" . + GS SLIDE 16
In front of you pages from a children's reader's diary. Created by my pupil. The guys write down the last name of the author and the title of the book, as a result it turns out a list of books he read, the names of the main characters, so that if necessary (for example, for storytelling in class), it was easier to remember book's contents. There are also drawings, extracts of favorite places, experiences, feelings (double diary), the opportunity to ask a question to . .. (triple diary)
.. (triple diary)
SLIDE 17
But someone from it was easier for the guys to use the pages of special sites for this purpose and their editors. In their Diaries, my young readers, again resurrect the lines of the read work, give him one more meaning, give him another option for a new life.
SLIDE 18
we pass to the next step - "Readers' portfolio". Reading bag helps work with a book not only in the library, in extracurricular classes activities, but also in all lessons. nine0007
SLIDE 19
portfolio "About Me", "My Achievements", children supplement its structure with sections, that distinguish a reader's portfolio from a student's portfolio: "Books that I I like to read”, “Reviews of books read”, “Reader's Dictionary”, “I want everything know", "Behind the pages of textbooks". My young readers come up with their own headings. For example, "Writers - anniversaries", Art cases where children select texts for the same topic (artistic, scientific, written by the guys themselves), pictures for these texts and even music. Some guys use computers for this. programs. Here's what happens. nine0217 SLIDE 20.
Some guys use computers for this. programs. Here's what happens. nine0217 SLIDE 20.
We can easily find out by flipping through the pages students' reading portfolios, which books, which authors, genres, they like to read.
Both the read books and the guys present their "Reader's portfolios" at the classroom reader conferences . ++
There are usually three of them, but the topics are different: “The wisest book”, The book that taught good”, “The book with which I do not I'm parting."
Speaking of Readers' Conferences, We have now reached the stage of information evaluation. nine0007
Very it’s good if the child reads not only within the walls of the school, but also, when he comes home, he sees reading their parents, relatives. Introducing my students to reading is more successful, if families have a tradition of collective reading aloud, discussions books read. So in our class team the idea of lessons was born family reading.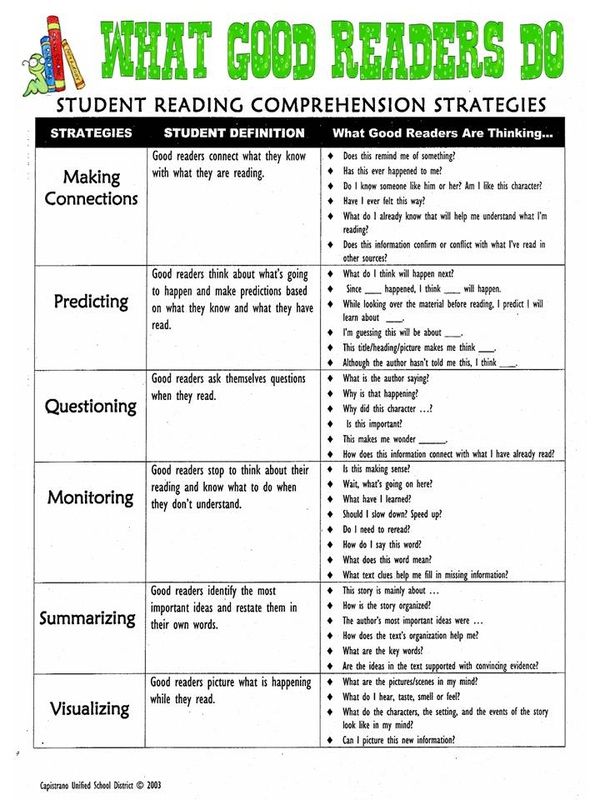 +
+
Such Lessons take place once a trimester. Thus, children are also involved in reading, and their parents.
++++ nine0220
This work involves both me and my children in the wonderful world of books, shapes the world reading my wards, liberates them, and at the same time teaches them to formulate thoughts and speak correctly, develops a culture of speech.
SLIDE 21
B at the end of the 2011 - 2012 academic year among parents and children was held repeated survey Interest in reading. It showed:
86% (57%) of children began to read daily, among parents 24% (68%) read the press, and 48% (11%) - fiction, 61% (23%) read to their children, and they all discuss read with children. nine0007
At this stage, I consider it very relevant using creative tasks when working with text . created by me a whole collection of such tasks is in the methodological recommendations:
I want to say about compositions in a separate line.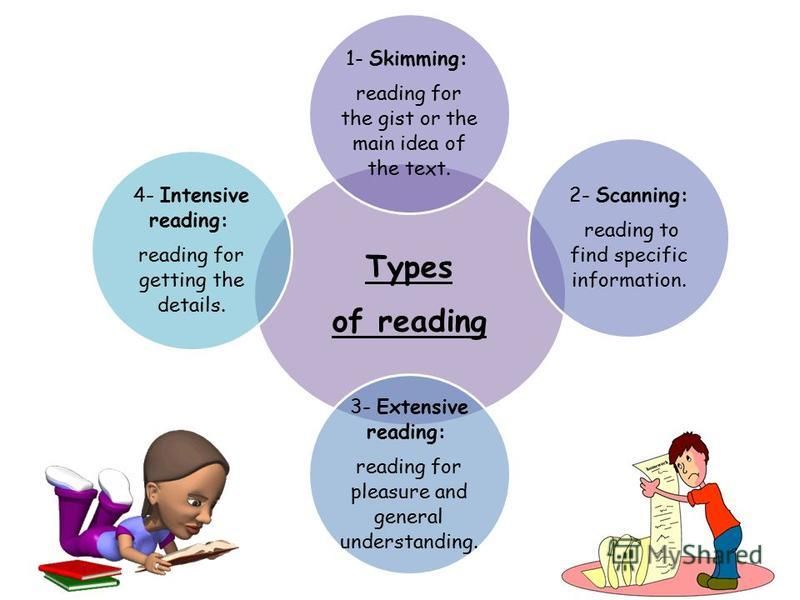 Essays are written in Russian language and literature lessons. However, they can be applied to any another lesson.
Essays are written in Russian language and literature lessons. However, they can be applied to any another lesson.
SLIDE 22 Essays-descriptions, essays-stories, essays-fairy tales, essays-riddles. nine0007
All tricks and tasks creative nature, which was discussed, help me in my pedagogical practice to significantly improve the quality of lessons, to intensify mental activity students, imagination, stimulates the development of the ability to learn, more fully perceive any work of art, any text.
So result of my work, I consider the positive dynamics of the level of training , as well as the fact that that high school students and their parents have an interest in reading in general. nine0007
B at the end of the 2011-2012 academic year, with the help of a school psychologist, final diagnosis.
Conclusions: SLIDE 23
1. The diagnostics of the formation of aspects of semantic reading showed that what
· there is a positive growth trend the level of school motivation, it increased by 5%; SLIDE 24
show positive growth results of the development of cognitive processes: SLIDE 25, 26, 27, thinking - by 14%, attention - by 11%, memory - by 12%, diagnostics of speech development - by 47%.
level of education for the period from 2009 to 2012 increased by 7%. SLIDE 28
Working on By creating the "Reader's Portfolio" my students got their first experience research activities. This allowed them to take part in academic readings. SLIDE 29
6 of my guys became winners and winners of the gymnasium stage of the Olympiads, and 3 people were winners and prize-winners municipal stage. We have become active participants in All-Russian competitions:
- "Russian bear cub - linguistics for all"
- Youth mathematical championship
- Youth philological championship
- team tournament "Znayki", etc.
SLIDE 30 a bank of methods and techniques for teaching semantic strategies was formed and tested reading, methodological recommendations for primary school teachers are given.
4. Created a model for the phased implementation of semantic reading strategies "Step by step". nine0007
All materials were presented to the team on the pedagogical council and posted on my personal website. STOP!!!
STOP!!!
A student came to his mentor said: “Master! I'll stop reading books." "What is it?" the mentor asked. "Yes I don’t understand what is written,” answered the monk. “Child,” the elder said to him then, sheep, when they find juicy grass, grab it greedily and swallow it, not chewing, trying only to grab as much as possible, then, having already eaten, chew it up. So you, as long as you have time and opportunity, as much as possible, read books without laziness, and the dark will be light for you. Through reading understand the incomprehensible. nine0007
And for my children unknown pages of books became light.
9000 recommendations
Comprehension exercises the meaning of the text.
Working with text: search information and reading comprehension
1. Vocabulary work. Reading words and explaining their lexical meaning.
2. Title text.
3. Determination of the topic of the text, main thought.
4. Selective reading. Find in description of the hero, nature, etc. in the text
5. Work on teacher issues, textbook or student.
6. Drawing up "thick" and "subtle" questions
7. Keyword selection
8. Yes-no
9. Fishbone
10. Content prediction
11. Brainstorming
12. Didactic games
13. Interactive games
14. Morphological box
15. Knowledge wheel 9002 9002 text: transformation and interpretation of information
1. Dividing the text into parts planning.
2. The retelling is detailed and concise.
1. "Missing word". Teacher reads the text and skips one word. Children must insert the correct word within the meaning of. nine0007
2. Recovery of logical text sequences. Articles from magazines, newspapers are cut into pieces, mixed and given to the student in an envelope.
3. Text restoration. A small text is written in large letters on a piece of paper, cut into small pieces. A team of 2-3 people restores the text. The task can complicate if pieces from other texts are put into the envelope or mixed several articles.
Text restoration. A small text is written in large letters on a piece of paper, cut into small pieces. A team of 2-3 people restores the text. The task can complicate if pieces from other texts are put into the envelope or mixed several articles.
4. Distribution of offers.
5. Cluster (visual brain assault)
6. Double (triple) diary
7. Reader's diary - briefcase
8. Parallel texts
9. I know - I want to know - I can
10. 6 thinking hats
11. Role, audience, form, theme (RAFT)
12. Reading with notes
13. Plus, minus, interesting
14. Create a portrait
Working with text: evaluation of information
1. Determining the type of text. nine0007
2. Drawing up a filmstrip. The text is divided into parts and distributed among the children. The student reads his an excerpt, draw a drawing for it and make a short caption. All drawings fastened together and used for a brief retelling.
3. Phantograms. Various fantasies when working with text:
a) in a well-known text one condition changes (hero, season, scene, etc.). Students fantasize how the content will change;
b) come up with a sequel story; nine0007
c) are distributed to all students sheets on which 2-3 phrases are written (the same). This is the beginning of the story. Then everyone continues in their own way. The stories are then read out and determined the best.
4. Compilation of crossword puzzles text.
5. Quizzes one by one a large work or several small ones.
6. Mini essays with a purpose analysis of the character or deed of the hero, essay-description, essay-fairy tale, essays, stories, essays, riddles.
7. Selection of riddles for words from text.
8. Selection of proverbs and proverbs that reveal the theme of the text.
9. Compilation of puzzles to words from the text.
10. Sincwine
11. Interactive games
12. Word associations
Word associations
13. Decision tree
14. Family reading lessons
15. Reader conferences
Creative assignments when working with text in the classroom.
- Work with an illustration to the text. nine0220
- Review drawings created by children.
This is the most a difficult but interesting kind of creative work with children's illustrations. I do it's like this:
o each the student, after parsing the text, goes deeper into creating his own illustration;
schoolchildren exchange drawings;
o received the drawing examines it and, rereading the text, tries to find this episode, to to which it refers. Having established to which place the illustration was created, the student signs it with the words of the text; nine0007
- matching the content of the illustration with the content of this episode, the student writes a review, which indicates whether or not the given figure corresponds to the text, marks the quality of the work performed.
 He backs up all his remarks. links to text. The review is signed by the student.
He backs up all his remarks. links to text. The review is signed by the student.
- Modeling and application.
This type of baby creativity is used more often in grades 1 and 2, when children do not perceive are still critical of the results of their images and see more in them than is given. Children can mold a fungus, a bird, a boat, a bunny, a dog, that is, a separate subject of the overall picture, and then combine into a common creative work. nine0007
- Homemade books.
One of the most interesting tasks for children - this is work with books - homemade, each of made by children with creativity and imagination. There are books in the form of a Christmas tree, fungus, house, boat, etc. The children made their own books. at home. Each book has its own title, which was represented and defended by the author on book competition in the classroom.
In these books - homemade children record works only of their own composition.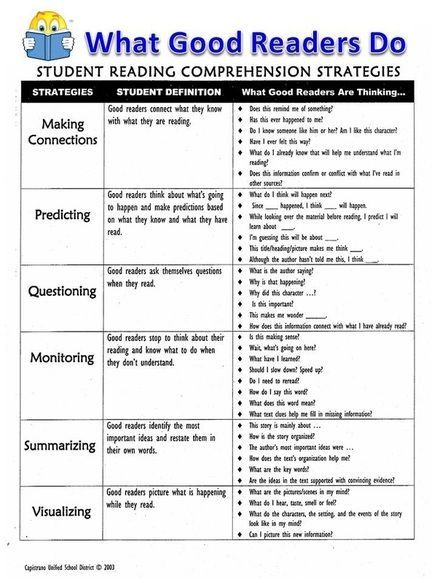 it the first steps in their work, although not always successful, but most of the guys are drawn to such work, trying to prove themselves. nine0007
it the first steps in their work, although not always successful, but most of the guys are drawn to such work, trying to prove themselves. nine0007
- Drafting questions and tests on this text.
From 1st class, I teach children not only to correctly answer the questions asked by the teacher, but and ask questions about the text. This work develops the ability to distinguish the main thing, both in general and in the specific case, is to compose interrogative sentences that require detailed or specific answers (yes, no).
Children are also very I like to make a test based on the read work, where you need to choose from 3 of the given answers one is correct. It is with great pleasure that we offer our questions and tests at the lessons of literary reading. nine0007
Creative retelling.
The goal of creative retelling - to evoke an emotional response in students to what they read work, to help them to understand the idea more deeply, to survive with the hero those feelings that are embedded in the work by the author. For creative retellings are selected works that allow the reader to put himself in position of a literary hero, understand his psychology, look through the eyes of a hero on those people and those events that are described in the work. Creative retelling can be carried out with a change in the face of the narrator or a creative addition to the text of the author. Almost always work is required to select material or adding to it, because the narrator is unaware of some facts or, conversely, he will need to talk about experiences that are not described by the author. nine0007
For creative retellings are selected works that allow the reader to put himself in position of a literary hero, understand his psychology, look through the eyes of a hero on those people and those events that are described in the work. Creative retelling can be carried out with a change in the face of the narrator or a creative addition to the text of the author. Almost always work is required to select material or adding to it, because the narrator is unaware of some facts or, conversely, he will need to talk about experiences that are not described by the author. nine0007
Such paraphrases require students to work with imagination based on the ideas received during reading and analysis of the work and will help to fully perceive the artistic text, contribute to a deeper understanding of what is read, develops creative abilities of students and bring interest and variety.
- Continued works (inventing the end)
Read work can sometimes serve as an impetus for independent creativity children: they come up with a continuation of the readable work, that is, their end. It can be a story, a fairy tale, or even a poem. Not all the work, of course, can be continued. However, to facilitate the work students take such works that are closer to the students themselves. nine0007
It can be a story, a fairy tale, or even a poem. Not all the work, of course, can be continued. However, to facilitate the work students take such works that are closer to the students themselves. nine0007
- Creative essay .
For development creative abilities I use writing essays by children. Creative the essay introduces students to reading and analyzing a literary work in a special way. way: they must try to solve a problem that is close to the one solved by writer in his work.
Meaning creative essay as a form of introductory classes:
- attraction students' attention to the topic of the studied literary work; nine0655 - mobilization of all knowledge related to the topic;
- exercises in self-construction of an essay.
All this must to exacerbate students' interest in reading and analysis of the work, to increase their observation, to draw their attention to such aspects of the literary works that they had not seen before.
Compositions for children write on separate sheets of paper and, if desired, can illustrate them, giving them an original shape: a leaf, a snowflake, a flower, etc. nine0007
All compositions with we read the consent of the authors aloud and discuss. Essays are read in full separate sentences, well-chosen words. The main thing is to celebrate everyone. Children listen with great attention to the compositions of their classmates.
- Word creation.
Very important a means of developing creative abilities is the compilation of fairy tales, stories, myths, fables, poems. Children themselves come up with plots, main characters. The best works are read out and discussed. nine0007
From 2nd class trying to write poetry. At first it was rhymes, the continuation of poetic lines. But much more for the guys themselves to be in the role of poets. On lessons literary reading, children are very fond of minutes of poetry, on which they read own poems.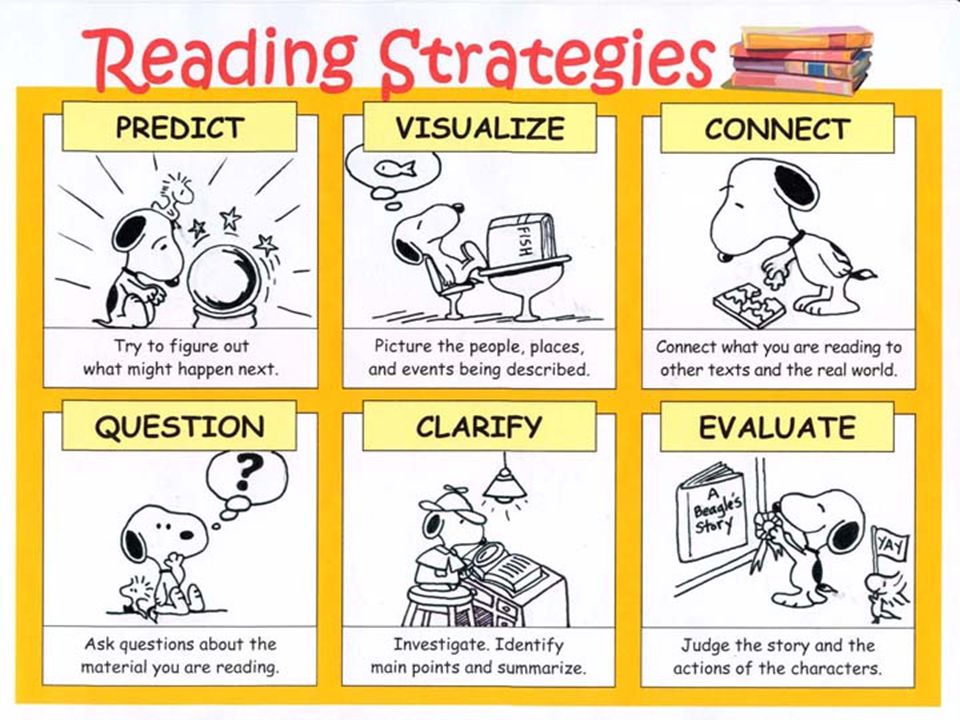
- Review-review.
One type essays that allow you to teach a child to express their own position on relation to the read work, is a review of the book. It has a student can not only express an assessment of what they read, but also learn more deeply the meaning works. nine0007
Structure variant recall:
1. Representation hero and expression of his attitude to the work.
2. Brief presentation of the plot of the work with an emotional assessment of events.
3. Characteristic the hero and the expression of his attitude towards him.
In my practice, I I will organize the feedback letter as follows. In the classroom, a sheet of cardboard is hung out with large envelope at the bottom. On the sheets, students put their feedback, compiled according to a certain plan. Then I check the submitted reviews, their students rewrite, then the leaflets are hung in the reading corner. Reviews are read comrades. After all students have read them, the reviews are added to envelope, new reviews are posted in their place. nine0007
nine0007
Such organization creative work activates extracurricular reading. Children will have to show creative approach to a work of art, to show the direction of their literary interests and the level of artistic taste.
Abstract .
Annotation in a book placed on the back of the title page. From it you can find out what is said in book, as the annotation contains a concise summary of the content. Often abstract written in such a way as to engage the reader. nine0007
For writing annotations to the book, I offer the children the following memo.
Instruction
1. Choose the book you like.
2. Do your best to interest future readers of this book.
3. Start annotation can be different:
This book tells about …
This story is about …
The writer … talks about …
The protagonist of this book is …
Amazing events take place in …
Do you like to read about …
Work with crosswords.
- Drafting quizzes.
- Dramatization
Molds dramatizations:
- finger theater;
- puppet theater;
- costume performances based on famous works;
- musical performances;
- performances based on their own scripts.
Dramatization is a special form of reincarnation in the depicted image. Therefore, it is necessary occasionally to encourage the usual desire of children to costume when dramatizing. nine0007
- Drafting fabulous announcements and telegrams.
There is a component creativity, without which the creation of something new is unthinkable. This is creative imagination. Imagination is the basis of any creativity. Great value in revitalization creative activity have game moments that introduce an element of entertainment into creative process.
One type The game is to compose fabulous ads and telegrams.
Develop creative imagination and literary games that give a more complete perceive works of art in the future.
Simple speech children's creativity is easily manifested in play activities.
Here are some examples of such games that I spend in literary reading classes with my children.
a. "Tree wisdom!”
Fast at first, but read the text carefully. Now everyone writes a note that asks text question. Then complete the note, attach it with a paperclip to the tree. The tree often changes - in turn, everyone approaches the tree, “rips off” the note and answer the question aloud. The rest rate the question and answer. This work can be in pairs, fours, in rows. Before plucking from the tree leaflets-questions, the children read the given text again. At the end are defined the best experts. nine0007
- “General poem".
compose poetry can be all together. To do this, everyone should have a piece of paper and a pen. Every conceives the first line of his poem and, at the signal of the teacher, transmits it neighbor on the left. The neighbor must understand and feel what he wanted to say party game, and try to continue the poem. And so on until the sheet with the completed poem will not be returned to the author. The author corrects poem and read it. Of course, it is imperfect, but it can become the basis for creating a deeper and more interesting work. nine0007
Every conceives the first line of his poem and, at the signal of the teacher, transmits it neighbor on the left. The neighbor must understand and feel what he wanted to say party game, and try to continue the poem. And so on until the sheet with the completed poem will not be returned to the author. The author corrects poem and read it. Of course, it is imperfect, but it can become the basis for creating a deeper and more interesting work. nine0007
- “ I I’ll start, and you continue…” (test of a poetic pen)
Teacher or the child is offered (pronounced and recorded) the beginning of poetic lines invented by themselves. Students must complete on their own by unfolding further plot started. To complete the game task is given certain time. You can divide all the guys into teams by offering to perform different verses.
After completion works of mini-poetic texts are discussed. It is proposed to carry out the author's protection of your creative work. Children are pleased, fascinated by such work, develops their verbal art. It is no coincidence that small masterpieces are born very often. nine0007
Children are pleased, fascinated by such work, develops their verbal art. It is no coincidence that small masterpieces are born very often. nine0007
“Fable in 10 minutes”
The teacher writes some phrase or several, then folds the sheet so that it is not visible written and handed over to the student. Now on a blank sheet the student writes his phrase. He also folds the sheet and gives it to another. Anything is allowed to be written. whatever, but there is one subtlety that you need to remember: all these phrases must answer (in order) the following questions:
1. Who it was (was)?
2. As looked like?
3. Where went (went)?
4. Whom met?
5. What told him/her?
6. What did he/she answer?
7. What was done to him/her?
8. What is was his/her reaction?
9. How is the whole story over?
10. Output or morality.
When recorded the answer to the last question, the whole sheet unfolds and is read with expression the resulting fiction.
So You can compose both a fairy tale and a story. nine0007
- “Digital dictation".
Children themselves compose digital dictations based on the read work and offer them in game to their classmates.
Children write only two digits:
0 - if the statement is false and 1 if it is true.
Digital dictation may be given orally or may be written on the board. This is one of the most interesting ways to activate the attention of children, more fully perceive a work of art. nine0007
Can be used any number of digital dictation sentences, but it is more convenient when their number is a multiple three.
Digital dictations may be a specific work or by works, on the general development.
- “Live images".
One reads work, and others with facial expressions, gestures, pantomime react to heard.
Or available children to read a specific text in the voice of a hero-sweet tooth, a grumbler, like a bear etc.

 Focuses on fluency and phonics with additional support for vocabulary.
Focuses on fluency and phonics with additional support for vocabulary.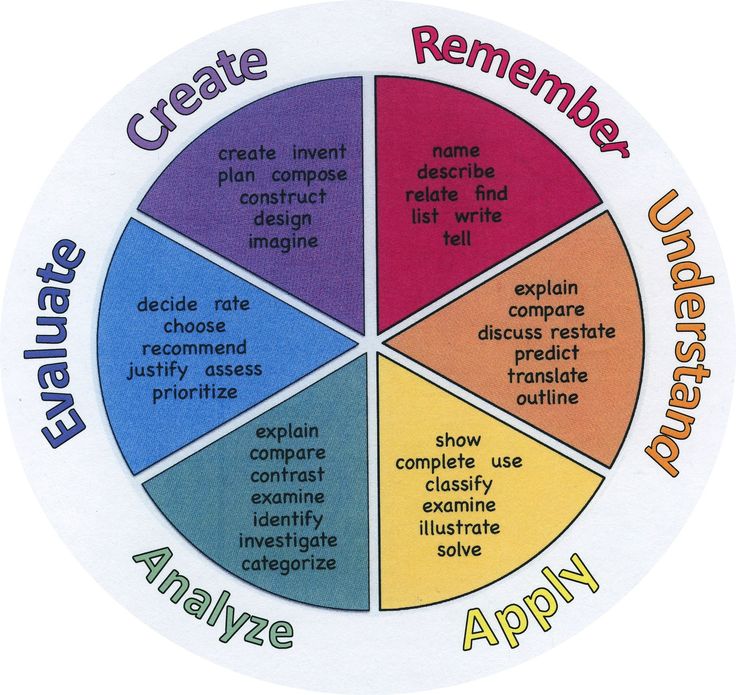
 p/n
p/n  N. Usanova, O.F. Potemkin
N. Usanova, O.F. Potemkin  Didactic games
Didactic games