Child learning skills
6 Life Skills Your Child Needs and How To Develop Them – Primrose Schools
Skip to main content
Primrose School Logo
To search type and hit enter
WANT MORE PARENTING TIPS?
Sign up for our newsletter to get advice and resources delivered to your inbox.
Sign Up
By Primrose Schools
Did you know you can help your child succeed in the future by encouraging a few simple skills at home? The foundation for executive function skills (like problem solving and self-control) is built in the earliest years of a child’s life and can ultimately lead to more success in a future career.
According to a recent survey, executive function skills are more highly valued in entry-level job candidates than technical abilities, academic background and other factors. Here are tips and resources to help foster these important skills: teamwork, adaptability, critical thinking, problem solving, self-control and working memory.
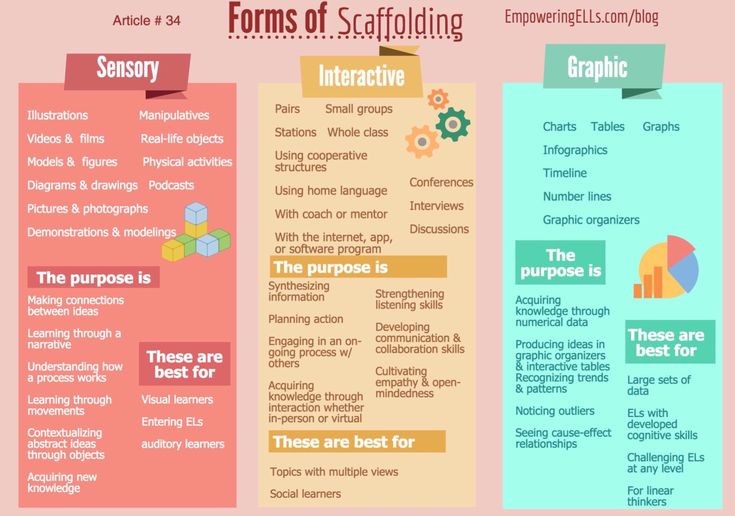
Teamwork
Teamwork is an essential skill for every young child to learn – it comes into play in many everyday situations, like during a playdate with a friend or when helping parents or siblings with chores. Encourage your child to strengthen her teamwork skills at home or on-the-go with these tips. Read More
Adaptability
Adaptability might seem like a skill that is too advanced for a toddler, but it’s actually important to nurture it early in life. Use these activities to help your child learn to adapt. Read More
Critical Thinking
Critical thinking – the ability to take in new information and determine how best to use it – plays a large role in the lives of young children. Playtime is a great time to naturally focus on this skill, so try these activities to intentionally nurture critical thinking at home. Read More
Problem Solving
All parents want their children to be excellent problem solvers, but did you know that nurturing skills like problem solving early in life can help children become more successful adults? Here are tips for encouraging problem solving at home. Read More
Read More
Self-Control
Whether it’s an argument between siblings, an angry outburst before bedtime or crying about not getting their way, all children struggle with self-control at some point. Try these activities to help your child build his self-control. Read More
Working Memory
Your child’s working memory does more than just help her remember information; it gives her the ability to put information to use, like following directions or rules and completing multi-step tasks. Help your child develop her working memory with these activities. Read More
Find a Primrose School Near You
Inspire a lifelong love of learning. Contact your local Primrose to schedule a tour.
Find A School
Get more parenting and early education tips.
Sign Up
SEARCH BLOG
Search Form>
New skills for kids & behaviour management
Helping children learn new skills as part of behaviour management
When children can do the things they want or need to do, they’re more likely to cooperate.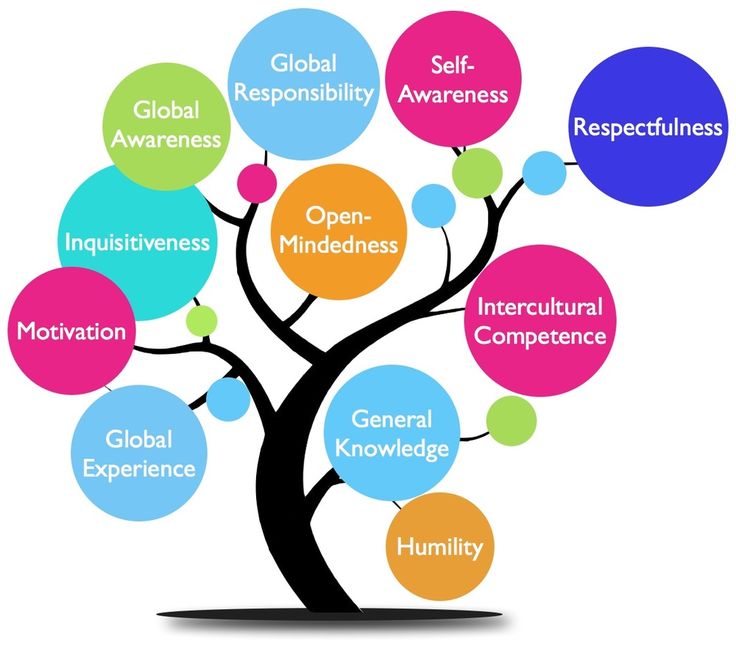 They’re also less likely to get frustrated and behave in challenging ways. This means that helping children learn new skills can be an important part of managing behaviour.
They’re also less likely to get frustrated and behave in challenging ways. This means that helping children learn new skills can be an important part of managing behaviour.
When children learn new skills, they also build independence, confidence and self-esteem. So helping children learn new skills can be an important part of supporting overall development too.
Here’s an example: if your child doesn’t know how to set the table, they might refuse to do it – because they can’t do it. But if you show your child how to set the table, they’re more likely to do it. They’ll also get a sense of achievement and feel good about helping to get your family meal ready.
There are 3 key ways you can help children learn everything from basic self-care to more complicated social skills:
- modelling
- instructions
- step by step.
Remember that skills take time to develop, and practice is important. But if you have any concerns about your child’s behaviour, development or ability to learn new skills, see your GP or your child and family health nurse.
When you’re helping your child learn a skill, you can use more than one teaching method at a time. For example, your child might find it easier to understand instructions if you also break down the skill or task into steps. Likewise, modelling might work better if you give instructions at the same time.
Modelling
Through watching you, your child learns what to do and how to do it. When this happens, you’re ‘modelling’.
Modelling is usually the most efficient way to help children learn a new skill. For example, you’re more likely to show rather than tell your child how to make a bed, sweep a floor or throw a ball.
Modelling can work for social skills. Prompting your child with phrases like ‘Thank you, Mum’, or ‘More please, Dad’ is an example of this.
You can also use modelling to show your child skills and behaviour that involve non-verbal communication, like body language and tone of voice. For example, you can show how you turn to face people when you talk to them, or look them in the eyes and smile when you thank them.
Children also learn by watching other children. For example, your child might try new foods with other children at preschool even though they might not do this at home with you.
How to make modelling work well
- Get your child’s attention, and make sure your child is looking at you.
- Move slowly through the steps of the skill so that your child can clearly see what you’re doing.
- Point out the important parts of what you’re doing – for example, ‘See how I am …’. You might want to do this later if you’re modelling social skills like greeting a guest.
- Give your child plenty of opportunities to practise the skill once they’ve seen you do it – for example, ‘OK, now you have a go’.
Instructions
You can help your child learn how to do something by explaining what to do or how to do it.
How to give good instructions
- Give instructions only when you have your child’s attention.
- Use your child’s name and encourage your child to look at you while you speak.
- Get down to your child’s physical level to speak.
- Remove any background distractions like the TV.
- Use language that your child understands. Keep your sentences short and simple.
- Use a clear, calm voice.
- Use gestures to emphasise things that you want your child to notice.
- Gradually phase out your instructions and reminders as your child gets better at remembering how to do the skill or task.
A picture that shows your child what to do can help them understand the instructions. Your child can check the picture when they’re ready to work through the instructions independently. This can also help children who have trouble understanding words.
Sometimes your child won’t follow instructions. This can happen for many reasons. Your child might not understand. Your child might not have the skills to do what you ask every time. Or your child just might not want to do what you’re asking. You can help your child learn to cooperate by balancing instructions and requests.
Step-by-step guidance: breaking down tasks
Some skills or tasks are complicated or involve a sequence of actions. You can break these skills or tasks into smaller steps. The idea is to help children learn the steps that make up a skill or task, one at a time.
How to do step-by-step guidance
- Start with the easiest step if you can.
- Show your child the step, then let them try it.
- Give your child more help with the rest of the task or do it for them.
- Give your child opportunities to practise the step.
- When your child can do the step reliably and without your help, teach them the next step, and so on.
- Keep going until your child can do the whole skill or task for themselves.
An example of step-by-step guidance
Here’s how you could break down the task of getting dressed:
- Get clothes out.
- Put on underpants.
- Put on socks.
- Put on shirt.

- Put on pants.
- Put on a jumper.
You could break down each of these steps into parts as well. This can help if a task is complex or if your child has learning difficulties. For example, ‘Put on a jumper’ could be broken down like this:
- Face the jumper the right way.
- Pull the jumper over your head.
- Put one arm through.
- Put your other arm through.
- Pull the jumper down.
Forwards or backwards steps?
You can help your child learn steps by moving:
- forwards – teaching your child the first step, then the next step and so on
- backwards – helping your child with all the steps until the last step, then teaching the last step, then the second last step and so on.
Learning backwards has some advantages. Your child is less likely to get frustrated because it’s easier and quicker to learn the last step. Also the task is finished as soon as your child completes the step. Often the most rewarding thing about a job or task is getting it finished!
Often the most rewarding thing about a job or task is getting it finished!
In the earlier example, you might teach your child to get dressed by starting with a jumper. You’d help your child get dressed until it came to the final step – the jumper.
You might help your child put the jumper over their head and put their arms in – then you might let your child pull the jumper down by themselves. Once your child can do this, you might encourage your child to put their arms through by themselves and then pull the jumper down. This would go on until your child can do each step, so they can do the whole task for themselves.
When your child is learning a new physical skill like getting dressed, it can help to put your hands over your child’s hands and guide your child through the movements. Phase out your help as your child begins to get the idea, but keep saying what to do. Then simply point or gesture. When your child is confident with the skill, you can phase out gestures too.
Tips to help children learn new skills
No matter which of the methods you use, these tips will help your child learn new skills:
- Make sure that your child has the physical ability and developmental maturity to handle the new skill. You might need to teach your child some basic skills before working on more complicated skills.
- Consider timing and environment. Children learn better when they’re alert and focused, so it can be good to work on new skills in the morning or after rest time. It’s also good to avoid distractions, like the TV or younger siblings.
- Give your child the chance to practise the skill. Skills take time to learn, and the more your child practises, the better.
- Give lots of praise and encouragement, especially in the early stages of learning. Praise your child when they follow your instruction, practise the skill or try hard, and say exactly what your child did well.
- Avoid giving negative feedback. Rather than saying your child has done it ‘wrong’, use words and gestures to explain 1-2 things your child could do differently next time.

Remember that behaviour might get worse before it improves, especially if you’re asking more from your child. A positive and constructive approach can help – for example, ‘Well done for getting the knots on your laces right! Would you like to do the loops together today?’
What skills to develop in a child and how it will help in the future
Photo: Nicolas Picard / Unsplash
85% of a person's success in a profession depends on soft skills. Together with Natalia Gatanova, psychologist, mother and scientific director of the MKEBI Foundation, we figure out what it is and how to develop it in young children
Scientists divide human skills into two conditional groups: professional hard skills and supraprofessional soft skills.
- Hard skills - highly specialized skills for performing certain tasks at work. For example, a programmer's skill is to write code in python. hard skills can be learned at school, university, at work, courses or trainings.
- Soft skills (“soft” skills) is a set of social skills that help a person solve problems in life: communication, leadership, teamwork, people management, emotional intelligence. Soft skills cannot be learned in training, they are formed in childhood and develop throughout life.
A simple model of professional competencies in the form of a doll. “Hard” skills inside, “flexible” skills outside (Photo: Moscow School of Management Skolkovo)
According to the results of a joint study by scientists from Harvard, Stanford and the Carnegie Endowment, soft skills determine the success of a person in the profession by 85%, and only 15% depends on highly specialized skills.
In a survey by the UK's Sutton Trust, 88% of young people, 94% of employers and 97% of teachers surveyed said they considered "life skills" as or more important than academic ones. The changing VUCA world requires a person to quickly adapt to the new. VUCA is an acronym for instability (volatility), uncertainty (uncertainty), complexity (complexity), and ambiguity (ambiguity). It is important now to pay attention to the development of soft skills in a child to help them cope with changes and not get lost in the future.
The changing VUCA world requires a person to quickly adapt to the new. VUCA is an acronym for instability (volatility), uncertainty (uncertainty), complexity (complexity), and ambiguity (ambiguity). It is important now to pay attention to the development of soft skills in a child to help them cope with changes and not get lost in the future.
Like adults, the most important skills for children are communication skills, while you need to pay attention to leadership and group work, says Natalia Gatanova, scientific director of the MKEBI Foundation.
- Communication skills. The child must learn to communicate: introduce themselves, get to know each other, agree to play together. If necessary, ask for help from adults or peers, offer to provide it yourself. Explain exactly what they need and why. By developing communication skills, the child learns to accept different points of view and argue his own.

- Leadership qualities. Leadership is confidence in yourself and your abilities. The child learns to take responsibility for the decisions made and the people around. If no one wants to play, he will offer to start. A toddler can feel invisible and unreal if he constantly waits for someone to organize the game for him or solve all the problems. Children should feel like full-fledged people who know how to achieve their goals and make the right decisions for this.
- Working in a group. The ability to work and be in a group with other children helps to achieve big goals, compete and negotiate, develops leadership and communication. Working in a group, the child is not afraid to accept the rules of the game, to maintain his role and enjoy it.
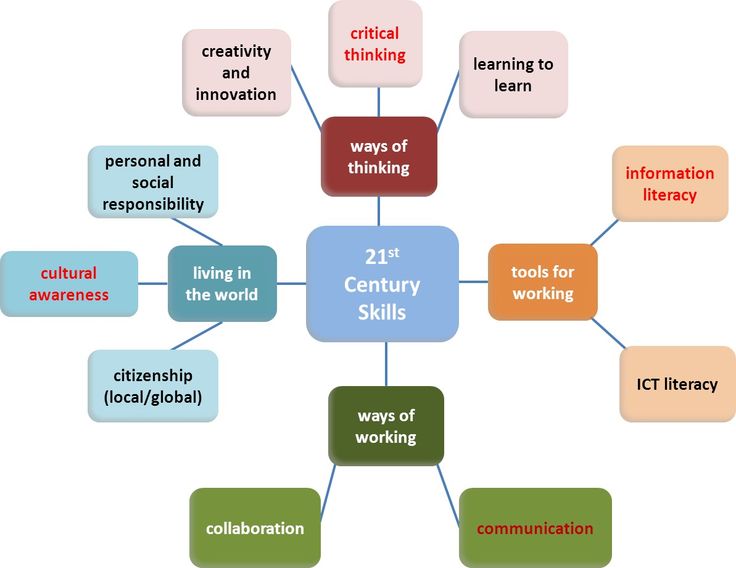
Six major megatrends that are changing the world. From the Skills of the Future report
Global Education Futures and WorldSkills Russia experts recommend developing ten key skills that people will need in the future:
- Attention control and concentration.
 Will help you cope with information noise and overload, manage processes and solve complex problems.
Will help you cope with information noise and overload, manage processes and solve complex problems. - Creative thinking. In the future, routine tasks will be automated, so the skills of creative thinking and the creation of creative ideas will help to remain a sought-after specialist in the labor market.
- Logic. Logic develops computational thinking. Helps to solve complex problems and make informed decisions.
- Spatial thinking and imagination. Helps to correlate oneself with the surrounding space, imagine new objects and navigate in it.
- Information handling skills. Digital literacy and programming skills are as important as reading skills. These are basic skills that everyone needs in a new complex world.
- Self-organization and time management. Zoomers and millennials are more likely to choose a free schedule and change jobs.
 Remote work is becoming the norm and sets a new era - self-organization. Skills will help you manage time, projects and life.
Remote work is becoming the norm and sets a new era - self-organization. Skills will help you manage time, projects and life. - Emotional intelligence. Through emotions we react to what is happening around us. The skill helps to manage your emotional state, avoid neurosis, depression and apathy.
- Intercultural communication. Global changes are forcing economies, corporations and communities to come together to solve common problems. Intercultural communication skills help build relationships with people from other areas and countries.
- The ability to learn, unlearn and relearn. Self-learning helps you learn skills on your own in a rapidly changing world and adapt to change.
- Critical thinking. The skill helps to think clearly and rationally, to look for a logical connection between facts and to formulate strong arguments.
In her TED talk, teacher Rimma Rappoport talks about how children can develop soft skills in Russian language lessons0097 RBC Trends ), the child understands his needs if the mother adequately responds to them. That is, if a mother feeds her son when he is cold, he develops an incorrect understanding of himself at an unconscious level. Already at the age of three, the child wants to decide for himself: what cartoon to watch, what to wear and what toys to play. He imagines that the world is built around his desires. If a child does not understand himself, he cannot satisfy his needs.
That is, if a mother feeds her son when he is cold, he develops an incorrect understanding of himself at an unconscious level. Already at the age of three, the child wants to decide for himself: what cartoon to watch, what to wear and what toys to play. He imagines that the world is built around his desires. If a child does not understand himself, he cannot satisfy his needs.
In the theory of self-determination, there are three basic human needs.
- To be accepted — the child plays with other children, feels needed and useful.
- To be independent - the child understands that he can change something if he wants to. For example, put toys in your own way or choose clothes.
- Be successful and competent - the child knows that if he is given a difficult task, he will cope with it. Adults may not pay attention to this, explaining with the phrase “you will grow up, you will understand,” but this is not true.
 You need to treat the child as a complete person.
You need to treat the child as a complete person.
Psychological comfort and health depend on the satisfaction of basic needs. If a child learns to understand and meet his needs in childhood, he will grow up to be an independent adult who responds calmly to difficulties. Such adults are sure that any problem can be solved.
Circles and sections develop, but you should not rely only on additional education. Soft skills are formed from birth, so it is better to set a personal example for a child and take him seriously.
- Personal example. The child adopts behavior patterns by imitating adults. Parents set patterns of communication if they openly communicate with people, express feelings, ask for help, solve problems. For example, if you want your child to say hello, say hello yourself.
- Attitude. A child is not a small adult who begins to live after 18 years of age, but a full-fledged person. Take your child seriously, ask his opinion.
 If you give a choice, it must be real. For example, the offer to choose a cup for milk is imaginary, because the child will still have to drink milk. Better ask what he wants to drink: tea, water, milk or juice.
If you give a choice, it must be real. For example, the offer to choose a cup for milk is imaginary, because the child will still have to drink milk. Better ask what he wants to drink: tea, water, milk or juice. - Inner environment. Relatives, friends and acquaintances are the inner circle of the child. They set patterns for all forms of communication that develop soft skills. If a child comes to a development group with an atmosphere of mutual respect and the opportunity for self-expression, soft skills will develop. At the same time, sending a shy child to a development group and expecting him to become a leader in it is not worth it. It is better to give the child a responsible task with the right to make mistakes. If there is a bakery on the ground floor of the house, assign a child to be responsible for the bread in the house. This is a task with real actions: take money, go to the store, choose bread and bring it home.
In order to see the difficulties with the development of soft skills in a child in time, look at his behavior. For example, if a child comes to a group of children, but cannot find a friend to play in 5-10 minutes, then he has difficulties. The child may not say hello, hide, or stand aside for a long time and watch other children play. Try to talk to him and find out the reasons for this behavior, contact a child psychologist.
For example, if a child comes to a group of children, but cannot find a friend to play in 5-10 minutes, then he has difficulties. The child may not say hello, hide, or stand aside for a long time and watch other children play. Try to talk to him and find out the reasons for this behavior, contact a child psychologist.
Talk to kindergarten teachers, school teachers or parents of classmates. If it is difficult for adults to work with a child: he refuses everything, bullies the guys, “pulls the blanket over himself” - and this is not a one-time phenomenon, then there are difficulties.
Psychotherapist Andrei Kurpatov in the book Happy Child. Universal Rules” writes that not understanding the reasons for children's crying, parents defiantly leave the child alone with his misfortune, making a lot of mistakes in emotional education
Soft skills develop gradually throughout life. Some skills form others. For example, communication develops emotional intelligence and the ability to manage people. There is no set age when a child will grow up and trade one set of soft skills for others.
There is no set age when a child will grow up and trade one set of soft skills for others.
In order for the child to understand his needs and be able to meet them, the mother must correctly respond to the emotions and demands of the child in childhood and give the right feedback in a timely manner. Then, if a child breaks a toy and cries, he will understand that he is crying because of a broken toy, and not a bad mother. You need to believe in your child, love him and give him the opportunity to live, and not prepare for life in the future.
To develop your child's soft skills:
- Respond correctly to needs at an early age, give timely feedback. So the child learns to understand himself and satisfy basic needs.
- Pay attention to communication, leadership and group work - these are the most important soft skills in a child.
- Lead by example in how you behave, communicate, and work with others.
- Treat your child like a complete adult with your own opinion.

- Watch your inner circle - ask relatives to set the right example, send the child to development groups with an atmosphere of mutual respect.
- See a specialist if your child has difficulty developing communication and soft skills.
- Love and respect your child.
8 skills that are useful for developing a preschooler and elementary school student
School preparation / Early childhood development
The LogicLike team talks about the skills that are important to master in preschool and primary school age in the first place.
LogicLike is an online platform for the development of children aged 5-12. We teach children to reason and work with information, develop logic and non-standard thinking.
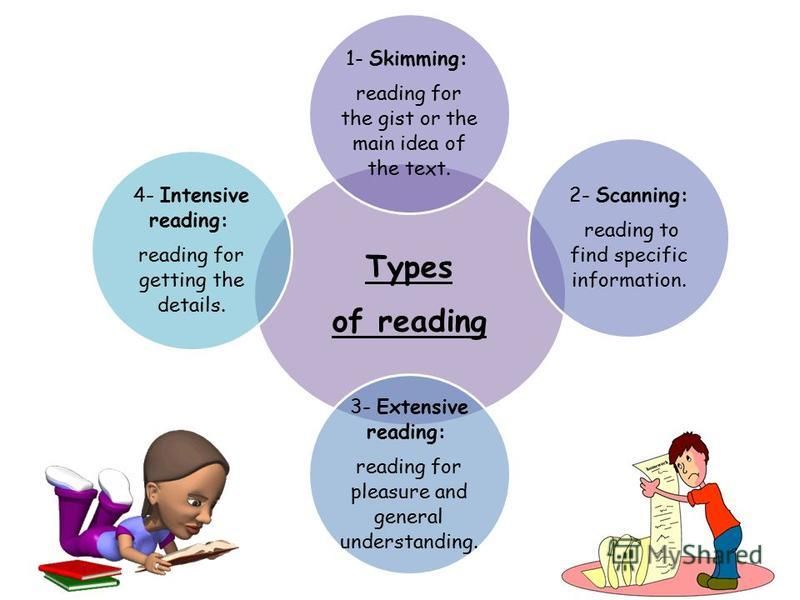
1. Ability and desire to learn: cognitive abilities and interest in learning
Perception, attention, memory, imagination, speech, thinking are mental cognitive processes that make up the ability and desire to learn. For most children, the development of cognitive interest is a natural process laid down by nature. At preschool age, inquisitive children most of all want to discover something new.
For most children, the development of cognitive interest is a natural process laid down by nature. At preschool age, inquisitive children most of all want to discover something new.
Closer to 5-7 years, the child no longer simply perceives information in finished form, as it was before. An inquisitive mind seeks to find answers to questions on its own. An inquisitive preschooler learns to bring different concepts into one system, analyzes them, compares them, looks for patterns and draws conclusions.
Hot interest and curiosity are the basis of independent motivation of a preschooler and a first grader to study.
The elementary school curriculum does not contain separate classes devoted to the development of cognitive abilities. Therefore, the task of teaching the child to learn largely falls on the parents.
High cognitive interest plus developed attention, memory, thinking and other cognitive abilities will help you get used to school without stress, become more independent, proactive and avoid chronic academic failure.
See also: The benefits of entertaining mathematics and solving logic problems.
The ability to learn independently cannot be overestimated. Technology is developing many times faster than it was 20 years ago, and specialists of any profession are in the race for new knowledge. Try to imagine what will happen in another 20 years.
2. Creative thinking: the ability to think outside the box, contrary to patterns
The ability to create something new, unconventional - this is how classical psychology defines the concept of "creative thinking". You should not associate it exclusively with art: extraordinary solutions are welcome in any field of activity, be it acting or mobile application development.
At the age of 5-7 years, thinking is not constrained by stereotypes and it is easier for a child to learn to be “creative”. This will help in the future to get out of any difficult situations, simply connecting creative thinking.
See also: 10 ideas and exercises to develop creativity.
The ability to think outside the box is useful not only in everyday life. For example, engineer and ornithologist Eiji Nakatsu developed a rounded nose for a bullet train. The idea came from observing the kingfisher, a bird whose streamlined beak allows it to fish easily, plunging into the water without splashing. This train design reduced air resistance and energy costs.
3. The ability to think logically: we develop logical and mathematical intelligence
Some everyday and educational problems can be solved creatively. But in most cases, when an objective, balanced approach is needed, creativity is not enough. Logical thinking comes to the rescue:
- ability to think;
- prove the truth or falsity of judgments;
- make informed decisions;
- explain your position to yourself and others.
When a child pumps logical thinking and mathematical abilities, he learns to use specific concepts, "weigh" options and make decisions.
Solving entertaining logic problems is a proven way to develop logic in preschoolers and younger students. Is your child 5-7 years old? This is the perfect time to start.
Day after day, more than 100,000 students
complete 10-20 assignments on the LogicLike website. And how much can you? Choose where to start:
Riddles and questions Riddles and questions
Logic tasks Logic tasks
Children with developed logical and mathematical intelligence can easily cope with school mathematics. In grades 3-4, they win mathematical olympiads and, in general, have more chances for a breakthrough in overall intellectual development.
4. Spatial thinking and imagination: developing visual-spatial intelligence
It is possible to create 3D pictures in your head, look at them in great detail and rotate them as you like with the help of spatial thinking and imagination. By developing these abilities, the child learns to navigate in space, recognize directions of movement, determine the sides of the horizon, understand the position of objects in space and perceive their shape.
This is interesting: Games and tasks for the development of spatial thinking of preschoolers.
Universal skills for success in any endeavors
The ability and desire to learn, creative, logical-mathematical and spatial thinking are components of the intellect and are absolutely necessary for both children and adults. However, this is not enough to achieve success.
Special, "hard" skills (hard skills) affect a person's success in a particular activity. They, too, can and should be developed from childhood, especially if the child has obvious inclinations and interests.
What can determine the success of a person in a variety of activities? General, "flexible" skills (soft skills) : the ability to learn, think outside the box, speak beautifully and correctly, correctly allocate time, etc. It is equally useful in study, work and personal affairs. “Soft” skills are the basis for the development of special skills and human efficiency in everything.
We have identified 4 universal skills, qualities (their groups) that will definitely be useful to your child at school and later in life.
5. Communication skills: the ability to communicate and speak in public
The ability to conduct a dialogue, negotiate, convince somewhere, and give in somewhere, helps to join the team and find a common language with any person. A sociable person is more likely to reveal his abilities and succeed than someone who is stuck in communication.
6. Ability to work with information
When the information in the head is not sorted out, but falls into a heap, it is much more difficult to find and use something valuable.
For effective work and study, it is important to be able to:
- evaluate information for accuracy and reliability;
- to sift out the superfluous and empty, to highlight the main thing;
- combine elements into semantic groups;
- memorize and find the right information in time.

"Who owns the information, he owns the world."
Nathan Rothschild
7. Self-organization, time management
Sometimes it seems that a person's life is organized by circumstances. School drives into the framework of lessons for 45 minutes, work creates the boundaries of an 8-10-hour working day.
But without the ability to plan things and manage your time, it is difficult to be productive. This is something that is not taught in school, but without which it is difficult to do without in life.
“I’ve been thinking about how to kill time more than once!” said Alice from Lewis Carroll's fairy tale to the Hatter. He answered her:
“How can he (time) like this? If you didn’t quarrel with him, you could ask him for anything you want.
8. Personal qualities: leadership, will, perseverance
Purposeful, stress-resistant, responsible, proactive, hardworking, able to cope with routine tasks - like a torn line from a resume of a top specialist, isn't it? All these qualities are classified as soft skills. They are not related to a specific profession, but without them any work is difficult.
They are not related to a specific profession, but without them any work is difficult.
Personal qualities are formed in childhood and depend on upbringing. It is important in this regard to correctly “distribute responsibilities” between the school and parents.
Abilities and skills open up a world of possibilities for the child
It all starts with the discovery of the inclinations laid down by nature, which are easiest to develop into abilities. But without effort, even rich inclinations run the risk of remaining in the stage of unsprouted grains.
A vivid example is in the biography of the Russian painter Vasily Surikov. His inclinations for drawing appeared early, but by the time he entered the art academy, they were not developed to a sufficient degree, according to teachers.
“Is this your work? Yes, for such drawings, you should even be forbidden to walk past the Academy!
, the examiner remarked sternly.
Surikov did not agree, in three months he completed a three-year course with the artist Dyakonov and successfully entered. To make this example even more revealing, imagine that Surikov never discovered his ability to draw.
To make this example even more revealing, imagine that Surikov never discovered his ability to draw.
How do you like it if your child agrees with the school teacher, they say, “well, there are no abilities for mathematics and logic - a humanist”?
At any age, it's not too early and not too late!
In childhood, the potential for the distant future is laid. But does this mean that it is already too late for adults to develop their abilities? Not at all.
This is confirmed by people who debunk myths by their example. Belarusian biathlete Daria Domracheva received two higher economic educations before realizing in sports.
Self-taught artist Henri Rousseau began painting at a mature age, with only military service and customs experience behind him. It is never too late to develop and discover a second wind.
What else is worth remembering?
- Listen to your child and help him develop in what he likes. Do not try to realize only your ambitions, do not strive to grow a new Hans Zimmer or Steve Jobs.

Learn more