Children's reading levels
How To Identify Your Children's Reading Levels + Which Books to Read
Want to know how to get your kids excited about reading? It starts with choosing appropriate books for their level. Here’s what you need to know about how to identify reading levels for kids!
How to Identify a Child’s Reading Level & Which Books Are Best for Each Reading LevelAre you looking for someone to explain reading levels in plain English?
Like, how you identify your child’s reading level and what they mean from the schools?
Some systems grade with numbers, while others are letters and scores. It’s no wonder it’s confusing.
I struggled with this too. I wanted to get my kids books that they could easily read but I didn’t understand what the levels meant and how to choose a book based on those. After lots of research and trial and error, I’ve finally cracked the code(s).
I’m here to answer all your questions so you can feel confident in understanding your child’s reading abilities and can continue to help them grow as readers.
By the time you are done reading this you will understand:
- What leveled reading is and why it’s used
- The 4 major reading level systems
- How you can identify your children’s reading levels
- What level your child should be at based on their age and grade
- And how to help them choose an appropriately leveled book that nurtures their love of reading
Let’s demystify these systems and help you gain confidence in helping your child improve their reading skills.
What is leveled reading and why is it used?
Reading is a skill that is developed over time. As your child is learning to read they need reading material that they can decode to help gain confidence in their reading skills.
This is where leveled reading comes into play. Leveled reading breaks down how difficult a particular book is and where a child’s reading ability is. This way they are given books and individualized reading instruction that help them become better readers.
While reading levels can indicate if a child is below grade level, on grade level, or above grade level, the most important job these levels provide is to help a teacher develop a good strategy and plan to improve that child’s reading skills.
I think the biggest takeaway is that your child’s reading level does not determine their intelligence or even how successful they will be in school. Instead, reading levels help teachers and homeschooling parents determine the best strategies to help your child succeed.
How to Identify Your Children’s Reading Levels
Most children who attend school sit down one on one with their teacher multiple times a year so that the teacher can identify your child’s reading level. The teacher has the child read books from gradually increasing reading levels.
While the child is reading, the teacher takes into account how fluently and accurately the child reads, as well as their comprehension level.
To put it another way:
- Fluency
means the child reads the text without many mistakes and can read it fluidly.
- Comprehension is how much the child is understanding from what they are reading.
A child who reads a book very fluently, without mistakes, can still not truly grasp what that book was about.
That lack of comprehension means that the book contains ideas, sentence structure, or vocabulary that is too difficult for them to understand and decipher. They would do better and enjoy reading more at a lower reading level.
How can you identify your child’s reading level at home?
Some websites advise parents to do an unofficial reading level assessment at home by making a running record. But I don’t think a running record is necessary at home. It’s overly complicated to just get an idea of your child’s reading skills.
A running record is basically making a copy of the page that your child is going to read and mark down anywhere your child makes a mistake. A teacher would use this to identify particular reading struggles to give them a more complete picture of the child’s reading abilities.
Instead, what I suggest is choosing a variety of books that hover right around their level. Choose books that are slightly below what you perceive your child’s reading level to be. Also, pick out books on their level as well as one or two steps above their reading level. This way they have material they can easily master as well as books that will challenge them.
I found this really great list at Scholastic that outlines books based on Guided Reading Levels (I’ll get more in-depth about the different reading level systems in just a minute).
Here is a list of my favorite books to use to gauge and practice reading levels at home:
- A-C – Bob Beginner Books 1 (you can’t beat them),
- D-F – David Board Books (Level D), Go, Dog, Go (Level E and a classic we all may remember from our own childhood), Pete the Cat: Too Cool for School (Level F)
- G-I – Biscuit book series (Level G), Big Shark, Little Shark (Level I), Elephant & Piggie series by Mo Willems
- J-M – Fly Guy series (level J), Pinkalicious Series (level K), The Book with No Pictures (level L), The Day the Crayons Quit (level M)
- N-P – Stellaluna (level N), Nancy Clancy series (level O), Horton Hears a Who! (Level P)
- R-S – Shiloh (Level R), Matilda (Level S)
- T-V – How to Train your Dragon (Level T), Bud, Not Buddy (Level U), Holes (Level V)
- W-Y – Walk Two Moons (Level W), The Little Prince (Guided Level X), Echo (Level Y)
In the Bob Books, your child should read a couple of the books as they progressively get more challenging. In other early reader short books, your child can either read the entire book or read a few pages.
In other early reader short books, your child can either read the entire book or read a few pages.
For longer books, one page is usually enough to get an idea if your child is mastering fluency and comprehension.
To gauge fluency, keep a simple tally count of mistakes as they are reading and notice if they are able to read with inflection and emotion. I keep track of mistakes by putting a clipboard on my lap under the table and making a small dot for each mistake. I make sure to do this completely out of the view of my child. The reason is simple: I don’t want them shutting down or losing the joy of reading simply because they see me marking mistakes.
Remember, the goal is to build a love for reading!
To evaluate their comprehension, you should pre-read the selection you are giving your child and have some ideas of a few questions you can ask them once they finish reading the selection.
When they get to a point that they are challenged but still comprehending with good fluency, you have found their approximate reading level.
At home, they should have access to books that are one or two levels below their reading level. This builds confidence for budding readers.
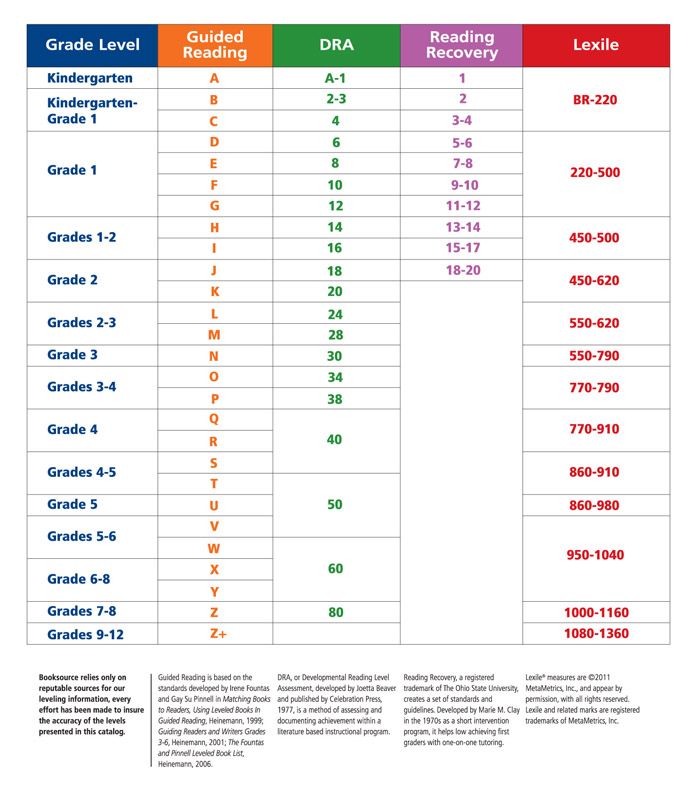
The 4 Major Reading Level Systems
As if this whole reading level thing wasn’t confusing enough, there isn’t just one reading level system. In fact, there are 4 major reading level systems, which different school districts use.
The 4 major reading level systems are guided reading level, accelerated reader, developmental reading assessment, and Lexile measurement levels.
Let’s break these different systems down so you can understand the one that your child’s school uses, or one that you may want to adopt to track your child’s progress.
Guided Level ReadingThis is the system that I used to make the list of books for you to do your home reading assessment above.
It is also one of the most popular systems through school districts. So it only makes sense to go over it first.
Guided Level Reading was developed by Irene Fountas and Gay Su Pinnell. It uses an alphabet system of dividing books into appropriate levels. Level A are the easiest books and they get progressively more challenging until you reach the most difficult books at Level Z.
For each grade level, there are multiple different reading levels so that as your child progresses they can get gradually more challenging books.
Children are tested on level by reading a benchmark book. That means a book that they have never read before is what you can use to determine their fluency and comprehension. The list of books I gave you above would be examples of benchmark books.
This system is popular because it gives a clear vision of where the child is with their reading skills but it isn’t as obvious to the child whether they are ahead, behind or on target with their peers. So it can be better for the child’s confidence and can reduce bullying or comparison.
This is by far my favorite system because once you know what letters correspond to which grade, it is very easy to understand.
Accelerated Reader
Accelerated reader is the system I remember from childhood. Books are based on grade level with a decimal system giving each grade a scale of 10. So what does that look like?
A book could be leveled at 1.8 meaning it’s a first grade level book but the difficulty is moving towards a second grade level book. The biggest difference between Accelerated Reader system versus the other systems is that it has a computer program that quizzes children on the books they read.
This can be problematic for children struggling with reading. Quizzes can cause anxiety even in young children, and cause a negative association with reading.
For that reason, I am not the biggest fan of this particular system, but it is still very popular in the school system.
Developmental Reading Assessment
This system also starts by testing a child by reading a benchmark book. Remember, a benchmark book is a book that helps test your child’s fluency and comprehension.
Developmental Reading Assessment (also called DRA) is a system of leveled books and tests created by Pearson (one of the most popular textbook and educational tools in the US).
I think this system is a little more confusing because it starts with a reading level labeled level A then immediately switches to numbers. So very beginning readers start with leveled A, then it switches to levels 1-80 with 80 being the most difficult.
This is also a very popular choice with school districts, so you may be used to seeing this.
This system ranks books and reading materials based on readability and how difficult it is to read them.
Lexile Measurement Levels
If your child’s reading levels look something like “200L”, then they are using the Lexile Measures system.
This system does not start with a benchmark book but with a standardized test. This system ranks books and reading materials based on readability and how difficult it is to read them.
Levels for the Lexile Measuring system start with BR for beginner readers and then transition into a number like 700L for more advanced readers. Let’s be honest…this makes this system a little more confusing for us parents.
This is a less popular option for schools, but a few do use it. So I want to cover it in case you fall in this group.
What Levels Should Your Child be Reading Based on Grade?
Overall, reading levels are supposed to help with small reading groups and interventions if necessary. They also help a teacher to develop tailored instruction based on each child’s reading level.
How do you know if your child is reading on grade level based on their reading level?
I am going to break this down by grade and I am going to cover all 4 reading level systems: guided reading level (GRL), accelerated reader (AR), developmental reading assessment (DRA), and Lexile measurement levels (Lexile).
Then you can compare your child’s reading level with the reading levels for their grade to get a better understanding of where your child is with learning to read.
You can also notice that for all the reading level systems, except for accelerated reader, reading levels overlap between grades. So, for example, GRL reading level S could be for fourth grade or fifth grade.
Remember, your child may fall outside of these boundaries – they are just general guidelines.
Kindergarten Reading Levels
- GRL: A-C
- AR: 0.1-0.9
- DRA: A-4
- Lexile: BR40l-230L
- GRL: C-I
- AR: 1.0-1.9
- DRA: 4-16
- Lexile: BR
- GRL: I-M
- AR: 2.0-2.9
- DRA: 16-24
- Lexile: 107L-1080L
- GRL: M-P
- AR: 3.0-3.9
- DRA: 24-38
- Lexile: 415L-760L
- GRL: P-S
- AR: 4.0-4.9
- DRA: 38-40
- Lexile: 635L-950L
- GRL: S-V
- AR: 5.
 0-5.9
0-5.9 - DRA: 40-50
- Lexile: 770L-1080L
- GRL: V-Y
- AR: 6.0-6.9
- DRA: 50-60
- Lexile: 855L-1165L
What to do if Your Child is Reading Below Their Grade Level
If you are told your child is reading below grade level, it can be a gut punch. So what do you if your child is reading below grade level?
First, don’t panic. Children develop their reading skills at different stages, some children are early readers and some children take a little longer to get there. Just like some children walk early and some children walk late.
Next, just continue encouraging reading at home by reading books together and discussing what you’re reading. You can also continue to provide them reading materials they can comfortably read and enjoy.
Positivity and encouragement, along with shared reading time will go a long way!
How to Help Your Child Choose a Book to Read
So now that you know what your child’s reading level is and what that means, how can you help your child choose a book to read?
The number one factor in helping your child choose a book is to pick something they are interested in, even if it is above or below their level.
You want to foster a love for reading because it’s enjoyable. With time and practice, the skills will come! Of course, if you are truly concerned, speaking with your child’s teacher to come up with a game plan may be helpful as well.
The Takeaway
At this point, I hope you feel more confident in understanding the different reading level systems and how they are used to help your child to become a better reader.
Remember, your child’s score is not an indicator of how successful they will be and all children develop reading skills at different ages.
Just continue to nurture a love for reading with your child by providing them books they are interested in and spending time reading to them and with them. You’ve got this!
More Resources On Positive Parenting & Screen Free Kids:
- Safety Tips for Kids: Books to Reinforce Safety Rules for Kids
- Pros and Cons of Homeschooling: Weighing School Options
- 10 Ways to Limit Screentime and Raise Unplugged Kids
- Creating Screentime Rules for Summer (Free Printable)
- 10 Screen-Free Alternatives Before Bedtime
- Printable Screen time Rules Checklist for Kids (PDF)
A Guide for Parents and Teachers
As a child starts school and begins learning to read, parents are likely to hear the term “reading level. ” A teacher might share that a student is reading at, above, or below level. They may also provide specific numbers, like 440L or GR J. Parents can find all this confusing, so we’ve put together this simple guide for teachers to share as they discuss what reading levels mean for their students.
” A teacher might share that a student is reading at, above, or below level. They may also provide specific numbers, like 440L or GR J. Parents can find all this confusing, so we’ve put together this simple guide for teachers to share as they discuss what reading levels mean for their students.
What are reading levels?
Source: Scholastic
Reading levels are a way of determining the reading skills a student already has. They measure a child’s reading comprehension and fluency, using a variety of factors like phoneme awareness, decoding, vocabulary, and more. Teachers use reading levels to understand what a student knows and what they need to work on. They might also be used to assemble kids into small reading groups.
Many children’s book publishers indicate reading levels on their books, so parents and kids can quickly find options to suit their needs. Choosing the right reading level can be key for many children. If the book they try to read is too difficult for them, they may give up. On the other hand, reading books that are too easy won’t challenge them to build their skills.
On the other hand, reading books that are too easy won’t challenge them to build their skills.
Suggestions, Not Rules
It’s extremely important to remember a few things about these levels. First of all, in some cases, the score evaluates the ease of reading of a book, but not the content. For instance, a book like Alice Walker’s The Color Purple earns a 4.0 score on the AR/ATOS scale, indicating it’s written at a fourth grade level. However, most people would agree that the content of this book isn’t right for fourth graders. In fact, this type of book is what’s known as “high-low,” meaning the content and interest level is meant for higher-grade students, while the readability score is low enough that less-skilled readers will find it within their range. (Learn more about high-low books here.)
So while level numbers can be helpful, they aren’t the only indicator you should use when choosing a book. In fact, many teachers caution against using levels to limit kids’ reading choices. If a child is willing to tackle a more difficult book because the subject matter interests them, go ahead and let them! On the other hand, if they want to reread old favorites just for fun, that’s great too. The most important thing is to get students reading, whenever and however possible.
If a child is willing to tackle a more difficult book because the subject matter interests them, go ahead and let them! On the other hand, if they want to reread old favorites just for fun, that’s great too. The most important thing is to get students reading, whenever and however possible.
ADVERTISEMENT
How To Determine Reading Levels
Source: The Groovy Teacher on Twitter
Schools give reading assessments one or more times each year. These assessments measure a student’s reading level based on one of several available systems. Each system has its own formula for determining a score, and your child might even be given a score in several different reading level systems.
Below are some of the most common systems you’ll find in schools, districts, and libraries. Every leveled book has a different score in each system, and you can find equivalency charts online to help you compare the various scores. Note that there are many systems out there, with different companies and publishers often designing their own. These basic four will cover most schools and students, though.
These basic four will cover most schools and students, though.
Lexile® Reading Levels
Lexile® is one of the most common reading level systems. These levels are indicated by a number followed by the capital letter L. They range from 10L for brand-new readers to 2000L and above for advanced readers. The first digit of the score roughly corresponds with grade level, so a book rated 370 would be appropriate for most third graders. When looking for “just right books” for Lexile levels, aim for those that are rated 100L below to 50L above your child’s current score.
Example Lexile measures include:
- David Goes to School: 210L
- Judy Moody and the Bad Luck Charm: 470L
- The Lightning Thief (Percy Jackson): 680L
- The Hobbit: 1000L
Guided Reading Levels (Fountas and Pinnell)
The GRL reading level system was developed by two Ohio State University professors, Irene Fountas and Gay Su Pinnell. You might hear it referred to by either of these names or by the abbreviation GRL. In recent years, this system has faced controversy as one of its core theories has been disproved by cognitive scientists. (Learn more about this dispute here.) Still, many schools and publishers continue to use the system, which grades books with letters from A (early readers) to Z+ (advanced). Choose books at the same letter level or one above to match kids with the best choices for their abilities.
In recent years, this system has faced controversy as one of its core theories has been disproved by cognitive scientists. (Learn more about this dispute here.) Still, many schools and publishers continue to use the system, which grades books with letters from A (early readers) to Z+ (advanced). Choose books at the same letter level or one above to match kids with the best choices for their abilities.
Example GRL scores include:
- David Goes to School: GR Level G
- Judy Moody and the Bad Luck Charm: GR Level M
- The Lightning Thief (Percy Jackson): GR Level W
- The Hobbit: GR Level Z
ATOS/AR Reading Levels
The Accelerated Reader level is also called the ATOS score. This system analyzes the average sentence and word length, the vocabulary grade level, and the number of words in a book. Books are scored using an X.X format, where the first number indicates the grade level (0 = kindergarten), and the second indicates the approximate month of that level. For instance, a score of 5.4 would indicate the book should readable for a student in the fourth month of fifth grade.
For instance, a score of 5.4 would indicate the book should readable for a student in the fourth month of fifth grade.
Example AR scores include:
- David Goes to School: ATOS/AR 0.9
- Judy Moody and the Bad Luck Charm: ATOS/AR 3.1
- The Lightning Thief (Percy Jackson): ATOS/AR 4.7
- The Hobbit: ATOS/AR 6.6
DRA Reading Levels
The Developmental Reading Assessment (DRA) tests various reading skills like phonemic awareness, phonics, and fluency. Student scores can range from A1 (for beginners) to 80 (advanced). Choose books at or slightly above a child’s DRA level to challenge them just enough, but not too much to frustrate them.
Example DRA scores include:
- David Goes to School: DRA 12
- Judy Moody and the Bad Luck Charm: DRA 24
- The Lightning Thief (Percy Jackson): DRA 60
- The Hobbit: DRA 70
Still have more questions about reading levels? Drop by the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook to chat and ask for advice.

Plus, check out What Is the Science of Reading?
Reading speed in children ✅ Blog IQsha.ru
What affects the high reading speed? To answer this question, let's understand what it is. Fast reading suggests that the skill of putting letters into words and translating printed characters into speech is automated. So, while reading, you can think not about finding out the meaning of each individual word, but about extracting meanings from the entire text. You can think, ask questions to the text, fantasize. That's why teachers around the world don't stop at learning letters and putting them into words, but encourage children to increase their reading speed.
Do you want to study online? Start right now
So, the faster the child reads, the better he/she:
-
understands the text more successfully;
-
learns unfamiliar words more reliably;
-
performs tasks faster in the lesson;
-
learns more information per lesson.
 .
.
What reading speed should be?
In elementary school, students are given a kind of reading speed test. It is believed that a child in grade 1 reads “normally” at a speed of 25 words per minute, in grade 2 - from 50 words per minute and faster, in grade 3 - from 75 and in grade 4 - from 95. A primary school graduate reads well if his reading speed approaches the speed of speech - 120-150 words per minute.
“Normal” speeds are achieved by some children solely due to natural learning abilities. For some, motivation in the form of family reading or interesting texts helps. And some do not like reading as a process (like adults, for example, do not like to draw or fish) - and it will not work to achieve a combination of “speed-quality-understanding” of reading with ordinary suggestion and notations from adults.
How to improve reading speed in children? Let's separate the two goals: reading aloud and "silently". Each of these goals will have different methods and practice exercises. It should be noted that the success of classes to increase the speed of reading does not depend on the duration of these classes, but on the regularity. It is better to practice every day without skipping three times a day for 5 minutes than once a week for 30 minutes.
It should be noted that the success of classes to increase the speed of reading does not depend on the duration of these classes, but on the regularity. It is better to practice every day without skipping three times a day for 5 minutes than once a week for 30 minutes.
Develop your working memory
Remembering a character or word you just read is a subtle but important point in increasing your reading speed. Working memory can and should be improved, this will require special exercises. For example:
-
Visual dictation. The child considers a set of characters or reads a short text for literally 10 seconds, and then draws or writes down what he remembers on a piece of paper.
-
Schulte tables. You can find a huge number of them on the web. The meaning of working on such tables is to visually find certain symbols or to find in order the numbers that are randomly scattered around the sheet. The child must remember where on the sheet he already looked for and counted the symbol, or where this or that number was when he was looking for a completely different one.

-
Name the objects. Show your child a group of real objects or picture cards, 5 to 10 pieces. Ask to turn away and name everything that the child saw and remembered.
-
Remember the figures. Draw shapes on a sheet of paper in a certain sequence and color them. Invite the child to look at the sample for 10-15 seconds, and then draw and color the figures in the same sequence on their sheet.
Complete online tasks from Aikyusha
Reading aloud speed
1. Reading with a stopwatch. Set a timer or hourglass for 1 minute and have your child read aloud. When the minute is over, you need to remember which word the child stopped on, and then start the timer again. Let the child read the same text and again remember at the end of the minute which word he stopped on. Repeat the stopwatch reading the next day. There is no need to draw any conclusions and comments, and there is no need to strive for a faster reading at this stage either. On a familiar text, automation of the reading skill will happen by itself!
On a familiar text, automation of the reading skill will happen by itself!
2. Reading tongue twisters. To get started, teach your child to quickly pronounce some simple tongue twisters by heart. When the principle “what to do with the language and everything else” becomes clear, invite the child to read unfamiliar tongue twisters - first slowly, and then several more times faster and faster. For example:
Staffordshire terrier is zealous, and black-haired Giant Schnauzer is frisky.
Beavers wander into the cheeses of the forests. Beavers are brave, but kind to beavers.
Our Polkan from Baikal lakal. Lakal Polkan, lakal, but not shallow Baikal.
3. Interrupted reading. Prepare a template from paper or cardboard with narrow vertical stripes that will cover part of the text. The task of the child is to “finish” the interrupted words to complete ones and understand the entire text. After reading through such a “cage”, be sure to ask the child to retell the text. With regular exercises of this kind, reading speed will soon improve.
With regular exercises of this kind, reading speed will soon improve.
4. Lightning. The child reads one text, but according to a prearranged signal (clap, snap of fingers), his task is to read either very quickly, or more slowly.
Silent reading speed
-
Selective reading. In any text editor, write down a short text, highlight it in a certain font, make the letters large. And between the letters of this text, place small gray letters. Ask your child to read only what is written in large black letters.
-
Tug. The text is read by an adult, changing the tempo from slow to fast and vice versa. The child must follow the text with his eyes.
-
Trap. The adult reads the text, the child follows the text with his eyes. Instead of some words, an adult pronounces synonyms aloud (for example, instead of a road - a path, instead of a white one - light, etc.), the child’s task is to immediately stop the adult and point to the word that is actually printed in the text.

-
Reversed reading. Everything is very simple: you just need to turn the book over ... and read to yourself)) After reading, ask the child to retell the meaning of the text.
Would you like to study online? Start Now
Reading Techniques for Grades 1-4
Reading is one of the basic skills for every child. Being able to read is important not only for the lessons of literature and the Russian language, but also for all other sciences. It will be difficult for a student to learn material in mathematics, English or the world around him if he does not know how to quickly familiarize himself with the text and understand what he read. It is reading that opens the door to the world of knowledge. Mastering cognitive texts or works of art, children learn to communicate, learn about the surrounding reality, and broaden their horizons. Cognitive abilities are also honed - memory, attention. Therefore, reading is considered the basis of success in further education.
But how do you know if a child reads well for his age or not? This can be done by checking the reading technique. Many parents do not quite understand the format and meaning of this test, believing that the determining criterion is speed, that is, the number of words read per minute. In fact, the test is focused on assessing not only the pace of reading, but also other skills. Let's try to deal with the requirements prescribed for reading technique in the Federal Standards.
Reading technique: basic criteria
How fast should you read? Is everything okay with a child with technology? Perhaps his skills do not meet some standards? These questions always concern responsible parents. And I must say that there is nothing wrong with this excitement, because involvement in the process of teaching children is in many ways the key to future success. But is it really worth worrying about reading speed?
To answer this question, it is necessary to understand in detail what exactly is assessed when testing reading technique.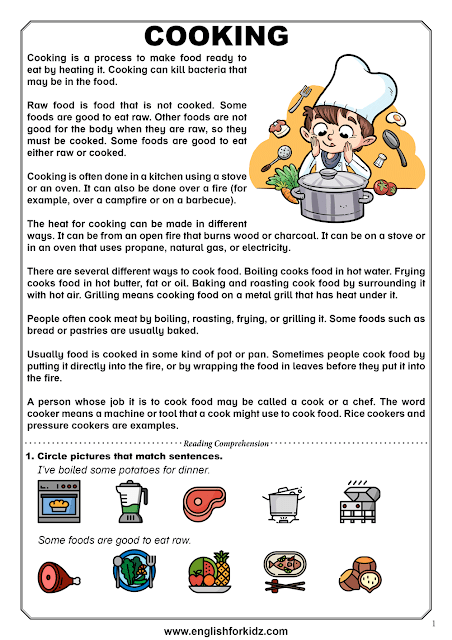 According to the requirements of the Federal State Educational Standard, the following are assessed:
According to the requirements of the Federal State Educational Standard, the following are assessed:
- reading speed - the number of characters that a child is able to read in one minute;
- way of reading - reading words by syllables or whole, smoothly;
- correctness - the absence of mistakes and hesitations made by a child when reading;
- awareness - the ability to understand the meaning and idea of what is read;
- expressiveness - the ability to correctly place stresses, observe intonation and maintain pauses when reading.
Analyzing the listed criteria, we can say that the test of reading technique is based on the assessment of two components: semantic and technical. At the same time, the technical side - tempo, expressiveness, correctness - is subordinated to the semantic, that is, the ability to understand the content of the text.
Reading technique: what is really important?
Reading is the most important type of speech activity, based on the ability to perceive and assimilate information. Unlike drawings, diagrams and video sequences, it activates the imagination. Scientists have proven that when reading poetry, other areas of the brain are involved than when mastering prose. This fact is explained by the different structure of phrases and phrases used in prose and poetry. Therefore, the ability to read can be considered as a tool for self-development. But this is not a basic skill, but acquired in the learning process. And here it is important not to force things, but to focus on the abilities and capabilities of the child.
Unlike drawings, diagrams and video sequences, it activates the imagination. Scientists have proven that when reading poetry, other areas of the brain are involved than when mastering prose. This fact is explained by the different structure of phrases and phrases used in prose and poetry. Therefore, the ability to read can be considered as a tool for self-development. But this is not a basic skill, but acquired in the learning process. And here it is important not to force things, but to focus on the abilities and capabilities of the child.
It must be understood that reading technique is just one of the criteria, and it is not necessary to focus only on it. Especially parents whose children are not yet in school. Don't just chase the pace. At this stage, it is more important to broaden your horizons, get acquainted with different topics, memorize new words. And the best way to achieve this is to read a lot, daily, but not to put speed at the forefront.
As far as schoolchildren are concerned, two parameters essentially matter here: technique and meaningfulness of reading. Technique is usually called the ability to distinguish letters, transform them into sounds, compose syllables and words. Meaningfulness is a deeper concept. It is based on understanding the meaning and content of the text.
Technique is usually called the ability to distinguish letters, transform them into sounds, compose syllables and words. Meaningfulness is a deeper concept. It is based on understanding the meaning and content of the text.
It would be erroneous to require a child to make sense of what they read until they have developed the skill of technical letter recognition. All the efforts of the crumbs, who are just learning to read, are aimed at memorizing and recognizing letters, syllables, words. In order to understand the essence of what is written in the text, he no longer has any intellectual strength or time. Therefore, primary education teachers first focus on technology, and only when it is brought to automatism, they begin to form a meaningful approach to reading.
Reading speed standards for elementary school
Reading speed standards adopted for elementary school students:
- Grade 1: 1st semester - 20-25 words per minute, 2nd semester - 30-40 words;
- Grade 2: I half-year - 40-50 words; II half-year - 50-60 words;
- Grade 3: I half-year - 60-70 words; II half-year - 70-80 words per minute;
- Grade 4: I half-year - 80-90 words per minute; end of the school year - 100-120 words.

In classes and schools for gifted children, the rate of reading may be higher. So, in the first grade, such children read more than 60 words per minute, in the second - 90-95, in the third - 95-105 words per minute. The pace when reading to yourself should be 20-50 words faster than when reading aloud.
Other test parameters
And a few more parameters that you should pay attention to:
- Grade 1 - the student can read a significant part of the text by syllables.
- Grade 2 - higher requirements are imposed on the reading technique: only complex words can be read by syllables, it is important to observe pauses and correctly place stresses.
- Grade 3 - reading must be conscious and expressive, with observance of intonation. In order to correctly assess the skills of the child, retelling is practiced.
- Grade 4 - the student should be able to analyze what he has read and express his personal opinion.
Focusing on the standard, we can draw some conclusions about the effectiveness of training. But even if the child cannot read the number of words prescribed in the standards, you should not worry too much about it. After all, these are just average standards developed on the basis of general data. Each student has their own level and pace of development. Checking the technique is rather information for the teacher and parents. After analyzing the results, you can understand in which aspects of training you need to show more diligence.
But even if the child cannot read the number of words prescribed in the standards, you should not worry too much about it. After all, these are just average standards developed on the basis of general data. Each student has their own level and pace of development. Checking the technique is rather information for the teacher and parents. After analyzing the results, you can understand in which aspects of training you need to show more diligence.
Testing your reading skills yourself
You can organize a reading test at home, but don't turn it into an exam. Some children are quite sensitive to any tests, and in stressful situations they cannot always demonstrate everything they are capable of. Come up with a game format or check the technique discreetly. If the child himself wants to know what success he has achieved, then no problems will arise.
Action sequence:
- Arm yourself with a watch with a second hand. To check, you can use a stopwatch on your smartphone, but it’s better to refuse an hourglass, since a child who has never seen such a thing will be distracted by them.
- Prepare a text and show it to the child.
- Ask to read the text aloud.
- The time should be recorded from the start of reading.
- If you notice that a child has made a mistake, do not stop him, but simply make a note for yourself.
- Rate the result. To get the most objective picture of the student's skills, you should conduct a control check and compare the results.
If you see that the child is not concentrated enough, he is in a bad mood or is not feeling well, check the reading technique on another day.
Correctly evaluate the result
Count the number of words read. Points to pay attention to when counting:
- conjunctions, particles, prepositions consisting of one or two letters are counted as one word;
- when wrapping, the word is counted not as one, but as two;
- words with a hyphen are counted differently: if there are three or more letters on both sides of the hyphen, then the word is counted as two, less than three letters - as one word.

Not only speed is important, but other criteria as well. Be sure to evaluate the correctness of the text you read. All mistakes made should be sorted out with the child. If you notice that there are a lot of hesitations, corrections, changes in endings and whole words, you should consult with the teacher. Perhaps professional correction of reading skills is needed.
It is also important to understand how well the child understood the meaning of the text. It is not necessary to ask the student to retell what they have read. It is enough that he describes the content in a few words. Ask him to identify the main idea. If there are problems with this, then you can resort to retelling.
Pay attention to expressiveness. The student should try to observe intonation, pause in accordance with punctuation marks. Unfortunately, not all children are able to read a passage with an expression. Tell the child in which places you need to increase the pace and emotionality, which words need to be emphasized.
Requirements for texts used to test reading skills
When choosing a text, adhere to the following recommendations:
- It should be a text unfamiliar to the child, but not too complex, age appropriate.
- Pay attention to the structure of sentences: they should be short, without dialogues and a lot of punctuation marks.
- It is better to choose text without pictures.
- Font size is also important - it should be large enough.
- Text should not be split into two pages.
Of course, you should not check your reading technique using the instructions for household appliances or a manual for housewives. The best option is short stories about nature, animals, seasons.
Tips for Improving Reading Technique
Don't be discouraged if your test results aren't up to standard. But what really needs to be done is to put more diligence and not be lazy to practice. You can seek help from specialists or deal with the child on your own. But just remember that you need to do at least 15 minutes every day.
But just remember that you need to do at least 15 minutes every day.
There are many exercises to improve reading technique:
- reading the same text several times in a row with a gradual increase in pace;
- "buzzing reading" - daily five minutes of reading in a low voice;
- "gibberish" - the use of texts in which some of the letters are written upside down;
- "word search" - an exercise to find a specific word in the text;
- exercise with syllabic tables.
This is just a part of the exercises to improve your reading technique. There are also recommendations for working on literacy, expressiveness, understanding the meaning of what is read:
- if there are problems with diction, emphasis should be placed on tongue twisters;
- in order for the child to better understand the meaning of what he read, ask him to retell texts more often, make plans, draw illustrations for any passage;
- Poems are most suitable for improving the expressiveness of reading.
Learn more