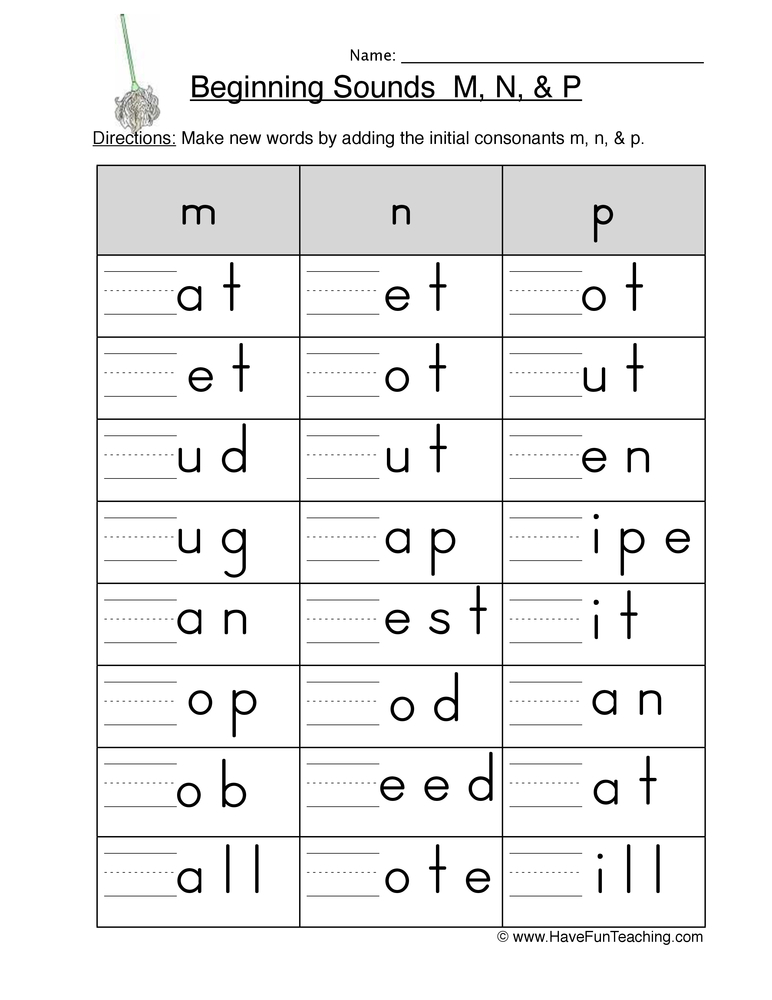
Consonants in words
What is a Consonant? Definition, Examples of Consonants in English
Definition of consonant: A consonant is a letter (sound) of the English alphabet that is not a vowel.
What is a Consonant?
What does consonant mean? A consonant is most often identified as a letter that is not a vowel.
More specifically, a consonant is a sound that when paired with a vowel makes a syllable.
A consonant is any sound that a letter makes that is not a vowel sound.
What Letters are Consonants?
English consonant letters: B, C, D, F, G, H, J, K, L, M, N, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, X, Y (sometimes), Z
Consonant Examples in Words:
- car
- “c” and “r” are consonants in this word
-
storm
- “s” “t” “r” “m” are consonants in this word
- day
- “d” is a consonant in this word
Consonants vs. Vowels
Consonants are not vowels. Vowels in the English language are A, E, I, O, U, (and sometimes Y).
Vowels, just like consonants, do not make syllables on their own. A vowel paired with a consonant makes a syllable.
Example of vowel in word:
- sit
- “i” is the vowel in this word
Forming Syllables
A syllable is a unit of sound that creates meaning in language. Consonants pair with vowels to create syllables.
Syllables can have more than one letter, more than on consonant, and more than one vowel, but they cannot have more than one sound.
Examples:
- maker
- two syllables
- “mak”: two consonants “m” “k” plus one vowel “a”
- “er”: one vowel “e” plus one consonant “r”
- slow
- one syllable
- three consonants “s” “l” “w” and one vowel “o”
- banana
- three syllables
- “ba”: one consonant “b” plus one vowel “a”
- “na”: one consonant “n” plus one vowel “a”
- “na : one consonant “n” plus one vowel “a”
- lean
- one syllable
- two consonants “l” “n” plus one vowel “n”
Literary Devices That Use Consonants
The sound specifically created from consonants is used in the literary device called
consonance.
Consonance is the repetition of similar consonant sounds within nearby words. It is, in a sense, the opposite literary device to alliteration.
Consonance, as with alliteration, is often used in poetry when writers use sound to create meaning.
Example of Consonance:
- the children seemed adorable and endearing
- the repetition of the “d” sound in these examples creates the consonance
The following is an example of consonance from American poet Emily Dickinson’s “’T was later when the summer went”:
‘T was later when the summer went
Than when the cricket came,
And yet we knew that gentle clock
Meant nought but going home.
The “t” sound in this example creates the consonance. Dickinson purposefully incorporates consonance into this poem to reflect her intention.
She wants to mimic the sound of the cricket and the sound of the clock. She does so, subtly, by including consonance.
Summary: What are Consonants?
Define consonant: the definition of consonant is one of a class of speech sounds that are enunciated by constricting or closing one or more points of the breath channel. Examples include, c, d, n, p, etc.
Examples include, c, d, n, p, etc.
In summary, a consonant is a unit of sound (a letter) in English.
- Consonants are not vowels.
- When consonants combine with vowels, they create syllables.
Contents
- 1 What is a Consonant?
- 2 What Letters are Consonants?
- 3 Consonants vs. Vowels
- 4 Forming Syllables
- 5 Literary Devices That Use Consonants
- 6 Summary: What are Consonants?
Consonants: Definition and Examples
by Craig Shrives
This Page Includes...
- Printable & Sendable Test
- Why Consonants Are Important
- Key Points
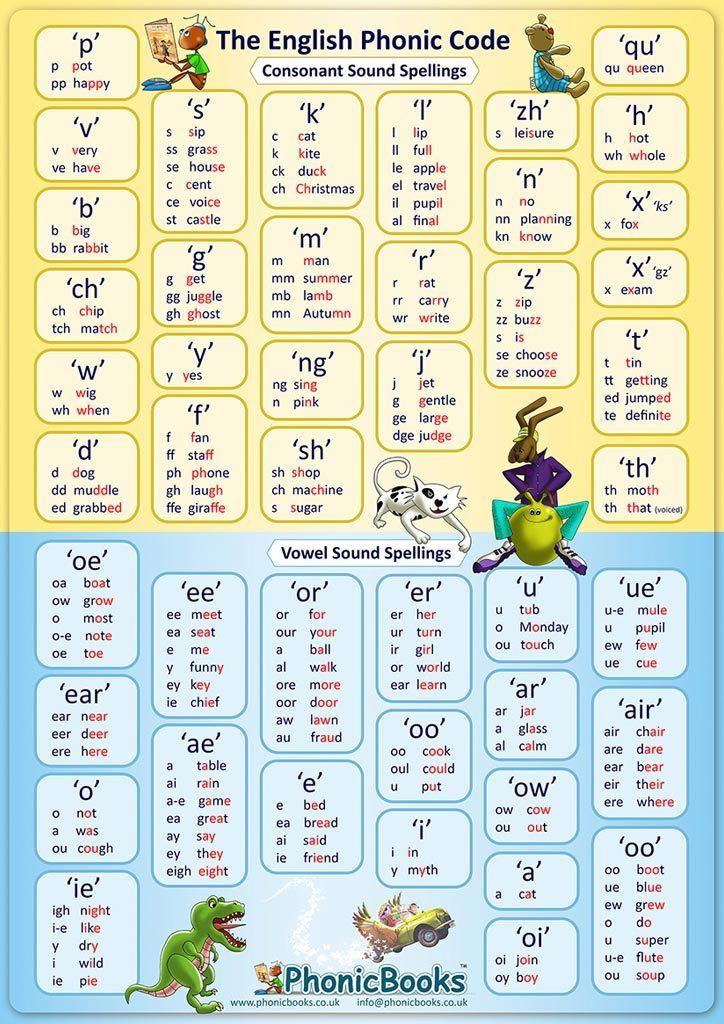
What Are Consonants? (with Examples)
A consonant is a letter of the alphabet that represents a basic speech sound produced by obstructing the breath in the vocal tract. All the letters in the alphabet apart from A, E, I, O, and U (called vowels) are known as consonants.
For example:
- T is pronounced using the tongue (front part)
- K is pronounced using the tongue (back part)
- B is pronounced with the lips
- H is pronounced in the throat
- F is pronounced by forcing air through a narrow gap
- M is pronounced using the nasal passage
A consonant can be combined with a vowel to form a syllable.
More about Consonants
With seven consonants, "rhythms" is the longest word without any vowels. There are three words with six consonants and no vowels:
- He moved very spryly. ("Spryly" means in a nimble or agile manner.)
- She is sylphy. ("Sylphy" means like a "sylph" (a slender graceful girl).)
- Eclipses occur at times of syzygy. ("Syzygy" is the straight-line configuration of three or more celestial bodies.
 )
)
Some might argue that these words do contain vowels because they include Y, which is often called a semi-vowel. (There is more on this on the vowels page.)
With no "vowels," we have crwth (a stringed instrument) and cwtch (a shed, cuddle, or hiding place). But, both of these words derive from Welsh, which typically treats W like the U in "cut."
Why Consonants Are Important
There are two good reasons to care about consonants.
(Reason 1) Use "a" and "an" correctly.
Use "a" (not "an") before a consonant sound. Note the word sound. (The ruling is not use "a" before a consonant.)
- It was a unique experience to receive an unequivocal answer. (Even though "unique" and "unequivocal" start with the same letter (the same two letters in fact), "unique" starts with a consonant sound (Y) while "unequivocal" starts with a vowel sound.
 Remember that you must use "a" (not "an") before a consonant sound.)
Remember that you must use "a" (not "an") before a consonant sound.)
- Becoming a eunuch wasn't a one-off deal it was a two-off deal. ("Eunuch" and "one-off" both start with vowels but with consonant sounds.)
Read more about "an" and "a" on the page about indefinite articles.
Be particularly careful with abbreviations.
- She was injured in a RTA.
- She was injured in an RTA. (The letter "R" is a consonant, but the initialism RTA is pronounced "ar-tee-ay," i.e., it starts with a vowel sound. Therefore, "an" is correct.)
- A MAFF official came to stuff an MRSA outbreak. (The acronym MAFF attracts "a" because it is pronounced "maf," i.e., it starts with a consonant sound. However, the initialism MRSA attracts "an" because it is pronounced "em-ar-ess-ay," i.e., it starts with a vowel sound.)
Read more about using "an" and "a" with abbreviations.
(Reason 2) Use consonance to add rhythm and musicality to your writing.
Consonance is a literary technique created by repeating the same consonant sound in neighboring words. It is used by poets and lyricists to compel their audiences to consider the near rhyme created by consonance. Consonance is not the same as alliteration, which sees neighboring words all starting with the same letter or sound.
- I earn my keep by cracking locks or picking a pockets.
- She swung her fist in angst against the beast.
- The new logo says boorish and English but also stylish.
Read more about consonance.
Key Points
Printable Test
Help Us Improve Grammar Monster
- Do you disagree with something on this page?
- Did you spot a typo?
Find Us Quicker!
- When using a search engine (e.
 g., Google, Bing), you will find Grammar Monster quicker if you add #gm to your search term.
g., Google, Bing), you will find Grammar Monster quicker if you add #gm to your search term.
Next lesson >
See Also
What is a diphthong?The top 10 spelling rulesThe top 20 misspelled wordsHow to improve your English spellingWhat is a schwa vowel?Using an and aDrag-and-drop test on the types of syllable
Page URL
Technical Help
- Download the latest grammar-checker app
Grammarly's app will help with:
(1) Avoiding spelling errors
(2) Correcting grammar errors
(3) Finding better words
(This free browser extension works with webmail, social media, and texting apps as well as online forms and Microsoft Office documents, like Word and Teams.)
Next lesson >
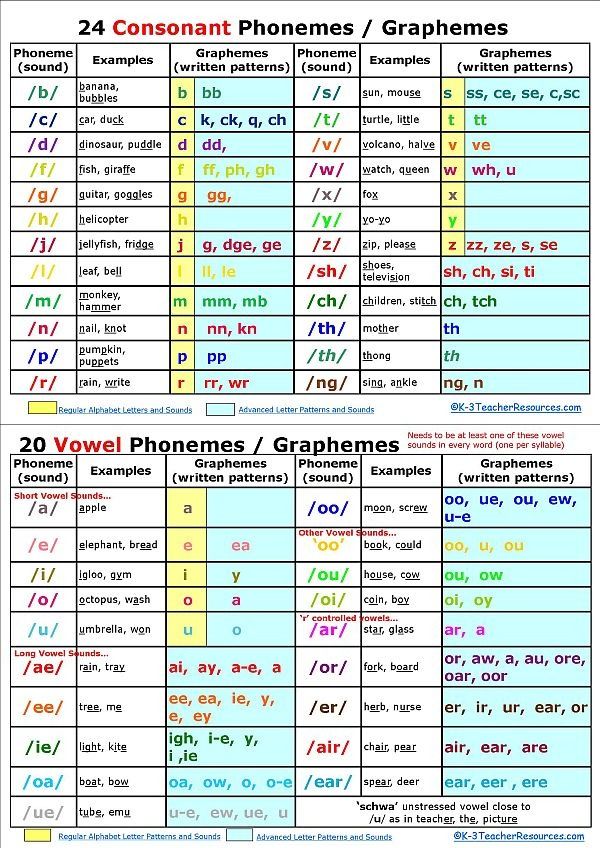
Consonant letters and consonant sounds of the Russian language - scheme, table
There are 21 consonant letters and 36 consonant sounds in Russian.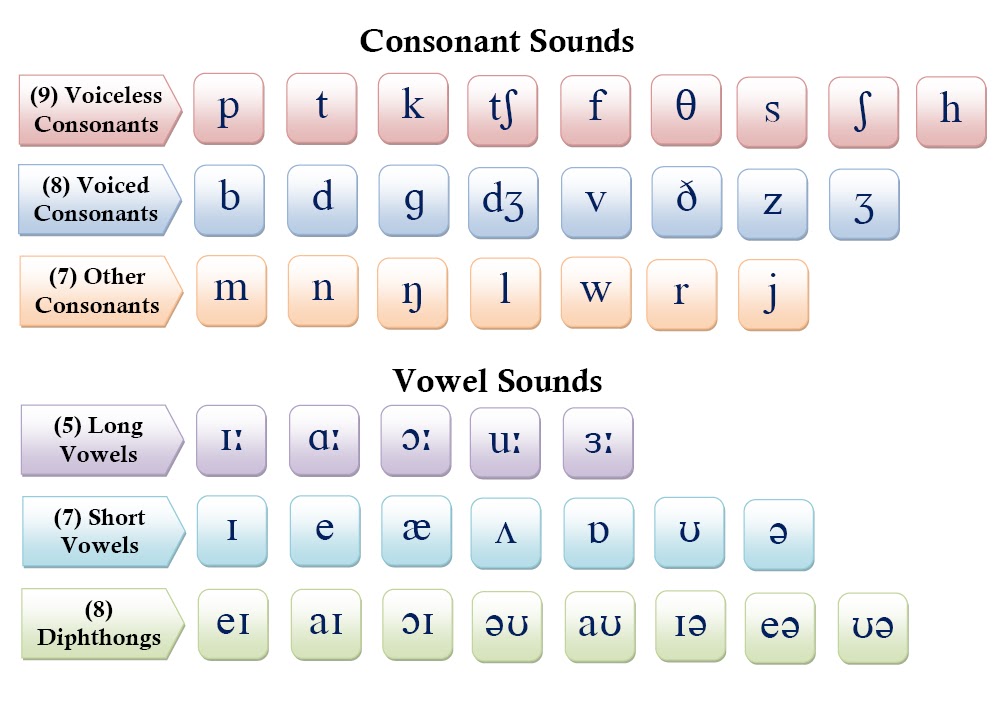 Consonants and their corresponding consonant sounds:
Consonants and their corresponding consonant sounds:
b - [b], c - [c], d - [g], d - [d], f - [g], d - [d], s - [h] , k - [k], l - [l], m - [m], n - [n], n - [n], p - [p], s - [s], t - [t], f - [f], x - [x], c - [c], h - [h], w - [w], u - [u].
Consonants are divided into voiced and voiceless, hard and soft. They are paired and unpaired. There are 36 different combinations of consonants in terms of pairing-unpairing of hard and soft, deaf and voiced: deaf - 16 (8 soft and 8 hard), voiced - 20 (10 soft and 10 hard).
Scheme 1. Consonant letters and consonant sounds of the Russian language.Hard and soft consonants
There are hard and soft consonants. They are divided into paired and unpaired. Paired hard and paired soft consonants help us distinguish between words. Compare: horse [kon '] - con [kon], bow [bow] - hatch [l'uk].
For understanding, let's explain "on the fingers". If a consonant letter in different words means either a soft or a hard sound, then the sound is paired. For example, in the word cat, the letter k denotes a hard sound [k], in the word whale, the letter k denotes a soft sound [k ']. We get: [k] - [k '] form a pair of hardness-softness. Sounds for different consonants cannot be attributed to a pair, for example [v] and [k '] do not make a pair in hardness-softness, but make a pair [v] - [v ']. If a consonant is always hard or always soft, then it belongs to unpaired consonants. For example, the sound [g] is always solid. There are no words in Russian where it would be soft [zh']. Since there is no pair [w] - [w ’], then it belongs to unpaired ones.
For example, in the word cat, the letter k denotes a hard sound [k], in the word whale, the letter k denotes a soft sound [k ']. We get: [k] - [k '] form a pair of hardness-softness. Sounds for different consonants cannot be attributed to a pair, for example [v] and [k '] do not make a pair in hardness-softness, but make a pair [v] - [v ']. If a consonant is always hard or always soft, then it belongs to unpaired consonants. For example, the sound [g] is always solid. There are no words in Russian where it would be soft [zh']. Since there is no pair [w] - [w ’], then it belongs to unpaired ones.
| unpaired | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Frudge | Soft | only solid | Only soft |
| [b], [B], [B], [g], [g], [g], [g], [g], [g], [g]. , [k], [l], [m], [n], [p], [r], [s], [t], [f], [x] | [b'], [c'], [g'], [d'], [h'], [k'], [l'], [m'], [n'], [p'] , [p'], [s'], [t'], [f'], [x'] | [w], [w], [c] | [h’], [u’], [y’] |
Voiced and voiceless consonants
There are voiced and voiceless consonants. Thanks to voiced and deaf consonants, we distinguish words. Compare: ball - heat, stake - goal, house - volume. Deaf consonants are pronounced with the mouth almost covered; when they are pronounced, the vocal cords do not work. For voiced consonants, more air is needed, the vocal cords work.
Thanks to voiced and deaf consonants, we distinguish words. Compare: ball - heat, stake - goal, house - volume. Deaf consonants are pronounced with the mouth almost covered; when they are pronounced, the vocal cords do not work. For voiced consonants, more air is needed, the vocal cords work.
Some consonants have a similar sound in terms of pronunciation, but are pronounced with different tonality - dull or voiced. Such sounds are combined in pairs and form a group of paired consonants. Accordingly, paired consonants are a pair of voiceless and voiced consonants.
- paired consonants: b-p, v-f, g-k, d-t, s-s, w-w.
- unpaired consonants: l, m, n, p, d, c, x, h, u.
| Parny | unpaired | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Little | Deaf | Only loud | only deaf |
| [b], [b '], [B'], [B '], [B' B], [B '], [B' B], [B '], [B'], BU d], [g'], [d], [e'], [g], [h], [h'] | [p], [p’], [f], [f’], [k], [k’], [t], [t’], [w], [s], [s’] | [d’], [l], [l’], [m], [m’], [n], [n’], [p], [p’] | [x], [x’], [c], [h’], [u’] |
Sonorant, noisy and hissing consonants
Sonorant - voiced unpaired consonants. There are 9 sonorous sounds: [th '], [l], [l '], [m], [m '], [n], [n '], [p], [p '].
There are 9 sonorous sounds: [th '], [l], [l '], [m], [m '], [n], [n '], [p], [p '].
Noisy consonants are voiced and voiceless:
- Noisy voiceless consonants (16): [k], [k'], [p], [p'], [s], [s'], [t] , [t'], [f], [f'], [x], [x'], [c], [h'], [w], [w'];
- Noisy voiced consonants (11): [b], [b'], [c], [c'], [g], [g'], [d], [e'], [g], [ h], [h'].
Hissing consonants (4): [g], [h’], [w], [u’].
Paired and unpaired consonants
Consonants (soft and hard, deaf and voiced) are divided into paired and unpaired. The tables above show the division. Let's summarize everything with the scheme:
Scheme 2. Paired and unpaired consonants. Scheme 2.1. Consonant sounds. Scheme 2.2. Paired consonants. Scheme 2.3. unpaired consonants.To be able to do phonetic analysis, in addition to consonants, you need to know vowels and the rules of phonetics.
Words with the letter ё must be written through ё. Phonetic parsing of the words "everything" and "everything" will be different!
Hard and soft consonants.
 How to determine? Table and examples
How to determine? Table and examples Free introductory Russian lesson
Sign up
You must have noticed that the same consonants can sound different. For example, in the words "childish" and "think" the letter "d" is not the same: we pronounce one softly, and the other firmly. It's time to figure out why this is happening. In this article, we will tell you what hard and soft consonants are and how to determine them so as not to make mistakes in phonetic analysis.
What consonants are called hard and soft
Consonants are those in which there is noise. When we pronounce them, the exhaled air encounters obstacles: the special position of the tongue, lips, teeth, palate. This is where the characteristic consonant sound comes from.
Consonants can be hard or soft, voiced or voiceless.
-
Soft consonants - sounds, during the pronunciation of which the middle of the tongue rises, and the tip approaches the teeth.
-
Solid consonants are sounds in which the tongue does not make additional movements.
Therefore, we pronounce hard and soft consonants differently. This can be seen if you say, for example, the words autumn and wasps . In the first case, the sound [s'] is soft and will sound appropriate. But in the second word [s] is a solid consonant sound, and this can also be heard from its sound.
Here are some more examples of the same consonants that represent hard and soft sounds.
| | | |
|---|---|---|
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
Interestingly, the hardness or softness of a consonant is related to which vowel follows it.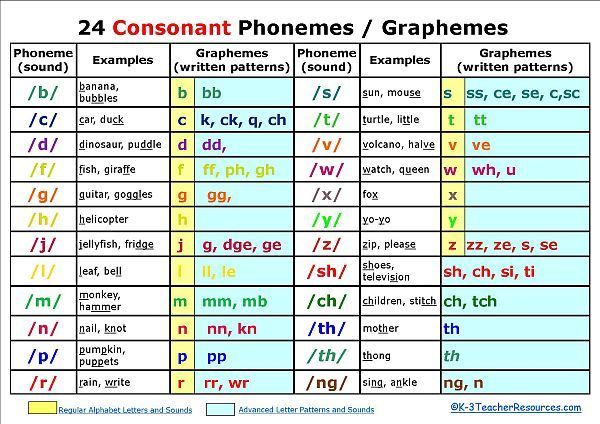 If after the consonant there are letters denoting the hardness of the sound ( a, o, y, s or e ), it will be hard, and if the letters denoting softness ( i, e, e, yu, and or b ), - soft. The exception is some borrowed words, for example pho[ne]tika .
If after the consonant there are letters denoting the hardness of the sound ( a, o, y, s or e ), it will be hard, and if the letters denoting softness ( i, e, e, yu, and or b ), - soft. The exception is some borrowed words, for example pho[ne]tika .
For example:
-
soft consonants: [d'e] revo, [v'e] black, when [b'e] reap, [v'a] knowledge, p[r'i] led, [l'u] dny etc. ;
-
hard consonants: me[ta], k[ry]sha, [du]mother, [me]r etc.
Test yourself!
Determine what consonant sound is used in these words - [d] or [d']: see, home, winner, businesslike, victory, pest, meditation, bear
Demo lesson in Russian
introductory lesson and find out what topics separate you from the "five" in Russian.
Paired and unpaired consonants in terms of hardness-softness
Consonants form pairs in terms of hardness-softness and are called, respectively, paired. Here is a table of all paired hard and soft consonants.
Here is a table of all paired hard and soft consonants.
| [b] | [c] | [g] | [d] | [h] | [s] | [k] | [l] | [m] | [n] | [p] | [p] | [t] | [f] | [x] |
| [b'] | [in'] | [g'] | [d'] | [z'] | [s'] | [k'] | [l'] | [m'] | [n'] | [n'] | [p'] | [t'] | [f'] | [x'] |
However, in Russian there are consonants that do not have such a pair: they can only be soft or only hard. Such sounds are called unpaired. For example, consonants [g], [w] and [c] do not have a pair, they are always solid. Even if in the word they are followed by letters that indicate the softness of consonants: i, e, e, u, and or b . For convenience, we collected all paired and unpaired consonants in the memo below. Save and enjoy!
Such sounds are called unpaired. For example, consonants [g], [w] and [c] do not have a pair, they are always solid. Even if in the word they are followed by letters that indicate the softness of consonants: i, e, e, u, and or b . For convenience, we collected all paired and unpaired consonants in the memo below. Save and enjoy!
Test Yourself
Test your understanding of hard and soft consonants and letters with the activities below.
Task 1
Name:
-
10 hard consonant words;
-
5 words that always contain hard consonants;
-
10 soft consonant words;
-
5 words with always soft consonants.
Assignment 2
Read the words below and mark hard consonant sounds in them, and indicate whether they are paired or unpaired in hardness-softness:
-
wind,
-
apple,
-
crawl,
-
Far East,
-
approaching,
-
cauterize,
-
pyramid,
-
appearance,
-
lure,
-
important,
-
cyclone,
-
athletic,
-
interferes.
Learn more