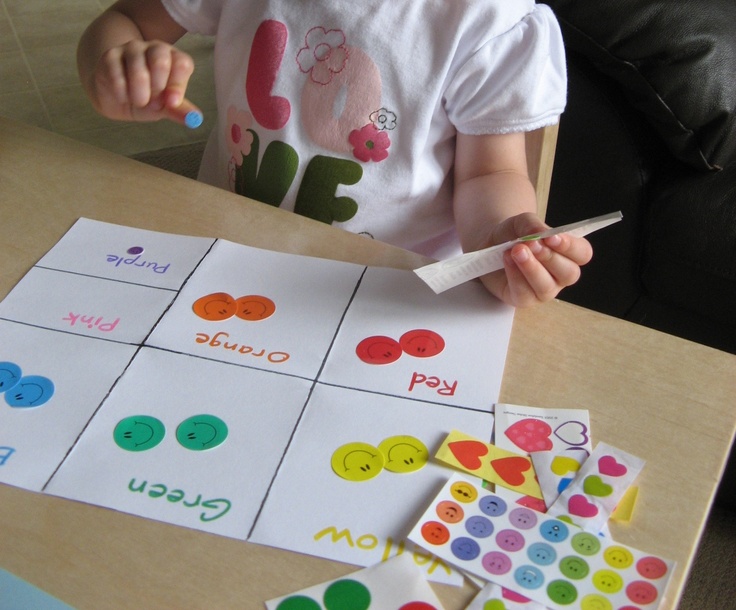
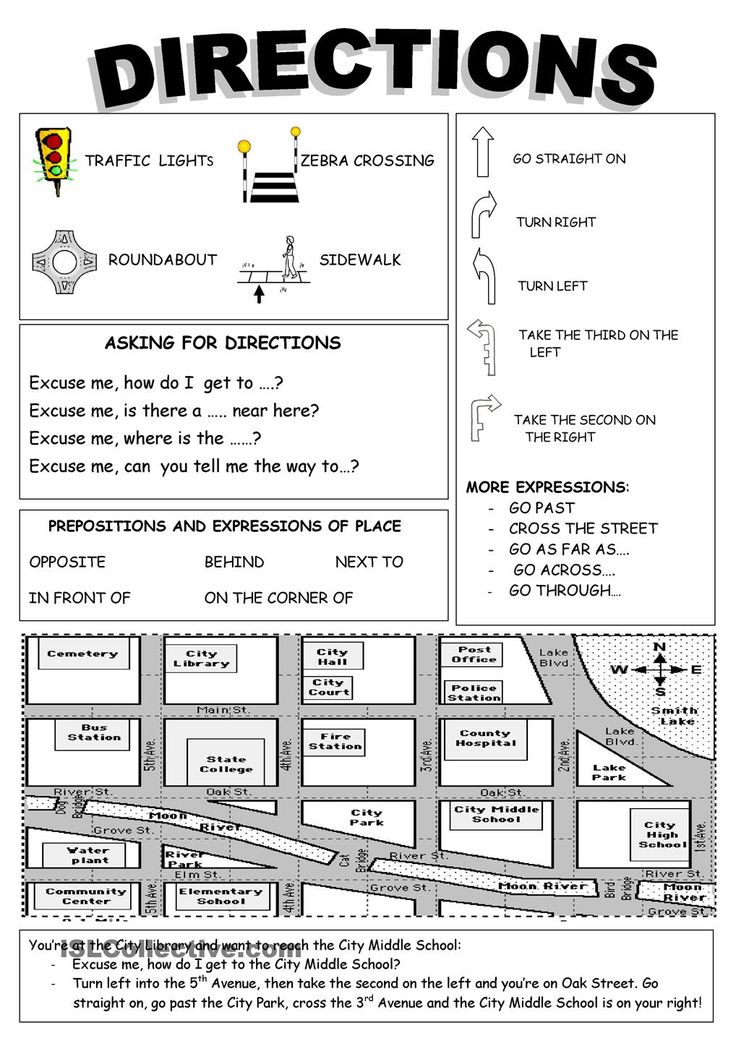
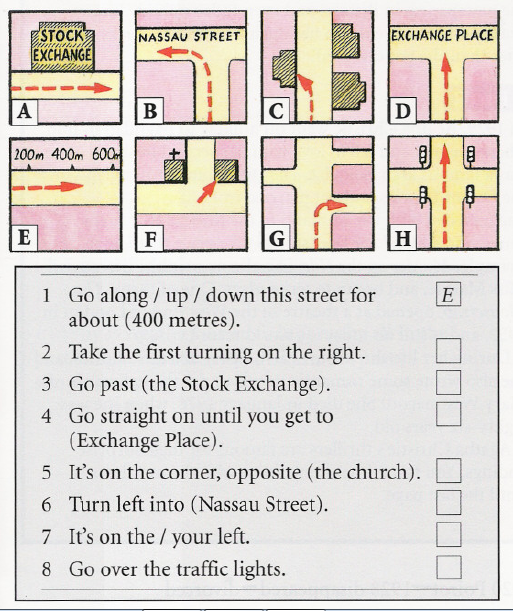
Following directions activity for elementary students
Lessons For Teaching Students To Follow Directions
As teachers, sometimes we give our students directions but then are surprised (or disappointed) that they don't follow them.
No names on papers? No titles on compositions? No answers rounded to the nearest tenth? We all face these problems in our students but we can correct some of these behaviors by teaching the skills required for students to be able to follow directions.
If you find yourself confronting such problems while grading papers, your students may not be paying attention to directions. Although most successful students recognize the importance of reading instructions thoroughly and following them, some students may master the skill slowly. Education World provides five intriguing lessons to help your students read, write, follow, and even evaluate directions. Included: Lessons that make following directions fruitful and fun!
Surprised to see a number of students suddenly leave the room only halfway through an exam, the professor followed them into the corridor. He discovered the students completing the balance of the questions while leaning against the walls. When he asked for an explanation, one student pointed to the third question, which asked "Describe Hemingway's The Old Man and the Sea. You may supply a drawing but please leave room to answer."
Sadly, this joke may not ring very true for many teachers today. Unfortunately, in the rush to complete assignments, students often race past directions to get to the "meat" of their work. In desperation, some teachers have hidden the answer to a simple question, or a hint to a tougher one, within the directions of an exam, just to encourage students to read the directions!
There are ways to help students recognize the value of reading instructions before beginning an assignment and following them throughout. Elementary teachers may hold a "bear hunt." Students bring in teddy bears, hide them within the classroom or school, and then create lists of directions for others to follow to locate the bears.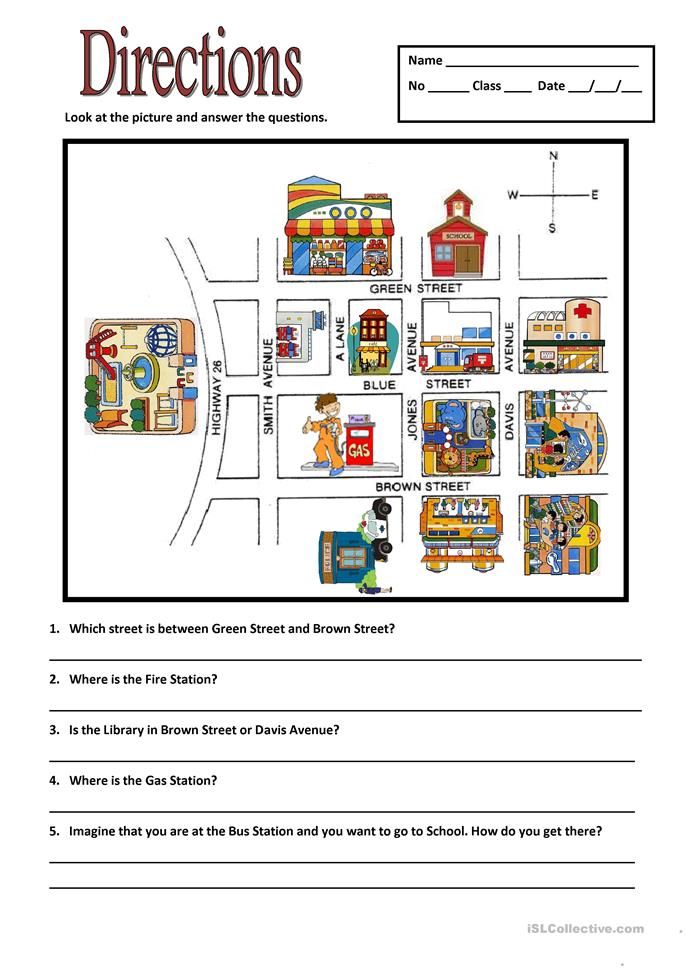 Teachers of older students may craft a page of instructions that students must read in their entirety before beginning to work and include as the last one, "Ignore all of the directions above and turn in your paper." The Internet provides even more opportunities to emphasize directions with lesson plans, how-to's, and recipes!
Teachers of older students may craft a page of instructions that students must read in their entirety before beginning to work and include as the last one, "Ignore all of the directions above and turn in your paper." The Internet provides even more opportunities to emphasize directions with lesson plans, how-to's, and recipes!
LESSONS FOR TEACHING STUDENTS TO FOLLOW DIRECTIONS
This week, Education World provides lessons about following directions. Click on each of the lesson headlines below for a complete teaching resource. Approximate grade levels are in parentheses.
How Well Do You Follow Directions?
This easy-to-use activity teaches valuable lessons about the importance of listening and following directions. (Grades K-12)
Phil's Fish Shop
Taking on the roles of new employees in a pet shop, students offer advice to customers, answer questions, and create a handbook of instructions for new fish owners. (Grades 3-8)
Critics of Cuisine
As food critics, students follow directions to create culinary delights and then critique the recipes and the flavor of their products. (Grades 3-12)
(Grades 3-12)
The Magician's Apprentice
Teaching the skill of following directions requires a little hocus-pocus in this lesson. Students re-create magic tricks, evaluate the clarity of the instructions, and teach an apprentice how to perform a trick. (Grades 3-8)
George Washington Teaches Map Directions
If students follow "directions," they'll have a picture of George Washington. (Grades 3-8)
Parachute Drop
Students experiment with gravity as they follow directions to create parachutes that will carry paperclip passengers safely to the ground. (Grades 1-3)
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES
30 Classroom Procedures to Head Off Behavior Problems
To keep your days running smoothly, establish consistency using these general procedures, daily tasks, and activities.
Free Following Directions Worksheets
Teach-nology provides several adorable coloring sheets with simple instructions to follow.
Last updated: 11/22/19
19 Activities for Middle School Students to Improve Following Directions
Whether 1-step directions or multi-step directions, students need practice and clear expectations. Students follow hundreds of directions every year at school and at home. In order to improve their ability to process oral directions and listening skills, you can incorporate fun activities into your school day.
Students follow hundreds of directions every year at school and at home. In order to improve their ability to process oral directions and listening skills, you can incorporate fun activities into your school day.
Try some of these 19 activities and notice the difference you will see over a period of time, as students improve with following directions.
1. Science Experiments
Incorporate your school curriculum into teaching kids to follow directions. Using science experiments in your school setting will improve academics, engage students, and strengthen students' following directions skills and abilities.
Learn More: Moms
2. Learn to Code
Further developing science skills and learning to code are beneficial for so many reasons. In addition to helping students learn computer science skills, they can also work on fine motor skills and improve following directions skills. Coding is ideal and appropriate for all grade levels.
Learn More: Teach Your Kids Code
3. Following Direction Logic Puzzle
This worksheet takes on the form of a riddle or secret code to be solved. For students who need a break from screen time, let them try to decipher the code by solving the riddles. The following directions worksheet is a good way to also encourage critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Learn More: Centervention
4. Paper Folding Activity
Simple instructions will be easy to follow and form a unique craft! This activity uses multi-step directions to have students create a paper masterpiece. Students will need to pay attention to directions and details to be successful in this awesome activity.
Learn More: Speech Snacks
5. Boat Craft
This fun and challenging activity allows some creative freedom but requires multi-step directions as well. This activity is great for upper elementary teachers or middle school teachers to use with their students.
Learn More: Pedia Staff
6. Building From Scratch
This activity will require key listening skills. Teaching students to make something with their hands is a great way to improve following directions. This is ideal for motor skills as well. Students may have a harder time working with their hands, so making the teacher aware of expectations is key.
Learn More: Moms
7. Coloring Worksheets
Giving the child directions for this printable activity is key. Lists of directions are included for students to read themselves or for the teacher to call out to them. Precise directions will help students know when to do each step in the process.
Learn More: Tam Aqua K12
8. Summer Olympics Following Directions Game
This adorable summer Olympics game is great for following directions. Perfectly themed activity sheets are designed for listening activities that focus on teaching students 1-step directions, 2-step sequential directions, and even 3-step sequential directions.
Learn More: Speech Time Fun
9. Leaf Craft
This leaf craft is a perfect hands-on activity for teaching students the importance of following directions. As they listen and perform each task in each step, students' following directions skills will improve with practice.
Learn More: Inspontaneous Speech
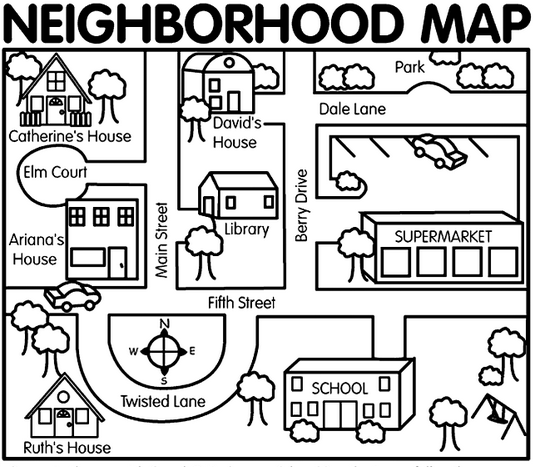
10. Following Directions Map
These easily printable maps are easy to use. There are several themes to choose from. Each is accompanied by a list of instructions. Students can read them or listen as teachers read them aloud.
Learn More: Making Learning Fun
11. Star Wars Directions Game
Fun games, like this Star Wars following directions game, are great for helping students practice how to properly follow directions. This interactive game allows students to work within groups and collaborate and interact with others.
Learn More: Teach This
12.
 Glyphs
Glyphs Glyphs are a fantastic resource for upper elementary and middle school students who need to practice following directions. Students will use white drawing paper to draw a picture, based on listening to directions and using what applies to them individually.
Learn More: Teach With Me
13. Before and After Statements
These before and after statements are great for older kids. This is a way to let students interact in groups and follow directions. On slips of paper, you will write in events and use them to complete this activity.
Learn More: Miss Barrett Speech Language
14. Listening Skills Holiday Sheet
These printable worksheets will be helpful for children with language skills needing improvement or for students to practice following directions. They are holiday themed and ideal for key listening skills and multi-step directions.
Learn More: Resources From Rachel
15.
 Can You Follow Directions Quiz Sheet
Can You Follow Directions Quiz Sheet This fun quiz-type sheet is helpful in assessing how well students follow directions. This is a great way to see if they can follow targeted directions and if not, where the breakdown occurs so you will know what to work on.
Learn More: The Worksheets
16. Following Directions: Directions Sheet
This directions sheet is a breakdown of 4-step directions. Each section requires students to look ahead to see what to do, when to do it, and how to do it. They are working to follow directions in each step.
Learn More: The Worksheets
17. Relay Races
Relay races get students up and moving. Teachers can customize this activity to get students to practice following directions in a nontraditional way. Students can follow directions and work with their teams to see who can win each challenge.
Students can follow directions and work with their teams to see who can win each challenge.
Learn More: Mr Physed
18. Following Direction Worksheet
This following directions activity is good for working on following directions and literal directions. Students can cut and place items in places, dependent on prepositional directions. This is especially good for bilingual students.
Learn More: The Worksheets
19. Paper Airplanes
Constructing paper airplanes is fun and ideal for practicing following directions. Let students use a template and guide for directions or orally tell them what to do. Either way, they will get good practice and finish with a nice end result.
Learn More: Speech Snacks
Principles and directions of the primary school teacher's work on the formation of the value of health in children. | Article on the topic:
Principles and directions of work of primary school teachers
on the formation of the value of health in children.
Elementary school teacher - subject and class teacher rolled into one. His work should be a purposeful and systematic activity, built on the basis of the education program of the educational institution. The new Federal State Educational Standard (FSES) for elementary school focuses teachers, first of all, on instilling in children the value of health and a healthy lifestyle culture.
The stable formation of the value of health in children is impossible without creating conditions for an independent and creative manifestation of a child. The very concept of education in this aspect is interpreted as “the formation of the image of the Self” and is based on special principles that can be called “health-creative”.
N. K. Smirnov lists the following principles, according to which work with younger schoolchildren should be built on the formation of the value of health and a healthy lifestyle:
1) the principle of formation of children's values for a healthy lifestyle;
2) the principle of natural conformity, which involves taking into account the age and individual characteristics of students based on the study of their needs and interests and, in connection with this, organizing their health-saving activities;
3) the principle of cultural conformity, that is, the inclusion of children in culture through specially oriented and organized health-creative activities;
4) the principle of focusing on the self-development of a culture of health, that is, recognition of the active principle in schoolchildren in health-creative activity;
5) the principle of health-creative activity - reliance on the active personal position of schoolchildren in the formation of a healthy lifestyle;
6) the principle of integration of educational influence, following which means the active interaction of all subjects of the pedagogical process - teachers, parents and children - aimed at ensuring the physical and mental health of each child.
To implement these principles, the primary school teacher must first of all create a comfortable environment for children. This will help children to fully realize their potential for maintaining health, developing individual abilities, inclinations and independence, developing the ability to manage and control their health-saving activities.
The managerial activity of the teacher in the formation of the value of health among students is recommended to be considered as a logical cycle. This cycle is formed by such interconnected and sequentially replacing each other types of activities (functions) as: analytical, constructive, organizational and executive, preventive-correctional and reflective-evaluative activities.
These activities are shown schematically.
Interaction of the functions of the class teacher in the formation of the value of health
Analytical constructive
Reflective and organizational and
Assignment performer
Prevention-
Correctional
Analytic activities of an elementary school teacher is aimed at obtaining and studying information on the state of health, psychophysiological characteristics, moral qualities of children, their children family environment.
When preparing for lessons and extracurricular activities, the teacher's constructive activity comes to the fore. It determines:
- goals, objectives, content of lessons and activities to form the value of health among students;
- selection of teaching, educational, as well as health-saving methods, techniques and means of training and education.
Organizational and executive activities - the main in the implementation of the planned lessons and extracurricular activities. It consists of the following components:0003
- organization of the assimilation of educational material, taking into account the individual characteristics and capabilities of each student;
- creating a situation of success, a positive emotional mood, a favorable psychological climate in the classroom;
- application of health-saving technologies aimed at protecting all aspects of children's health.
The preventive and corrective activity of a primary school teacher is revealed in the special measures taken to prevent, eliminate or reduce deviations from the norms of medical or social health in children. Realizing the preventive function, the teacher solves such problems as:
Realizing the preventive function, the teacher solves such problems as:
- creating a psycho-emotional mood of students for work, mobilizing their psychological resources through psycho-gymnastics, music, movement, etc.;
- removal of psycho-emotional stress;
- prevention of mental and visual fatigue in children.
In addition to these aspects (they can be called applied), the teacher should focus on the most important task of shaping and correcting the spiritual and moral development of students' personality. Forms and methods of corrective action are determined depending on the degree of deviation and individual developmental features of children.
The reflexive and evaluative activity of the teacher contributes to the creation of the necessary conditions for self-knowledge and self-analysis by children of their actions, actions, intentions.
All of the listed functions of an elementary school teacher accompany the entire educational cycle - from preparing classes and extracurricular activities to summing up their results.
In accordance with the listed principles and functions, the following specific areas of activity of a primary school teacher in the formation of the value of health in children are built:
1) monitoring student health indicators;
2) disease prevention;
3) organization of psychological and theoretical support;
4) prevention of bad habits;
5) physical education;
6) spiritual and moral education.
Thus, these principles, functions and activities of a primary school teacher are necessary prerequisites for the formation of the value of health among younger students.
The managerial activity of the teacher in the formation of the value of health among students is recommended to be considered as a cycle formed by the following types of activities (functions) of the teacher, as: analytical, constructive, organizational and executive, corrective and reflective-evaluative. The target part is a necessary prerequisite for working with the value sphere of children.
Forms of extracurricular activities under the conditions of GEF IEO
Teachers' Council - a community for those who teach and study . Professionals grow with us.
Do you want to keep up with the world and trends, be the first to learn about new approaches, methods, learn how to apply them in practice, or even undergo retraining and master a new specialty? Everything is possible in our Training Center.
There are already more than 40 online retraining and additional education courses on our platform.
See
Forms of extracurricular activities under the conditions of GEF IEO
In accordance with the Federal State Educational Standard for Primary General Education (FSES IEO), the main educational program of primary general education is implemented by an educational institution, including through extracurricular activities.
Extracurricular activities of students, as well as activities within the lessons, are aimed at achieving the results of mastering the main educational program of the school.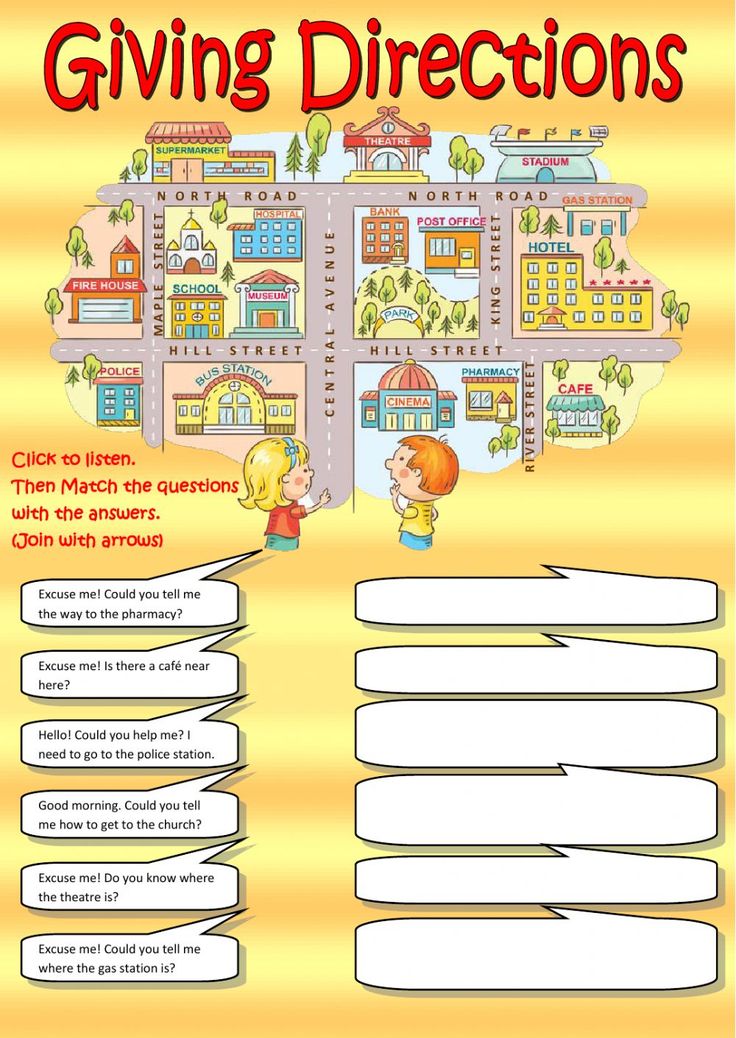 Particular attention in the second generation GEF IEO is focused on achieving personal and meta-subject results, which determines the specifics of extracurricular activities, during which the student not only and not even so much should learn how to learn to act, feel, make decisions, etc.
Particular attention in the second generation GEF IEO is focused on achieving personal and meta-subject results, which determines the specifics of extracurricular activities, during which the student not only and not even so much should learn how to learn to act, feel, make decisions, etc.
The purpose of organizing extracurricular activities in accordance with the Federal State Educational Standard of the IEO is to create conditions for students to achieve the social experience necessary for life in society and to form a system of values accepted by society, to create conditions for the multifaceted development and socialization of each student in their free time from study; creation of an educational environment that ensures the activation of social, intellectual interests of students, the development of a healthy, creatively growing personality, with a formed civic responsibility and legal self-awareness, prepared for life in new conditions, capable of socially significant practical activities.
Extracurricular activities of an educational institution are aimed at achieving educational results:
- students acquire social experience;
- formation of a positive attitude towards basic social values;
- acquisition by schoolchildren of the experience of independent social action.
The planned results of mastering the program of extracurricular activities include:
- personal results - the readiness and ability of students for self-development, the formation of motivation for learning and cognition, the value-semantic attitudes of primary school graduates, reflecting their individual and personal positions, social competencies, personal qualities; the formation of the foundations of Russian, civic identity;
- meta-subject results - mastered by students UUD (cognitive, regulatory and communicative).
In addition, extracurricular activities in elementary school allow the teaching staff to solve a number of very important problems. 0131 tasks :
0131 tasks :
- to ensure a favorable adaptation of the child in school;
- optimize student workload;
- improve the conditions for the development of the child;
- take into account the age and individual characteristics of children.
The structure of extracurricular activities
Extracurricular activities in elementary school are carried out through:
- curriculum of an educational institution;
- additional educational programs of a general education institution;
- educational programs of institutions of additional education for children;
- cool guide.
Directions, types and forms of extracurricular activities
According to the Federal State Educational Standard of the IEO of the Russian Federation, the organization of classes in the areas of extracurricular activities is an integral part of the educational process at school. Hours allocated for extracurricular activities are used at the request of students and in forms other than the lesson system of education.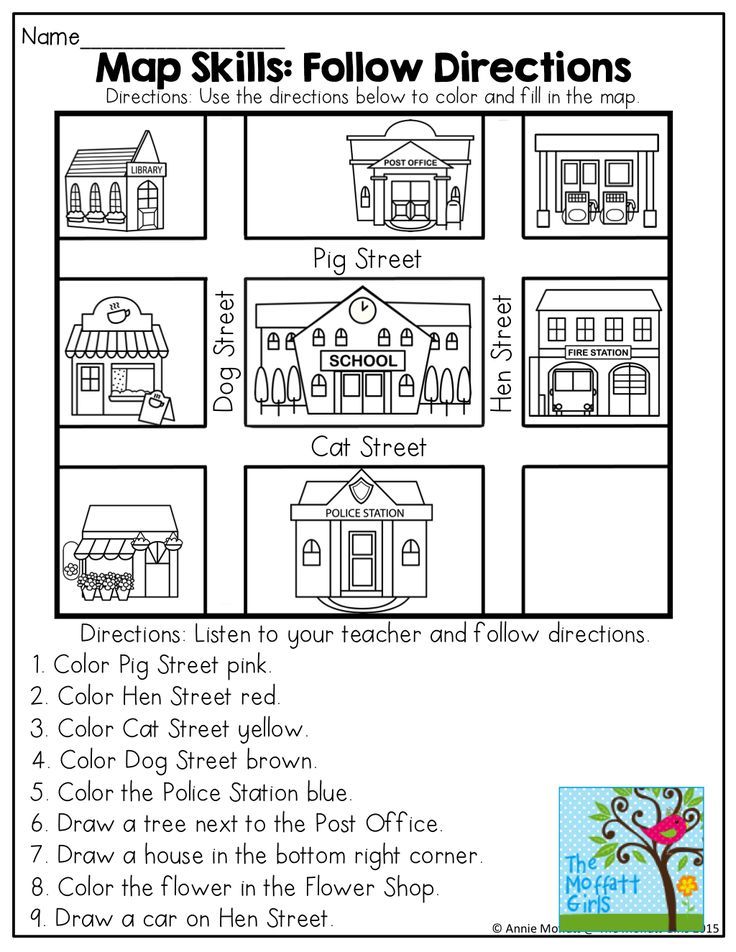 The Federal State Educational Standard of the IEO of the Russian Federation determines the main directions of extracurricular activities.
The Federal State Educational Standard of the IEO of the Russian Federation determines the main directions of extracurricular activities.
Directions, types and forms of extracurricular activities are very closely interconnected.
Areas of extracurricular activities:
- Sports and recreation
- Spiritual and moral
- General Intellectual
- General cultural
- Social
Types of extracurricular activities:
- Gaming activities
- Cognitive activity
- Problematic - valuable communication
- Leisure - entertainment activities
- Artistic creation
- Social creativity
- Labor activity
- Sports and recreation activities
- Tourism and local history activities
Forms of extracurricular activities:
- Circle
- Studio
- Section
- Club
- Association
- Optional
- Scientific Society
- Conference
- Slet
- Game
- Competition
- Tournament
- Meeting
- Concert
- Performance
- Practice
- Excursion
- Cult trip
- Camping trip
- Subbotnik
- Landing
Forms of extracurricular activities in areas:
Sports and recreation:
- Visiting sports sections
- Organization of excursions, Health Days and other sports competitions.
- Conducting health talks.
- Application of game moments, physical education minutes in lessons, exercises before lessons.
- Dynamic pauses and walks in elementary school.
- Participation in sports competitions.
- The work of the summer health camp day stay.
General cultural:
- Organization of excursions to theaters and museums, exhibitions of children's drawings, crafts and creative works of students;
- Conducting thematic classes on the aesthetics of the student's appearance, culture of behavior and speech;
- Participation in competitions, exhibitions of children's creativity of the aesthetic cycle at the level of school, district, region.
General intellectual:
- Subject weeks;
- Library lessons;
- Competitions, excursions, olympiads, conferences, business and role-playing;
- Project activities;
- Participation in research conferences;
- Development of projects for lessons.
Spiritual and moral:
- Meetings with veterans of the Second World War and labor, lessons of courage, visiting the school museum.
- Exhibitions of drawings.
- Design of newspapers about the military and labor glory of Russians,
- Themed class hours.
- Preparation for participation in the military sports game "Zarnitsa".
- Patriotic song festivals, parades of formation and song.
Social:
- Subbotniks.
- Work at the school site.
- Breeding and care of indoor plants.
- "Plant a Tree", "White Flower", "Feed the Birds", etc.
Forms of extracurricular activities by type:
Verbal-logical
The main means of influence is the word (persuasion with a word), which evokes response emotions in children.
- Talks on various topics
- Discussions
- Assemblies
- Conferences
- Lectures
The main thing here is the exchange of information, messages from teachers, students and other adults. Discussion of problematic issues.
Discussion of problematic issues.
Figurative art forms
- Concerts
- Performances
- Holidays
- KTD
The main means of influence is a joint, mainly aesthetic experience. The main thing here is to evoke strong, deep and ennobling collective emotions.
Employment forms of extracurricular activities
- Work at the school site
- Work on the design and cleaning of the office
- Houseplant Care
- Organization of duty at recess and in the school canteen
- Help for the school librarian
- Labor troops
In modern conditions, it is necessary to emphasize the personal significance of work, when the child realizes that the acquired skill will be useful to him in life, when he is interested in the result of his work there.
Game (leisure) forms of work
- Joint holidays
- Preparation of concerts, performances
- Week of theater, dance, vocals
- Watching and discussing films, performances
- Competitions
- Competitions
- KVNy
- Hiking trips
- Excursion walks in the park
- Excursion trips
The role of play in the organization of leisure occupies an important place in the life of a child, and therefore is considered by teachers as one of the main means of education. Games can be sports, educational, competitive, competitive, intellectual, etc.
Games can be sports, educational, competitive, competitive, intellectual, etc.
Psychological forms
- Lectures
- Conversations
- Discussions
- Psychological exercises
- Consulting
- Trainings
In forms of this type, the main means of influence are elements of psychological training, methods of practical psychology, individual and group psychotherapy. These forms require special knowledge and skills.
Results of extracurricular activities
All types, directions and forms of extracurricular activities of students at the level of primary general education are strictly focused on educational results.
The educational result of extracurricular activities is the direct spiritual and moral acquisition of the child through his participation in one or another type of activity.
The educational effect of extracurricular activities is the influence (consequence) of one or another spiritual and moral acquisition on the development of the child's personality.
Levels of results of extracurricular activities
First level. 1st class
The student knows and understands social life
Acquiring social knowledge by a schoolchild (about social norms, about the structure of society, about socially approved and unapproved forms of behavior in society, etc.), understanding of social reality and everyday life. Achieved in cooperation with a teacher
Second level. 2-3 grades
The student appreciates social life
Getting a student experience of experiencing and the formation of positive attitudes of schoolchildren to the basic values of society (person, family, Fatherland, nature, peace, knowledge, work, culture). Achieved in a friendly children's environment.
Third level. 4th grade
The student acts independently in public life
Obtaining by the student the experience of independent social action. It is achieved in interaction with the social subject.