Helping reading fluency
How to Improve Reading Fluency for Better Comprehension
You’ve spent years reading storybooks, store signs, and cereal boxes to your child. But now that they're learning to read out loud by themselves, story time might feel like new territory. When your growing reader furrows their brow with every word and stumbles through most sentences, there are certain steps you can take to set them up for lifelong reading success.
Reading fluency is the ability to read out loud accurately, at a good pace (not too slow or too fast), and with expression. “Although it’s typically measured in school when children start reading on their own, such as at the end of first grade, reading fluency is something you can start working on with them even before then,” says Helen Maniates, Ph.D., associate professor of teacher education at the University of San Francisco.
And it certainly pays to, because reading skills can help your child get more out of every subject in school. “Reading fluency contributes to reading comprehension,” says Maniates. “When children read slowly, don’t pay attention to punctuation, or struggle with particular words, they lose track of the ideas in the text.” Set your child up for academic success with these easy — and fun! — reading approaches.
1. Show them your own fluent reading.
The more often your child hears fluent reading, the more likely they are to pick it up. “Start by reading a paragraph or a full page from a book, and then ask your child to read it,” says Brook Sawyer, Ph.D., an associate professor focusing on language and literacy development at the College of Education at Lehigh University. “When you provide that model, it’s an opportunity for the child to get familiar with the story, understand the pacing, and then mimic you.”
As you model, channel your high school drama class: Read with exuberant, Oscar-worthy expression and pause at the appropriate times (at commas, periods, etc.) to demonstrate the cadence of our language. It’s also helpful to play audiobooks in the car to squeeze in extra modeling time when you’re on the go, says Sawyer.
2. Teach your child how to track words.
If you’ve ever learned a new language, you know how difficult it can be to decipher where one word ends and the next begins when listening to a conversation. Your little learner might feel the same way when they try to follow along during story time. That’s where tracking — or running your finger under words as you read them — comes in handy. You can track while you’re reading to your child, or ask them to track when they're reading out loud.
“When kids are first learning to read, it’s really important for them to touch each word to understand the correspondence between the spoken and written language,” says Maniates. “It’s a stepping-stone strategy. Eventually, they’ll be able to tackle larger phrases without reading word by word.” To make tracking words more fun for your child, equip them with plastic Martian or witch fingers!
3. Try choral reading together.
Not to worry: No singing skills required! Choral reading simply means you read a story out loud, and ask your child to read along with you at the same pace. This helps them understand what fluent reading feels like, and gives them the chance to practice it themselves at your pace, says Sawyer. It’s OK if you’re a tiny bit ahead of them — just be sure to pick a book that they can already read themselves. That way, they're working on pacing and accuracy rather than decoding new words.
This helps them understand what fluent reading feels like, and gives them the chance to practice it themselves at your pace, says Sawyer. It’s OK if you’re a tiny bit ahead of them — just be sure to pick a book that they can already read themselves. That way, they're working on pacing and accuracy rather than decoding new words.
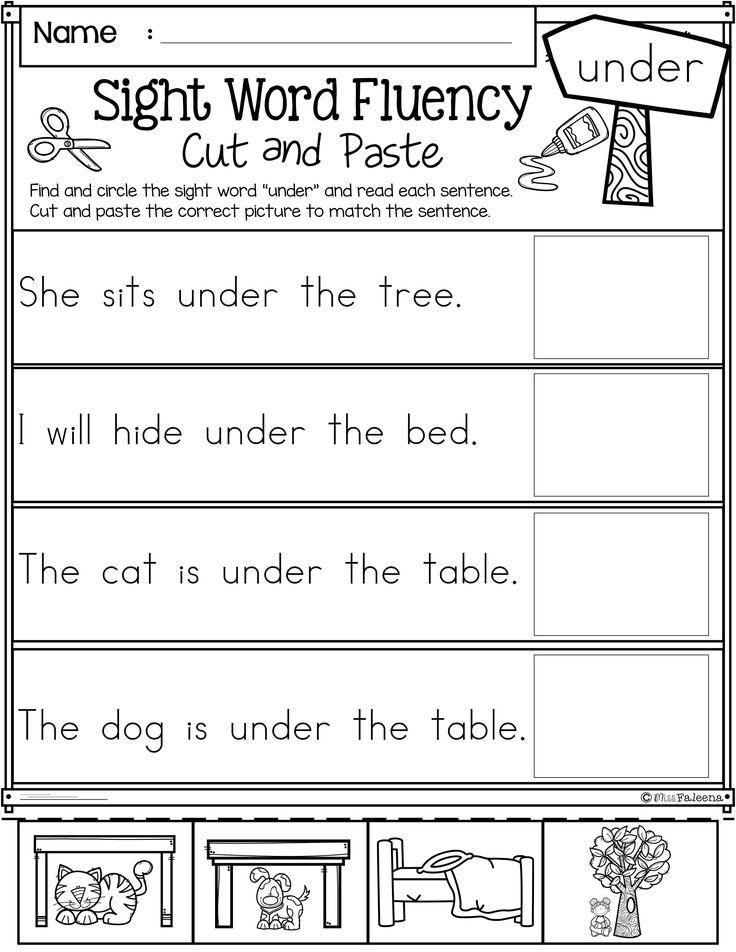
4. Focus on sight words.
You may notice that your child struggles with certain words like “walk” or “house,” also known as sight words. “These are words that are not decodable by sounding them out phonetically,” says Maniates. “They often overlap with high-frequency words, which are those that appear very often in children’s texts.” When your child memorizes what these words look like and can instantly recognize them, they won’t have to spend valuable reading time (and brainpower!) trying to sound them out.
Turn teaching sight words into a game: Spell the words out with magnetic letters; write them on a large piece of paper and ask your child to splat the correct word with a fly swatter when you say it; or use activity packs to help them easily learn them anywhere.
5. Recruit a friendly audience.
Just like us grown-ups, kids are more likely to fumble over their words when they feel nervous or uncomfortable. Set up an inviting stage for them to practice reading stories out loud by creating an audience out of their favorite stuffed animals or recruiting your family pet to listen along. “Some kids really don’t like to read in front of other people, either because they feel shy or feel pressure around it,” says Sawyer. “Start by reading a story together, and then for extra practice, set up a pretend audience that they can read out loud for.”
Eventually, this might also help your child read with more expression. “Reading out loud is almost like a performance, because you’re thinking about your voice, the volume, the pitch, the tone, and you might even be making facial expressions or gestures,” says Maniates. “We want kids to do this when they’re young because that’s how they’ll internalize stories when they read silently to themselves later on. ”
”
6. Record, evaluate, and repeat!
Every so often, when your child is reading out loud, record a passage and then listen to it together. You might celebrate that they read on pace, then record it a second time while aiming for more expression. “Set a specific goal for the session, and decide together what you want to do a little better,” says Sawyer. Just be sure to make it a relaxed setting (this is something you can do in jammies and on the sofa!) and focus on the positive strides your child is making.
It's also a good time to incorporate texts that are easy for your child to read. “Parents are often concerned with getting their kids ahead in reading, but when they’re struggling, going back to easier texts can be really helpful,” says Maniates. “It builds confidence and consolidates their skills so they can expand upon them.”
Shop books that build fluency skills below! You can find all books and activities at The Scholastic Store.
Five Evidence-Based Ways to Improve Reading Fluency in Elementary and Secondary Grades
Imagine this conversation between an instructional coach and a sixth-grade social studies teacher concerned about student performance on unit tests.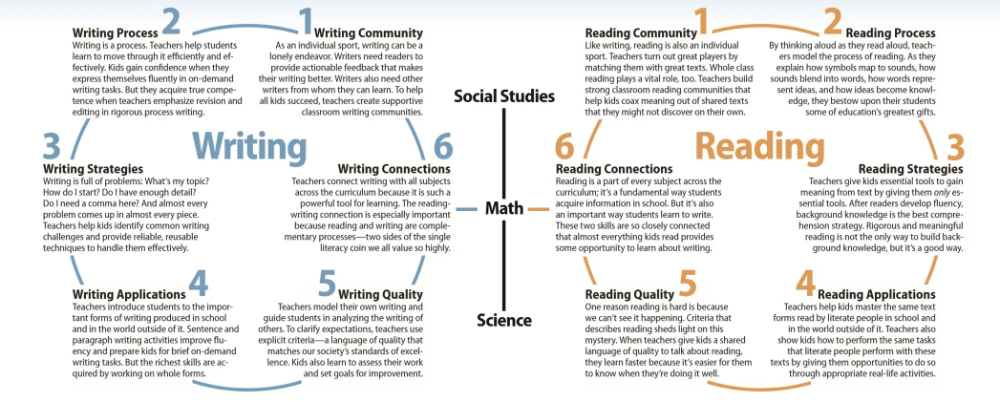
Instructional Coach: When we spoke last week, we decided that you would interview a few students to learn why they struggle with their social studies unit tests and talk to other teachers to see if they are noticing similar trends. What did you learn?
Teacher: I began by talking to colleagues, and they are experiencing similar things. I then spoke to a few students and learned that they often struggle on unit tests because they have difficulty reading and understanding the questions.
Coach: How do students perform when working on daily activities?
Teacher: Students usually do well and can answer the questions that I ask about what we are reading. This is why I am confused by their poor performance on the unit tests.
Coach: When students are reading during daily activities, what do you notice?
Teacher: Well, some have low reading levels, so I often read the material to them.
Coach: Do you read the material when it comes time for the test?
Teacher: No, I want to see what they can do independently.
Coach: What I heard you say is that students perform well on daily activities when you read the material to them, but they struggle when they are expected to read and answer questions on their own. We may need to dig into their reading fluency skills and help them develop their skills in this area in order to help them perform better on their social studies unit tests.
Teacher: I see what you mean, and I will need help thinking about how to better support my students’ reading fluency.
In this blog post, we focus on reading fluency in elementary and secondary classrooms. Reading fluency is a critical reading skill that facilitates reading for understanding and is our ultimate goal for teaching reading. It involves reading with appropriate rate, accuracy, and expression (National Reading Panel, 2002). Pikulski and Chard defined reading fluency as “efficient, effective word-recognition skills that permit a reader to construct the meaning of text. Fluency is manifested in accurate, rapid, expressive oral reading and is applied during, and makes possible, silent reading comprehension” (2011, p. 510).
510).
The importance of reading fluency for students’ reading comprehension is further supported by a recent National Assessment of Educational Progress report (NAEP, 2021). The NAEP study found that oral reading fluency was consistently and positively related to fourth-grade students’ performance on the NAEP reading test, which measures reading comprehension and is used to evaluate our nation’s progress in reading. In particular, students who scored low on the NAEP reading test showed difficulty with reading fluency, word-level reading skills, and text comprehension. Despite the importance of reading fluency, many teachers may be unsure how to best support the students they teach who struggle with reading. In this blog post, we share five evidence-based recommendations for improving reading fluency among struggling readers.
5 Recommendations for Improving Reading Fluency Among Struggling Readers
1. Develop students’ ability to decode words.
Many students who struggle with reading fall behind early in their education because they struggle with skills such as letter identification, letter-sound correspondence, or word recognition. These underlying word-reading skills are foundational for reading fluency. For students with significant reading difficulties, this word-level instruction is key to unlocking passage-level reading fluency.
These underlying word-reading skills are foundational for reading fluency. For students with significant reading difficulties, this word-level instruction is key to unlocking passage-level reading fluency.
When teaching these skills, it is important to deliver instruction that is explicit and systematic. Instruction should be explicit in the sense that the teacher must implement familiar routines, include many examples, and explain each skill in ways that are clear, visible, and consistent for students. Instruction should be systematic in that it should move from easier to more complex, build on higher-utility skills and what students know, and be appropriate for the task or lesson goal. The "I do, we do, you do” model is often used to plan an explicit and systematic lesson.
What foundational reading skills are important to teach in each grade? Here are some examples (The Meadows Center for Preventing Educational Risk [MCPER], 2016) of specific activities teachers might use when teaching one or more of these skills (this is not meant to be an exhaustive list):
- Kindergarten: Introduce new and review previously learned letters and sounds; make or build words; introduce new and review previously learned high frequency words; use fluency practice with skills.
- Grade 1: Review phonological awareness skills; introduce sound, spelling partners, and morphemes; make or build words; introduce new and review previously learned high-frequency words; use fluency practice with skills.
- Grade 2: Make or build words; introduce new high-frequency words; use fluency practice with skills.
- Grades 3–5: Make or build words; use fluency practice with skills.
2. Ensure that each student reads connected text every day to support reading rate, accuracy, and expression.
Students may be proficient enough at reading lists of individual words, but they must also practice their skills in books or passages (i.e., connected text) to become fluent readers. Reading familiar books or passages allows students’ skills to become more automatic, which enables them to free up their attention to connect ideas in the text to background knowledge and increase their reading comprehension.
To get better at reading requires more time reading. When developing lesson plans, it is important that teachers identify opportunities for students to practice reading. This can, of course, happen in English and language arts classes, but it also should happen across content areas. Students often are motivated to read more when they are interested in the reading material and when they have adequate support.
When developing lesson plans, it is important that teachers identify opportunities for students to practice reading. This can, of course, happen in English and language arts classes, but it also should happen across content areas. Students often are motivated to read more when they are interested in the reading material and when they have adequate support.
At home, parents can encourage more reading each day by scheduling dedicated time for students to read independently (i.e., reading material independently with 95% to 100% accuracy) and by establishing a purpose for reading. For example, children can select a book to read that is of interest to them, and each day they can document what they read in a reading log. Daily entries in this reading log might include recording progress toward achieving a goal (e.g., increasing the number of words or pages read each day), brief summaries, connections made, difficulty vocabulary encountered, etc. Entries could be used to create a presentation to be shared with a student’s peers. Schoenbach, Greenleaf, and Murphy’s Reading for Understanding (2012) provides additional recommendations for reading logs (what they refer to as metacognitive logs).
Schoenbach, Greenleaf, and Murphy’s Reading for Understanding (2012) provides additional recommendations for reading logs (what they refer to as metacognitive logs).
3. Model reading fluency for your students.
Read-alouds are a powerful and useful instructional tool that model important foundational skills (i.e., prosody, vocabulary, and that print conveys a message) for children in a way that explicitly and unambiguously teaches something (Roberts & Burchinal, 2001; Trelease, 2001). When paired with think-alouds, teachers can promote vocabulary acquisition and help students make sense of or make connections between ideas beyond the classroom (Beck, McKeown, & Kucan, 2013; Gold & Gibson, 2001; Massaro, 2017).
Read-alouds can be used to model reading fluency. For example, before reading a text, a teacher might say, “Follow along as I read. Listen to how I read the words at a steady pace and how I pause to take a quick breath at each period." Modeling reading fluency has been found to be an effective tool for improving reading fluency. Teachers or parents who are interested in incorporating this modeling within their read-aloud routines may find this read-aloud resource, developed by The Meadows Center for Preventing Educational Risk, to be helpful.
Teachers or parents who are interested in incorporating this modeling within their read-aloud routines may find this read-aloud resource, developed by The Meadows Center for Preventing Educational Risk, to be helpful.
4. Take advantage of repeated reading routines.
Repeated reading is reading and rereading material to match the (a) purpose of the lesson and (b) student’s reading ability. For example, if the purpose is to enhance reading rate, then select a text that is appropriate and at the student’s decoding level. The teacher and student can monitor the number of words read correctly and can discuss the story to check comprehension. Discussions after each read can change to focus on a different reading element (e.g., character, main idea).
Teachers who are interested in this routine can find lesson plans here that show how this routine can be taught following an explicit instructional approach (see page 59 of the PDF, which is page 196 in the original resource book).
- Students select a passage.
- The higher-performing student reads the lower-performing student’s passage first to provide a model.
- The lower-performing student practices reading through the passage three times with their partner. The partner marks student errors on a copy of the passage and provides feedback on student errors.
- Students read the passage a fourth time as quickly as possible. Partners time the student reading for 1 minute. This time is referred to as the “first timing.”
- Students record progress on their individual graphs in their workbooks.
5. Set fluency goals and use progress-monitoring data to inform instruction.
The combination of reading accuracy and rate (automaticity) is considered a student’s oral reading fluency (ORF). Beginning in the middle of first grade, ORF is a complex skill that develops gradually, measures accuracy without regard to reading rate, and is one way to screen students quickly to monitor progress and determine whether additional support is needed. Measuring ORF provides valuable information about the child’s ability to read connected text fluently. Below are a few resources to use when setting fluency goals and monitoring student progress:
Measuring ORF provides valuable information about the child’s ability to read connected text fluently. Below are a few resources to use when setting fluency goals and monitoring student progress:
- Reading Fluency Goal Setting template (Iowa Reading Research Center, n.d.a)
- Oral Reading Fluency Reflection Guide (Iowa Reading Research Center, n.d.b)
- Oral Reading Fluency Norms (Reading A-Z, 2021
Tracking or monitoring progress is important to determine student reading growth and is closely linked to both screening and diagnostic assessment. Progress monitoring, administered weekly or biweekly, is a systematic process to formatively track the progress of student growth of an intervention skill (e.g., fluency). It additionally provides information about the appropriate levels of text to use (The University of Texas Center for Reading and Language Arts, 2002). Progress monitoring can help you answer a number of questions, such as: Is learning happening? Is my teaching helping students make progress?
Take Action
- Review current or historical school and classroom data to determine how information and resources included in this blog might be used to further student learning.

- Choose one of the resources, routines, or strategies to implement in your classroom. Write and share reflections. How did the routine improve or strengthen your current practices? How did students respond differently to this routine versus what you normally do?
- Select one of the five recommendations about which to learn more. Based on this new learning, make adjustments in one of your current classes to target one or more student’s needs.
- Review one or more of the additional resources below and choose one to add to your existing classroom practices.
| Resource | Content |
|---|---|
| Fluency Practice: Techniques for Building Automaticity in Foundational Knowledge and Skills Authors: Datchuk & Hier, 2019 Audience: Elementary | Learn about the components of fluency practice, gain access to a checklist of steps to use when implementing a fluency practice session (i. |
| FCRR Student Center Activities Author: Florida Center for Reading Research, 2004-2010 Audience: Elementary | Materials to use during whole- or small-group instruction, centers/workstations, or for extended learning. Fluency materials include (but are not limited to) letter recognition, letter-sound correspondence, word parts, words, phrases, chunked text, and connected text. |
| Effective Fluency Instruction and Progress Monitoring Author: The University of Texas Center for Reading and Language Arts, 2004 Audience: Elementary | Gain access to a presentation focused on fluency instruction, as well as strategy sets to teach letter sounds, regular word reading, irregular word reading, and fluency in connected text. |
| Essential Reading Strategies for the Struggling Reader: Activities for an Accelerated Reading Program Author: The University of Texas Center for Reading and Language Arts, 2001 Audience: Elementary, Secondary | Learn about and access supplemental literacy resources to support the five components of reading instruction. |
| Sight Word Fluency Lists Author: The Meadows Center for Preventing Educational Risk, 2017 Audience: Elementary | Access lesson materials that focus on sight word fluency and word recognition. Use materials for routines such as reading words aloud as a group, partner reading, repeated reading, paired reading, and more. |
| 10 Key Policies and Practices for Reading Intervention (The Key Strategies in Action 2: Use universal screening to identify students experiencing reading difficulties) Author: The Meadows Center for Preventing Educational Risks, 2020 Audience: Elementary, Secondary | Learn about policies and practices for reading intervention, as well as key strategies in action. |
References
Beck, I., McKeown, M., & Kucan, L. (2013). Bringing words to life: Robust vocabulary instruction (2nd ed.). The Guilford Press.
Datchuk, S., & Hier, B. (2019). Fluency practice: Techniques for building automaticity in foundational knowledge and skills. Exceptional Children, 51(6), 424-435.
Duke, N. & Pearson, D. (2008). Effective practices for developing reading comprehension. Journal of Education, 189(1/2), 107-122.
Florida Center for Reading Research. (n.d.). FCRR student center activities. https://www.fcrr.org/student-center-activities
Glaser, D. (2002). High school tutors: Their impact on elementary students’ reading fluency through implementing a research-based instruction model [Doctoral dissertation, Boise State University]. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global.
ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global.
Gold, J., & Gibson, A. (2001, June 14). Reading aloud to build comprehension. Reading Rockets. https://www.readingrockets.org/article/reading-aloud-build-comprehension
Iowa Reading Research Center. (n.d.a ). Oral reading fluency skills goal setting template. https://iowareadingresearch.org/oral-reading-fluency-goal-setting-template
Iowa Reading Research Center. (n.d.b). Oral reading fluency reflection guide. https://iowareadingresearch.org/oral-reading-fluency-reflection-guide
Massaro, D. (2017). Reading aloud to children: Benefits and implications for acquiring literacy before schooling begins. The American Journal of Psychology, 130(1), 63-72.
The Meadows Center for Preventing Educational Risk. (2014). Read-aloud routine for building vocabulary and comprehension skills in kindergarten through third grade. https://meadowscenter.org/files/resources/FlipBook_Screen1. pdf
pdf
The Meadows Center for Preventing Educational Risk. (2016). Sample literacy blocks, K-5. https://buildingrti.utexas.org/instructional-materials/sample-literacy-blocks-k-5
The Meadows Center for Preventing Educational Risk. (2017). Sight word fluency lists. https://texasldcenter.org/lesson-plans/detail/sight-word-fluency-lists
The Meadows Center for Preventing Educational Risk. (2020). 10 key policies and practices for reading intervention. https://www.meadowscenter.org/files/resources/10Key_ReadingIntervention_WEB-Rev2.pdf
National Assessment of Educational Progress. (2021). The 2018 NAEP oral reading fluency study. https://nces.ed.gov/nationsreportcard/subject/studies/pdf/2021025_2018_orf_study.pdf
National Reading Panel. (2002). Teaching children to read: An evidence-based assessment of the scientific research literature on reading and its implications for reading instruction. https://www.nichd.nih.gov/sites/default/files/publications/pubs/nrp/Documents/report. pdf
pdf
Pikulski, J., & Chard, D. (2005). Fluency: Bridge between decoding and reading comprehension. The Reading Teacher, 58(6), 510-519.
Reading A-Z. (2021). Fluency standards table. https://www.readinga-z.com/fluency/fluency-standards-table/
Roberts, J., & Burchinal, M. (2001). The complex interplay between biology and environment: Otitis media and mediating effects on early literacy development. In S. B. Neuman & D. K. Dickinson (Eds.), Handbook of early literacy research (pp. 232-241). The Guilford Press.
Schoenbach, R., Greenleaf, C., & Murphy, L. (2012). Reading for understanding: How Reading Apprenticeship improves disciplinary learning in secondary and college classrooms. Jossey-Bass.
The University of Texas Center for Reading and Language Arts. (2001). Essential reading strategies for the struggling reader: Activities for an accelerated reading program. https://texasldcenter.org/files/lesson-plans/Essential_Strategies_web. pdf
pdf
The University of Texas Center for Reading and Language Arts. (2002). Effective instruction for struggling readers: Research-based practices.
The University of Texas Center for Reading and Language Arts. (2004). Effective fluency instruction and progress monitoring. https://meadowscenter.org/files/resources/Fluency_Guide.PDF
Trelease, J. (2001). The read-aloud handbook (5th ed.). Penguin Books.
5 Simple and Effective Ways to Improve Reading Fluency
Reading fluently means reading at a natural pace, with expression, and at the same time understanding what you read. How can you help your students and children learn to read fluently? Isn't it enough just to read more?
In fact, non-verbal reading (note: reading to oneself, not out loud) does not help people who have difficulty reading fluently. The National Reading Panel states: "Empirical studies show that independent non-verbal reading has little effect on the development of reading speed. " In this case, it is necessary to consider whether the student should continue to read in the wrong way in the hope of gradually improving his skills if he has difficulty reading?
" In this case, it is necessary to consider whether the student should continue to read in the wrong way in the hope of gradually improving his skills if he has difficulty reading?
This is very similar to learning to paint. Having received some useful advice from the teacher, the student begins to understand the basic techniques of painting. The teacher breaks down each step and then checks how each one works to make sure the students have understood everything correctly.
Should we do the same for our students - make sure they read diligently, progressing step by step, the way an art teacher approaches each student to make sure that our technique will lead us to the desired result? Would a student have a better understanding of the technique of the art of painting if he silently and clumsily tried to draw something on his own? This is exactly what happens to the student who does not talk about his reading problems.
Despite this, non-verbal reading plays an important role in a student's life. Once he reaches the level of fluent reading, he should continue to read everything that comes to hand at his usual speed.
Once he reaches the level of fluent reading, he should continue to read everything that comes to hand at his usual speed.
Here are the best ways to improve reading fluency:
-
Show an example of fluent reading: demonstrate how to read aloud correctly. Other adults can help with this too: tutors, parents, siblings, etc. In this way, the student will hear how the text should sound in order to get a clearer understanding of how speech is built, including correctly spaced pauses at the end of sentences, rising intonation when using questions, etc.
-
Reading aloud: have your students read aloud loudly and clearly, not necessarily fast. As you gain experience in reading and improve his skills, the speed will most likely increase as well.
-
Choral reading (or reading in unison): this is a group practice in which you read a passage of text to your students and they repeat it in unison. This provides group reading practice and can also help a child who is too shy to read aloud in front of others.

-
Reader's Theatre: This is a fun transformation of ordinary reading into a kind of performance. Each student should work as a team with their classmates, reading with expression and conveying the meaning of what is written. This will help improve not only reading efficiency, but also teamwork skills.
-
Praise for fluent reading: a little praise sometimes works wonders. Remember to also gently point out problem areas so that students know what to work on. Reading is extremely difficult for some, so do not forget to encourage them to continue their work!
Now that you know that independent non-verbal reading does not help students with reading difficulties, what approach would you take for literature lessons to make them more effective? Pay attention to the FAST FORWORD software package, which now includes the Reading Assistant Plus program, which is:
-
demonstrates a sample of correct reading (reads aloud to a student)
-
listens and analyzes how the child reads aloud
-
helps you practice the correct pronunciation of
-
helps build vocabulary
-
helps to understand the meanings of unfamiliar words
This is a kind of personal reading tutor built into your computer, and this program is very effective, especially for children who are not helped by silent reading.
Practice, backed by the right methods and the right support, is the key to the success of beginning readers.
Source
Fluent reading - recommendations for beginners
When parents pick up the alphabet, the image of a fluent reading child appears in their dreams. Everyone wants their child to be able to read at the speed of conversational speech, accurately and expressively. My son is a first grader, but he already reads fluently. In this we were helped by the recommendations of Noel Janis-Norton, which I want to talk about.
In this article you can find:
- recommendations for teaching the basics of fluent reading;
- reading difficult words;
- help in learning to read words of several syllables;
- work on errors due to inattention;
- Acceleration of reading fluency;
- the friendship of a child with a book - how to achieve this.
Recommendations for teaching the basics of fluent reading
Recommendation 1. Choosing a method. The problem of lack of fluent reading touched many children. Some parents hope that at school they will teach their children everything perfectly, but this is not so. If a child studies independently from the first school days, he will have a “great” opportunity to memorize mistakes and not complete all tasks. Therefore, at first it is better to control the completion of homework. Many schoolchildren need to improve their reading technique, and not only lagging behind students. Using the same books and methods as in school is ineffective, and here's why. The more techniques you teach, the more areas of the brain will be involved, and the speed of mastering the material and the formation of skills directly depends on this. That is why the same material must be studied in various ways, the more methods you apply, the higher the efficiency will be.
Choosing a method. The problem of lack of fluent reading touched many children. Some parents hope that at school they will teach their children everything perfectly, but this is not so. If a child studies independently from the first school days, he will have a “great” opportunity to memorize mistakes and not complete all tasks. Therefore, at first it is better to control the completion of homework. Many schoolchildren need to improve their reading technique, and not only lagging behind students. Using the same books and methods as in school is ineffective, and here's why. The more techniques you teach, the more areas of the brain will be involved, and the speed of mastering the material and the formation of skills directly depends on this. That is why the same material must be studied in various ways, the more methods you apply, the higher the efficiency will be.
Recommendation 2. Play to improve reading speed. Now I will tell you about my son and my favorite games - exercises that will be interesting and useful for both beginners in reading and elementary school students.
Gemini game.
This game is great for developing reaction speed. For her, you need to prepare - make two sets of cards. Choose 3-4 words that the child can read, write one word each on a piece of paper, and then duplicate the sheets with inscriptions - this way you will have two copies of one word. You put all the cards on the table and ask the child to find the twin words. You can complicate the game by adding words that differ in only one letter, for example: tok and tick; hand and river; sheep and candle. When the child already copes with the tasks quickly enough, it can be complicated by using a different font size and color, as well as writing one of the paired words in capital letters, and the second in block letters.
Total Recall Game
We play it if we have difficulty memorizing a definition or passage of a poem by heart. Since memorability directly depends on reading comprehension, we go from the opposite. On pieces of paper, I write down all the words from a difficult sentence and lay them out in random order. Then I ask the child to listen carefully as I read this sentence, and then collect the cards in the correct order. Thus, we do not memorize like parrots, but we learn by understanding the meaning of each word.
On pieces of paper, I write down all the words from a difficult sentence and lay them out in random order. Then I ask the child to listen carefully as I read this sentence, and then collect the cards in the correct order. Thus, we do not memorize like parrots, but we learn by understanding the meaning of each word.
Oral game "Scribbler".
In this game, participants exchange rhymes and then write down all the rhymes they hear. The winner is the one who remembers and writes more rhymes.
These games are not recommended for more than ten minutes, even if your child asks you to.
Suggestion 3. Sing karaoke more often. Choosing a song that you can confidently sing together is very important. A child who knows the words well will have time to sing at the right pace, and at the same time follow the text on the screen.
Reading difficult words.
There are two approaches to teaching reading.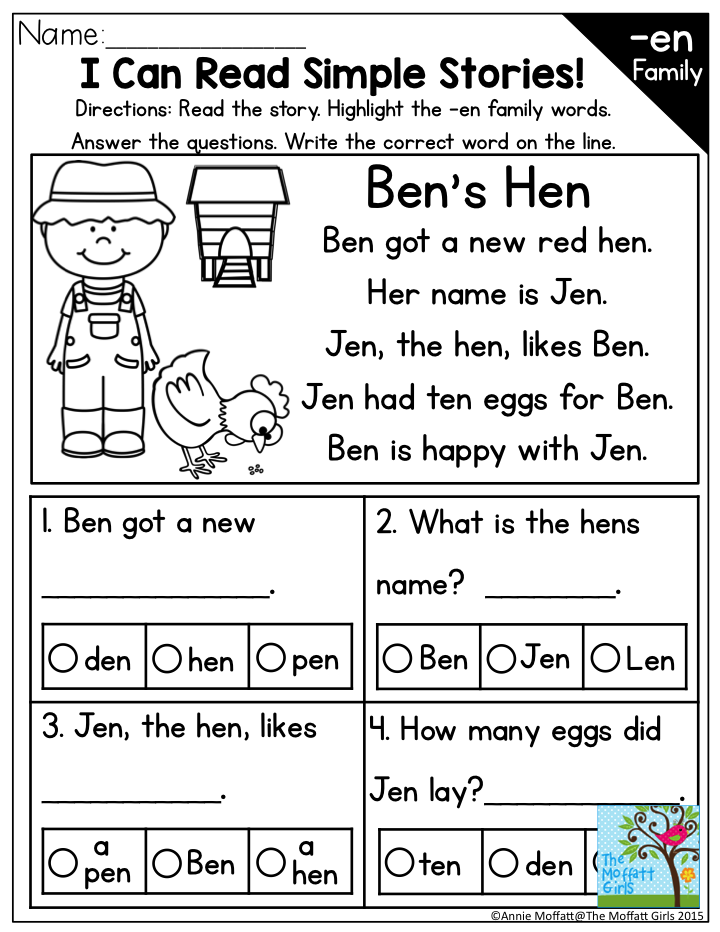 The first approach is based on the recognition of the word as a whole unit, the rules of phonetics are not explained. First, they are taught to read words on cards with the image of the word, then the child is given a very colorful book with simple words and a predictable plot. Encountering unfamiliar words, the child must guess from the clues of the illustrations or the context. The second approach to teaching reading is phonetic, based on the pronunciation of letters and sounds. Children are taught to combine sounds first into syllables, then into words. The best learning option is the interaction of these two methods.
The first approach is based on the recognition of the word as a whole unit, the rules of phonetics are not explained. First, they are taught to read words on cards with the image of the word, then the child is given a very colorful book with simple words and a predictable plot. Encountering unfamiliar words, the child must guess from the clues of the illustrations or the context. The second approach to teaching reading is phonetic, based on the pronunciation of letters and sounds. Children are taught to combine sounds first into syllables, then into words. The best learning option is the interaction of these two methods.
If the child is stuck on one word that is difficult for him, try prompting using the context. Usually the choice of words according to the meaning helps to cope with this problem. If you ask a child to traditionally spell a word, then you need to be prepared for mistakes, because when the last sound of the word is pronounced, the first is already forgotten. Sometimes it helps to write this word in large letters and, leaving the first three letters and covering the rest, ask the child to guess the end of the word.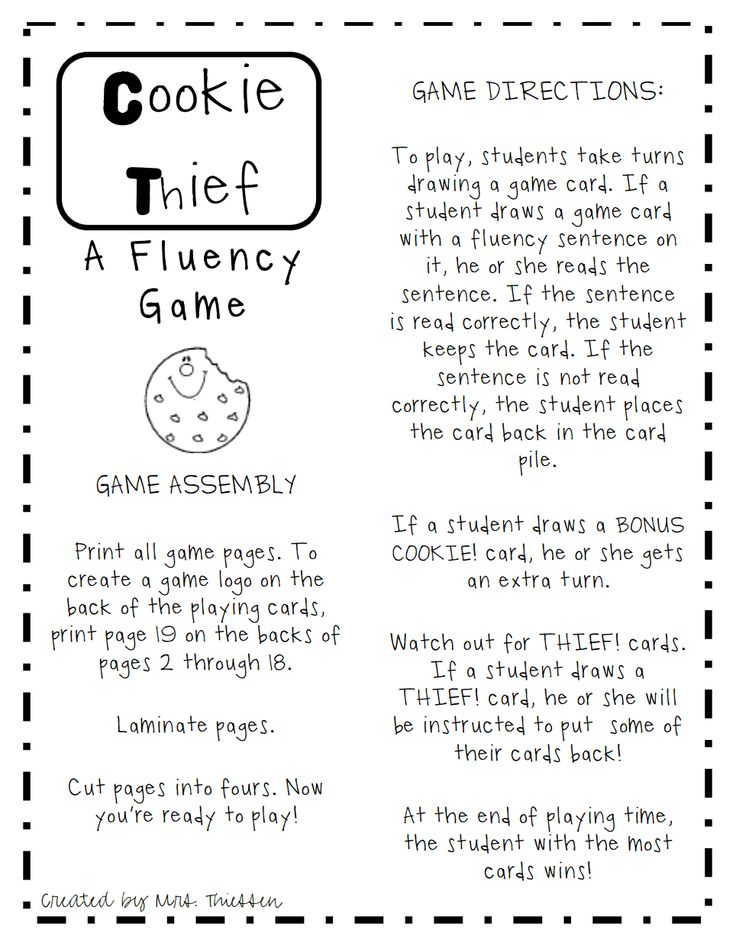 If you recall the context of the text, or at least the last sentence, the child will definitely cope with this harmful word.
If you recall the context of the text, or at least the last sentence, the child will definitely cope with this harmful word.
Help in learning to read words with several syllables.
Start learning to read polysyllabic words from words with two syllables, gradually increasing the number of syllables over time. I want to talk about ten steps that helped us learn to read polysyllabic words quite easily.
Step 1. Choose a few simple two-syllable words, the meaning of which the child knows, but does not yet read freely, for example: cup, song, compote.
Step 2. Write a word on a piece of paper and cut it in half - cup / ka, song / nya, com / sweat.
Step 3. Connect all three words on the table and read them, indicating the location with your finger.
Step 4. Ask the child to repeat what they just saw and heard.
Step 5. Cover the second syllable with a sheet of paper, and read the first syllable aloud, pointing at it with your finger. Then do the opposite - cover the first syllable with a sheet of paper, and read the second syllable out loud, pointing at it with your finger.
Then do the opposite - cover the first syllable with a sheet of paper, and read the second syllable out loud, pointing at it with your finger.
Step 6. Ask the child to repeat what they just saw and heard. This will be more difficult to do, since some syllables are difficult to read separately.
Step 7. Mix all the syllables on the table. The task of the child is to compose words and read them.
Step 8. Repeat this exercise after a couple of days. You will see, even if the child has forgotten some syllables, it will take much less time to complete the task.
Step 9. As soon as the child learns to read these syllables without hesitation, it's time to add new cards with new syllable words to the cards already studied.
Step 10. Ask them to spell the words by closing their eyes and imagining the letters as written.
We used words with basic syllables from N. A. Zaitsev. My son read his first words at the age of four.
A. Zaitsev. My son read his first words at the age of four.
Working on mistakes by inattention
Children often replace words in a sentence by guessing them from the context, especially when they are in a hurry to finish reading. In this case, an interesting process takes place in the brain - the eyes do not perceive letters and do not send a signal for decoding to that part of the brain that is responsible for reading. The part of the brain that guesses the desired sequence works, like in a mobile phone with the fast typing function. Many professionals recommend not to correct these errors, as they do not affect the meaning of the text read, and the child will go astray. Another important factor is that children are usually corrected in a nervous tone, which can discourage reading. We all agree that learning should not be frustrating, otherwise the desire to learn will disappear. Therefore, it is better to introduce a new rule - joint reading in turn. The next sentence can only be read if the previous one was read verbatim correctly. If there were inaccuracies or errors, you need to silently wait for the correct version. Sometimes I deliberately make mistakes when reading together in order to please my son and test his attentiveness.
The next sentence can only be read if the previous one was read verbatim correctly. If there were inaccuracies or errors, you need to silently wait for the correct version. Sometimes I deliberately make mistakes when reading together in order to please my son and test his attentiveness.
Acceleration of reading fluency.
When children begin to read, they slowly pronounce syllables like robots. This way of reading can become an unpleasant habit. If we want to instill a conversational style of reading, then we need to read together in the following way. Choose a simple text that the child has already heard repeatedly. Ask him for help - you will read, and he will move his finger where you read. Read the text with expression and emotion. Then ask the child to show how it looked from the outside - let him read now, and you will move your finger. If you make such a five-minute reading traditional, the results will impress you.
Child's friendship with a book – how to achieve it.

And now some useful, in my opinion, tips.
- Keep reading to your children, even when they learn to read silently. If you read to them before going to bed, putting your arms around their shoulders, they will look forward to these evening tales.
- The children's library should have a well-groomed appearance - the books should be within the child's reach, arranged and glued.
- Visit libraries. Let them wander around the library on their own and choose books to read.
- Go to the bookstore. Usually children always ask for something in the store, and this trip is unlikely to be an exception. The best option is to buy a book that interests the child, presenting it as a reward for some good deed. Think of buying books not as an expense, but as a long-term investment.
- Play theater with your child. Children are happy about the idea of role-playing their favorite fairy tale.
- Teach children by your personal example.
Learn more

 e., before, during, and after), and see examples of scoring and graphing oral reading.
e., before, during, and after), and see examples of scoring and graphing oral reading. For fluency, activities include basic steps to teach reading fluency, partner reading, fluency word cards, page races, repeated readings, fast phrases, independent reading, and more.
For fluency, activities include basic steps to teach reading fluency, partner reading, fluency word cards, page races, repeated readings, fast phrases, independent reading, and more. Practices for reading fluency include (but are not limited to) text reading, partner reading, fast phrases, diagnostic assessments, progress monitoring, and providing feedback.
Practices for reading fluency include (but are not limited to) text reading, partner reading, fast phrases, diagnostic assessments, progress monitoring, and providing feedback.