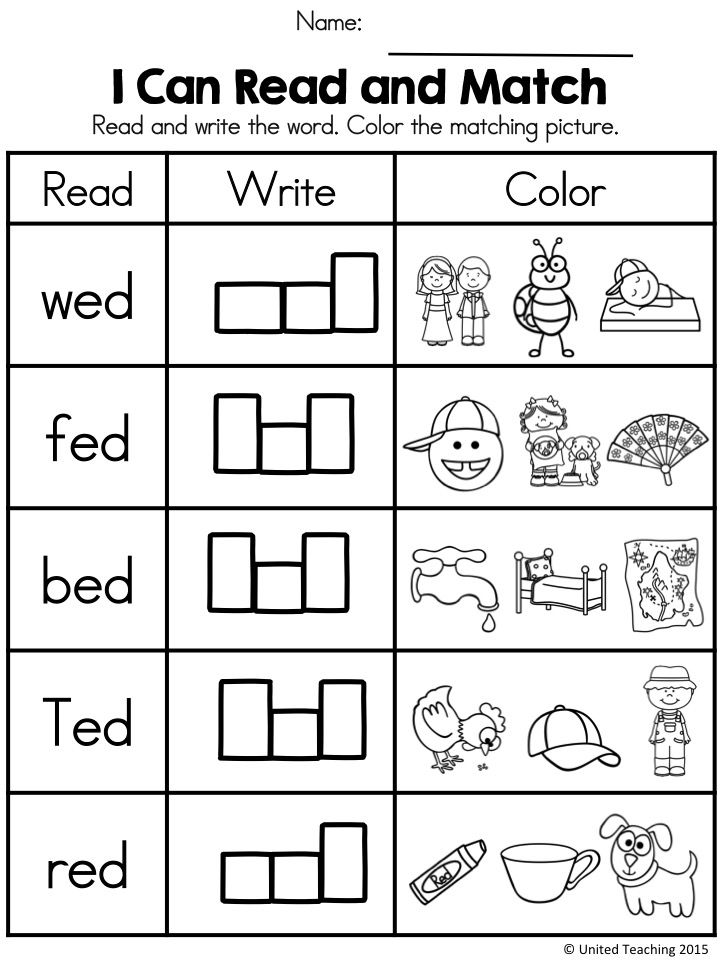
Kindergarten word activities
48 Fun Sight Word Activities That Work
Teachers are always on the hunt for great sight word activities. Sight words are any words readers recognize automatically “by sight”—for fluent readers, that’s almost all words! High-frequency words, the most commonly occurring words in written English like those on the Dolch list, are often thought of as the most crucial sight words.
It’s a myth that blindly memorizing every letter in a sight word is the only way to learn it. The science of reading tells us that linking sounds and letters is the most effective way for kids’ brains to learn any word. Many common words are easy to tackle using beginning phonics skills (like “at,” “can,” “him,” etc.), so staying true to a strong phonics curriculum is one way to support kids’ sight word learning. Even irregularly spelled words have decodable parts, e.g., kids can use the sounds of “s” and “d” to help with “said,” even if the “ai” is unexpected. Experts often call these words “heart words” to call out for kids that they should learn the unexpected word parts “by heart.
” (If all this is unfamiliar to you, it can feel overwhelming, but you’ve got this! Check out teaching guru Jillian Starr’s explanation for more help.)
Check out these low-prep and engaging sight word activities for both teaching and practicing words.
1. Map it and drive it
This is a genius way to introduce words with appealing materials: Say the word, represent each sound with a LEGO brick, write letters for each sound, and “drive” to read it.
Source: @droppinknowledgewithheidi
2. Smush play dough for each sound
Set up a routine that works for any word. Play dough squishing for each sound is the ultimate multi-sensory component.
ADVERTISEMENT
Source: @playdough3plato
3. Map words with a magnet wand
It is so super-satisfying to drag those magnetic dots around! Watch the video below for lots of tips on introducing a word using this process.
Source: @warriorsforliteracy
4.
 Make a mini book
Make a mini bookLots of handy info in one place for your little learners.
Source: @hughesheartforfirst
5. Tap it, pop it, learn it!
Hardwire those words in kids’ brains with this comprehensive word intro routine. (You had us with the pop its!)
Source: @hellojenjones
6. Find and swat words
An oldie but such a goodie. Find a word in an array and WHACK! Swat it with a fly swatter!
Source: @kids_play_learn_laugh
7. Flip word pancakes
Serve up sight word pancakes while practicing spelling them aloud.
Source: @bee_happy_teaching
8. Wear heart word bracelets
Make kids feel like sight word VIPs.
Source: @teachingmoore
9. Search for sight word balls
Write sight words on ball pit balls with a chalk marker or dry-erase marker. Kids can race around hunting for balls to read and toss in a basket, or hunt through a big tub of balls for a certain word.
Source: @preschoolforyou
10.
 Start a sight word band
Start a sight word bandLoud but oh-so-fun! Feel the rhythm while tapping and reading sight words stuck to homemade percussion instruments.
Source: @earlyyears_withmrsg
11. Drive on a sight word path
This is one of many fun ways to use magnetic tiles for learning! Kids love “knocking down” word tiles with a toy car as they read each one.
Source: @travisntyler
12. Use sticky notes to inspire sight word sentences
Have kids stick words on items that give them ideas for sentences. “My Mom said to wear a helmet!” = so good!
Source: @kinneypodlearning
13. Write words on a sensory bag
So easy: Fill a zip-top bag with a small amount of kid-safe paint, seal well, and have kids practice “writing” sight words with their finger or a cotton swab.
Source: @makeitmultisensory
14. Wear a sight word crown
Wear your word proudly and practice reading others’ words. Fun in person or virtually.
Source: @mrsjonescreationstation
15. Play a magnetic-tile board game
We love new ideas for ways to use magnetic tiles for sight word activities. Easy to set up and fun to play.
Source: @twotolove_bairantwins
16. Spell words to a familiar tune
Get sight words stuck in everyone’s head, in a good way. We’d add a line for chanting the sounds in the word!
Source: @saysbre
17. Feed a word monster
Nom, nom, nom.
Source: @ecplayandlearn
18. Search for the pom-pom under sight word cups
Read all the words as you try to find the cup that hides the prize.
Source: @la.la.learning
19. Play sight word KABOOM
This classroom classic is perfect for sight words. If you need a refresher on the rules, Jillian Starr covers them.
Source: @essentiallykinder
20. Roll and write words
Roll, write, repeat.
Source: @mylittlepandamonium
21. Write words with rainbow colors
Bonus points for aromatic markers.
Source: @mylittlepandamonium
22. Trace words with flashlights
Stock up on batteries because kids never get tired of this!
Source: @giggleswithgerg
23. Find words in plastic eggs
Give kids a checklist of words to find as they open each egg.
Source: @blooming_tots1
24. Spy words around the classroom
Just add a magnifying glass and clipboard to make kids feel like supersleuths!
Source: @readingcorneronline
25. Find words in the morning message
Don’t forget about old standbys! This is one of our favorite ways to get kids to recognize sight words in connected text.
Source: @tales_of_a_kinder_classroom
26. Build words with bricks
Such a great use of extra building bricks!
Source: @raysinkinder
27. Write words in sand
Easy-peasy to set up and keep neat if you use plastic pencil boxes.
Source: @teacherhacks
28. Spell words on a construction site
Bulldozing over each word to read it is the best part!
Source: @planningplaytime
29.
 Spell words with toy cars
Spell words with toy carsDrive on over!
Source: @lozlovesprep
30. Park in a sight word “parking lot”
This one is easy to modify based on whatever toys are available in the classroom or at home.
Source: @msbendersclassroom
31. “Plant” words in play dough
Watch those reading skills grow!
Source: @planningplaytime
32. Build words in a sensory tub
Because spelling is just more fun when your hands are covered in beans!
Source: @coffeeandspitup
33. Write words on a magnetic drawing board
That eraser track makes for a perfect word card holder!
Source: @moffattgirls
34. Or write words on the window!
Everyone wants a turn to write on the window!
Source: @kindergarten_matters
35. Shhh! Discover words written in invisible ink
Write words in white crayon and reveal them with watercolors on top!
Source: @teachstarter
36.
 Dot-paint words with a cotton swab
Dot-paint words with a cotton swabCalming and effective.
Source: @sightwordactivities
37. “Type” words on a keyboard
Busy day at the sight word office! Use a keyboard cover or any old keyboard.
Source: @lifebetweensummers
38. Read words before heading through the door
The line leader can double as the word pointer during transitions.
Source: @ms.rowekinder
39. Read the word the teacher’s wearing!
Wait, is there something on my shirt?
Source: @theprimarypartner
40. Take a sight word cakewalk
Choose a winning word when the music stops!
Source: @joyfulinkinder
41. Play sight word hopscotch
If you can’t get outdoors, tape on the floor works just as well.
Source: @wheretheliteracygrows
42. Play tic-tac-toe
I’ll be team “the.”
Source: @create_n_teach
43. Go sight word bowling
No bowling pins? Use half-filled plastic water bottles instead.
Source: @thecreativeteacher_
44. Ready, aim, read
Just throw a beanbag at a word target if foam darts are a no-go.
Source: @laurens_lil_learners
45. Play muffin tin ball toss
Toss and read. It’s easy to use colored muffin cups to prep different sets of words.
Source: @homeschooling_fun_with_lynda
46. DIY sentence flash cards
Authentic use of words in context for the win.
Source: @teachertipsandtales
47. Play sight word checkers
King me! If kids don’t have a partner available, they can “play” with a stuffed animal and get double practice.
Source: @sightwordactivities
48. Play sight word Guess Who?
Set up this game once and use it forever.
Source: @lessons_and_lattes
We’d love to hear—what are your favorite sight word activities? Share in the comments below.
Want more articles like this? Be sure to sign up for our newsletters.
Plus, what are sight words?
7+ Hands-On Sight Word Activities for Kindergarten
Learning letter sounds, how to blend and segment words, and various phonics skills are foundational for early reading. However, there are just some words that can’t be sounded out. Sight words are commonly used words that young readers are taught to memorize. Since these words are used in high frequency, students are encouraged to recognize them by sight. Hands-on sight word activities merge students’ kinesthetic learning with visual learning.
However, there are just some words that can’t be sounded out. Sight words are commonly used words that young readers are taught to memorize. Since these words are used in high frequency, students are encouraged to recognize them by sight. Hands-on sight word activities merge students’ kinesthetic learning with visual learning.
For many kids, sight words are one of the first steps in learning to read. And what better way to learn sight words than with some fun sight word games that don’t require worksheets?
Learning to read is complicated and intricate, especially for kindergarten students. While learning to read sight words is only one component of reading development, it is a necessary and important component.
What are sight words?
Words like the, of, you, was are all words that need to be memorized and recognized by sight. They cannot be decoded using general phonics patterns.
Some words that we consider sight words are decodable words, but occur frequently. Those are often called high-frequency words, although I have found that “sight words” and “high frequency words” are terms that are used interchangeably. Words like, and, that, as, on, in are all decodable words, but are also often taught as sight words.
Which words should you consider sight words?
Well, there are a couple of different answers. If your school district is assessing a list of words, consider that your list. If your school or district is not providing a list of words, you can find various lists online, including Dolch Lists and Fry’s Lists. While Dolch and Fry’s are some of the more common lists, each reading program seems to develop its own list. Most lists are very similar.
Since it takes students so long to learn sight words, you might consider limiting sight word instruction to words that are common and irregular or not decodable. If you are teaching a phonics-based reading program alongside teaching students to memorize sight words, then they will learn how to decode and, had, last, then, with, not, much, etc. as they progress through the reading program. Don’t waste valuable time on teaching students to memorize decodable words if you don’t have to.
If you are teaching a phonics-based reading program alongside teaching students to memorize sight words, then they will learn how to decode and, had, last, then, with, not, much, etc. as they progress through the reading program. Don’t waste valuable time on teaching students to memorize decodable words if you don’t have to.
Sight Word Cards
Consider using blending cards for sight words to learn decodable high-frequency words. These sight word cards have blending cues for decodable sight words. They can enhance your sight word activities and can be used with small groups or whole group instruction to help students see the phonetic connection between the sounds and symbols.
How do You Learn Sight Words in the Classroom?
There are a variety of ways for students to learn sight words, including the new Science of Reading Heart Method. Once students have learned a word, frequent exposure is the key. Creating fun ways to learn the words helps too!
Creating fun ways to learn the words helps too!
All students will also benefit from using more hands-on sight word activities during your word work stations.
Here are 5 sight word activities for kindergarteners that help young learners remember high-frequency words while having fun!
1. Block Building Game
Turn a classic block-building game, like Jenga, into a way for students to learn their sight words. Start by writing a high-frequency word on each block. Playing the normal Jenga rules, where a player removes a block from the tower and places it on top, have the student who removes the block successfully use the sight word in a sentence before the next player takes their turn. Or for an easier version, have players read and spell the words while moving blocks.
Download the game rules from education.com.
2. Tic-Tac-Toe Sight Word Activities
Kids love to play Tic-Tac-Toe! Add a twist by having the student read a sight word and use it in a sentence or read and spell it before adding an X or O to the board. Use sight word flashcards.
Use sight word flashcards.
Try a variation by having students write the words along with an X or O on the board. Check out the templates and rules from sightwords.com.
3. Shaving Cream Fun Sight Words Activities
Sometimes learning is messy! Break out the shaving cream on desks and tables, and have your students write out their sight words with their fingers. Save money on supplies by checking out a local dollar store or buying in bulk at a warehouse club store.
Clean-up is easy. Just wipe down the tables and spray clean. One additional benefit is that the shaving cream acts as a soap and cleans up your tabletop!
A sand or salt box is another great tool to use, but a little less messy than shaving cream. Fill a small box with sand or salt. Using flashcards or sight word cards, have students turn over a card and draw the letters for the word in the box. The feel of the rough sand or salt helps kinesthetic learners memorize the words.
The feel of the rough sand or salt helps kinesthetic learners memorize the words.
4. Use Manipulatives to Form Letters
For kinesthetic learners, using tangible items to physically form words can be an important way to show what they know! Try using Wikki Stix, play dough, or bendable straws to form words on mats or flat surfaces. Playdough is also a great medium for stamping letters to form sight words.
5. Journaling
Although open journaling or free writing may seem a little advanced for kindergarteners, you’ll be surprised with how much they can write even in the beginning stages.
Give students a list of sight words and markers. Ask students to generate a story with a drawing. Or give students a seasonal topic with words and a few sight words.
Save these in a digital or paper portfolio throughout the year to measure growth. Tools like Seesaw are incredible for keeping portfolios of student work via video and other mediums.
6. Word Ladder Game
This game is perfect for kids who are just starting to learn sight words. To play, choose a simple sight word like “at” or “had.” Then, see how many other words you can make by changing just one letter. For example, starting with “at,” you might get “bat,” “cat,” “hat,” and so on. The player with the most words at the end of the game wins! This is also a great way to focus on word family words, short vowel word families, and rhyming.
To make this game kinesthetic, create hopscotch-like boxes on your classroom floor. Have students move up the ladder as they create new words.
7. Musical Sight Words
This sight word activity is similar to Musical Chairs, but with a sight word twist. To play, write several sight words on slips of paper and put them in a hat or bowl. Then, play some music while everyone walks around the room. When the music stops, everyone must grab a slip of paper.
Once everyone has a word, they must stand up and spell it out loud. The player who spells their word correctly first gets to stay in the game; the rest are out! The last player standing is the winner.
Instead of requiring spelling, you can just ask students to read the word. Remove one word each round to eliminate students as you would during a regular musical chairs game.
These 5 7 sight word activities for kindergarteners will help your students learn their first sight words in no time. These are just a few ideas to get you started. With a little creativity, you can come up with all sorts of fun games to help your child learn their sight words.
Do you want some more ideas?
More Low-Prep Fun Ways to Practice Sight Words
To make learning sight words fun for kids, here are some more great sight word activities These ideas may be great for some of your more advanced learners.
- Write sight words in alphabetical order.
- Write the same sight word in multiple different colors. They can even create a rainbow of colors!
- Have students trace a sight word worksheet with their fingers before writing it down on a separate sheet of paper.
- Create a silly sentence with the sight words, then have students rewrite it.
- Have students spell out individual letters of the sight words, then put them together to spell out the whole word.
- Give students blank pieces of paper and have them practice writing each sight word multiple times in a row until they can write it correctly without looking at another reference source.
- Encourage students to make up stories or riddles using the sight words they need to practice and write it down afterward as practice.
- Ask students to use each letter of their chosen sight word to start a new sentence and complete the sentence with their own words after that
- Draw pictures around each of their chosen sight words and encourage them to label what was drawn for further practice writing it down correctly
- Give students an index card for each sight word and have them write that particular word several times on both sides
- Create sight word puzzles by writing each sight word on an index card, cutting the cards into pieces, and having students put the pieces back together.

- Play a game of I Spy using sight words around the room
- Have a scavenger hunt with sight words: hide index cards around the classroom with each card containing a different sight word written on it.
- Construct simple sentences using sight words and have students identify all of the words in it as they read it aloud.
- Give each student a list of 10-20 Sight Words and have them draw pictures to represent each word; then go over the list together to practice pronouncing each one correctly and discuss what the pictures represent based off of context clues gleaned from their drawings.
- Practice writing sentences with specific targets like “I can see ______” and have students fill in the blank with different Sight Words along with other appropriate vocabulary from list of words.
- Play Simon Says using Sight Words: The teacher or student calls out a Sight Word for others to act out (i..e hop if you hear ‘jump’).
Here are five more additional resources to help teach sight words in your classroom!
- Dolch Sight Word Lists
- Dolch Sight Word Assessment
- Fry Sight Word Lists
- Online Sight Word Games
If you are looking for a tool for parents to use at home, these Sight Word Practice Cards provide small doses of daily practice and a routine for parents to easily implement.
I created these phonics readers to use with my own kindergartener at home. Although they focus on specific word families and phonics patterns, the resource also introduces two new sight words per word family. Sight words are learned and read along with the phonics patterns.
What activities do you use to teach sight words in your classroom? I’d love to hear about them in the comments below!
Are you interested in additional blog posts about teaching early reading? Here are a few more!
Methods and techniques of teaching in kindergarten. | Methodological development (junior, middle, senior, preparatory group) on the topic:
Methods and techniques of teaching in kindergarten.
Definition of the term "teaching method". The essence of the activity of a teacher in kindergarten. Classification of methods and techniques for teaching preschoolers and a methodology for choosing methods and techniques for teaching in kindergarten. Characteristics of verbal methods and teaching methods.
Characteristics of verbal methods and teaching methods.
OVERVIEW
Plan:
Introduction
1. Characteristics of verbal teaching methods and techniques
2. Selection of teaching methods
3. Practical task
Conclusion
References
Introduction
Introduction
learning in kindergarten. The activity of a teacher in kindergarten is to organize the development, upbringing and education of children. This activity is carried out with the help of teaching methods and techniques.
Training is carried out in various ways. Translated from Greek, “method” means the way to something, the way to achieve the goal. teaching teacher preschooler method
Teaching method is a system of sequential interrelated ways of work of a teacher and taught children, which are aimed at achieving didactic tasks.
Each method consists of certain techniques of the teacher and students. The method of learning, unlike the method, is aimed at solving a narrower learning problem. A combination of techniques form a method. Methods and techniques for teaching preschoolers can be practical, visual, verbal and gaming
A combination of techniques form a method. Methods and techniques for teaching preschoolers can be practical, visual, verbal and gaming
Techniques are implemented through the use of a certain method. One method or technique always complements, develops or corrects another.
With the help of upbringing methods, the behavior of children is corrected, personal qualities are formed, the experience of their activities, communication and relationships is enriched.
1. Characteristics of verbal teaching methods and techniques
Teaching methods are subdivided:
Table 1.0048
Type of the method
The characteristic of the method
The task of the teacher
The purpose in teaching children
Story is the most important verbal method, which allows the form accessible to children to the educational material.
These can be stories about current events, seasons, writers, composers, and so on. Literary works are used. Can be combined with visual methods (objects and their image)
Do not overload with details, clearly trace the main idea, idea. Using facial expressions, gestures, expressive speech for narration.
Develop speech, understanding ability, ability to listen, respond to content, answer questions, retell.
Conversation is a dialogical teaching method, which assumes that all participants in the conversation can ask questions and answer, express their point of view.
Distinguish between introductory and summarizing conversations.
Questions are the main technique in its implementation.
Topics are determined by specific educational tasks, their age characteristics. It is used when children have some experience and knowledge about the objects and phenomena to which it is dedicated.
It is used when children have some experience and knowledge about the objects and phenomena to which it is dedicated.
The purpose of the introductory conversation is to prepare children for the upcoming activity.
Generalizing conversation - conducted to clarify, summarize the knowledge acquired on a particular topic.
The effectiveness of the conversation largely depends on the teacher's ability to purposefully lead the children, direct the child's thoughts and activate speech activity. To achieve - that all children would actively take part in the discussion of the issue posed to them.
Pedagogically substantiate the content and contribute to solving the problems of comprehensive education.
Develop thinking, speech, restraint, politeness. And in general, the culture of speech communication.
Reading fiction.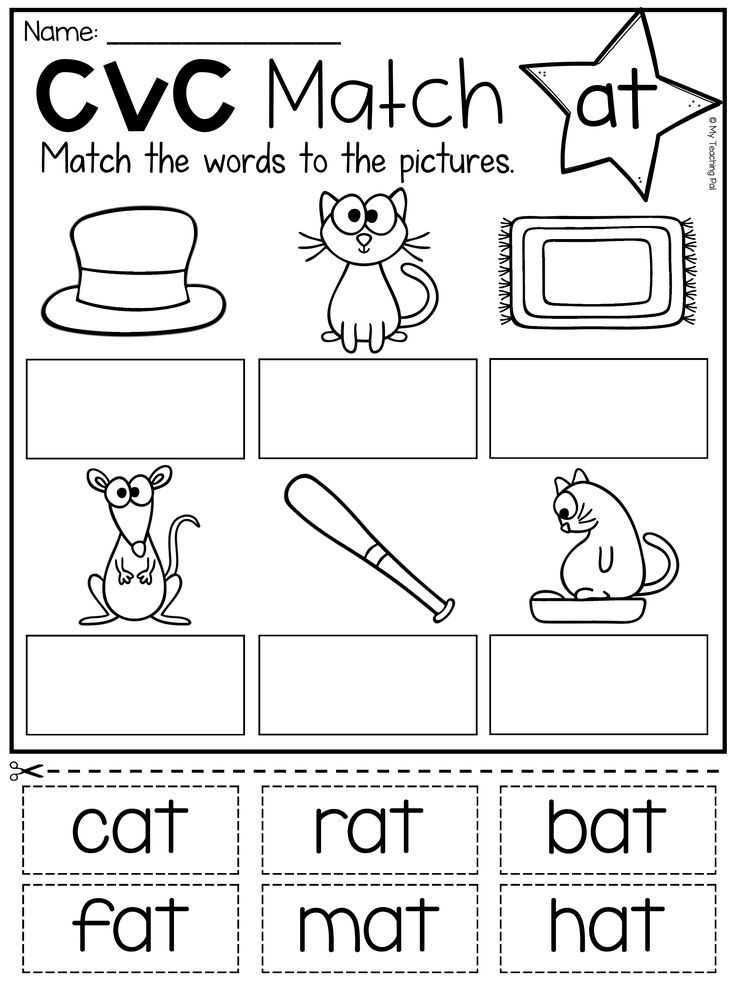 Fiction is a source of knowledge about the world around us.
Fiction is a source of knowledge about the world around us.
From books the child learns many new words, figurative expressions, his speech is enriched with emotional and poetic vocabulary.
The main method is the teacher's reading from a book.
Methods are used: questions, instructions, explanation, explanation, pedagogical assessment.
Prepare children with a short conversation, set an educational and cognitive task.
Select works that are valuable in educational terms, corresponding to the age and level of development of children.
Education of feelings, development of thinking, speech, imagination, memory. Formation of the ability to perceive and comprehend a work of art.
Conclusion:
Verbal methods and techniques are used in teaching preschoolers, but due to childhood, visual material is needed.
The success of verbal teaching methods directly depends on the mastery of them by the educator himself. And on how correctly and in what form it is presented to children.
The main instrument is the word. All verbal methods and techniques are aimed at the development of speech, thinking and memory.
To achieve results in teaching children, verbal methods and techniques are best combined with visual, as well as playful and practical.
2. The choice of teaching methods
When choosing a teaching method, the teacher must follow some rules:
Conclusion: When choosing one or another method, the educator needs to take into account many dependencies each time. No way of education can be declared in advance effective or ineffective without taking into account the conditions in which it is applied.
First of all, the choice of methods must be prepared and assume real conditions for implementation. Then the goal is determined, and specific tasks are set. Next, the optimal choice of the solution to the problem.
Next, the optimal choice of the solution to the problem.
The educator starts from the reasons that influence the choice of the method indicated in the table.
In kindergarten, the task of educators is to give children the necessary skills for later development. The use of various educational methods allows you to achieve the desired and take into account the individual characteristics of each member of the group.
The program formulates the main goals and objectives of education. And educational methods in kindergarten help to achieve the goals.
3. Practical task:
Monitor the organized forms of education in kindergarten (class), highlight the teaching methods and techniques that were used in the lesson.
| What was observed | Course of the lesson | Methods and techniques | |
| Surveillance was carried out at the lesson in the senior group No. The lesson was conducted by tutors Suvorova S.S. and Loskutova N.A. on the topic: "Autumn" The lesson was held on September 27th. Children 5-6 years old, in the amount of 14 people. | Guys, let's look out the window. What season is it now? (autumn). Today we will talk about autumn. -After what season does autumn come? - What are the autumn months. -Which autumn is early or late now? -What happens in autumn in nature, the life of animals and birds? - What kind of clothes and shoes do you wear in autumn? Why? -What kind of trees grow in the forest? (oaks, birches, aspens, maples) | The verbal method is used. Uses such techniques as questions that require ascertaining, encouraging mental activity. Expand your horizons, develop cognitive activity. | |
| -Look who came to us? (surprise moment, a hare comes, asks questions) - Guys, now I'll play with you. -Autumn months - February, June, March? (none) -Autumn months - September, October, November? (yes) - Is the weather clear, sunny, warm in autumn? (yes) - When does this weather happen: at the beginning or end of autumn? (beginning) -Now tell me which of the two sentences is correct: "In autumn, children wear panama hats, T-shirts, shorts and sandals" or "In autumn, children wear raincoats, jackets and boots." -What would happen if you went outside in Panama hats, T-shirts, shorts and sandals? Bunny praises the children and shows the letter. | The game method is used. The sudden appearance of a hare, questions in a playful way - tricks. The role is used as a component of the game. Formed thinking perseverance, attentiveness, consolidation of previously acquired knowledge. | ||
| - Look what I have. This letter. It was sent to me yesterday from the forest by forest dwellers. Look who? He opens the envelope and takes out pictures. Name them (squirrel, hedgehog, bear, and mouse). -How do these animals prepare for winter in autumn? -What kind of stock do you make? (a squirrel puts cones, nuts, berries and mushrooms in a hollow; a hedgehog hides mushrooms; a bear digs a den; a mouse drags spikelets into a mink). -Why do animals stock up for the winter? -What color is the grass and leaves in autumn? (yellow, red, green, brown, orange). Bunny praises the children and leaves. | The game method is used - a didactic game, in combination with a visual method - pictures in an envelope. | ||
| - And now guys, we will turn into leaves! We are autumn leaves, We are sitting on the branches. The wind blew - they flew. (run in circles) We flew, we flew And quietly sat on the ground. (sat down) The wind came up again And picked up all the leaves. (stood up) We swirled, flew. (circled, ran) And they sat down on the ground again. (sat down) | Physical education minute. A visual method, a verbal method, a practical method associated with the practical motor activity of children are used. Game method, close to the leading activity of preschool children, the most specific. It enables the simultaneous improvement of a variety of motor skills, independence of action, quick response to changing conditions, manifestation of creative initiative. | ||
| - What did we talk about today? - What did you learn about autumn? - Who came to visit us? - What did you play today? | Summary of the lesson. | ||
So you can look at each method and find that each of them has certain possibilities, its own zone of influence. The educator, starting from the program appropriate for the age of the children, implements the activity in the form that is most easily assimilated by the children. The game form of training is used.
Children received and acquired knowledge on the subject of autumn. During the lesson, the tasks planned by the teacher were solved.
Methods and techniques were used by caregivers effectively. Since they are used in the process of organized, diverse activities.
References:
1. Bolotina L.R., Komarova T.S., Baranov S.P. Preschool pedagogy: [Text] / Textbook for students of secondary pedagogical educational institutions.- M .: Publishing Center "Academy", 1997.-240 p.-ISBN 5-7695-0038-8
Bolotina L.R., Komarova T.S., Baranov S.P. Preschool pedagogy: [Text] / Textbook for students of secondary pedagogical educational institutions.- M .: Publishing Center "Academy", 1997.-240 p.-ISBN 5-7695-0038-8
2. I. O. Karelina , Methods of training and education in the field of preschool education
: [Text] / course of lectures: teaching aid / comp. - Rybinsk: branch of YAGPU, 2012. - 68s.
3. I.P. Vile, Pedagogy. New course: [Text] / - M .: Humanit. ed. center VLADOS, 1999.-Kn.2: General principles. Teaching process.-576 p.: ISBN5-691-00174-4
., isp. - M.: Publishing Center "Academy", 1998.- 400s. ISBN 5-7695-0029-8
5. Pedagogy. [Text] / Ed. P.I. Pidkasistogo - M .: Pedagogical Society of Russia, 1998.- 640s. ISBN 5-93134-001-7
6. S.A. Kozlova, T.A. Kulikova Preschool pedagogy [Text] / - 3rd ed. -7695-0 816-7
Word games and exercises for children in kindergarten, Card file of word games in kindergarten
Game activity of a preschooler > Games for children area
“What is round and what is oval?”
Game progress: The teacher asks the child to name as many round and oval objects as possible. The child starts the game.
The child starts the game.
If he cannot name, the teacher starts: “I remembered that an apple is round and a testicle is oval. Now you go on. Remember what shape is a plum, and what is a gooseberry? That's right, the plum is oval, and the gooseberry is round. (Helps the child name objects and compare them in shape: ring-fish, hedgehog-ball, cherry-leaf cherry, watermelon-melon, acorn-raspberry, tomato-eggplant, sunflower-seed, zucchini-apple) .
In case of difficulty, the teacher shows the child a set of pictures and together they arrange them into two groups.
“Flies - does not fly”
Game progress: The teacher asks the children to quickly name objects when he says the word “flies”, and then name other objects when he says the word “does not fly”.
The teacher says: “Flies”.
Children call: “Crow, plane, butterfly, mosquito, fly, rocket, dove”, etc. Then the teacher says: “Does not fly”. Children call: “Bicycle, chamomile, cup, dog, pencil, kitten”, etc. The game continues: the words “flies”, “does not fly” are called by one of the children, and the teacher names the objects together with the children. The game can be played while walking.
Children call: “Bicycle, chamomile, cup, dog, pencil, kitten”, etc. The game continues: the words “flies”, “does not fly” are called by one of the children, and the teacher names the objects together with the children. The game can be played while walking.
"Edible - inedible"
The game is played by analogy with the previous one.
"Alive-non-living"
Game progress: First, we explain that we call all living objects "WHO", and inanimate objects "WHAT". Here are some examples.
Then we play questions and answers. You can use picture books.
What is growing? Who is growing?
Who flies? What flies?
Who swims? What is floating?
Who is the biggest? What is the biggest?
Etc.
“What happens below and what happens above?”
Game progress: The teacher invites the children to think and name something that happens only upstairs.
If the children find it difficult, he prompts: “Let's look up, above us is the sky. Does it happen below? No, it always happens only at the top. And what else happens only at the top? Where are the clouds? (stars, moon) . Now think about what happens only below? Look at the ground. Where does the grass grow? Where does she go?” (plants, ponds, earth, sand, stones, etc.) .
Does it happen below? No, it always happens only at the top. And what else happens only at the top? Where are the clouds? (stars, moon) . Now think about what happens only below? Look at the ground. Where does the grass grow? Where does she go?” (plants, ponds, earth, sand, stones, etc.) .
After that, the children independently enumerate the objects of nature that exist only above and those that exist only below.
"What can be sweet?"
Game progress:
The teacher offers the children: Listen carefully, I will call something that is sweet. And if I make a mistake, then I must be stopped, I must say: “Stop!”
The teacher says: "Sugar, marshmallows, raspberries, strawberries, lemons."
The children listen attentively and stop him on the word where he “wrong”. Then the children themselves name what is sweet.
“Answer quickly”
Game progress: The teacher, holding the ball in his hands, becomes a circle with the children and explains the rules of the game: “Now I will name some color and throw it to one of you ball. The one who catches the ball must name an object of the same color. Then he himself calls any other color and throws the ball to the next one. He also catches the ball, names the object, then his color, etc.”
The one who catches the ball must name an object of the same color. Then he himself calls any other color and throws the ball to the next one. He also catches the ball, names the object, then his color, etc.”
For example, “Green,” says the teacher (makes a short pause, giving the children the opportunity to remember green objects) and throws the ball to Vitya.
"Grass", - Vitya answers and, having said: "Yellow", throws the ball to the next one.
The same color can be repeated several times, as there are many objects of the same color.
The main feature for classification can be not only the color, but also the quality of the object.
The beginner says, for example: "Wooden", and throws the ball.
“Table,” answers the child who caught the ball and offers his word: “Stone”.
"Home" - the next player answers and says: "Iron", etc.
The next time the form is taken as the main feature. The teacher says the word "round" and throws the ball to any player.
"Sun" - he answers and calls another shape, for example "square", throwing the ball to the next player.
He names a square-shaped object (window, handkerchief, book) and suggests some form. The same shape can be repeated several times, since many objects have the same shape. When repeating, the game can be made more difficult by offering to name not one, but two or more objects.
“How are they similar?”
Game progress: The teacher invites the children to look around and find two objects that are somewhat similar to each other.
He says: “I will call: the sun-chicken. How do you think they are similar to each other? Yes, that's right, they are similar in color to each other. And here are two more items: a glass and a window. How are they similar to each other? And now each of you will name your two similar objects.
Games to eliminate the fourth "extra" word
“Be careful!”
Game progress: The teacher says to the children: I will name four words, one word does not fit here. You must listen carefully and name the "extra" word. For example: matryoshka, tumbler, cup, doll; table, sofa, flower, chair; chamomile, hare, dandelion, cornflower; horse, bus, tram, trolleybus; wolf, crow, dog, fox; sparrow, crow, dove, chicken; apple, tree, carrot, cucumber.
You must listen carefully and name the "extra" word. For example: matryoshka, tumbler, cup, doll; table, sofa, flower, chair; chamomile, hare, dandelion, cornflower; horse, bus, tram, trolleybus; wolf, crow, dog, fox; sparrow, crow, dove, chicken; apple, tree, carrot, cucumber.
After each highlighted "extra" word, the teacher asks the child to explain why this word does not fit into this group of words, i.e., to explain the principle of grouping.
“Listen carefully!”
Game progress: The teacher says to the child: “I will name the words, and you will say which word does not fit: cat, fox, horse, cow; tractor, car, rocket, bus; pear, turnip, beet, carrot; book, pencil case, ball, notebook; water, thermometer, medicine, cotton wool.
In case of difficulty, he slowly repeats a certain set of words and helps the child to highlight the unsuitable for some reason.
Find out!
Game progress: What kind of berries do you know? Now I will name the words, if among them you hear the word for a berry, then clap your hands.
Presentation words - cabbage, strawberry, apple, pear, currant, raspberry, carrot, strawberry, potato, dill, blueberry, lingonberry, plum, cranberry, apricot, marrow, orange.
"Now I'm going to name the words, if you hear a word related to berries, clap once, if it's about fruits - twice."
(Words can be used the same, you can come up with others.)
As a basis for systematization, there can be a theme - tools, furniture, clothes, flowers, etc.
Tell me, what are the similarities in taste? color? size?
- lemon and pear
- raspberry and strawberry
- apple and plum
- currant and gooseberry
What is the difference in taste? color? size?
Divided into groups
Game progress: "What groups do you think these words can be divided into? Sasha, Kolya, Lena, Olya, Igor, Natasha.
What groups can be made from these words: dove, sparrow, carp, titmouse , pike, bullfinch, zander".
“Pick up the words”
Game progress:
- Match as many words as possible that can be attributed to the wild animals group (pets, fish, flowers, weather phenomena, seasons, tools and etc.) .
- Another version of the same task.
Use arrows to connect words that match the meaning:
ball | furniture
poplar | flower
cabinet | insects
plate | wood
coat | clothing
ant | crockery
pike | toy
rose | fish
"Similarities and differences"
Game progress: Invite the child to indicate the similarities and differences of the following pairs of words:
Book - notebook | Day - night
Horse - cow | Tree - bush
Telephone - radio | Tomato - cucumber
Airplane - rocket | Table - chair
"Find the opposite object"
Game progress: Calling any object (for example, sugar) , you need to name as many others as possible that are opposite to this one.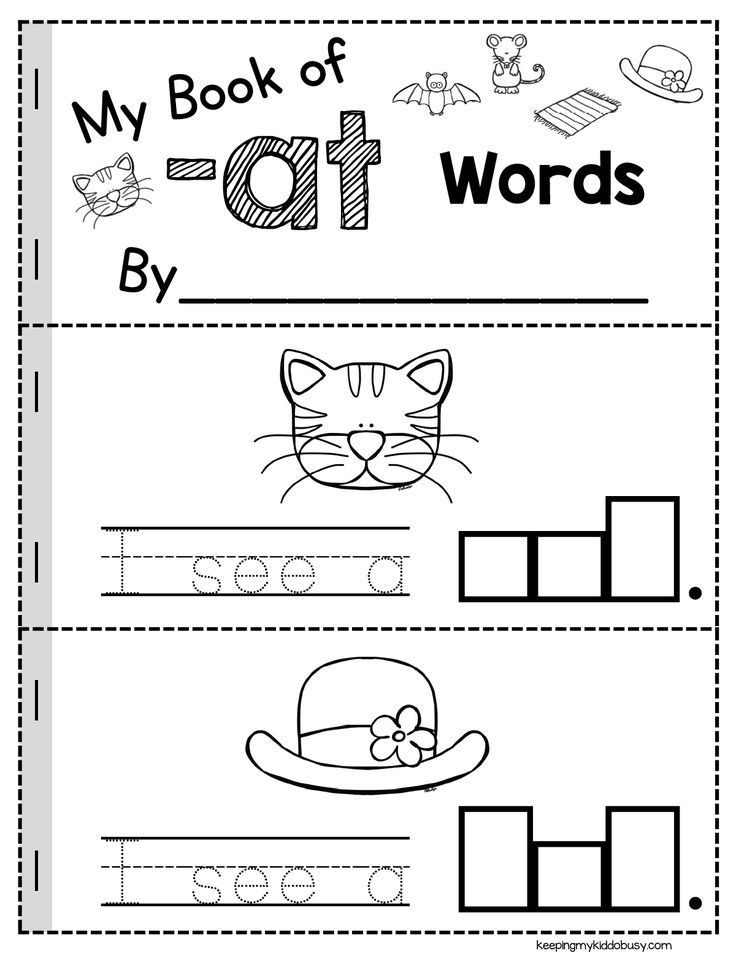 It is necessary to find opposite objects according to the function "edible - inedible", "useful - harmful", etc., on the basis of (size, shape, condition) , etc.
It is necessary to find opposite objects according to the function "edible - inedible", "useful - harmful", etc., on the basis of (size, shape, condition) , etc.
“Search for an analogy”
Game progress: A word is called, for example, a briefcase. It is necessary to come up with as many "analogues" as possible, i.e. other items similar to it in various essential features (bag, sack, backpack, etc.) Game progress: Invite the child to name a group of objects in one word. We call many specific objects with one word. For example, birch, pine, oak, etc. we call trees.
Invite the child to name in one word:
- a table, a chair, a cupboard are...
- a dog, a cat, a cow are...
- a cup, a saucer, a plate are...
- cornflower, chamomile, tulip - this.
"Find a common word"
Game progress: This task contains words that are united by a common meaning. It is necessary to try to convey this general meaning in one word.
What is the common word for the following words:
- Faith, Hope, Love, Elena
- a, b, c, c, n
- table, sofa, armchair, chair
- Monday, Sunday, Wednesday, Thursday
- January, March, July, September.
The generalizing word can be "spring months", or it can be "months of the year", etc.
A more complex version of the exercise contains only two words for which it is necessary to find a common concept.
Find out what the following words have in common:
a) bread and butter (food)
b) nose and eyes (parts of the face, sensory organs)
c) apple and strawberries (fruits)
d) watch and thermometer 903 devices)
d) Kit and lion (animals)
E) Echo and mirror (reflection)
“Words-twin”
Game: This exercise is related to the same. a phenomenon of the Russian language, like homonymy, that is, when words have different meanings, but are the same in spelling.
Which word means the same as the words:
1) a spring and something that opens the door;
2) the girl's hair and a grass cutter;
3) a branch of grapes and a drawing tool.
Think of words that are the same in sound but different in meaning.
Additional tasks for the exercise:
4) a crying vegetable and a weapon for shooting arrows (burning vegetable and small arms) ;
5) part of a gun and part of a tree;
6) things to paint on and greenery on the branches;
7) a construction site hoist and a mechanism that must be opened to allow water to flow.
“What is needed”
Game progress: The car runs on gasoline or other fuel; tram, trolleybus or electric train are powered by electricity. All this together can be attributed to the group "transport".
Seeing an unfamiliar car (e.g. truck crane) , they ask: what is it? Why?
Similar exercises are performed with other concepts: tools, utensils, plants, animals, furniture, etc.
“Why?”
Game progress: Now I will tell you words, and you will answer me, which is more, which is less, which is longer, which is shorter.
- Pencil or pencil? Which one is shorter? Why?
- Cat or whale? Which one is more? Why?
- Boa constrictor or worm? Which one is longer? Why?
- Tail or ponytail? Which one is shorter? Why?"
The teacher can come up with his own questions, focusing on the above.
"Choose the main thing"
Game progress: An adult says to the children: Now I will read a series of words. From these words you will have to choose only two, denoting the main features of the main word, i.e., without which this object cannot exist.
Other words are also related to the main word, but they are not the main ones.0003
For example, a garden... What do you think, which of these words are the main ones: plants, gardener, dog, fence, earth, i.e. something without which a garden cannot exist? Can there be a garden without plants? Why?. .. Without a gardener... a dog... a fence... land?.. Why?
.. Without a gardener... a dog... a fence... land?.. Why?
Each of the proposed words is analyzed in detail. The main thing is that children understand why this or that word is the main, essential feature of this concept.
Sample tasks:
a) Boots (laces, sole, heel, zipper, shaft)
b) River (shore, fish, angler, mud, water)
c) City (car, building, crowd, street, bicycle)
d) Barn (hayloft, horses, roof, livestock, walls)
e) Cube (corners, drawing, side, stone, wood)
f) Division (class, divisible, pencil, divider, paper)
g) Game (cards, players, fines, penalties, rules)
h) Reading (eyes, book, picture, print, word)
and) war (plane, guns, battles, guns, soldiers)
“Dunette”
Crowd games: The host thinks of a word or tells the conditions of some completely unusual situation, and the players (children or adults) must guess the word or explain the situation by asking questions that can be answered with one of five answers: "yes"; "No"; "Yes and no"; "there is no information about it"; "it's not significant. "
"
For example: "I thought of a plant in the middle zone. In ten questions, determine the plant that I thought of."
Themes for "danetok" and possible continuation of the game.
What vegetable did I have in mind?
- Is it a root vegetable? (Carrot, beetroot, radish)
- Is it a leafy vegetable? (Cabbage, lettuce)
- Is it a fruit vegetable? (Tomatoes, cucumbers)
What name did I think of?
- Is it a male name?
- Does the name begin with a vowel?
- Is there such a name in our group?
What piece of clothing did I have in mind?
- Is this outerwear?
- Are these men's clothes?
What fairy tale did I have in mind?
- Is this a Russian fairy tale?
What historical figure did I have in mind?
- Is this a man?
What must I do in the morning?
What color do I have in mind?
What property of ice cream, light bulb, watermelon, pencil did I guess?
What country did I have in mind?
What kind of writer, storyteller, poet, scientist did I have in mind?
What famous battle did I have in mind?
"Black box"
Game progress: Children are shown a "black box" or just a bag, briefcase and they are asked to guess in 10 questions - what is there? Etc.
- Is there a man-made object? Is there something soft? Is there something metallic? Etc.
List the items
Game progress: One leader is selected from the group of children. He leaves the room for 2 minutes. At this time, 7 objects are placed on the table in the room and the situation is thought about. For example, children think of the situation "I'm going for a walk", then 7 items of clothing should lie on the table.
The driver is invited, the situation is told to him and he is allowed to inspect the table for 1-2 minutes. Then he turns his back to the table and faces the group of children and starts listing the things on the table. After each correct answer, the group says "Correct!", after the wrong - "Wrong!". If the driver has not listed all the items, the group says which items he forgot.
“Opposite”
Game progress: The leader calls the group of children a word. The task is to name a word denoting the opposite object.
For example, the facilitator says the word "cup". Children can name the following items: "board" (the cup is convex, and the board is straight) , "sun" (the cup is made by a person, and the sun is part of nature) , "water" (water is a filler, and a cup is a shape) etc.
Each child in turn offers his answer and always explains why he chose that particular subject.
"Come up with a riddle"
Game progress: A leader is selected from a group of children. His task is to come up with a riddle. The group must solve this riddle. Then another child comes up with a riddle, and so on. Children of 6 years old love to come up with riddles, the game is lively.
"Who is whom (than) will be?
Game progress: The good thing about the game is that you can play with the company and with your child anywhere. Ask each other questions, make sure that the baby answers the question correctly.
Who will the egg be? (can be a chick, crocodile, turtle, snake.)
- chicken - rooster;
- a boy - a man;
- calf - cow or bull - paper - book;
- snow - water;
- water - ice;
- seed - flower;
- flour - pancakes;
etc.
Reverse game: "Who was who?".
- horse - foal
- flower - seed
"Third extra"
Game progress: Adult says three words - owl, crow, fox. The child should quickly analyze these three words in his mind and determine that all three words refer to wildlife, however, an owl and a crow are birds, and a fox is not. Therefore, the fox is superfluous here.
More examples for younger preschoolers:
- milk, juice, bread - all three words mean edible. But they drink milk and juice, but eat bread;
- car, horse, tram;
- hat, scarf, boots;
- rose, birch, tree.
For children aged 5-7 the tasks become more difficult:
- rain, snow, river;
- doctor, tourist, driver;
- shadow, sun, planet;
- frost, blizzard, January;
- stone, clay, glass;
- door, carpet, window;
- sea, river, pool.
“What happens?”
Game progress: First, the adult asks questions, and the child answers. Then you need to give the child the opportunity to express themselves.
Examples:
- What is high? (tree, pole, man, house) . Here it is appropriate to ask which is higher - a tree or a house; person or pole.
- What is long? (short)
- What is wide (narrow) ?
- What is round (square) ?
A variety of concepts can be included in the game: what is fluffy, soft, hard, sharp, cold, white, black, etc.
“What is outside, what is inside?”
Game progress: The adult names a couple of objects, and the child says what can be outside and what can be inside. House - closet; book - cabinet; purse; wallet-money; pan - porridge; aquarium - fish; booth - dog; nora - fox.
Then switch roles - let the child think of pairs of words.
Who is this?
Game progress:
Option 1: We ask questions: who treats the sick? Who teaches children at school? Who is preparing dinner? Who is working on the tractor? Who delivers letters and newspapers? Who sews the dress?
Option 2: Questions: what does the janitor do? What does the doctor do? What does an electrician do? What does the teacher do? What does the driver do? What does a painter do? What does a hairdresser do?
3rd option: We come up with riddles. For example: this person works on the street, he has a broom, a shovel.
4th option: "Who needs what?" What does the postman need? What does a hairdresser need? And vice versa: who needs scissors? Who needs a needle?
"Guess the object by its parts"
Game progress: Children name the parts of the object. The first person to guess what it is about gets one point. This option is good because you can play together with your child anywhere. For example, on the way to kindergarten, while waiting in line to see a doctor, etc.
Examples:
Four legs, backrest, seat.
Numbers, arrows.
Letters, pictures, sheets.
Trunk, branches, leaves.
Root, stem, leaves, petals.
Screen, buttons, electric cord, remote control.
Spout, handle, lid, electric cord.
Paws, tail, collar.
Paws, tail, trunk.
Does everything seem too simple at first glance? But in fact, not all children can describe objects. Try it!
"Guess the item from the description"
Game progress: Game conditions are the same as in the previous one. But the task here is more difficult. It is necessary not only to find the correct definitions of objects, but also to correctly coordinate adjectives and nouns by gender, as well as to know such concepts as furniture, vegetables, fruits, insects, domestic and wild animals, etc.
Wild animal, lives in the forest , big, shaggy, likes honey.
Wild animal, sly, red, with a fluffy tail.
Insect, with colorful wings, similar to a flower.
Transport, large, heavy, with wings and tail.
Vegetable, red, round, put in salads and soups.
Sweet, small, in a beautiful paper.
“Think and choose!”
Game progress: Now I will read you a proverb, and you try to find a suitable phrase for it that reflects the general meaning of the proverb, for example:
Measure seven times, and cut once
a) If you cut it wrong yourself, then do not blame the scissors
b) Before you do it, you need to think carefully
c) The seller measured seven meters of fabric and cut it off
The right choice here is "Before you do, you need to think carefully"
Example tasks:
1. Less is better.
a) One good book is more useful to read than seven bad ones.
b) One delicious cake is worth ten bad ones.
c) What matters is not quantity, but quality.
2. If you hurry, you will make people laugh.
a) The clown makes people laugh.
b) To do a job better, you need to think about it well.
c) Haste can lead to ridiculous results.
3. Strike while the iron is hot.
a) A blacksmith forges hot iron.
b) If there are favorable opportunities for business, you should immediately use them.
c) A blacksmith who works slowly often gets more done than one who is in a hurry.
4. There is nothing to blame on the mirror, if the face is crooked.
a) You should not blame the cause of failures on circumstances, if the problem is in yourself.
b) A good quality mirror does not depend on the frame, but on the glass itself.
c) The mirror hangs crooked.
5. The hut is not red in the corners, but red in the pies.

 5, kindergarten No. 15.
5, kindergarten No. 15.  The game is called: "Fix the mistakes." I will say what I know about autumn, and if I am mistaken, you will correct me!
The game is called: "Fix the mistakes." I will say what I know about autumn, and if I am mistaken, you will correct me! 
 (Squat down)
(Squat down)  In conclusion, the teacher uses the verbal method of conversation. Questions lie in the reception of the verbal method. Summarizing conversation to summarize the knowledge gained, and recent events.
In conclusion, the teacher uses the verbal method of conversation. Questions lie in the reception of the verbal method. Summarizing conversation to summarize the knowledge gained, and recent events.