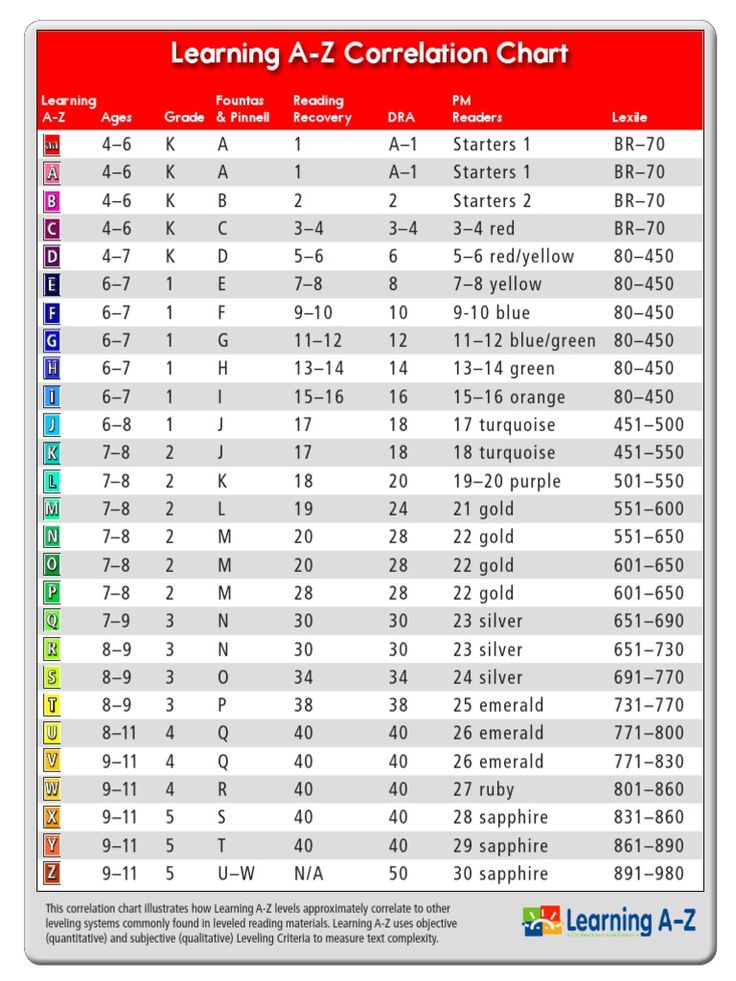
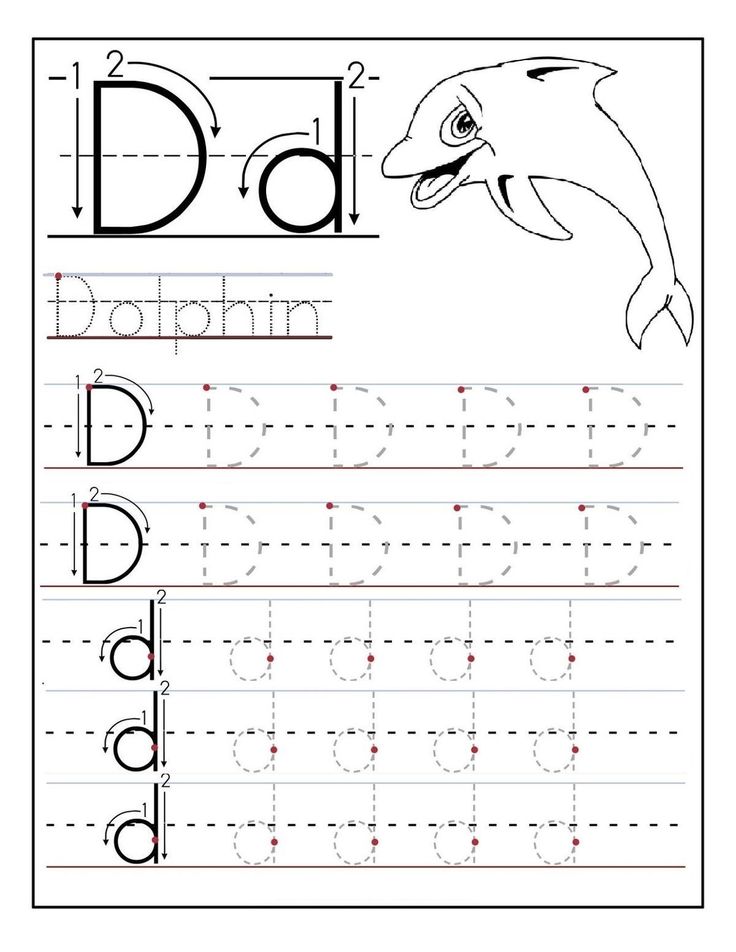
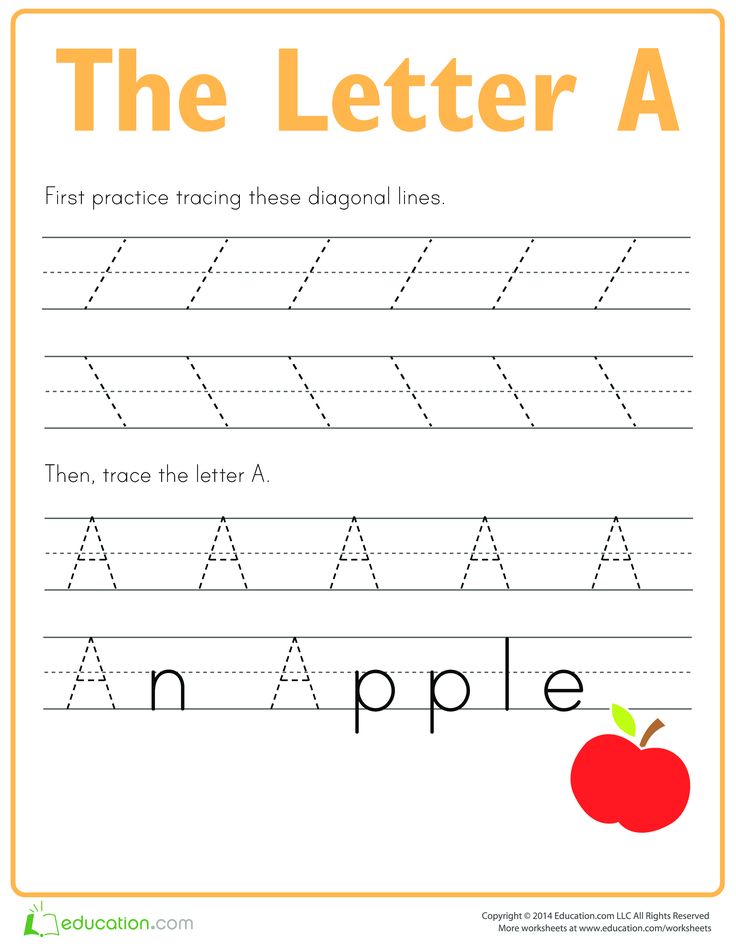
Learning writing letters
Browse Writing Letter Educational Resources
Entire LibraryPrintable WorksheetsGamesGuided LessonsLesson PlansHands-on ActivitiesInteractive StoriesOnline ExercisesPrintable WorkbooksScience ProjectsSong Videos
408 filtered results
408 filtered results
Writing Letters
Sort byPopularityMost RecentTitleRelevance
-
Filter Results
- clear all filters
By Grade
- Preschool
- Kindergarten
- 1st grade
- 2nd grade
- 3rd grade
- 4th grade
- 5th grade
- 6th grade
- 7th grade
- 8th grade
By Subject
- Coding
- Fine arts
- Foreign language
- Math
Reading & Writing
- Leveled Books
Reading
Early Literacy
- Concepts of Print
- Early Writing Practice
Writing Letters
- Writing Names
- Picture Comprehension
- Communicating Through Symbols
- Alphabet
- Reading Comprehension Strategies
- Reading Genres and Types
- Writing
- Grammar
- Science
- Social emotional
- Social studies
- Typing
By Topic
- Arts & crafts
- Coloring
- Holidays
- Offline games
- Seasonal
By Standard
- Common Core
Short A 1
Guided Lesson
Short A 1
Bag, cat and cap are all examples of short A words that kindergarteners will be learning to read this year. You can support this learning with a guided exploration of the short A sound. Kids will be taught how to identify the short A within text, in addition to the corresponding sound. Check out our short A printables for more phonics practice.
Kindergarten
Reading & Writing
Guided Lesson
Search Writing Letter Educational Resources
Young students can train their hands and fine motor skills with support from the Learning Library's tools on writing letters. The ABCs are broken down into simple steps so kindergartners learn to build letters line by line. There is a large supply of tracing assignments, lessons on letter sounds, and much more that familiarize kids with the 26 little letters that create a robust language.
Simple as ABC: Writing Letter Resources
In preschool through first grade, young students learn their ABCs, the building blocks to the world's greatest novels, moving speeches and profound poetry. It all starts with mastering each letter, its sound and shape. The Learning Library provides alphabet writing resources for new students to practice this powerful fundamental.
It all starts with mastering each letter, its sound and shape. The Learning Library provides alphabet writing resources for new students to practice this powerful fundamental.
Handwriting may be a dying art form now that keyboards have largely replaced pencils. But there are still many instances where penning words down occurs, like when filling out a doctor form or writing a personal letter. Recognizing letter shapes is essential for reading, too. Education.com provides printable worksheets and teacher-created lesson plans that teach specific letters, such as Practicing P and Z is for Zookeeper. A preparatory lesson plan, Get Ready to Write! trains students' hand coordination and finger strength by instructing them to write different lines that commonly appear in letters.
Kids can leave the pencil and eraser at home and practice letter writing digitally with the resource center's online games that include a look at short A, E and U. An active hands-on activity, Fine Motor Practice, includes different exercise stations that smooths small-scale coordination capabilities, such as stringing beads and cutting paper with scissors. Guided lessons and printable workbooks on writing the alphabet can also be accessed in the library. Students will be masters of the alphabet—from A to Z—with Education.com's writing letter resources.
Guided lessons and printable workbooks on writing the alphabet can also be accessed in the library. Students will be masters of the alphabet—from A to Z—with Education.com's writing letter resources.
An Introduction to Letter Writing
By: My Child magazine
Introduction
Letter writing is an essential skill. Despite the prevalence of emails and text messages, everyone has to write letters at some point. Letters of complaint, job applications, thank you letters, letters requesting changes or making suggestions — the list goes on and on. Encouraging children to write letters from an early age will improve their communication, social and handwriting skills, and teach them what they need to know about writing and structuring letters.
In this article:
What's so special about receiving a handwritten letter?
Quite apart from curriculum requirements, being asked to write letters is a task that will appeal to children. The sheer fun of sending and receiving letters appeals to every child. There is something special about putting letters into the post box and then having letters delivered by the postman… the brightly colored stamps, seeing your name on the envelope and knowing that inside is a long awaited letter from a friend or member of the family. It shows someone cares and has taken the time to sit down and think about you.
There is something special about putting letters into the post box and then having letters delivered by the postman… the brightly colored stamps, seeing your name on the envelope and knowing that inside is a long awaited letter from a friend or member of the family. It shows someone cares and has taken the time to sit down and think about you.
Handwritten letters have a charm of their own. You can take time to think about what you want to say. You can keep letters to read again and again. You can admire the handwriting; share dreams and thoughts. Responding by letter is very different to the immediacy of a text message or an email.
Back to Top
Activity 1: Warming up to letter writting
Use the above themes to encourage the children to discuss letter-writing. Ask the children to put their hands up if they have ever received a personal letter. Ask for one or more volunteers to talk about how they felt to receive the letter. Here are some initial questions that may help:
- What was in your mind as you read the letter?
- Did you keep the letter to read again?
- Did you share your letter with anyone?
- Did you write back?
And some questions for whole class or group discussions:
- Can the class describe any differences between the handwritten letter and an email?
- Do the children think there is ever a time when only a handwritten letter will do?
Ask the class to interview each other to find out each individual's experiences of writing and sending letters. This can be recorded in a chart.
This can be recorded in a chart.
Back to Top
Activity 2: Introducing letter writing
Collect a supply of different types of letters — both formal and informal. Ask the children to sort them out into two groups. Which were written to friends? Which are formal letters from businesses? Which features or characteristics distinguish formal from informal?
Having done that ask the children to look for differences between the two groups. This allows a discussion to take place about the different types of letter. Draw up a chart for each group covering:
- Address — business or private?
- Greeting — formal or informal?
- Style of letter — friendly or business?
- What is the message?
- How does the letter end?
This will allow the children to find out for themselves the differences between formal and informal letters.
This could be followed by a discussion of the type of letters the children or their families write.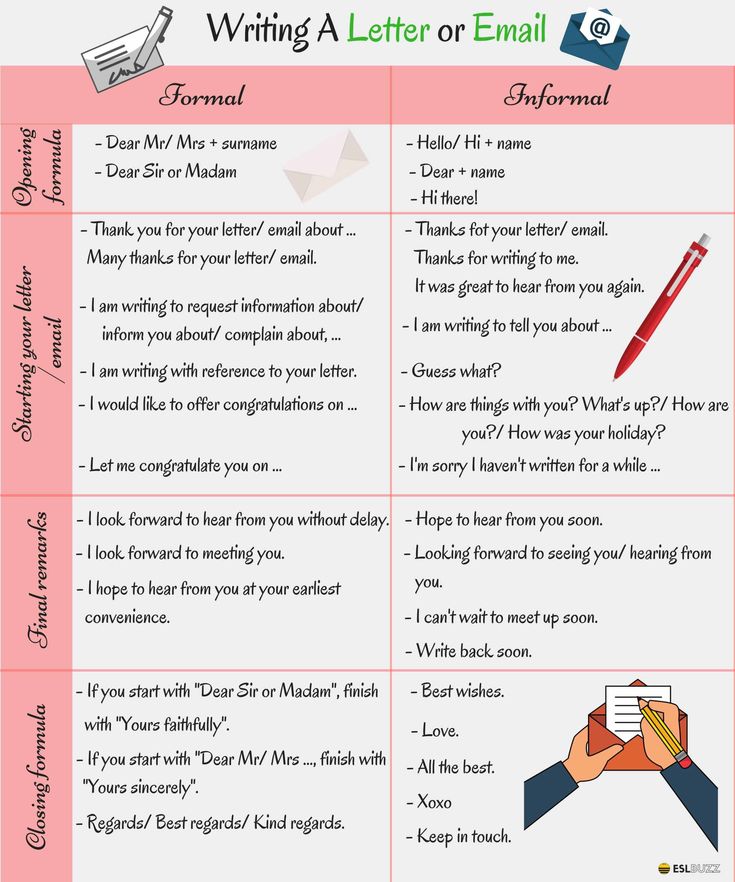 How many occasions can they think of which would deserve a letter to be written? For example:
How many occasions can they think of which would deserve a letter to be written? For example:
- Letters of congratulation
- Exchanging news
- Writing to friends
- Letters saying sorry for doing something wrong
- Making appointments
- Asking for information
- Dealing with banks or stores
- Letters to family members who live some way away
- Letters to Santa Claus
- Thank you letters
- Letters showing how much you appreciate someone
- Letters responding to someone who has had bad news — showing how much you care by trying to share their sadness
- Letters of complaint
- Letters to newspapers and magazines
In each case the children should decide what type of letter would be most appropriate in each case — formal or informal? Draw up a chart for each group.
Back to Top
Activity 3: Formal letters
These are sometimes known as business letters. They are written in a strictly formal style.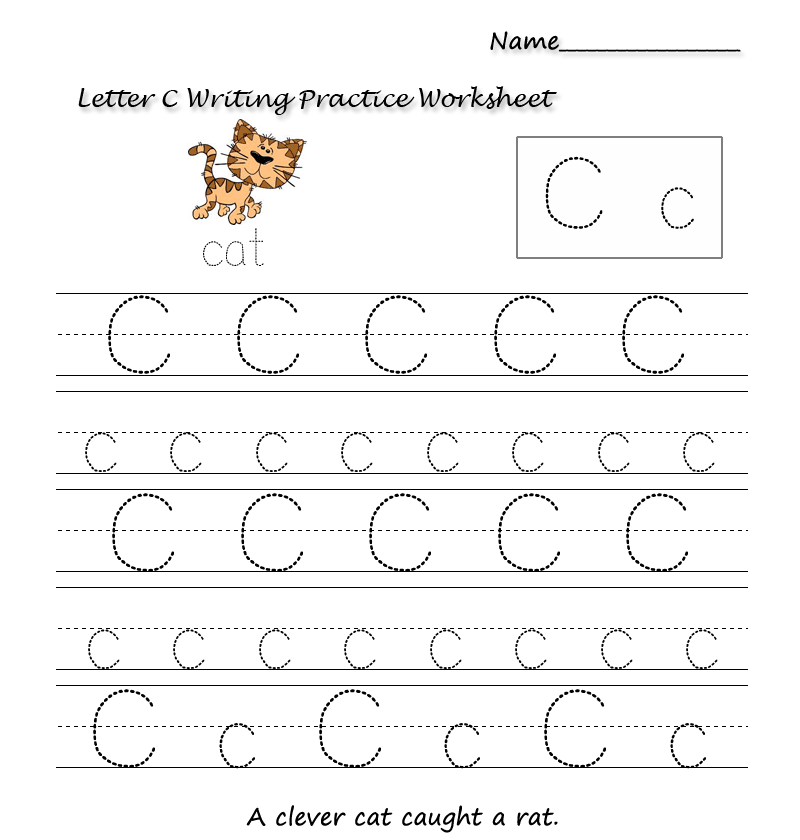 Such letters are always written on an A4 (8" x 11") sheet of paper. They can be folded three times so that the address to which the letter is being sent can appear in the window of a business envelope. The layout is always the same.
Such letters are always written on an A4 (8" x 11") sheet of paper. They can be folded three times so that the address to which the letter is being sent can appear in the window of a business envelope. The layout is always the same.
Structure:
- The senders address is put at the top right hand side
- Include telephone number and email if available
- The address of the person receiving the letter goes on the left hand side below the sender's address
- The date
- Greeting — Dear Sir or Madam. You can use the titles Miss, Mrs. or Mr. if you know the name of the person to whom you are writing
- The message
- Complimentary close — Yours faithfully or Yours sincerely
- Signature
- Write name in block letters (this is to ensure that the person receiving the letter knows exactly who has sent it. Signatures may not be very clear)
Back to Top
Activity 4: Informal letters
These are letters to friends and relations, or people you know well. Structure:
Structure:
- The sender's address should always appear on the top right hand corner of the page.
- Include telephone number and email if available
- Greeting — There are several variations that can be used depending on how well you know the person: Dear Mary, Hi Mary, Greetings
- Complimentary close — short comment, for example Love, Lots of love, With thanks, See you soon
Tips for writing good letters
- Make sure that they are well written. It can be very annoying for someone to have to struggle to read handwriting. Always use your best and clearest handwriting.
- Make sure all your contact details are clearly written down at the top of the letter. If they are not, then you might not get a reply. The correct address is essential.
- Think about what you want to say. If necessary make some notes on a separate sheet of paper first. This will ensure that you do not forget anything.
- Think about to whom you are writing the letter.
 Use the right style of writing and language — formal or informal, business like or friendly.
Use the right style of writing and language — formal or informal, business like or friendly. - Lay out your letter using paragraphs. This makes it easier for the reader.
Back to Top
Activity 5: Letter of inquiry and letters providing information
Suitable for school, children ages 7-9
These are formal letters and messages need to be precise and detailed, covering all the required information. Two types of letters can be undertaken — a letter requesting information; and a reply providing it.
Out in the Milky Way, there is an alien curious about Earth. He writes a letter asking for information about liquids and gases. These do not exist on his planet and he finds it hard to understand what they are.
Write a letter explaining what liquids and gases are. How do they work? What examples could be included? What would be confusing about them? This could link to your science curriculum and could act as a revision exercise giving an opportunity for a discussion about gases and liquids.
The following day, give the children a thank you letter from the alien!
You could link up with another class in the school. One class could write letters of inquiry. These would be delivered to the second class for answering.
Back to Top
Activity 6: Thank you letters
Suitable for school, children ages 5-7 and 7-9
Thank you letters are very important and can be used in lots of ways: thanking organisations for helping, thanking people for helping you, thanking someone for a lovely time. They make a good follow up exercise after receiving presents or going on a visit.
Your class has just been out on a school visit to a farm. Write a thank you letter to the farmer. You will need to say thank you and how much you enjoyed the visit. Give some examples of what you enjoyed best about the day? Was it feeding the lambs? Pond dipping? Seeing the young animals?
Back to Top
Activity 7: Letters of invitation
Suitable for school, children ages 5-7 and 7-9
Everyone likes receiving invitations. Receiving a hand written letter asking you to a party or a special event makes you feel very special.
Receiving a hand written letter asking you to a party or a special event makes you feel very special.
Discuss what type of event might create a need to write letters of invitation. There are plenty of examples — birthday parties, Christmas parties, a visit to a beach with friends; going out to a farm or to the cinema, a wedding or when a new baby is christened; or simply inviting a friend to stay overnight at your house.
Choose a special event and write a letter inviting a friend. What do you need to include in the letter so that they have all the necessary information? You need to be clear on the date and the time, as well as the location. Your friend would be very upset if he or she went to the wrong place. Does he or she need to bring anything with them? Does he or she need to be collected at a set time? Will outdoor clothing be needed if the weather is bad? How will your friend reach the location of the event? Should a parent bring them or will you provide transport?
Remember to ask them to reply saying yes or no. Give a date by which you must have their reply. This is important if food and drink are being provided, or if you need to know exactly how many people are coming.
Give a date by which you must have their reply. This is important if food and drink are being provided, or if you need to know exactly how many people are coming.
Back to Top
Activity 8: Letters of complaint
Suitable for school or home, children ages 5-7 and 7-9
When might a letter of complaint be sent? It might be when someone has done something wrong. Sometimes people write letters to organisations or the newspapers to complain about litter or poor service.
Just imagine what Mr. Bear must have been thinking at the end of the story of Goldilocks and the Three Bears. A naughty girl had broken into his home, eaten his porridge; broken a chair and then gone to sleep on his child's bed. Then she had run away without even saying sorry when the bears came back.
Write a letter of complaint from Mr. Bear to the parents of Goldilocks. What would he say? He would need to get his complaint across very strongly. There would be a list of Goldilocks' misdeeds. He would ask for an apology. Would he ask for payment for the broken chair? Would he ask for action to be taken against Goldilocks? Discuss the various possibilities with the children. What might he ask? Would it be a formal or informal letter?
He would ask for an apology. Would he ask for payment for the broken chair? Would he ask for action to be taken against Goldilocks? Discuss the various possibilities with the children. What might he ask? Would it be a formal or informal letter?
Back to Top
Activity 9: Letters to Santa
Suitable for school, children ages 5-7 and 7-9
Every year children write letters to Santa Claus, asking for special toys at Christmas time. But how many children think about Santa Claus himself? What is his life like? What are the problems of living amid all that snow and ice?
This is an exercise that could involve two classes within a school. Both classes should prepare for the task by listening to some unusual letters. J R Tolkein wrote a lovely book entitled Letters from Father Christmas. Every December a letter would appear telling wonderful tales of life at the North Pole — how the reindeer got loose and scattered presents all over the place; how the accident-prone Polar Bear climbed the North Pole and fell through the roof of Santa Claus's house.
Children in the younger class should write letters to Santa. They should ask about life at the North Pole. What do they think it is like? What sort of characters live there? How does Santa Claus occupy his time for the rest of the year? Consider how they would feel living in a land of snow and ice all year round? Would they want a holiday somewhere warmer?
Once the letters are written, gather them up and take them to an older group of children. Give each child a letter and ask them to write a reply. This would give them the opportunity to use their imagination and create imaginative responses, possibly little stories about life at the North Pole. They could also add in their own ideas. But care should be taken to make sure that all the questions in the original letters are answered.
Finally, take the answers back to the original class for reading and discussing.
Back to Top
Activity 10: Letters to newspapers and magazines
Suitable for school, children ages 7-9
These are letters that aim to pass on an opinion or a message. Examples can be easily obtained from local newspapers or from children's magazines such as DK Find Out or Aquila. They are written slightly differently to normal letters and are always addressed Dear Sir, or Dear — (name of magazine).
Examples can be easily obtained from local newspapers or from children's magazines such as DK Find Out or Aquila. They are written slightly differently to normal letters and are always addressed Dear Sir, or Dear — (name of magazine).
These are letters that are directed at a wide audience — anyone who happens to read it. The sender never gets a direct letter back through the post. Sometimes people are so interested in a letter, which has appeared in a magazine that they want to express their opinions. So they then write a letter to the magazine giving their comments.
So what might go into a letter to a newspaper or magazine? It might be a request — could you provide more stories about skate boarding, or nature? It might be a way of thanking people for providing help. Sometimes letters to local newspapers are used to thank people who helped find a lost dog or help after an accident; but who did not leave their names. By writing to the paper, the sender hopes that the message will reach the people concerned. Sometimes such letters are used to express opinions such as on climate change, treatment of animals, poor services, not enough buses, and human rights.
Sometimes such letters are used to express opinions such as on climate change, treatment of animals, poor services, not enough buses, and human rights.
Letters of this kind need to be very precise. Arguments should be clearly made. Requests for action should be clearly indicated. From reading the letter, everyone should know exactly what the sender is asking.
A major issue is recycling and energy conservation. Everyone is trying to reduce the amount of energy we use. Look at all the reasons why energy conservation is so important. Then, write a letter to a paper or magazine saying why you believe we should avoid wasting energy. Give examples of how energy can be saved? What measures should we take in our homes or schools? Could anything more be done?
Back to Top
Learning to write block letters of the Russian alphabet. Trainer
Electronic library
Raising children, today's parents educate the future history of our country, and hence the history of the world.
- A.S. Makarenko
Learning to write block letters of the Russian alphabet. Trainer
- A
- B
- B
- G
- D
- E
- Yo
- F
- Z
- and
- Y
- K
- L
- M
- H
- O
- P
- R
- C
- T
- W
- F
- X
- C
- H
- W
- W
- b
- S
- b
- E
- Yu
- I
- Tasks
This section contains a simulator that teaches preschoolers 5-6 years old how to write the correct block letters of the Russian alphabet. The simulator consists of a collection of developing children's recipes, arranged in alphabetical order on colored tabs.
Red tabs contain copybooks for studying vowels, blue tabs for studying consonants, gray tabs for studying separating marks. The green tab contains developmental tasks and exercises for consolidating and practical application of writing skills in block letters.
The green tab contains developmental tasks and exercises for consolidating and practical application of writing skills in block letters.
Printing is part of learning to read and write early. This lesson develops attention, fine motor skills, graphic skills, promotes better memorization of the alphabet and improves literacy.
Performing developmental tasks and exercises, the child will get acquainted with block letters, learn how to write them, and also learn the Russian alphabet.
You can print as many copybooks as you need to repeatedly practice writing letters, reinforce your skills, and get a successful learning outcome.
Here various methods of teaching writing in block letters are proposed, which allows you to individually select the most suitable option for your child or put into practice all the proposed methods, making the learning process more interesting and varied for a preschooler.
Tips for working with spelling:
- Let's learn the vowels first.
 They are simpler and easier to pronounce and remember, at this stage of learning there are no problems even for children with speech disorders. Letters denoting the same vowel sound are recommended to be studied in pairs A - I, O - E, U - Yu, E - E, Y - I.
They are simpler and easier to pronounce and remember, at this stage of learning there are no problems even for children with speech disorders. Letters denoting the same vowel sound are recommended to be studied in pairs A - I, O - E, U - Yu, E - E, Y - I. - After vowels, we study consonants. The sequence of study does not matter. As a rule, the letter P and other letters, the pronunciation of which is still difficult for the baby, are studied at the end. It is not recommended to study paired consonants in a row (B - P, G - K, D - T, Z - C, V - F, F - W) - it is difficult for a child at this age not to confuse them by ear.
- There are different approaches to the order of learning the letters, so you can use another, in your opinion, the most acceptable variant of the sequence of letters.
- Practice with your child for no more than 15 to 20 minutes.
- When completing tasks, the preschooler should hold the pen or pencil correctly, without straining the fingers too much.

- It is very important to properly organize the child's workplace: be sure to pay attention to whether it is comfortable for the child to sit at the table, and also where the light source is located. For right-handers, the lamp should be on the left side, and for left-handers, on the right.
- Don't forget to praise your child, even if he doesn't do well on tasks. From classes, a preschooler should receive only positive emotions. This is a prerequisite for further successful learning.
- Remember that learning should be in the form of an exciting game. In no case should a child be forced to fill out prescriptions - this can consolidate an aversion to learning to read and write for many years.
* Methods V.G. were used to create the simulator. Dmitrieva , O.S. Zhukova , M.O. Georgieva , M.P. Tumanovskaya .
- Views: 601576
Children speak
| “When will you play with me? Dad from work - right behind the TV. - Yana, 6 years old |
New
- Lego speech games
- Neurologopedic prescriptions. Learning to read and developing speech
- Become a letter! Dynamic pauses in teaching literacy to preschoolers and younger schoolchildren
- 7 Inexpensive Educational Gifts for Kids
- Speed reading for kids and more
Recommended
Prescriptions for children
| Preparing for school | |
| Hand development | |
| Teaching writing | |
| Interesting tasks | |
| Modern techniques |
Privacy Policy
Prescription.
 Learning to write and draw. Funny letters
Learning to write and draw. Funny letters - Description
- Characteristics
- Product reviews
-
FUNNY LETTERS Compiled by L. Mavrina Artists: A. Bannykh, A. Artyukh, E. Nemirova, D. Goncharova Cover art by E. Efremova
Do you want to teach your child to write? Our recipes will help you with this. Let the baby first practice his hand, circling the fragments of pictures, funny hooks and curls. Then he will be able to draw beautiful even letters on the lines. This will help him in the future to receive only “five” at school.
-
Format 60х90/8 ISBN 978-8-9951-4836-4 Author Mavrina L. Painter A. Bannykh. A. Artyukh. E. Nemirova. D. Goncharova Cover illustration by E.  Efremova
Efremova Series Recipe. Learning to write and draw Number of pages eight The year of publishing 2021 Age restrictions 0+
No comments yet
Leave a review
- Recommended
- Similar items
-
-
New Year in the Little Mouse's house. Book in a case.
available
2 500 rub
More
-
The smallest snowman Four winter tales
available
1 100 rub
More
-
Tractor for Santa Claus
available
550 rub
More
-
And Santa Claus is not real!
available
550 rub
More
-
When Santa Claus was little
available
550 rub
More
-
The smallest snowman Icicle of Desire
available
550 rub
More
-
Letter from Santa Claus.

Learn more
-

 And my mother is a lady! - immediately erase the beginnings "
And my mother is a lady! - immediately erase the beginnings "