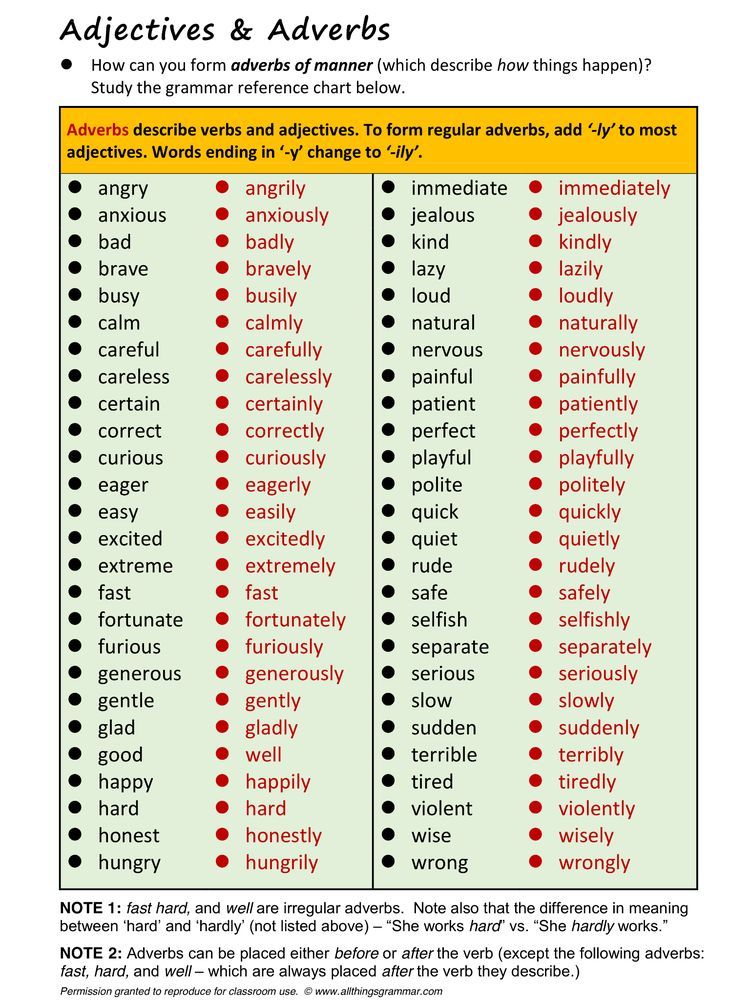
Letter reading levels
Leveling Chart | Scholastic Guided Reading Program for the Classroom
Use the grid below to shop by Guided Reading, Developmental Reading Assessment (DRA), and Lexile® Levels. This chart includes Lexile level recommendations and may also be used as a general leveling guide.
Click on links to shop the Teacher Store!
| Grade | Scholastic Guided Reading Level | DRA Level | Lexile® Levels |
|---|
| Grade | Scholastic Guided Reading Level | DRA Level | Lexile® Levels | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kindergarten |
| Beginning Reader | |||||||||||||||||||
| 1 |
|
| 190L-530L | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2 |
|
| 420L-650L | ||||||||||||||||||
| 3 |
|
| 520L-820L | ||||||||||||||||||
| 4 |
|
| 740L-940L | ||||||||||||||||||
| 5 |
|
| 830L-1010L | ||||||||||||||||||
| 6 |
|
| 925L–1070L |
Back to Top
Web
%PDF-1. 6
%
1 0 obj
>/OCGs[10 0 R 147 0 R]>>/Pages 3 0 R/Type/Catalog>>
endobj
2 0 obj
>stream
application/pdf
 did:15db8152-68a8-46d5-a5b7-6acdab2bb30fuuid:efea4095-1096-4349-8fa2-74f3dc71acefxmp.iid:2c85fddd-02a1-460a-8def-ea2058bc4e49xmp.did:2c85fddd-02a1-460a-8def-ea2058bc4e49uuid:65E6390686CF11DBA6E2D887CEACB407default
did:15db8152-68a8-46d5-a5b7-6acdab2bb30fuuid:efea4095-1096-4349-8fa2-74f3dc71acefxmp.iid:2c85fddd-02a1-460a-8def-ea2058bc4e49xmp.did:2c85fddd-02a1-460a-8def-ea2058bc4e49uuid:65E6390686CF11DBA6E2D887CEACB407default png00
png00 200 BasicFalseGothamNarrow-Black.otf
200 BasicFalseGothamNarrow-Black.otf 10612481.6037180.0000000.000000
10612481.6037180.0000000.000000 6639190.00000099.7680600.009155
6639190.00000099.7680600.009155 55405098.4557870.9826810.228885
55405098.4557870.9826810.228885 65964738.37643963.6499521.181048
65964738.37643963.6499521.181048 60699966.66818965.24300078.234529
60699966.66818965.24300078.234529 7079422.4628062.4628060.000000
7079422.4628062.4628060.000000 20000--OpenType - PS1677719684GothamNarrow-Medium1677719684
20000--OpenType - PS1677719684GothamNarrow-Medium1677719684 0 0.0 612.0 792.0]/Type/Page>>
endobj
12 0 obj
>/Resources>/ExtGState>/Font>/ProcSet[/PDF/Text/ImageC/ImageI]/Properties>/XObject>>>/Thumb 210 0 R/TrimBox[0.0 0.0 612.0 792.0]/Type/Page>>
endobj
208 0 obj
>stream
HWnH}WdE:bx`'bXĶ18ߪfSsA(vu]N:Õxs5o٠?A6_!\@ٛ1맳@?5Lr:o땸[ٗr1sފ%Dkx"E98[RGÅ8'%üe2~4O˺L >}e(h8&cz'R/J+M2Ɨ GiM>ԈXtUVcU*Ax=Q46FhYӢ6"7HŰ?Rjn`?}j%v.@+rkƼcGsq2UP㹍:_H.]XM!D IrqD_t
0 0.0 612.0 792.0]/Type/Page>>
endobj
12 0 obj
>/Resources>/ExtGState>/Font>/ProcSet[/PDF/Text/ImageC/ImageI]/Properties>/XObject>>>/Thumb 210 0 R/TrimBox[0.0 0.0 612.0 792.0]/Type/Page>>
endobj
208 0 obj
>stream
HWnH}WdE:bx`'bXĶ18ߪfSsA(vu]N:Õxs5o٠?A6_!\@ٛ1맳@?5Lr:o땸[ٗr1sފ%Dkx"E98[RGÅ8'%üe2~4O˺L >}e(h8&cz'R/J+M2Ɨ GiM>ԈXtUVcU*Ax=Q46FhYӢ6"7HŰ?Rjn`?}j%v.@+rkƼcGsq2UP㹍:_H.]XM!D IrqD_tReading analyst - reading levels.
CONTENT
- Group 1. Teaching the technique of semantic reading
- Beginner level (letter reading)
- Developing level (reading by syllable)
- Advanced level (reading in whole words and syllables with compound words)
- Free level (reading in whole words)
- Group 2. Development of reading competencies for subject education nine0006
- Weak level
- Training level
- Independent level
The "Reading Analyst" system makes it possible to assess the level of reading competence for two groups - the group for teaching the technique of semantic reading (Group 1) and the group for developing reading competence for subject education (Group 2).
Although we assume that the first group will most likely include elementary school students from grades 1 to 4, and the second group will include secondary school children from grades 5 to 7, we strongly recommend taking into account the individual characteristics of children: if a child elementary school reads very well, test his reading competencies on tests of the secondary school group, but if a child in the fifth grade reads with a lot of technical errors, it may make sense to check his competencies on tests for group 1 elementary school and then select texts for reading corresponding to its level. nine0005
Below we offer brief descriptions of the levels that are determined during testing and evaluation of texts, and also give recommendations on the selection of texts for each level.
Group 1. Education of semantic reading technique
Description of the levels of competence of reading words. The reading speed is low, there is a recall of each letter separately. In some cases, there may be a breakdown in reading a word due to the large time interval between reading letters. Reading comprehension is limited to a word or phrase. The teacher's help is needed both in the name of the letters and their reduction into a word, and in keeping the attention on the text. Reading speed per minute - 10-15 words. nine0005
In some cases, there may be a breakdown in reading a word due to the large time interval between reading letters. Reading comprehension is limited to a word or phrase. The teacher's help is needed both in the name of the letters and their reduction into a word, and in keeping the attention on the text. Reading speed per minute - 10-15 words. nine0005
Recommendations for the selection of texts for the initial level of reading technique:
Texts of the initial level of reading technique are intended for mastering the reading skill from scratch and represent various types of alphabets and short texts necessary to consolidate the skill of recognizing and reading letters and short words. The transfer of the plot is carried out by 2-3 sentences connected sequentially with each other.
Features of texts suitable for this level:
Short texts of 30 words are suitable for beginners, the length of words should not exceed 5–6 letters. It is good if as many words as possible correspond to the following features.
- Words of one or two syllables.
- Three-syllable words must be open syllable (e.g. white ). Stressed vowels must be at the beginning of a word.
- Words begin with a consonant
- Words end in consonant
Very short and simple texts are required for this level of reading. Such texts are not evaluated by the Reading Analyst system, but are selected independently.
Developing level (reading by syllable)
Description of the level
Reading by syllables, in difficult places - spelling. There are many errors such as omissions of syllables and words, substitutions of letters and syllables. There is almost no orientation to punctuation, the intonation when reading does not correspond much to the content. Reading comprehension is low and fragmented. Reading speed is slow. There is a decrease in motivation to read when faced with difficulties. A teacher's help is needed to read words that have more than three syllables and have articulations of three consonants. Reading speed per minute - 35-50 words. nine0005
Reading speed per minute - 35-50 words. nine0005
Recommendations for the selection of texts for the developing level of reading technique:
Texts for the developing level of reading technique are designed to strengthen reading skills, as well as for corrective work in the presence of difficulties in mastering it. May contain a short simple linear plot with a main character or main idea and a small number of secondary additional ideas. If necessary, the narrative can be divided into several small parts without compromising reading comprehension. nine0005
Features of texts suitable for this level:
Texts consisting of 70 words are suitable for the developing level, the length of words should not exceed 10 letters. The text may contain words that have the following features:
- Words with one closed three-letter syllable
- One-syllable words and two-syllable words with a combination of consonants at the beginning of the word (for example: coward , hello )
- Stress on the first syllable in two-syllable words and on the second syllable in three-syllable words (for example: lamp, candy )
- Words of three syllables and four syllables (alternating vowels and consonants) (for example: steamboat , ran )
- Nominative, accusative, dative and prepositional words
- Sentences with simple syntax: definition, subject, predicate.
 (For example: The white bird has arrived. )
(For example: The white bird has arrived. ) - Offers with 2 homogeneous members
- Offers with 3 homogeneous members
- Impersonal offers
- Compound sentences
- Personal verbs
- Introductory words
Texts that are suitable for this level of reading, the "Reading Analyst" system refers to texts for developing reading level .
Advanced level (reading in whole words and syllables with compound words)
Description of level
Whole-word reading of easy words can switch to syllable-by-syllable reading in case of occurrence of polysyllabic, difficult or infrequent words. When reading, there may be errors in the repetition of words and syllables, difficulties in understanding some parts of the text. There is unevenness in the speed of reading and the transfer of expressiveness. Need help reading obsolete words, words with more than 5-6 syllables and texts of 3 levels of complexity. The understanding of the text is adequate, but fragmentary, there is an assimilation of the general plot of the narration, but the details and secondary ideas are not fixed. Reading speed per minute - 65-75 words. nine0005
The understanding of the text is adequate, but fragmentary, there is an assimilation of the general plot of the narration, but the details and secondary ideas are not fixed. Reading speed per minute - 65-75 words. nine0005
Recommendations for the selection of texts for advanced reading skills:
Texts for advanced reading skills can be used to introduce new knowledge and develop competence in meaningful reading, in particular, reading comprehension and formulating answers to questions about the text. The narrative may contain several storylines or ideas, the number of secondary elements of the narrative may increase, but should remain within 5. The text should be divided into semantic parts. These texts can be offered to read for leisure reading to schoolchildren who have developed and fluent levels of reading technique. nine0005
Features of texts suitable for this level:
Texts of about 100 words are best for the advanced level, the length of words should not exceed 14 letters. The text may contain words with the following properties:
The text may contain words with the following properties:
- Monosyllabic words with a combination of consonants at the end of the word (for example: scarf )
- Two-syllable words with a combination of consonants in the middle of the word (for example: srot ) nine0007 Three-syllable words with a combination of consonants at the beginning, middle or end of a word (for example: beauty, harness)
- Words of four or five syllables (alternating vowels and consonants) (for example: drawing)
- Adverbs
- Genitive and instrumental words
- Complex sentences, sentences with coordinating conjunctions and sentences with direct speech
- Reverse word order in a sentence. (For example: Vasya came home late. -
- The presence of cardinal numerals, pronominal adjectives and pronominal nouns
Texts that are suitable for this level of reading, the system "Reading Analyst" refers to texts for advanced reading level.
Free level (reading in whole words)
Description of the level
Reading in whole words with a small number of errors in new terms, obsolete words or polysyllabic words, infrequently occurring words. Errors can be noticed by the reader and corrected. There is respect for intonation and expressiveness. Comprehension of the text is complete, answers to questions are detailed. The reader understands causal relationships, can predict linear events. Reading does not require the help of a teacher. Reading speed per minute - more than 100 words. nine0005
Recommendations for the selection of texts for the free level of reading technique:
Texts for the free level of reading technique are suitable for studying the subject and forming mental operations of analysis and forecasting when working with text, which are part of the reading competence. The plot in the text may be non-linear with additional inclusions of secondary storylines or ideas.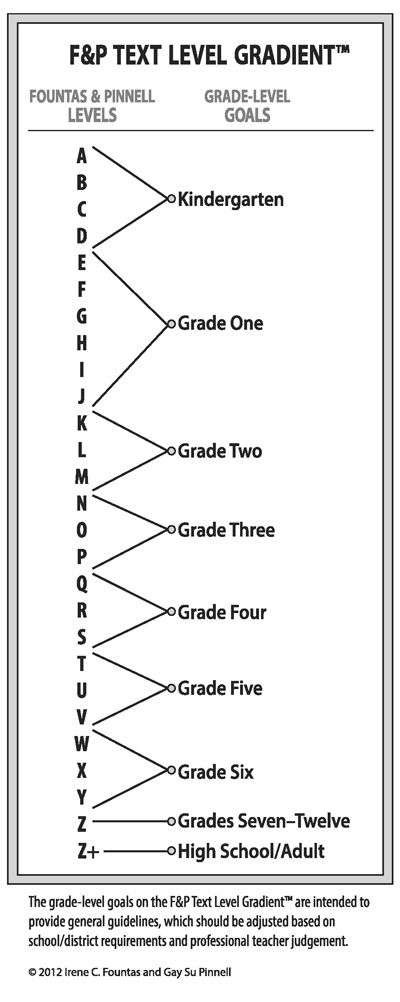 The story should be broken down into small semantic parts. For students with a free level of reading technique, to maintain motivation, the selection of texts includes the thematic interests of schoolchildren. Students can read such texts for pleasure. nine0005
The story should be broken down into small semantic parts. For students with a free level of reading technique, to maintain motivation, the selection of texts includes the thematic interests of schoolchildren. Students can read such texts for pleasure. nine0005
Features of texts suitable for this level:
The free reading level allows you to read texts of 100 words, but words in the text can contain up to 18 letters. Words with the following parameters can be included in the text:
- Sentences with adversarial conjunctions
- Rarely used, obsolete words
- Foreign words
- The presence of participial phrases
Texts that are suitable in their parameters for this level of reading, the Reading Analyst system refers to texts for free reading .
Group 2. Development of reading competencies for subject training
Description of levels in the formation of reading competencies for subject training
Weak level
Reading level
It is difficult, no smooth, there are no smooth inaccuracies, mistakes. Comprehension of the text occurs at a superficial level. Most often, there is just voice-over of the text. Can read light text independently. Reading more complex texts requires the help of an adult. Reading accuracy is below 85%, error rate is more than 20 words. He can correct 1 mistake out of 5 on his own. Reading speed is slow, there is no orientation to punctuation marks. Understanding is not adequate, fragmentary, there are errors in understanding both the text itself, and the subtext, and beyond the text. There is no way to generalize and use the information read. There are answers to factual questions like: Who? What? When? Where? How much? Is not it? nine0005
Comprehension of the text occurs at a superficial level. Most often, there is just voice-over of the text. Can read light text independently. Reading more complex texts requires the help of an adult. Reading accuracy is below 85%, error rate is more than 20 words. He can correct 1 mistake out of 5 on his own. Reading speed is slow, there is no orientation to punctuation marks. Understanding is not adequate, fragmentary, there are errors in understanding both the text itself, and the subtext, and beyond the text. There is no way to generalize and use the information read. There are answers to factual questions like: Who? What? When? Where? How much? Is not it? nine0005
Recommendations for the selection of texts for a weak level of reading for subject teaching:
Texts suitable for a weak level are intended primarily for correcting reading skills and competencies, especially in cases where there are: a large number of errors, misunderstanding of what has been read, inability to answer factual questions.
For a weak level of reading competence, texts with the following properties are suitable for subject teaching:
- The text consists of 2-3 paragraphs.
- The text consists of short sentences without complex constructions and special language tools.
- There are no more than 3-4 terms in the text.
- The main idea is clear, simple, clearly formulated at the beginning of the text.
Texts that are suitable for this level of reading, the system "Reading Analyst" refers to texts for a weak level of reading for subject teaching. nine0004
Educational level
Description of the level
Reading has an average level, which is reflected in errors in words and intonations when reading. There is smoothness, except for those moments when complex words and phrases occur. Reading flexibility and expressiveness are present when reading light texts. For more complex texts, adult assistance is required. Understanding of the text is adequate, but fragmentary. You can meet errors in understanding subtext and overtext. The accuracy of reading technique exceeds 85%, the error rate is 1 in 20 words. Ability to correct your reading errors - 2 out of 5. Reading speed is average. Can use information from the text within a narrow framework, generalize and find causal relationships, which allows answering questions of evaluative and convergent types. (Why? How? How? What do you think?)
Understanding of the text is adequate, but fragmentary. You can meet errors in understanding subtext and overtext. The accuracy of reading technique exceeds 85%, the error rate is 1 in 20 words. Ability to correct your reading errors - 2 out of 5. Reading speed is average. Can use information from the text within a narrow framework, generalize and find causal relationships, which allows answering questions of evaluative and convergent types. (Why? How? How? What do you think?)
Recommendations for the selection of texts for the academic level of reading for subject education:
Texts suitable for the academic level are intended to introduce you to the topic of the academic subject, to start studying the topic. Texts of this level can be used to develop the technique of semantic reading, as well as to develop the skills of reproducing the content of the understood text and answering questions about it. In addition, students who experience some difficulty in reading can read such texts for pleasure, which helps to strengthen the motivation to read. nine0005
nine0005
Texts for the intermediate level should have the following characteristics:
- The text has a simple logical and semantic structure.
- The main idea of the text is clear and precise.
- The main idea of the text is located either at its beginning or at the end.
- Each paragraph is linked to the previous one by the corresponding means of communication.
- The volume of terms does not exceed 5–7 words.
Texts that are suitable in terms of their parameters for this reading level are classified by the Reading Analyst system as Reading level texts for subject teaching.
Independent level
Level description
Reading is easy. It is characterized by fluency, ease, a small number of errors, expressiveness. Able to discuss what has been read. The help of the teacher is not required when reading texts of any complexity.
The independent level of reading competence for subject education is characterized by the following student skills: complete (basic thoughts and details), precise (meanings of words are known), distinct (all linguistic ways of expressing meaning are known), deep (understanding of text, subtext, overtext, context) understanding of a rather long text, often containing conflicting information, from unfamiliar and unfamiliar subject areas. Inaccuracies in one of the four parameters are allowed. The ability to determine the difficulties of reading and understanding the text, as well as the quality of one's reading and understanding of the text, analyzing the quality of full and short answers to questions. Positive and interested attitude towards free, abundant reading. nine0005
Inaccuracies in one of the four parameters are allowed. The ability to determine the difficulties of reading and understanding the text, as well as the quality of one's reading and understanding of the text, analyzing the quality of full and short answers to questions. Positive and interested attitude towards free, abundant reading. nine0005
Recommendations for the selection of texts for the independent level of reading competence for subject education:
A text suitable for the independent level can be designed to deepen knowledge in a particular academic subject, it introduces a large number of facts and terms. In addition, texts of an independent level are suitable for the formation and development of mental operations of analysis and forecasting when working with text, as well as the ability to make annotations, questions, formulate full and short answers to them. nine0005
Texts suitable for independent reading competence for subject-specific learning are characterized by the following properties:
- The text contains the author's opinion, is emotionally colored.

- The structure of the text can be complex, complex, the main idea is read from the text and can be located anywhere in it.
- The text contains a problem that the reader formulates independently based on its content. nine0007 Understanding the text requires background knowledge hidden in the text.
Texts that are suitable for this level of reading, the system "Reading Analyst" refers to texts for independent reading level for subject education.
Rule for reading English letters C & G (exercises and word tables)
Posted or Updated on . Author Tatiana
In lesson 4 of the course "English: repeating the rules of reading." Part 2 we will continue to learn to read in English. In this lesson, we'll look at rule for reading English letters Cc and Gg . As usual, exercises with audio are waiting for you.
Different reading (discrepancy) in English is when the same letter is read differently depending on which letter it is BEFORE.
* * *
Later in the lesson, we'll look at how the consonants Cc and Gg are read in English. You will learn the general rule and will be able to practice by doing the exercises. nine0005
Lesson content:
- Reading rule for English letters Cc and Gg
- Exercises for reading words with the letter Cc
- Exercises for reading words with the letter Cc
* * *
General rule for reading C & G in English
There is a general rule for reading C [ci] & G [ʤi] in English.
If the letters c & g come before i, e, y, then they read as in the alphabet: [s] and [ʤ]. Otherwise, like [k] and [g].