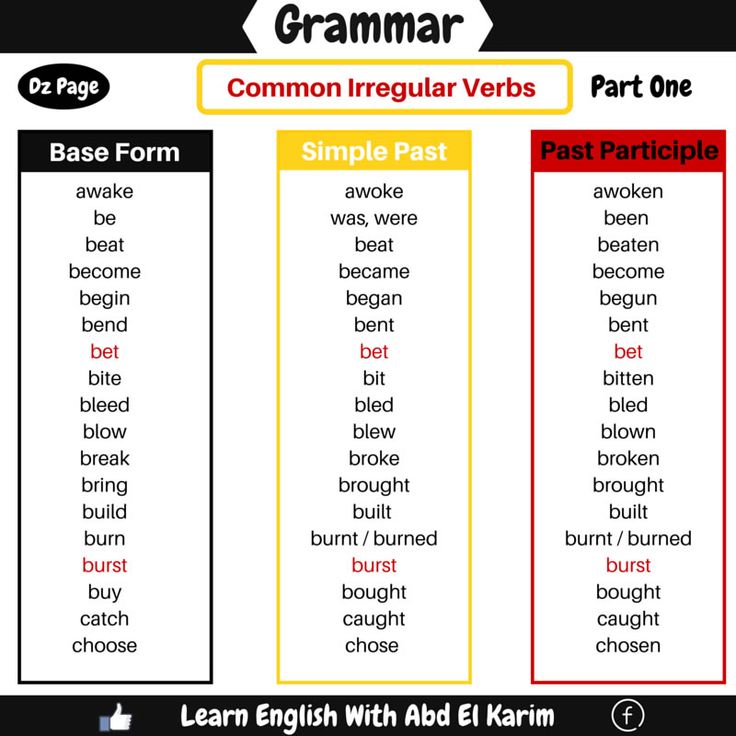
Math is first
First In Math Online Math Practice
Since schools closed, students have solved 3,420,270,287 problems.
28,585,540,416 math problems solved — and counting!
"I was truly amazed at the interest and determination First in Math created in my students, motivation was NO problem! Not only did they learn math and improve their ability to focus, they also learned the importance of setting and achieving daily short-term goals to eventually achieve things that in the beginning were only dreams."
Joel Stockton — 5th-grade Teacher, Cavazos Elementary, La Joya ISD, TX LEARN MORE
First In Math reaches all K-8 students, from intervention to gifted, and all demographics, making it an invaluable
supplement to any curriculum.
LEARN MORE >>
More than 200 self-paced activities offer immediate feedback to help students master procedural skills—and help
educators assess where intervention is needed.
LEARN MORE >>
"There is such a value in First In Math. It allows kids who need a little extra help a chance to work on their skills and it allows kids who excel to go beyond what is taught in the classroom."
Dr. Frank Fischel — Principal, Mountain View Elementary School, Flanders, NJ
Setting and achieving goals, as well as ongoing opportunities for recognition, keeps students energized to sustain accelerated effort over time.
LEARN MORE >>
First In Math Demo
Teachers, enroll one classroom for free! If you love First In Math and decide to buy, your students can continue without missing a beat.
Math Success Stories
Read informative articles from our library, including educational theory about why First In Math works,
case studies,
success stories,
testimonials, and
results.
Watch Video
See the power of First In Math! This four-minute video shows you how engaging FIM games are for both students and educators.
- show password
Access your educator account
OR
OR
Why don't you try a lorem ipsum game today?
First In Math Online Math Practice
Since schools closed, students have solved 3,420,270,287 problems.
28,585,540,416 math problems solved — and counting!
"I was truly amazed at the interest and determination First in Math created in my students, motivation was NO problem! Not only did they learn math and improve their ability to focus, they also learned the importance of setting and achieving daily short-term goals to eventually achieve things that in the beginning were only dreams. "
"
Joel Stockton — 5th-grade Teacher, Cavazos Elementary, La Joya ISD, TX LEARN MORE
First In Math reaches all K-8 students, from intervention to gifted, and all demographics, making it an invaluable
supplement to any curriculum.
LEARN MORE >>
More than 200 self-paced activities offer immediate feedback to help students master procedural skills—and help
educators assess where intervention is needed.
LEARN MORE >>
"There is such a value in First In Math. It allows kids who need a little extra help a chance to work on their skills and it allows kids who excel to go beyond what is taught in the classroom."
Dr. Frank Fischel — Principal, Mountain View Elementary School, Flanders, NJ
Setting and achieving goals, as well as ongoing opportunities for recognition, keeps students energized to sustain accelerated effort over time.
LEARN MORE >>
First In Math Demo
Teachers, enroll one classroom for free! If you love First In Math and decide to buy, your students can continue without missing a beat.
Math Success Stories
Read informative articles from our library, including educational theory about why First In Math works, case studies, success stories, testimonials, and results.
Watch Video
See the power of First In Math! This four-minute video shows you how engaging FIM games are for both students and educators.
- show password
Login required.
Access your educator account
OR
OR
Why don't you try a lorem ipsum game today?
Table of digits and classes of numbers in mathematics
Numbers and figures
Numbers are counting units. With the help of numbers, you can count the number of objects and determine various values.
Special characters are used to write numbers - numbers . There are ten of them in total: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0.
There are ten of them in total: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0.
The natural numbers are the numbers that we use when counting. Here they are: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, …
- One (1) is the smallest number, and there is no largest number.
- Zero (0) means no item. Zero is not a natural number.
The name of the number depends on the number of digits.
A number that consists of one character is called single digit . The smallest single-digit is 1, the largest is 9.
A number that consists of two digits is called two-digit . The smallest two-digit is 10, the largest is 99.
Numbers written with two, three, four or more digits are called two-digit , three-digit , four-digit or multi-digit . The smallest three-digit number is 100, the largest is 999.
The smallest three-digit number is 100, the largest is 999.
Each digit in a multi-digit number takes a certain place - position .
Solve your math homework for 5.
Detailed solutions will help you understand the most difficult topic.
Number classes
Digits in the notation of multi-digit numbers are divided from right to left into groups of three digits each. These groups are called classes . In each class, the numbers from right to left represent the units, tens, and hundreds of that class.
Class table:
Names of classes of multi-digit numbers from right to left:
- the first is the class of units,
- second - thousand class,
- third - million class,
- fourth - billion class,
- fifth - trillion class,
- sixth - quadrillion class,
- seventh - quintillion class,
- the eighth is the sextillion class.

To make it convenient to read a multi-digit number entry, a small gap is left between the classes. For example, to read the number 1253296, it is convenient to first highlight the classes in it:
- 125 911 723 296.
And now read the number of units of each class from left to right:
- 125 billion 911 million 723 thousand 296.
When reading a class of units, there is no need to add the word "units" at the end.
Digits of numbers
The position of a digit in a number entry determines its value. For example:
- 1 123 contains: 3 units, 2 tens, 1 hundred, 1 thousand.
We can put it another way and say that in a given number 1123, the number 3 is in the ones place, 2 is in the tens place, 1 is in the hundreds place, and 1 is the value of the thousands place.
Let's clarify what a discharge is in mathematics. Digit is the position or location of a digit in a natural number notation.
Each category has its own name. The higher digits always live on the left, and the lower digits always live on the right. To remember faster, you can use a table.
The number of digits always corresponds to the number of digits in the number. This table has the names of all the digits for a number that consists of 15 characters. The following digits also have names, but they are rarely used.
The lowest (lowest) digit of a multi-digit natural number is the units digit.
The highest (highest) digit of a multi-digit natural number is the digit corresponding to the leftmost digit in the given number.
Bit units are designated as follows:
- Units are units of the first digit (or simple units) and are written in the first place on the right.
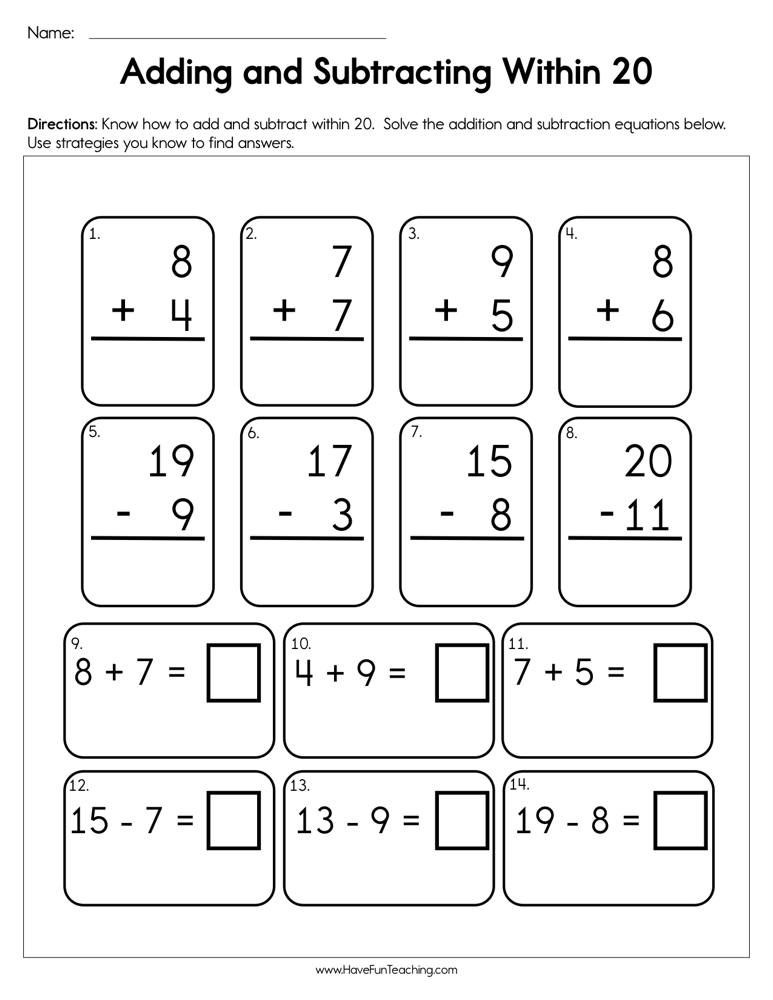
- Tens - units of the second digit and are written in the number in second place from the right.
- Hundreds are units of the third digit and are written in third place from the right.
- Thousand units are units of the fourth digit and are written in fourth place from the right.
- Tens of thousands are units of the fifth digit and are written in fifth place from the right.
- Hundreds of thousands - units of the sixth digit and are written in the number in the sixth place from the right, and so on.
Every three consecutive digits constitute a class. The first three digits: units, tens and hundreds, form a class of units (first class). The next three digits: units of thousands, tens of thousands and hundreds of thousands - form the class of thousands (second class). The third class will be units, tens and thousands of millions and so on.
| To make it easier to understand mathematics - sign up for our courses in mathematics! |
Let's practice
Example 1. Write down the number containing:
Write down the number containing:
- 55 units of the second class and 100 units of the first class;
- 110 units of the second class and 5 units of the first class;
- 7 second class units and 13 first class units.
Answer:
- 55 100;
- 110 005;
- 7013.
All bit units other than simple units are called compound units . Every ten units of any digit equals one unit of the next higher digit:
- 10 units equals 1 ten;
- 10 tens equals 1 hundred;
- 10 hundreds equals 1 thousand;
- 10 thousand equals 1 ten thousand;
- 10 tens of thousands equals 1 hundred thousand;
- 10 hundred thousand equals 1 million.

To find out how many units of any digit are in a number, you need to discard all the digits denoting units of the lowest digits and read the number that is expressed by the remaining digits.
Example 2. How many hundreds are there in 6284?
As we argue:
In the number 6284, the third place in the class of units is the number 2, which means that there are two hundred in the number.
The next digit from the left is 6, meaning thousands. Since every thousand contains 10 hundreds, there are 60 in 6 thousand of them.
This means that this number contains 62 hundreds.
The number 0 in any digit means the absence of units in this digit.
Simply put, the number 0 in the tens place means the absence of tens, in the hundreds place - the absence of hundreds, etc. In the place where 0 stands, nothing is said when reading the number:
- 11 627 - eleven thousand six hundred and twenty seven.
- 31 502 - thirty one thousand five hundred two.
To help you understand this topic, you can print out the Year 4 Grade Chart and refer to it if you have any problems.
Ranking of countries by the quality of mathematics and science education
In its annual report The Global Competitiveness Report, the World Economic Forum (WEF) collects various indicators of the world's economies and compares them with each other. One of the parameters that affects the country's final score in this study is the level of education. At the same time, the report provides data on the quality of mathematics and science education in schools and universities around the world. We are talking about the level of teaching exact disciplines, such as mathematics, physics, chemistry, biology. Thus, these statistics do not include the humanities, such as history, languages, law, economics or literature.
According to the study, the level of teaching in the exact sciences is the highest in European countries. Moreover, the former Soviet countries, such as Estonia, Ukraine, Russia and Armenia, turned out to be unexpectedly high in the ranking. It is curious that in the humanities our countries are traditionally at the bottom of the ranking, while the exact sciences continue to be at a high level of teaching for many years in a row. Below you can see the corresponding list where the countries of the world are located, depending on the level of teaching of natural sciences. The higher the index value for a country, the higher the level of teaching. Also attached is the original report detailing each country's score on the selected indicator. Latest version of rating Quality of math and science education was released in 2018.
Moreover, the former Soviet countries, such as Estonia, Ukraine, Russia and Armenia, turned out to be unexpectedly high in the ranking. It is curious that in the humanities our countries are traditionally at the bottom of the ranking, while the exact sciences continue to be at a high level of teaching for many years in a row. Below you can see the corresponding list where the countries of the world are located, depending on the level of teaching of natural sciences. The higher the index value for a country, the higher the level of teaching. Also attached is the original report detailing each country's score on the selected indicator. Latest version of rating Quality of math and science education was released in 2018.
Reports: GCR2018.pdf

 1
1  1
1  6
6  4
4  1
1  7
7  2
2