Math terms starting with k
Learn Definition, Facts and Examples
The vocabulary of mathematics contains words that start with the letter ‘K’. There are a lot of words used in mathematics. It is important to have knowledge of the vocabulary of maths as it is helpful for us to know the terminologies and their meaning which are eventually helpful in grabbing concepts.
Math Words Starting with K
In this article, we will discuss some of the words that start with the letter ‘K’. The list of the words is provided with a detailed explanation of each word so that students can understand the meaning of the words and use them in maths.
List of Words
The list of words that start with the letter K is given below.
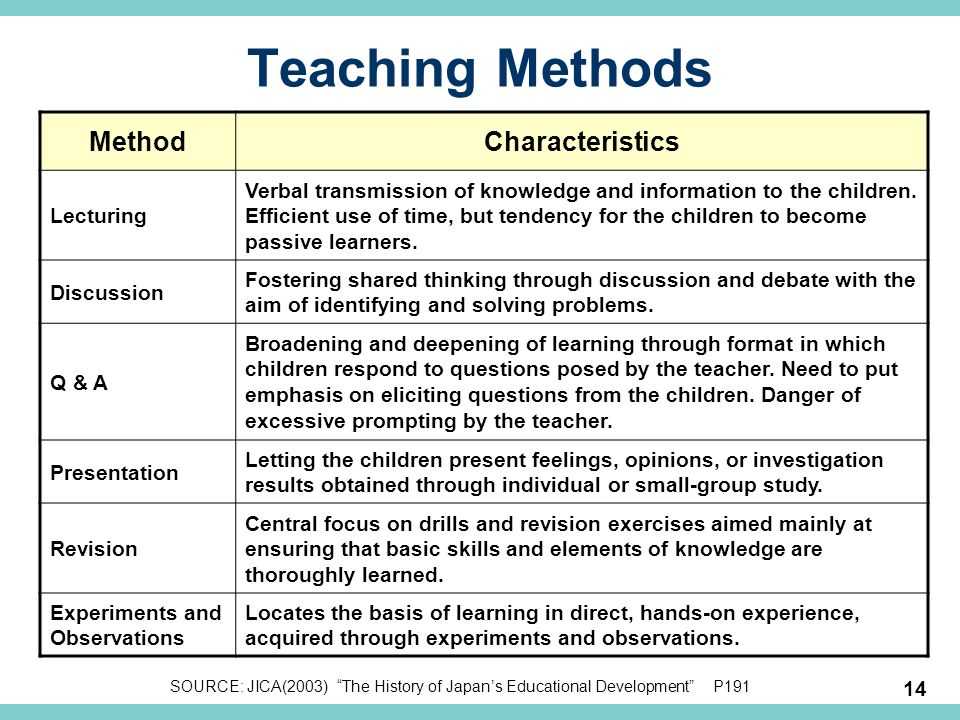
S.No. | Words |
1 | Kilogram |
2 | Kilometer |
3 | Kelvin |
4 | Kilobyte |
5 | Key |
Let’s understand these terms in detail.
Kilogram
When we go to the market we bought things in some kind of measurement. You may have heard the term kilogram which is a type of unit to measure weight. The kilogram can be written as kg. Hence it is a measure of mass. 1 Kilogram is equal to 1,000 grams.
Things That Weigh in Kg
Kilometer
A kilometer is used for the measurement of distance. 1 kilometer is equal to 1000 meters. Hence it is a metric unit of distance which can also be written as km.
Kelvin
Kelvin is a unit of measurement of temperature. Kelvin scale is used on some thermometers to measure temperature.
Kilobyte
It is a unit of data measurement for computers. 1 kilobyte equal to 1000 bytes. This is a very important concept for computer technology and digital electronics which you will learn in higher classes in depth.
1 kilobyte equal to 1000 bytes. This is a very important concept for computer technology and digital electronics which you will learn in higher classes in depth.
Key
A key in maths is defined as a list or note which describes the meaning of each symbol on a graph.
Conclusion
In this article the discussion about the math words that start with K is done. The list of words is provided as well words are explained in detail. Students are required to know these terminologies as it will help them to understand the complex concept of maths.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dictionary of terms in mathematics from A to Z - POCHEMUKHA.
 RU answers to questions.
RU answers to questions. Axiom is a statement accepted without proof.
The algebraic expression is a number of numbers, denoted by letters or numbers, and connected using the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, raising to a power, and extracting a root.
Abcissa (French word). One of the Cartesian coordinate points. Is the first. It is usually denoted by the symbol "X". First used by G. Leibniz in 1675 (German scientist).
Additivity. Some property of quantities. He speaks about the following: the value of a certain quantity corresponding to a full-fledged object is equal to the sum of the values of such a quantity that correspond to its parts in any division of a full-fledged object into parts.
Adjunct. Fully corresponds to algebraic addition.
Axonometric. One of the ways to represent spatial figures on a plane.
Algebra. Part of mathematics that studies problems and solutions of algebraic equations. The term was first seen in the 11th century. Applied Muhammed ben-Musa al-Khwarizmi (mathematician and astronomer).
Argument (function). Variable value (independent) with which the value of the function is determined.
Arithmetic. The science that studies operations on numbers. Originated in Babylon, India, China, Egypt.
Asymmetric. Absence or violation of symmetry (inverse of symmetry).
Infinitely large value is greater than any given number.
An infinitely small value is less than any finite value.
Billion. One thousand million (one followed by nine zeros).
Bisector. A ray starting at the corner vertex (divides the corner into two parts).
Vector. Directed straight line segment. One end is the beginning of the vector; the other is the end of the vector. For the first time the term was used by W. Hamilton (an Irish scientist).
Directed straight line segment. One end is the beginning of the vector; the other is the end of the vector. For the first time the term was used by W. Hamilton (an Irish scientist).
Vertical corners. A pair of corners that has a common vertex (formed by the intersection of two lines in such a way that the side of one corner is a direct continuation of the second).
Vector is a quantity characterized not only by its numerical value, but also by its direction.
Graph - a drawing that clearly depicts the dependence of one value on another, a line that gives a visual representation of the nature of the change in the function.
Hexahedron. Hexagon. The term was first used by Pappus of Alexandria (Ancient Greek scholar).
Geometry. Part of mathematics that studies spatial forms and relationships. The term was first used in Babylon/Egypt (5th century BC).
Hyperbole. Open curve (consists of two unrestricted branches). The term appeared thanks to Apollonius of Perm (ancient Greek scientist).
Hypocycloid. This is the curve that the point of the circle describes.
Homothety. An arrangement between figures (similar), in which the lines connecting the points of these figures intersect at the same point (this is called the center of the homothety).
Degree. Unit for flat corner. Equal to 1/90 of a right angle. Measuring angles in degrees began more than 3 centuries ago. For the first time such measurements were used in Babylon.
Deduction. Form of thinking. With its help, any statement is deduced logically (based on the rules of the modern science of "logic").
Diagonal. A line segment that connects the vertices of a triangle (they do not lie on the same side). First used the term Euclid (3rd century BC).
Discriminant. An expression made up of the values that define the function.
Fraction is a number made up of a whole number of fractions of one. It is expressed as the ratio of two integers m/n, where m is the numerator showing how many parts of the unit are in the fraction, and n is the denominator showing how many parts the unit is divided into.
Denominator. Numbers that make up a fraction.
The golden ratio is the division of a segment into two parts so that the larger part is related to the smaller one, as the entire segment is to the larger part. Approximately equal to 1.618. The criterion of beauty, used in architecture, etc. The term was introduced by Leonardo da Vinci.
Index. Alphabetic or numeric index. With its help, mathematical expressions are supplied (this is done in order to distinguish from each other).
Induction. Method for proving a mathematical equation.
Int. Basic concept of mathematical analysis. It arose due to the fact that it took to measure volumes and areas.
Irrational number. A number that is not rational.
Leg. One of the sides of a right triangle that is adjacent to a right angle.
Square Regular quadrilateral (or rhombus). Each corner of the square is a straight line. All angles in a square are equal (by 90 degrees).
Mathematical constant. A value that never changes in its value. A constant is the opposite of a variable.
Cone. A body that is bounded by a single cavity by means of a conical surface. It intersects a plane (the plane is perpendicular to its axis).
Cosine. Is one of the trigonometric functions. The designation in mathematics/higher mathematics is cos.
Equation root - solution, the value of the unknown, found through known coefficients.
The constant is a constant value.
Coordinates are numbers that define the position of a point on a plane, surface, or in space.
Logarithm. Exponent "m". It must be raised to the "a" power in order to get some NT. For the first time, the logarithm was proposed by J. Napier.
Line is the common part of two adjacent surface areas.
Max. Highest value of the function.
Scale. The ratio of two linear dimensions to each other. Used in many modern industries. The main - cartography, geodesy.
Matrix. Rectangular table. It is formed using the set of a number (definite). Includes columns and rows (matrix structure). For the first time, the term "matrix" appeared with the scientist J. Sylvester.
Median. A segment that connects the vertex of a triangle and its midpoint on the opposite side.
Minimum. Smallest value of the function.
Polygon. Geometric figure. The definition is a closed broken line.
Module. Absolute value (real number).
The set is a collection of elements united by some attribute.
Norm. The absolute value of the number.
The inequality is two numbers or expressions connected by signs (greater than) or (less than).
Oval. Convex, closed figure (flat).
Circle. Numerous points located on a plane.
Ordinate. One of the Cartesian coordinates. It is usually designated as the second.
Octahedron. Geometric figure. One of the five polyhedra (regular). The octahedron includes 8 faces (regular), 6 vertices and 12 edges.
Parallelepiped. Prism. The base is a parallelogram or a polyhedron (equivalent concepts). Has 6 edges. Each face is a parallelogram.
Has 6 edges. Each face is a parallelogram.
Parallelogram. Quadrilateral. Its opposite sides are parallel (in pairs). At the moment, there are 2 special cases of a parallelogram: a rhombus and a square. The main property of this geometric figure:
• Opposite sides are equal;
• Opposite angles are equal.
Perimeter. The sum of all sides of a geometric figure. For the first time it was possible to meet at Archimedes and Heron (ancient Greek scientists).
Perpendicular. A straight line that intersects a plane (any) at a right angle.
Pyramid. Polyhedron. Its base is a polygon. Any other face is a triangle (these faces have a common vertex). At the moment, pyramids can be of various types: triangular, quadrangular, and so on (they are distinguished by determining the number of corners).
Planimetry. One of the most important parts of elementary (simple) geometry. Planimetry studies the properties of figures that are on a plane. For the first time, the term was designated by Eculid (an ancient Greek scientist).
Planimetry studies the properties of figures that are on a plane. For the first time, the term was designated by Eculid (an ancient Greek scientist).
Plus. A sign that denotes a mathematical operation - addition. In addition, positive numbers are denoted with a plus. For the first time, the sign was introduced by J. Vidman (a famous Czech scientist).
Limit. The basic concept of mathematics. Denotes: a variable value approaches a constant value (defined) indefinitely. The term was first used by the famous scientist Newton.
Prism. Polyhedron. The first 2 faces are equal angles (these are the bases of the prism). The rest is the side faces.
Projection. One of the ways to depict spatial and flat figures.
Variable is a value whose numerical value changes according to a certain, known or unknown law.
Plane is the simplest surface. Any line connecting two of its points belongs entirely to it.
Any line connecting two of its points belongs entirely to it.
Line is a set of points common to two intersecting planes.
Percentage is a hundredth of a number.
Radian. Angle unit.
Rhombus. Parallelogram. All sides of this figure are equal. A rhombus having right angles has the term "square".
Segment. Part of a circle (limited by a chord that connects the ends of the arc).
Secant. Trigonometric function. The designation in mathematics/higher mathematics is sec.
Sector. Part of a circle. Constrained by a circle + two radii (connects the ends of one arc to the center of the circle).
Symmetry - match.
Sinus. Trigonometric function. The designation in mathematics / higher mathematics is sin.
Stereometry. Part of elementary geometry. Engaged in the study of full-fledged spatial figures.
Part of elementary geometry. Engaged in the study of full-fledged spatial figures.
Tangent. Trigonometric function. The designation in mathematics/higher mathematics is tg.
Tetrahedron. Polyhedron, includes 4 triangular faces. Each vertex has 3 faces (converge at the vertices). A tetrahedron has 4 faces + 6 edges + 4 vertices.
Dot. Has no definite and final concept. Any point is denoted by letters A, B, C.
Triangle. Polygon (simple). Includes 3 tops + 3 sides;
Theorem is a statement to be proved based on axioms and previously proven theorems.
Identity is an equality valid for all values of the coefficients included in it.
Topology is a branch of mathematics that studies the properties of figures that do not change under any deformations carried out without ruptures and gluing.
An equation is a mathematical notation of the problem of finding the values of unknowns under which the values of two given functions are equal.
Angle. Geometric figure (flat). It is formed by two rays that come out of one point (the points are the corner vertices).
Factorial is the product of natural numbers from 1 to any given natural number n. Denoted n!. Factorial of zero o! = 1.
The formula is a combination of mathematical symbols that expresses a sentence.
Function is a numerical relationship between elements of two sets, in which one element of one set corresponds to a certain element of another set. Can be given by formula or graph.
Chord. A segment that connects 2 points on a circle.
Digits are symbols for numbers.
Central The middle of something (for example: a circle).
Cyl. A body bounded by a cylindrical surface + parallel planes (two). For the first time, the concept of "cylinder" could be found in Euclid and Aristarchus.
Compass. Special instrument designed for drawing arcs, linear measurements and circles.
Numerator. A specific number with which a fraction is composed. The term was first used by Maxim Planuda (Byzantine scholar).
The number is one of the basic concepts of mathematics that arose in connection with the counting of individual objects.
Ball. Geometric body. It is the total set of all points in a certain space.
Exhibitor. Same as exponential function. The term was first introduced by G. Leibniz (a German scientist).
Ellipse. Oval curve. For the first time this term was introduced by Apollonius of Perga (an ancient Greek scientist).
Dictionary of mathematical terms (letters A - D) - Talim / Education
Mathematics (Old Greek μᾰθημᾰτικά < Ancient Greek μάθημα - study, science) is the science of structures, order and relationships, historically based on the operations of counting, measuring and describing the shape of objects. Mathematical objects are created by idealizing the properties of real or other mathematical objects and writing these properties in a formal language.
Mathematical objects are created by idealizing the properties of real or other mathematical objects and writing these properties in a formal language.
Mathematics does not belong to the natural sciences, but is widely used in them both to accurately formulate their content and to obtain new results. Mathematics is a fundamental science that provides (common) linguistic means to other sciences; thus, it reveals their structural interrelation and contributes to the discovery of the most general laws of nature.
We present to your attention a dictionary of mathematical terms.
Abscissa - (Latin word abscissa - "cut off"). Loans. from the French lang. at the beginning of the 19th century Franz. abscisse - from lat. This is one of the point's Cartesian coordinates, usually the first one, denoted by x. In the modern sense, T. was first used by the German scientist G. Leibniz (1675).
Additivity - (Latin word additivus - “added”). The property of quantities, consisting in the fact that the value of the quantity corresponding to the whole object is equal to the sum of the values of the quantities corresponding to its parts in any division of the object into parts.
The property of quantities, consisting in the fact that the value of the quantity corresponding to the whole object is equal to the sum of the values of the quantities corresponding to its parts in any division of the object into parts.
Adjunct - (Latin word adjunctus - "attached"). This is the same as the algebraic addition.
Axiom - (Greek word axios - valuable; axioma - “asserting a position”, “honor”, “respect”, “authority”). In Russian - since Peter's times. This is a basic proposition, a self-evident principle. For the first time T. is found in Aristotle. Used in Euclid's Elements. An important role was played by the works of the ancient Greek scientist Archimedes, who formulated the axioms related to the measurement of quantities. Lobachevsky, Pash, Peano contributed to axiomatics. A logically impeccable list of the axioms of geometry was indicated by the German mathematician Hilbert at the turn of the 19and 20 centuries.
Axonometry - (from the Greek words akon - "axis" and metrio - "measure"). This is one of the ways to depict spatial figures on a plane.
Algebra - (Arabic word "al-jabr"). This is a part of mathematics that develops in connection with the problem of solving algebraic equations. T. first appears in the work of the outstanding mathematician and astronomer of the 11th century, Mohammed bin Musa al-Khwarizmi.
Analysis - (Greek word analozis - "decision", "permission"). T. "analytical" goes back to Vieta, who rejected the word "algebra" as barbaric, replacing it with the word "analysis".
Analogy - (Greek word analogia - "correspondence", "similarity"). This is a conclusion based on the similarity of particular properties that two mathematical concepts have.
Antilogarithm - (Latin word nummerus - "number"). This number, which has a given tabular value of the logarithm, is denoted by the letter N.
Antje - (French word entiere - "whole"). This is the same as the integer part of a real number.
Apothem - (Greek word apothema, apo - "from", "from"; thema - "applied", "delivered").
1. In a regular polygon, apothem is a segment of a perpendicular dropped from its center to any of its sides, as well as its length.
2. In a regular pyramid, apothem is the height of any of its side faces.
3. In a regular truncated pyramid, apothem is the height of any of its side faces.
Applicata - (Latin word applicata - "applied"). This is one of the Cartesian coordinates of a point in space, usually the third, denoted by the letter Z.
Approximation - (lat. word approximo - “approaching”). Replacing some mathematical objects with others, in one sense or another close to the original ones.
Function argument (Latin word argumentum - “object”, “sign”). This is an independent variable, the values of which determine the values of the function.
This is an independent variable, the values of which determine the values of the function.
Arithmetic (Greek word arithmos - "number"). This is the science that studies operations on numbers. Arithmetic originated in the countries of Dr. East, Babylon, China, India, Egypt. Special contributions were made by: Anaxagoras and Zeno, Euclid, Eratosthenes, Diophantus, Pythagoras, L. Pisa and others.
Arctangens, Arcsinus (the prefix "arc" is the Latin word arcus - "bow", "arc"). Arcsin and arctg appear in 1772 in the works of the Viennese mathematician Schaeffer and the famous French scientist J.L. Lagrange, although D. Bernoulli had already considered them a little earlier, but who used a different symbolism.
Asymmetry (Greek word asymmetria - "disproportion"). This is the absence or violation of symmetry.
Asymptote (Greek word asymptotes - "not coinciding"). It is a straight line to which the points of some curve approach indefinitely as these points move away to infinity.
Astroid (Greek word astron - "star"). Algebraic curve.
Associativity (Latin word associatio - “connection”). Associative law of numbers. T. was introduced by W. Hamilton (1843).
Billion (French word for billion, or billion - milliard). This is a thousand million, the number represented by a unit with 9 zeros, i.e. number 10 9 . In some countries, a billion is a number equal to 10 12.
Binomial (Latin words bi - “double”, nomen - “name) is the sum or difference of two numbers or algebraic expressions, called members of the binomial.
Bisector (Latin words bis - "twice" and sectrix - "secant"). Loans. In the 19th century from the French lang. where bissectrice - goes back to lat. phrase. This is a straight line passing through the vertex of the angle and dividing it in half.
Vector (Latin word vector – “carrier”, “carrier”). This is a directed segment of a straight line, in which one end is called the beginning of the vector, the other end is called the end of the vector. This term was introduced by the Irish scientist W. Hamilton (1845).
This is a directed segment of a straight line, in which one end is called the beginning of the vector, the other end is called the end of the vector. This term was introduced by the Irish scientist W. Hamilton (1845).
Vertical corners (lat. words verticalis - "top"). These are pairs of angles with a common vertex, formed by the intersection of two lines so that the sides of one angle are a continuation of the sides of the other.
Hexahedron (Greek words geks – “six” and edra – “edge”). This is a hexagon. This T. is attributed to the ancient Greek scientist Pappus of Alexandria (3rd century).
Geometry (Greek words geo - "Earth" and metreo - "I measure"). Other Russian loans. from Greek The part of mathematics that studies spatial relationships and shapes. T. appeared in the 5th century BC. in Egypt, Babylon.
Hyperbole (Greek word hyperballo - “going through something”). Loans. in the 18th century from lat. lang. This is a non-closed curve of two unboundedly extending branches. T. was introduced by the ancient Greek scientist Apollonius of Perm.
lang. This is a non-closed curve of two unboundedly extending branches. T. was introduced by the ancient Greek scientist Apollonius of Perm.
Hypotenuse Zamstvo from lat. lang. in the 18th century, in which hypotenusa - from the Greek. the side of a right triangle that is opposite the right angle. The ancient Greek scientist Euclid (3rd century BC) instead of this term wrote, "the side that pulls together a right angle."
Hypocycloid (Greek word gipo – “under”, “below”). A curve that is described by a point on a circle.
Goniometry (Latin word gonio – angle). This is the doctrine of "trigonometric" functions. However, this name did not stick.
Homothety (Greek word homos- "equal", "same", thetos - "located"). This is an arrangement of figures similar to each other, in which the lines connecting the points of the figures corresponding to each other intersect at the same point, called the center of the homothety.
Degree (lat. word gradus - “step”, “step”). A unit of measure for a flat angle, equal to 1/90 of a right angle. Measurement of angles in degrees appeared more than 3 years ago in Babylon. Designations reminiscent of modern ones were used by the ancient Greek scholar Ptolemy.
Graph (Greek word graphikos- “inscribed”). This is a graph of a function - a curve on a plane, depicting the dependence of a function on an argument.
Deduction (Latin word deductio - “derivation”). This is a form of thinking through which a statement is derived purely logically (according to the rules of logic) from some given statements - premises.
Deferents (Latin word defero- “I carry”, “I move”). This is the circle along which the epicycloids of each planet rotate. According to Ptolemy, the planets revolve in circles - epicycles, and the centers of the epicycles of each planet revolve around the Earth in large circles - deferents.
Diagonal (Greek word dia - "through" and gonium - "angle"). This is a line segment connecting two vertices of a polygon that do not lie on the same side. T. is found in the ancient Greek scientist Euclid (3rd century BC).
Diameter (Greek word diametros - "diameter", "through", "measuring" and the word dia - "between", "through"). T. "division" in Russian is first found in L.F. Magnitsky.
Headmistress (Latin word directrix – “guide”).
Discreteness (Latin word discretus – “divided”, “discontinuous”). This is discontinuity; opposed to continuity.
Discriminant (Latin word discriminans- “distinguishing”, “separating”). This is an expression composed of quantities defined by a given function, the conversion of which to zero characterizes one or another deviation of the function from the norm.
Distributivity (Latin word distributivus - "distributive").