Maths creative activities
7 Classroom Math Activities That Will Make Math Engaging and Fun
Back to Articles
Fun, hands‑on math games are a great way to make early math concepts clear and keep your students engaged.Introducing math games into the classroom is a great way to make learning fun, engaging and motivating for young learners.
And the best part about starting early (kindergarten to grade 2) is that it helps your students to develop a positive attitude toward math from an early age, setting them up for a successful academic future.
Here are some fun classroom math activities that will have your students begging to do more.
Math Bingo
This math game is sure to become a fast favorite with your students. You can choose whatever skill you want to review, such as addition, subtraction, or number sequencing. The game works just like regular bingo, except students have to solve math problems in order to know what number to mark off of their sheet.
To prepare, make a list of 25 math problems (e.g. 2+1, 3–0, or 2, 4, 6, _ ). Write the answers on the same sheet of paper.
Create your own 5x5 bingo cards or generate them online. At random, write the answers on the cards using the solutions from your list. There should be a bingo card for each student playing. You can laminate the cards to use for next time and have students place pennies or rocks to mark their answers.
Make a paper plate clock
Are your students learning to tell time this year? This hands‑on craft activity is a fantastic way to practice this important skill.
Start with a paper plate and make a small hole at the center. Students should write the numbers in the correct places. Using colored paper, they can then cut the clock hands to the right size and secure them using a split pin from the center. You can even use a second plate (different color) for students to write the minutes. Glue the second plate to the bottom of the first so that it creates a rim.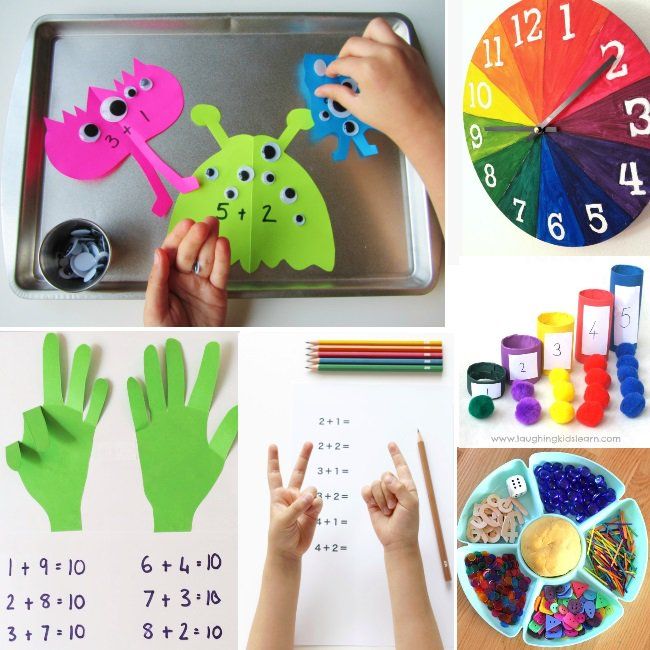
Guess the weight
Children love playing guessing games, and when it comes to whether something is heavy or light, there can certainly be a few surprises in store for them.
Gather several items and spread them across a table. One at a time, ask students to guess the weight of each item and write their predictions in one column on a page (you can create a simple template for this too). Using kitchen scales, invite individual students to weigh each item and record the correct answers in a second column. You can also add a column in between and pass each item around the class, so students can guess the weight after holding each in their hand.
Hopscotch math
This game is a great way to get your students outside on a nice sunny day. Using a piece of chalk, draw a hopscotch grid on the pavement mimicking a calculator layout. Ask students to form a line and one by one, give them a simple operation (e.g. 2+3, 5–0). Students should take turns hopping on each element of the equation in the correct order, landing finally on the answer.
In another game, you can call out a number and ask students to hop on any equation that equals to that number. For a fun twist, ask students to hop on one leg for odd numbers, and two legs for even numbers.
Hopscotch math is a fun activity which helps students to practice simple operations.Pizza fractions
Fractions can be tricky, so this activity can really help students to visualize key concepts. Create an instruction sheet with five different fractions on each (you can create several so different students get a different set). Students should create a pizza (using construction paper, or even the inside of an empty pizza box) and decorate the toppings to represent each fraction.
For example, if they had a quarter (fourth), they should cover one-quarter of the pizza with a specific ingredient (e.g. mushrooms or pepperoni).
'Lengthy' scavenger hunt
Divide students into groups and give each group a list of measurements and a measuring tool (e.g. a ruler, tape, trundle wheel). Instruct students to find items that are exactly the length of what they have listed. For younger students who haven't yet been introduced to measurement, draw various lines on their sheet and ask them to find items that are exactly the same length.
Instruct students to find items that are exactly the length of what they have listed. For younger students who haven't yet been introduced to measurement, draw various lines on their sheet and ask them to find items that are exactly the same length.
Make sure you prepare items beforehand and place them in a safe and visible spot. This activity can be done outside or in the classroom.
Survey and graph
Ask each student to think of a question they’d like to survey their fellow classmates on. For example, they might like to ask their classmates what their favorite animal is out of a dog, monkey, pig, or chicken. Give students time to walk around the classroom quizzing each other and recording their data.
Once students have collected enough data, ask them to represent their results by building a bar graph using linking cubes, blocks, or Legos. They can use sticky notes or bits of paper to create labels above each bar. Take a photo of each student's graph, which you can later print out to create a class collage to display.
Looking for new ways to make elementary math fun? Mathseeds is a research-based online math program specifically designed for students in grades K–2. Created by a highly experienced team of elementary teachers, Mathseeds provides self-paced lessons, fun games, automated reporting, and a range of teaching tools to help your elementary math students succeed. Sign up for a free trial today.
35 Active Math Games and Activities for Kids Who Love To Move
Tired of hearing groans when you announce it’s time for math? These active math games and activities will spice up your learning game. They get kids up and moving, using their whole bodies to learn facts and skills. Lots of these ideas can be adapted to suit a variety of math concepts, so choose a few to try out with your own math students.
1. Throw snowballs inside or out
Clip flash cards to plastic tubs, then challenge kids to throw the correct number of large white pom-poms (“snowballs”) in from a distance. If there’s snow on the ground, bundle up and take this one outside to use real snowballs!
If there’s snow on the ground, bundle up and take this one outside to use real snowballs!
Learn more: Frugal Fun 4 Boys and Girls
2. Stack sticks to practice tally marks
Small sticks are perfect for practicing tally marks. Kids will have fun checking the ground under trees for twigs, then breaking them into pieces and creating tally piles.
Learn more: @amysam623
3. Fish for numbers
It’s so easy to make your own magnet fishing pole. Float some numbered foam fish with paper clips attached, then try to catch the numbers in the right order! (Don’t want to get wet? Just lay the fish on the ground instead.)
Learn more: Buggy and Buddy/Fishing Math
4. Draw and measure shapes on the sidewalk
First, give kids some sidewalk chalk and let them draw a variety of shapes, as big or small as they like. Then, arm them with measuring tapes and have them practice taking measurements.
Learn more: @playexploregrow
5.
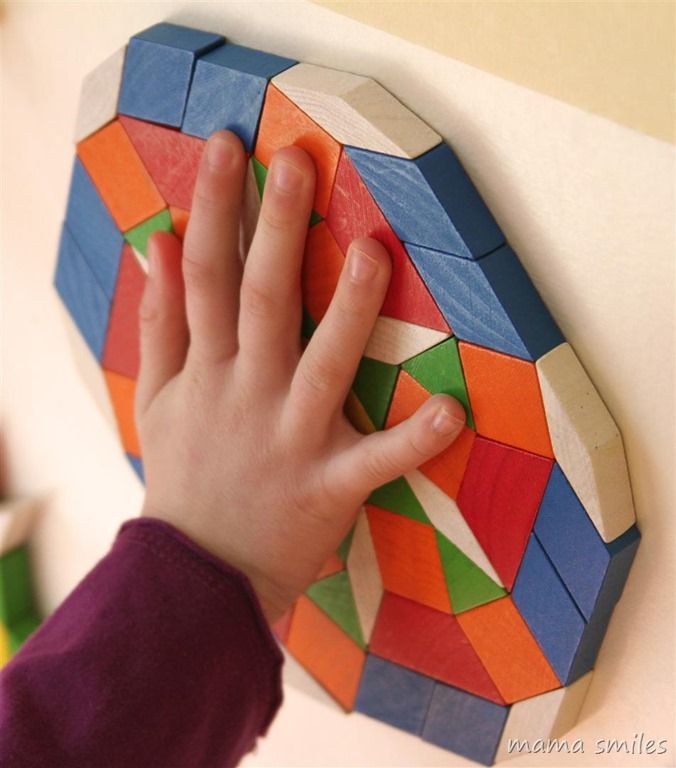 Stomp and smash on a number line
Stomp and smash on a number lineGrab some paper bags and number them, then shake them out and lay them in a number line. Now, call out an addition or subtraction problem, like 3 + 2. Have a student stomp on the bag labeled three, then on the next two to arrive at an answer of five. (Feeling brave? Try this one with balloons!)
Learn more: Schooltime Snippets
6. Grow fact-family flowers
Pick up colorful fall leaves and write math facts on them. Gather them around a numbered rock to make pretty flowers.
Learn more: @discoverwildlearning
7. Toss beanbags to learn place value
Label bins with place values like ones, tens, and hundreds. Kids toss beanbags into the bins, then count them and see what number they’ve created.
Learn more: Saddle Up for Second Grade/Place Value Toss
8. Form paper-plate number bonds
Pass out numbered paper plates, then have students mix and mingle to see how many number bonds they can form.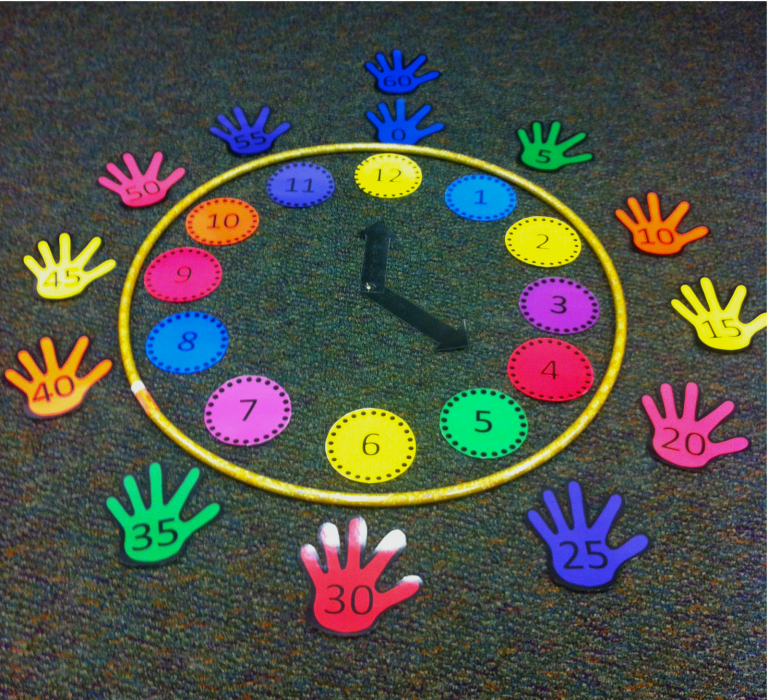
Learn more: The Schroeder Page
9. Create a life-size number line
Number lines are wonderful for all sorts of math games and activities. Make one big enough for kids to stand and jump around on using sidewalk chalk (or painter’s tape indoors). You’ll use it over and over again.
Learn more: Childhood Beckons
10. Hit the target and graph
You can teach graphing in lots of ways, so why not make it active? Students throw balls onto a target, graphing and analyzing their throws as they go.
Learn more: Amy Lemons
11. Head out on a plot graph scavenger hunt
Create a map of your school, playground, or other area using graph paper (or even better, have kids help you do it). Then choose plot points for them to visit to find notes or small prizes. They’ll feel like real treasure hunters!
Learn more: Edventures With Kids
12. Roll the dice to count and move
Get practice with low-number counting and addition using action dice. Write activities like “jump,” “clap,” or “stomp” on a small wooden block, then roll it along with a pair of dice. Kids add them up (or subtract if you prefer) and complete the activity the number of times shown.
Write activities like “jump,” “clap,” or “stomp” on a small wooden block, then roll it along with a pair of dice. Kids add them up (or subtract if you prefer) and complete the activity the number of times shown.
Learn more: Buggy and Buddy/Math Dice
13. Whack a ball to subtract
You know your elementary math students are going to love this! Build your own whack-a-mole 10-frame with a shoebox and Ping-Pong balls. Then, have kids whack the balls to practice their subtraction facts. So fun!
Learn more: Planning Playtime
14. Make a splash with water balloons
You’re going to need to be willing to get a little wet for this one, but kids simply adore math games (or any games!) with water balloons. Fill and label balloons numbered 1 through 20 (or whatever numbers you’re working on). Draw the numbers in a big circle on the playground. Then, have a student choose a balloon, find the matching number, and head off to make a splash!
Learn more: Little Bins for Little Hands
15.
 Tell time on a giant clock
Tell time on a giant clockDraw a giant clock face with hours and minutes on the playground with sidewalk chalk. Choose two students to be the hour and minute hands, then call out a time and send them out to become the clock. Add more complicated elements by having them add to or subtract from the initial time too. (“Now it’s 23 minutes later!”)
Learn more: Creative Family Fun/Sidewalk Chalk Clock
16. Measure your frog jumps
Have your students hop like frogs, leap like gazelles, or jump like kangaroos. Then, pull out the ruler or measuring tape so they can measure the distances they’ve covered.
Learn more: Coffee Cups and Crayons
17. Jump to math facts practice
Lay out a grid like the one shown that has the answers to whatever set of math flash cards you’re currently working with. (This teacher used masking tape; you could also do sidewalk chalk on the playground.) Two players face off, one on each side of the board. Show the flash card, and kids race to be the first to jump to the correct square with both feet inside the lines. Get all the rules at the link below.
Get all the rules at the link below.
Learn more: Teaching and Tapas
18. Run a flash-card race
Tape a series of flash cards to the floor and challenge kids to see who can correctly make their way from start to finish the fastest. They can call out the answers or write them down, but they have to get it right before they move on. Kids can race side by side or work independently to beat their own best time.
Learn more: There’s Just One Mommy
19. Catch a math beach ball
Beach balls are so much fun in the classroom. Scribble numbers all over one with a Sharpie, then toss it to a student. Wherever their thumbs land, they add (or subtract or multiply) those two numbers together before tossing the ball to the next student.
Learn more: Saddle Up for Second Grade/Beach Ball Math
20. Do a number dance
Kids who love “Dance Dance Revolution” will get into this one. Make a number mat for each student like the ones shown. Flash an equation with an answer between 10 and 99 on the screen. Kids figure out the answer and jump to put their left foot on the correct tens place, right foot on the ones. They’ll be dancing and spinning as they learn!
Flash an equation with an answer between 10 and 99 on the screen. Kids figure out the answer and jump to put their left foot on the correct tens place, right foot on the ones. They’ll be dancing and spinning as they learn!
Learn more: Number Loving
21. Groove with angles
Teach kids about transversals and the angles they create with some fun dance moves! Get the details for “Dance Dance Transversal” at the link below.
Learn more: Communicating Mathematically
22. Add and subtract by stacking cups
We’re not sure why, but kids simply love stacking cups. Label yours with math problems and answers, then have kids build pyramids and towers galore!
Learn more: The Kindergarten Smorgasboard
23. Measure the height of a tree (no ladder needed)
Kids will be amazed to learn they can measure the tallest tree while keeping their feet on the ground. The link below walks you through the steps with a free printable.
Learn more: From ABCs to ACTs
24. Count and learn on a nature walk
Take an outdoor stroll and practice basic math along the way. This works indoors too—walk the school hallways (quietly) and count doors, windows, posters, and more.
Learn more: Creative Family Fun/Math Walk
25. Hunt for shapes in the world around you
Looking for super-simple and fun active math games? Give students a sheet with shapes to find as you walk around the school or playground. Each time they find the shape, have them trace it on their worksheet and then make a mark to keep track of how many times they’ve seen it.
Learn more: Hands-On Teaching Ideas
26. Steal the balls with addition robbery
Kids compete to see whose basket of balls will add up to the highest amount. The trick? They don’t know at the beginning which balls are worth the most. Learn how to play at the link below.
Learn more: That After School Life
27. Puddle-jump from number to number
Lay out a series of construction paper puddles labeled with numbers. You can call out numbers and have kids jump to the correct one, or have them jump from one to the next in order forward or backward, or even try some skip counting.
You can call out numbers and have kids jump to the correct one, or have them jump from one to the next in order forward or backward, or even try some skip counting.
Learn more: NurtureStore
28. Paint and hide number rocks
Painted rocks are always a big hit! Have your class help you make these, then hide them around the playground and send kids off to find and answer equations.
Learn more: The OT Toolbox
29. Skip-count along a hopscotch board
A hopscotch board can be used for a lot of fun and active math games. Try it for skip counting: Kids hop along counting by 2s, 5s, 10s, or whatever you’re currently working on. Learn more at the link below.
Learn more: Math Geek Mama/Skip-Counting Hopscotch
30. Aim and throw to practice math skills
Pick up a set of Sticky Darts and draw two dartboards side by side. You can label the rings with any numbers you like. Kids throw the darts and then add, subtract, multiply, or divide the numbers—your choice!
Learn more: Inspiration Labs
31.
 Design an outdoor board game
Design an outdoor board gameDraw a winding path and fill the spaces with math equations. Kids roll the dice and move from space to space (have them jump, skip, or twirl to mix things up). If they get the answer right, they move to the new space. If not, their turn is over. Customizable math games like this can be used at any level.
Learn more: Look! We’re Learning!
32. Turn UNO into an active math game
Grab your UNO deck and get ready to move! Assign each color a movement (hop, touch toes, etc.). As kids draw the cards, everyone completes the movement the correct number of times. Skip and Reverse work as usual, but anyone who gets Draw Two has to draw two more cards and complete the actions on their own while others cheer them on. See more at the link below.
Learn more: Still Playing School
33. Bowl them over while learning math facts
Active math games using recycled materials are economical and good for the environment. Set up empty plastic bottles labeled 1 through 10, then roll the ball to see how many you can knock down. Add up the numbers of the knocked-over bottles to get your score.
Set up empty plastic bottles labeled 1 through 10, then roll the ball to see how many you can knock down. Add up the numbers of the knocked-over bottles to get your score.
Learn more: Learn With Play at Home
34. Compete to win at putt-putt math
Pick up a few dollar-store supplies and make your own putt-putt course. This can be a simple game where kids simply shoot for the highest (or lowest) number. But you can also drive up the complexity by putting equations on the cups that kids have to solve first to determine which is the best cup to aim for.
Learn more: My Catch a Star Classroom!
35. Give a classic game a math twist
Create active math games that give new life to existing resources. For example, add numbers to Twister! For more advanced players, instead of saying “Right hand 5,” try saying “Right hand 14 – 9” to make them think.
Learn more: Math Geek Mama/Twister Math
If you like these active math games and are looking for more ways to move in the classroom, try these 21 Kinesthetic Reading Activities for your most active learners.
Plus, sign up for our free newsletters to get all the best teaching tips and ideas!
Development of creative activity of students in mathematics lessons (author's concept)
If the student at school did not learn on his own do nothing,
then in life he will always only imitate,
copy, as there are few who would,
having learned to copy, they knew how to make
independent application of this information.
Tolstoy L.N.
Formation and development of cognitive interests are part of the broad problem of education a well-rounded personality. That's why the need to form cognitive interests at school has a social, pedagogical and psychological significance. Development of the formation problem cognitive interests of schoolchildren for modern construction of the educational process determined by the tasks of modern society, concerned with the preparation of the younger generations only for the present, but also for the future. Already in The school needs to instill in the student the desire to constantly updating their knowledge with the help of self-education, nurture his inner incentives to expand your general and special outlook to rise to the rank of intelligent a worker capable of not only being good executor of the production task, but also improve your work, raise it to level of creativity. If a graduate schools will work in science, technology, culture, all the more he needs knowledge, multiplied by practical guidelines to transform reality, and in that and in otherwise, he will be able to help brought up in school interest in cognitive activities, development on this basis of inclination, ability in any conditions to keep up with the times, with science, culture. This is the reason for my choice themes - the formation of creative activity students in math class.
Already in The school needs to instill in the student the desire to constantly updating their knowledge with the help of self-education, nurture his inner incentives to expand your general and special outlook to rise to the rank of intelligent a worker capable of not only being good executor of the production task, but also improve your work, raise it to level of creativity. If a graduate schools will work in science, technology, culture, all the more he needs knowledge, multiplied by practical guidelines to transform reality, and in that and in otherwise, he will be able to help brought up in school interest in cognitive activities, development on this basis of inclination, ability in any conditions to keep up with the times, with science, culture. This is the reason for my choice themes - the formation of creative activity students in math class.
Mathematics has always been integral and an essential part of human culture, it is the key to knowledge environment, the base of scientific and technical progress and an important component of development personality. Very often under the main target mathematics education imply preparation for a future profession, for admission to university But it is equally important to educate in a person ability to understand the meaning of the tasks, the ability to correctly, logically reason, learn the skills of algorithmic thinking. Everyone needs to learn to analyze to distinguish hypothesis from fact, to criticize, to schematize, express one's thoughts clearly, on the other hand, develop imagination and intuition (spatial representation, ability anticipate the outcome and predict the path solutions). In other words, mathematics is necessary for intellectual development of the individual.
Very often under the main target mathematics education imply preparation for a future profession, for admission to university But it is equally important to educate in a person ability to understand the meaning of the tasks, the ability to correctly, logically reason, learn the skills of algorithmic thinking. Everyone needs to learn to analyze to distinguish hypothesis from fact, to criticize, to schematize, express one's thoughts clearly, on the other hand, develop imagination and intuition (spatial representation, ability anticipate the outcome and predict the path solutions). In other words, mathematics is necessary for intellectual development of the individual.
The task of the teacher is to organize the process learning in such a way that every effort knowledge acquisition proceeded in conditions development of cognitive abilities of students, the formation of such basic techniques mental activity, such as analysis, synthesis, abstraction, generalization, comparison.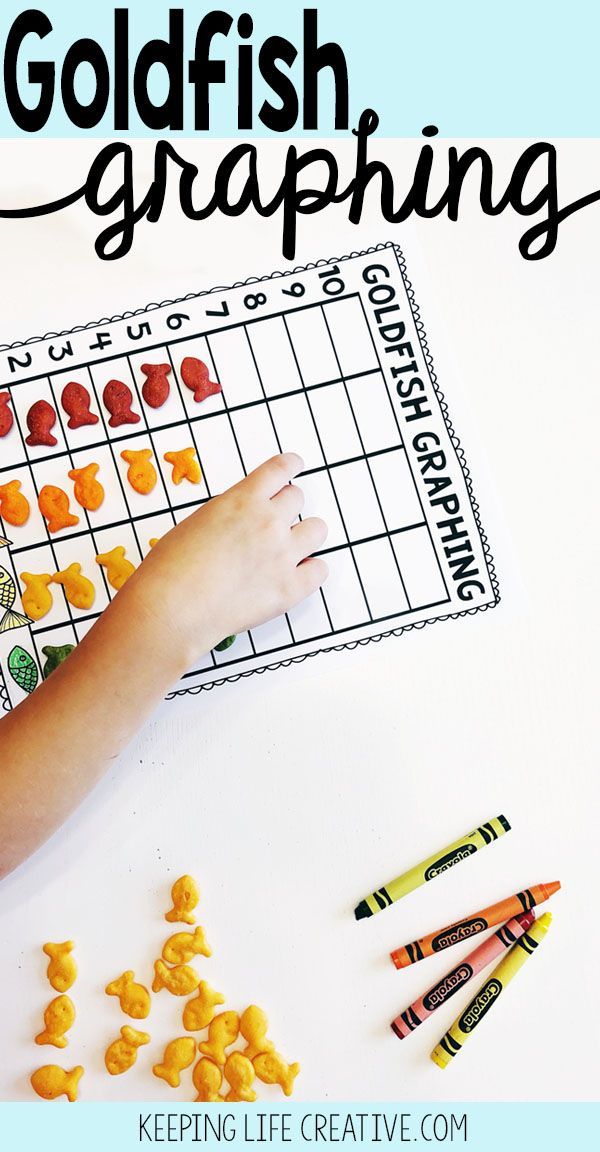 Students need to learn on their own work, make and test assumptions, guesses, be able to make generalizations of the studied facts, creatively apply knowledge in new situations.
Students need to learn on their own work, make and test assumptions, guesses, be able to make generalizations of the studied facts, creatively apply knowledge in new situations.
Creative activity of students is not limited to buying a new one. The work will be creative when it shows students' own idea, new tasks and they are independently solved with the help of acquired knowledge.
The teacher must marvel at beauty and power mathematical methods and infect their students. Equally, it must be very patient, because they have no right to wait instant results. However, if all done professionally and honestly, sooner or later late, the student will show himself. Mathematics is science "wonderful". It needs to be noticed, and for this should encourage students to seek truth. This means that at every stage of the school math education need to teach children observe, compare, notice patterns, formulate a hypothesis, teach to prove or abandon the hypothesis.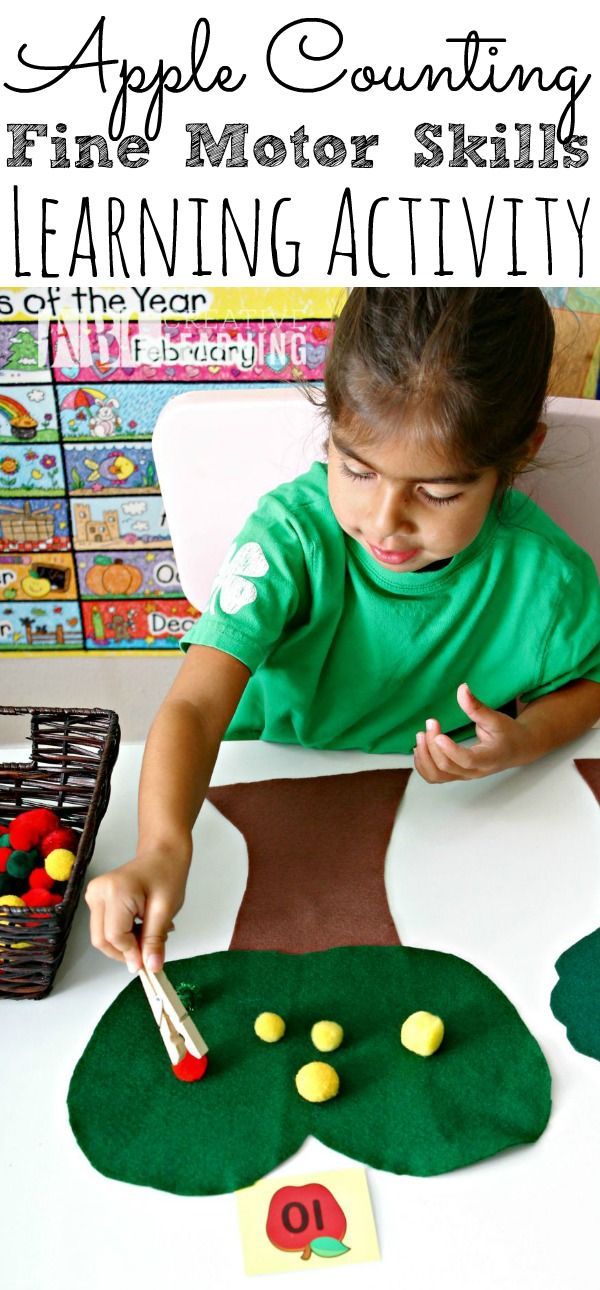 It is important to teach students build definitions and denial. Show that in mathematics almost nothing needs to be memorized - it should be understood learn to apply and then everything will be remembered by itself yourself.
It is important to teach students build definitions and denial. Show that in mathematics almost nothing needs to be memorized - it should be understood learn to apply and then everything will be remembered by itself yourself.
Methods and forms of development of creative activities of students
The teacher must remember that when meeting even with a very gifted student, he prepares from him not mathematics, and above all a comprehensively developed personality, and this work he performs in close unity with teachers of other disciplines. AT learning process at school is formed human consciousness, views, worldview, beliefs, develop creativity students. For this it is useful to use non-standard math problems as well as historical and illustrative materials.
I never start a new topic, speaking of a new branch of mathematics, without proper introductory part, arousing interest and students' attention. The introductory part can and should be a 3-5 minute fascinating story, associated with the history of mathematics.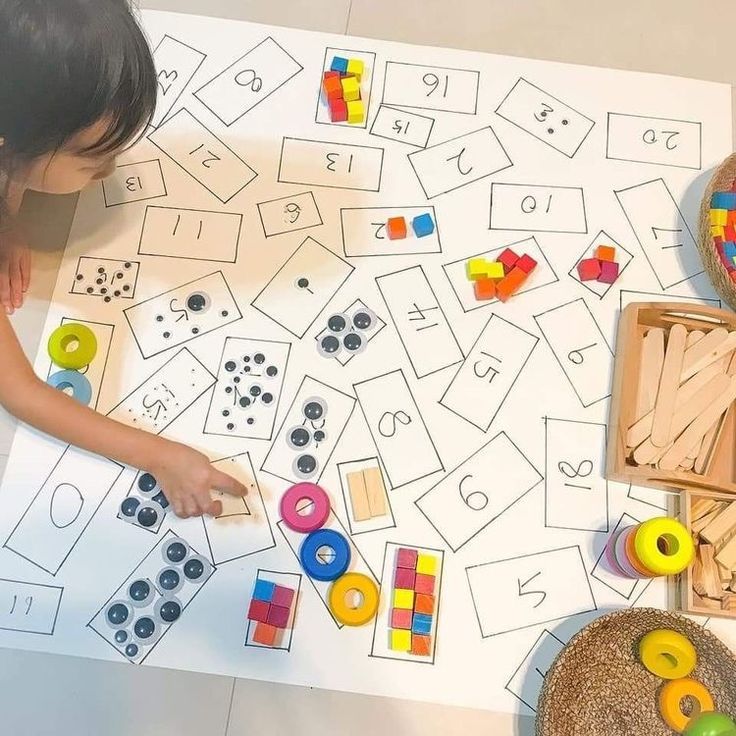 Such a presentation gives students the opportunity to show each new section or topic that math how science arose and developed in connection with human practical activity. Studied at school properties, rules, theorems - there are generalization of the thousand-year experience of mankind. The pedagogical process is always associated with interaction of the student not only with the teacher, but also with “the apparently not present teacher.” AT as “absent” teachers successfully various eminent figures of science and cultures, including mathematicians. studying life and work of a scientist - mathematician, students have a worthy role model, which encourages them to be creative, to research work in the study of new material.
Such a presentation gives students the opportunity to show each new section or topic that math how science arose and developed in connection with human practical activity. Studied at school properties, rules, theorems - there are generalization of the thousand-year experience of mankind. The pedagogical process is always associated with interaction of the student not only with the teacher, but also with “the apparently not present teacher.” AT as “absent” teachers successfully various eminent figures of science and cultures, including mathematicians. studying life and work of a scientist - mathematician, students have a worthy role model, which encourages them to be creative, to research work in the study of new material.
First geometry lesson in 7th grade talk about the origin of geometric knowledge in Egypt, on their further development in Greece, on Greek scientist Euclid, who all created before him, in geometry, brought into a single harmonious system. A more complete study of the works Euclid is conducted by students. Students explore not only the mathematical works of the scientist, but also historical background, Euclid's contribution to development of other sciences. As a result of the studies draw conclusions about the significance of the work Euclid, about the need to study them on this stage of learning. One of these studies provided in the appendix.
A more complete study of the works Euclid is conducted by students. Students explore not only the mathematical works of the scientist, but also historical background, Euclid's contribution to development of other sciences. As a result of the studies draw conclusions about the significance of the work Euclid, about the need to study them on this stage of learning. One of these studies provided in the appendix.
In order for a teenager to develop an attitude towards people, to oneself, developed creative abilities, it is necessary that the surrounding life, his activities required him to be active expressions for this relationship. One of the effective means is solution of mathematical problems . According to S. Schwarzburd, the purpose of studying school course of mathematics consists in the assimilation by students mathematical theories on modern scientific level and in mastering the ability to apply mathematics in the real world. Therefore, in the system of exercises of the mathematics course I include tasks containing the most useful and interesting educational information from general technical disciplines, biology, geography.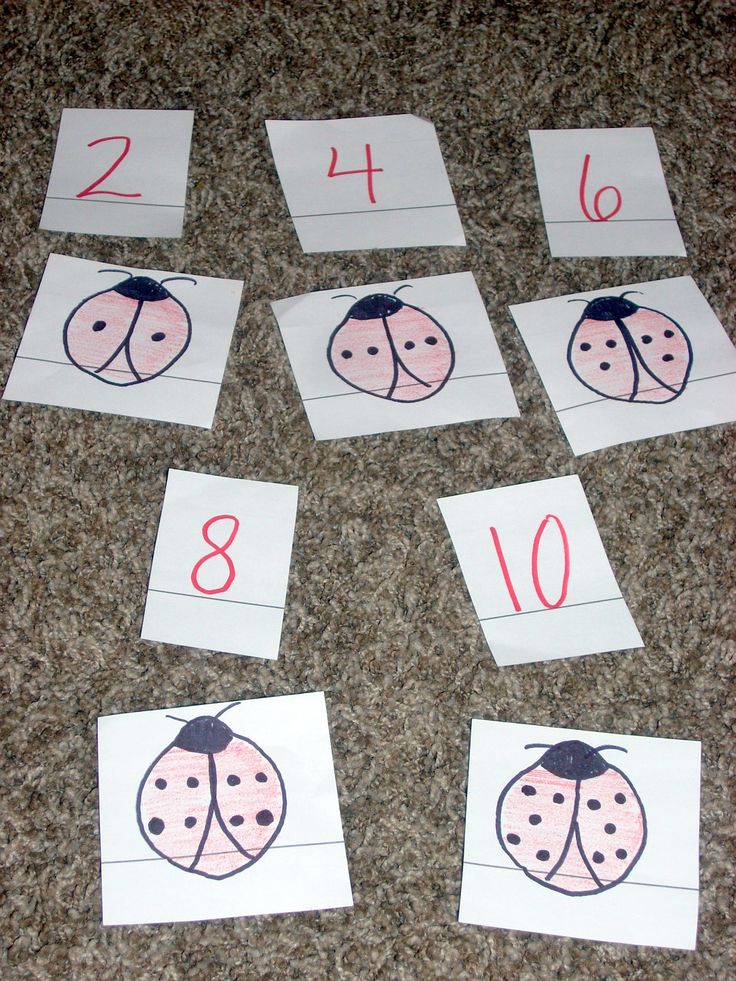
EXAMPLES
less than the period of their feeding, and the total time incubation and feeding is 38 days. What is the duration of each period?
2. 1 quintal of milk produces 9 kg of cheese. How much cheese can be made from milk obtained from 150 cows for 5 months, if the average milk yield from each cows 16kg per day?
I try to select tasks so that they have several solutions. Students should find these solutions (that is, creative minutes). I welcome and appreciate each new thought.
A positive role in the development of mathematical thinking and creative activity of schoolchildren play labs . In the course of their performance of students, working with visual manuals, tools, graphs and tables, making calculations, “open” and formulate new mathematical definitions. I strive to ensure that in the process of work students as much as possible “discovered” themselves. An important step in this direction is conducting laboratory work in the classroom.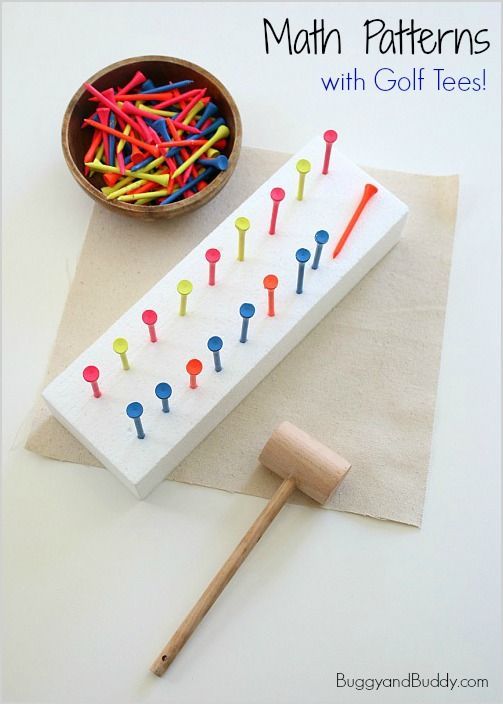
Example
Lab, in progress which students “discover” the number and derive the length formula circles.
Students are encouraged to make and bring to class circles of various diameters made of cardboard, and threads. In the lesson, I ask students to circle one from circles with a pencil, then this circle “Girdle” the thread, and then straighten it. Length thread will be approximately equal to the length of this circles. They do the same with the rest of the circles. The students themselves conclude that the larger the diameter of a circle, the larger it length.
Then for each case I propose to find the ratio of the circumference of a circle to the length of its diameter. This ratio is the same for all circles (output done by the students). Further I propose this the ratio is denoted by the Greek letter, the circumference - with the letter C, and the length of the diameter with the letter d. Formula circumference students formulate on one's own.
Great opportunities for the development of creative student activities provide practical student work . In the course of their implementation students improve their knowledge develop the ability to use discover the connection between mathematics and life.
Examples of practical work:
1) tasks for calculating volumes, areas;
2) drawing diagrams;
3) drawing up various kinds of estimates;
4) measuring work on the ground;
5) modeling.
Of great importance for the development of creative activities of students play didactic games that can be used on various lesson stages.
Didactic games can be widely be used as a means of education, upbringing and development. Main learning impact belongs to the material, play actions, which, as it were, automatically conduct educational process, directing the activity of children in a certain direction. The game form of classes can be use at various stages of the lessons. Determination of the place of the didactic game in the structure of the lesson and the combination of elements of the game and teachings depend to a large extent on correct the teacher's understanding of the functions of didactic games and their classifications. First of all, collective games in the classroom should be divided into didactic lesson tasks. It is above all games educational, controlling, summarizing.
Determination of the place of the didactic game in the structure of the lesson and the combination of elements of the game and teachings depend to a large extent on correct the teacher's understanding of the functions of didactic games and their classifications. First of all, collective games in the classroom should be divided into didactic lesson tasks. It is above all games educational, controlling, summarizing.
A game will be educational if the students participating in which they acquire new knowledge, skills and abilities or forced to acquire them in the process preparation for the game.
Example.
I ask for a week to study an independent topic "Trapezoid". Why a trapezoid? little about her material. We play the auction “Teacher and students”. Students find so much material about her and her lines that you wonder. Then together we sum up all those new facts that are not in textbook, and learn to comprehend them.
The control will be a game, didactic the purpose of which is to repeat, reinforce, verification of previously acquired knowledge.
Example
the need to repeat all the axioms, check how students learned them. Regular poll is not arouses due interest. Therefore, I use game form of classes “Competition of geometers”. I prepare codas in advance with assignments - drawings to the axioms. The task is is to establish, an illustration of which an axiom is every drawing as well notice which elements on each of them missing. You need to draw the desired element, and then formulate the corresponding axiom. I offer similar tasks to students when repetition of concepts such as segment, half-line, angle, equality of figures, etc.
General games require the integration of knowledge. They contribute to the establishment of interdisciplinary connections aimed at acquiring skills act in different learning situations.
Example
At the first geometry lessons in the 7th grade, the guys get acquainted with various simple figures. New terminology is emerging, which is not easy absorbed by them. In this regard, oral exercises include the following tasks. Describe the drawing (drawing) using the data which are set. Recording can be done symbolically. The description of the figure includes more complex figures that students get acquainted with in the lessons, that is, the drawing becomes more complicated. In this manner not only the mind develops, but also speech. The mathematical culture of speech is developing, which is difficult to achieve by other methods. A homework assignment is proposed: come up with a drawing and describe it. At the beginning of the geometry lesson, students show the task one by one. They see creativity of others, and this encourages to create more better. To do this, you need to know deeply educational material.
In this regard, oral exercises include the following tasks. Describe the drawing (drawing) using the data which are set. Recording can be done symbolically. The description of the figure includes more complex figures that students get acquainted with in the lessons, that is, the drawing becomes more complicated. In this manner not only the mind develops, but also speech. The mathematical culture of speech is developing, which is difficult to achieve by other methods. A homework assignment is proposed: come up with a drawing and describe it. At the beginning of the geometry lesson, students show the task one by one. They see creativity of others, and this encourages to create more better. To do this, you need to know deeply educational material.
Game-creativity, game-work. During the game, children develop the habit of thinking self, desire for knowledge, feeling self-esteem, empathy for a friend. Carried away, children do not notice that they are learning learning, remembering new things.
In turn, didactic games in depending on the content of the material, method organization, level of preparation of schoolchildren, goals Lessons can take on a variety of forms. To be productive, reproductive, creative, constructive, practical, educational.
It cannot be considered that the use of gaming situations in the classroom gives students the opportunity master mathematics “easily and simply”. Lungs there are no paths in science. But you need to use all so that children learn with interest. Didactic game is not an end in itself, but a means training and education, development of creative personality.
I offer small creative tasks on holidays:
1. Illustrate the application of mathematical concepts, terms on examples from life, fiction, on various school subjects.
In 5th grade, students are encouraged to do collection of proverbs and sayings which includes a number.
Measure seven times, cut once.
Chasing two hares, not one catch up.
Seven villages and one horse.
2. Come up with your own problem, complete it and solve it on this topic. Classify jobs by this topic according to the level of difficulty and make exemplary test work for comrades.
3. Write a fairy tale, poetry, fable, sketch on math topic. This task is unusual for mathematics lesson and therefore is of interest.
Example
numbers” a 6th grade student wrote the following fairy tale.
“In a certain kingdom, in a certain state lived a positive Number, and this number had daughter - Fraction and son - Percentage. Son and daughter always arguing among themselves about which of them was the most important, who dearer than Number. But even though they lived in the Mathematical city, they did not know mathematics at all, they were unaware that the Percentage and the Fraction are part of the Number, and therefore they are equally dear to Number.”
An important part of the process of teaching mathematics is the control of knowledge and skills of schoolchildren. From how it is organized, what it aims at, significantly depends on the effectiveness of training work. That is why in my work I devote serious attention to ways of organizing control, its content.
From how it is organized, what it aims at, significantly depends on the effectiveness of training work. That is why in my work I devote serious attention to ways of organizing control, its content.
The form of organization of control has chosen a level differentiation.
The goals of level differentiation are ensure that all students achieve basic level of training, representing is the state standard of education, and simultaneous creation of conditions for the development students who are interested in and able to mathematics. Its main feature is differentiation of requirements for knowledge and skills students: the level of compulsory preparation, which sets the lower bound assimilation of the material. This level is available available to all students. Based on it higher levels of mastery of the course are formed.
Students are given the right and opportunity to studying in one class and according to one program, choose the level that suits them needs, interests, abilities.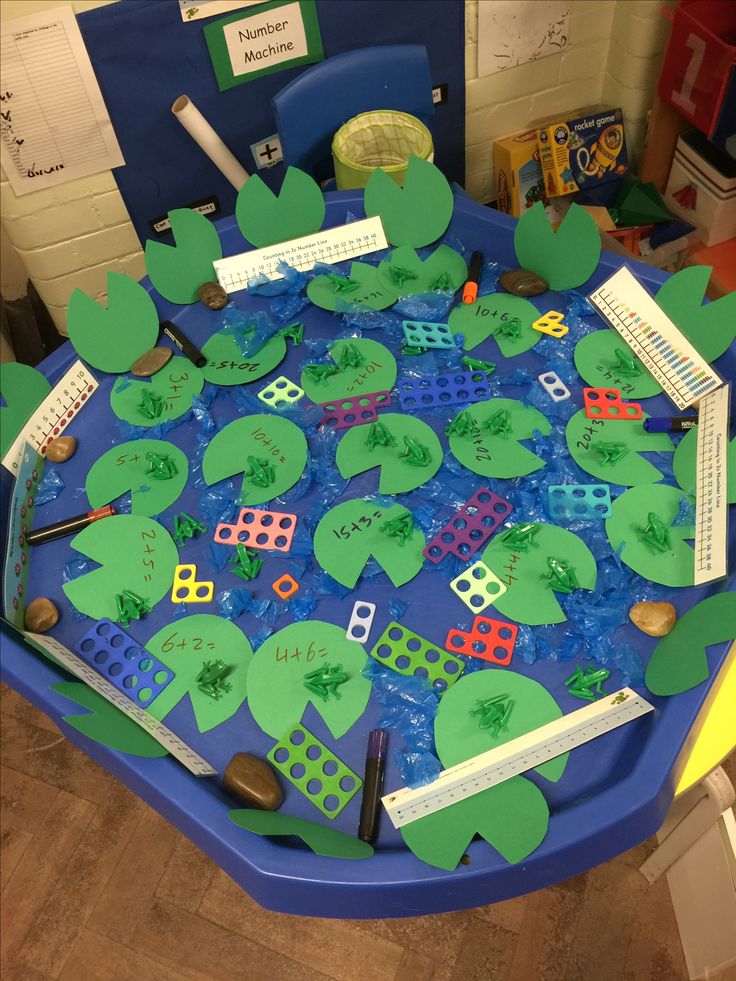 Exactly This approach contributes to the psychological comfort of the student at school, forms his a sense of respect for oneself and others, builds responsibility and capacity for decision-making, contributes to the development creative activity. For each topic I develop various control systems: offsets, control work, tests. For implementation current control, it is advisable to choose such validation form like offset . I will pass the test in open form. I give students so many tasks. and examples of how many students are in the class. By The content of the problem is easy, medium, difficult. Preparation time is one to two weeks. Appreciated creative approach to the solution, the number of ways solving one problem.
Exactly This approach contributes to the psychological comfort of the student at school, forms his a sense of respect for oneself and others, builds responsibility and capacity for decision-making, contributes to the development creative activity. For each topic I develop various control systems: offsets, control work, tests. For implementation current control, it is advisable to choose such validation form like offset . I will pass the test in open form. I give students so many tasks. and examples of how many students are in the class. By The content of the problem is easy, medium, difficult. Preparation time is one to two weeks. Appreciated creative approach to the solution, the number of ways solving one problem.
Examinations.
Tasks are divided into three levels of difficulty A B C. Level A complies with mandatory program requirements, B- medium level complexity, level B tasks are intended for students with an increased interest in mathematics.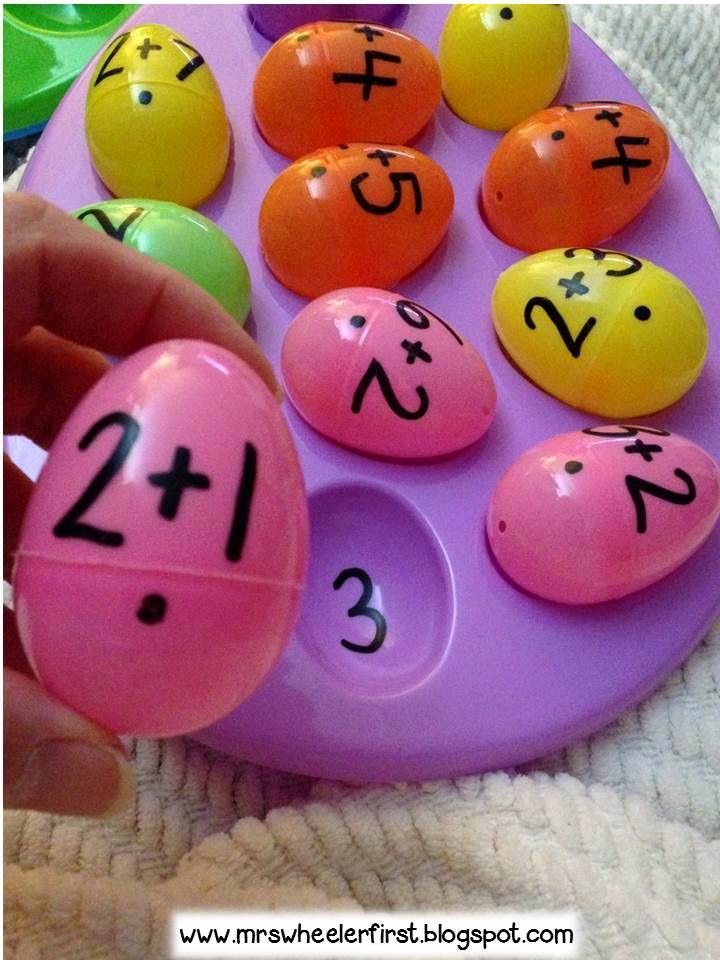 Students can compare assignments different levels and, with the permission of the teacher, choose the level of difficulty that suits you.
Students can compare assignments different levels and, with the permission of the teacher, choose the level of difficulty that suits you.
Example
Sample test on the topic: "Perpendicular lines".
Level A:
1. Define adjacent corners.
2. In the figure, lines AK and BC intersect at the point O.
a) Among the angles obtained by crossing straight lines AC and BK, find and write down the angles adjacent to AOC angle.
b) Find the degree measure of the angle SOC, if the angle AOB is equal to 58 0 .
Level B.
A) What is the sum of adjacent angles?
B) What is the angle if it is 43 0 more corner adjacent to it?
Level B.
A) The sum of two angles is 178 0 . Prove that angles cannot be adjacent.
B) Prove that the bisectors of the angles formed at the intersection of two lines are perpendicular.
Testing.
The main advantage of the test form of control is simplicity and speed. with which is done the first assessment of the level of training in this a specific topic, which also allows real evaluate readiness for final control in other, traditional forms and, if necessary, edit certain elements of the theme. I would like to note one feature of the tests - tests are perceived by most students as kind of game. This removes a whole series psychological problems - fears, stress, nervous breakdowns that are characteristic of ordinary forms of control. Good test results help prepare students mentally for a test or test.
Research work of students as the most important means of developing creativity activities.
At present, the world of education has become task to update the content of education. Due with this great importance is given research activities of students.
Under research activities refers to the activities of students the guidance of the teacher, associated with the decision students of a creative, research task with a previously unknown solution and assuming the presence of the main stages characteristic of scientific research: problem statement, studying the theory, mastering the methodology research, collection of own material, its analysis and generalization, own conclusions and their comparison with literature data. Student independently draws a conclusion, conducts an analysis, solves non-standard problems, experiments, based on experience. Laboratory, practical works brings out some new for his position, studies primary sources, special literature and on this basis draws up reports, theses, abstracts containing their generalizations, solutions. Teacher - organizer, children work on one's own. In research activities, the main goal is to obtain objectively new knowledge. The criteria are also changing. the success of the mandatory process.
Student independently draws a conclusion, conducts an analysis, solves non-standard problems, experiments, based on experience. Laboratory, practical works brings out some new for his position, studies primary sources, special literature and on this basis draws up reports, theses, abstracts containing their generalizations, solutions. Teacher - organizer, children work on one's own. In research activities, the main goal is to obtain objectively new knowledge. The criteria are also changing. the success of the mandatory process.
I evaluate not only knowledge, but also others indicators:
- participation in discussions;
- the ability to express one's point of view;
- collection of material from various sources;
- activity in the discussion of issues;
- the ability to ask questions;
- an opportunity to express one's attitude towards the material being studied.
In the educational process, the student must, be able and willing to show their active participation. From previous consumption by students issued by a teacher, textbook, technical means of teaching information there is a turn to learning how obtain the necessary information and to be able to express his attitude towards her.
From previous consumption by students issued by a teacher, textbook, technical means of teaching information there is a turn to learning how obtain the necessary information and to be able to express his attitude towards her.
Consider that the research method inaccessible to most students and is the lot of the few. Such a judgment is not correct. Speech It's about elementary methods of search work - no one requires students to make a discovery, enriching science. It's about creative work. Children need to be taught to think to search for oneself, to find oneself some solutions. Such a creative approach is necessary for every worker: a physicist, a doctor, and teacher, and locksmith, and field grower, and cutter. And creativity should be taught from childhood. Exactly at school lays the foundation for creative human abilities.
Most successful research work performed by students of grade 6:
1. “Development of mathematics: stages, problems, achievements. primitive society”. Choice topics due to the fact that mathematics is an integral part of human culture, and so it's good for everyone to know fragments of the history of this science, the names of its creators, the essence of their contribution to the course of evolution.
primitive society”. Choice topics due to the fact that mathematics is an integral part of human culture, and so it's good for everyone to know fragments of the history of this science, the names of its creators, the essence of their contribution to the course of evolution.
2. “Mathematical transformations”. Laboratory research work. Target work - to show that mathematics is experimental science. Success does not bring so much use of ready-made recipes and tough models, how much mathematical approach to phenomena of the real world.
Teaching is a difficult and responsible profession. Great joy is to form a person, to give him knowledge, to educate character, to sow good. But it's not easy work! Is it possible to be good teacher? Yes, you can if you love children. Teaching skills are learned how to learn the art of a musician, surgeon, pilot, steelworker. We need knowledge, we need skills, we need character. It is necessary to acquire professional skills, develop mastery in yourself, do not stoop to handicraft. What is needed for this? Before just know the subject. But this is not enough. To successfully to teach, it is necessary to master the techniques teaching: methods of explanation, questioning, organization of independent work of students.
What is needed for this? Before just know the subject. But this is not enough. To successfully to teach, it is necessary to master the techniques teaching: methods of explanation, questioning, organization of independent work of students.
The principle of my work can be formulated as principle of "four COs".
A lesson in mathematics is:
- Collaboration,
- Empathy,
- Joy,
- Creation.
This is how the teacher appears to me mathematics.
Development of students' creative abilities in extracurricular activities in mathematics - NovaInfo 41
Secondary school No. 8 with in-depth study of individual subjects, Vologda
Novainfo 41 , p.177-179 , download PDFPublished 9000 the problem of developing the creative abilities of students in the study of mathematics.
 Methodological ways of developing the creative abilities of students in optional classes in mathematics, as well as the problems of selecting the content of optional courses that contribute to the development of students' creative abilities are considered.
Methodological ways of developing the creative abilities of students in optional classes in mathematics, as well as the problems of selecting the content of optional courses that contribute to the development of students' creative abilities are considered. Keywords
EXTRA-COURSE CLASSES, OPTIONAL COURSES, TEACHING METHODS, CREATIVITY, CREATIVE ACTIVITY
Text of scientific work
Extra-curricular classes in mathematics for schoolchildren are constantly developing, enriching and need more and more qualified guidance from teachers. In the activities of students in extracurricular activities in mathematics, creative activity should prevail over reproducing. In these classes, more than in the classroom, it is possible to use partially exploratory and research teaching methods, which requires the teacher to possess appropriate teaching methods and high skill [5].
The main goal of extracurricular activities in mathematics is to expand and deepen knowledge, develop students' interest in the subject, develop their mathematical abilities, instill in students an interest in independent mathematics, educate and develop their initiative and creativity. Extracurricular activities with their inherent specifics (freer distribution of time, fewer students, the possibility of adjusting the program in the process of its implementation, etc.) make it possible to devote much more opportunities for the creative assimilation of mathematics and for the development of students' abilities.
Extracurricular activities with their inherent specifics (freer distribution of time, fewer students, the possibility of adjusting the program in the process of its implementation, etc.) make it possible to devote much more opportunities for the creative assimilation of mathematics and for the development of students' abilities.
What are the specific methodological ways of developing the creative abilities of students in optional classes in mathematics? The well-known Russian psychologist V.A. answered this question in relation to the lesson. Krutetsky. He believes that the development of creative learning abilities of schoolchildren is associated with independent creative mastery of mathematics, with independent formulation of simple mathematical problems, with finding ways and methods for solving them, with the “invention” of proofs of theorems, independent derivation of formulas, with finding original ways to solve non-standard problems. All this applies to extracurricular activities as well [1].
What should be the content of optional courses in order to promote the development of students' creative abilities? The content of the studied material should to a certain extent reflect the process of formation of the corresponding mathematical theory in mathematical science, reflect the creative activity of mathematicians. This provision is difficult to implement when studying individual topics of a compulsory school course, but in a system of optional classes united by a common goal, this is possible.
Elective courses should include self-study - exercises that are tasked with "discovering" a fact or mode of action unfamiliar to students. At the same time, students must observe, compare, put forward hypotheses, check their proposals. The importance of the emotional factor, both in the work of a scientist, inventor, and in the creative cognitive activity of students, is well known. For the development of creative activity of students, interest in the material being studied is important, it is interest that can encourage students to active imagination and fruitful intuition. Creative activity is connected with the problem of the development of creative abilities, tk. creative abilities develop in creative activity, manifest themselves in it [4].
Creative activity is connected with the problem of the development of creative abilities, tk. creative abilities develop in creative activity, manifest themselves in it [4].
Learning tasks can be divided into standard and search tasks. A standard task is considered to be such a task, the solution of which requires students to apply one or another algorithm known to them or perform a solution according to a model. A search task is understood as a task, upon presentation of which students do not know in advance how to solve it. This implies the expediency of presenting an optional course in the form of a series of successively arranged search tasks.
In this case, the study of the course is not limited to understanding and memorizing the educational material, it primarily consists in mastering the search results and solving cognitive problems, while the factual material acts as an auxiliary material for the implementation of very complex thought processes, as a result students develop the qualities of a creative personality.
Russian psychologist A.M. Matyushkin writes that a teacher who creates such learning conditions under which students discover acquired knowledge and actions can rightfully say that he not only imparts knowledge to students, but also develops their creative abilities [2].
The ability to define is an essential element of creative thinking. The search for definitions in optional classes contributes to the development of the ingenuity of schoolchildren. When studying all the topics included in the system of optional courses, it is necessary to strive to ensure that students independently construct definitions of concepts. In this case, of course, more time is spent than when the teacher formulates a ready-made definition. However, this time cannot be considered lost, because. students will gain experience in thinking management, which they successfully use in further education.
In addition, effectively organized learning activities of students in the process of solving non-standard problems is the most important means of forming a mathematical culture, such qualities of mathematical thinking as flexibility, criticality, rationality, logic; their organic combination is manifested in the special abilities of a person, giving him the opportunity to successfully carry out creative activity [3].
Thus, the use of such ways of managing the creative activity of students as increasing the emotionality of teaching, solving problems that require creative use of knowledge, creating problem situations, presenting an optional course in the form of a sequence of tasks, “designing” definitions by students increases interest in the material being studied and creates conditions favorable for the education of creative activity and independence of students.
Read also
References
- Krutetsky V.A. Psychology of mathematical abilities of schoolchildren. Moscow: Education, 1968. 481 p.
- Matyushkin A.M. Problem situations in thinking and learning. Moscow: Knowledge, 1985. 257 p.
- Miteneva S.F. Development of creative abilities of students in the process of solving non-standard problems in mathematics: monograph. Vologda, 2008. 150 p.
- Miteneva S.