Maths games for kindergarten in the classroom
Kindergarten Math Games That Make Learning Fun from the Start
Looking for ways to make math fun for young learners? Check out these kindergarten math games! They teach all the basic math skills kindergartners need to master and are sure to engage every kid in the learning process.
(Just a heads up, WeAreTeachers may collect a share of sales from the links on this page. We only recommend items our team loves!)
1. Conquer cardinality with penguin dominoes
Kindergarten math students work to master cardinality, understanding that written numerals correspond to the number of items pictured. These free printable penguin dominoes make the concept fun to practice.
Learn more: Playdough to Plato
2. Put together puzzles to gain number sense
Kindergarten math students learn to understand that numbers can be represented in a variety of ways. These free printable puzzles help them practice those skills.
Learn more: Tickled Pink in Primary
ADVERTISEMENT
3.
This free printable game helps little ones master their numbers from 11 to 20, both as numerals and represented on ten-frames.
Learn more: The Measured Mom
4. Stack cups and count to 100
Kids love stacking things, so they’ll get a kick out of kindergarten math games that make use of stackable cups. This one has them doing it with 100 cups while they count! Turn it into a competition by putting them in teams and timing them to see who can finish the task the fastest.
Learn more: Kindergarten Smorgasboard/100 Cups
5. Visit the skip-counting store
How fun is this? Grab some toys and label them with price tags in increments of 10 cents. Give kids a handful of plastic dimes, and have them count out the amount needed for each “purchase.”
Learn more: Creative Family Fun/Skip Counting Store
6. Have a rubber duck race
In this game, kids race to see who can be the first to get their rubber duckies to 10 (or any number you choose).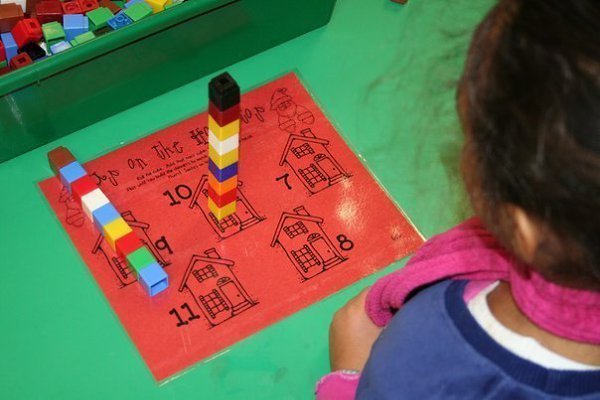 They roll a die and lay out tiles to move their duck. The twist? To get to 10 at the end, they must roll the exact number they need—no going over! Kindergarten math games like this one are terrific for practicing counting on, basic addition, and making 10.
They roll a die and lay out tiles to move their duck. The twist? To get to 10 at the end, they must roll the exact number they need—no going over! Kindergarten math games like this one are terrific for practicing counting on, basic addition, and making 10.
Learn more: Happy Toddler Playtime
7. Practice counting on with cards and dice
Remove the face cards from a deck of playing cards and grab a pair of dice. The first player turns over a card and then rolls the dice. The number on the dice indicates how far they “count on” from the card. (For example, a player turns over a three and rolls a four. They say, “Three: four, five, six, seven.”) If the player gets it right, they keep the card, and the other player(s) get a turn.
Learn more: Creative Family Fun/Counting On
8. Skip-count with craft sticks
There are endless ways to use craft sticks in the classroom. For this game, number a series of colorful sticks by fives, as shown. Kids can practice by putting them in order first.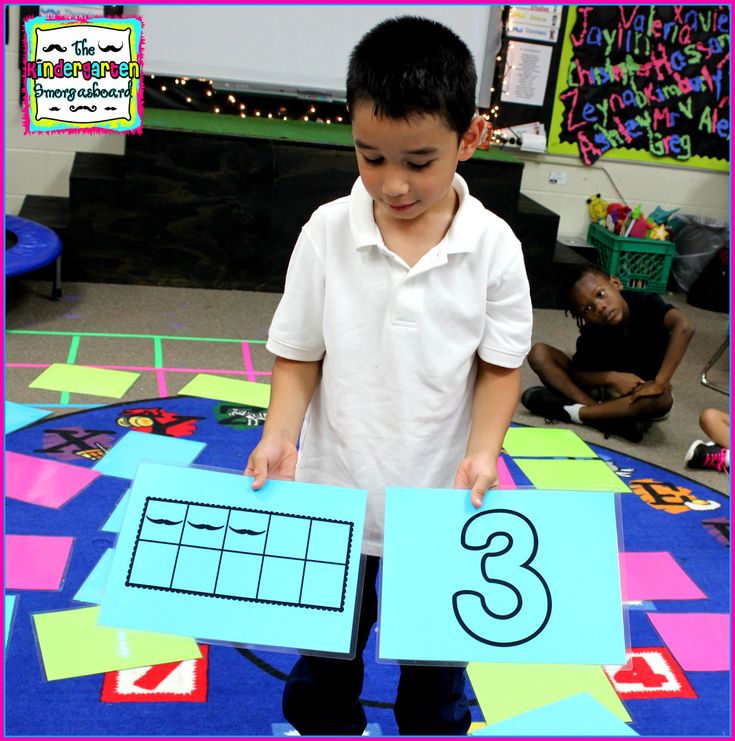 Then, have a student draw a stick and count on by fives from that number to 100—if they draw 75, they then count 75, 80, 85, 90, 95, 100. If they get it right, they keep the stick, and the next player takes a turn.
Then, have a student draw a stick and count on by fives from that number to 100—if they draw 75, they then count 75, 80, 85, 90, 95, 100. If they get it right, they keep the stick, and the next player takes a turn.
Learn more: Simply Kinder
9. Match teen numbers
Once they’ve mastered the numbers 1 to 10, it’s time to understand how those numerals add up to make bigger numbers. These free printable cards show numerals and matching bundles of sticks that deconstruct each teen number into tens and ones.
Learn more: The Kindergarten Connection
10. Compare numbers with dominoes
Kindergartners learn to compare numbers to determine which is larger and which smaller. Stacking math cubes based on the numbers on dominoes is a fun, hands-on way to compare the two numbers side by side, making it easier to see the difference.
Learn more: My Fabulous Class
11. Face off and compare numbers
You’ll need some small toys for this game, as well as polyhedral dice. Kids roll and place the number of items on their side. Then, they compare the two to see which is bigger.
Kids roll and place the number of items on their side. Then, they compare the two to see which is bigger.
Learn more: Natalie Lynn Kindergarten
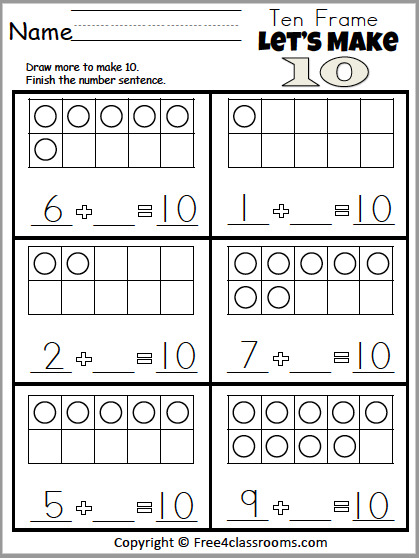
12. Make 10 with two-sided chips
You’ll need counting chips that are a different color on each side for this activity. Kids shake up 10 chips in a cup and pour them out on the table. Then they see how many they have of each color and write that number bond to make 10.
Learn more: First Grade Fairytales
13. Throw snowballs to make 10
Make “snowballs” from paper (or any way you like), then place them in a bucket at one end of the room. Start kids out by having them toss snowballs into another bucket until they reach 10 (or any target number). Then, up the challenge by placing some snowballs in each bucket and have kids figure out how many more they need to toss in to make 10.
Learn more: Frugal Fun for Boys and Girls—Snowball Math Games
14. Use Uno cards to play addition war
In the card game War, players each flip an Uno card, and the one whose card is greatest takes them both.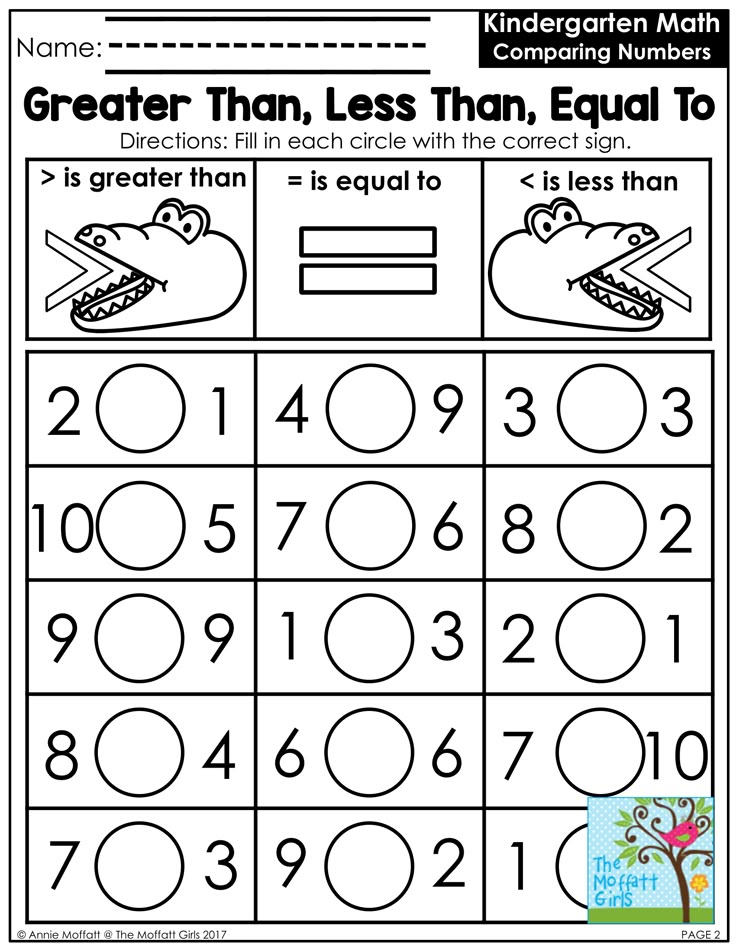 In this twist on one of our favorite kindergarten games, players each flip two cards. They then use counting blocks to represent the numbers and count on or add to find the sum. The largest sum wins the hand, and play continues.
In this twist on one of our favorite kindergarten games, players each flip two cards. They then use counting blocks to represent the numbers and count on or add to find the sum. The largest sum wins the hand, and play continues.
Learn more: Planning Playtime—Addition Game
15. Roll and add for fluency within 5
Kindergarten math students work to become fluent in adding and subtracting within 5. This free printable board game makes it fun!
Learn more: Liz’s Early Learning Spot
16. Get four in a row and learn place value
This customizable game helps teach the early place-value concept of tens plus ones. Get it for free at the link.
Learn more: Two Boys and a Dad
17. Bowl and subtract within 10
Set up a toy bowling pin set (or make one from plastic bottles or toilet-paper tubes). Kids bowl and see how many pins they knock down, subtracting that number from 10. Then they repeat, this time subtracting from the previous answer. First to get to zero wins!
First to get to zero wins!
Learn more: Planning Playtime—Subtraction Worksheets
18. Get off my boat!
So simple, so engaging, so fun! Use tape to outline a boat shape on the floor (or try this outside with sidewalk chalk). Let some kids board the “boat,” then make some get off. Use those numbers to write a subtraction number sentence and solve the equation!
Learn more: Kindergarten Smorgasboard—Get Off My Boat!
19. Drive and compare numbers to music
Prep for this game by using dot markers on paper plates as shown (visit the link below for more examples). Each kid takes a plate then uses it to “drive” around the room as you play music. When the music stops, they find a nearby partner and compare what they see on each other’s plates (e.g., “8 dots is more than 4 dots. 1 green dot is less than 4 green dots.” Then start the music up and repeat!
20. Build a weigh station
Use a hanger and plastic cups to build a super-simple weigh station. Kids will love dropping items into the cups to see which weighs more or less. Turn it into a game by having them try to guess which object weighs more first or how many of one item equals another.
Kids will love dropping items into the cups to see which weighs more or less. Turn it into a game by having them try to guess which object weighs more first or how many of one item equals another.
21. Battle it out in ribbon war
Looking for kindergarten math games that teach non-standard measurement? This idea is fun and easy. Cut colorful ribbons into a variety of lengths and place them in a bag. Each student pulls a ribbon from the bag. Then, put students in pairs and have them compare their ribbons to identify the longer one. The student with the longer ribbon keeps both, and the game continues.
22. Hold a shape scavenger hunt
Kindergarten math students are learning to recognize shapes in their environment and also to categorize and sort. This scavenger hunt does it all! Send them out to find objects in the room that match the shapes. Then count and compare to see how many you have in each category.
Learn more: Frugal Fun for Boys and Girls—Shape Scavenger Hunt
23.
 Hop along a shapes maze
Hop along a shapes mazeUse sidewalk chalk to lay out a shape maze on the playground or driveway. Choose a shape and hop from one to the next, or call out a different shape for every jump!
Learn more: Creative Family Fun—Shape Maze
24. Make a match to learn shapes
Grab these free printable memory cards at the link. Then play and learn the basic shapes.
Learn more: Life Over C’s
25. Guess the mystery shapes
Work on geometry terms like “sides” and “vertices” when you sort shapes using these attributes. Start by placing 3D shapes into paper bags and asking students questions like “The shape in this bag has 4 sides. What could it be?”
Learn more: Susan Jones Teaching
Love these kindergarten math games? You’ll also enjoy these 50 Kindergarten Math Word Problems of the Day!
Want more articles like this? Subscribe to our newsletters!
22 Kindergarten Math Games You Should Play With Your Kids
In Kindergarten, it is important to make students excited to learn about maths in the world around them. Kindergarten students need to have the space to explore, make connections and come to their own realizations about numbers and shapes – and games are a great way to do this! Whether you are homeschooling or teaching a class, here are 23 math games perfect for Kindergarten-aged students. Try them out and watch the maths magic happen!
Kindergarten students need to have the space to explore, make connections and come to their own realizations about numbers and shapes – and games are a great way to do this! Whether you are homeschooling or teaching a class, here are 23 math games perfect for Kindergarten-aged students. Try them out and watch the maths magic happen!
1. Online Math Games
Looking for an easy lesson activity with no preparation? Then these online games are perfect! Here you will find 70 free online games for your students to play, covering the 8 main topic areas.
Learn more: education.com
2. PBS Online Math Games
The PBS website is free and has games linked to a range of topics to engage students in their math learning. Students will find over 100 games here featuring many familiar and friendly characters, such as Curious George, Elmo, and Dr. Seuss!
Learn more: pbskids.org
3. Splash Learn
Splash Learn online games are free and super fun! There are 61 games that cover a wide range of Kindergarten topics, including place value and number sense, addition and subtraction, time, money, measurement, data, and geometry.
Learn more: splashlearn.com
4. Cool Kindergarten Online Games
Another great online resource for Kindergarten students. On this site, there are four key learning themes that students can explore through interactive videos and games. The graphics are engaging and super kid-friendly.
Learn more: coolkindergarten.com
5. Counting Game!
Materials: dice, small items to count, small bowls or cups
This game is great for students to play in pairs or individually. Students will roll the dice and place that many items into their bowl. Take turns and keep going until one person has put all of their items into their bowl!
Learn more: buggyandbuddy.com
6. Addition and Subtraction Tower
Materials: dice, 2x2 Duplo blocks
Roll the dice and see who can make the tallest tower in this addition and subtraction tower game! Students simply roll the dice and add that many bricks to their tower. Or, if your students need a subtraction challenge, get them to build two equal-sized towers, roll the dice and then remove that many bricks. This time the shortest tower wins.
This time the shortest tower wins.
Learn more: frugalfun4boys.com
7. Play Dough Stamp and Count
Materials: playdoh, various Duplo blocks, scrap paper, pen, a tray (optional)
Engage your students with stamping fun while they learn addition pairs! Simply write numbers on pieces of paper and tell students to stamp that amount on their playdough using Duplo bricks with 1, 2, 4, or 8 dots. Challenge them to make a number like 17 – if they have already stamped 8 dots, how many more to go? As an added bonus, this game helps to build students' fine motor skills at the same time as their maths skills!
Learn more: frugalfun4boys.com
8. Number Matching with Cups
Materials: paper cups, markers
This game is great for students who are learning to count. Draw circles with a different number of dots inside. Label the bottom of the cups with numbers 1 to 10 and students can try to match the cup to the correct circle on the paper.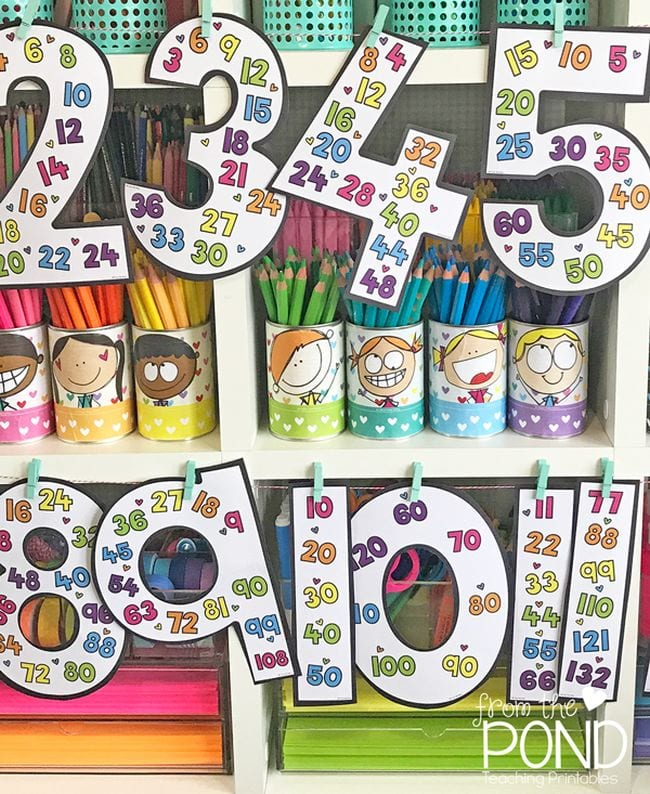
Learn more: funlearningforkids.com
9. Playdough Subtraction Smash
Materials: subtraction playdoh mat, playdoh, markers
Let the students roll 10 balls of playdough and place them down on the mat handout. Give students an amount to subtract and students can smash that number of balls to reveal the answer. This activity is a great way to learn subtraction and release some anger!
Learn more: 123homeschool4me.com
10. Play Dough Numbers
Materials: playdough, printable numbers.
Optional Materials: beads, seeds, dry beans
Help your students to learn their numbers with this fun sensory activity! Simply place a number mat on the table and ask the children to manipulate the playdoh to create that number with the dough. A great game to support students’ fine motor skills and number recognition.
Learn more: howwelearn.com
11. Snowman Counting
Materials: snowman cut out, markers, buttons, hat cut-outs
In this game, students simply cut out a snowman and some hats from cardstock. Write numbers on the snowmans’ hats and let the students place the hat on the snowman by matching the number of buttons to the number on the hat.
Write numbers on the snowmans’ hats and let the students place the hat on the snowman by matching the number of buttons to the number on the hat.
Learn more: cbc.ca
12. Counting with Unifix Cubes
Materials: addition flashcards, unit cubes
Counting with unfix cubes is a great way for students to practice addition. Simply place flashcards on the floor or table and let the students solve the questions by collecting the correct amount of unit cubes.
Learn more: homegrownlearners.com
13. Spin and Collect
Materials: worksheet, paper clip, unit cubes
In this activity, students each spin the spinner 10 times and circle the number they land on each time. When the students land on a number, they must collect the same number of cubes. In the end, the students will count all of their cubes and see who collected the most.
Learn more: susanjonesteaching.com
14. Animal Pattern Block Mats
Materials: colored blocks, free animal pattern mat
Do your students love learning about the ocean? Then this super fun hands-on activity is for you! In this activity, students use colored blocks to make animal patterns. In addition to learning about shapes and patterns, extend your students by talking about the features of each animal and use this activity as a chance to practice fine motor skills and visual discrimination.
In addition to learning about shapes and patterns, extend your students by talking about the features of each animal and use this activity as a chance to practice fine motor skills and visual discrimination.
Learn more: lifeovercs.com
15. Make That Number
Materials needed: worksheet, dice
This game can be used to practice both subtraction and addition! Students will roll dice, generating numbers for addition and subtraction sums. Then, students color in or use a do-a-dot marker to mark the totals they have made. When a student gets four in a row, the game is over.
Learn more: themeasuredmom.com
16. Frog Jump Game
Materials: painters tape, tape measure
Optional Material: frog cut out
Students will practice their counting and measuring skills in this fun jumping game. Students will jump like a frog a certain number of times and measure how far they traveled. Use rulers to introduce standard units of measure or a piece of string or other objects to reinforce the students’ understanding of non-standard units.
Learn more: coffeecupsandcrayons.com
17. Goldfish Counting
Materials: goldfish crackers, counting cards
Do your students like eating goldfish crackers? If so, entice them into this activity by using the crackers to learn and practice counting! Hand out a range of goldfish bowl counting cards and have the students cover each fish picture with a goldfish cracker – just be sure students don’t eat them instead!
Learn more: lifeovercs.com
18. Matching Game Obstacle Course
Materials: string, chairs, pegs, deck of cards or sticky notes
Weave string back and forth between a hallway of chairs to create an obstacle course for your students. Peg cards or sticky notes with numbers onto the string and give students a number to navigate their way through the obstacle course to collect.
Learn more: handsonaswegrow.com
19. Marshmallow Subtraction
Materials: marshmallows, markers, free printable worksheet
Another great activity for hungry students – and in this activity, eating is encouraged! Students can learn subtraction with marshmallows, counting out the total number, and eating the amount subtracted to discover the total amount left behind.
Learn more: lifeovercs.com
20. Sunglasses Addition
Materials required: Sunglasses printable, scissors, glue
Let students learn addition in this practical activity. Students must find the matching addition sum and total to make a complete pair of sunglasses!
Learn more: adabofgluewilldo.com
21. One More One Less
Materials: free worksheet, dice, crayons or color pencils
This activity is a great way to practice one more or one less than. Students take turns to roll a dice and color the hexagon that is either one more or one less than the number on the dice.
Learn more: susanjonesteaching.com
22. Number Sense
Materials: worksheet, scissors, color pencils, glue
Through this game, students in Kindergarten can further develop their number sense through sorting through cards showing different representations of a number and other numbers.
Learn more: themoffattgirls.com
The math games reviewed in this article cover a whole host of math topics for Kindergarten, including place value, number sense, shape, and measurements. The hands-on nature of the activities is sure to engage young learners and help them to become more comfortable with difficult math concepts. So what are you waiting for? Start trying them out and building your students’ love of math today!
The hands-on nature of the activities is sure to engage young learners and help them to become more comfortable with difficult math concepts. So what are you waiting for? Start trying them out and building your students’ love of math today!
Frequently Asked Questions
How high can a 5-year-old count?
Most students of this age are able to recognize and count to 10. However, students that are closer to 6 or who have engaged in extra tuition may also be able to count to 100, although this is not expected.
How can you make math fun?
Playing fun math games and building in opportunities for hands-on learning is the best way to keep students active and engaged while also supporting the development of their understanding of complex math topics.
What kind of math do Kindergarteners learn?
The key areas covered in Kindergarten include counting, addition, subtraction, measurement, and geometry.
Didactic games in mathematics in kindergarten: goals and objectives
Didactic games in mathematics in kindergarten: goals and objectives
Didactic games are held to increase the child's awareness of the world around. They develop observation skills, teach them to fix and find differences between objects, comparing them according to different characteristics. During the game process, children learn to find elementary cause-and-effect relationships. nine0005
They develop observation skills, teach them to fix and find differences between objects, comparing them according to different characteristics. During the game process, children learn to find elementary cause-and-effect relationships. nine0005
Didactic games in mathematics in preschool educational institutions can be very different, their choice depends on the goal:
1 The use of numbers and numbers in games contributes to familiarization with the concept of counting, the history of numbers, improving counting and comparison skills.
These didactic math games for preschoolers help:
improve the skill of using single digits independently; nine0005
-
education of mindfulness, memory, thinking;
-
learning how to distribute natural numbers, improving counting skills.
-
Games designed to study the time make children familiar with the days of the week, the names of the months, learn to remember their position in the calendar.
-
Orientation development games allow pupils to learn to fix and state their own position on the ground, to determine and name the location of any object relative to another. With the educational task achieved, preschoolers are able to use words to name the location of objects. nine0005
-
Games with figures are used to strengthen knowledge about the shape of various geometric shapes, improve the skill of finding them in nearby things. Such games are conducive to the education of attention and the formation of creative imagination in preschoolers.
-
Didactic mathematical games that develop logical thinking are originally intended to form the components of scientific thinking: making judgments, bringing arguments, summing up. They also help develop creativity and out-of-the-box thinking It is important to know
Didactic games should not be played for a long time .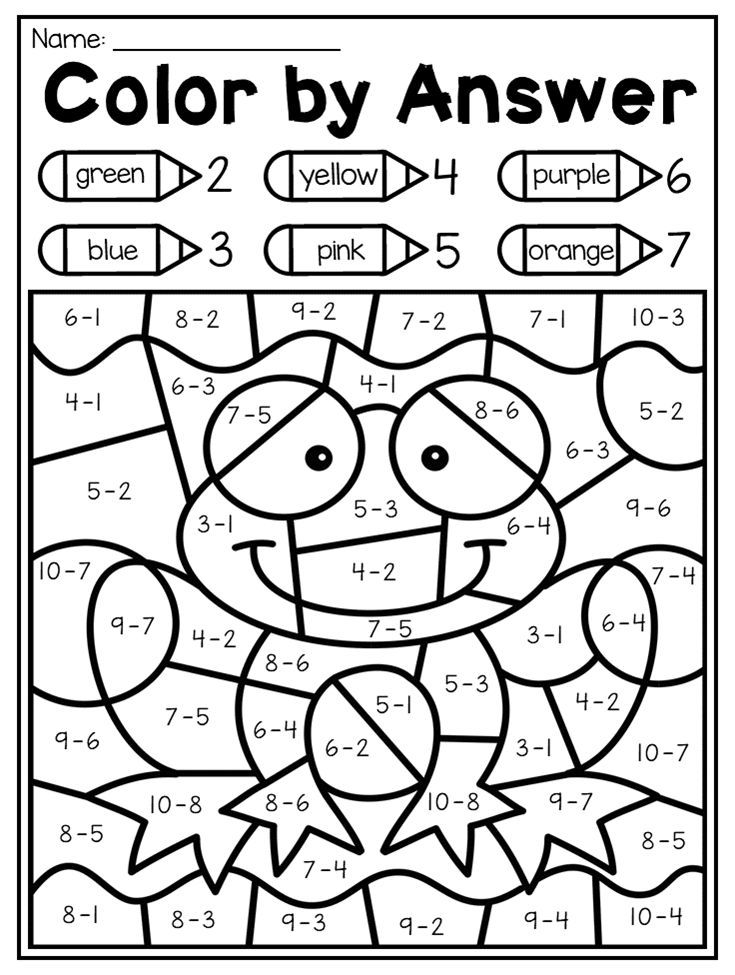 For younger children, it is enough to allocate 5 minutes for them. Didactic games in mathematics in the senior group can last no more than 15 minutes. Exceeding this time may lead to a decrease in activity and a weakening of cognitive interest, which may adversely affect the result.
For younger children, it is enough to allocate 5 minutes for them. Didactic games in mathematics in the senior group can last no more than 15 minutes. Exceeding this time may lead to a decrease in activity and a weakening of cognitive interest, which may adversely affect the result.
-
If a team takes part in the game, attention should be paid to the individual abilities of each , and, if necessary, to provide assistance to the underachieving for a successful outcome of the educational problem.
DIDACTIC Games for preschool children
In order to grow cognitive interest of educated teachers, teachers should try to diversify the course of teaching. To do this, many develop and produce their own training sessions. In the manufacture of visibility, everything that is at hand can be useful, the main condition is harmlessness for kindergarten students. nine0005
nine0005
Materials for creating didactic games can be as follows:
-
improvised materials - fabric, yarn, buttons;
-
natural raw materials - leaves, flowers, grass, cones;
-
stationery - glue, gouache, colored paper, cardboard;
-
imagination is the most important component.
Do-it-yourself didactic math games in pictures
Making do-it-yourself didactic games is not at all difficult. Here are examples of such mathematical games.
004
"Describe the pattern"
Purpose: training of orientation in space, improvement of communication skills.
Game progress. Each preschooler has a drawing depicting a carpet. Pupils are required to describe the position of the parts of the pattern in the figure: on the left side, on the right, at the top or bottom.
"Solve an example"
Purpose: training to perform addition and subtraction within ten. nine0005
Game in progress. The teacher throws a ball to a preschooler and calls an example. The pupil, having caught it, answers and returns the ball. Then the teacher throws the ball to the next one.
"Find the mistake"
Purpose : analysis of geometric shapes, comparison and finding the excess.
Game progress . The preschooler is invited to analyze the rows of geometric shapes and point out the error, offering a correction option with an explanation. A mistake can be a circle in a row of squares, or a red figure among yellow ones. nine0005
nine0005
"Show"
Purpose: improvement of the ability to recognize a geometric figure according to a given criterion.
Game progress. In front of a preschooler, several figures are randomly laid out, differing in color, shape and size. The teacher proposes to determine the figure according to the named criterion: a small square, a large red circle, etc.
"One property"
Purpose: to consolidate knowledge about the properties of geometric shapes, to develop the ability to characterize and distinguish figures by their characteristics. nine0005
Game progress: players must provide the same set of geometric shapes. One of the players puts one of them on the table. The task of the second player is to choose from his set a figure that differs from the one laid out by the previous player in only one of some signs. For example, if the first figure laid out is a large red circle, then the next one can be laid out a large red square or a large blue circle, or a small red circle. The game should be built on the principle of playing dominoes. nine0005
For example, if the first figure laid out is a large red circle, then the next one can be laid out a large red square or a large blue circle, or a small red circle. The game should be built on the principle of playing dominoes. nine0005
"Who are the neighbors?"
Game progress . Participants become in a circle. The teacher throws the ball and calls a random number. The child, having caught the ball, names the neighbors of this number. The ball is then thrown to the next player.
"Let's Harvest"
Goal : Practice comparing objects by size.
Game progress . The teacher advises the children to harvest in different baskets - large vegetables and fruits in one basket, small ones in the other. "Shop and Geometry" Purpose: training in recognizing basic geometric shapes, improving communication skills.
Game progress. On the table are objects of various shapes, put up for sale.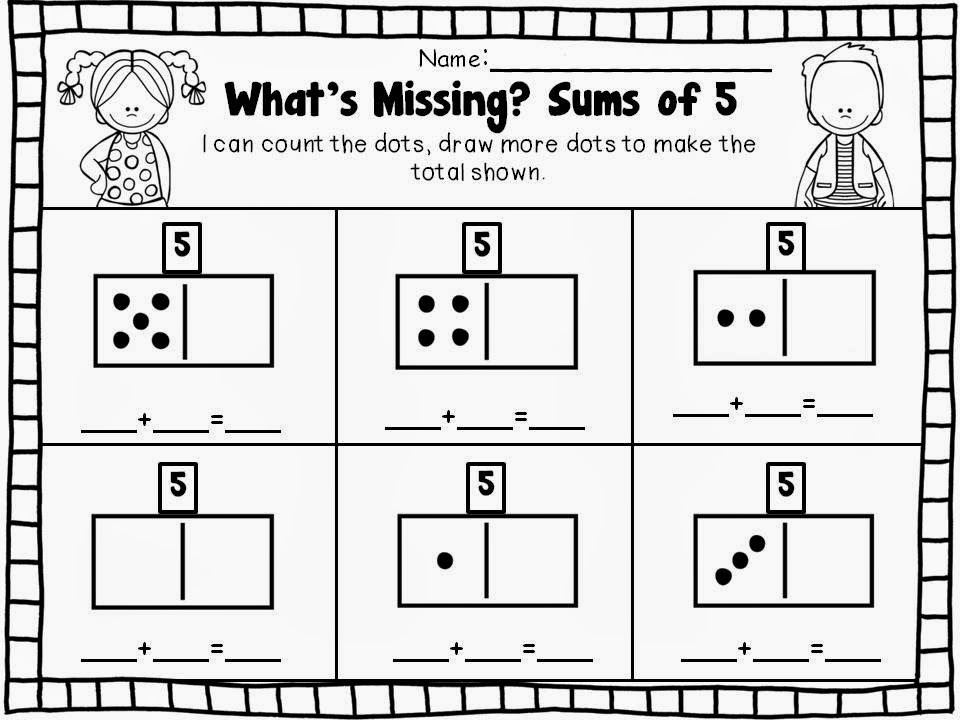 Each pupil - the buyer receives a card - a check on which a figure is drawn: a circle, a triangle, a square or a rectangle. He can purchase any thing, provided that the shape of the goods corresponds to the picture on the card. Having made an unmistakable choice and proving it, the child receives a purchase. nine0004
Each pupil - the buyer receives a card - a check on which a figure is drawn: a circle, a triangle, a square or a rectangle. He can purchase any thing, provided that the shape of the goods corresponds to the picture on the card. Having made an unmistakable choice and proving it, the child receives a purchase. nine0004
Mathematical game library Game with a cube .
Purpose : exercise in forward and backward counting.
Material: cube with numbers or circles on the sides.
Game progress.
Children form a circle. with the help of a counting rhyme, a leader is chosen.
He throws the cube, calls the number on the edge and continues to count further, after which he throws the cube to another child and gives the task: “Count further” or “Count backwards”. nine0005
Which hand is how much?.
Purpose : To train children in the ability to make a number from two smaller numbers.
Material: small toys to fit in hands or counting sticks.
Game progress:
The teacher offers to count the items in his hands.
-How many toys (sticks) do I have?
After the teacher divides the objects in two hands behind his back. nine0005
- Guess how many toys (sticks) I have in my left (right) hand? (helps with the words "more", "less" to guess the first number)
Having guessed how many objects are in one hand, the child must say how many objects are in the other hand and how many together.
The game "Remove the numbers on the assignment."
Purpose: learn to set variable characteristics using quantitative and spatial relationships, meaningful and visual images. nine0005
Material: number cards.
Game progress.
Number cards in front of each player. It is proposed to arrange the cards in order. The game consists in the fact that the children remove the card with the number that is guessed. For example, the teacher says: “Remove the number showing how many times a year a person has a birthday”, “Remove the number that denotes a number greater than 7 on 1", etc.
For example, the teacher says: “Remove the number showing how many times a year a person has a birthday”, “Remove the number that denotes a number greater than 7 on 1", etc.
Game "Let's check attention". nine0004
Purpose: to develop memory and the ability to correctly name the attributes of the game (geometric shapes of different sizes and colors, cards with numbers)
Material : geometric shapes of different sizes and colors, cards with numbers.
Game progress.
The facilitator lays out several items. The player carefully examines them, remembers. The leader counts (to himself) to ten. Then the items are covered with a napkin. The player lists the items he has memorized. nine0005
Reverse game.
Goal : To encourage children to use antonyms in speech.
Material: ball.
Game progress.
Children stand in a circle. the teacher throws the ball and says: "Low." The child catches the ball and, returning it, answers: “High”.
the teacher throws the ball and says: "Low." The child catches the ball and, returning it, answers: “High”.
Deep - shallow
Bitter - sweet
Far - close
Cold - hot, etc. nine0005
Guessing game
Objectives: improve the experience of spatial orientation and counting skills. Develop the ability to ask questions, determining the color, shape, location of objects.
Material: flannelgraph, images of homogeneous, identical objects that differ in quantity, size, shape, color (for example: snails, dragonflies, butterflies of different colors). Tray with the same spare pictures.
Game progress.
The game consists of two parts (if desired, each of them can be used independently.)
1 part . The players are located next to the panel and examine it. The leader is chosen by counting. He asks his question to all the children and invites one to answer.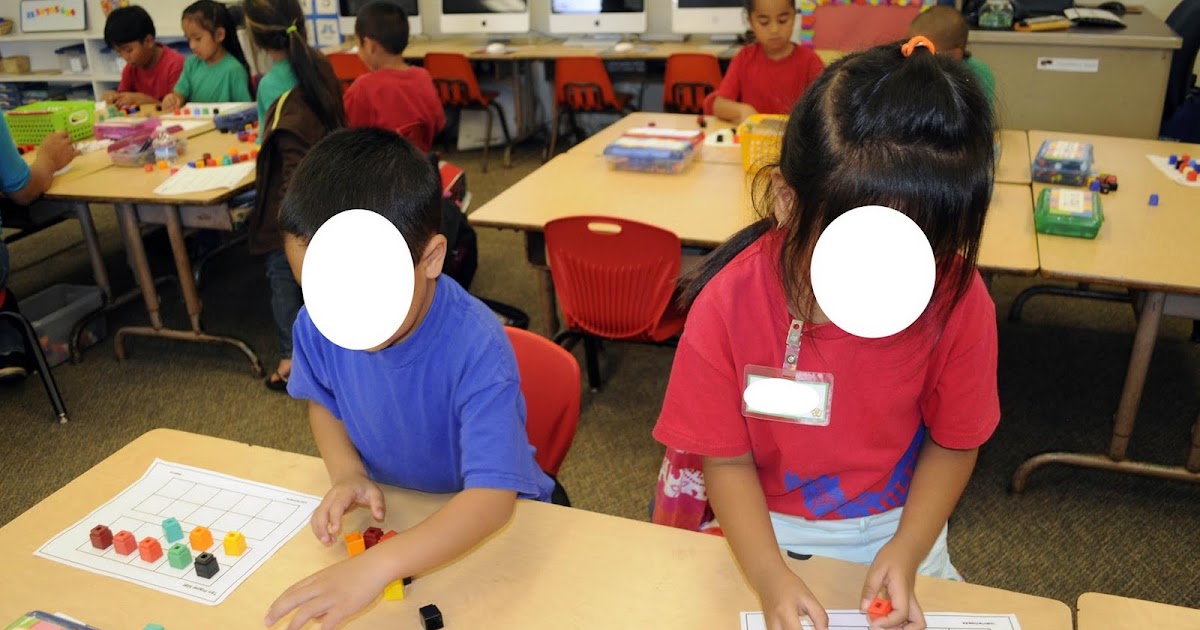 If he answers correctly, he becomes the leader and asks his question. So gradually the move passes from one player to another. The educator encourages original and varied questions, helps to formulate them clearly and briefly. The questions encode the name, quantity, location or quality of the objects presented on the panel. nine0005
If he answers correctly, he becomes the leader and asks his question. So gradually the move passes from one player to another. The educator encourages original and varied questions, helps to formulate them clearly and briefly. The questions encode the name, quantity, location or quality of the objects presented on the panel. nine0005
Part 2 . On the tray are additional parts for the game. On the instructions of the host, the player adds details to the panel and arranges them according to the instructions; replaces one part with another; moves elements on the panel.
We count in the kitchen.
Purpose : practice counting.
Game progress.
In the kitchen, without looking up from work, you can ask your child to count: the legs of the table, chair, stools, deep and small plates, cups, glasses, saucers, jars, burners by the stove, drawers by the cabinet, handles by the furniture and much more. You can compare two groups of objects, what is more, what is less. nine0005
nine0005
Account by ear.
Purpose: develop auditory attention, practice counting.
Game progress.
Knock so that the child does not see the movement (the child closes his eyes or turns away).
- I'll knock, and you tell me how many times.
- I will knock, and you will knock the same number of times.
- I will tell you how many times, you will knock as many times.
- Count only strong blows (tambourine). nine0005
- Count only weak hits.
Didactic games in mathematics lessons
Didactic games in mathematics lessons not only captivates, makes you think, but also develops independence, initiative and will of the child, teaches to reckon with the interests of comrades. I want to talk about some didactic math games that I use in my lessons.
MBOU "Tonkinskaya secondary school", elementary teacher
class Toropova Galina Nikolaevna
"A child is not a vessel to be filled,
but a torch to be lit. " (Francois Rabelais)
" (Francois Rabelais)
Mathematics becomes the most difficult and, for some children, the least favorite subject in the first years of schooling. This is due to the fact that some children have not yet developed such functions of mental activity as analysis, synthesis, generalization, the ability to compare, classify, and differentiate. For the successful education of children, it is necessary at the very first stages to arouse their interest in educational activities, to captivate, to intensify their activities. One of the most effective means of awakening a keen interest in a subject is a didactic game. nine0005
The implementation of game techniques and situations in the lesson takes place in the following main areas: the didactic goal is set for students in the form of a game task; educational activity is subject to the rules of the game; educational material is used as its means, an element of competition is introduced into educational activity, which translates the didactic task into a game one; successful completion of the didactic task is associated with the gaming result.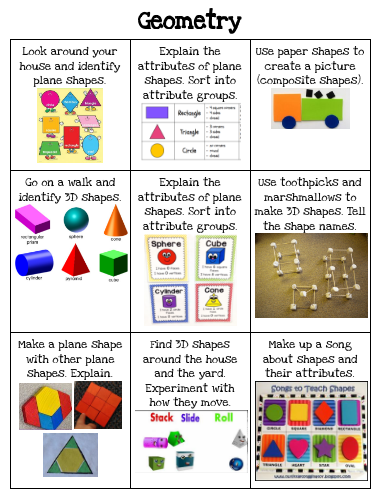
Didactic game in mathematics lessons not only captivates, makes you think, but also develops independence, initiative and will of the child, teaches to reckon with the interests of comrades. Enthusiastic children learn the program material more easily, acquire certain knowledge, skills and abilities. Therefore, the inclusion of games and game exercises in the lesson of mathematics makes the learning process interesting, creates a cheerful mood among the children, helps to overcome difficulties in mastering the material, relieves fatigue and maintains attention. nine0005
Significance of didactic games:
- significantly increases the cognitive interest of younger students;
- the lesson becomes brighter, more emotionally saturated;
- positive motivation for learning is formed;
- Arbitrary attention develops, working capacity increases;
- the ability to work in a team is formed
The place and role of gaming technology in the educational process, the combination of game and learning elements largely depend on the teacher's understanding of the functions and classification of pedagogical games. nine0005
nine0005
According to the nature of cognitive activity, didactic games can be classified into the following groups:
- games that require executive activity from children. With the help of these games, children perform actions according to the model (come up with numerical expressions, lay out a pattern, draw a figure similar to this one)
- games that require action replay. They are aimed at the formation of computational skills (“Mathematical fishing”, “Labyrinth”, “How to get to the top”, “Fill in the window”, “Determine the course of the ship”)
- games that include exploration and creativity (Collect Circle Examples, Math Caterpillar)
According to the nature of the material used, didactic games are conditionally divided into games with objects, board games and word games.
According to the functions didactic games are divided into:
- educational;
- controlling;
- generalizing.

A game will be educational if the students who participate in it acquire new knowledge, skills and abilities or are forced to acquire them in the process of preparing for the game. Moreover, the result of mastering knowledge will be the better, the more clearly the motive of cognitive activity is expressed not only in the game, but also in the very content of the mathematical material.
Controlling will be a game, the didactic purpose of which is to repeat, consolidate, test previously acquired knowledge. To participate in it, each student needs a certain mathematical background. nine0005
Generalizing games require knowledge integration. They contribute to the establishment of interdisciplinary connections, are aimed at acquiring the skills to act in various educational situations.
According to the number of participants didactic games can be: collective, group and individual.
Didactic games can be used at separate stages of the lesson, acting as game moments.
I want to tell you about some didactic math games that I use in my lessons. I am currently working with 3rd grade students. The central theme of the mathematics course in grade 3 is the study of tabular multiplication and division. The technique requires that children not only know the table, but also understand the principles of its compilation, which make it possible to find any work. Computing skills, as you know, are acquired as a result of repeated repetitions of the same operations. To avoid monotony in working out tabular cases of multiplication and division, I conduct exercises in a playful, entertaining way. nine0005
I determine the value of a didactic game not by what kind of reaction it evokes from children, but by how effectively it helps to solve a learning problem in relation to each student.
Choosing some didactic game for the lesson, I think over the following questions :
- Purpose of the game.
 What skills and abilities will be formed in the process of its implementation? What educational goals are pursued during the game?
What skills and abilities will be formed in the process of its implementation? What educational goals are pursued during the game? - Is it feasible for students in my class? nine0030
- Will all children participate equally in the game?
- Summing up the game.
To conduct a didactic game in the lesson, if necessary, I make groups in advance so that each group includes students with both strong and weak learning abilities. In each group, I appoint a responsible person. As a rule, this is a student with good learning opportunities or the most organized one who can organize the work of the group. nine0005
I assign an important role in the lessons to oral exercises. In order to involve all students in this, I use signal cards. They help to discipline students and at the same time receive information about the assimilation of the material. With their help, you can do a lot of oral exercises in the form of a game.
In my lessons I use the following games.
Game “Yes. No.”
Examples are given on the board: 4x6, 8x3, 4x5, 7x3, 9x4, 5x6. I show cards with numbers. If the number is the answer, the students say “Yes” in chorus, then say the example 4x6=24. if the number is not the answer, say "No". nine0005
Live Math
All students have a card with numbers from 0 to 9. Reading an example (3×2). The student who has a card with the number 6 stands up or raises his hand. It is best to give examples for division, since single-digit numbers are obtained in the answers.
The game requires physical activity, so it can be done instead of a physical minute in the middle of the lesson.
“I won’t tell”
The game is structured like this: children count, for example, from 20 to 50 one by one. Instead of numbers that are divisible by, for example, 6, they say: “I won’t tell!” !«. I write these numbers on the board. A record appears: 24, 30, 36, 42, 48. Then, with each of the numbers written down, students name examples: 24:6=4, 30:6=5, etc.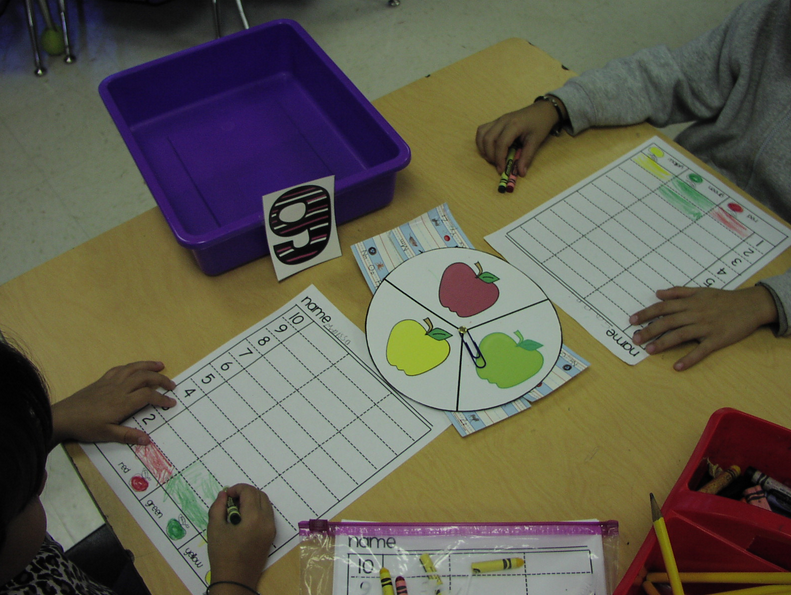 nine0005
nine0005
This game contributes to the purposeful formation of attention switching mechanisms.
“Test yourself”
I prepare cards with the results of multiplying some numbers, for example 18. I show the card, and the students write down an example for multiplication with such an answer.
“Who is faster, who is more correct?!”
I distribute one set of numbers from 0 to 9 for each row of desks, so that one student in the row gets the number 0, the other 1, etc. I read examples (4×4; 9× 2 or 40: 4, etc.), and the children must quickly figure out how much it will turn out, and those who have the numbers 1 and 6 go to the board and make the number 16. For each example, a point is scored for the row in which the faster and answered correctly. The row with the most points wins.
The game not only helps to consolidate a certain computational skill, in particular tabular multiplication and division, but in the course of it the understanding of the local meaning of numbers is clarified - students need to stand up so that one number stands for units, the other for tens. Mixing places is seen as a loss. nine0005
Mixing places is seen as a loss. nine0005
"Don't let your friend down!"
Two (four) students go to the blackboard at the same time. I read an example, for example: 6 × 7. I propose to make four examples of multiplication and division with the same numbers. The first student writes examples for multiplication, and the other - for division. If the examples are compiled and solved correctly, I applaud the guys for their coherence in their work. The entry on the board looks like this:
6×7=42 7×6=42
42:7=6 42:6=7
Example 7×6 =42 implies 42:7=6, 42:6=7. nine0005
“Divisible - not divisible”
I say different numbers, and the students clap their hands if the number is divisible, for example, by (4, 5) without a remainder.
"Collect the word"
The same number of examples are written on the board on the right and on the left. Two teams come to the board. On a signal, each of those called solves one of the examples and chooses among the prepared cards a card with a number corresponding to the answer of the example (a letter is written on the back of the card). The first team to make up the words wins. nine0005
The first team to make up the words wins. nine0005
Interdisciplinary communication is also carried out in this game, since dictionary words or words for any rule can be composed.
"Silence"
Examples for multiplication and division are written on the board. I show an example, the children on the cards are the answers. (Each student has a number set.)
"The best counter"
A circle with numbers is attached to the board. I give the task: to increase (or decrease) these numbers several times. Children write down answers in notebooks. This is followed by a check (the student who completed the task first reads the answers and everyone checks their notes.). nine0005
“In order”
Examples given:
8×3
3×2
3×6
7×3
5×3
3×9
Name the values of expressions in ascending (or descending) order.
“Circular examples”
I prepare cards with examples in advance, selecting them so that the answer of the previous example is the beginning of the next one.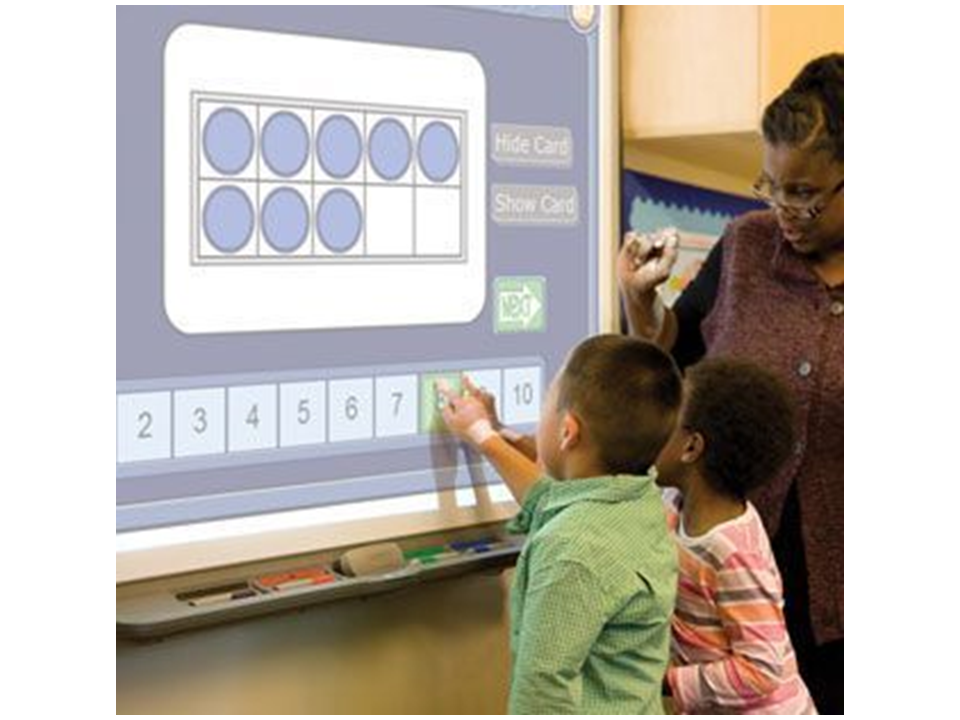 Each student in the same row receives such a card. It is very important not to make a mistake here! In the next lesson, these circular examples are given to the children of another row. nine0005
Each student in the same row receives such a card. It is very important not to make a mistake here! In the next lesson, these circular examples are given to the children of another row. nine0005
“Which row is better?”
Students in the first row ask questions to the students in the second row on the multiplication table (including cases of division). Then the students of the second row prepare examples for the children of the third row. On the board, I count the number of correct answers in each row.
"Which row will fly to the moon faster?"
I have 3 rockets cut from heavy paper folded in half. Each rocket has windows for the number of students in a row. In the middle of the rocket, I insert a sheet cut out along the contour of the rocket, and in the windows I write examples for multiplication and division. Students in each row quickly solve one example by passing the rocket to each other. We check the examples collectively. The rocket, in which all the tasks are completed correctly, “flies into space” first! I throw away the used sheets with examples and insert new ones. Tomorrow the rocket is ready to fly again! nine0005
Tomorrow the rocket is ready to fly again! nine0005
Similarly, the games "Who will be on the mysterious island faster?"
"Chain"
Write on a board or poster.
I give the task:
- find the last number if the first number is 18, 24;
- find the first number if the last is 16, 72.
"Mathematical Dominoes"
Each student receives a card. It is divided into 2 parts: in the first part, an example for multiplication or division is written, in the second part, the answer to another task. The first student reads his example. The one who has a card with the answer to the sounded task calls this answer and says a new example. The next student answers and names his task, etc. nine0005
Math Lotto
All students take one card. I have 24 of them. The results of the multiplication table are written on them (4 answers each). I show the class a card with an expression, for example 5x3, and the guys on their cards cover the answers with circles. The winner is the one who closes all the numbers on his card first. Students make chips at a labor training lesson.
The winner is the one who closes all the numbers on his card first. Students make chips at a labor training lesson.
"Find a Pair"
3 students from each row come to the board in turn. Task: write down the numbers in the boxes to get the correct equalities. nine0005
9×4 = ? +?
42 : 6 = ? —?
76 - 44 = ? X ?
27 + 27 = ? X ?
These are just some of the types of work in mathematics lessons that activate students' activity. When performing the tasks described above, the guys think, compare, analyze. And this contributes to a more solid and conscious assimilation of knowledge.
The children really like the game "I am a photographer", in which I show the children a strip with numbers, signs, and the students have to memorize them in 5 seconds and "take a picture" in a notebook. nine0005
Author: Galina Toropova
The Pedagogical Council is a community for those who teach and study . Professionals grow with us.











