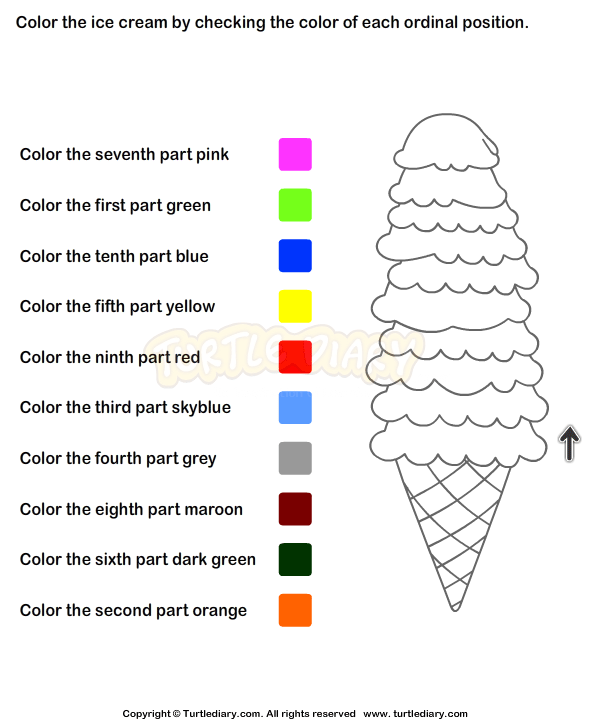
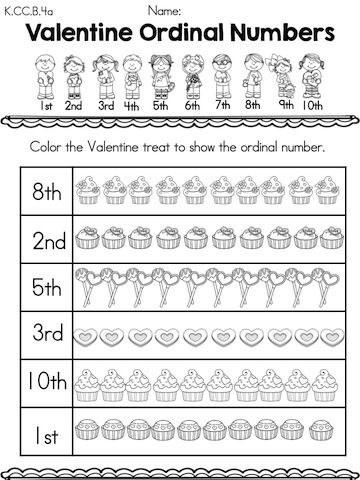
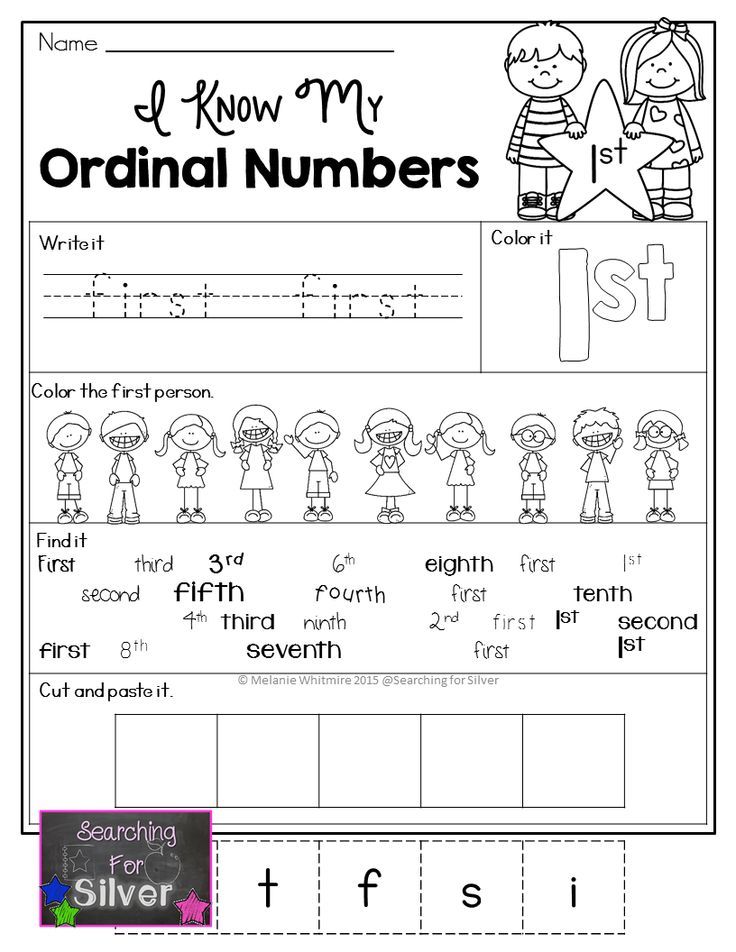
Preschool ordinal numbers
Definition And Activities For Kids
Learning mathematical skills is a vital part of early childhood development. And understanding ordinal numbers and how they work is part of building this competency.
Before we dive deeper into what ordinal numbers are and how you can assist your child with learning them, it’s important to know that we use them in our everyday lives.
This means your child has probably already come across this numerical concept, even though they may not know how to put it into words yet.
To help your young learner reach a stage where they fully comprehend and can use these numbers correctly, we’ve prepared five effective activities for you to try at home.
Let’s begin!
What Are Ordinal Numbers?
Ordinal numbers help us communicate the order of objects in a series. For example, first, second, third, and so on.
In theory, this sounds easy, but explaining it to children can be a little challenging. For instance, you can show a child the number “2,” and they may be able to understand what it means to have two of something (e. g., two eyes, two ears).
But when we talk about ordinal numbers, second (the ordinal number) is very different from two (the integer).
That’s because these numbers are not just about counting — they are more about things in relation to one another. And we have to look at a whole series or set for us to determine which object is first, second, third, etc.
The good news? Most children come across these types of numbers when watching a race or playing a game. They may be able to say:
Tommy came first.
Suzi was second.
Lorna was third.
Mike was last.
Children also spend a lot of time working with ordinal numbers in their early years at school because they connect with other critical mathematical concepts, such as sequencing and counting. So, helping your child understand them is part of a good foundation.
How Do You Write Them?
There are many different ways to write numbers, depending on what you are trying to show or solve. In the case of ordinal numbers, here are a few things to consider.
In the case of ordinal numbers, here are a few things to consider.
Let’s take a look at the first 10 ordinal numbers:
- First (1st)
- Second (2nd)
- Third (3rd)
- Fourth (4th)
- Fifth (5th)
- Sixth (6th)
- Seventh (7th)
- Eighth (8th)
- Ninth (9th)
- Tenth (10th)
From the above list, you can see that we write ordinal numbers by using the last two letters of the word. For example, fifth = 5th.
When looking at compound numbers, we apply the following:
- Numbers ending with 1: Only add “st” (e.g., twenty-first = 21st, thirty-first = 31st)
- Numbers ending with 2: Only add “nd” (e.g., twenty-second = 22nd, thirty-second = 32nd)
- Numbers ending with 3: o/Only add “rd” (e.g., twenty-third = 23rd, thirty-third = 33rd)
- Numbers ending with 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, or 0: Only add “th” (e.g., twenty-fourth = 24th, thirty-fifth = 35th)
Some people add “ly” at the end of an ordinal number when it’s written out (e. g., firstly, secondly, thirdly, etc.). However, when dealing with larger numbers (from 9th upwards), it’s best to avoid the “ly” altogether.
g., firstly, secondly, thirdly, etc.). However, when dealing with larger numbers (from 9th upwards), it’s best to avoid the “ly” altogether.
Ordinal Vs. Cardinal Numbers
We can’t look at ordinal numbers without also identifying what cardinal numbers are and how they relate.
In a nutshell, cardinal numbers tell us how many there are of something. For example, you have two ears. We also use these numbers for counting. Ordinal numbers, on the other hand, tell us the order of things in a set. For example, Timothy is second in the line.
Distinguishing between these two concepts can sometimes be tricky, especially for young learners. For instance, they might say, “The number three question was so easy,” instead of, “The third question was so easy.”
Activities are a great way to help our children identify the differences between these two concepts. With that in mind, here’s our list of five fun and effective games you can play with your child at home!
5 Activities To Learn Ordinal Numbers For Kids
1) Toy Lineup
What You’ll Need:
- Index cards
- Marker
- Any toys of your choice
What To Do:
The simplest way to introduce ordinal numbers to children is by placing some of their favorite toys in a line.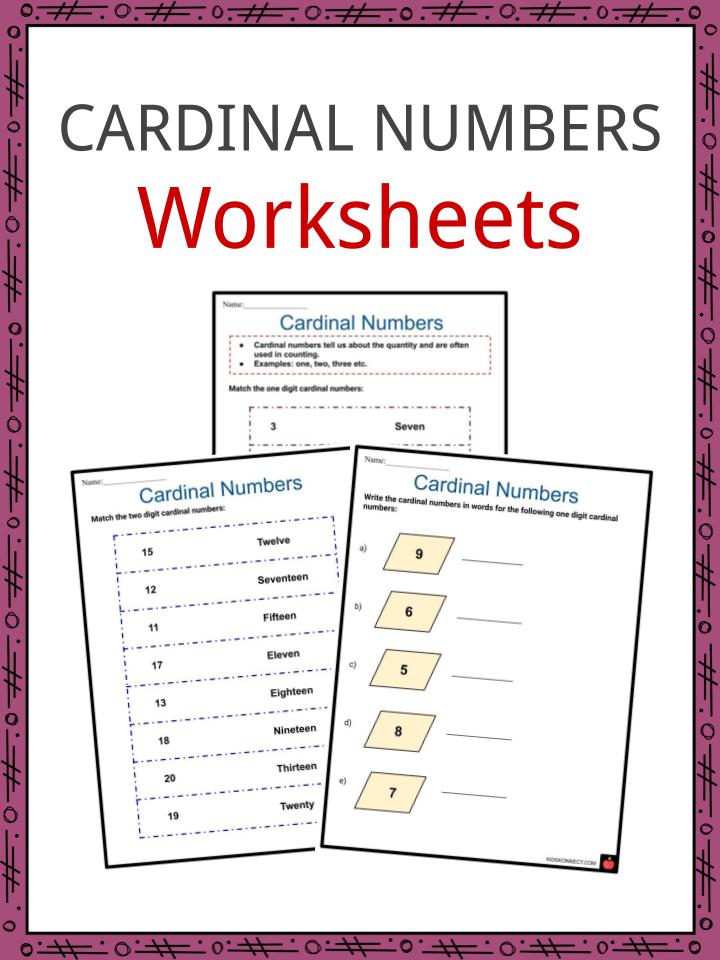
For this activity, you can use anything — dolls, toy cars, trains, legos — basically, anything you have an abundance of. After placing these items in a line, write ordinal numbers on your index cards (one number on each card).
To start playing, hand your child the index cards. Then, have them match the correct number card with each toy. For example, if they point at the fourth toy, they need to show you the card labeled “4th.”
You can start with just three to five items and, as they improve their skills, increase the line to 10 items or more.
This is a great way for children to get comfortable with what ordinal numbers look like in their numerical form.
2) Change The Lineup
What You’ll Need:
- Index cards
- Marker
- Any toy of your choice
What To Do:
As the name suggests, this activity is all about changing the positions of your lined-up objects. You can use the same toys you used in the previous game.
Start with changing the position of one object.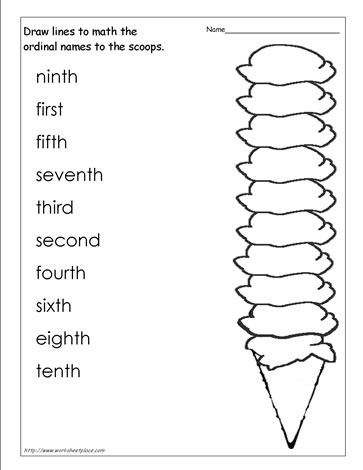 For example, move one item from the third to the last spot. Then, ask your child:
For example, move one item from the third to the last spot. Then, ask your child:
Which toy is third in line now?
Which toy is last in line now?
Continue moving just one object at a time, and encourage your child to re-evaluate their positions.
This game allows children to grasp that just one change is enough to influence the whole series. It also encourages them to think beyond memorization. As you switch things up, they’ll have to focus on which object is now the first, second, third, and so on.
3) Story Plot Map
What You’ll Need:
- A sheet of paper
- Marker
What To Do:
To begin, draw four boxes on your sheet of paper and label them with ordinal numbers (1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th). Next, tell a story in parts. For example, it might look something like this:
First, a girl named Emily wanted to get a cat.
Second, she went to a store and found the cutest little kitty.
Third, she asked her parents to get the cat.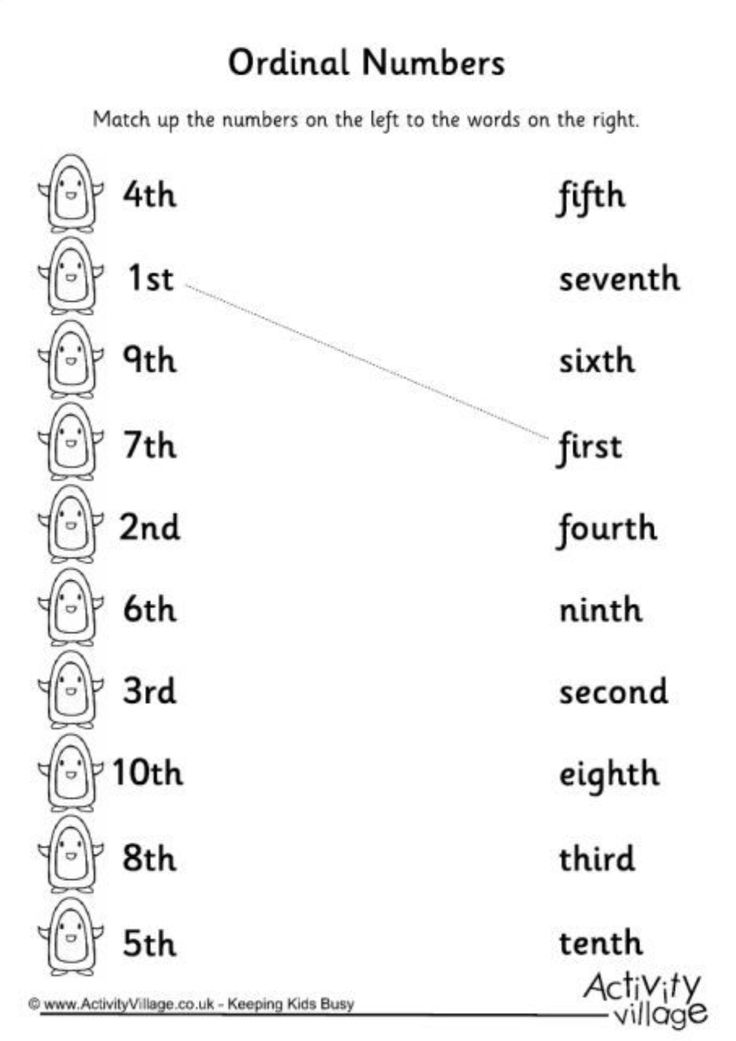
Fourth, they told her…
You can also write (or help your child write) what happens in each box as you tell the story. (So, “First, a girl named Emily wanted to get a cat” would go in the box labeled “1st”).
Point to each box as you tell that part of the story to give a visual representation of the events and emphasize the ordinal numbers (e.g., first, second, and so on).
Your story can take any direction you wish, and you can also encourage your child to give their input on what happens next.
One challenge with this game is ending the story on the last box. If there are four boxes, for example, then the fourth has to end it all. We recommend beginning by modeling all four boxes yourself first.
After that, your child thinks of box one, you get box two, they get box three, and you conclude the story for box four. After trying this a few times, let your child try the fourth box.
4) Color The Rainbow
What You’ll Need:
- White sheet of paper
- Pencil
- Crayons
What To Do:
Start by drawing eight lines in the shape of a rainbow on your sheet of paper. Then, hand the paper to your child. To play, have them listen to and follow directions as you tell them which stripe to color in.
Then, hand the paper to your child. To play, have them listen to and follow directions as you tell them which stripe to color in.
For example:
Color the third stripe green.
Color the fifth stripe orange.
Continue giving instructions until the rainbow has all of its seven colors.
Don’t be surprised if your child has to count each time they color in a stripe. This is all part of practicing and learning as they go, and this activity reinforces that ordinal numbers are about looking at the order of a whole set.
5) Wrong Order
What You’ll Need:
- Index cards
- Marker
What To Do:
Start by writing 1st-10th down on your index cards (one number on each card). Then, shuffle the cards and line them up in the wrong order. Very simply, the object of the game is for your child to place the cards in the correct order.
They might need a little help in the beginning, but as they get more comfortable, you can add a timer to keep things interesting: Let’s see if you can line these up in their correct order in under 30 seconds!
This is a great activity for children to practice identifying ordinal numbers in their numerical form (1st, 2nd, 3rd, etc. ).
).
Ordinal Numbers Are Not So Ordinary!
While we may use the concept and language of ordinal numbers every day, there’s nothing ordinary about them.
And as you can now see, helping children learn to correctly identify these numbers is crucial because they form part of other important concepts, such as sequencing. The above activities allow your child to work on and solidify their knowledge of ordinal numbers with you at home.
In addition, our Wacky Slide game from the HOMER Learn & Grow app is specially designed to help reinforce the fundamentals of understanding and working with ordinal numbers.
By using these activities — and with lots of time and practice — your young learner will be an ordinal number pro in no time!
Author
10 Free Ways to Teach This Skill
This post contains affiliate links. If you click & make a purchase, I receive a commission at no additional cost to you! Thanks! As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. Read my full disclosure here.
Read my full disclosure here.
Ordinal numbers are a concept that we use every single day. So, obviously, we need to make sure that our kids understand what they are and what they mean. But, you may be thinking, “It’s been a few years since I was in school, and I can’t remember what the heck an ordinal number is!”
Well, don’t worry because I’m going to tell you what they are, and I’m going to share 10 ordinal numbers activities to help you teach this skill across all the different subjects!
What are Ordinal Numbers?
Ordinal numbers are simply “a thing’s position in a series.” (As in, first, second, third, so on and so forth.) That’s it!! Yet, understanding what they are in your mind and knowing how to explain ordinal numbers to kids are entirely different.
You can say, “one” and show a child one object. That’s pretty straightforward.
However, ordinal numbers are relational and a completely abstract concept to little kids.
What I mean is that the relationship between the positions of 2 different objects is the foundation of ordinal numbers. In other words, you have to have a second to have a first.
In other words, you have to have a second to have a first.
That’s why you need engaging activities and ordinal number exercises that provide a solid foundation! But, don’t think you have to learn all sorts of new information. It’s very likely that you’re already doing some and don’t even realize it.
So, let’s get to it!
Ordinal Numbers Activities
1. Line It Up
One of the first and easiest ordinal number activities for preschool is lining objects up in a row. My favorite thing about this activity is that you can use anything of which you have an abundance. (So, at our house, we would use LEGOs because we own about 10,000 LEGO bricks.)
You can use stuffed animals, cars, trains, or any other objects that interest your kiddos. Start out with 3-5 objects and my free printable ordinal number cards. Let your kiddos point to the object and match the correct number card. It’s that easy!!
As a classroom teacher, you can extend this lesson by having your students line up. However, there is a trick to this. Make sure to take a picture of everyone in the line, and then show the image to the class. Otherwise, everyone will be stepping out of line to see the first person, Jimmy won’t be able to see around Susie, and pushing will ensue. Trust me, classroom management will be a nightmare.
However, there is a trick to this. Make sure to take a picture of everyone in the line, and then show the image to the class. Otherwise, everyone will be stepping out of line to see the first person, Jimmy won’t be able to see around Susie, and pushing will ensue. Trust me, classroom management will be a nightmare.
Print out several sets of the image and ordinal number cards. Then have your students work together to match the student and the position. (Joey is first. Cindy is second.)
2. Days of the Week
Another one of my favorite ordinal number activities is using the days of the week. If you do any sort of calendar time, you may already be teaching them without even knowing it! You probably say something along the lines of, “Sunday is the first day of the week. Monday is the second day of the week.”
If not, just start doing this daily. You’ll be amazed at how the consistent practice helps. If you want visuals to go along with the sentences, I have a free “Days of the Week” printable you can use with your ordinal number cards.
See how easy this is? You can do it!
3. Months of the Year
This is another quick way to practice ordinal numbers on a day-to-day basis. When you are discussing the current month, use my free printable months of the year pages to show the position of each month.
Just print out the months and point to the current month. Let’s say we are in the month of March, point to March and say, “This is March. It is the third month of the year.” Then you can write 3rd beside March. Continue this same cycle of sentences and discussion until you have talked about every month and practiced the concepts of first through twelfth.
4. Sequencing
Remember, teaching ordinal numbers doesn’t have to be super-complex. By simply talking about consistent, sequential daily activities, you are teaching ordinal numbers. Think about it like this. What are the events that kids do every day? First, wake up. Second, put on your clothes. Third, put your pajamas away. Fourth, eat breakfast.
See? You don’t need an expensive set of sequencing cards. You can either draw pictures or let your child draw them. Just have your kids put the pictures in order and match the ordinal number cards to them! Easy peasy.
5. Following Recipes
Following recipes is another one of my favorite ordinal number activities. Obviously, you need to use your judgment on the intricacy of the recipe, but for young children let them make something like pudding.
Go ahead and have all of the tools out for them. Then allow them to complete the steps as independently as they can. For those just learning the concept of ordinal numbers, let them complete 3 steps. “First, pour in the pudding mix. Second, pour in 2 cups of milk. Third, stir it all together.”
For older kids, let them give you a running commentary on every step. “First I get out my bowl. Second, I get out the pudding mix and milk. Third, I pour the pudding mix into the bowl.”
To extend this activity, you can allow them to video themselves and then write the sequence into their own written recipe. Think about what a fun family activity this would be! Your kids could make an entire cookbook and then give them to family members as Christmas gifts.
Think about what a fun family activity this would be! Your kids could make an entire cookbook and then give them to family members as Christmas gifts.
By the way, I recently found a recipe that I had written when I was in second grade, and it should have been a foreshadowing to my future issues with cooking. I was able to explain (in detail) how to cook “spasketty” in 3 steps. It was hilarious! Obviously, my understanding of cooking and ordinal numbers wasn’t really vast.
6. ABC Order
This is a great way to combine reading and math! You can either make your own alphabet flashcards with index cards and a sharpie or get a pack of simple alphabet flashcards. Then let your littles match the first 12 letters of the alphabet with the appropriate ordinal number. You can mix them up to make it more challenging for your more advanced learners.
To add another level of difficulty, have your kids write their spelling words or vocabulary words and cut them out. Then have them mix the words up and put the words into alphabetical order while matching the correct ordinal number. This is another one of my favorite ordinal number activities!
This is another one of my favorite ordinal number activities!
7. Sports
If you have a child that loves sports, then get them thinking about how each sport makes use of ordinal numbers. Here are two examples…
- Football-1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th downs: 1st-4th quarters: rankings of the favored teams in the NFL
- Baseball-1st, 2nd, 3rd base: 1st-8th innings: rankings of the favored MLB teams
This is extremely useful when you get the dreaded “When am I ever going to use this skill in real life?” Well, now they know!!
8. Competition
Because I’ve taught boys, and am raising two boys of my own, I am keenly aware of how much they love competition. They can make a competition out of literally ANYTHING.
So, take advantage of this and let them compete in any category they want. Then have them give out the prizes to the appropriate winner. (Depending on how many participants, you may be able to give out all 12 of the ordinal number tags.)
Any time you can make learning into a game, you have a winning combination.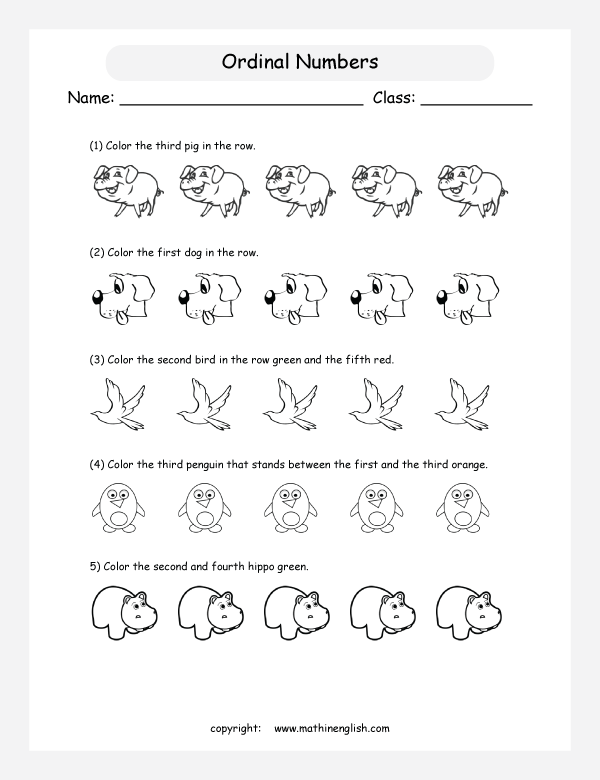
9. Order of Events
If you have older kids, they will be required to understand and create timelines. So, this is the perfect opportunity to incorporate math into history!
There is a distinct relationship between historical events and ordinal numbers, and this is a great time to get kids thinking about that fact. Have them write out several significant events from history, mix them up, and then ask them to put the events into order.
To challenge your kiddos even more, ask them to explain the cause and effect relationship between the events. This gets them thinking more deeply about “why” the events happened in that specific order.
10. Paragraph Structure
We all know the importance of good writing, but sometimes we don’t really know what that looks like at different levels. Honestly, it can be pretty tricky, but one thing that is necessary to good writing is the use of ordinal numbers! (I bet you knew I was going to say that.)
Think of it like this, if you want your kids to be able to have a coherent piece of writing, they need to include a sequence of events or a distinct order to their paragraphs.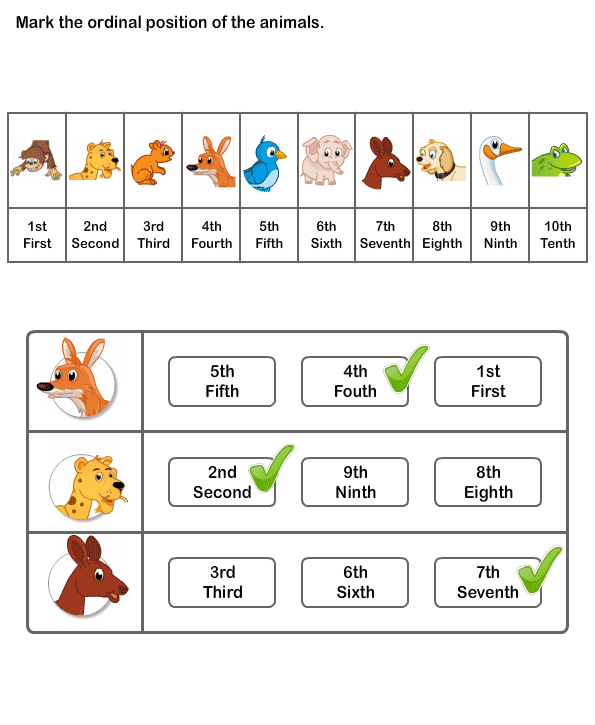 So, you teach them how to write sentences and put those sentences into order. “First, the man gave the dog a bone. Second, the dog dug a hole to hide the bone.”
So, you teach them how to write sentences and put those sentences into order. “First, the man gave the dog a bone. Second, the dog dug a hole to hide the bone.”
Then when they’ve mastered that skill, you apply this same technique to creating paragraphs and essays!
So, there you have it!
Ten activities for teaching ordinal numbers in all content areas, and all of them are completely FREE!! Was it easier than you thought it was going to be? Do you think you can use some of these simple ideas?
Teaching counting to preschool children :: 0
Evseeva Irina Vladislavovna - teacher-defectologist
Teaching counting to preschool children
The formation of quantitative ideas is an important stage in the development of a preschool child. To successfully master the skills of counting, children need the help of adults.
Parents should use every opportunity to ask a child the question, "How much?" For example: “How many plates are on the table?”, “Bring 5 spoons”, “How many spoons did you bring? Why did you bring 5 spoons?”, “How many cars are in the parking lot?” etc. Please note that it is necessary to count not only sets arranged in a row, but also those where the elements are located, for example, in a circle or in the form of another figure, or generally asymmetric. It is necessary to explain to the child that the location of objects does not affect the result of the count, but it is very important not to miss a single element.
Please note that it is necessary to count not only sets arranged in a row, but also those where the elements are located, for example, in a circle or in the form of another figure, or generally asymmetric. It is necessary to explain to the child that the location of objects does not affect the result of the count, but it is very important not to miss a single element.
Before a child is aware of the relationship between numbers, he must learn to compare adjacent sets, groups of objects that differ from each other by one. At first, each group of objects or drawings should be placed in a row. Then the two compared sets will be arranged in two rows. Each element of the second set will be strictly under the corresponding element of the first. The child first lays out the first set, for example, five cubes in a row, at some distance from each other and counts them. Recounting objects is the simplest means by which you can find out how consciously the child uses the numeral. After the child has counted the cubes, invite him to put a typewriter under each cube and count. For example, there were four cars. Ask the child to compare which objects are larger (less), cubes or cars. The child should answer like this: “There are more cubes than cars, because there are five of them, and there are four cars” or “There are fewer cars than cubes, because there are 4 of them, and there are 5 cubes. The number 4 is less than the number 5.
For example, there were four cars. Ask the child to compare which objects are larger (less), cubes or cars. The child should answer like this: “There are more cubes than cars, because there are five of them, and there are four cars” or “There are fewer cars than cubes, because there are 4 of them, and there are 5 cubes. The number 4 is less than the number 5.
Exercises for comparing adjacent sets lead the child to understand the basic principle of constructing a natural series of numbers, where each subsequent number is greater than the previous one by one, and vice versa, each previous one is less than the next by one.
Play with your child the game "Name the number more (less) by one." The adult shows the picture to the child, and the child counts the objects on it and calls the number one more (less) than the result of the count.
Another game "Name it soon". At the beginning of the game, they agree on the condition: to name the numbers one more. An adult throws a ball to a child and calls a number. The child catches the ball and, throwing it back, calls the number one more. The game is played at a fast pace. Another option for the task: name the number 1 less.
The child catches the ball and, throwing it back, calls the number one more. The game is played at a fast pace. Another option for the task: name the number 1 less.
Many children do not distinguish between ordinal and cardinal numbers, do not realize their meaning. The child should have an idea of the cases in which people use the ordinal account. The kid needs to explain that the questions "which?", "What is the number?" require special recalculation. In this case, each item receives its number in the row, and to answer the question "in which place" or "which one?" the direction of the account is essential. When determining the serial number, it is customary to count from left to right, and in other cases - to indicate in which direction the count was kept.
Please note that often children find it difficult to agree on numerals with nouns. Select masculine and feminine objects for counting, for example, color images of an apple, plum and pineapple, and show how, depending on which objects are counted, the words one, two, and so on change. One apple, one plum, one pineapple. Two apples, two plums, two pineapples, and so on. Very often, children replace the numeral one with the word times. When the child begins to count: "One, two, three," stop him, pick up, for example, a ball and ask: "How many balls?" "One ball," the child replies. - "That's right, one ball. You can't say "one ball". And you need to count like this: one, two ...".
One apple, one plum, one pineapple. Two apples, two plums, two pineapples, and so on. Very often, children replace the numeral one with the word times. When the child begins to count: "One, two, three," stop him, pick up, for example, a ball and ask: "How many balls?" "One ball," the child replies. - "That's right, one ball. You can't say "one ball". And you need to count like this: one, two ...".
Introduction to numbers
In order for the assimilation of numbers to be not mechanical, but conscious, it is necessary to introduce the child to them after he has formed an idea of \u200b\u200bthe relationship between number and quantity. Invite the child to put, for example, a cube on the table and ask: how many cubes are on the table? The number of items is indicated by a sign. This sign is called "number". The number "one" denotes the number of items - one cube. Next, you can show the child the number 1, offer to color it. In the same way, you can introduce the child to other numbers.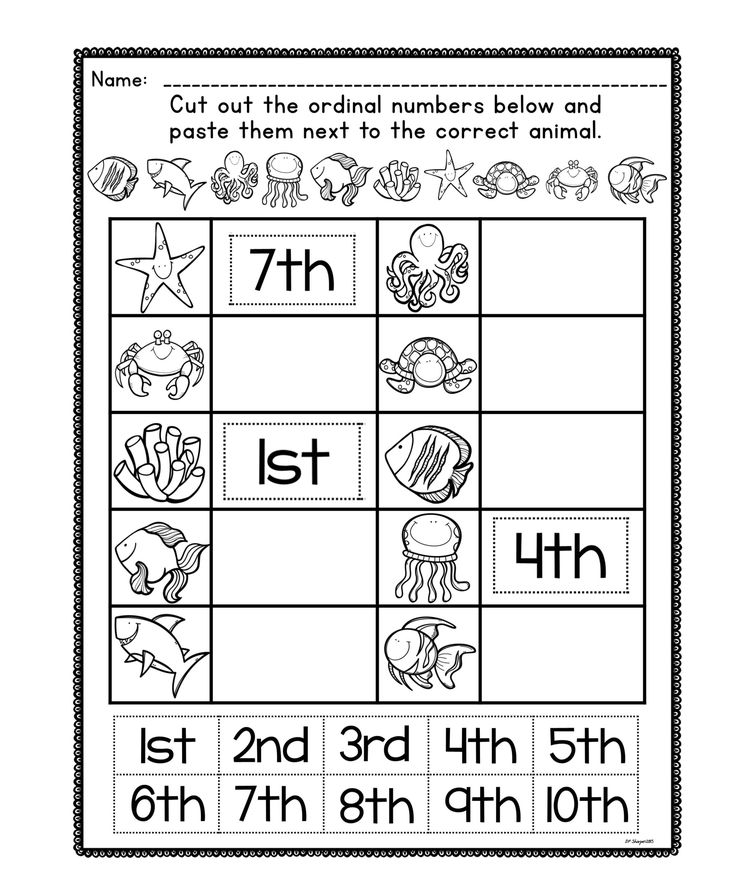 Before introducing the child to the number 0, invite the child to count, for example, candies in a box (4 pieces), and then treat them to their relatives: one candy for mom, another for dad, a third for grandma, a fourth for grandpa. There was nothing left in the box. This can be written as a number. On the letter "nothing" is denoted by the number 0. Zero is placed very first on the left in a series of other numbers.
Before introducing the child to the number 0, invite the child to count, for example, candies in a box (4 pieces), and then treat them to their relatives: one candy for mom, another for dad, a third for grandma, a fourth for grandpa. There was nothing left in the box. This can be written as a number. On the letter "nothing" is denoted by the number 0. Zero is placed very first on the left in a series of other numbers.
To fix the numbers, various exercises are used:
-
swipe, pencil,
-
shading contour numbers,
-
sculpting numbers,
-
laying out with sticks, sand, pebbles, etc.,
-
reading literary works
Play with your child the game "Put the numbers in order!". First, the child is offered cards with drawn dots (number cards) and they need to be arranged in order (from 1 to 10 or within a number familiar to the child, for example, from 1 to 6). The child is then given numbers and asked to arrange them under the appropriate number card. This game can be repeated several times as the child learns new numbers and the numbers they represent. Thus, the child will gradually learn the number series not formally, but based on visual material.
The child is then given numbers and asked to arrange them under the appropriate number card. This game can be repeated several times as the child learns new numbers and the numbers they represent. Thus, the child will gradually learn the number series not formally, but based on visual material.
Literature:
Mathematics for preschoolers: Book. For a kindergarten teacher / T.I. Erofeeva and others - M., 1997
Shcherbakova E.I. About mathematics for kids, 1984
Back to section
Documents - Government of Russia
Site search optionsClose
Next news
Previous news
- Small font size
- Normal font size
- Large font size
- Enable/disable image display On Off
Government of Russia
-
- Demographics
- Health
- Education
- Culture
- Society
- State
-
- Employment and labor
- Technological development
- Economics.
 Regulation
Regulation - Finance
- Social Services
-
- Ecology
- Housing and cities
- Transport and communications
- Energy
- Industry
- Agriculture
-
- Regional development
- Far East
- Russia and the world
- Security
- Law and Justice
- Selected documents with references to them
- Search across all documents
Type of document
Decree of the Government of the Russian FederationOrder of the Government of the Russian FederationOrder of the President of the Russian FederationDecree of the President of the Russian FederationFederal lawFederal constitutional lawCode
Number
Title or text of the document
Signing date
October 29, Saturday
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 29, 2022 No.
 1932
1932 On amendments to the Instruction on the procedure for admitting officials and citizens of the Russian Federation to state secrets
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 29, 2022 No. 1930
On Amendments to Appendix No. 3 to the Rules of the Wholesale Electricity and Power Market
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 29, 2022 No. 1926
On amendments to the annex to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 7, 2014 No. 778
778
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 29.10.2022 No. 1927
On approval of the Rules for providing a grant in the form of a subsidy from the federal budget to the autonomous non-profit organization "Directorate of Sports and Social Projects" in order to financially support activities related to the preparation and holding of the "Games of the Future" project in the Russian Federation in 2024
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 29, 2022 No.
 1925
1925 On Amendments to the Regulations on the Federal State Land Control (Supervision) and the Regulations on the Federal State Veterinary Control (Supervision)
October 28, Friday
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 28, 2022 No. 1917
On Amendments to Certain Acts of the Government of the Russian Federation
October 26, Wednesday
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 26, 2022 No.
 1899
1899 On submitting for ratification the Agreement between the Government of the Russian Federation and the Government of the Republic of India on measures for the protection of technologies in connection with cooperation in the field of exploration and use of outer space for peaceful purposes and in the creation and operation of launch vehicles and ground-based space infrastructure
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 26, 2022 No. 1901
On the introduction of amendments to certain acts of the Government of the Russian Federation on the powers of federal executive authorities in the electric power industry and the invalidation of subparagraph "a" of paragraph 1 of the changes that are made to the acts of the Government of the Russian Federation on ensuring the readiness of employees to perform labor functions in the electric power industry and the field of heat supply and certification on safety issues, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 28, 2022 No. 768
768
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 26, 2022 No. 1900
On Amendments to the Regulations on the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 26, 2022 No. 1907
On amendments to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated September 1, 2005 No. 549
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 26, 2022 No.
 1909
1909 On approval of the Rules for the provision in 2022 of another interbudgetary transfer from the federal budget to the budget of the Saratov region, the source of financial support for which is the budgetary allocations of the reserve fund of the Government of the Russian Federation, in order to reimburse the expenses of the budget of the Saratov region made in 2021 for the implementation of capital investments in the capital construction object "State Health Institution "Saratov City Polyclinic No. 20", Saratov (construction of a polyclinic for 500 beds in the village of Yubileiny in the Volzhsky district of Saratov)"
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 26, 2022 No.
 1911
1911 On amendments to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of September 15, 2017 No. 1104
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 26, 2022 No. 1910
On amendments to the Basic Provisions for the Formation and State Regulation of Gas Prices, Tariffs for Gas Transportation Services, Payments for Technological Connection of Gas-Using Equipment to Gas Distribution Networks in the Russian Federation and Payments for Technological Connection to Main Gas Pipelines of Gas Pipelines Under Construction and Reconstruction Designed for Transportation gas from main gas pipelines to capital construction facilities, and gas pipelines designed to transport gas from natural gas fields to the main gas pipeline
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 26, 2022 No.
 1906
1906 On amendments to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 24, 2015 No. 390
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 26, 2022 No. 1904
On making changes to the list of types of objects, the placement of which can be carried out on lands or land plots that are in state or municipal ownership, without the provision of land plots and the establishment of servitudes
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 26, 2022 No.
 1905
1905 On amendments to the Rules for granting subsidies from the federal budget to a management company that manages the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation, as well as territories of advanced socio-economic development in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation that are part of the Far Eastern Federal District, the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation and the free port of Vladivostok , and subsidies from the federal budget to the management company, which performs the functions of managing territories of advanced socio-economic development and state support for entrepreneurial activity in the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 26, 2022 No.
 1912
1912 On Amendments to Certain Acts of the Government of the Russian Federation
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 26, 2022 No. 1908
On Amendments to Certain Acts of the Government of the Russian Federation
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 26, 2022 No. 1902
On amendments to the Rules for the provision in 2022 of another interbudgetary transfer from the federal budget to the budget of the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania in order to co-finance the expenditure obligations of the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania arising from the implementation of measures to upgrade the tram fleet
Tuesday October 25
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 25, 2022 No.