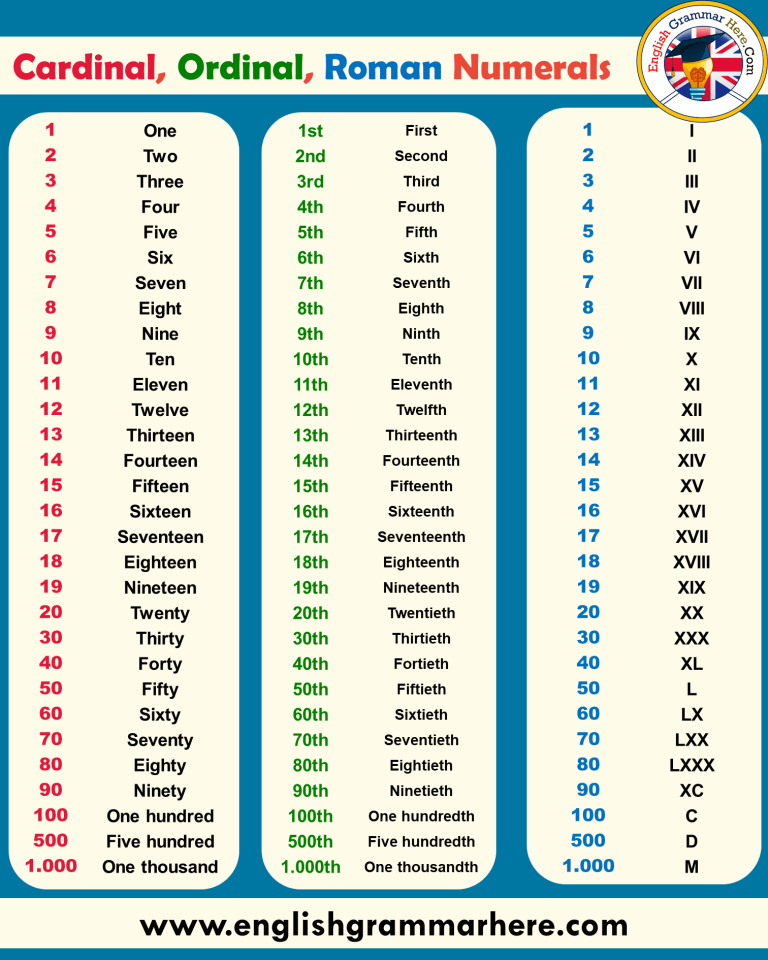
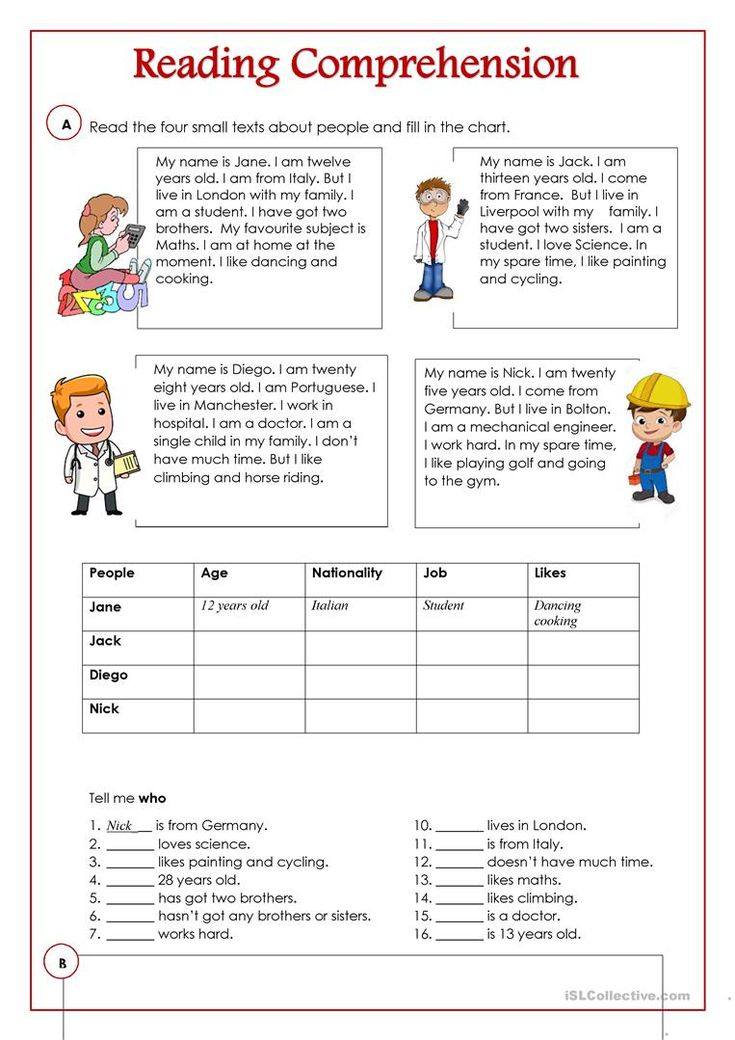
Reading activity for beginners
Beginners Reading Comprehension - GrammarBank
Read the passages and choose the correct options according to the readings.
One of my favorite vacation places is Mexico. I really like the weather there because it never gets cold. The people are very nice too. They never laugh at my bad Spanish. The food is really good. Mexico City is a very interesting place to visit. It has some great museums and lots of fascinating old buildings. The hotels are too expensive to stay but there are more affordable options. For example, you can stay at one of the beach resorts like Acapulco. If you are planning to visit Mexico, you should definitely see the Mayan temples near Merida.
1.Sam likes warm weather
Sam doesn't like warm weather at all
Sam hates warm water
Sam likes cold weather
2.
His Spanish is very goodHe speaks Spanish very well
He is Spanish
He doesn't speak Spanish very well
3.
There's a lot to see and do in MexicoThere aren't a lof of beautiful places in Mexico
Mexico is a dirty place
Tourists never come to Mexico
4.
The hotels aren't comfortable there
Hotels are all poor in Mexico
The hotels in Mexico are pretty expensive
Last summer, we decided to spend our vacation at the beach because the weather was very hot in the mountains. The travel agent said that traveling by bus was the cheapest way, but we went by plane because it was faster. We wanted to have more time to spend at the beach. The weather was beautiful and we had a great time.
5. We decided to go to the beach because ----.it was cheaper than going to the mountains
the travel agent said that it was the cheapest
of the hot weather in the mountains
we wanted to spend time at the beach
best
easiest
cheapest
slowest
more fun
cheaper
expensive
faster
hated
didn't like
enjoyed
regretted

good
freezing
terrible
cold
Correct answers:
You are here: >> Home >> Beginners ESL Reading >> Reading Comprehension Test - Beginners
Print exercises and lessons:Hint: For exercises, you can reveal the answers first ("Submit Worksheet") and print the page to have the exercise and the answers. Print This Page
↑▲▲▲▲▲▲▲↑
- Home
Grammar
- PDF eBooks
- Grammar Lessons
- Grammar Exercises
- Grammar Quizzes
- Mixed Tests
- PDF Worksheets
Beginners ESL
- Beginners Lessons
- Easy Worksheets
- Beginners Tests
- Reading Exercises
- Drag & Drop Grammar
For Kids
- English For Kids
- Kids Word Games
- Picture Vocabulary
Reading Skills
- Reading Tests
- Short Dialogues
- Short Sentences
- Closest in Meaning
- Irrelevant Sentence
- ESL Paragraphs
Major Exams
- GRE Reading
- Text Completion
- GRE Equivalence
- SAT Sentence
- TOEFL
Writing & Vocab
- Essay Writing
- Vocabulary Exercises
- Study Skills Tips
- Drag & Drop Vocab
25 Activities for Reading and Writing Fun
These activities have been developed by national reading experts for you to use with children, ages birth to Grade 6. The activities are meant to be used in addition to reading with children every day.
The activities are meant to be used in addition to reading with children every day.
In using these activities, your main goal will be to develop great enthusiasm in the reader for reading and writing. You are the child's cheerleader. It is less important for the reader to get every word exactly right. It is more important for the child to learn to love reading itself. If the reader finishes one book and asks for another, you know you are succeeding! If your reader writes even once a week and comes back for more, you know you have accomplished your beginning goals.
Activities for birth to preschool: the early years
Activity 1: Books and babies
Babies love to listen to the human voice. What better way than through reading!
What you'll need:
Some books written especially for babies (books made of cardboard or cloth with flaps to lift and holes to peek through).
What to do:
- Start out by singing lullabies and folk songs to your baby.
 When your baby is about six months old, choose books with brightly colored, simple pictures and lots of rhythm in the text. (Mother Goose rhymes are perfect.) Hold your baby in your lap so he/she can see the colorful pages of the book. Include books that show pictures and names of familiar objects.
When your baby is about six months old, choose books with brightly colored, simple pictures and lots of rhythm in the text. (Mother Goose rhymes are perfect.) Hold your baby in your lap so he/she can see the colorful pages of the book. Include books that show pictures and names of familiar objects. - As you read with your baby, point out objects in the pictures and make sure your baby sees all the things that are fun to do with books. (Pat the Bunny by Dorothy Kunhardt is a classic touch-and-feel book for babies.)
- Vary the tone of your voice with different characters in the stories, sing nursery rhymes, make funny faces, do whatever special effects you can to stimulate your baby's interest.
- Allow your child to touch and hold cloth and sturdy cardboard books.
- When reading to a baby, keep the sessions brief but read daily and often.
As you read to your baby, your child is forming an association between books and what is most loved – your voice and closeness.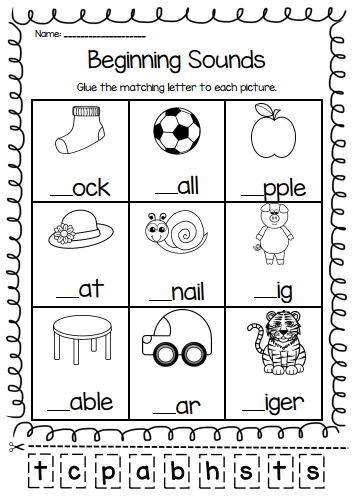 Allowing babies to handle books deepens their attachment even more.
Allowing babies to handle books deepens their attachment even more.
Activity 2: Tot talk
What's "old hat" to you can be new and exciting to toddlers and preschoolers. When you talk about everyday experiences, you help children connect their world to language and enable them to go beyond that world to new ideas.
What you'll need:
Yourself and your child
What to do:
- As you get dinner ready, talk to your child about things that are happening. When your 2- or 3-year-old "helps" by taking out all the pots and pans, talk about them. "Which one is the biggest?" "Can you find a lid for that one?" "What color is this one?"
- When walking down the street and your toddler or preschooler stops to collect leaves, stop and ask questions that require more than a "yes" or "no" answer. "Which leaves are the same?" "Which leaves are different?" "What else grows on trees?"
- Ask "what if" questions. "What would happen if we didn't shovel the snow?" "What if that butterfly lands on your nose?"
- Answer your child's endless "why" questions patiently.
 When you say, "I don't know, let's look it up," you show how important books are as resources for answering questions.
When you say, "I don't know, let's look it up," you show how important books are as resources for answering questions. - After your child tells you a story, ask questions so you can understand better. That way children learn how to tell complete stories and know you are interested in what they have to say.
- Expose your child to varied experiences – trips to the library, museum, or zoo; walks in the park; or visits with friends and relatives. Surround these events with lots of comments, questions, and answers.
Talking enables children to expand their vocabulary and understanding of the world. The ability to carry on a conversation is important for reading development. Remember, it is better to talk too much rather than too little with a small child.
Activity 3: R and R – repetition and rhyme
Repetition makes books predictable, and young readers love knowing what comes next.
What you'll need:
- Books with repeated phrases (Favorites are: Alexander and the Terrible, Horrible, No Good, Very Bad Day by Judith Viorst; Brown Bear, Brown Bear, What Do You See? by Bill Martin, Jr.
 ; Horton Hatches the Egg by Dr. Seuss; and The Little Engine That Could by Watty Piper.
; Horton Hatches the Egg by Dr. Seuss; and The Little Engine That Could by Watty Piper. - Short rhyming poems.
What to do:
- Pick a story with repeated phrases or a poem you and your child like. For example, read:
(Wolf voice:) "Little pig, little pig, let me come in."
(Little pig:) "Not by the hair on my chinny-chin-chin."
(Wolf voice:) "Then I'll huff and I'll puff and I'll blow your house in!" - After the wolf has blown down the first pig's house, your child will soon join in with the refrain.
- Read slowly, and with a smile or a nod, let your child know you appreciate his or her participation.
- As the child grows more familiar with the story, pause and give him or her a chance to fill in the blanks and phrases.
- Encourage your child to pretend to read, especially books that contain repetition and rhyme. Most children who enjoy reading will eventually memorize all or parts of a book and imitate your reading.
 This is a normal part of reading development.
This is a normal part of reading development.
When children anticipate what's coming next in a story or poem, they have a sense of mastery over books. When children feel power, they have the courage to try. Pretending to read is an important step in the process of learning to read.
Activity 4: Poetry in motion
When children "act out" a good poem, they learn to love its rhyme, rhythm, and the pictures it paints with a few well-chosen words. They grow as readers by connecting feelings with the written word.
What you'll need:
Poems that rhyme, tell a story, and/or are written from a child's point of view.
What to do:
- Read a poem slowly to your child, and bring all your dramatic talents to the reading. (In other words, "ham it up.")
- If there is a poem your child is particularly fond of, suggest acting out a favorite line. Be sure to award such efforts with delighted enthusiasm.
- Suggest acting out a verse, a stanza, or the entire poem.
 Ask your child to make a face the way the character in the poem is feeling. Remember that facial expressions bring emotion into the performer's voice.
Ask your child to make a face the way the character in the poem is feeling. Remember that facial expressions bring emotion into the performer's voice. - Be an enthusiastic audience for your child. Applause is always nice.
- If your child is comfortable with the idea, look for a larger setting with an attentive, appreciative audience. Perhaps an after-dinner "recital" for family members would appeal to your child.
- Mistakes are a fact of life, so ignore them.
Poems are often short with lots of white space on the page. This makes them manageable for new readers and helps to build their confidence.
Activity 5: Story talk
Talking about what you read is another way to help children develop language and thinking skills. You won't need to plan the talk, discuss every story, or expect an answer.
What you'll need:
Storybooks
What to do:
- Read slowly and pause occasionally to think aloud about a story. You can say: "I wonder what's going to happen next!" Or ask a question: "Do you know what a palace is?" Or point out: "Look where the little mouse is now.
 "
" - Answer your children's questions, and if you think they don't understand something, stop and ask them. Don't worry if you break into the flow of a story to make something clear. But keep the story flowing as smooth as possible.
- Talking about stories they read helps children develop their vocabularies, link stories to everyday life, and use what they know about the world to make sense out of stories.
Activity 6: Now hear this
Children are great mimics. When you tell stories, your child will begin to tell stories, too.
What you'll need:
Your imagination
What to do:
- Have your child tell stories like those you have told. Ask: "And then what happened?" to urge the story along.
- Listen closely when your child speaks. Be enthusiastic and responsive. Give your child full attention.
- If you don't understand some part of the story, take the time to get your child to explain. This will help your child understand the relationship between a speaker and a listener and an author and a reader.

- Encourage your child to express himself or herself. This will help your child develop a richer vocabulary. It can also help with pronouncing words clearly.
Having a good audience is very helpful for a child to improve language skills, as well as confidence in speaking. Parents can be the best audience a child will ever have.
Activity 7: TV
Television can be a great tool for education. The keys to successful TV viewing are setting limits, making good choices, taking time to watch together, discussing what you view, and encouraging follow-up reading.
What you'll need:
A weekly TV schedule
What to do:
- Limit your child's TV viewing and make your rules and reasons clear. Involve your child in choosing which programs to watch. Read the TV schedule together to choose.
- Monitor what your child is watching, and whenever possible, watch the programs with your child.
- When you watch programs with your child, discuss what you have seen so your child can better understand the programs.

- Look for programs that will stimulate your child's interests and encourage reading (such as dramatizations of children's literature and programs on wildlife and science.)
Many experts recommend that children watch no more than 10 hours of TV each week. Limiting TV viewing frees up time for reading and writing activities.
It is worth noting that captioned TV shows can be especially helpful for children who are deaf or hard-of-hearing, studying English as a second language, or having difficulty learning to read.
Activities for preschool to grade two: moving into reading
Check out Reading Rockets' new summer website, Start with a Book. You'll find a treasure trove of themed children's books, parent–child activities, and other great resources for summer learning.
Activity 8: World of words
Here are a few ways to create a home rich in words.
What you'll need:
- Paper
- Pencils, crayons, markers
- Glue
- Newspapers, magazines
- Safety scissors
What to do:
- Hang posters of the alphabet on the bedroom walls or make an alphabet poster with your child.
 Print the letters in large type. Capital letters are usually easier for young children to learn first.
Print the letters in large type. Capital letters are usually easier for young children to learn first. - Label the things in your child's pictures. If your child draws a picture of a house, label it with "This is a house." and put it on the refrigerator.
- Have your child watch you write when you make a shopping list or a "what to do" list. Say the words aloud and carefully print each letter.
- Let your child make lists, too. Help your child form the letters and spell the words.
- Look at newspapers and magazines with your child. Find an interesting picture and show it to your child as you read the caption aloud.
- Create a scrapbook. Cut out pictures of people and places and label them.
- By exposing your child to words and letters often, your child will begin to recognize the shapes of letters. The world of words will become friendly.
Activity 9: Write on
Writing helps a child become a better reader, and reading helps a child become a better writer.
What you'll need:
- Pencils, crayons, or markers
- Paper or notebook
- Chalkboard and chalk
What to do:
- Ask your child to dictate a story to you. It could include descriptions of your outings and activities, along with mementos such as fall leaves and flowers, birthday cards, and photographs. Older children can do these activities on their own.
- Use a chalkboard or a family message board as an exciting way to involve children in writing with a purpose.
- Keep supplies of paper, pencils, markers, and the like within easy reach.
- Encourage beginning and developing writers to keep journals and write stories. Ask questions that will help children organize the stories, and respond to their questions about letters and spelling. Suggest they share the activity with a smaller brother, sister, or friend.
- Respond to the content of children's writing, and don't be overly concerned with misspellings. Over time you can help your child concentrate on learning to spell correctly.

- When children begin to write, they run the risk of criticism, and it takes courage to continue. Our job as parents is to help children find the courage. We can do it by expressing our appreciation of their efforts.
Activity 10: Look for books
The main thing is to find books you both love. They will shape your child's first impression of the world of reading.
What you'll need:
Good books
What to do:
- Ask friends, neighbors, and teachers to share the titles of their favorite books.
- Visit your local public library, and as early as possible, get your child a library card. Ask the librarian for help in selecting books. Have your child join you in browsing for books and making selections.
- Look for award-winning books. Each year the American Library Association selects children's books for the Caldecott Medal for illustrations and the Newbery Medal for writing.
- Check the book review section of the newspapers and magazines for the recommended new children's books.

- If you and your child don't enjoy reading a particular book, put it aside and pick up another one.
- Keep in mind that your child's reading level and listening level are different. When you read easy books, beginning readers will soon be reading along with you. When you read more advanced books, you instill a love of stories, and you build the motivation that transforms children into lifelong readers.
Activity 11: Read to me
It's important to read to your child, but equally important to listen to them read to you. Children thrive on having someone appreciate their developing skills.
What you'll need:
Books at your child's reading level
What to do:
- Listen carefully as your child reads.
- Take turns. You read a paragraph and have your child read the next one or you read half the page and your child reads the other half. As your child becomes more at ease with reading aloud, take turns reading a full page. Keep in mind that your child may be focusing more on how to read the words than what they mean, and your reading helps to keep the story alive.

- If your child has trouble reading words, you can help him or her in several ways:
- Ask the child to skip over the word, read the rest of the sentence, and then say what would make sense in the story for the missing word.
- Guide the child to use what he or she knows about letter sounds.
- Supply the correct word.
- Tell your child how proud you are of his or her efforts and skills.
Listening to your child read aloud provides opportunities for you to express appreciation of his or her new skills and for them to practice their reading. Most importantly, this is another way to enjoy reading together.
Activity 12: Family stories
Family stories enrich the relationship between parent and child.
What you'll need:
Time set aside for talking with your child.
What to do:
- Tell your child stories about your parents and grandparents. You might even put these stories in a book and add old family photographs.

- Have your child tell you stories about what happened on special days, such as holidays, birthdays, and family vacations.
- Reminisce about when you were little. Describe things that happened at school involving teachers and subjects you were studying. Talk about your brothers, sisters, or friends.
- Write a trip journal with your child to create a new family story. Recording the day's events and pasting the photographs into the journal ties the family story to a written record. You can include everyday trips like going to the market or the park.
- It helps for children to know that stories come from real people and are about real events. When children listen to stories, they hear the voice of the storyteller. This helps them hear the words when they learn to read aloud or read silently.
Activity 13: P.S. I love you
Something important happens when children receive and write letters. They realize that the printed word has a purpose.
What you'll need:
- Paper
- Pencil, crayon, or marker
What to do:
Language is speaking listening, reading, and writing. Each element supports and enriches the others. Sending letters will help children become better writers, and writing will make them better readers.
Activities for grades 3–6: encouraging the young reader
Activity 14: Good books make reading fun
Stories for young children should be of all kinds – folktales, funny tales, exciting tales, tales of the wondrous and stories that tell of everyday things.
What you'll need:
A variety of interesting books
What to do:
- An essential step in learning to read is good books read aloud. Parents who read aloud to their children are teaching literacy concepts simply by sharing books. Encourage your children to listen, ponder, make comments, and ask questions.
- Be flexible enough to quickly abandon a book that does not appeal after a reasonable try at reading it.
 No one is meant to enjoy every book. And no one, especially a child, should be forced to read or listen to books that bore.
No one is meant to enjoy every book. And no one, especially a child, should be forced to read or listen to books that bore. - Even after children have outgrown picture books they still enjoy hearing a story read aloud. Hearing a good story read well, especially if it is just a little beyond a child's own capabilities, is an excellent way to encourage independent reading. Not all books are best read aloud; some are better enjoyed silently.
- There are plenty of children's books that are twice as satisfying when they are shared a chapter at a time before bed or during long car rides. There are some books that children should not miss, books that they will want to hear many times and ultimately read for themselves.
- Young children want to read what makes them laugh or cry, shiver and gasp. They must have stories and poems that reflect what they themselves have felt. They need the thrill of imagining, of being for a time in some character's shoes for a spine-tingling adventure.
 They want to experience the delight and amazement that comes with hearing playful language. For children, reading must be equated with enjoying, imagining, wondering, and reacting with feeling. If not, we should not be surprised if they refuse to read. So let your child sometime choose the story or book that they want you to read to them.
They want to experience the delight and amazement that comes with hearing playful language. For children, reading must be equated with enjoying, imagining, wondering, and reacting with feeling. If not, we should not be surprised if they refuse to read. So let your child sometime choose the story or book that they want you to read to them.
Give your child many opportunities to read and write stories, lists, messages, letters, notes, and postcards to relatives and friends. Since the skills for reading and writing reinforce one another, your child's skills and proficiency in reading and writing will be strengthened if you help your child connect reading to writing and writing to reading.
Activity 15: Artful artists
Children love to be creative when it comes to drawing, and illustrations add visual imagery to stories.
What you'll need:
- Drawing paper
- Pens and pencils
- Magic markers or crayons
What to do:
Find a fable, fairy tale, or other short story for your child to read. Then ask your child to illustrate a part of the story he or she likes best or describe a favorite character. Have the child dictate or write a few sentences that tell about this picture.
Then ask your child to illustrate a part of the story he or she likes best or describe a favorite character. Have the child dictate or write a few sentences that tell about this picture.
Activity 16: Shopping your way with words
Use your weekly shopping trip as an opportunity to help your child develop reading and writing skills.
What you'll need:
- Paper and pencils
- Newspaper ads
- Supermarket coupons
What to do:
As you make out your grocery shopping list, give your child a sheet of paper and read the items to him or her. If the child asks for spelling help, write the words correctly for him or her to copy or spell the words aloud as your child writes them.
Ask your child to look through the newspaper ads to find the prices of as many items as possible. Your child can write these prices on the list and then look through your coupons to select the ones you can use. Take your child to the supermarket and ask him or her to read each item to you as you shop.
Activity 17: Cookbooking
Cooking is always a delight for children, especially when they can eat the results!
What you'll need:
- Easy-to-read recipes
- Cooking utensils
- Paper and pencils
What to do:
Show your child a recipe and go over it together. Ask your child to read the recipe to you as you work, and tell the child that each step must be done in a special order. Let your child help mix the ingredients. Allow your child to write down other recipes from the cookbook that he or she would like to help make.
Activity 18: Dictionary words
A dictionary is a valuable learning tool, especially if your child makes up his or her own booklet of words that are challenging.
What you'll need:
- Paper and pencils
- A stapler
- Old magazines
- Newspaper and supplements
What to do:
Encourage your child to make a dictionary by putting together several sheets of paper for a booklet. Ask your child to write at the top of each page a new word he or she has recently learned. If the word can be shown in a picture, have him or her look through magazines and newspapers to find pictures that illustrate the words and paste them on the correct pages.
Ask your child to write at the top of each page a new word he or she has recently learned. If the word can be shown in a picture, have him or her look through magazines and newspapers to find pictures that illustrate the words and paste them on the correct pages.
Have your child write the meaning of each word and a sentence using each new word. Your child can then use some or all of these sentences as the basis for a creative story. Have your child read this story to you and other family members.
Activity 19: Journals
Keeping a journal is a way for your child to write down daily events and record his or her thoughts.
What you'll need:
Two notebooks - one for your child and one for you!
What to do:
Help your child start a journal. Say what it is and discuss topics that can be written about, such as making a new friend, an interesting school or home activity just completed, or how your child felt on the first day of school. Encourage your child to come up with other ideas. Keep a journal yourself and compare notes at the end of the week. You and your child each can read aloud parts of your journals that you want to share.
Keep a journal yourself and compare notes at the end of the week. You and your child each can read aloud parts of your journals that you want to share.
Activity 20: Greetings and salutations
Everyone loves to get mail, especially when the card has been personally designed.
What you'll need:
- Paper and pencils
- Crayons and magic markers
- Stamps and envelopes
What to do:
Ask your child to list the birthdays of family members, relatives, and friends. Show your child some store-bought birthday cards with funny, serious, or thought-provoking messages. Your child can then create his or her own birthday card by using a folded piece of paper, making an attractive cover, and writing a short verse inside. Then your child can mail the cards to friends and relatives for their birthdays.
Activity 21: Giving the gift of reading
Reading a book is more fun when you have a homemade bookmark to mark your spot.
What you'll need:
- Pieces of lightweight cardboard
- Pens and pencils
- Paper
- Crayons and magic markers
What to do:
Provide your child with a piece of cardboard about 6" long and 2" wide. On one side of the bookmark, have your child draw a picture of a scene from a book he or she has read. On the other side, ask your child to write the name of the book, its author, publisher, publication date, and a few sentences about the book. After making several of these bookmarks, you might ask the child to send them to friends and relatives as gifts accompanied by a short note.
On one side of the bookmark, have your child draw a picture of a scene from a book he or she has read. On the other side, ask your child to write the name of the book, its author, publisher, publication date, and a few sentences about the book. After making several of these bookmarks, you might ask the child to send them to friends and relatives as gifts accompanied by a short note.
Activity 22: Let your fingers do the walking
The telephone book contains a wealth of information and is a good tool for reading and writing.
What you'll need:
- A telephone book, including the yellow pages
- Paper and pencils
What to do:
Have your child look through the yellow pages of the telephone directory, select a particular service, and write a clever or funny ad for it. Have your child read this ad to you. Help your child to find your own or a friend's listing in the white pages of the telephone book. Explain the different entries (for example, last name and address), along with the abbreviations commonly used.
Activity 23: Map your way to success
Children love to read road maps and this activity actually helps them with geography.
What you'll need:
- A road map or atlas
- Paper and pencil
- Stamps and envelopes
What to do:
When planning a vacation, let your child see the road map and help you plan where you will drive. Talk about where you will start and where you will end up. Let your child follow the route between these two points. Encourage your child to write to the Chamber of Commerce for brochures about places you will see on your trip.
Activity 24: What's in the news?
Newspapers are a form of daily communication with the outside world, and provide lots of learning activities for children.
What you'll need:
- Newspapers
- Scissors
- Colored pencils
What to do:
- Clip out an interesting news story and cut the paragraphs apart. Ask your child to read the paragraphs and put them in order.

- Ask your child to read a short editorial printed in your local newspaper and to underline all the facts with a green pencil and all the opinions with an orange pencil.
- Pictures fascinate children of all ages. Clip pictures in the newspaper. Ask your child to tell you about the picture or list adjectives to describe the picture.
- Do you take your child to the movies? Have your child first look up the movie page by using the index in the newspaper. After a movie has been chosen, have your child study the picture or text in the ad and tell you what he or she thinks the movie is about.
- Have your child pick a headline and turn it into a question. Then the child can read the article to see if the question is answered.
- Ask your child to clip food coupons from the newspaper for your grocery shopping trips. First, talk about which products you use and which you do not. Then the child can cut out the right coupons and putt hem into categories such as drinks and breakfast items.
 You can then cash in the coupons at the store.
You can then cash in the coupons at the store. - Pick out an interesting article from the newspaper. As you are preparing lunch or dinner, tell your child that you are busy and ask him or her to read the article to you.
- Many newspapers publish materials especially written for children, such as the syndicated "Mini Page," "Pennywhistle Press," and "Dynamite Kids." In addition, some newspapers publish weekly columns for children, as well as tabloids and summer supplements written by educators.
Activity 25: Using television to stimulate reading
What child doesn't enjoy watching TV? Capitalize on this form of entertainment and use TV to help rather than hinder your child's learning.
Some important ideas to consider before turning on the TV: Limit in some way the amount of TV your child watches so as to leave time for reading and other activities. Decide how much time should be set aside for watching TV each day.
Serve as an example by limiting the amount of TV you yourself watch. Have time when the TV set is off and the entire family reads something. You may want to watch TV only for special shows. Before the TV set is turned on, encourage your child to select the programs he or she wishes to watch. Ask your child to give you the reason for the choices made.
Have time when the TV set is off and the entire family reads something. You may want to watch TV only for special shows. Before the TV set is turned on, encourage your child to select the programs he or she wishes to watch. Ask your child to give you the reason for the choices made.
In addition, watch some of the same TV programs your child watches. This helps you as a parent share in some of your child's daily activities.
What you'll need:
- A TV
- A TV selection guide
- Colored highlighters
- A calendar page for each month
- Paper and pencils
What to do:
- Ask your child to tell you about favorite TV characters using different kinds of words.
- As your child watches commercials on television, ask him or her to invent a product and write slogans or an ad for it.
- Encourage your child to watch such programs as Reading Rainbow. Urge older children to watch such programs as 60 Minutes and selected documentaries.
 These programs are informative. Discuss interesting ideas covered in the programs and direct your child to maps, encyclopedias, fiction, or popular children's magazines for more information.
These programs are informative. Discuss interesting ideas covered in the programs and direct your child to maps, encyclopedias, fiction, or popular children's magazines for more information. - Have your child name 10 of his or her favorite shows. Ask your child to put them into categories according to the type of show they are, such as family shows, cartoons, situation comedies, sports, science fiction, or news and information. If you find the selection is not varied enough, you might suggest a few others that would broaden experiences.
- Prepare a monthly calendar with symbols such as a picture of the sun to represent an outdoor activity or a picture of a book to represent reading. Each time your child engages in a daily free time activity, encourage him or her to paste a symbol on the correct calendar date. This will give you an idea of how your child spends his or her free time. It also encourages a varied schedule.
- Ask each child in your family to pick a different color.
 Using the TV listing, have each child use this color to circle one TV program that he or she wants to watch each day. Alternate who gets first choice. This serves two purposes. It limits the amount of time watching TV and it encourages discriminating viewing.
Using the TV listing, have each child use this color to circle one TV program that he or she wants to watch each day. Alternate who gets first choice. This serves two purposes. It limits the amount of time watching TV and it encourages discriminating viewing. - Devise a rating scale from 1 to 5. Ask your child to give a number to a certain TV program and to explain why such a rating was given.
- Have your child keep a weekly TV log and write down five unfamiliar words heard or seen each week. Encourage your child to look up the meanings of these words in the dictionary or talk about them with you.
20 reading texts for children aged 5-6-7-8
A child who has learned to put sounds into syllables, syllables into words, and words into sentences needs to improve his reading skills through systematic training. But reading is a rather laborious and monotonous activity, and many children lose interest in it. Therefore, we offer texts of small size , the words in them are divided into syllables.
First read the work to the child yourself, and if it is long, you can read its beginning. This will interest the child. Then invite him to read the text. After each work, questions are given that help the child to understand what they have read and comprehend the basic information that they have learned from the text. After discussing the text, suggest reading it again.
Mo-lo-dets Vo-va
Ma-ma and Vo-va gu-la-li.
In-va ran-sting and fell.
It hurts no-ha, but Vo-va does not cry.
Wow!
B. Korsunskaya
Answer questions .
1. What happened to Vova?
2. What made him sick?
3. Why is Vova doing well?
Clever Bo-beak
Co-nya and co-ba-ka Bo-beak gu-la-li.
So-nya played-ra-la with a doll.
That's why So-nya in-be-zha-la to-my, and the doll for-would-la.
Bo-beek found a doll-lu and brought it to So-ne.
B. Korsunskaya
Answer the questions.
1. Who did Sonya walk with?
2. Where did Sonya leave the doll?
3. Who brought the doll home?
The bird made a nest on a bush. De-ti our nest-up and took off on the ground.
- Look, Vasya, three birds!
In the morning, deti came, and the nest was empty. It would be a pity.
L. Tolstoy
Answer questions.
1. What did the children do with the nest?
2. Why was the nest empty in the morning?
3. Did the children do well? How would you do?
4. Do you think this work is a fairy tale, a story or a poem?
Pete and Mi-sha had a horse. They began to argue: whose horse. Did they tear each other apart.
- Give me - my horse.
- No, you give me - the horse is not yours, but mine.
Mother came, took a horse, and became nobody's horse.
L. Tolstoy
Tolstoy
Answer the questions.
1. Why did Petya and Misha quarrel?
2. What did mother do?
3. Did the children play horse well? Why do you think so
?
9000 9000
9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000
015
9 9000 9000
FILVORDA for the development of reading, View here.
It will be interesting for children to read selected texts, they affect the emotional world of the child, develop his moral feelings and imagination . Children will get acquainted with the works of L. Tolstoy, K. Ushinsky, A. Barto, S. Mikhalkov, E. Blaginina, V. Bianchi, E. Charushin, A. Usachyov, E. Uspensky, G. Snegiryov, G. Oster, R. Rozhdestvensky, as well as fairy tales of different nations.
Blaginina, V. Bianchi, E. Charushin, A. Usachyov, E. Uspensky, G. Snegiryov, G. Oster, R. Rozhdestvensky, as well as fairy tales of different nations.
It is advisable to show children the genre features of poems, stories and fairy tales using the example of these works.
Fairy tale is a genre of oral fiction containing events unusual in the everyday sense (fantastic, wonderful or worldly) and distinguished by a special compositional and stylistic construction. In fairy tales there are fairy-tale characters, talking animals, unprecedented miracles happen.
Poem is a short poetic work in verse. The verses are read smoothly and musically, they have rhythm, meter and rhyme.
Story — small literary form; a narrative work of small volume with a small number of characters and the short duration of the events depicted. The story describes a case from life, some bright event that really happened or could happen.
In order not to discourage reading, do not force him to read texts that are uninteresting and inaccessible to his understanding. It happens that a child takes a book he knows and reads it “by heart”. Mandatory every day read to your child poems, fairy tales, stories.
Daily reading enhances emotionality, develops culture, horizons and intellect, helps to cognize human experience.
Literature:
Koldina D.N. I read on my own. - M .: TC Sphere, 2011. - 32 p. (Candy).
TOP 14 Best Books 📗 in English for Beginners
Why is it important to read books in English
When we read, our brain works hard. Even the shortest, medium-sized article in the native language is a good warm-up for the human brain prone to idleness, accustomed to shirking and pretending to be busy.
And reading books in English is no longer just a warm-up for the brain, but a real strength training with a bench press and the rest attached. In addition to the fact that reading itself increases memory capacity, develops communication skills and imagination, reading books in English is useful for the following reasons:
In addition to the fact that reading itself increases memory capacity, develops communication skills and imagination, reading books in English is useful for the following reasons:
Vocabulary increases. Cramming foreign words is not a very effective exercise. But when we memorize words in context, we are more likely that at the right moment that very phrase or expression will pop up in our head. The more English words you see, the better - something will surely be remembered. How to do this simply and fun, we will tell a little later.
The passive vocabulary is activated. The set of phrases that you use constantly and remember which is not difficult for you is your active vocabulary. Reading will help bring the passive reserve into working condition - these are the phrases, words, expressions that gather dust on the mezzanines of your RAM. Thus, your speech will become more diverse, and the list of possible topics for conversation will expand significantly.
Writing skills develop. When we read, our visual memory turns on. It is she who is responsible for spelling - you remember how the English word is spelled correctly and automatically repeat it in the same form in writing.
Grammar is being pumped. For beginners to learn English, tenses and passive constructions of the language may not be given as much as you like, but once you start reading, you will not leave them a chance. Your brain "reads" grammatical structures from the text, and you absorb them more naturally.
Pronunciation improves. Pronunciation is often neglected. All forces are thrown at grammar and vocabulary, and the pronunciation remains “from rush visa lave”. It would be nice to take care of that right away. Reading English literature aloud will give you confidence in speaking. There are many books for beginners with additional audio materials on sale: after listening to the recording, try to repeat the intonation and nuances of pronunciation. Before you have time to look back, you will speak no worse than any "native".
Before you have time to look back, you will speak no worse than any "native".
Increased self-esteem. There is no feeling that can be compared to when you finish reading your first book in English. Pride in yourself and understanding that much in the world is inaccessible without knowing English can become a strong motivation from the first to the last page.
English proficiency test
This English proficiency test was compiled by the Skysmart online school tutors. They prepared interesting and relevant tasks on modern topics to make the test both useful and interesting
How to read in English: life hacks
To keep the interest in reading in English at the very beginning, follow a few simple recommendations. These simple rules will help you make the reading process easier and more efficient.
1. The most important step is choosing the right book. Remember, a simple book does not mean at all - uninteresting. Here it is important to honestly assess your level and choose the appropriate book. It is better if the first book is as simple and understandable as possible - do not take up Ulysses right away, it is better that at the very beginning it was more interesting than difficult for you. Choose adapted literature for beginners - such books are specially published for those who begin to learn the language. They come with a translation, a dictionary and, sometimes, audio materials. Great book choice for first time readers!
Remember, a simple book does not mean at all - uninteresting. Here it is important to honestly assess your level and choose the appropriate book. It is better if the first book is as simple and understandable as possible - do not take up Ulysses right away, it is better that at the very beginning it was more interesting than difficult for you. Choose adapted literature for beginners - such books are specially published for those who begin to learn the language. They come with a translation, a dictionary and, sometimes, audio materials. Great book choice for first time readers!
2. Set a reading schedule. Who among us has not heard “better more often, but less than once a week, but two hours at once”? So, this really works. Read every day for 20 minutes - so you do not hate the book after the first hour and a half reading session, and the efficiency will only grow. Start a timer. At first, read strictly for no more than 20 minutes - this method will help you quickly move forward at your comfortable pace.
3. No dictionary. If you have chosen the right book, and it fully corresponds to your level of English, there should be no need for a dictionary. Effective reading begins when the meaning of unfamiliar words is guessed from the context. Guess, guess, err, go back and guess again. But. None. Dictionaries.
4. Write out phrases, not single words. Memorize the whole phrase from the sentence, not individual words. From now on, context is your best friend.
5. Retell. This ancient practice goes back to the Druids and turns Elementary into Intermediate faster than an American can say a Russian tongue twister. After every 20 minutes of reading, summarize everything with a retelling.
6. Reinforce with listening. If the text is not only read, but also listened to, you will achieve maximum efficiency from the process. Get as much out of the book as possible.
Get as much out of the book as possible.
New material is easier to learn when there is constant practice. Come to English language courses for teenagers and consolidate your knowledge in practice!
How many English words do you already know?
Let's define your vocabulary - without complex questions and with the help of smart algorithms.
List of the best books to read in English
You can read not only fiction. Reading articles, magazine columns, newspapers, and even user manuals is also helpful and effective. But for those who are just starting to learn English, it is better to opt for fiction.
Even if you are not a reader in principle, it will not be difficult for you to find a book for beginners that will be of any interest to you. The choice among fiction is great and inexhaustible: children's fairy tales, fantasy, detective stories, bestsellers, immortal classics, biographies, memoirs.
You need to progress in reading according to the level of the language: the higher the level, the more difficult the book. Start with an easy, adapted book, and when you feel ready to move on to more difficult books, choose from a variety of options according to your interests.
The variety of genres at the middle level is slightly higher than at the previous one. However, all the rules for effective reading at this level remain the same. The advanced level assumes that you are already "on you" with the chosen book, and you have access to the world of great literature.
Of course, there are a lot of rules and recommendations, but here's the most important thing: remember that reading is the most enjoyable and exciting way to learn a language. Don't treat books like hard work. Read with pleasure.
Free English lessons with a native speaker
Practice 15 minutes a day. Learn English grammar and vocabulary. Make language a part of life.
Level of difficulty for beginners
For beginners, there are many interesting books in English. Here are four books that you will definitely be interested in reading.
1. Anne of Green Gables by Lucy Maud Montgomery. "Anne of Green Gables", Lucy Maud Montgomery.
A novel by a Canadian writer about Ann "with two n": a red-haired girl adopted by a single brother and sister who live on a farm. Touching, exciting, full of funny and exciting moments, a book about love, honor, growing up, friendship. In total, three novels have been written about different periods of Anya's life: from the most tender childhood to blossoming maturity. By the way, Netflix released the series "Ann" based on the novel - it will be great to read the book first, and then watch the film adaptation.
Source: Anne of Green Gables
2. Tracey Beaker's Diary by Jacqueline Wilson. "Starring Tracy Beaker", Jacqueline Wilson.
"Starring Tracy Beaker", Jacqueline Wilson.
Perhaps all the books of this writer deserve to be read. She writes about English teenagers, their problems, family relationships. Not only a child, but also any adult will find it useful and interesting to read Wilson with her sharp humor, sharp phrases and really related topics.
For a language beginner, Jacqueline Wilson's books are just a gift. Easy language, an abundance of colloquial phrases, idioms and a plot that you can't tear yourself away from. Tracey Beaker's diary is Jacqueline's star book. The quintessence of humor and unique author's style. By the way, based on Tracy Beaker, a series was shot, the characters of which speak in simple language. Try to read first, and then get acquainted with the film adaptation.
Source: Tracy Beaker's Diary
3. No such list is complete without Lewis Carroll and his Alice in Wonderland.
Find an edition of the book adapted for language learning according to the method of Ilya Frank - this is a text divided into paragraphs, accompanied by a translation and a dictionary. Alice is on the must-read list. Therefore, if you have only seen the film adaptation with Johnny Depp so far, then be sure to read it - you definitely won’t be bored.
Alice is on the must-read list. Therefore, if you have only seen the film adaptation with Johnny Depp so far, then be sure to read it - you definitely won’t be bored.
Source: Alice in Wonderland
4. “Three in a boat, not counting the dog”, Jerome. K. Jerome.
“Three Men in a Boat (To Say Nothing of the Dog)”, Jerome Klapka Jerome. This book is studied in the first years of linguistic faculties and, in general, it is clear why - easy, funny and very useful for the language. You will spend the whole story on the water surface of the Thames, in a boat with the main characters. Read, watch film adaptations - there are at least two of them. At the same time, you will find out how many heroes are still in the boat.
Source: Three in a boat, not counting the dog
Demo lesson in English
Determine the level and set a goal, and then learn to speak English fluently.
Intermediate
For Pre-Intermediate and Intermediate, the choice of books in English is much wider than for beginners.
5. Catcher in the Rye by Jerome Salinger. “The catcher in the Rye”, J.D. Salinger.
A cult item. A poignant, gripping story of Holden Colfid, a child of a lost generation. A rebellious teenager who doesn't feel at home anywhere, drops out of another school and sets off to wander around winter New York.
Gets into adventures, shares his thoughts, makes the reader fall in love with himself, because each of us is a bit of Holden Caulfield. Even the classic translation of The Catcher in the Rye does not half convey the Salinger atmosphere of the novel. Reading a book in English is worth at least for this amazing sense of belonging.
Source: Catcher in the Rye
6. On the Road by Jack Kerouac. "On the road", Jack Kerouac.
Roman-journey, endless hitchhiking across the USA in the early 50s. Together with the main character, you race along Route 60 in California, spend the night under the starry sky of Colorado, meet fellow writers in New York. It seems that you are about to arrive somewhere, and the journey will end, but it still continues.
It seems that you are about to arrive somewhere, and the journey will end, but it still continues.
Source: On the Road
7. Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone, J. Rowling. “Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone”, Joanne Rowling.
That's really who does not need ideas and descriptions. Lucky for someone who has not yet read Harry Potter, and this whole amazing tale is ahead of him. And if you have already read Potter from cover to cover in Russian, feel free to proceed with the book in English. There is nothing better than immersing yourself in your favorite fantasy world again.
Source: Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone
8. Thirteen Reasons Why by Jay Asher. “Thirteen Reasons Why”, Jey Asher.
The cult Netflix series is based on this novel. A story that raises topical social problems in the life of adolescents around the world. Fascinating, exciting, sometimes creepy, a book after which everyone will find something to think about.
Fascinating, exciting, sometimes creepy, a book after which everyone will find something to think about.
Source: Thirteen Reasons Why
9. The Lord of the Rings trilogy by John Tolkien. "The Lord of the Rings", J. R. R. Tolkien. As in the case of Harry Potter - a great opportunity to get acquainted with the Tolkien universe for those who are not yet familiar with it. And devoted Tolkienists who have mastered English at the Intermediate level will be able to plunge into it again, but already in the “true” one - that is, the original version.
Source: The Lord of the Rings
10. The Devil Wears Prada by Lauren Weisberger.
“The Devil wears Prada”, L. Weisberger. It seems that everyone has seen the adaptation with Anne Hathaway and Meryl Streep. The book in English is full of modern vocabulary, interesting phrases, idioms and constructions that you will have to rack your brains over. After this book, you will have a wealth of language material that will come in handy in any conversation.
After this book, you will have a wealth of language material that will come in handy in any conversation.
Source: The Devil Wears Prada
11. Gone with the Wind by Margaret Mitchell. “Gone with the wind”, Margaret Mitchell.
Immortal classic, epic novel about war, love and friendship. It is read in one breath, both in translation and in the original. If you still haven't heard about the brave Scarlett O'Hara, who "will think about everything tomorrow", then rather start reading.
Source: Gone with the Wind
12. Classic detective stories can often be found in such lists. Not in vain The Adventures of Sherlock Holmes and Hercule Poirot. "Sherlock Holmes stories", Arthur Conan Doyle; "Hercule Poirot novels", Agatha Christie occupy a special place among adapted literature. In addition to the fact that you are probably already familiar with many plots, the simple style of presentation and the availability of a dictionary in adapted editions will add ease and pleasure.