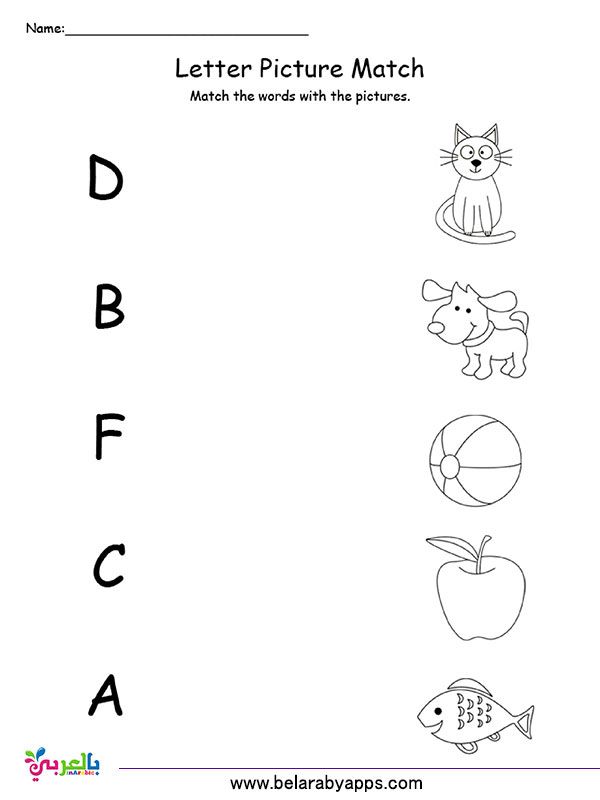
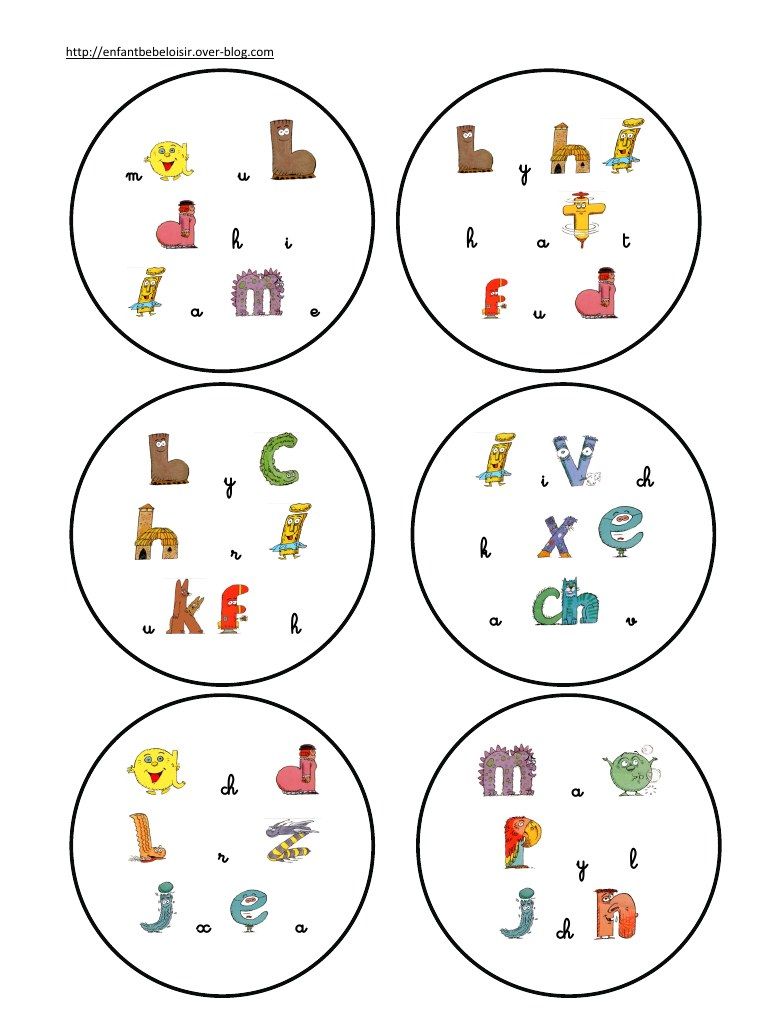
Reading words for preschoolers
The Basic Spelling Vocabulary List
By: Steve Graham, Karen R. Harris, Connie Loynachan
This list was created to help teachers know which spelling words should be taught to kids in grades 1–5. The list contains 850 words that account for 80 percent of the words children use in their writing — the ones they need to be able to spell correctly.
This list was devised to help educators know which spelling words should be taught to children. The list contains 850 words that account for 80 percent of the words children use in their writing — the ones they need to be able to spell correctly.
Mastering this relatively small corpus of words yields a high rate of return. For example, the most common 1,000 words are used 13 times more frequently than the next most common 1,000 words. It also provides teachers flexibility in planning spelling instruction, providing an opportunity to give children the "basics" while supplementing with other spelling words germane to classroom activities.
Grade level for each word was determined based upon difficulty, pattern of occurrence in children's writing across grades, and grade placement on current vocabulary lists and spelling materials.
Words that children have difficulty spelling correctly are marked with an asterisk.
Grade 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| a | fat | like* | sat
|
Back to Top
Grade 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| about* | father* | lives | set |
Back to Top
Grade 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| able | even | mind | spelling |
Back to Top
Grade 4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| across | during | mountain | sure* |
Back to Top
Grade 5 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| although | different* | planet | suddenly
|
Back to Top
Graham, S. , Harris, K.R. and Loynachan, C. (1993). The Basic Spelling Vocabulary List. Journal of Educational Research 86(6) 363-368.
, Harris, K.R. and Loynachan, C. (1993). The Basic Spelling Vocabulary List. Journal of Educational Research 86(6) 363-368.
Reprints
You are welcome to print copies for non-commercial use, or a limited number for educational purposes, as long as credit is given to Reading Rockets and the author(s). For commercial use, please contact the author or publisher listed.
Related Topics
Early Literacy Development
Spelling and Word Study
Vocabulary
Writing
New and Popular
Print-to-Speech and Speech-to-Print: Mapping Early Literacy
100 Children’s Authors and Illustrators Everyone Should Know
A New Model for Teaching High-Frequency Words
7 Great Ways to Encourage Your Child's Writing
Screening, Diagnosing, and Progress Monitoring for Fluency: The Details
Phonemic Activities for the Preschool or Elementary Classroom
Our Literacy Blogs
Shared Reading in the Structured Literacy Era
Kids and educational media
Meet Ali Kamanda and Jorge Redmond, authors of Black Boy, Black Boy: Celebrating the Power of You
Get Widget |
Subscribe
Vocabulary: Activities for Your Pre-K Child
Talking to and reading with your pre-K child are two terrific ways to help them hear new words. Conversations and questions about interesting words are easy ways to get new words into everyday talk.
Conversations and questions about interesting words are easy ways to get new words into everyday talk.
Even very young children love to hear and learn new words! Help your child expand their word bank and knowledge of the world by using interesting and vivid words instead of simpler language in your everyday conversations. For example, instead of saying, "this pizza is good" you might say, "this pepperoni pizza tastes spicy."
Reading aloud exposes your child to lots of vivid language that is not found in books for beginning readers. When you come upon a new and interesting word, take the time to stop and ask your child what they think that word might mean in the context of the story. Then offer a kid-friendly definition of the word and connect it to a similar word and a shared experience.
Word learning and vocabulary growth takes time and patience. Don't expect your child to learn a new word after one conversation or one read aloud. True word learning happens after being exposed to words several times. We all learn about words throughout our lifetime. You're getting your child off to a great start by developing an early interest in words.
We all learn about words throughout our lifetime. You're getting your child off to a great start by developing an early interest in words.
Try these vocabulary activities at home!
Read aloud every day
Reading aloud to your child and having your child read books on their own is the best way to increase their vocabulary. Books provide words they won’t encounter in everyday conversations as the language of books is more complete and formal than talking. A great story also provides context and illustrations for learning a new word.
Bring in the nonfiction
Nonfiction and informational books (such as the picture books by Gail Gibbons and Sneed Collard) offer young children a treasure chest of new and interesting words about our world. If the book has a glossary, spend some time discussing the words with your child, and as you read aloud stop as often as needed to think about new words and how they connect to what your child already knows about.
Grocery store vocabulary
Use the items on the grocery shelf to give your child practice finding something above their belly button, below their nose, on the bottom shelf, and between other items on a shelf. Opportunities to use superlatives, those little endings that help describe size, are all around the grocery store. Have your child find a big fruit, a bigger fruit and the biggest fruit in the produce section. What's the smallest item in the cart? The largest item?
Opportunities to use superlatives, those little endings that help describe size, are all around the grocery store. Have your child find a big fruit, a bigger fruit and the biggest fruit in the produce section. What's the smallest item in the cart? The largest item?
Explore your world
Visits to a museum, the zoo, the botanical garden, historical sites, and even your neighborhood park are terrific opportunities to introduce your child to new words. Spend some time looking at the signage and identifying new words, then connecting them to what you see right there.
How can I help my four year old learn more words?
Literacy expert Sandra Wilborn shares three key ways to build your young child's vocabulary: lots of family talk, narrating your every day activities such as cooking or shopping, and reading to your child — while pointing out new words and then using them in your conversations. (From our video series Reading SOS: Expert Answers to Family Questions About Reading.)
(From our video series Reading SOS: Expert Answers to Family Questions About Reading.)
Talk about new words during read alouds
Talking to and reading with your child are two terrific ways to help them hear and read new words. Conversations and questions about interesting words ("The book says, 'The boy tumbled down the hill,' and look at the picture! How do you think he went down the hill?") are easy ways to get new words into everyday talk.
Sharing a new word with your child doesn't have to take a long time: just a few minutes to talk about the word and then focus back on the book or conversation. Choose which words to talk about carefully — choosing every new word might make reading seem like a chore. The best words to explore with your child are ones that are common among adult speakers but are less common to see in the books your child might read.
When introducing new words to your young learner, keep the following four helpful hints in mind:
First, provide a simple, kid-friendly definition for the new word:
Enormous means that something is really, really big.
Second, provide a simple, kid-friendly example that makes sense within their daily life:
Remember that really big watermelon we got at the grocery store? That was an enormous watermelon!
Third, encourage your child to develop their own example:
What enormous thing can you think of? Can you think of something really big that you saw today? That's right! The bulldozer near the park was enormous! Those tires were huge.
Lastly, keep your new words active within your house.
Over the next few days and weeks, take advantage of opportunities to use each new vocabulary word in conversation. Kids often need to hear a new word in context ten times or more before they "know" that word.
Antonyms: another word
Try this activity from the Florida Center for Reading Research (FCRR). The FCRR "At Home" series was developed especially for families! Watch the video and then download the activity: Antonyms: Another Word. See all FCRR vocabulary activities here.
A powerful technique for growing your child’s vocabulary
This video is from Home Reading Helper, a resource for parents to elevate children’s reading at home provided by Read Charlotte. Find more video, parent activities, printables, and other resources at Home Reading Helper.
More vocabulary resources
Vocabulary apps
Reviews provided by Common Sense Media.
20 reading texts for children aged 5-6-7-8
A child who has learned to put sounds into syllables, syllables into words, and words into sentences needs to improve his reading skills through systematic training. But reading is a rather laborious and monotonous activity, and many children lose interest in it. Therefore, we offer texts of small size , the words in them are divided into syllables.
First read the work to the child yourself, and if it is long, you can read its beginning. This will interest the child. Then invite him to read the text. After each work, questions are given that help the child to understand what they have read and comprehend the basic information that they have learned from the text. After discussing the text, suggest reading it again. nine0005
Mo-lo-dets Vo-va
Ma-ma and Vo-va gu-la-li.
In-va ran-sting and fell.
It hurts no-ha, but Vo-va does not cry.
Wow!
B. Korsunskaya
Korsunskaya
Answer questions .
1. What happened to Vova?
2. What made him sick?
3. Why is Vova doing well?
Clever Bo-beak
Co-nya and co-ba-ka Bo-beak gu-la-li.
So-nya played-ra-la with a doll.
That's why So-nya in-be-zha-la to-my, and the doll for-would-la. nine0015 Bo-beek found a doll-lu and brought it to So-ne.
B. Korsunskaya
Answer the questions.
1. Who did Sonya walk with?
2. Where did Sonya leave the doll?
3. Who brought the doll home?
The bird made a nest on a bush. De-ti our nest-up and took off on the ground.
- Look, Vasya, three birds!
In the morning, deti came, and the nest was empty. It would be a pity.
L. Tolstoy
Answer questions.
1. What did the children do with the nest?
2. Why was the nest empty in the morning?
Why was the nest empty in the morning?
3. Did the children do well? How would you do?
4. Do you think this work is a fairy tale, a story or a poem?
Pete and Mi-sha had a horse. They began to argue: whose horse. Did they tear each other apart.
- Give me - my horse.
- No, you give me - the horse is not yours, but mine.
Mother came, took a horse, and became nobody's horse. nine0015 L. Tolstoy
Answer the questions.
1. Why did Petya and Misha quarrel?
2. What did mother do?
3. Did the children play horse well? Why do you think so
?
9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000
015
9 9000 9000
FILVORDA for the development of reading, View here.
It will be interesting for children to read selected texts, they affect the emotional world of the child, develop his moral feelings and imagination . Children will get acquainted with the works of L. Tolstoy, K. Ushinsky, A. Barto, S. Mikhalkov, E. Blaginina, V. Bianchi, E. Charushin, A. Usachyov, E. Uspensky, G. Snegiryov, G. Oster, R. Rozhdestvensky, as well as fairy tales of different nations.
It is advisable to show children the genre features of poems, stories and fairy tales using the example of these works.
Fairy tale is a genre of oral fiction containing events unusual in the everyday sense (fantastic, wonderful or worldly) and distinguished by a special compositional and stylistic construction. In fairy tales there are fairy-tale characters, talking animals, unprecedented miracles happen. nine0005
Poem is a short poetic work in verse. The verses are read smoothly and musically, they have rhythm, meter and rhyme.
Story — small literary form; a narrative work of small volume with a small number of characters and the short duration of the events depicted. The story describes a case from life, some bright event that really happened or could happen.
In order not to discourage reading, do not force him to read texts that are uninteresting and inaccessible to his understanding. It happens that a child takes a book he knows and reads it “by heart”. Mandatory every day read to your child poems, fairy tales, stories.
Daily reading enhances emotionality, develops culture, horizons and intellect, helps to cognize human experience.
Literature:
Koldina D.N. I read on my own. - M .: TC Sphere, 2011. - 32 p. (Candy).
How easy it is to teach a child 4-6 years old to read - the best methods and exercises
How to understand that it's time
To the question "When is it time for a child to be able to read?" there is no ready answer, but we want to immediately warn against two misconceptions:
-
“You don't have to teach your child to read at home, they will teach you at school anyway.
 ” Yes, they will. But remember: the first year at school is the most intense in all 11 years of study. For some 4-5 months in the 1st grade, the child goes through the alphabet "from" and "to", learns to read, write, and the rest of the time he studies the basics of the Russian language. Therefore, it will be great if he has a reading skill before school. This will reduce the burden on the child.
” Yes, they will. But remember: the first year at school is the most intense in all 11 years of study. For some 4-5 months in the 1st grade, the child goes through the alphabet "from" and "to", learns to read, write, and the rest of the time he studies the basics of the Russian language. Therefore, it will be great if he has a reading skill before school. This will reduce the burden on the child. -
"There is no time to waste - the sooner the baby begins to read, the better." All children are different and develop at their own pace. Therefore, you should not impose teaching reading to a preschooler as soon as he is 4-5 years old, if the student himself does not yet show interest in this activity. Instead, you can begin to develop an interest in reading through bright and engaging books. A good option would also be games that involve letters. nine0005
The indicator to be guided by is not the age of the preschooler, but his speech skills.
It's time to learn to read if…
If the speech development of a preschooler proceeds without gross violations. Let's figure out what criteria will help you find out if a child is ready to learn to read:
-
Understanding addressed speech. The kid must understand sentences, phrases, individual words that others around him turn to. nine0005
-
Vocabulary. The more words a child knows, the better he will understand what he read. It will also help him communicate with adults and other children.
-
Grammar. The ability to correctly build sentences, select and change words is important for children who are learning to read.
-
Pronunciation.
 For learning to be effective, the child must know how to pronounce words without gross errors.
For learning to be effective, the child must know how to pronounce words without gross errors.
Remember: at preschool age, a child may have minor flaws in grammar and pronunciation - this is normal. Over time, these violations will be corrected, and they should not be considered an obstacle to reading. But if the baby is not yet very confident in speaking, do not rush him to read - this will not help develop speech, but only demotivate.
Practicing child psychologist Ekaterina Murashova
Free course for modern moms and dads from Ekaterina Murashova. Sign up and participate in the draw 8 lessons
How to make learning to read easier for preschoolers
-
Praise more and never scold
It's hard for us adults to imagine how difficult it really is for a baby to learn from scratch such a complex skill as reading.
 After all, being able to read means being able to correlate a sound with a letter or a combination of letters, connect sounds, understand the meanings of the words read and the meaning behind the text.
After all, being able to read means being able to correlate a sound with a letter or a combination of letters, connect sounds, understand the meanings of the words read and the meaning behind the text. If parents take the child's progress for granted and express dissatisfaction when the child does not understand something, this will not push the future student to development, but will only complicate the process. Therefore, it is important to praise for small victories: I learned the letter that was passed last time - great, I coped without my father's help with the word as much as two syllables - clever. nine0005
Do not take failures as a consequence of the negligence of the little student. When a child does not understand the first time, this is an occasion to look for another explanation or give more time to practice. If you feel tired and irritated, you should stop the activity and return to it in a good mood.
-
Exercise little but regularly
Do not expect perseverance and a desire to spend hours figuring out unfamiliar letters from your baby.
 It is difficult for preschoolers to keep their attention in a lesson for more than 25 minutes, and even such small classes should be interrupted with physical education minutes and games so that the child does not get bored. This is exactly how Skysmart prepares for school: 25-minute classes with breaks for outdoor games. nine0005
It is difficult for preschoolers to keep their attention in a lesson for more than 25 minutes, and even such small classes should be interrupted with physical education minutes and games so that the child does not get bored. This is exactly how Skysmart prepares for school: 25-minute classes with breaks for outdoor games. nine0005 But regular practice is important - much more important than the duration of the session. And it doesn’t have to be just lessons: you can look for familiar letters on signs during a walk, on a door plate in a children’s clinic, on a package of your favorite corn flakes.
-
Read books aloud
In a series of studies conducted by Dr. Victoria Purcell-Gates among five-year-olds who could not yet read, those children to whom their parents read aloud regularly for two years, expressed their thoughts in more literary language, built longer phrases and used more complex syntax.
 nine0005
nine0005 In addition, reading aloud with adults contributed to the expansion of the children's vocabulary, as parents explained the meanings of new words that children did not encounter in everyday life.
Expert Opinion
According to neuroscientist Marianne Wolfe, book evenings with parents help develop a love of reading because the child establishes a connection between reading aloud and feelings of love and warmth.
- nine0258 Discuss read
The role of communication in teaching literacy cannot be overestimated. At first, it is important to ask if the future student is interested, if he is tired, what was remembered from the lesson. When a preschooler learns to read coherent texts, be sure to ask questions about their content.
It's great if the child reads on his own and without the prompting of the parents, but even in this case, do not deprive him of the opportunity to discuss what he read with you.
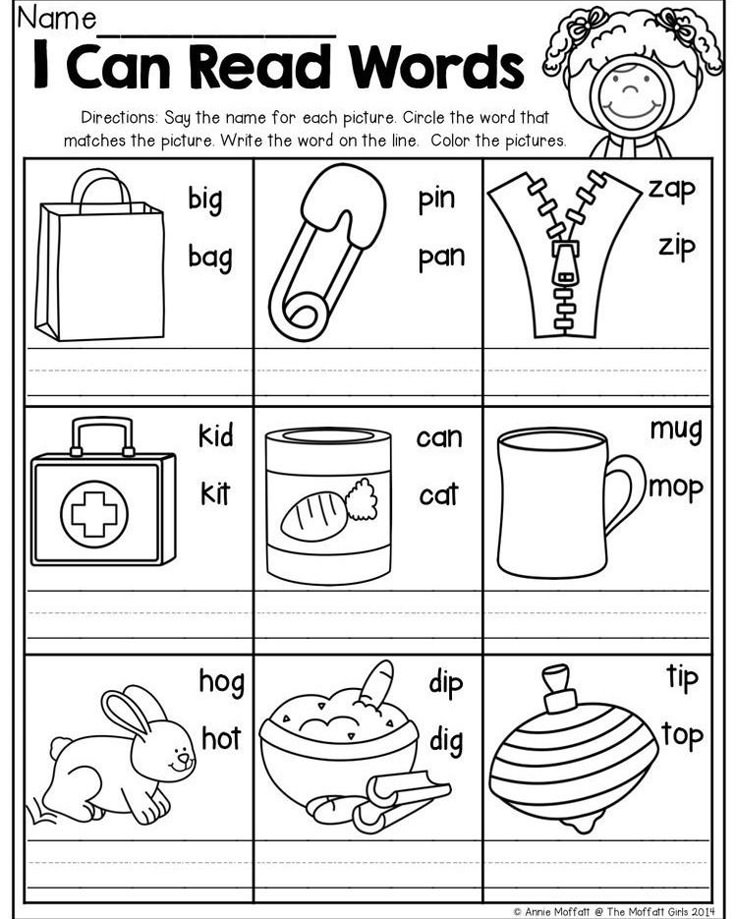 For example, you might ask:
For example, you might ask: -
Which of the characters do you like?
-
Do you think this character is like you? Would you like to be like her?
-
What would you do if you were a hero?
-
Why did the described event happen? How are these two events related?
-
How did what you read make you feel?
-
What do you remember most from what you read? nine0005
-
What do you think the author wanted to teach? Why did he write this? Do you agree with the author?
-
-
Go from simple to complex
From the correspondence between sounds and letters to syllables, from short words to longer and more complex words. It would seem that this is obvious, but no: sometimes parents are so happy with the success of the child at first that they push him to study more complex topics than he is ready to accept. Of course, the program should adapt to the future student, but you should not skip steps, even if the child is making progress.
nine0202 There are methods that offer to teach a child to read by memorizing whole words. Alas, experiments show that such techniques generally work worse. For example, a group of scientists from the United States came up with an artificial alphabet and offered subjects to learn it, and then read the words written using this alphabet. At the same time, some subjects were immediately explained the principles of correspondence between sounds and letters, while others had to derive reading rules on their own based on whole words. It turned out that the first group copes with reading new, previously unfamiliar words better than the second. nine0005
At the same time, some subjects were immediately explained the principles of correspondence between sounds and letters, while others had to derive reading rules on their own based on whole words. It turned out that the first group copes with reading new, previously unfamiliar words better than the second. nine0005 Therefore, we advise you to choose those teaching methods that involve clear instructions about the relationship between sound and letter - and this is especially important for those children who have difficulty reading. Below we have compiled a few of these techniques that you can use to teach your preschooler at home.
It is important to select questions individually, based on the age of the child. With younger children, discuss everything together, ask simple questions, direct their attention to some facts. The complexity of the questions should increase in proportion to the age of the child. The older he is, the more difficult the tasks should be, and the questions can already affect the "reflection" of their feelings and experiences. nine0005
The complexity of the questions should increase in proportion to the age of the child. The older he is, the more difficult the tasks should be, and the questions can already affect the "reflection" of their feelings and experiences. nine0005
Methods of teaching preschoolers to read
Warehouse reading
The method of teaching a child to read through warehouses was actually used in Rus', but for modern parents this technique is associated with the name of the philologist Nikolai Aleksandrovich Zaitsev. nine0005
nine0005
Zaitsev suggests not focusing on the study of individual letters, as it can be difficult for students to understand how letters can merge into syllables and words. Teaching a child to read by syllables is also not always easy: one syllable can be quite long ( shine, ruble ), and the boundaries of syllables are not obvious ( Lun-tik or Lu-ntik ?). Therefore, in Zaitsev's methodology, a warehouse is used as the main unit.
Warehouse can be a combination of a consonant and a vowel (pa-pa, ma-ma), a single consonant or vowel (de- d , i-s -li, A -le-sha), as well as a combination of a consonant with a hard or soft sign (ma- l -chi-k, use d -yem).
In order for a preschooler to understand the differences between the recording of voiced and soft, vowels and consonants, different types of warehouses have their own cube size, color and content, thanks to which the cubes sound when they are shaken. Cubes affect several channels of perception at once, and warehouses should not just be pronounced, but sung - this way, according to the author of the methodology, learning is more interesting and effective. nine0005
Cubes affect several channels of perception at once, and warehouses should not just be pronounced, but sung - this way, according to the author of the methodology, learning is more interesting and effective. nine0005
One of the advantages of the technique is that children willingly play with blocks themselves, and the process of learning to read becomes active, mobile.
Syllabic reading
This technique, according to some sources, was developed by the Romans. Later, Nadezhda Sergeevna Zhukova, a Soviet and Russian speech therapist, created a primer based on it. In it, she built her own system in which sounds and letters are sequentially introduced into speech.
Due to the fact that the concept of a syllable is introduced at an early stage, it is faster and easier to teach a child to read syllables together. By the way, as in Zaitsev's technique, it is proposed to sing syllables, and not just pronounce them. nine0005
nine0005
Based on the syllabic method, Zhukova developed a set of teaching aids - copybooks, copybooks and a book for reading. Benefits will help teach children to read correctly 6 and 7 years old at home.
Both techniques for teaching preschoolers to read are used in the Skysmart Ready for School course. The course consists of two stages: first, children get acquainted with letters and warehouses, which allows them to quickly start reading simple words, and then they learn what a syllable is. Gradually, we introduce more complex syllabic constructions, move on to reading phrases and sentences. nine0005
Sound analytical-synthetic teaching method
This method originated in the USSR and is still considered the main one in Russian schools and kindergartens. It was developed by the Soviet teacher and Russian language methodologist Voskresenskaya Alexandra Ilyinichna.
Same as N.S. Zhukova, Voskresenskaya proposed her own order in which children should learn letters and sounds. The principle of this sequence was that the child first learned the letters that can be combined into simple syllables, and then moved forward in the level of complexity. As a result, children learn syllables in this order:
The principle of this sequence was that the child first learned the letters that can be combined into simple syllables, and then moved forward in the level of complexity. As a result, children learn syllables in this order:
-
Two-letter syllables (including one consonant): am, ma, ra, etc. and simple words from them: ra-ma, ma-sha, Pa-sha, etc.
-
Three-letter syllables with a vowel in the center: poppy, lat, etc.
-
The combination of the first two stages into words: sa-lat, earth-la, etc.
-
Words of three syllables and six letters: az-bu-ka, ve-se-lo, etc.
-
Words of two syllables and six letters: question-ros, tea-nick, etc.
nine0205
Words with a combination of vowels at the beginning and at the end of the word: chair, March, etc.
In this way, children simultaneously prepare for more complex syllables at each stage and reinforce what they have learned earlier.
Exercises for learning to read
Learning to read usually takes place in several stages. First, the child listens to the sound, visually remembers the letters. Different games will help with this, where you need to look for letters, invent words, etc. When this stage is over, you can move on to syllables and games to work them out. And only after that it will be possible to proceed to words, and then to sentences and texts. nine0005
Letter memory exercises
The first step is to teach your child to recognize letters. To do this, you can use pictures with hidden letters. We use such exercises in the preparation for school lessons in Skysmart.
Ask your child to identify what letter a word begins with, or name as many words as possible that begin with a certain letter.
Next, we train to distinguish correctly written letters from incorrect ones. This is also important for learning to write: preschoolers often mirror letters or distort individual elements. nine0005
Exercises for vowels and consonants
To learn how to distinguish between vowels and consonants, tasks will help you determine the sound with which a word begins.
It will also help to remember the difference between vowels and consonants and search for an extra letter.
Word building exercises
When your child can read short words, ask him to make a word out of letters on his own.
Composing words from syllables is convenient if you have cubes at hand, but you can also try on paper.
Another good exercise is to fill in the missing letter in the word.

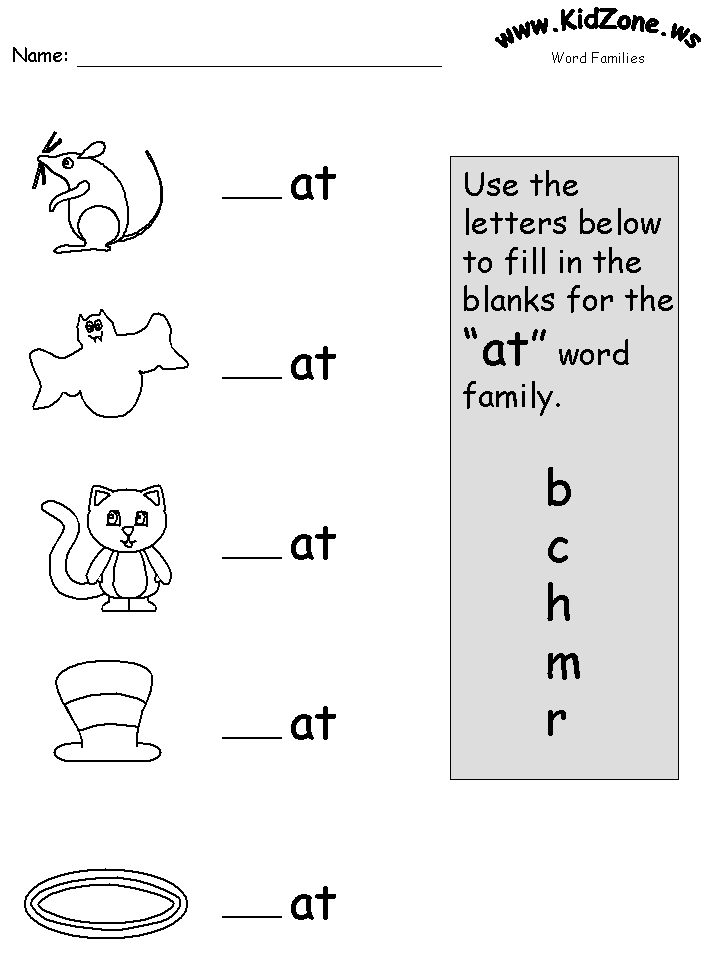 *
*