Shapes to learn
25 Creative Activities and Ideas For Learning Shapes
Learning shapes is one of the earliest concepts we teach kids. This readies them for geometry in the years ahead, but it’s also an important skill for learning how to write and draw. We’ve rounded up our favorite activities for learning shapes, both 2-D and 3-D. They all work well in the classroom or at home.
1. Start with an anchor chart
Colorful anchor charts like these are terrific reference tools for kids learning shapes. Have kids help you come up with examples for each one.
Learn more: A Spoonful of Learning/Kindergarten Kindergarten
2. Sort items by shape
Collect items from around the classroom or house, then sort them by their shapes. This is a fun way for kids to realize that the world around them is full of circles, squares, triangles, and more.
Learn more: Busy Toddler/Shape-Sorting
3. Snack on some shapes
Everyone loves a learning activity you can eat! Some food items are already the perfect shape; for others, you’ll have to get a little creative.
Learn more: Chieu Anh Urban
4. Print with shape blocks
Grab your shape blocks and some washable paint, then stamp shapes to form a design or picture.
Learn more: Pocket of Preschool
5. Go on a shape hunt
These “magnifying glasses” make an adventure of learning shapes! Tip: Laminate them for long-term use.
Learn more: Nurture Store UK
6. Hop along a shape maze
Use sidewalk chalk to lay out a shape maze on the playground or driveway. Choose a shape and hop from one to the next, or call out a different shape for every jump!
Learn more: Creative Family Fun
7. Assemble a truck from shapes
Cut out a variety of shapes (excellent scissors skills practice!), then assemble a series of trucks and other vehicles.
Learn more: Little Family Fun
8. Stretch out shapes on geoboards
Teachers and kids love geoboards, and they’re a great tool for learning shapes. Give students example cards to follow, or ask them to figure out the method on their own.
Give students example cards to follow, or ask them to figure out the method on their own.
Learn more: Mrs. Jones’ Creation Station
9. Drive on shaped roads
Use these free printable road mats to work on shapes. Bonus: Make your own road shapes from sentence strips!
Learn more: PK Preschool Mom
10. Find shapes in nature
Take your shape hunt outside and look for circles, rectangles, and more in nature. For another fun activity, gather items and use them to make shapes too.
Learn more: Nurture Store UK
11. Put together craft stick shapes
Add Velcro dots to the ends of wood craft sticks for quick and easy math toys. Write the names of each shape on the sticks for a self-correcting center activity.
Learn more: Surviving a Teacher’s Salary
12. Blow 3-D shape bubbles
This is a STEM activity that’s sure to fascinate everyone. Make 3-D shapes from straws and pipe cleaners, then dip them in a bubble solution to create tensile bubbles. So cool!
Make 3-D shapes from straws and pipe cleaners, then dip them in a bubble solution to create tensile bubbles. So cool!
Learn more: Babble Dabble Do
13. Prep a shape pizza
Cover a paper plate “pizza” with lots of shape toppings, then count the number of each. Simple, but lots of fun and very effective.
Learn more: Mrs. Thompson’s Treasures
14. Construct shapes from toothpicks and Play-Doh
This is an excellent STEM challenge: how many shapes can you make using toothpicks and Play-Doh? Marshmallows work well for this activity too.
Learn more: Childhood 101
15. Outline shapes with stickers
Kids adore stickers, so they’ll enjoy filling in the outlines of the shapes they’re learning. They won’t realize it, but this gives them fine motor skills practice too!
Learn more: Busy Toddler/Sticker Shapes
16. Lace shapes
Lacing cards have long been a classic, but we really like this version that uses drinking straws. Just cut them into pieces and glue them along the edges of the cards.
Just cut them into pieces and glue them along the edges of the cards.
Learn more: Planning Playtime
17. Make shapes with LEGO bricks
LEGO math is always a winner! This activity also makes a good STEM challenge. Can your students figure out how to make a circle from straight-sided blocks?
Learn more: Pocket of Preschool
18. Categorize shapes by their attributes
Work on geometry terms like “sides” and “vertices” when you sort shapes using these attributes. Start by placing shapes into paper bags and asking students questions like, “The shape in this bag has 4 sides. What could it be?”
Learn more: Susan Jones Teaching
19. Count and graph shapes
These free printable worksheets challenge kids to identify shapes, then count and graph them. Lots of math skills, all in one!
Learn more: Playdough to Plato
20. Create a shape monster
Add arms, legs, and faces to create cheery (or scary) shape monsters! These make for a fun classroom display.
Learn more: Fantastic Fun and Learning
21. Sift through rice for shapes
Sure, kids can identify their shapes by sight, but what about by touch? Bury blocks in a bowl of rice or sand, then have kids dig them out and guess the shape without seeing them first.
Learn more: Fun With Mama
22. Craft an ice cream cone
Ice cream cones are made up of several shapes. Encourage kids to see how many different ways they can make a sphere of “ice cream.”
Learn more: Extremely Good Parenting
23. Ask “What does the shape say?”
If you don’t mind the risk of getting that song stuck in your kids’ heads, this is such a neat way to combine writing and math.
Learn more: Around the Kampfire
24. Piece together shape puzzles
Use wood craft sticks to make simple puzzles for kids who are learning their shapes. These are inexpensive enough that you can make full sets for each of your students.
Learn more: Toddler at Play
25. Feed a shape monster
Turn paper bags into shape-eating monsters, then let kids fill their hungry bellies!
Learn more: Teach Pre-K
From teaching shapes to long division and everything in between, these are the 25 Must-Have Elementary Classroom Math Supplies You Can Count On.
Plus, 22 Active Math Games and Activities For Kids Who Love to Move.
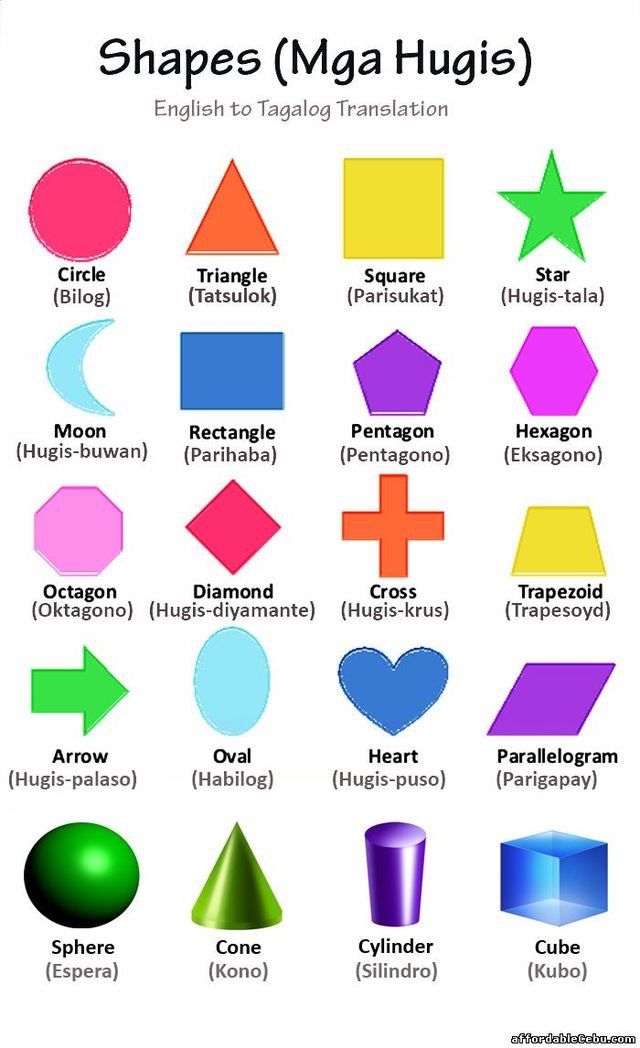
Teaching Basic Shapes to Kids In an Interesting Way
Table of Contents
| 1. | Introduction |
| 2. | Why is teaching shapes so important? |
| 3. | What are the different types of shapes for kids? |
| 4. | How to teach kids with the help of games and activities |
5. |
Conclusion |
| 6. | About Cuemath |
| 7. | Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) |
| 8. | External References |
Introduction
Kids have dynamic learning capabilities that are enhanced by their observation skills. However, parents need to take tiny steps while teaching preschool kids. Basic shapes and colors impact children. They try to understand their surroundings by looking at the different objects around them. All kinds of objects and structures help kids in learning shapes. As a parent one should introduce different shapes for kids at an early age. There are various shapes activities for kindergarten that can help kids learn and understand basic shapes.
Shapes for Kids
Here is a downloadable PDF that lists out various shapes for kids. Teaching basic shapes for kids helps them understand their own observations. Different types of shapes for kids. Click on the download button to explore them.
Teaching basic shapes for kids helps them understand their own observations. Different types of shapes for kids. Click on the download button to explore them.
Why is teaching shapes important?
Basic shapes for kids are being taught at every preschool today. It is important to understand the necessity of shaping activities for kindergarten kids. Few ways in which kids are impacted by basic shapes are:
- Visual Information
- Sign and symbols
- Alphabets and numbers
- Mathematical concepts
- Categorization and comparison
- Problem-solving
- Symmetry
- Kids Learn how to organize visual information
Children observe their surroundings very keenly and encounter different shapes every single day. Teaching basic shapes for kids helps them understand their own observations.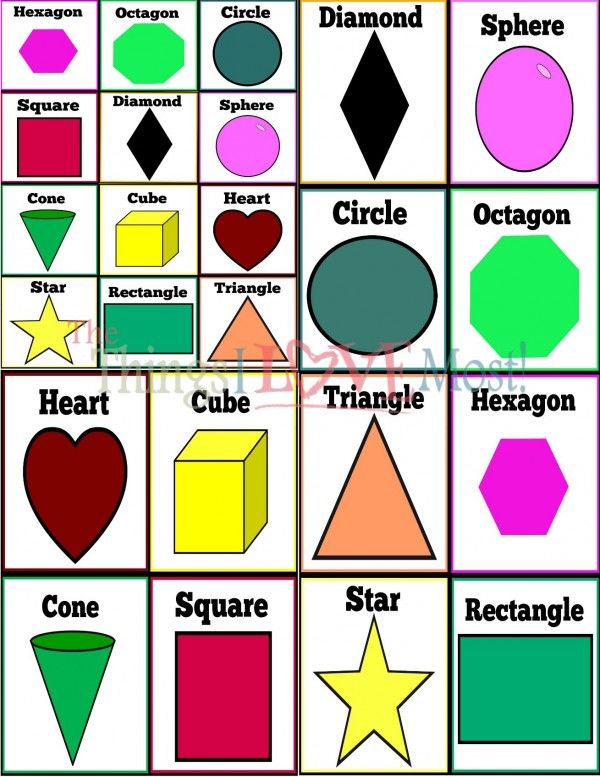 The visual information they gather comprises compound shapes that are formed by a combination of basic shapes. Shapes’ names for kids enable them to identify the basic shapes in compound shapes. For instance, when a child looks at a car it appears to be a rectangular box. However, children will learn to identify the compound shapes in a car once they learn basic shapes.
The visual information they gather comprises compound shapes that are formed by a combination of basic shapes. Shapes’ names for kids enable them to identify the basic shapes in compound shapes. For instance, when a child looks at a car it appears to be a rectangular box. However, children will learn to identify the compound shapes in a car once they learn basic shapes.
- Helps to teach signs and symbols
Symbols are very important for kids. But it will take some time for kids to get used to it. Kids take some time before they can actually name the shapes they see. However, this does not indicate that the kid is unable to comprehend basic shapes. Signs on the other hand impart certain information and details. Basic shapes for kids help them store information in their minds. Kids are usually 5 to 6 years old when they start following signs and symbols
.
- Help kids identify different alphabets and numbers
Toddlers may get confused among all the alphabets they see. As parents, it can be challenging to teach various letters and numbers. Kids tend to mix up similar-shaped letters like “b” and “d”. Patience is important while correcting these mistakes. Learning shapes for kids help them differentiate among the letters. Therefore all the preschools cover learning shapes for kids before moving into Alphabets and numbers.
As parents, it can be challenging to teach various letters and numbers. Kids tend to mix up similar-shaped letters like “b” and “d”. Patience is important while correcting these mistakes. Learning shapes for kids help them differentiate among the letters. Therefore all the preschools cover learning shapes for kids before moving into Alphabets and numbers.
- Basic mathematical concepts can be taught
Once a child is comfortable identifying shapes for his /her own, they can start learning simple mathematical operations like addition and subtraction. It is always easier to teach addition than subtraction. Therefore we advise parents to start teaching addition and then venture into subtraction. Basic shapes for kids include balls, matchboxes, dice, etc. So you can pick the object of your choice and start teaching simple maths to your kids.
- Categorization and comparison
Facial recognition and navigation skills are swiftly developed among kids who can categorize and compare various shapes. As kids learn to differentiate shapes, they understand facial features and their differences. It is also important to note that different shapes for kids imply different geographical locations or features. Have you noticed, in kids’ drawing- mountains and hills are always triangles and houses have a square or rectangle structure with a triangular roof? We do suggest you take a look and understand how kids observe and compare the shapes around them.
As kids learn to differentiate shapes, they understand facial features and their differences. It is also important to note that different shapes for kids imply different geographical locations or features. Have you noticed, in kids’ drawing- mountains and hills are always triangles and houses have a square or rectangle structure with a triangular roof? We do suggest you take a look and understand how kids observe and compare the shapes around them.
- Problem-solving
Brain development and thinking skills are really important for a kid in preschool or kindergarten. Shapes and colors are directly responsible for brain development. Kids analyze structures and start with 2-D mental mapping and then gradually, as the year progresses, they start 3-D mapping. These mental mapping of shapes plays a crucial role in the development of problem-solving abilities in children.
- Symmetry
Kids love to play around the parks or fields. This is important for the development of their motor skills. However, kids tend to lose their balance more often than adults. Growing up, we all had cuts and bruises on our knees Over the years these injuries started disappearing even when sports activities became more rigorous. This happens when kids are unable to understand the basic concept of balance and center of gravity. Now even though terms like the center of gravity feel fancy for kids, it is important to teach symmetry with the help of basic shapes for kids. This will help them understand how to position themselves and develop motor skills.
This is important for the development of their motor skills. However, kids tend to lose their balance more often than adults. Growing up, we all had cuts and bruises on our knees Over the years these injuries started disappearing even when sports activities became more rigorous. This happens when kids are unable to understand the basic concept of balance and center of gravity. Now even though terms like the center of gravity feel fancy for kids, it is important to teach symmetry with the help of basic shapes for kids. This will help them understand how to position themselves and develop motor skills.
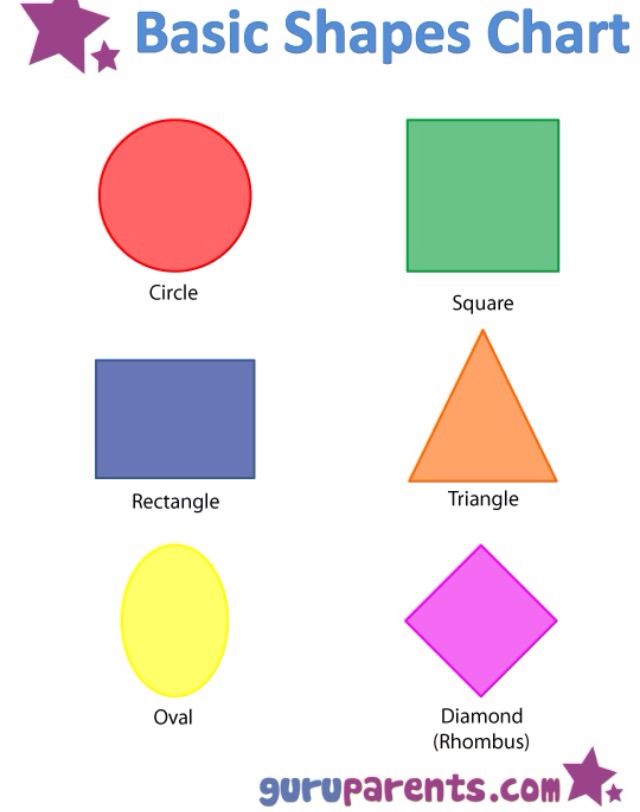
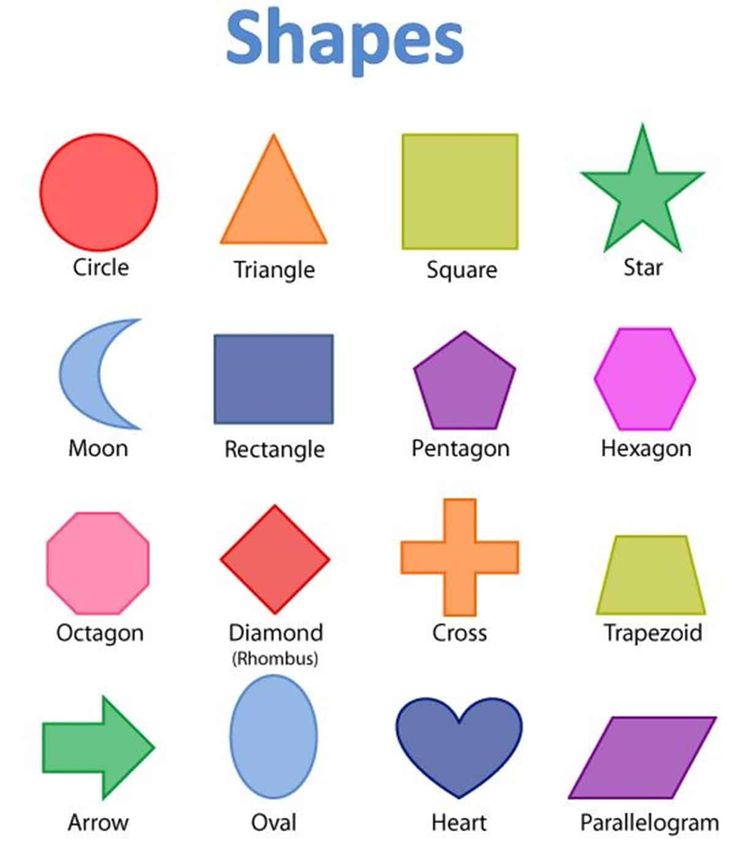
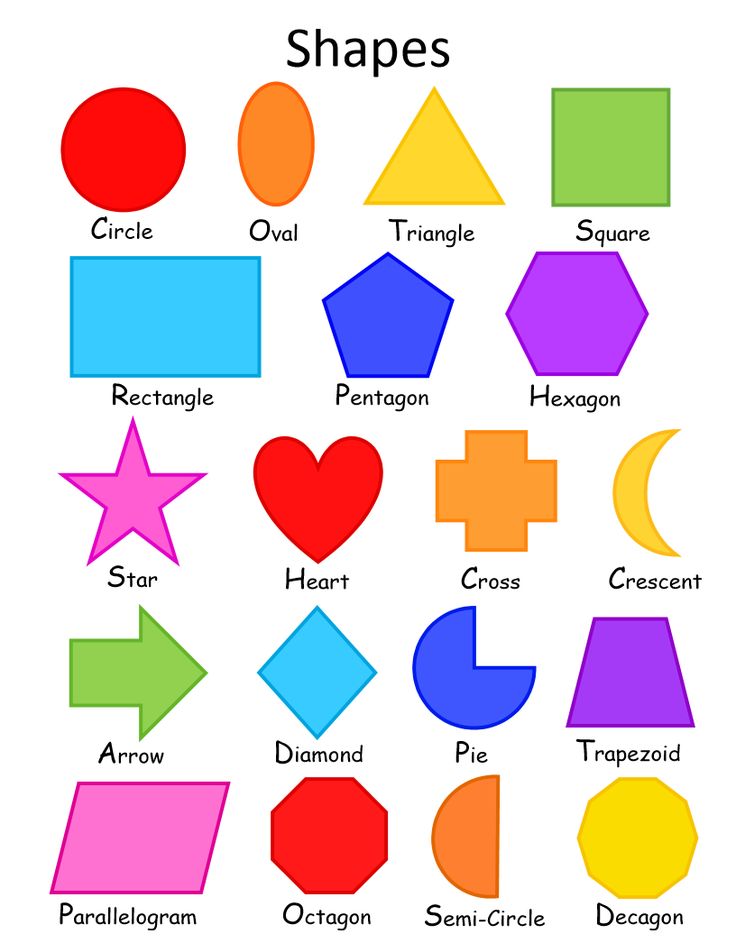
What are the different types of shapes for kids?
Different shapes for kids are available ranging from basic shapes to compound shapes. Basic shapes are simple shapes that can not be broken down into simpler shapes by general conventions, examples include square, circle, triangle, etc. Compound shapes can be split into simpler shapes, examples include Arrows, Starts, etc. Let us go through a few shapes to understand better.
Let us go through a few shapes to understand better.
|
Shape |
Image |
Number of Sides |
Example: |
|
Triangle |
3 Sides |
Mountains and Hills are Triangle in shape |
|
|
Square |
4 Sides |
Small houses or huts are square in shape |
|
|
Rectangle |
4 Sides |
Cars and buses are rectangle in shape |
|
|
Circle |
No Sides |
Wheels and Balls are circle in shape |
|
|
Arrow |
7 Sides |
Signs boards have an arrow shape |
|
|
Star |
10 Sides |
Starfish and star anise are star-shaped |
|
|
Diamond |
4 Sides |
Kites and crystals have diamond shape |
|
|
Heart |
No Sides |
Strawberries are heart-shaped. |
- Basic Shapes for kids
Shapes like squares, triangles, circles, and rectangles are taught first to kids. Once a child learns how to categorize and name these shapes, they are taught more complex shapes. However, it suggested that ample time is spent on basic shapes for kids. This is because all the shapes are taught at a later stage depending upon the concepts developed during learning basic shapes for kids. It may require a little while for kids to pick up the concept but we suggest parents be patient.
- Advanced Shapes for kids
Once a child is familiar with basic shapes he/she is ready to learn advanced shapes for kids. These shapes include arrows, stars, and hearts. Advanced shapes do not include 3-D structures in preschool as it may confuse them.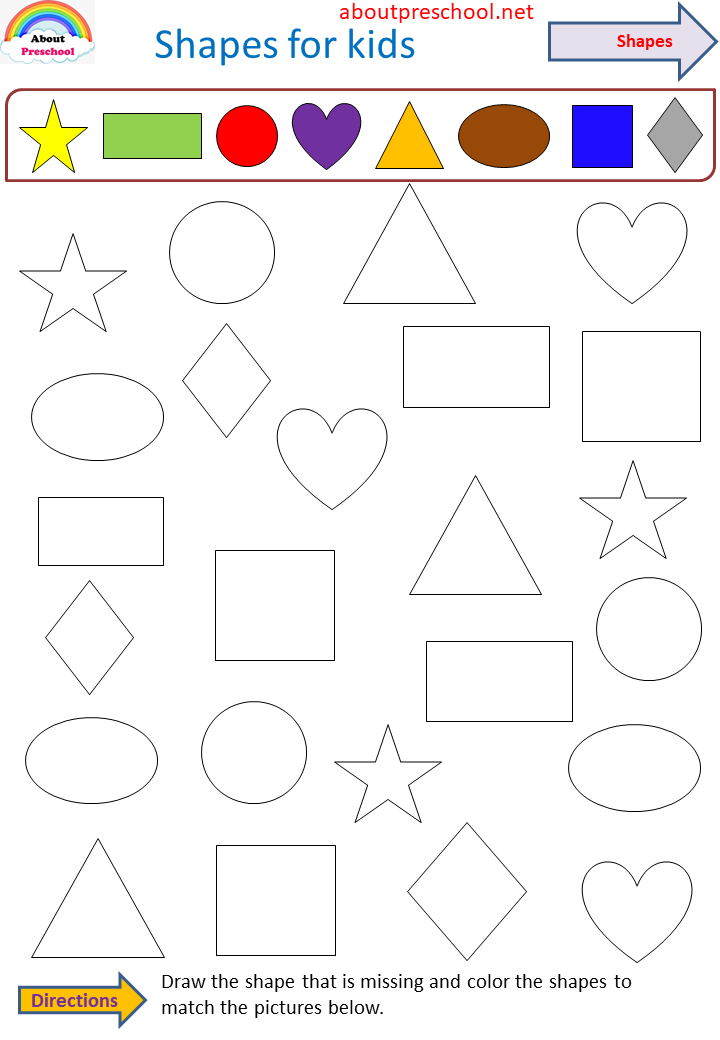 Kids with a clear conception of basic shapes will be able to ace this topic quickly.
Kids with a clear conception of basic shapes will be able to ace this topic quickly.
How to teach shapes to kids with the help of games and activities?
Till now, we saw how important basic shapes can be for a child's brain development. Teaching shapes can be cumbersome without activities as children find it difficult to comprehend something that can not be observed. Activities and games will help kids learn while having fun.
Now, we will look into a few activities and games to help your child play and learn.
- Flashcard shapes for kids
Flashcards are a really fun and interactive tool while teaching kids. They can be purchased in stores or prepared by hand. You can draw different shapes on cards made out of thick paper to prepare a set of flashcards. Use these cards to play with your child. Ask your kid to pick up a card and name the shape drawn on the card. Maintain a scoreboard and let them beat their own high scores.
Maintain a scoreboard and let them beat their own high scores.
- Shapes for kids chart
Bright and colorful shape names for kid's charts are available in the market. To prepare them at home, you need to draw shapes and write down their names. Colorful shapes are easier to remember for kids. Ask your kids to look at the beautiful chart every day in the morning before going to preschool or kindergarten.
- Shapes hunt
Just like a treasure hunt, shapes hunting is fun and easy for preschoolers. Use a set of flashcards with different shapes on them. Ask your kid to pick up one card and identify the shape and once he or she has identified the shape, ask them to find an object of the same shape around the house. This will keep the kids engaged and help them relate basic shapes to their surroundings.
- Puzzle games
Two types of puzzles are available for kids to learn basic shapes. The first one contains pieces of brightly colored basic shapes for kids. These shapes need to be fitted onboard with hollows similar to the shapes. These boards with pieces of basic shape for kids are available in preschool supply shops and toy shops.
The second type is a conventional puzzle with bigger pieces. Once a child is proficient in basic shapes for kids they can try to join the pieces of a picture together.
We suggest you go for basic puzzles with pictures of fruits and flowers to keep the level easy for your child.
Conclusion
In the former section, we came across the various benefits of teaching basic shapes for kids. It is one of the most important topics covered in the kindergarten and preschool syllabus. Even though your child may be learning shapes for kids in school, it is suggested that parents help them out with shapes games for kids. This is because the identification of shapes and naming shapes are two different objectives. Kids tend to forget shape names.
Even though your child may be learning shapes for kids in school, it is suggested that parents help them out with shapes games for kids. This is because the identification of shapes and naming shapes are two different objectives. Kids tend to forget shape names.
Start teaching basic shapes to your child and try to relate them with the objects around you. This will help kids relate the concept of basic shapes with their surroundings. We suggest parents start with basic shapes and gradually move into advanced shapes. Spend more time on basic shapes for kids to build the foundation for advanced shapes.
About Cuemath
Cuemath, a student-friendly mathematics and coding platform, conducts regular Online Live Classes for academics and skill-development, and their Mental Math App, on both iOS and Android, is a one-stop solution for kids to develop multiple skills. Understand the Cuemath Fee structure and sign up for a free trial.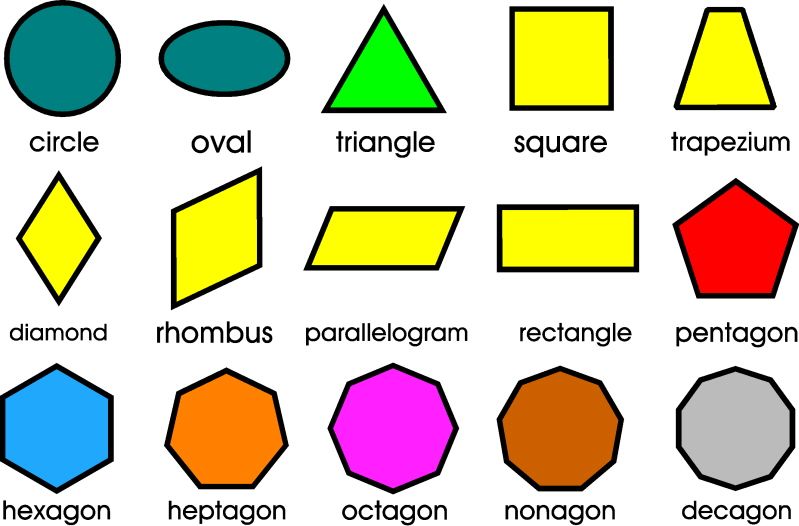
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between regular and irregular shapes?
- Regular Shapes are those which have equal sides as well as equal angles. Irregular Shapes are just the opposite,i.e, their angles and sides vary.
- Examples of Regular Shapes are Square, Circle, Equilateral Triangle, etc.
- Examples of Irregular Shapes are Rectangle, Heart, Right-angled triangle, etc.
- Cylinder - Circles
- Cuboid - Rectangles
- Cube - Squares
- Pyramid - Rectangles and Circles
- Tetrahedron - Triangles
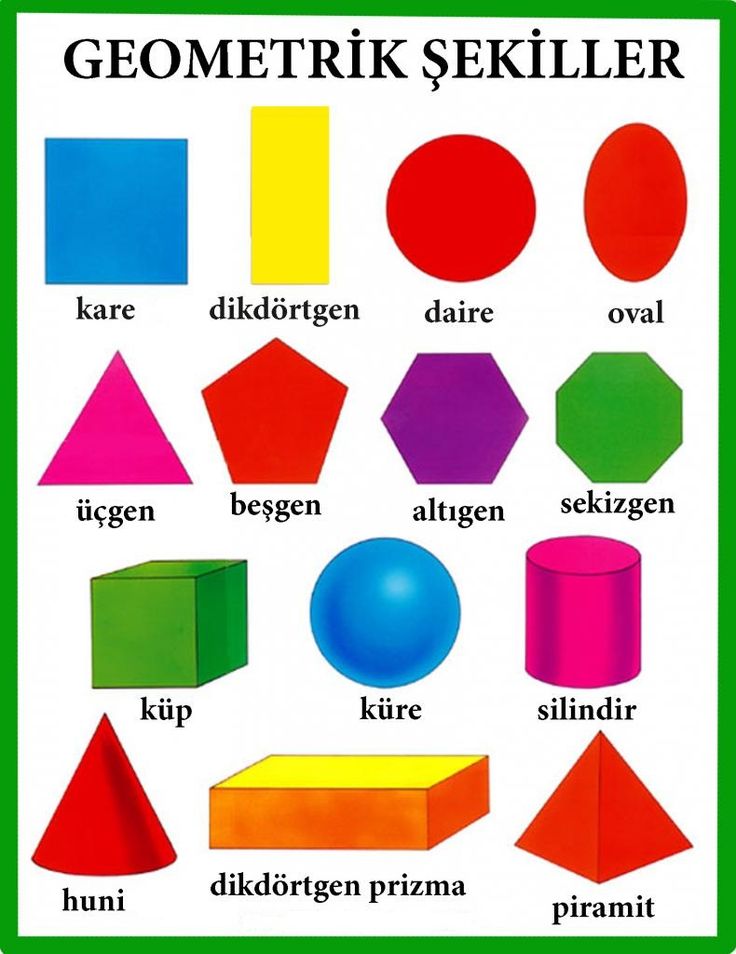
- Geometric: These are simple shapes like rectangle, square, triangle, etc. which are geometric in nature.
 They form the basis of other types of shapes.
They form the basis of other types of shapes. - Organic: These shapes are curvier in nature and have a natural feel to them (for example, the shape made after the ink is spilled on a paper is of organic type). These are more soothing and relaxing to the eyes.
- Abstract: These shapes are complex in nature and are mostly used in graphics designing purposes. They are aesthetically beautiful but are not naturally found.
Forms of study at a university, college or technical school
When entering a university or college, an applicant has to choose the form of education.
In this section we will consider the main question:
What are the forms of education?
The main forms of conducting the educational process are:
- Full-time ("daytime") form of education
- Part-time (often referred to as "evening education")
- Correspondence (it is also often positioned by universities as a "remote form")
- Externat
It should be noted that each form is unique in its own way and has its own advantages and disadvantages.
"
What form of education to choose when entering a university or college? "1. Full-time (full-time) form of education at a university or college.
Full-time provides a systematic curriculum in which students regularly attend classes 5-6 days a week. Classes are usually visited in the morning. But there are times when educational institutions are forced to put classes for students on the second shift. This may be due, for example, to the desire of the educational institution to provide students with the opportunity to work part-time in the morning, or to the lack of a classroom fund, the irrational distribution of faculty and other reasons.
The full-time study program involves a large amount of theoretical material, lectures and seminars, control, laboratory and practical work. The student has the opportunity to listen to all the necessary material, ask questions to the teacher, and consolidate the knowledge gained.
In their last years, students of higher education institutions and colleges undergo industrial practice at enterprises and receive the primary necessary work experience in a particular field.
Total term of study full-time (full-time) is 4 years for the undergraduate program, 5 years for the specialist's program, and 2 years for the master's program. In the case when a graduate of a college or technical school enters a university for full-time education in a specialized specialty, it is possible to reduce the period of study to 3 years.
In initial vocational education programs, the term of study at a college or technical school is usually from 1 to 3 years.
Normative period of full-time college education, upon admission after 9class, basically, ranges from 2 years 10 months to 4 years 10 months, depending on the level of secondary vocational education received: basic or advanced. Upon admission to a college or technical school, secondary vocational education programs, after grade 11, the full-time study period is from 1 year 10 months to 3 years 10 months, depending on the level of secondary vocational education received: basic or advanced
Advantages:
- Serious theoretical training of a specialist
- When studying full-time, students are granted a deferment from military service (in the event that he uses the deferment only for the first time.
 If the student has reached the age of 18 and has previously received one deferral, for example, in college, then when studying for full-time, the student will no longer receive a second deferment)
If the student has reached the age of 18 and has previously received one deferral, for example, in college, then when studying for full-time, the student will no longer receive a second deferment) - Bright student life, participation in competitions, events and holidays of the educational institution, the possibility of self-realization.
- When studying at a free department, good students are paid a scholarship.
Disadvantages:
- The theory obtained at a university does not always correspond to the real situation at enterprises.
- When graduating from a university, a specialist has no or minimal work experience, and in most cases can count, upon employment, only on starting positions.
2. Part-time (evening) form of education at a university or college.
Part-time education involves a fairly large number of classroom lessons, but of course less than full-time.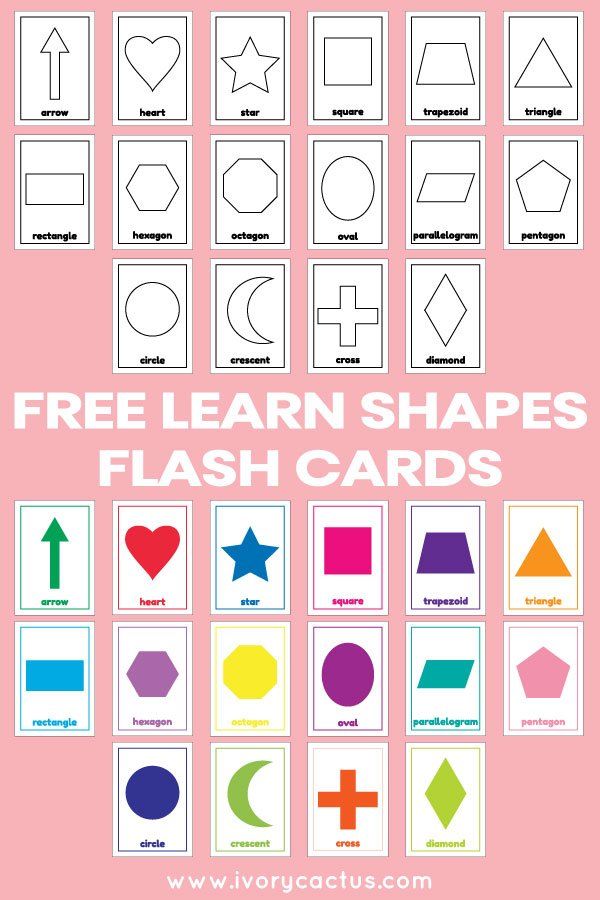 With such training, students usually attend classes 2-4 days a week (mostly on weekdays, less often on weekends) in the evening. It is usually assumed that in this way students will be able to safely combine work and gain knowledge and skills within the framework of a higher professional education program. Thus, the student has the opportunity to receive the necessary material, discuss it with the teacher and use it in their work. This combination contributes to the rapid acquisition of useful experience and the development of a specialist.
With such training, students usually attend classes 2-4 days a week (mostly on weekdays, less often on weekends) in the evening. It is usually assumed that in this way students will be able to safely combine work and gain knowledge and skills within the framework of a higher professional education program. Thus, the student has the opportunity to receive the necessary material, discuss it with the teacher and use it in their work. This combination contributes to the rapid acquisition of useful experience and the development of a specialist.
Part-time classes are usually held in the form of systematic classroom lessons throughout the academic year, followed by a credit and examination session.
The normative period of study for part-time (evening) form at the university for a bachelor's program is 4.5 years, for a specialist's program from 5.5 years, and for a master's program 2 years. The term of study after a college or technical school, according to an abbreviated program, is usually from 3 years.
The normative period of study in part-time (evening) form in college, upon admission after grade 9, basically ranges from 2 years 10 months to 4 years 10 months, depending on the level of secondary vocational education received: basic or advanced. admission to a college or technical school, to programs of secondary vocational education, after grade 11, the term of study in full-time (evening) form is from 1 year 10 months to 3 years 10 months, depending on the level of secondary vocational education received: basic or elevated.
In initial vocational education programs, the term of study at a college or technical school is usually 1 to 3 years.
Benefits:
- Possibility of independent income, effective combination of work and study
- Upon graduation from a university or college, a specialist already has work experience and can apply for career advancement
Disadvantages:
- When studying at the part-time (evening) department, deferment from the army is not provided
- Due to lack of time, students of the evening department are unable to participate in the student life of the educational institution.

- Lack of opportunity to receive a scholarship when studying in the field, funded from the state budget of the Russian Federation
3. Part-time education at a university or college.
The educational process for part-time education provides for a small number of classroom hours. The main part of the material is studied by students on their own, and then, the educational institution, conducts knowledge control in the form of tests and sessions.
Currently, in each educational institution, the process of distance learning is built differently. Some universities and colleges conduct classes throughout the year, for example, once a week on a weekday or weekend (weekend groups), and upon studying the discipline, they immediately conduct a test or an exam on it. Such a system is called "modular".
Other universities and colleges adhere to the classical correspondence form of education , where students are "read" orientation lectures immediately before the session, and then students, after listening to the course and additionally studying the necessary literature, pass attestation control in the form of tests and exams.
The correspondence form is convenient for those categories of citizens who are not able to regularly attend classes at a college or university. This form is also suitable for combining study and work in an enterprise. At the same time, at the request of the student, during the session, the educational institution may issue a certificate-call, which is the basis for employers to grant study leave to the student.
A separate item should be highlighted "Correspondence education using information technology" or "Distance learning"
This form of organization of the educational process involves the use of a computer with access to the Internet. There are various ways for students to obtain study materials. In most cases, these are online lectures using special software, webinars.
Attestation activities for this form of education can also be carried out online, using information technology, but more often teachers send students control and practical work by e-mail or to the personal account of an educational Internet resource. To help students remote form provide access to the electronic library of the educational institution, where everyone can find the necessary material on the topics studied.
To help students remote form provide access to the electronic library of the educational institution, where everyone can find the necessary material on the topics studied.
The duration of part-time college education in secondary vocational education programs is from 3.5 to 5 years.
The term of study at a university for undergraduate programs is usually 4.5-5.5 years, for specialist programs on average 5.5-6 years, for master's programs 2-2.5 years.
As well as full-time and part-time forms of education, part-time education can be implemented with a reduction in the term of study for graduates of colleges and technical schools entering a specialized field of study, or students receiving a 2nd higher education under a bachelor's or specialist's program at a university.
Benefits:
- Opportunity to combine work and education
- Relatively little time is devoted to the study of disciplines - often only this option is suitable for pregnant women or students already caring for young children.
 This form is in great demand among people working in an irregular schedule.
This form is in great demand among people working in an irregular schedule.
Disadvantages:
- Low educational attainment
- No respite from the army
- Inability to receive a scholarship
- Students of the correspondence department practically do not participate in the activities and student life of the educational institution
4. External study at a college or university.
This form assumes that a student of a college or university independently masters the educational program, and the educational institution conducts control and certification of the student, followed by the issuance of a document confirming the level of qualification of the graduate.
i.e. the educational institution does not conduct classroom lectures in which the student could master the material.
The term of study is calculated based on the requirements of the state standard, where, as a limit on the number of possible disciplines passed by a student, there is a figure - 20 disciplines per year.
Benefits:
- The fastest way to get education and qualifications.
Drawbacks:
- Difficulty of self-study
- Unable to use student benefits
what are the types of education at school in the Russian Federation, what is suitable for your child
Forms of education in Russia
Basic general education in our country is compulsory (Article 66 of the Federal Law "On Education in the Russian Federation"). Every citizen must complete at least 9 classes.
There are two forms of education (Article 17 of the Federal Law "On Education in the Russian Federation"):
- in organizations engaged in educational activities, simply - in schools;
- outside of such organizations.
What forms of education exist?
Outside educational institutions, education takes place in the form of family education (from grades 1 to 9) and self-education (grades 10–11).
Let's consider each form of education in more detail.
Forms of education in the organization
Public or traditional private schools offer three forms of education: full-time, part-time or part-time. You can go to any of them both in the primary grades, and in the middle and senior levels.
<
What is full-time education
In full-time education, the child goes to school five or six days a week, obeys its schedule, regularly receives grades and is certified. In legal language, this is called "being in the contingent of an educational organization."
Ideally, a student, like a blotter, absorbs the teacher's knowledge and wisdom, and during breaks has fun with classmates. In life, many parents are dissatisfied with the quality of school education, and children are faced with bullying.
Full-time education is suitable if:
- the child likes going to school, he cannot imagine himself without his class;
- you cannot devote much time and resources to your child's education;
- the child is not accustomed to discipline and needs a rigid framework from the outside.
Home-based education is a variation of full-time education. It is organized for children who, due to illness, cannot attend classes within the walls of the school. Please note: a variation, but not an independent form of learning.
What is part-time education
In part-time education, the child is enrolled in school, but goes there several times a week or less to turn in and receive homework. At the same time, he must be certified together with the class: if today they write a control, you must be present.
Schools transfer children to part-time education reluctantly and quite rarely. Firstly, because of unnecessary trouble for teachers, and secondly, so as not to create precedents. “Why can’t Petrov go to school, but I can’t ?!”
Part-time education is suitable if:
- the child easily learns the program from textbooks, without the help of teachers;
- you want your child to have a little more free time, but not lose contact with peers;
- The child's sports or creative schedule does not coincide with the school schedule.
Part-time education
In part-time education, the child does not go to school and masters the program on his own, with the help of tutors or online resources. But he is in the contingent of the school, which means that you cannot change the program, skip classes, and you will have to adhere to the certification schedule.
True, tests can be taken remotely: through the school website or, for example, via Skype. In the law, this is called "implementation of educational programs using e-learning and distance learning technologies." In other words, distance learning is not its independent form, it is only a way of organizing the educational process.
Public schools are reluctant to transfer students to part-time education. After all, legally, when receiving education at school (no matter in what form), the responsibility for its quality lies with the administration and teachers. If the correspondence student is poorly prepared and does not pass the certification, they will ask the teachers.
Distance learning is suitable if:
- the child masters the program very well;
- the family moves frequently or travels a lot;
- the child is professionally involved in sports or creative work.
Forms of education outside the organization
The main difference from education in the organization is that the responsibility for the quality of knowledge lies not with the school, but with the parents or the student himself.
Parents are obliged to provide the child with basic general education. Therefore, before receiving a certificate for grade 9, education outside of school is called family education. The decision to switch to this form is made by mom and dad, taking into account the interests of the child.
In grades 10–11, and also if an adult person did not finish his studies at one time and decided to catch up, this form is called self-education. Responsibility is on the student.
What is family education
Family education (FO) as a form of education is flexible and variable. Parents have the right to choose any program and organize the educational process in different ways. No one will ask how the child specifically learns, the main thing is that he passes certification.
Parents have the right to choose any program and organize the educational process in different ways. No one will ask how the child specifically learns, the main thing is that he passes certification.
Attestations on the family form and on self-education are taken externally. After all, external studies are not a separate form of education, but a form of certification in family education and self-education.
<>
Let's look at the main types of family education.
- Homeschooling . The child studies in the family and is attached to the school several times a year to pass intermediate certifications. Parents can teach themselves, hire tutors or connect online schools. In the latter case, family education is often confused with home and distance learning, but, as you already understood, these are different things.
- Unschooling . The same, only the child does not adhere to any program and is not attached to the school for certification until 9class.
- Alternative schools . Parents almost completely delegate the education of the child, but carefully choose the system. These can be Montessori or Waldorf schools, democratic schools or one-day schools, educational institutions working according to various author's methods, and, of course, digital schools.
The family form of education is suitable if:
- the child is closely in the classical school, he wants to learn more, better and faster;
- the child combines professional sports or concert activity with studies;
- he cannot keep up with the pace of other children and needs a special approach;
- the child has conflicts with classmates or teachers;
- the child is in poor health but does not have a disability, or does not like the option of home schooling;
- the family is not satisfied with the traditional school system, there is no contact with the school administration and teachers;
- the family often moves or lives in another country, but wants the child to have a Russian certificate.

<