Social skills at school
Social Skills: Promoting Positive Behavior, Academic Success, and School Safety
Good social skills are critical to successful functioning in life. These skills enable us to know what to say, how to make good choices, and how to behave in diverse situations. The extent to which children and adolescents possess good social skills can influence their academic performance, behavior, social and family relationships, and involvement in extracurricular activities. Social skills are also linked to the quality of the school environment and school safety.
While most children pick up positive skills through their everyday interactions with adults and peers, it is important that educators and parents reinforce this casual learning with direct and indirect instruction. We must also recognize when and where children pick up behaviors that might be detrimental to their development or safety. In the past, schools have relied exclusively on families to teach children important interpersonal and conflict resolution skills.
However, increased negative societal influences and demands on family life make it imperative that schools partner with parents to facilitate this social learning process. This is particularly true today given the critical role that social skills play in maintaining a positive school environment and reducing school violence.�
Contents
- 0.1 Consequences of Good Social Skills�
- 0.2 Consequences of Poor Social Skills
- 0.3 Impact on School Safety
- 0.4 Defining Types of Social Skills
- 0.5 Identifying Social Skills Deficits�
- 0.6 Social Skills Interventions
- 0.7 Examples of evidence-based social skills programs
- 1 Related
With a full repertoire of social skills, students will have the ability to make social choices that will strengthen their interpersonal relationships and facilitate success in school. Some consequences of good social skills include:
- Positive and safe school environment.
- Child resiliency in the face of future crises or other stressful life events.
- Students who seek appropriate and safe avenues for aggression and frustration.
- Children who take personal responsibility for promoting school safety.
Consequences of Poor Social SkillsREAD MORE: Best Appetite Suppressant: 5 Hunger Control Supplements Complete Guide
Students with poor social skills have been shown to:
- Experience difficulties in interpersonal relationships with parents, teachers, and peers.
- Evoke highly negative responses from others that lead to high levels of peer rejection.� Peer rejection has been linked on several occasions with school violence.
- Show signs of depression, aggression and anxiety.
- Demonstrate poor academic performance as an indirect consequence.
- Show a higher incidence of involvement in the criminal justice system as adults.

Given the demonstrated relationship between social skills and school safety, schools are increasingly seeking ways to help students develop positive social skills, both in school and in the community. Social skills related to school safety include:
- Anger management
- Recognizing/understanding others' point of view
- Social problem solving
- Peer negotiation
- Conflict management
- Peer resistance skills
- Active listening
- Effective communication
- Increased acceptance and tolerance of diverse groups
In isolation, social skills are not sufficient to ensure school safety; interventions should not be limited to student instruction and training. Change in the school culture should be facilitated by infusing social skills training into a comprehensive system of school safety and discipline policies, emphasizing relationship-building between students and faculty (teachers and administrators) and between schools and families, and providing effective behavior management and academic instruction.
Defining Types of Social SkillsREAD MORE: Red Boost Reviews – Ingredients, Benefits, Pros and Cons
While there are hundreds of important social skills for students to learn, we can organize them into skill areas to make it easier to identify and determine appropriate interventions. For example, the “Stop and Think” program organizes skills into four areas:
- Survival skills (e.g., listening, following directions, ignoring distractions, using nice or brave talk, rewarding yourself)
- Interpersonal skills (e.g., sharing, asking for permission, joining an activity, waiting your turn)
- Problem-solving skills (e.g., asking for help, apologizing, accepting consequences, deciding what to do)
- Conflict resolution skills (e.g., dealing with teasing, losing, accusations, being left out, peer pressure)
Prior to determining the best means to help a student develop better social skills, it is important to understand specifically what a student can and can't do. It is crucial to assess and classify the nature of a child's social skill deficits in order to devise and implement the most appropriate intervention.�
It is crucial to assess and classify the nature of a child's social skill deficits in order to devise and implement the most appropriate intervention.�
Children may experience difficulty performing a skill:
- Due to lack of knowledge (acquisition deficits), e.g., the child does not know the skills or does not discriminate when a skill is appropriate. For example, a child grabs a pencil from a peer in class when she needs one because she does not know how to appropriately ask to borrow it.
- Consistently despite knowledge (performance deficits), e.g., the child knows how to perform the skills but fails to do so consistently or at an acceptable level of competence. For example, although the child understand that he should raise his hand to speak in class, and does so much of the time, he will sometimes blurt out a comment without raising his hand.
- To a sufficient degree or level of strength (fluency deficits), e.
 g., the child knows how to perform skill and is motivated to perform, but demonstrates inadequate performance due to lack of practice or adequate feedback. For example, a student has learned what to say and do when confronted with bullying behavior, but her responses are not yet strong enough to be successful.
g., the child knows how to perform skill and is motivated to perform, but demonstrates inadequate performance due to lack of practice or adequate feedback. For example, a student has learned what to say and do when confronted with bullying behavior, but her responses are not yet strong enough to be successful. - Due to competing skill deficits or behaviors, e.g., internal or external factors interfere with the child demonstrating a learned skill appropriately. For example, depression, anxiety, hyperactivity, or negative motivation can interfere with demonstration of appropriate conflict resolution skills, even though the skills have been taught and learned.
Social Skills InterventionsREAD MORE: Exipure Review : Weight loss Pills Dosage, Works, Uses
Effective social skills programs are comprised of two essential elements: a teaching process that uses a behavioral/social learning approach and a universal language or set of steps that facilitates the learning of new behavior. Interventions can be implemented at a school-wide, specific setting, classroom, or individual level, but at all levels the emphasis is on teaching the desired skill, not punishing negative behaviors.
Interventions can be implemented at a school-wide, specific setting, classroom, or individual level, but at all levels the emphasis is on teaching the desired skill, not punishing negative behaviors.
Facilitate learning through normal activities. Teachers and parents must take advantage of incidental learning, in which naturally occurring behaviors or events are used to teach and reinforce appropriate social behavior. Adults can reinforce demonstrated positive social skills by praising children when they behave correctly, or offer alternatives to poor decisions to teach the more appropriate behavior. It may be necessary when working with children who have particular difficulty to intentionally “catch” them doing the right thing or devise situations in which they can make a good choice.�
Address environmental factors. The school or home environment can affect a child's ability to learn and perform good social skills. If a child is experiencing difficulty demonstrating a particular skill, it is best to first evaluate the environment to determine what might interfere with the child's appropriate acquisition of that skill. For instance, a student may be unruly at the beginning of the day because the teacher needs to establish more specific routines for coming into class, hanging up coats, checking in, etc. Addressing environmental obstacles like this also will benefit all children in that environment.
For instance, a student may be unruly at the beginning of the day because the teacher needs to establish more specific routines for coming into class, hanging up coats, checking in, etc. Addressing environmental obstacles like this also will benefit all children in that environment.
Address individual factors. Some children need more intensive, personalized training because of individual factors, such as a disability. These interventions might be aimed at children experiencing a specific difficulty or those who have previously been identified as at risk for behavior problems. For example, studies have shown that children with mild disabilities tend to exhibit deficient social skills and excess problem behaviors more than students without such disabilities. Interventions aimed at at-risk students are based on individual assessment of the particular child's skills and deficits.� Selected interventions aim to prevent existing behavior problems from developing into more serious ones.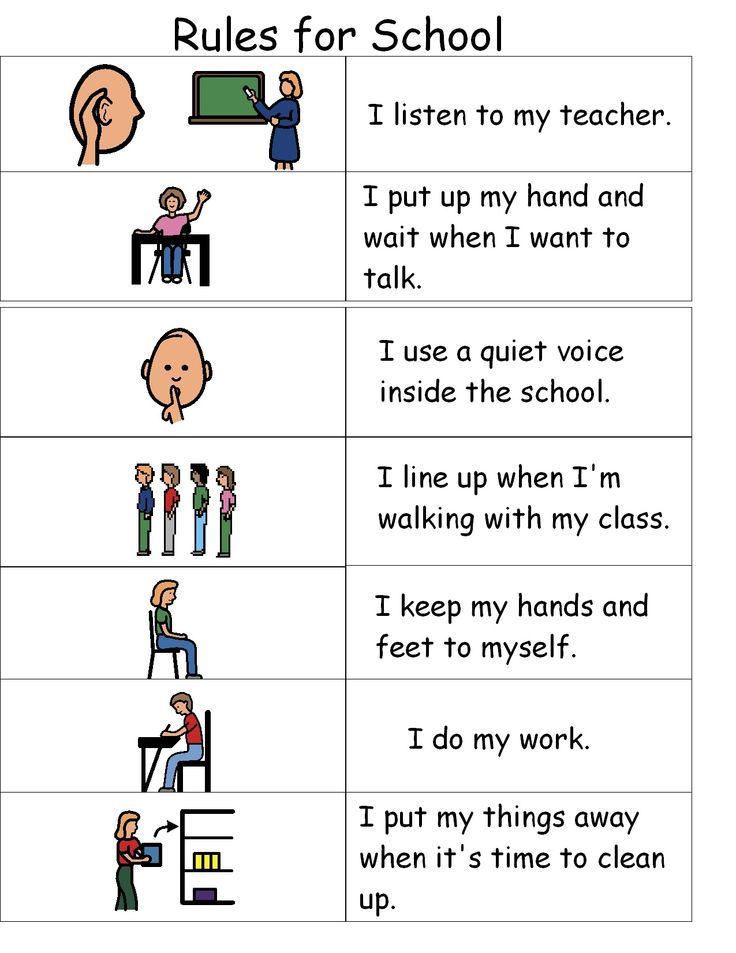
Social skills training should:
- Focus on facilitating the desirable behavior as well as eliminating the undesirable behavior.
- Emphasize the learning, performance, generalization, and maintenance of appropriate behaviors through modeling, coaching, and role-playing. It is also crucial to provide students with immediate performance feedback.
- Employ primarily positive strategies and add punitive strategies only if the positive approach is unsuccessful and the behavior is of a serious and/or dangerous nature.
- Provide training and practice opportunities in a wide range of settings with different groups and individuals in order to encourage students to generalize new skills to multiple, real life situations.
- Draw on assessment strategies, including functional assessments of behavior, to identify those children in need of more intensive interventions as well as target skills for instruction.

- Look to enhance social skills by increasing the frequency of an appropriate behavior in a particular situation. This should take place in “normal” environments to address the naturally occurring causes and consequences.
When planning social skills training programs, schools should:
- Include parents and other caregivers, both to help develop and select interventions and as significant participants in interventions. (Parents and caregivers can help reinforce the skills taught at school to further promote generalization across settings.)
- Focus on all age groups, including children below the age of 9 who are often bypassed due to the erroneous belief that they will “grow out of it.”
- Avoid a “one size fits all” approach and adapt the intervention to meet the individual or particular group needs. Students who speak English as a Second Language might need intensive social skill instruction to promote acculturation and peer acceptance.
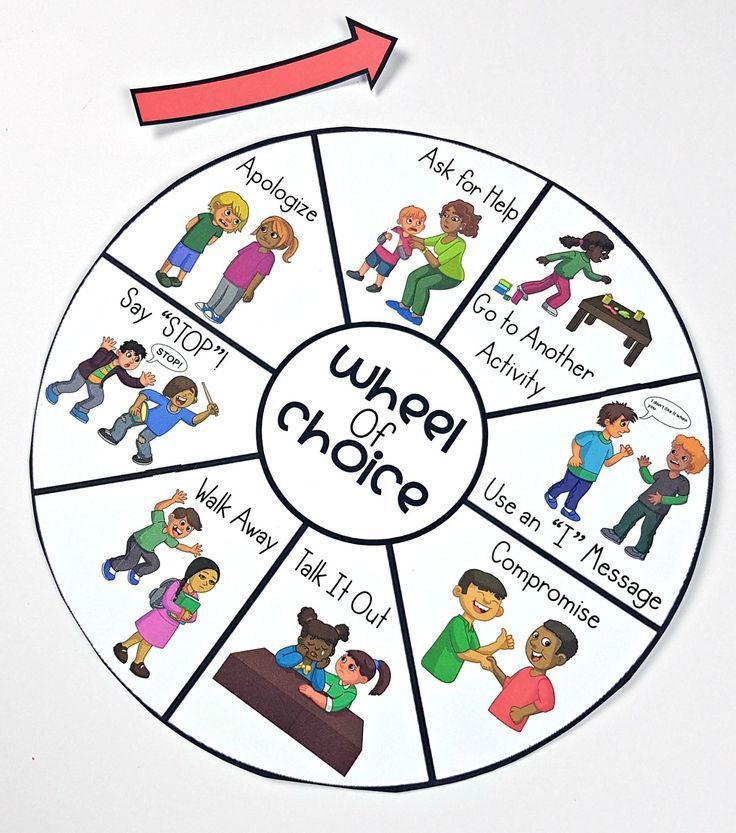 Children with disabilities might need adaptive curriculum and learning strategies. Most children will need a combination of different strategies that are matched to their particular deficits and backgrounds.
Children with disabilities might need adaptive curriculum and learning strategies. Most children will need a combination of different strategies that are matched to their particular deficits and backgrounds.
Often school administrators or mental health professionals opt to introduce one of the many empirically supported, commercially published programs into their schools. Effective existing social skills training programs include:
- “Stop and Think” Social Skills Program (Knoff): Part of Project ACHIEVE (Knoff and Batsche). Has demonstrated success in reducing student discipline referrals to the principal's office, school suspensions, and expulsions; fostering positive school climates and prosocial interactions; increasing students' on-task behavior; and improving academic performance. http://www.projectachieve.info
- Primary Mental Health Project (Cowen et al.
 )� Targets children K-3 and addresses social and emotional problems that interfere with effective learning.� It has been shown to improve learning and social skills, reduce acting, shyness and anxious behaviors, and increase frustration tolerances.� http://www.sharingsuccess.org/code/eptw/profiles/48.html
)� Targets children K-3 and addresses social and emotional problems that interfere with effective learning.� It has been shown to improve learning and social skills, reduce acting, shyness and anxious behaviors, and increase frustration tolerances.� http://www.sharingsuccess.org/code/eptw/profiles/48.html - The EQUIP Program (Gibbs, Potter, & Goldstein) Offers a three-part intervention method for working with antisocial or behavior disordered adolescents. The approach includes training in moral judgment, anger management/correction of thinking errors, and prosocial skills. http://www.researchpress.com/scripts/product.asp?item=4848#5134
- The PREPARE Curriculum (Goldstein) Presents a series of 10 course-length interventions grouped into three areas: reducing aggression, reducing stress, and reducing prejudice. It is designed for use with middle school and high school students but can be adapted for use with younger students.
 http://www.researchpress.com/scripts/product.asp?item=5063
http://www.researchpress.com/scripts/product.asp?item=5063 - The ACCEPTS Program (Walker et al) Offers a complete curriculum for teaching effective social skills to students at middle and high school levels. The program teaches peer-to-peer skills, skills for relating to adults, and self-management skills.
For further resources go to www.nasponline.org.
� 2002, National Association of School Psychologists, 4340 East West Highway, Suite 402,�Bethesda, MD, 20814, (301) 657-0270, fax (301) 657-0275, TTY (301) 657-4155.
Why Social Skills Are Key to Learning
You may be hoping your child will learn how to read and write in the first few months of preschool or kindergarten. But there are many other skills that she needs to master before an academic focus is appropriate. Studies show that the most important skills to learn in the beginning of the year are social: cooperation, self-control, confidence, independence, curiosity, empathy, and communication.
The First Basic Skills: The Four Cs
Here are a few examples of teachers' goals for the beginning of the school year. Ask your child's teacher to tell you about her objectives and her suggestions on how you can support these skills at home.
- Confidence: One of the first skills teachers focus on is the development of your child's sense of confidence or self-esteem. This means helping her feel good about who she is, both individually and in relationship to others. This is a lifelong skill that will help her feel competent now and as she continues in her schooling.
- Cooperation: Games, stories, and songs help your child learn how to work with others — no small task at this age! This teaches him how to empathize and to get along with others.
- Curiosity: Perhaps one of the most important skills she needs to develop at this stage is a true thirst for learning. Her teacher will use a wide variety of interesting materials and ideas to engage your child's natural curiosity.
- Communication: Expressing himself and representing his ideas, feelings, and knowledge about the world is a key skill for your child. It is at the core of all reading, writing, math, and science skills.
What You Can Do
Help your child develop essential social and emotional skills by making connections with school friends at home. Ask her whom she would like to invite for a playdate. It is often easier for children to make friends in their own space, one on one, than in school. Many teachers have found that a child who is having difficulties making friends or sharing in a large group often can make a close connection to a new friend on her "home turf." This relationship can then carry over to the classroom setting. Once there is a connection to one child in the classroom, more are soon to follow!
The Importance of Play
For your young child, play is important work. He grows, learns, and investigates the world through play. This happens through complex play activities that invite him to think, problem-solve, and participate in fantasy. When your child engages in play, he has to plan, create a focus, and strive for a goal — all essential life and work skills. Your child's teacher should provide play situations throughout your child's day. She may first introduce letters and numbers through meaningful dramatic play, block-building, and literature/music experiences. So don't fret if your child comes home saying he played all day! You can be sure that with his teacher's guidance and his own innate curiosity, he was applying very important problem-solving, reading, math, and science skills right in the midst of his play.
This happens through complex play activities that invite him to think, problem-solve, and participate in fantasy. When your child engages in play, he has to plan, create a focus, and strive for a goal — all essential life and work skills. Your child's teacher should provide play situations throughout your child's day. She may first introduce letters and numbers through meaningful dramatic play, block-building, and literature/music experiences. So don't fret if your child comes home saying he played all day! You can be sure that with his teacher's guidance and his own innate curiosity, he was applying very important problem-solving, reading, math, and science skills right in the midst of his play.
The experiences your child receives in the beginning of the year provide the foundation that will enable her to become an enthusiastic lifelong learner — enthusiastic because she has discovered that learning is fun as well as meaningful.
Soft skills or social skills for a student: 85% of success in life
Harvard and Stanford believe that a student's academic knowledge is only 15% of success in his further education, in building a career and in life.
Russian schools actively download knowledge into the heads of our children, but do not teach them social skills, the so-called soft skills - leadership, teamwork, organizational skills, etc. Namely, they allow you to apply the acquired knowledge and achieve your goals: a prestigious university, a successful career, a happy family and true friendship. nine0003
A study of Fortune 500 CEOs found that long-term and sustained job success was 75% social skills and only 25% academic.
Therefore, European education has long included the training of soft skills, without which it is difficult to succeed in the modern world. Many of these traits are innate and inherent in every child, but they need to be cultivated and developed. Here are some critical social skills that will help any student reach their goals in life. nine0003
TEAM WORK
The ability to listen, the ability to see a common goal and find common ground between a common idea and personal ambitions.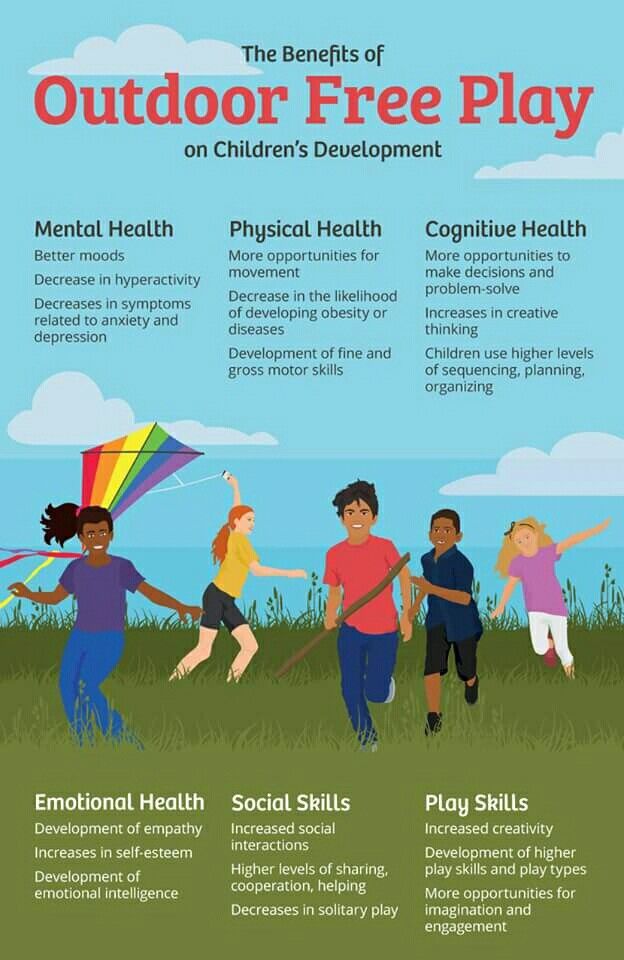 Willingness to help others and support in a difficult situation, the ability to convince and find a compromise.
Willingness to help others and support in a difficult situation, the ability to convince and find a compromise.
Check if your child can:
- do things with other children?
- help someone solve their study question?
- to make sure that not only he, but his entire team achieves the goal? nine0024
How it is taught in a foreign school:
- team activities: games, performance, volunteer programs;
- joint academic projects, when the project can be defended only by the whole team;
- competitions between "Houses" for students studying on a full board basis.
Join our Telegram channel!
Be the first to know about discounts, events and important news. nine0045 We promise - it will be interesting!
LEADERSHIP
To be a leader means to be a person whom everyone else recognizes as having the right to make responsible decisions for the entire team.
Check if your child can:
- to become a leader for other children: inspire and lead them?
- understand and feel other people?
- to set other children tasks corresponding to their abilities and character and to achieve their fulfillment? nine0024
How it is taught in a foreign school:
- Supervision of junior schoolchildren and beginners by high school students;
- Numerous clubs and hobby classes are sure to resonate in the soul of any student, and he will take the initiative in the area that interests him and gather his team of like-minded people.
We are looking for leaders, but not from the category of "president of the chess club", but from those who, faced with a problem, can at the right time take the lead of the team and lead it to the goal
- Laszlo Bock, Vice President of Recruitment, Google
CREATIVITY
A creative person is able to find non-standard, completely new solutions in familiar situations, he is able to invent and implement new ideas.
Check if your child can:
- Suggest an idea for a gala evening, fashion design or pop star poster?
- tell your friends the story he made up? nine0024
- come up with an idea for a new computer game or mobile application?
How it is taught in a foreign school:
- When solving a problem, the student will be asked not only to give the correct answer, but also to find 10 different solutions;
- Students focus on both academic knowledge and extracurricular activities - music classes, theater productions and acting skills, development of artistic skills. It is easier for a child with a broad outlook to find a non-standard approach to solving a problem. nine0024
COMMUNICATION
The ability to communicate, openness and the ability to establish contact with other people, as well as to make the right impression on them.
Check if your child can:
- Is it clear and interesting to express your ideas and thoughts?
- speak confidently with a group of your peers, with a school principal, with other adults?
- perform in front of an audience of 100 people?
How it is taught in a foreign school:
- Students are encouraged to actively participate in discussions in the classroom.
 And the final assessment is influenced by the student's involvement in lectures and seminars and his ability to defend his point of view;
And the final assessment is influenced by the student's involvement in lectures and seminars and his ability to defend his point of view; - Schoolchildren are constantly surrounded by their peers and implement academic projects together, participate in sports and creative events, attend hobby groups;
- Career days and meetings with universities are regularly held for high school students. Schools set aside time to develop a personal resume, self-presentation skills and interviews. nine0024
MANAGEMENT
This is the ability to bring people together to achieve a goal and inspire yourself and others to action. Initiative, demanding of oneself and others, attention to detail, the ability to delegate or do it yourself - all these are important qualities of an organizer.
Check if your child can:
- organize your time so that you can keep up with your studies and take part in extra school activities? nine0024
- put together a team to run cross country together or organize a party?
- make quick decisions when things don't go as planned?
How it is taught in a foreign school:
- time management skills are the first thing a student learns.
 Unlike Russian students, European students do not study from morning to evening. The whole day is scheduled by the clock, there is time for study, sports, hobbies, homework and, of course, time for rest; nine0024
Unlike Russian students, European students do not study from morning to evening. The whole day is scheduled by the clock, there is time for study, sports, hobbies, homework and, of course, time for rest; nine0024 - Participation in numerous school events requires a variety of skills from a student, including the ability to organize an exhibition, a holiday, a performance, a debate, a sports match, and much more.
POSITIVE
Faith in yourself and in other people. This is such a view of the world in which a person can look at events from different angles and prefers to find positive in everything that surrounds him.
Check if your child can:
- keep a smile on your face despite the challenges?
- to fight and not give up, even when you fail to achieve the goal?
- try to solve your problems on your own, without immediately resorting to your help?
How it is taught in a foreign school:
- Support and attention of teachers, mentors and high school students.
 The school is well aware of the difficulties students face and is always ready to help with advice and pay attention to positive events. nine0024
The school is well aware of the difficulties students face and is always ready to help with advice and pay attention to positive events. nine0024 - A healthy competitive environment helps students focus on their goals and not on temporary setbacks.
CURIOSITY
Intellectual curiosity, thirst for new knowledge, interest in the world around and desire for new experiences. This is a natural quality of any child and it is important to preserve it.
Check if your child can:
- look up from your phone or tablet and look around when you are driving? nine0024
- when you find yourself in a new place, try to find out something about it?
- ask questions about how the world works?
How it is taught in a foreign school:
- The task of every teacher is not only to prepare a student for the final exams, but also to make him fall in love with his subject. The first thing that Russian children and parents notice is that students in European schools love to study.

- Well-equipped classrooms and laboratories - here you can study not only theory, but also try everything in practice. Chemistry, physics, biology become especially exciting. nine0024
- School activities also include guest lecturers and thematic excursions. Children can learn first-hand about the subject and specialties: who you can become in the future, how you can apply the acquired knowledge in practice, what kind of employees employers want to see.
Most children are not very self-confident. They worry about entering a new social situation, about learning new skills, about having to complete a new task, even more difficult. They seek help and support from friends, parents, teachers, and this is natural. nine0003
Studying in European schools, students develop their social skills, becoming more self-confident. These skills have nothing to do with intelligence, the ability to quote Shakespeare in the original, or mentally multiply three-digit numbers. But the ability of a child to clearly formulate thoughts, offer alternatives and respect someone else's point of view will make him successful in all areas of life. After all, as Henry Ford said, confidence is half the battle.
After all, as Henry Ford said, confidence is half the battle.
European schools help students develop their social skills. nine0003
They will not appear on your high school diploma or university degree.
But these abilities are important in order to enter a good university, successfully complete it and find a dream job, which means getting a pass to a happy life.
Contact the manager and choose school
by phone +7 (495) 935-85-45
through the request form on the website
See also:
What the school should develop (5 key skills) | British School MCS from MAGIC CASTLE Education
British education in the center of Moscow
Knowledge. Responsibility. Character.
SPECIAL PROJECT
The world is changing so fast that we cannot say with certainty what our life will be like in a year. What can we say about a more distant future - in 10-20 years. How to plan the education of a child so that he finds himself in a new world unknown to us, overcomes any difficulties and succeeds?
How to plan the education of a child so that he finds himself in a new world unknown to us, overcomes any difficulties and succeeds?
The overwhelming majority of experts agree on one thing: the main thing that we must give the child is a set of flexible skills that will determine his future success. The world's leading schools have integrated the development of soft skills into their curricula. Experts say that education, which is aimed not only at the academic result, but also at the development of the child's personality, opens up new horizons. nine0003
Natalie Kaminsky, founder and director of Magic Castle International School in Moscow, spoke to Forbes Education about why soft skills are so important, which ones need to be developed at school, and how high academic standards can be combined with the development of a child's personality.
Soft skills are needed everywhere: in business, art, science, family life. Thanks to them, a person becomes a leader, inspires, leads others, finds non-standard solutions and does not give up in difficult situations. It is important to think about their development at the earliest stages: most of the soft skills are laid from childhood. nine0003
It is important to think about their development at the earliest stages: most of the soft skills are laid from childhood. nine0003
With the right curriculum, school is an ideal environment for personal development. In addition to academic goals, Magic Castle International School aims to develop key soft skills in its students: a positive and effective attitude to learning, growth and overcoming difficulties, creativity, responsibility, social communication skills.
Self-confidence
The vast majority of people can formulate life goals that they would like to achieve. Unfortunately, when it comes to the implementation of the plan, everything is not so simple. Scientists* have found that self-confidence plays a key role in success. People who believe in their abilities are much more likely to achieve goals: they approach problems more constructively, do not give up when faced with difficulties, and remain optimistic. The task of the school is to teach the child not to be afraid of difficulties, to show that he can achieve high results. nine0045
The task of the school is to teach the child not to be afraid of difficulties, to show that he can achieve high results. nine0045
An overly complex educational program causes the child to lose faith in himself. Too simple - causes boredom and demotivates. In both cases, the child does not feel joy from completing tasks and pride in the result.
All children are different, they need different time to complete tasks and different levels of support from the teacher. We have seen from personal experience that with the right organization of education, every child can believe in himself and achieve outstanding academic results. The task of our teachers is not only to explain the material clearly, visually and as interactively as possible, but also to make sure that each student can independently cope with the completed task. We adapt the program for each student: we add non-standard and complicated tasks if the child easily copes with the topic, and we provide additional support in cases where the material causes difficulties
Motivation
It always seems impossible until it's done (Nelson Mandella).
Have you ever noticed that it costs one person to set a new world record, which seemed unattainable for many years, as less than a month passes - there are people who are able to repeat the achievement. So it was with the conquest of Everest, the 10-second barrier in the 100 meters, the triple Axel in figure skating. Why it happens? When we know that the goal is achievable, it is easier for us to motivate ourselves on the way to it. What makes leaders different? They strive for ambitious goals and find motivation within themselves, even if everyone around them finds the task incredibly difficult. Self-motivation helps to find the energy and desire to achieve your goals. nine0003
It is important to teach children to be constructive about failures and achievements . The words we say when we praise or criticize, inspire and encourage the child, the way the student thinks in situations of difficulty or success, are the key points of development throughout life.
Not only words, but also the environment, the atmosphere can contribute to the development of intrinsic motivation. Even elementary inscriptions on the walls of the school with motivating statements do their job. Moreover, the “Rules for cultivating self-confidence, responsibility and motivation” have become a mandatory annex to the contract. nine0003
All Magic Castle teachers are trained in how to praise and give feedback to children, and every phrase we use with students is carefully chosen to ensure a growth mindset.
The teacher must distinguish between praise and encouragement. It is necessary to encourage children constantly, and to praise - for concrete successes. Don't tell your child that he is smart. Tell him, “You did a great job! You did well." If the child did something wrong, first emphasize the positive aspects of this experience: “It's great that you are experimenting with paints. Let's make sure that after any experiments, your room remains clean. nine0003
Give your child a positive and personal growth mindset by paraphrasing his language - changing pessimistic scenarios.
"I can't do it."
"I'm stupid."
"I made a mistake again."
"I give up."
"I can't."
"I'm great at this."
"I need time. I'll try different strategies to solve this problem."
"I need more time. If I put in the effort, I'll get there."
"Mistakes help me learn." nine0045 "I can always do better. I will keep trying."
"I can't do it yet, but I'll learn. I'll put in more effort and I'll succeed."
"I tried and learned to do it. I got results because I put in the effort."
Responsibility
To be responsible means to be able to make decisions and bear responsibility for them, to lead people and organize the achievement of a common goal, to fulfill given promises, to be obligatory. The formation of responsibility in children begins at the age of 3-4 and is inextricably linked with the ability to show independence and initiative. nine0045
nine0045
An environment where a child is overprotected or where every step is planned in advance by an adult does not give the child the opportunity to make choices, learn from their mistakes, take initiative and, as a result, develop responsibility. After all, how can you be responsible for other people's decisions?
It is important to observe the principle: "More duties - more rights."
Each child should have an area of responsibility. For example, household chores might include cleaning, caring for pets or plants, loading/unloading the dishwasher or washing machine, or ironing your own clothes. nine0003
At Magic Castle International School, children not only take responsibility for their own learning, but also initiate new dishes on the menu, supervise equipment and order on school grounds, organize events and charity fairs, participate in decision-making regarding the eco-organization of school life and much more.
In today's world, the success of business and personal life is based on the ethics of decision making. That is why mindfulness, emotional intelligence and an open view of the world are of particular importance. We help our students to formulate their life position and values, including through participation in debates on important issues of politics, economics, ecology, and social development. nine0045
Creativity and critical thinking
The ability to think creatively is required not only for representatives of creative professions. This skill is becoming more and more in demand in a variety of professional fields. And there is nothing to be surprised at: the ability to find non-standard solutions and quickly respond to the situation is exactly what is needed in the face of constant change and instability. Creative and critical thinking can be developed and trained. And where else to do this, if not at school - after all, it is here that the child faces new challenges every day. nine0045
nine0045
The standard Russian school curriculum does not always give a child the opportunity to realize their creative potential, as it is primarily focused on the development of technical and standardized skills. Unfortunately, not all teachers are willing to make extra efforts to develop students' creativity.
We want our students to be able to critically evaluate information, generate new ideas, find innovative solutions and bring them to life. nine0003
A variety of practical and creative activities are an integral part of the British curriculum. Our students have the opportunity to realize their ideas in design or art classes; express their own point of view and ask questions in the lessons of history, physics, geography; look for non-standard solutions to practical problems; write your own poems and stories. We try to create an atmosphere of creativity: the school newspaper, mood board, meetings with interesting and inspiring people, career days, a literary magazine, a wall of poetry, annual video reports about class life - all this is an integral part of learning at our school. In addition, at Magic Castle, students discover their many talents during additional classes in art, music, vocals, sports, choreography, design, cooking, IT and many other subjects. nine0045
In addition, at Magic Castle, students discover their many talents during additional classes in art, music, vocals, sports, choreography, design, cooking, IT and many other subjects. nine0045
Communication skills
Negotiation, conflict resolution, building relationships - all these skills are considered key in the business environment and often predetermine a person's success not only in career but also in personal life. It is at school through communication with peers that children develop their social skills and form a model of behavior that they will follow in the future when resolving conflicts, persuading, and working in a team.
An atmosphere where the child does not feel safe and sees negative examples of communication - forceful resolution of disputes, aggression, bullying.
The task of the school is to create a comfortable environment where children, on the one hand, independently build relationships with their peers, resolve conflicts and prove their point of view, and on the other hand, always feel the support of a mentor and are confident in their safety. The school must define the boundaries and rules within which children learn through experience effective and ethical communication. nine0003
The school must define the boundaries and rules within which children learn through experience effective and ethical communication. nine0003
In addition to creating a comfortable environment, we purposefully practice social skills in the classroom.
In addition to creating a comfortable environment, we purposefully practice social skills in the classroom.
Presentations . Children develop the ability to organize information, illustrate it and present it to various audiences. Our students master different types of presentations - elevator pitch, powerpoint, TED TALKS.
Debate . Through participation in debates, children learn to understand the interests of the audience, find persuasive arguments, develop them and structure the information presented logically.
Negotiation . The ability to find a solution acceptable to both parties and to prevent a conflict situation is an indispensable skill both in everyday life and in future professional life.
The ability to find a solution acceptable to both parties and to prevent a conflict situation is an indispensable skill both in everyday life and in future professional life.
Storytelling / Storytelling is one of the most important skills in the world today. The ability to make your story exciting, emotional, and memorable will come in handy during presentations, debates, negotiations, and essay writing. nine0003
* Bandura, A. (in press). self-efficacy. In D. Matsumoto (Ed.) Cambridge dictionary of psychology . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
July 15 / 2020
#PARTNER_MATERIAL
OTHER SPECIAL PROJECT MATERIAL
What should school education be like to provide a child with a successful future? Parents are talking.
Dual certificate.