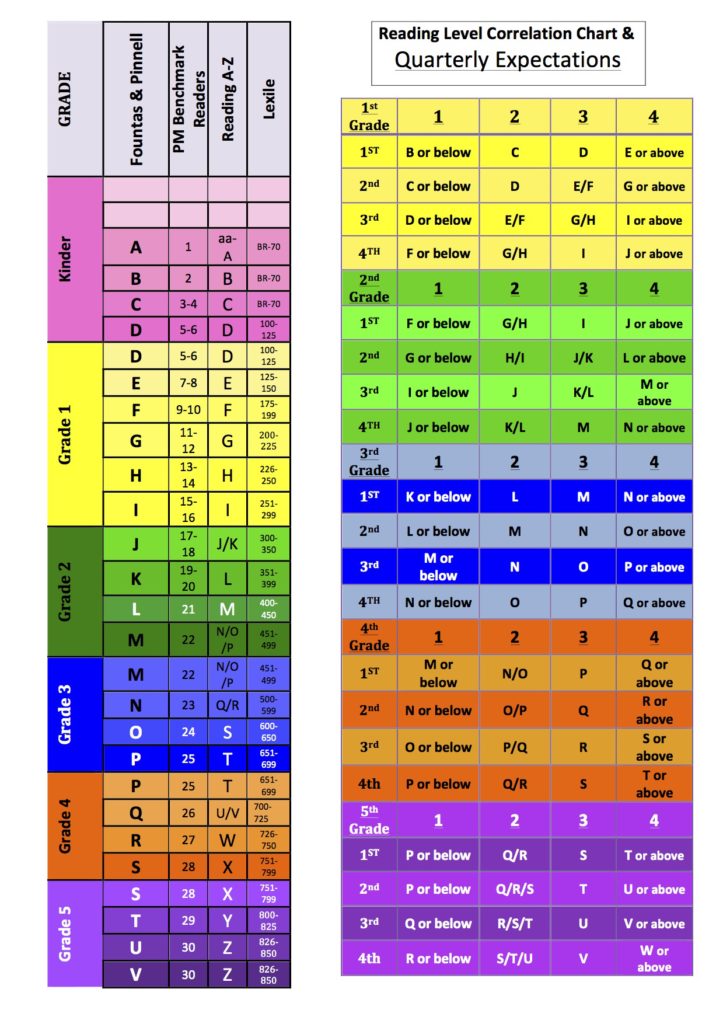
Student reading level chart
Determine Reading Ability Using a Reading Level Chart
A Reading level chart is an incredibly useful tool in the academic setting. It helps you make a lot of important reading decisions and figure out which reading level is right for you.
What Is a Reading Level Chart?
A reading level chart measures the word and sentence lengths based on grade-level ranges. Education experts create this system to communicate the difficulty of a text.
It can be helpful to determine what level of education a reader should ideally have before they would be able to comprehend the text. There are different level reading requirements associated with different age groups.
This chart determines what level a person should be based on their age and ability. It helps teachers and parents serve the children better by indicating how the text is most likely to be comprehended.
How Does Guided Reading Work?
Guided reading employs a standard scale to measure a child’s reading ability and works within a child’s instructional level.
A child is assessed and assigned a reading level based upon word knowledge, comprehension, and fluency. Levels range from A to Z, with level A representing the lowest level of difficulty and level Z representing the highest.
Reading anything above a certain level is frustrating, while anything below doesn’t allow enough learning.
However, teachers can work closely with their students to help them become better readers. They introduce increasingly challenging books that meet the instructional needs of each child based on their ability.
Does Reading Level Measure Intelligence?
Reading level is a tool for determining a person’s reading comprehension. It is calculated using a specific scale based on the standard text. This scale is by no means a measure of intelligence.
It is a guide for measuring which books are appropriate for what age range. As a reader grows older, their reading level increases.
Reading levels can also vary depending on the grade level the book is targeted for. It indicates how much a child knows compared to their peers at a particular grade level.
It indicates how much a child knows compared to their peers at a particular grade level.
Different Levels of Guided Reading
The reading level is determined by looking at the approximate grade level required to read a text comfortably. It is determined by how much schooling a reader needs to grasp the text altogether.
Leveled reading utilizes various assessment tools to determine how well a child reads. It then matches kids to books that are challenging enough for them to make progress.
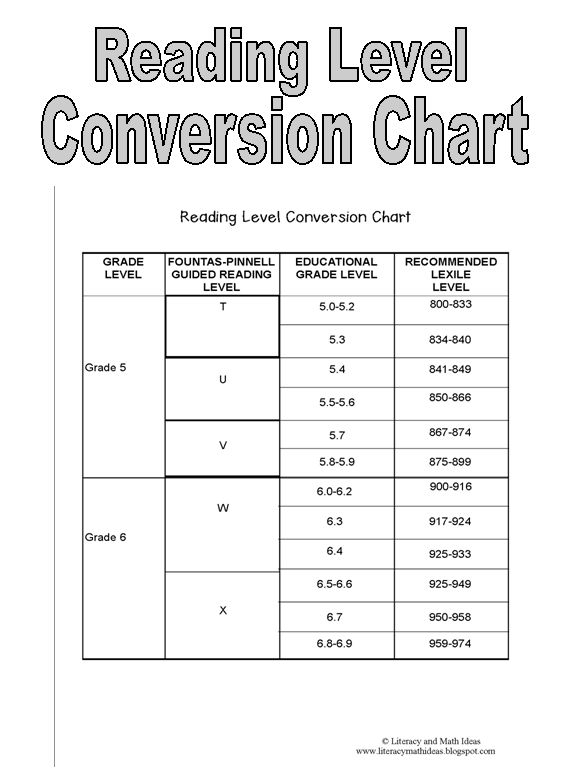
Teachers carefully select leveled texts for students using their current literacy behaviors and previous knowledge of content. They often use a conversion chart to show the correspondence of different reading levels to the parents.
The four most common leveled reading methods are:
- Guided Reading Level (GRL)
- Developmental Reading Assessment (DRA)
- Lexile Measures
- Accelerated Reader Level (AR)
Conclusion
A reading level chart is a tool to measure an individual’s reading ability. It provides them with appropriate reading material based on their age, developmental stage, and comprehension skills.
It provides them with appropriate reading material based on their age, developmental stage, and comprehension skills.
There are different approaches for measuring reading ability. The Guided Reading Level method is the most popular approach. It employs small guided reading books followed by reading levels for subsequent readings of large texts.
This chart is also helpful to determine appropriate materials to aid further development and reading efficacy of a child.
Frequently asked questions
What reading level should a grade 1 be at?
| Learning A-Z Text Leveling System | Grade | Reading Recovery |
|---|---|---|
| D | 1 | 5-6 |
| E | 1 | 7-8 |
| F | 1 | 9-10 |
| G | 1 | 11-12 |
What grade is a Level 3 reader?
Level 3 is for third and fourth grades.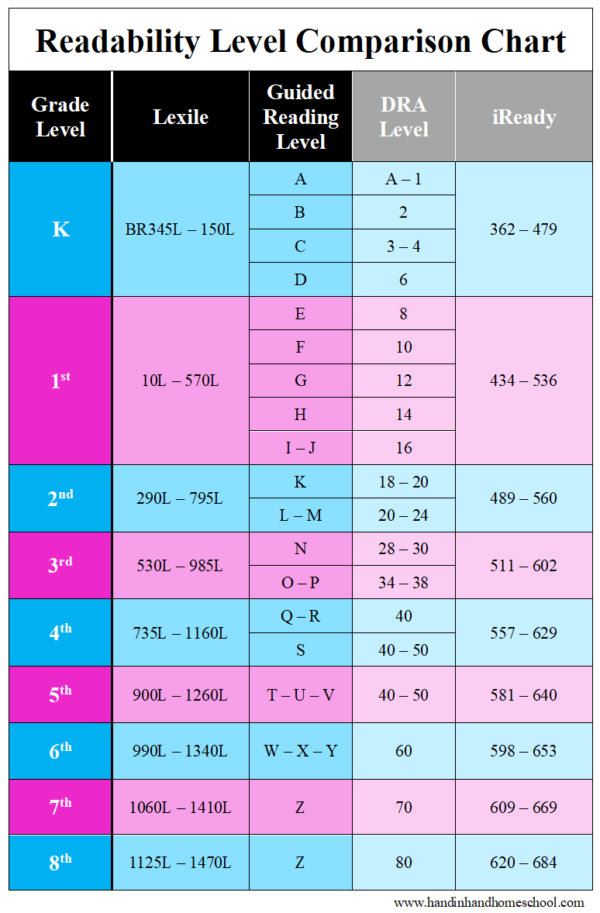
What are the levels of reading called?
The four levels of reading are elementary reading, inspectional reading, analytical reading, and syntopic reading. With Adler’s guide and some time and practice, you can reach syntopic reading level as well. Take a look at each of the four levels of reading below.
What reading level is a 10 year old?
Pre-K to 12 years old or 4th- to 6th graders. Children read sentences of approximately 10 words, with a maximum of 20 words per paragraph. An average book written at this level is between 20,000 and 40,000 words.
How do you determine a student’s instructional reading level?
- Levels A-J will assign a Benchmark Book.
- Levels Aa-Z2 are required to pass a benchmark.
- Listen to students’ recordings from reading a book or passage.
- Score all student recording via an online recording tool.
- A student’s recording of retellings helps you.
What level of reading should a 5 year old be on?
5 year olds should be able to read short vowel words like: ham, hat, lad, pet, vet, Ben, him, nip, wit, hop, Bob, dot,. You should keep in mind, I am talking about a 5 year old attending kindergarten for a few months. This content is not for your 5 year old yet (you won’t find it useful at this point).
What are the 5 levels of reading?
Readers undergo five stages of literacy development: emergent literacy, alphabetic fluency, word patterns, intermediate reading, and advanced reading.
What age is level 4 reader?
The typical reading age range: 4, 5 and 6 (Year 1 & Year 2). Levels 4 and 5 are also known as levels. Reading more words and sentences without having to use any power. Children who go to blue books should have confidence to sound out longer words, and they will be able to read with much less help than before.
What should a 6 year old be able to read?
- Draw a story to demonstrate comprehension.
- Do not sound out unfamiliar words.
- Find unfamiliar words by using images and context.
- When reading aloud, they self-correct.
- read familiar stories
- You will need to use some common punctuation and capitalization.
What does Level 1 mean in reading?
I read mostly short texts (eight to sixteen pages) and some short illustrated chapters (40 to sixty pages). Students have to maintain attention and memory over a long period of time while reading these books. These books have longer and harder sentences.
What is a Grade 4 reading level?
Kindergarten: A – 4. 1st Grade: 4 – 16. 2nd Grade: 16 – 24. 3rd Grade: 24 – 38. 4th Grade: 38 – 40.
What level should my 7 year old be reading at?
Level 7.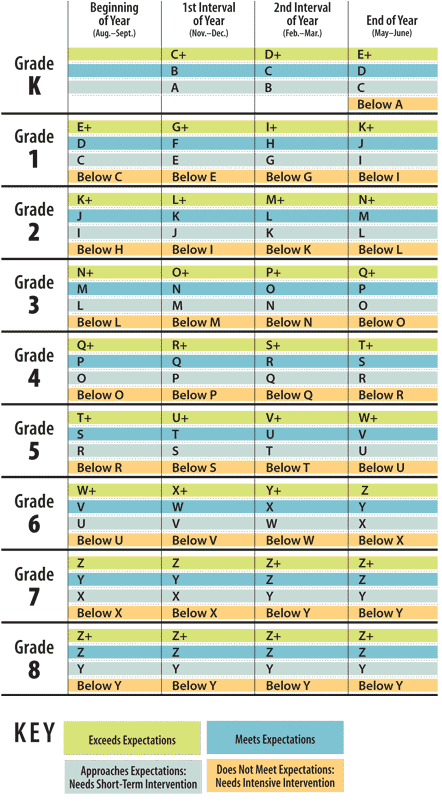 Age 6 – 7 years is recommended. Children can read complex sentences fairly fluently, observing punctuation. In addition to using expression, they don’t use illustrations.
Age 6 – 7 years is recommended. Children can read complex sentences fairly fluently, observing punctuation. In addition to using expression, they don’t use illustrations.
How do you evaluate reading level?
Children are guided by their teacher to read from a book that is considered standard for their grade level (a “benchmark” book) in order to determine reading levels using GRL. GRL books range from A to Z, with A being easiest.
What grade is all about reading level 1?
Pre-Reading (PK or K) and Levels 1 4 (grades K 3rd/4th) are included in the complete program. The teaching and lesson activities are multisensory with a strong emphasis on mastery learning based on reinforcement by game and review.
What are the 4 types of reading assessment?
There are four types of reading assessments that students use: Screening, Diagnostic, Progress Monitoring, and Summative.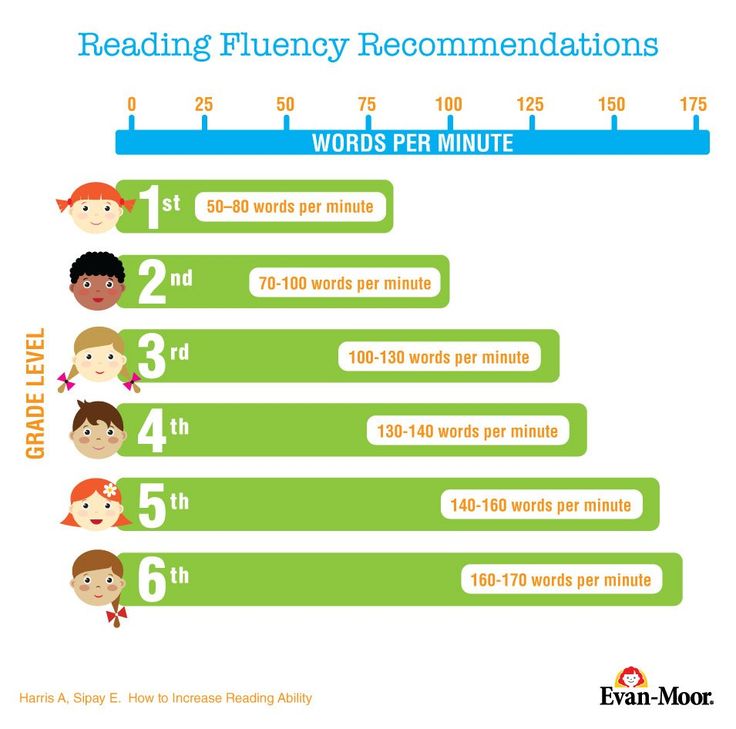
How do you determine reading difficulties?
- Assertion of single words is difficult.
- Problems with understanding sounds in words, sound order, or rhymes.
- Problems with spelling
- Writing letters into words.
- Substituting or omitting words.
- Poor reading comprehension
- Reading speeds (oral or silent) are slow.
What does Level 2 reading mean?
This level is for readers who are growing confident, but still need some assistance. These books, such as Frog and Toad Are Friends and Amelia Bedelia, feature more complex story lines, longer sentences, and more challenging words. Stories about mysteries and adventure, like Plants vs.
How does a teacher determine a student’s performance level?
The information about student learning can be assessed both through direct and indirect measures. Homework, quizzes, exams, reports, essays, research projects, case study analysis, and rubrics may cover direct measures.
Homework, quizzes, exams, reports, essays, research projects, case study analysis, and rubrics may cover direct measures.
What is the normal reading level?
Generally speaking, a person’s readability level is comparable to that of a seventh/8th grader (12 to 14 years old). A medical industry benchmark is actively held to this level as a standard for written guidelines.
What is a typical 2nd grade reading level?
Should a child read 50 to 60 words a minute in the beginning of the year and 90 words per minute by the end of the school year, 2nd grade readers should read 75 to 80 words / minute. Test this by giving your child a book from her reading list that she has not read, but will pique her interest.
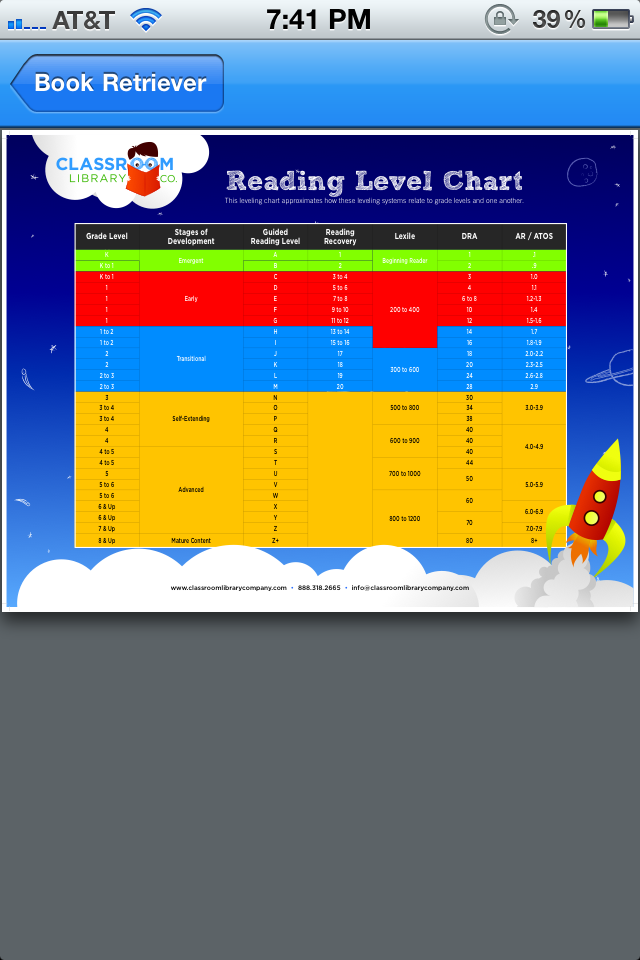
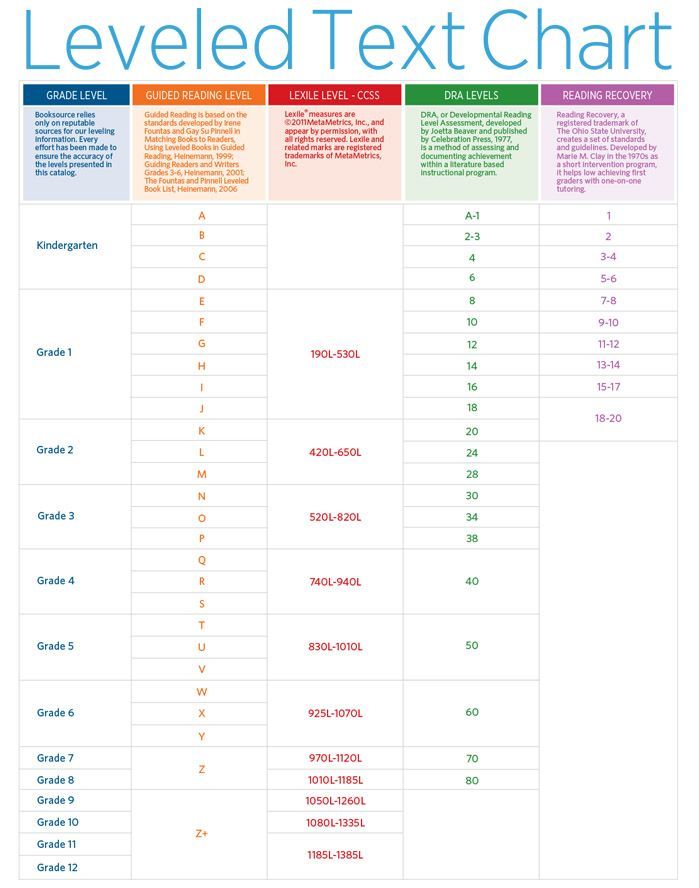
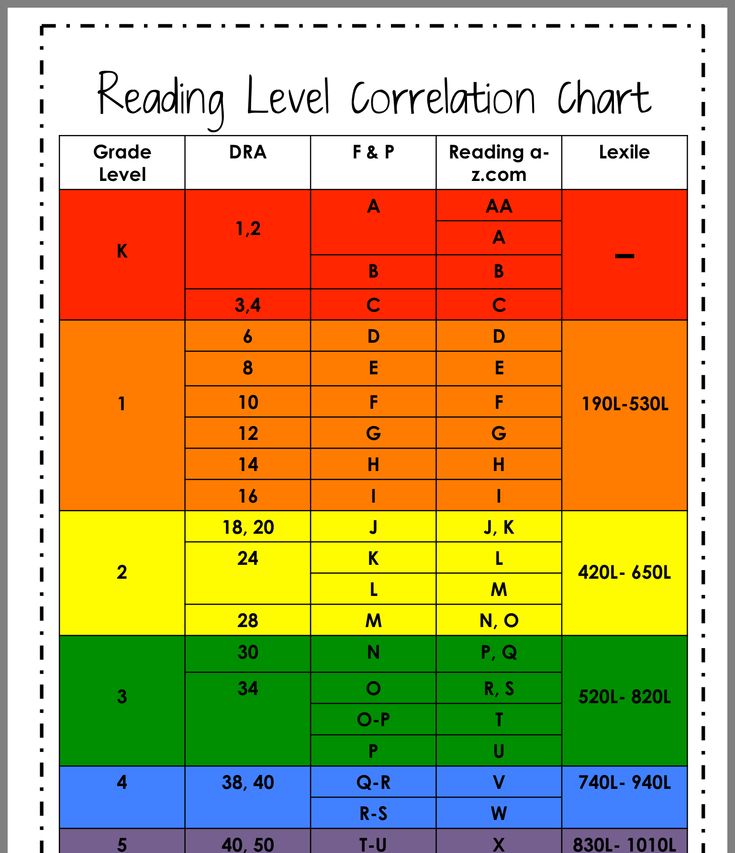
Booksource Reading Level Correlation Chart
Despite global supply chain issues, Booksource is making sure customers get their book orders.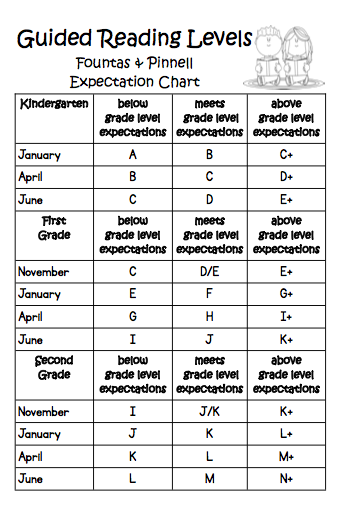 Click to learn more.
Click to learn more.
Reading Level Chart
Booksource knows that reading levels can serve as a helpful tool for educators. Use this Reading Level Chart to better understand how the common leveling systems correlate to one another and match students to texts that can be read with success. To start shopping for books by reading level, click on your desired Grade, Guided Reading or Lexile Level below.
Print PDF
To shop for books, tap on your desired Grade, Guided Reading or Lexile Level below. View more information by swiping left and right.|
Grade |
Guided |
Lexile |
DRA |
Reading |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Asset 5 Booksource relies only on reputable sources for our leveling information. |
|||||
|
Asset 5 Guided Reading is based on standards developed by Irene Fountas and Gay Su Pinnell. When leveling a title, Fountas & Pinnell consider factors such as text difficulty, vocabulary and developmental appropriateness. For example, a level P book is appropriate for grade three students in terms of both content and complexity. When necessary, Booksource relies on publisher guided reading levels. Every effort is made to ensure that reading levels designated by publishers are comparable to Fountas & Pinnell reading levels. |
|||||
|
Asset 5 Lexile levels are determined through quantitative evaluation of sentence length and difficulty. |
|||||
|
Asset 5 Developmental Reading Level Assessment, better known as DRA, was developed by Joetta Beaver and published by Celebration Press, 1977. DRA is a method of assessing and documenting achievement within a literature-based instructional program. |
|||||
|
Asset 5 Developed by Marie M. Clay in the 1970s as a short intervention program, Reading Recovery helps low achieving first-graders reach grade level standards through one-on-one tutoring. |
|||||
|
Emergent Asset 5Books for emergent readers tell simple stories, with one to two lines per page. They follow patterns and use repeated vocabulary. Emergent readers “read” from picture cues, and from hearing the story read aloud. Concepts are familiar. Emergent readers are developing an understanding of the alphabet and will recognize beginning letters and some sight words. They can attend to short read alouds featuring familiar narratives and concepts. Emergent readers may “pretend” read, as they recount a familiar story or rely heavily on picture cues. |
Kindergarten |
A |
BR |
A-1 |
1 |
|
B |
2-3 |
2 |
|||
|
C |
4 |
3-4 |
|||
|
D |
6 |
5-6 |
|||
|
Early Asset 5Books for early readers contain more pages and longer sentences. Early readers start to read simple stories and can sound out new words with one or two syllables. They will recognize and read some high-frequency words and begin self-monitoring for some comprehension. They predict words based on beginning sounds and picture cues. |
Grade 1 |
E |
190L-530L |
8 |
7-8 |
|
F |
10 |
9-10 |
|||
|
G |
12 |
11-12 |
|||
|
H |
14 |
13-14 |
|||
|
I |
16 |
15-17 |
|||
|
J |
18 |
18-20 |
|||
|
Transitional Asset 5Books for transitional readers include a larger core of frequently-used words, new vocabulary and longer words that require chunking. Transitional readers have developed several reading strategies for decoding and monitoring comprehension. They read longer, more complex texts, including narratives and informational texts, with fluency and phrasing. Their rate of reading has increased, and they are transitioning from reading to decode to reading to comprehend and learn. |
Grade 2 |
K |
420L-650L |
20 |
18-20 |
|
L |
24 |
||||
|
M |
28 |
||||
|
Grade 3 |
N |
520L-820L |
30 |
||
|
O |
34 |
||||
|
P |
38 |
||||
|
Fluent Asset 5Books for fluent readers come from different genres and sources. Fluent readers read fluently with phrasing, inflection and expression. They read independently and silently. They will read for longer durations and maintain comprehension of the text over several days or weeks. They set purposes for reading, and react to text. Fluent readers understand that reading will build knowledge, and influence ideas and attitudes. |
Grade 4 |
Q |
740L-940L |
40 |
|
|
R |
|||||
|
S |
|||||
|
Grade 5 |
T |
830L-1010L |
50 |
||
|
U |
|||||
|
V |
|||||
|
Grade 6 |
W |
925L-1070L |
60 |
||
|
X |
|||||
|
Y |
|||||
|
Proficient Asset 5Proficient readers continue to read for a variety of purposes, including learning or enjoyment. Proficient readers read across a wide variety of materials and for multiple purposes. They make adjustments to their reading style based on the text and their purpose. They read regularly, for enjoyment and knowledge, and synthesize information from reading. Due to mature content, the Z+ titles should be reserved for high school and adult readers. Reader discretion is advised. |
Grade 7 |
Z |
970L-1120L |
70 |
|
|
Grade 8 |
Z |
1010L-1185L |
80 |
||
|
Grade 9-12 |
Z (+) |
1050L-1385L |
|||
Reading Technique Table - AST partner
Reading Technique Tables
Rate 680 1
Reading Technique
It is customary at school to check students' reading technique.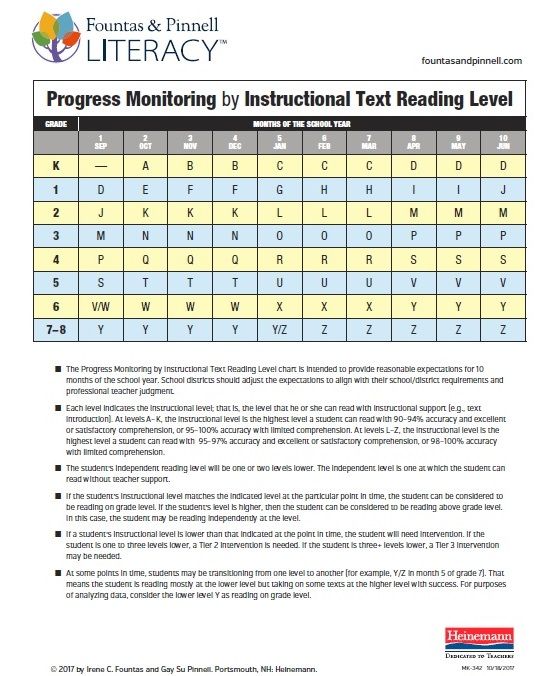 The child is given a text that he reads for one minute, and then the number of words read is counted. Given that reading skills are constantly being formed, reading technique is tested 2 times a year.
The child is given a text that he reads for one minute, and then the number of words read is counted. Given that reading skills are constantly being formed, reading technique is tested 2 times a year.
Reading Standards
Grade
1st semester
2nd semester
1
Correct, conscious and fluent syllabic reading with clear pronunciation of syllables and words. Reading speed - at least 20 - 25 words per minute.
Conscious, correct reading in whole words. Words of a complex syllabic structure are read syllable by syllable. Reading speed - at least 35 - 40 words per minute.
2
Conscious, correct reading of whole words with logical stress. Words of a complex syllabic structure are read syllable by syllable. Reading speed - at least 40 - 50 words per minute.
Conscious, correct reading in whole words, observing logical stresses, pauses and intonations.![]() Reading speed - at least 55 - 60 words per minute.
Reading speed - at least 55 - 60 words per minute.
3
Conscious, correct reading in whole words, observing pauses and intonations, through which the student expresses understanding of the meaning of the text being read. Reading speed - at least 60 - 70 words per minute.
Conscious, correct reading in whole words, observing pauses and intonations, through which the student expresses understanding of the meaning of the text being read. Reading speed - at least 70 - 75 words per minute.
4
Conscious, correct reading in whole words with pauses and intonations, through which the student expresses not only understanding of the meaning of the text being read, but also his attitude to its content. Reading speed - at least 75 - 80 words per minute.
Conscious, correct reading in whole words, observing pauses and intonations, through which the student expresses not only understanding of the meaning of the text being read, but also his attitude to its content.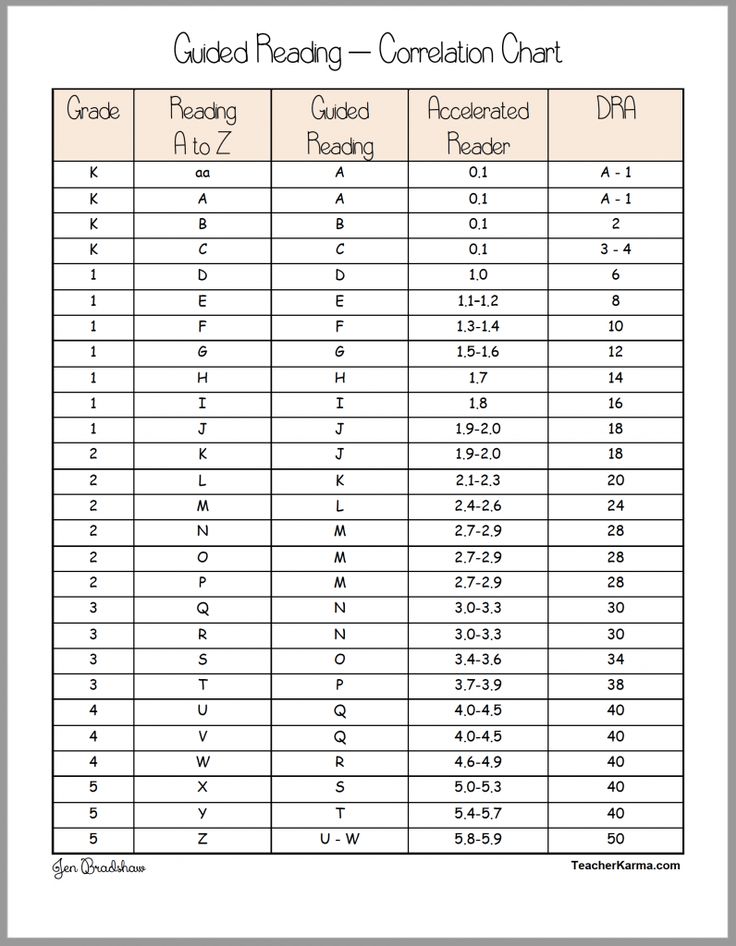 Reading pace - at least 85 - 95 words per minute.
Reading pace - at least 85 - 95 words per minute.
You don't have enough rights to add comments
You need to log in to post comments.
If you don't have an account on our site yet, we invite you to register.
This will take no more than 5 minutes.
This methodological material has a practical orientation and significance in the work of a primary school teacher. Guidelines are presented in checking the reading technique in primary school children (at the beginning of the 1st half of the year and at the end of the 2nd half of the year), criteria for checking the reading technique are prescribed.
To download materials from the site, you must log in to the site (log in with your username and password)
If you have not registered before, you can register.
After authorization/registration on the site, you will be able to download the material necessary for the work.
Order Review of methodological development
Available here
An excellent lesson in social and communicative development.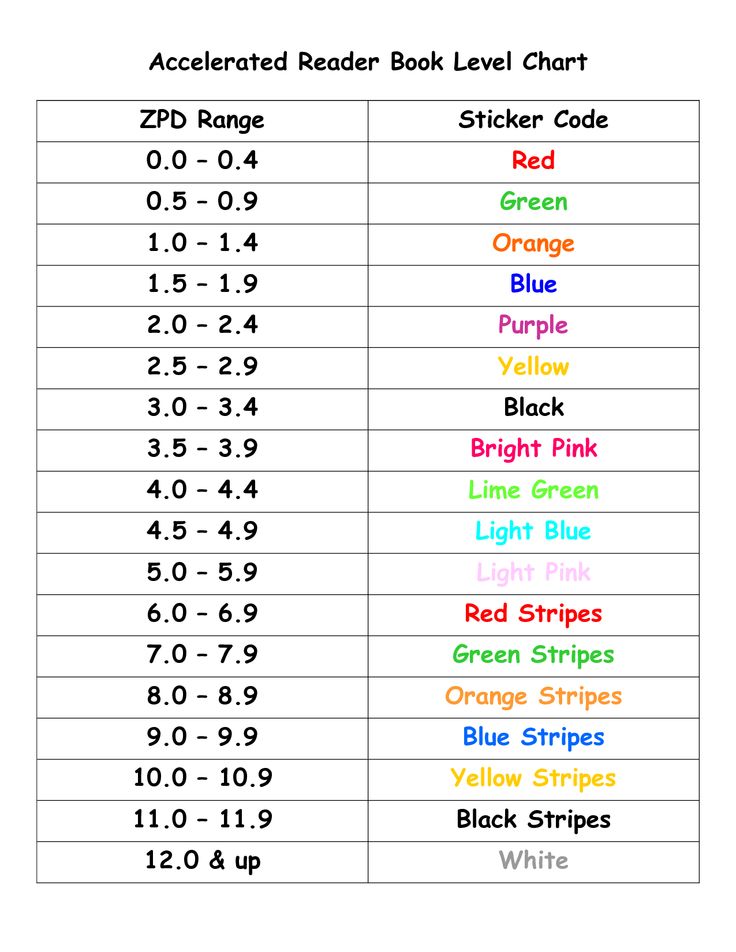 The author's work is aimed at activating re. More.
The author's work is aimed at activating re. More.
Interesting material to expand and systematize children's knowledge about the representatives of the seabed outside. More.
Nadezhda Mikhailovna is developing a process map for the lesson "Family Budget". Spanish lesson More.
An excellent lesson in the formation of ideas about pets, their appearance, lifestyle. Av. More.
Lesson on a hot topic. The author gives children an idea of causal relationships in an animal. More.
First aid in educational institutions Complete training
Gratitude to the leadership of the educational institution for the support and development of the professional potential of the teaching staff
Diploma for excellent knowledge and effective application of modern pedagogical methods in the context of the implementation of the Federal State Educational Standard
- Mass media registration certificate EL No. FS 77 - 58841 dated July 28, 2014 issued by the Federal Service for Supervision of Communications, Information Technology and Mass Communications (Roskomnadzor).
 License for educational activities No. 4276 dated 19.11.2020. Series 78 LO No. 0000171 Issued by the Education Committee of the Government of St. Petersburg In accordance with the Federal Target Program for the Development of the Education System for 2011–2015. and the draft concept of the federal target program for the development of education for 2016–2020.
License for educational activities No. 4276 dated 19.11.2020. Series 78 LO No. 0000171 Issued by the Education Committee of the Government of St. Petersburg In accordance with the Federal Target Program for the Development of the Education System for 2011–2015. and the draft concept of the federal target program for the development of education for 2016–2020. Reprinting of materials and their use in any form, including in electronic media, is possible only with the written permission of the site administration. The link to the site www. prodlenka. org is required. If you find that materials are illegally used on our site, inform the administrator - the materials will be removed. The opinion of the editors may not coincide with the point of view of the author.
Founder: Kovalev Denis Sergeevich. Editor-in-Chief: Kovalev D.S. Phone: +7 (812) 318-72-63
E-mail: info@prodlenka. org
Certificate of conformity for the quality of services provided reg. No. 04 ЕАС1. SU.01217 dated November 19, 2019. Service: Additional professional education. Based on the results of the evaluation of the provision of services, the evaluation of the process of rendering services and the verification of the results of the services provided, this document confirms the compliance of the services provided by the Center for the Development of Pedagogics LLC with all regulatory requirements.
SU.01217 dated November 19, 2019. Service: Additional professional education. Based on the results of the evaluation of the provision of services, the evaluation of the process of rendering services and the verification of the results of the services provided, this document confirms the compliance of the services provided by the Center for the Development of Pedagogics LLC with all regulatory requirements.
- Mass media registration certificate EL No. FS 77 - 58841 dated July 28, 2014 issued by the Federal Service for Supervision of Communications, Information Technology and Mass Media (Roskomnadzor). License for educational activities No. 4276 dated November 19, 2020. Series 78 LO No. 0000171 Issued by the Education Committee of the Government of St. Petersburg In accordance with the Federal Target Program for the Development of the Education System for 2011–2015. and the draft concept of the federal target program for the development of education for 2016–2020.
Evaluate 680 1
It is customary in the school to check students' reading skills.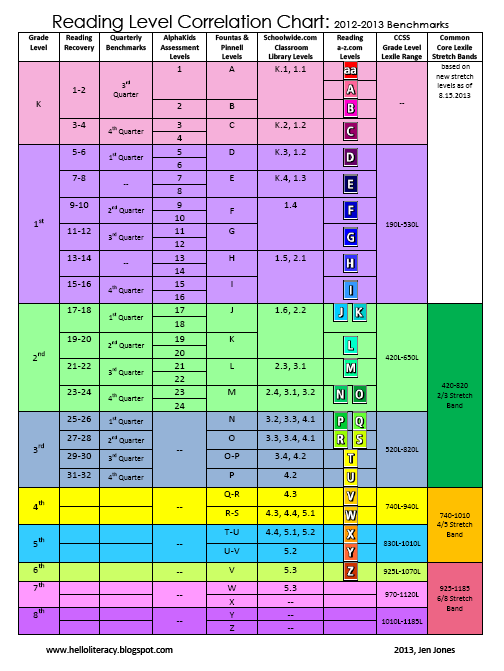 The child is given a text that he reads for one minute, and then the number of words read is counted. Given that reading skills are constantly being formed, reading technique is tested 2 times a year.
The child is given a text that he reads for one minute, and then the number of words read is counted. Given that reading skills are constantly being formed, reading technique is tested 2 times a year.
Reading speed - at least 85 - 95 words per minute.
www. prodlenka. org
08/23/2017 5:38:55
2017-08-23 05:38:55
Sources:
prodlenka. org/metodicheskie-razrabotki/277306-tablica-po-tehnike-chtenija
Reading technique (table) | Reading material (Grade 4): | Educational social network » /> » /> .keyword { color: red; }
Reading technique tables
On the topic: methodological developments, presentations and notes
Reading technique check (summary table for the whole class)
This table allows you to quickly note errors and correct reading of all children, as well as see the overall picture of the class.
Reading test chart.
I recommend using this table when checking reading technique.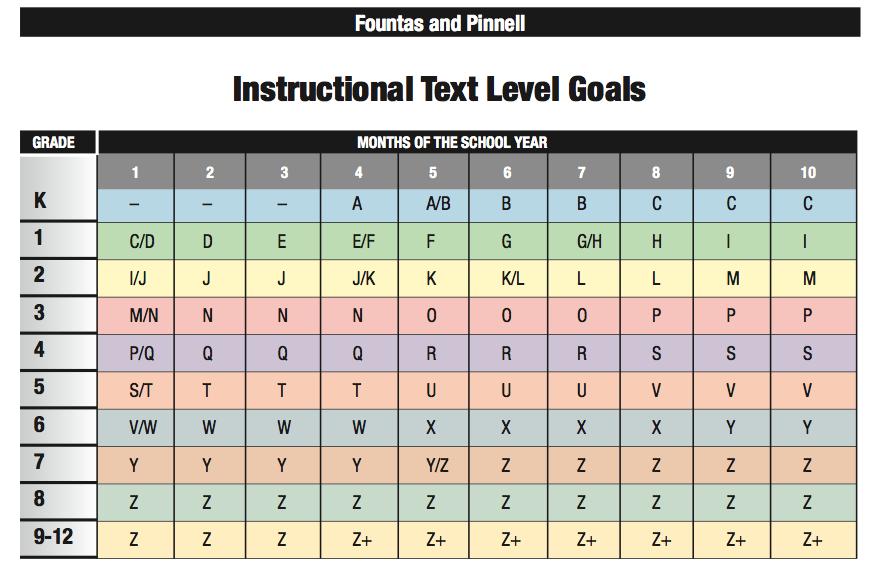
Tables to improve reading skills
The presentation is intended for students in grades 1-2. It is used both in reading lessons and for individual lessons with poorly reading students. Each slide is designed for one session of 5-7 minutes.
Checking reading technique (summary table for the whole class)
This table allows you to quickly mark errors and correct reading of all children, as well as see the overall picture of the class.
Reading technique checklist.
I recommend using this table when checking reading technique.
Tables to improve reading skills
The presentation is intended for students in grades 1-2. It is used both in reading lessons and for individual lessons with poorly reading students. Each slide is designed for one session of 5-7 minutes.
Reading technique checklist.
Nsportal. en
03/09/2019 3:33:20
2019-03-09 03:33:20
Sources:
Https://nsportal. ru/nachalnaya-shkola/chtenie/2020/09/26/tehnika-chteniya-tablitsa
ru/nachalnaya-shkola/chtenie/2020/09/26/tehnika-chteniya-tablitsa
Checklist table (reading technique, diagnostic work, writing speed) | Material on the topic: | Educational social network » /> » /> .keyword { color: red; }
Reading technique tables
On the topic: methodological developments, presentations and abstracts
Evaluation sheet for reading technique Grade 1
Evaluation sheet for reading technique.
Reading Technique Table
Convenient table for fixing reading technique results.
Tables Reading technique grades 1-4
Individual tables to monitor the dynamics of students' reading technique. Pasted in a diary. Reading test is carried out once a month. Children and parents can see the level of development of the nava.
Table (Reading Technique)
Reading Technique Table Grade 2 Vasilievka for the first half of the 2018-2019 academic year Purpose: to check the pace (speed) of reading teaching.

Norms of reading technique, counting and writing speed
Material for primary school teachers, which contains information on reading technique, speed of computing and writing skills.
Increasing your reading speed or 10 magical exercises to develop reading skills.
Reading speed is a very important aspect of academic achievement, and the task of parents is to help their child learn to read quickly. To do this, I propose 10 interesting exercises for the development of technique Thurs.
Evaluation sheet for reading technique Grade 1
Evaluation sheet for reading technique.
Reading Technique Table
Convenient table for fixing reading technique results.
Tables Reading technique grades 1-4
Individual tables to monitor the dynamics of students' reading technique. Pasted in a diary. Reading test is carried out once a month. Children and parents can see the level of development of the nava.
Table (Reading Technique)
Reading Technique Table Grade 2 Vasilievka for the first half of 2018-2019academic year Purpose: to check the pace (speed) of reading teaching.
Norms of reading technique, counting and writing speed
Material for elementary school teachers, which contains information on reading technique, speed of computing and writing skills.
Increasing reading speed or 10 magical exercises to develop reading skills.
Reading speed is a very important aspect of academic achievement, and the task of parents is to help their child learn to read quickly. To do this, I propose 10 interesting exercises for the development of technique Thurs.
Norms of reading technique, speed of counting and writing
Table of reading technique Grade 2.
Nsportal. en
08/13/2019 11:14:22
2019-08-13 11:14:22
Sources:
Https://nsportal. ru/nachalnaya-shkola/raznoe/2016/01/07/kontrolnyy-list-tablitsa-tehnika-chteniya-diagnosticheskaya
Reading technique.
 Norms 1-4 class.
Norms 1-4 class. Since many parents stubbornly refuse to understand what is the point of testing reading technique in elementary school (grades 1-4), I give up and post reading norms. At the same time, I ask you to carefully read not only the quantitative norm of words per minute, but also my explanations both in the table and below it.
Reading speed standards 1-4 grades
→ The number of words may vary slightly depending on the curriculum. Increased rates are given in parentheses.
→ Grade 1: no mark is given, the student "did it" or "did not do it". In the first half of the year, the reading technique may not be carried out.
| Grade | at the end of the first half of the year | at the end of the second half of the year |
| 1 cl. | at least 10 - 15 (20 - 25) wpm | by 2 -> less than 15 (25) words per minute by 3 -> 15-19 (25-34) words by 4 -> 20-24 (35-40) words by 5 -> from 25 ( 41) words |
| 2 cl. | by 2 -> less than 25 (40) words per minute by 3 -> 25-29 (40-48) words by 4 -> 30-34 (49-54) words by 5 -> from 35 ( 55) words | by 2 -> less than 40 (50) words per minute by 3 -> 40-44 (50-58) words by 4 -> 45-49 (59-64) words by 5 -> from 50 ( 65) words |
| 3 cells | by 2 -> less than 40 (55) words per minute by 3 -> 40-49 (55-64) words by 4 -> 50-59 (65-69) words by 5 -> from 60 (70) ) words | by 2 -> less than 65 (70) words per minute by 3 -> 65-69 (70-79) words by 4 -> 70-74 (80-84) words by 5 -> from 75 (85) ) words |
| 4 cl. | in 2 -> less than 65 (85) words per minute in 3 -> 65-74 (85-99) words by 4 -> 75-84 (100-114) words by 5 -> from 85 (115) words | by 2 -> less than 70 (100) words per minute by 3 -> 70-88 (100-115) words by 4 -> 89-94 (116-124) words by 5 -> from 95 (125) words |
Other reading parameters 1-4 class
| Grade | at the end of the first half of the year | at the end of the second half of the year |
| 1 cl. | Conscious, correct reading, simple words are read as a word. Words with a complex syllabic structure can be read syllable by syllable. | |
| 2 cl. | Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. Compliance with logical stresses. Words of a complex syllabic structure can be read syllable by syllable. | Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of logical stresses, pauses and intonations. Syllabic reading is undesirable. |
| 3 cells | Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the student expresses understanding of the meaning of what is being read. | Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the student expresses understanding of the meaning of what is being read. |
| 4 cl. | Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the student expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is read, and his attitude to the content of what is read. | Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the student expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is read, and his attitude to the content of what is read. |
Criteria for grading for reading technique:
- reading by syllables or a full word,
- presence of reading errors,
- number of words per minute,
- expressiveness
can be clicked to enlarge
As you can see, the number of words read is not decisive.
That is, parents need to understand what a concept such as reading speed , is only one of the criteria for determining the state of the art reading . way of reading is being checked : the child reads by syllables or the word is read by him smoothly, in its entirety. It is mandatory to check reading comprehension , in other words, whether the student understands what he has read or not. To do this, after reading, a question can be asked about the text, most often “What did you just read about?” and requires a simple answer (a detailed retelling is not needed 😉)
To do this, after reading, a question can be asked about the text, most often “What did you just read about?” and requires a simple answer (a detailed retelling is not needed 😉)
The expressiveness of reading, the presence of errors and / or stammers are also taken into account. Sometimes there is a return to re-reading the previous word, this indicates a lack of awareness and is considered a mistake.
It should also be taken into account that the standards of speed (rate) of reading may differ depending on the educational institution, the requirements for a student of a gymnasium will be higher, for a student of a correctional class - lower.
The frequency of checking reading technique in elementary school is usually 2 times a year: the end of the first half of the year and the end of the second half of the year. However, in some schools the reading level is checked at the end of each quarter or trimester.
And again! I warn, I exhort - and all the same, the "lion's" part of the students and parents steps on the rake, from which I try to warn.

 Each reading level system is designed independently, using various metrics to determine grade level targets. Every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of the levels presented.
Each reading level system is designed independently, using various metrics to determine grade level targets. Every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of the levels presented. Theme and developmental appropriateness are not considered. Lexile measures are from @2011 Metametrics, Inc., and appear by permission with all rights reserved. Lexile and related marks are registered trademarks of MetaMetrics, Inc.
Theme and developmental appropriateness are not considered. Lexile measures are from @2011 Metametrics, Inc., and appear by permission with all rights reserved. Lexile and related marks are registered trademarks of MetaMetrics, Inc. Reading Recovery is a registered trademark of The Ohio State University.
Reading Recovery is a registered trademark of The Ohio State University.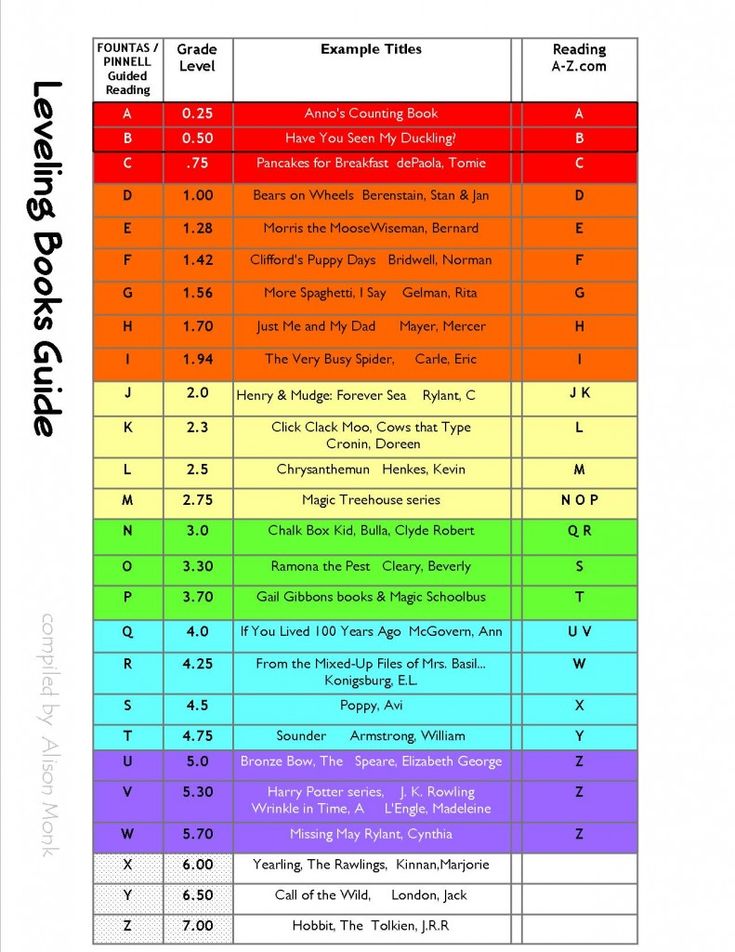 There is more variety in sentence structure. They include high-frequency words and picture cues to provide support while introducing early readers to new vocabulary. Concepts are familiar.
There is more variety in sentence structure. They include high-frequency words and picture cues to provide support while introducing early readers to new vocabulary. Concepts are familiar.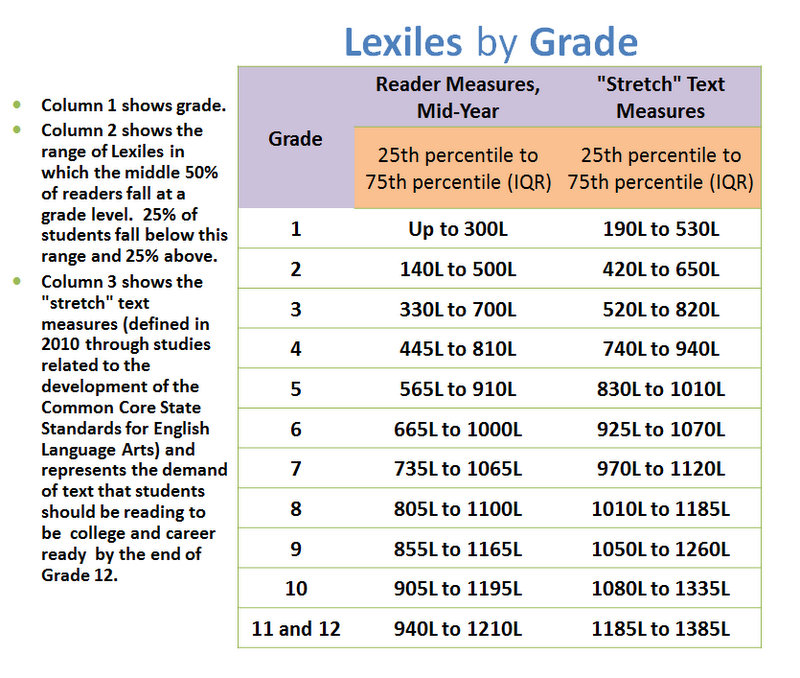 These books include text features and are on varied topics and from multiple genres. Transitional books can be short chapter books or more complex picture books. Concepts are less familiar and the text encourages readers to make connections.
These books include text features and are on varied topics and from multiple genres. Transitional books can be short chapter books or more complex picture books. Concepts are less familiar and the text encourages readers to make connections. The text is longer and more complex and requires sustained understanding over a few days or weeks of reading. Text features are used to gain and infer meaning. Fluent readers read for purposes such as enjoyment or for learning. Many concepts are new, as fluent readers read to gain new ideas and explore new perspectives.
The text is longer and more complex and requires sustained understanding over a few days or weeks of reading. Text features are used to gain and infer meaning. Fluent readers read for purposes such as enjoyment or for learning. Many concepts are new, as fluent readers read to gain new ideas and explore new perspectives.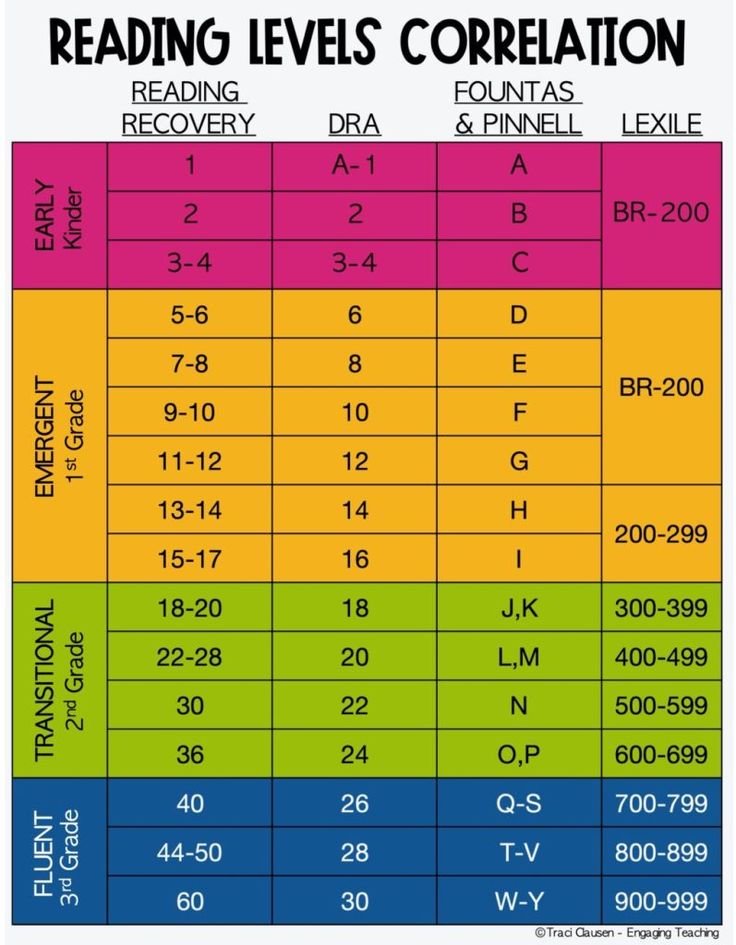 Books are specific to subject matter, such as the sciences or the humanities. Text is in different styles and lengths and includes different genres, contents and authors to meet a range of self-set purposes for reading.
Books are specific to subject matter, such as the sciences or the humanities. Text is in different styles and lengths and includes different genres, contents and authors to meet a range of self-set purposes for reading.