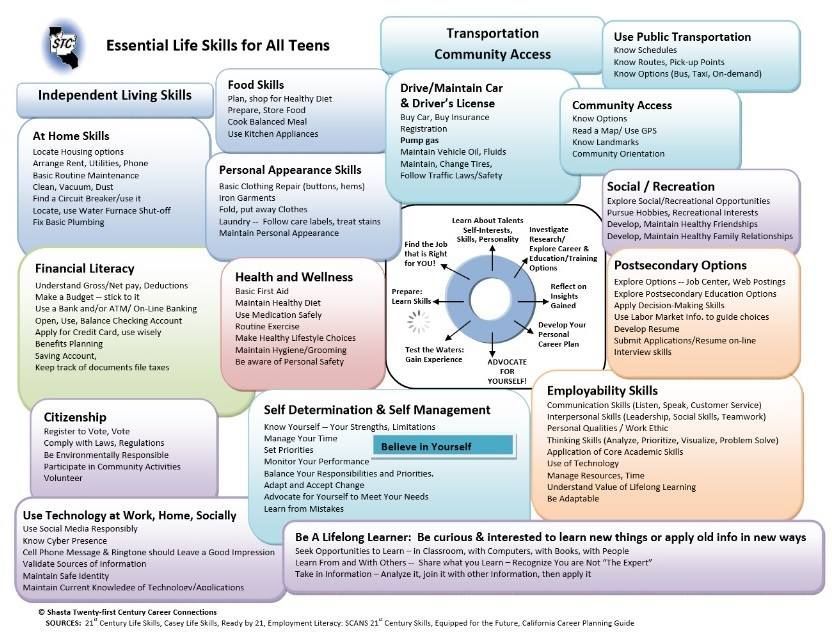
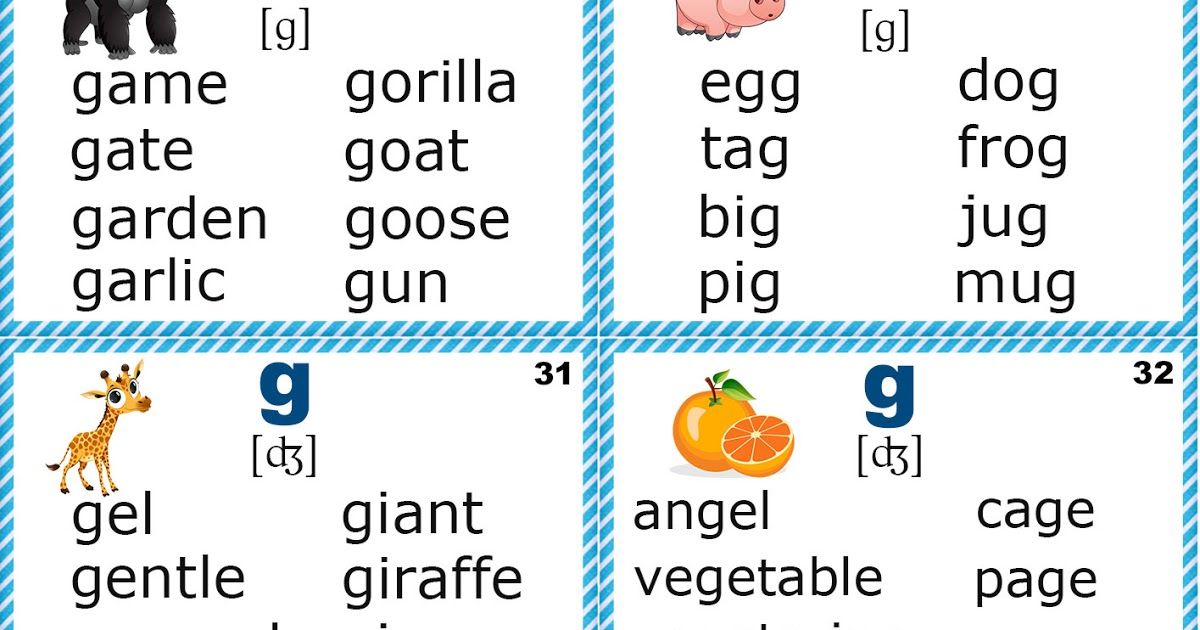
Teaching the letters
5 Easy ways to teach the alphabet to preschoolers | Daycare Blog
Teaching children the alphabet is foundational to learning how to read. Before children can put together sounds or draw together lines that make words, they need to know what they are. If you’ve never taught the alphabet before, the concept may sound abstract: how do you teach something that comes so naturally to you? Teaching letters can be really fun and simple. In this article, we’ll give you easy ways to teach the alphabet to preschoolers.
1) Sing alphabet songs
Obviously, we all know the English-language, “A-B-C-D, E-F-G,” song. That’s a great place to start. However, there are more alphabet songs, which can add variety to your tunes, and help kids learn the alphabet in different ways.
This article lists a whole bunch of alphabet songs to try. And, if you saw our article on YouTube channels for toddlers and preschoolers, you can find letter-related songs there too. The visuals in videos can show objects that start with each letter, and sometimes the songs also pronounce sounds too.
One important note brought up by this early childhood educator, is that kids should go from singing the song, to being able to say and point out the letters without a tune. So don’t stop at singing!
2) Play letter matching games
Letter matching games are easy to set up. You can have a poster board with the alphabet printed on it in large letters. Have separate letter magnets or paper letters cut out at the same size as the print letters. Ask the preschoolers to match their cut outs to the letters on the chart. Where does “A” go? Place the letter “A” cut out on top of the printed “A” on the poster board. Get them to practice doing this with all the other letters.
As the early childhood educator mentioned above noted, you can also have an alphabet ‘arc,’ where one end of a half-circle shows the letter “A”, and the other end the letter “Z”. In between you can have other letters in the alphabet shown, but not all of them. Ask the preschoolers to put down their block letters in the right sequence, using the pre-filled in letters as clues.
3) Open a new ‘alphabet box’ each week
You may have seen us post on Facebook that a certain week is brought to you by a letter we’re covering. It may be “C,” and you’ll see photos of us painting the letter C at daycare, or learning about animals that start with the letter “C.” Weekly letter themes are common in preschools.
You can take your weekly letter curriculum a step further by creating a box that children can open to discover objects that relate to that letter.
For example, on the week covering the letter “A,” your preschoolers can open (or even unlock) a box that contains an apple, a toy airplane, a toy alligator, an acorn, an arrow (a safe one!), and so on. In fact, don’t tell the children right away what letter the box of ‘treasures’ represents. Ask them if they can guess the letter they’ll cover that week by observing the objects in the box alone. This can be a fun and whimsical way to have your children get excited about the week ahead, and work together to come up with an answer.
3) Use interdisciplinary learning with each letter, to strengthen letter associations
Since repeating a letter over and over again can get boring, you can mix it up a little by bringing in related lessons. You can start with a week’s letter as your core subject. Then, throughout the day, teach interdisciplinary subjects that still relate.
For example, if you are on the letter “R,” you can learn about the colour “red” too, since it starts with “R.” Ask the children, ‘what things are red?’ If you are on the letter “A,” you can learn about apples. We’ve done this before, where we teach children about the types of apples there are, as well as explain that seeds are inside an apple, and so on.
This blogger lists a whole bunch of crafts you can you incorporate into your letter learning. For example, you can make holes with a hole punch for the letter “H.” This can then lead into learning about the circle shape. You get the idea…
4) If you use flashcards to teach the alphabet, use logical ones
Flashcards are a great memorization tool, and the alphabet is all about memorizing. However, this teacher warns that sometimes, pre-made flashcards can get really confusing. If you are teaching the letter “D” and there is an image of something that simply uses the sound of “D” somewhere in the word, but doesn’t start with “D”… well you can quickly see how even adults would be confused by that.
However, this teacher warns that sometimes, pre-made flashcards can get really confusing. If you are teaching the letter “D” and there is an image of something that simply uses the sound of “D” somewhere in the word, but doesn’t start with “D”… well you can quickly see how even adults would be confused by that.
Remember, at this stage, you’re not teaching phonetics or complex vocabulary and pronunciation. First, children need to recognize and know the alphabet. Use the simplest flash cards, with the simplest pictures of the objects and animals that preschoolers can recognize.
That said, sometimes you want to use lowercase and uppercase letters in your flashcards…and yes, that can be confusing for the very young learners, especially when the upper and lowercase look so different, but are called the same thing. But if you’re using a set of magnets, for example, you can just use their uppercase versions, that’s ok (they may only come in that form). For very early learners, you can start really basic.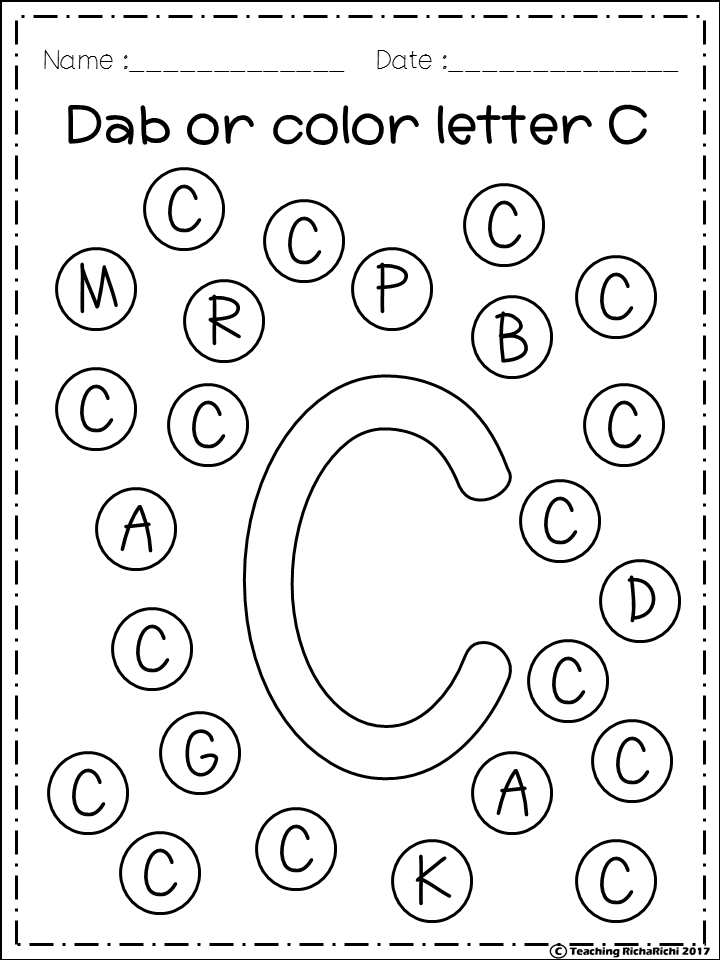 Just don’t forget to start showing them the lowercase and uppercase letters together at some point in their alphabet learning journey.
Just don’t forget to start showing them the lowercase and uppercase letters together at some point in their alphabet learning journey.
5) Eat foods shaped like letters to help preschoolers learn their alphabet
Speaking of interdisciplinary alphabet learning, why not do a baking session with the kids at preschool? They can use letter-shaped cookie cutters to make a fun and yummy snack. Meanwhile, there is a host of lessons you can teach with the baking activity. Chemistry, cooking, nutrition…the list goes on.
If you want the easy route, try commercially-sold letter-shaped biscuits. IKEA has a version of these. Ask your toddler or preschooler to name the alphabet letter they’re about to eat. Eating it can be the reward for getting it right!
And of course, there is alphabet soup, or noodles shaped like letters. You can make mealtime fun, and educational, with these edible alphabet manipulatives.
So there you have it, 5 easy ways to teach the alphabet to preschoolers.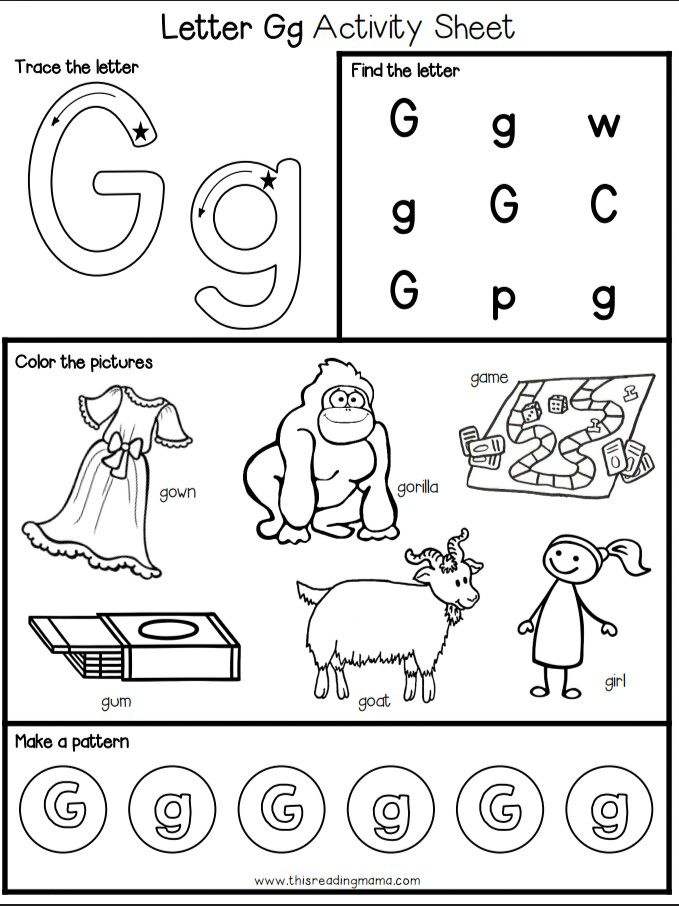 They may even be fun for you, too! It is super cute to hear little ones pronounce letters, and guess what object goes with each letter. When your preschoolers are learning the alphabet, be sure to take every teachable opportunity you can to encourage them to recognize letters in the world around them. If you’re on a field trip, ask the children if they can spot their letter-of-the-week on a street or building sign. If you’re reading a book, see if they can spot the letters you’re reading to them. Keep pushing letter recognition throughout the day, so the lessons can really sink into their memory.
They may even be fun for you, too! It is super cute to hear little ones pronounce letters, and guess what object goes with each letter. When your preschoolers are learning the alphabet, be sure to take every teachable opportunity you can to encourage them to recognize letters in the world around them. If you’re on a field trip, ask the children if they can spot their letter-of-the-week on a street or building sign. If you’re reading a book, see if they can spot the letters you’re reading to them. Keep pushing letter recognition throughout the day, so the lessons can really sink into their memory.
See more on our blog:
- How to teach digraphs to preschool children (6 ways)
- What is the best way to teach word recognition to early childhood readers?
- Why is literacy crucial in the early years? How can parents and preschools help with reading skills?
- How to teach toddlers and preschoolers to count, and learn their numbers
- Ideas for teaching shapes in preschool and daycare
5 Ways to Teach the Alphabet
Disclosure: This post contains affiliate links to Amazon. See my disclosure for details.
See my disclosure for details.
Teaching the alphabet is foundational for reading and writing. Around the age of 2, children begin showing interest in learning alphabet letters. While some kids learn letters very quickly, others need more repetition and time to learn letters. Today I’m going to share with you some of my favorite ways to teach the alphabet to little ones.
Here’s what a preschooler should know before kindergarten:
- Recite/sing the alphabet
- Identify uppercase letters
- Identify lowercase letters
- Match uppercase letters to lowercase letters
- Identify the sounds each letter makes
- Traces letters
- Write some alphabet letters
Here are my five favorite ways to teach the alphabet to children.
1. Read Alphabet Books
Read all sorts of alphabet books to your children, even starting as babies. The repetition will really help your child learn the alphabet at a young age. When my oldest was born, I was surprised at how many alphabet books we had been given as gifts. We loved reading all of them because they were different from each other. I found that around 18 months both my kids really started enjoyed reading alphabet books. Here are a few of our alphabet books:
When my oldest was born, I was surprised at how many alphabet books we had been given as gifts. We loved reading all of them because they were different from each other. I found that around 18 months both my kids really started enjoyed reading alphabet books. Here are a few of our alphabet books:
Here are some of our favorite alphabet books.
The Three Bears ABCChicka Chicka Boom Boom (Board Book)Eating the AlphabetThe Farm Alphabet BookG is for GoatHarold’s ABC (Purple Crayon Book)I Stink! (Kate and Jim Mcmullan)Bad KittyThe Letters Are Lost!AlphaOops!: The Day Z Went FirstZ Is for Moose (Booklist Editor’s Choice. Books for Youth (Awards))Q Is for Duck: An Alphabet Guessing GameABC T-RexWork: An Occupational ABC
2. Sandpaper Letters
Using sandpaper letters is a great way to introduce letters to children. My favorite ones are Didax Sandpaper Tracing Letters or School Supply Tactile Letters Kit. This is a perfect pre-writing activity because children use their finger to trace the sandpaper letters. I love that the cards tell the child where to start and which direction to go.
I love that the cards tell the child where to start and which direction to go.
Sandpaper letters are part of the Montessori approach to learning how to read. These letters provide a tactile and visual way to help children learn the alphabet. In the Montessori method, you teach letters to a child in the 3-period lesson.
1st period is introducing the letter (“this is” period). Show your child the letters. Have them trace the sandpaper letters. The best way to teach children alphabet letters is by telling them their phonetic sound. So each time they trace the letter, say the phonetic sound.
2nd period is association (“show me” stage). Ask your child to follow simple directions with the letters. For example, please pick up the /m/ and set it by the window. Continue to do this with each letter several times to reinforce this. If it is too difficult, return to the first period.
3rd period is recall (“what is this?” period). Only go to this period when they’ve mastered the other two periods. Put a letter in front of the child and say “Can you trace this and tell me what it is?” Continue with the other letters in the same way.
Only go to this period when they’ve mastered the other two periods. Put a letter in front of the child and say “Can you trace this and tell me what it is?” Continue with the other letters in the same way.
When you use these sandpaper letters, you are teaching them 3 things: the shape of letters, the feel of its shape and how its written, and how you pronounce its sound.
3. Alphabet Puzzles
I think teaching letters with alphabet puzzles are an amazing tool for teaching the alphabet. This is my favorite puzzle, from Melissa and Doug. It’s a beautiful wooden puzzle with neat pictures. This is a great way to practice vocabulary and verbal skills, too.
4. Sensory Activities
While some kids learn letters very quickly, others need more repetition and time to learn letters. I’ve always said that children learn best when they have many multisensory experiences with letters.
I love to incorporate sensory play into learning alphabet letters. When children have meaningful activities with repeated exposure, they start to pick up on letter names. One way is this alphabet ice excavation activity.
When children have meaningful activities with repeated exposure, they start to pick up on letter names. One way is this alphabet ice excavation activity.
You could also make a colorful sensory bin!
Or practice writing letters in the sand, like this sensory writing tray.
5. Alphabet Printables
I have quite a few alphabet printables on my blog, but here is a set that is easy and fun for preschoolers. You will need Do a Dot Markers or dot stickers to fill in the circles.
I love pulling printables out for a quick and easy activity. I’m always advocating for hands-on learning, but sometimes it’s nice to do a few paper activities. Using Do a Dot markers or dot stickers is great for hand-eye coordination and fine motor skills.
If you’d like to download this printable, just click the button below.
Learning the alphabet: methods, exercises and games for children
The alphabet is the foundation of reading. Therefore, before you start reading and writing, teach your children the letters.
Therefore, before you start reading and writing, teach your children the letters.
Children can start learning to read as early as preschool age. Parents and teachers need to teach their child how to pronounce sounds correctly in their native language. These are important prerequisites for learning letters and learning to read successfully. The educational process of preschool children is based on visual, acoustic and tactile exercises. The use of various channels of perception in the educational process increases its effectiveness and stimulates long-term memorization of letters.
Learning the alphabet: introducing the child to the alphabet.
To master reading, a child must learn and recognize not only the graphic form of letters, but also be able to compare them with their corresponding sounds. This means that the child must be able to write letters and pronounce them. When the child learns to correctly pronounce all the sounds in his native language and distinguish letters by visual form, go directly to reading. As a rule, at the age of 5-6 years, most children no longer experience difficulties in this.
As a rule, at the age of 5-6 years, most children no longer experience difficulties in this.
See also: Reading and bilingualism. Bilingualism in children
From the age of 5 to 6, children begin to understand that there is a lot of information encoded in language using letters. Thus, they are interested in learning to read by then, as they are naturally curious.
Of course, babies can learn and memorize individual letters quite early. However, their interest, mostly spontaneous, is directed to individual words and letters. Here it is important to gently motivate the child by encouraging him to learn through games and a comfortable environment. However, too much pressure can lead to stress, causing little ones to lose any motivation to learn letters.
Alphabet learning games
The first rule of learning the alphabet: learn the letters one by one!
Don't forget, each letter is made up of visually similar elements. If you try to teach a child several letters at a time, he may become confused. Learn the letters one by one. One lesson - one letter.
If you try to teach a child several letters at a time, he may become confused. Learn the letters one by one. One lesson - one letter.
Second rule of learning the alphabet: take your time!
Give your child enough time for each letter. Plan 1-2 lessons for each new letter. Organize the lesson in a form that is interesting for the child with the help of games.
Tactile method: from studying letters to reading
The child sees something abstract in a letter. Chains of associations will help in learning letters. Associating each letter with something specific or familiar helps the child fix it in his memory.
1. Make a letter out of plasticine
Let's memorize what a letter looks like and develop fine motor skills.
We will need: plasticine (should be elastic), modeling board and a disposable plastic knife.
Together with your child, roll out 8 approximately identical sausages from plasticine. 2 - divide in half, 2 - divide into 3 parts. From the remaining 4, make rings by blinding their edges and cut 2 of them in half, creating semicircles. Thus, you should get a set of elements to compose any letters of the alphabet. Show the child a couple of examples and ask them to repeat, collecting previously passed letters.
2 - divide in half, 2 - divide into 3 parts. From the remaining 4, make rings by blinding their edges and cut 2 of them in half, creating semicircles. Thus, you should get a set of elements to compose any letters of the alphabet. Show the child a couple of examples and ask them to repeat, collecting previously passed letters.
2. Magic wands
Let's memorize letters, learn how to make letters from sticks, learn how to transform letters.
We need: a set of counting sticks. If not, you can replace with matches or toothpicks.
The easiest way is to lay out letters from sticks according to a pattern or without a pattern (according to the idea). When the child learns to lay out all the letters, you can complicate the task by laying out objects familiar to the child from them, and then ask them to change them, for example, make a figure resembling a door out of sticks, and then ask the child to remove 2 sticks to make the letter P.
3.
 Tactile letters
Tactile letters Memorize letters and develop fine motor skills
We will need: sandpaper, velvet paper, scissors.
Cut out letters from sandpaper or velvet paper. The child will have to close his eyes to identify the letter by touch.
4. Draw a letter on the semolina
Memorize letters, develop fine motor skills
We will need: bright dish tray, semolina
Pour sand or semolina in a thin layer on the tray. Set an example for your child, show how to write letters on the croup with a finger or a stick. Ask him to write next to the letter, the same as you wrote, to write a letter more or less than yours, to add an unfinished letter, or to erase the extra detail of the "wrong" letter. Children will like this game, just shake the tray a little, and the mistake or inaccuracy made disappears!
5. Mirror letter
Memorize letters and train attention
We will need: cardboard, pencil and scissors
Prepare identical cards cards, 2 pieces for each letter.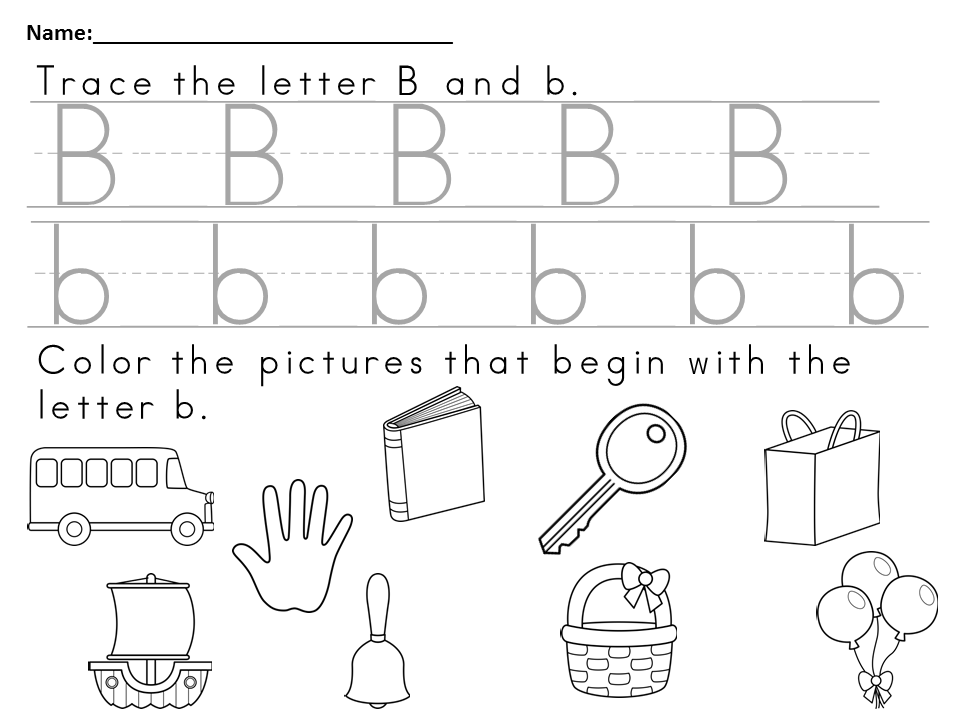 Write 1 letter on each card. Write the letters in mirror image and correctly. Lay out cards with the same letter in front of the child and offer to choose the correct one.
Write 1 letter on each card. Write the letters in mirror image and correctly. Lay out cards with the same letter in front of the child and offer to choose the correct one.
6. Memory test game
Train memory
We will need: scissors, cardboard and a pencil
The game "Memory Test" will challenge even older children. Write each capital letter on one card and lowercase letter on the other card. Turn over all the cards and place them on the table. Ask your child to match uppercase and lowercase letters. You can complicate and add a dictionary element. Have the children match the letter of the alphabet with the picture that starts with that letter.
7. Bean bag
Memory training
We will need: a bag of beans or other bulk material, a tablecloth or a large piece of paper.
If you want to warm up a bit while you study the letters, play a game of Beanbag. Write the alphabet randomly on a large piece of paper.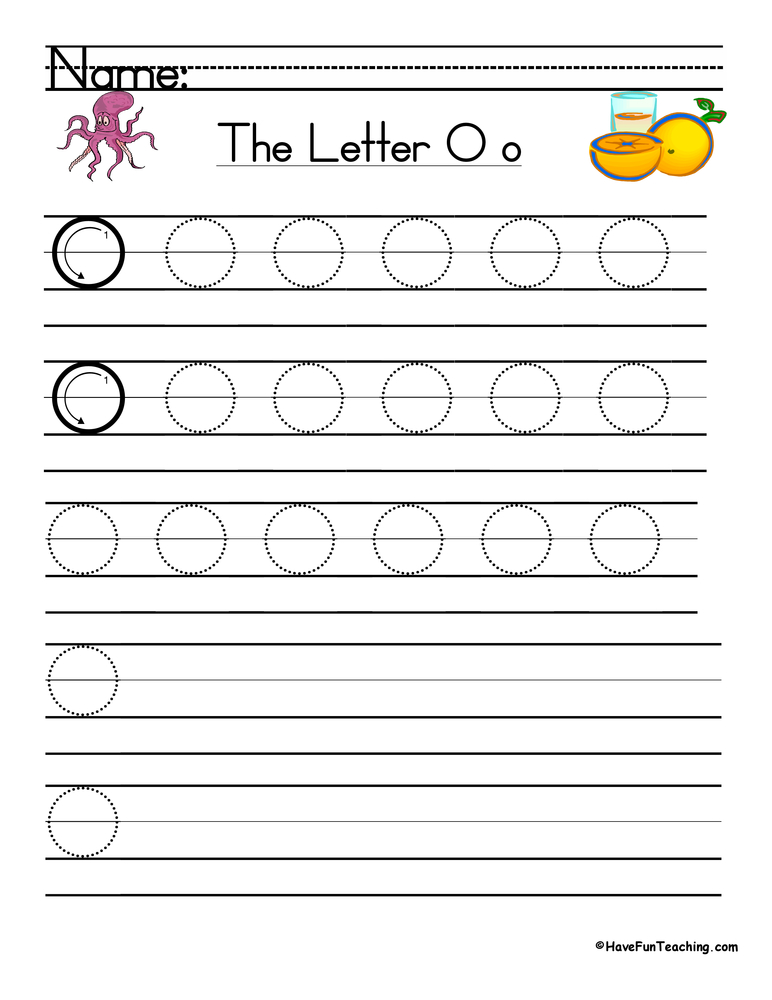 Give the children a bean bag and ask them to put it on paper. The child must name a word that begins with the letter on which the bag fell. If a student is stuck, help him.
Give the children a bean bag and ask them to put it on paper. The child must name a word that begins with the letter on which the bag fell. If a student is stuck, help him.
Ask the child to check the chosen letter with letters from the alphabet. Be sure to ask the name of the letter. The exercise will help children learn to distinguish visually similar letters and avoid mistakes when writing them in the future.
Drawing, coloring, cutting letters out of paper and gluing them together develop fine motor skills in children. Self-made flash cards with letters facilitate memory and associative thinking, creating the basis for tactile games. You can make postcards alone or with your child. Letters can be cut out of paper of various textures and pasted onto cards made of cardboard or paper. Then you can ask the child to pick up letters from 2-3 cards with their eyes closed.
Literacy begins with learning the letters of the alphabet. Combine different perceptual styles. The alphabet learning games described above help children to learn letters at different levels. Moreover, fine motor skills play a crucial role in the formation of systematic connections in the mind of the child and create the basis for the development of reading and writing.
The alphabet learning games described above help children to learn letters at different levels. Moreover, fine motor skills play a crucial role in the formation of systematic connections in the mind of the child and create the basis for the development of reading and writing.
How to quickly learn the alphabet - learning letters with a child
Letters are all around us. The child sees them in books and magazines, on product packaging, in shop windows. He can't help wondering what it is. Over time, he begins to understand that adults can read, begins to copy his parents, having learned a poem or a fairy tale by heart, and pretending that he is reading a book.
Experts recommend teaching a child to read shortly before school, since at an earlier age his brain is not yet ready to perceive such information. You can learn sounds with it, learn to distinguish them in oral speech, start mastering the alphabet. This pre-letter period is very important, because thanks to it the child will be able to learn to read fluently and understand what he read.
At what age do you start learning letters?
Many parents are sure that a child's development should start almost from the cradle. But neuropsychologists warn that learning letters and numbers before the age of 3 is harmful. At this age, the emotional and sensory sphere should be formed. If we force a child to learn, then we violate the laws of brain development, which can have negative consequences.
No specialist will tell you that at the age of 3 or 4 a child should know all the letters. Of course, if you wish, you can force him to learn the alphabet, but this will not be useful, but, on the contrary, can harm. The brain is ready for reading most often by the age of 5-6, and only in 20% of babies - by 4-5. Before this time, it is not worth studying letters.
But this does not mean that you can forget about the development of the child. At 3-4 years old, you need to work on the development of speech, teach the baby to ask and answer questions correctly, pronounce words, and study the world around him. You need to work on fine motor skills, teach him to dance, form a sense of rhythm, and so on.
You need to work on fine motor skills, teach him to dance, form a sense of rhythm, and so on.
These are the recommendations. However, all children are different. If a child has shown a sudden interest in letters, it means it's time to start learning. And it does not matter if it manifested itself late, for example, at 6 years old. The child should want to read, only after that you can study with him.
Psychologists note several signs that indicate a child's readiness for learning:
- The child perceives what he read by ear well, he can tell what the book is about.
- He knows how to build phrases, pronounce all sounds.
- Interested in what is written in a children's magazine, book or poster.
- Pretends to read, imitating adults.
If all these signs appear, you can start classes. You can’t put pressure on a child, force him to study, bribe him (“learn the letters - I’ll give you a chocolate bar”) - this will not achieve anything.
In those cases where the interest in letters appeared early, there is no need to give up classes. But do not overload the baby, work with him for no longer than 7 minutes, classes do not have to be done every day, you can take breaks of 2-3 days.
How to start learning the alphabet?
The child began to show interest in letters. No need to immediately load it with knowledge, cramming the alphabet. Move a little. The easiest way for children to remember the first letter of their name. Explain to him what this letter is, what it is called. You can ask him to find this letter in the text. Gradually, he will learn to highlight it, will pay attention to it. The first step has been taken.
Parents now trust their children's education to various children's tablets, phones and other similar toys. Remember that they are teaching letters, not sounds. Toddlers need to be taught precisely sounds, so it will be easier for them to master reading.
A letter is a graphic representation of sound, each has its own name. But learning to read, knowing only the names of the letters, is very difficult. Imagine that the child will need to read the word "ball". How will he do it? Just as he was taught: "beael". And all because he pronounces letters, not sounds.
But learning to read, knowing only the names of the letters, is very difficult. Imagine that the child will need to read the word "ball". How will he do it? Just as he was taught: "beael". And all because he pronounces letters, not sounds.
It is better to start learning with sounds, pronouncing them with the child. Parents themselves should not confuse sound and letter. Sound is what we hear. A bumblebee buzzes - this is a sound, a hammer knocks - this is also a sound. But far from all sounds we can get words. If we clap our hands, the sound will appear, but the word will not.
You can create a word from special sounds called speech sounds. Make sure that the child does not confuse the letter and sound. Explain to him that a letter is an icon that can be seen in a book or drawn on paper. Letters can be seen with the eyes and sounds can be heard.
General recommendations for teaching a child
If you decide to work with a child, remember the basic rule - he should be interested. You can't force him. At this age, the easiest and most accessible way of learning is through the game.
You can't force him. At this age, the easiest and most accessible way of learning is through the game.
It is difficult for kids to concentrate, to sit in one place for a long time, so classes should be short, 5-10 minutes each. As soon as you notice that he has become bored, switch to something else. If he forgot everything that you went through, do not get annoyed, repeat again until he remembers. If you overload your child with information, he will develop an aversion to learning.
At an early age, a child develops visual-figurative thinking, and only then - abstract-logical. This means that it is useless to draw letters on paper or a board. So you can't learn them. For him, it will be just a set of dashes.
The child needs a visual association. For example, if you are learning the sound "a", you can show him a picture of a watermelon or any other item that starts with that letter. Stock up in advance with soft cubes with letters, bright cards, coloring books, beautiful colored primers.
Do not learn letters in alphabetical order. It is better to start learning with vowel sounds. The letters that are most often found in speech are studied first, then you can move on to rarer ones.
How to learn vowels?
First, explain to your child that all words are made of sounds, just as houses are made of bricks. The more sounds in a word, the longer it is. After that, you can proceed to the study of sounds.
Start with "a" . You can show the baby pictures that show objects whose names begin with this letter. Draw with him the mouth that makes this sound, note how we open it wide. Let him try to name the words that begin with this letter. Do not overload the child: 1 lesson - 1 letter.
Try to consolidate the acquired knowledge. So you go to the kindergarten, you saw a pharmacy, let the kid try to find the letter that you studied. Bought a children's magazine, see if the title has the letter "a" . You can mold a letter from plasticine or dough, cut it out of paper. You can lay it out of sticks or sand.
You can mold a letter from plasticine or dough, cut it out of paper. You can lay it out of sticks or sand.
It will be much easier for you to captivate your baby if you always have blocks with letters, bright books, cards at hand. You can sing a song about a letter or listen to a funny verse.
So, study all the vowels one by one. At the end, you can explain that the sounds that you have already learned are called vowels. These are sounds that can be sung. Try to sing together "a-a-a" or "u-u-u" .
Remember that we have 6 vowels ( a , o , y , e , s , and ) and 10 vowels. The letters i , e , i , i consist of 2 sounds. It is better to postpone the study of the latter for later, because there is no sound "i" , i is a letter consisting of 2 sounds. Do not confuse the child so that later educators and teachers do not have to retrain him.
Do not confuse the child so that later educators and teachers do not have to retrain him.
How to learn consonants?
After you have learned the basic vowels ( a , y , and , o ) you can move on to consonants. You need to start with the simplest consonants ( b , p , m , n , t , g ). And here again we remember that we are teaching the child sounds, not letters. We know what to say0012 em ”, “ en ”, “ be ”, but children do not need to know this yet. The child must learn that this is the sound " mm " or the sound " nn ". After the baby learns simple consonants, you can proceed to the study of hissing.
Just like with vowels, knowledge needs to be consolidated. Children may confuse letters. To prevent this from happening, play associations. You can ask the children to think of what this letter looks like. Look for objects on the street that resemble this letter. For example, you walked past the horizontal bar, it is shaped like the letter " p ”, or look at the doorway, also resembles “ p ” in shape. Fold it out of pencils, look for it in store signs.
You can ask the children to think of what this letter looks like. Look for objects on the street that resemble this letter. For example, you walked past the horizontal bar, it is shaped like the letter " p ”, or look at the doorway, also resembles “ p ” in shape. Fold it out of pencils, look for it in store signs.
Alphabet learning techniques
There are several popular methods for teaching children to read and memorize the letters of the alphabet. You can use them, especially since specialists worked on them. But, no matter what method you work with, it is important to remember that your classes should not resemble lessons at school.
Children at this age should play and get the information they need through games. Therefore, after a short training part, immediately proceed to an interesting, gaming one. Creative activities are also very useful, with the help of which you not only study letters, but also develop the child’s fine motor skills, improve his drawing and coloring skills, and strengthen the ability to use scissors.
Games and games
There are many games to help you consolidate your knowledge. We will give a few examples.
1. Find the words with the right sound . You need to prepare cards that show different objects. The child must choose among them those in which there is a studied sound. First, you can simplify the task: ask him to find words that begin with this letter.
2. Catch the sound . To stretch a little, mother and child walk around the room. Mom calls different words. As soon as the child hears a word with the desired sound, he stops and claps his hands.
3. Think of the word . Ask your child to come up with as many words as possible with a certain sound. You can do this in turn, for example, first the mother calls the word, then the baby.
The task needs to be complicated, that is, the sound can be not only at the beginning of the word, ask him to come up with a word in which this sound will be at the end or in the middle. For example, you are learning the sound "a". First, you select words that begin with this letter - apricot, orange, then those that end in "a" - Moscow, jellyfish or contain the sound "a" in the middle - mosaic, eye.
For example, you are learning the sound "a". First, you select words that begin with this letter - apricot, orange, then those that end in "a" - Moscow, jellyfish or contain the sound "a" in the middle - mosaic, eye.
4. Determine where the sound is hidden. You need to draw a simple word scheme: three squares connected to each other. Each square denotes its own: the beginning of the word, the middle and the end. Put this word scheme in front of the child, give him a chip.
You name different words, and he must show on the diagram where the sound that you pass is located. For example, if you called the word "watermelon" (you can show a picture), the child must put the chip in 1 cell, and if the word "fox" - then in the 3rd cell.
5. Ball game . An adult throws a ball to the child and calls different words. If they have a letter being studied, he catches the ball, if not, then he does not catch it. To begin with, you can use words in which this letter is at the beginning, then complicate the task, that is, it can be in the middle or end.
Author's methods of learning the alphabet
There are several recognized methods of teaching reading, each of which can be devoted to a separate article.
Zaitsev's cubes
The basis of Zaitsev's technique is a game, that is, children simply play with cubes (there are 52 cubes of different sizes in the set) and at the same time learn to read without making any effort. These games can be started from 6-12 months old, but up to 2 years old they are used like regular blocks, and children after 2 years old can start making words.
Zaitsev's main unit is a warehouse. It can consist of a consonant and a vowel, or a single letter. The basis of this method is the warehouse principle of reading. In addition to cubes, a large warehouse table is also used.
This technique has many advantages, the main of which is that any child can be taught to read. But there are also disadvantages, for example, over time, children will have to be retrained, because they remember that letters are indicated by one color, and the teacher enters his own colors, for example, red is a vowel. In addition, the child is used to the fact that words are divided into warehouses, and not into syllables. Yes, the benefits are very expensive.
In addition, the child is used to the fact that words are divided into warehouses, and not into syllables. Yes, the benefits are very expensive.
Doman's cards
Neurosurgeon Glen Doman developed his own technique for children with CNS disorders, but then it was also used to teach healthy kids. He recommends teaching children to read not by letter, but by words, since letters mean nothing to him, and words have real designations.
For this, whole words are written on the cards in large print (at least 7-10 cm), for example, “mother” or “dad”, which must be quickly shown to the child, voicing each word. With the help of this method, even a small child can be taught to read. Training is necessarily carried out at an early age; after 5 years, the Glenn Doman method no longer works.
Olga Soboleva's Methodology
The principle of this training is based on the "two-hemispheric" work of the brain. The teacher tries to use the dominant type of memory, that is, the material is divided into 3 groups: for kinesthetics, visuals and auditory.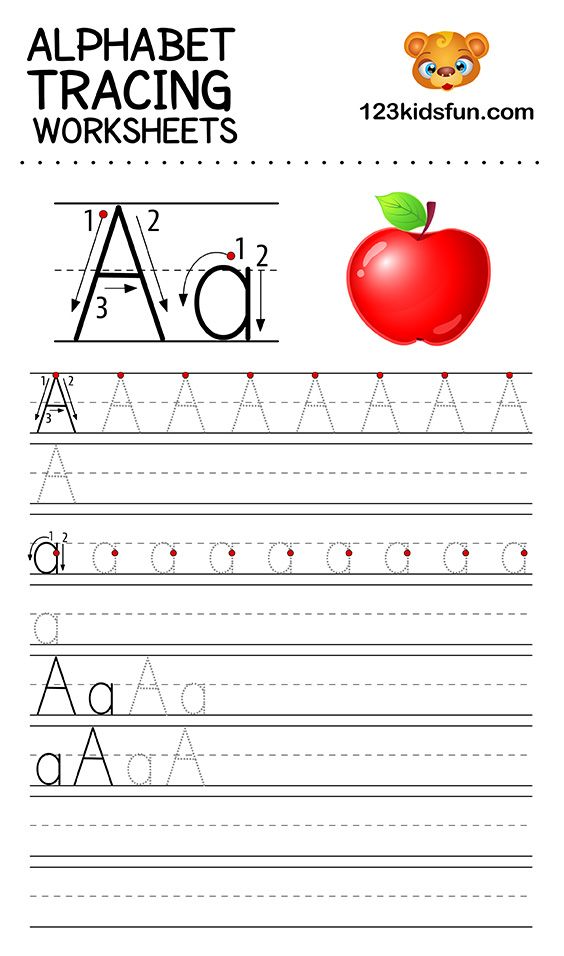
Many of its techniques are also used by ordinary teachers when teaching traditional methods to make it more interesting for children to study. Well suited for creative children and parents, it is not recommended for families where logic and structure come first.
Polyakov's method
Its author came up with 7 steps of learning to read, 70 lessons in total. Each lesson is detailed. They are held in the form of a game, take no more than 10 minutes. Stages 1 and 2 are the study of letters, warehouses, reading in warehouses.
Sergei Nikolaevich Polyakov himself, unfortunately, is no longer alive, but his work was continued by his son, as well as teachers who practice this method. If you wish, you can purchase books that describe in detail how to conduct classes, as well as video files with examples of classes.
Creative exercises
To reinforce the acquired knowledge, it is useful to conduct creative activities. For example, you can make a beautiful alphabet together. We studied the letter - cut it out of cardboard. It is better to choose a dense material. If it is difficult for the baby, you can help him, and the child will decorate - attach beads, groats, sequins, beautiful fabric, etc. to it.
We studied the letter - cut it out of cardboard. It is better to choose a dense material. If it is difficult for the baby, you can help him, and the child will decorate - attach beads, groats, sequins, beautiful fabric, etc. to it.
When you have collected the entire alphabet, you can decorate the children's room with it by connecting the letters into garlands, or hang it on the Christmas tree instead of toys. You can cut out paper blanks for letters, and the child must fold the whole letter from these parts.
Preschoolers love to draw and color. You can buy coloring books with letters, he will color them and remember what kind of letter it is. Or ask him to draw with felt-tip pens on paper, with chalk on a blackboard what you have already studied. But at this age, children should not be taught writing, this should be done by teachers in elementary school. The only thing you can teach your baby is to write in block letters.
If you are baking pies, ask your child to make familiar letters out of the dough.