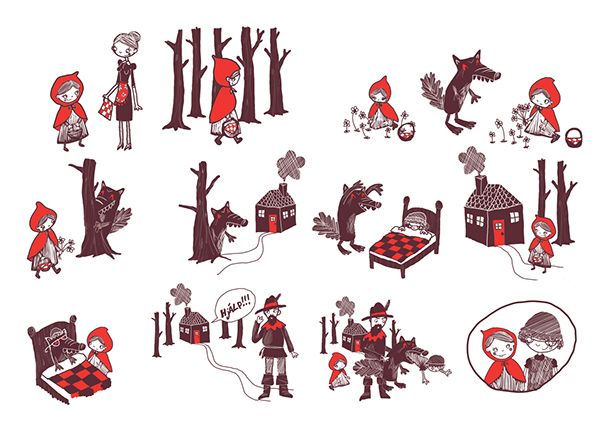
The story of red riding hood
Little Red Riding Hood
This story is featured in Favorite Fairy Tales and Short Stories for Children.
You may want to compare it to The Brothers Grimm version, Little Red-Cap.
Once upon a time there was a dear little girl who was loved by every one who looked at her, but most of all by her grandmother, and there was nothing that she would not have given to the child. Once she gave her a little cap of red velvet, which suited her so well that she would never wear anything else. So she was always called Little Red Riding Hood.
One day her mother said to her, "Come, Little Red Riding Hood, here is a piece of cake and a bottle of wine. Take them to your grandmother, she is ill and weak, and they will do her good. Set out before it gets hot, and when you are going, walk nicely and quietly and do not run off the path, or you may fall and break the bottle, and then your grandmother will get nothing. And when you go into her room, don't forget to say, good-morning, and don't peep into every corner before you do it.
"
I will take great care, said Little Red Riding Hood to her mother, and gave her hand on it.
The grandmother lived out in the wood, half a league from the village, and just as Little Red Riding Hood entered the wood, a wolf met her. Little Red Riding Hood did not know what a wicked creature he was, and was not at all afraid of him.
"Good-day, Little Red Riding Hood," said he.
"Thank you kindly, wolf."
"Whither away so early, Little Red Riding Hood?"
"To my grandmother's."
"What have you got in your apron?"
"Cake and wine. Yesterday was baking-day, so poor sick grandmother is to have something good, to make her stronger."
"Where does your grandmother live, Little Red Riding Hood?"
"A good quarter of a league farther on in the wood. Her house stands under the three large oak-trees, the nut-trees are just below. You surely must know it," replied Little Red Riding Hood.
The wolf thought to himself, "What a tender young creature. What a nice plump mouthful, she will be better to eat than the old woman. I must act craftily, so as to catch both." So he walked for a short time by the side of Little Red Riding Hood, and then he said, "see Little Red Riding Hood, how pretty the flowers are about here. Why do you not look round. I believe, too, that you do not hear how sweetly the little birds are singing. You walk gravely along as if you were going to school, while everything else out here in the wood is merry."
What a nice plump mouthful, she will be better to eat than the old woman. I must act craftily, so as to catch both." So he walked for a short time by the side of Little Red Riding Hood, and then he said, "see Little Red Riding Hood, how pretty the flowers are about here. Why do you not look round. I believe, too, that you do not hear how sweetly the little birds are singing. You walk gravely along as if you were going to school, while everything else out here in the wood is merry."
Little Red Riding Hood raised her eyes, and when she saw the sunbeams dancing here and there through the trees, and pretty flowers growing everywhere, she thought, suppose I take grandmother a fresh nosegay. That would please her too. It is so early in the day that I shall still get there in good time. And so she ran from the path into the wood to look for flowers. And whenever she had picked one, she fancied that she saw a still prettier one farther on, and ran after it, and so got deeper and deeper into the wood.
Meanwhile the wolf ran straight to the grandmother's house and knocked at the door.
"Who is there?"
"Little Red Riding Hood," replied the wolf. "She is bringing cake and wine. Open the door."
"Lift the latch," called out the grandmother, "I am too weak, and cannot get up."
The wolf lifted the latch, the door sprang open, and without saying a word he went straight to the grandmother's bed, and devoured her. Then he put on her clothes, dressed himself in her cap, laid himself in bed and drew the curtains.
Little Red Riding Hood, however, had been running about picking flowers, and when she had gathered so many that she could carry no more, she remembered her grandmother, and set out on the way to her.
She was surprised to find the cottage-door standing open, and when she went into the room, she had such a strange feeling that she said to herself, oh dear, how uneasy I feel to-day, and at other times I like being with grandmother so much.
She called out, "Good morning," but received no answer. So she went to the bed and drew back the curtains. There lay her grandmother with her cap pulled far over her face, and looking very strange.
So she went to the bed and drew back the curtains. There lay her grandmother with her cap pulled far over her face, and looking very strange.
"Oh, grandmother," she said, "what big ears you have."
"The better to hear you with, my child," was the reply.
"But, grandmother, what big eyes you have," she said.
"The better to see you with, my dear."
"But, grandmother, what large hands you have."
"The better to hug you with."
"Oh, but, grandmother, what a terrible big mouth you have."
"The better to eat you with."
And scarcely had the wolf said this, than with one bound he was out of bed and swallowed up Little Red Riding Hood.
When the wolf had appeased his appetite, he lay down again in the bed, fell asleep and began to snore very loud. The huntsman was just passing the house, and thought to himself, how the old woman is snoring. I must just see if she wants anything.
So he went into the room, and when he came to the bed, he saw that the wolf was lying in it.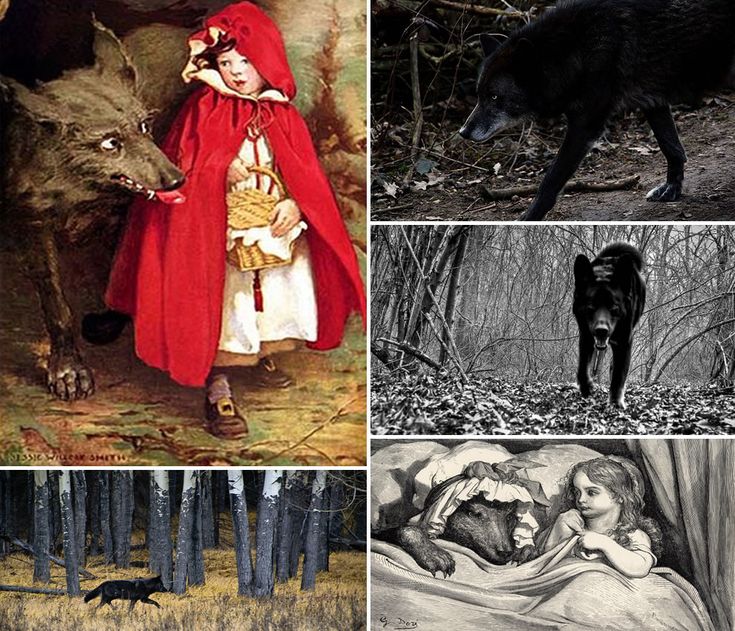 "Do I find you here, you old sinner," said he. "I have long sought you."
"Do I find you here, you old sinner," said he. "I have long sought you."
Then just as he was going to fire at him, it occurred to him that the wolf might have devoured the grandmother, and that she might still be saved, so he did not fire, but took a pair of scissors, and began to cut open the stomach of the sleeping wolf.
When he had made two snips, he saw the Little Red Riding Hood shining, and then he made two snips more, and the little girl sprang out, crying, "Ah, how frightened I have been. How dark it was inside the wolf."
And after that the aged grandmother came out alive also, but scarcely able to breathe. Little Red Riding Hood, however, quickly fetched great stones with which they filled the wolf's belly, and when he awoke, he wanted to run away, but the stones were so heavy that he collapsed at once, and fell dead.
Then all three were delighted. The huntsman drew off the wolf's skin and went home with it. The grandmother ate the cake and drank the wine which Little Red Riding Hood had brought, and revived, but Little Red Riding Hood thought to herself, as long as I live, I will never by myself leave the path, to run into the wood, when my mother has forbidden me to do so.
It is also related that once when Little Red Riding Hood was again taking cakes to the old grandmother, another wolf spoke to her, and tried to entice her from the path. Little Red Riding Hood, however, was on her guard, and went straight forward on her way, and told her grandmother that she had met the wolf, and that he had said good-morning to her, but with such a wicked look in his eyes, that if they had not been on the public road she was certain he would have eaten her up. "Well," said the grandmother, "we will shut the door, that he may not come in."
Soon afterwards the wolf knocked, and cried, "open the door, grandmother, I am Little Red Riding Hood, and am bringing you some cakes."
But they did not speak, or open the door, so the grey-beard stole twice or thrice round the house, and at last jumped on the roof, intending to wait until Little Red Riding Hood went home in the evening, and then to steal after her and devour her in the darkness. But the grandmother saw what was in his thoughts. In front of the house was a great stone trough, so she said to the child, take the pail, Little Red Riding Hood. I made some sausages yesterday, so carry the water in which I boiled them to the trough. Little Red Riding Hood carried until the great trough was quite full. Then the smell of the sausages reached the wolf, and he sniffed and peeped down, and at last stretched out his neck so far that he could no longer keep his footing and began to slip, and slipped down from the roof straight into the great trough, and was drowned. But Little Red Riding Hood went joyously home, and no one ever did anything to harm her again.
In front of the house was a great stone trough, so she said to the child, take the pail, Little Red Riding Hood. I made some sausages yesterday, so carry the water in which I boiled them to the trough. Little Red Riding Hood carried until the great trough was quite full. Then the smell of the sausages reached the wolf, and he sniffed and peeped down, and at last stretched out his neck so far that he could no longer keep his footing and began to slip, and slipped down from the roof straight into the great trough, and was drowned. But Little Red Riding Hood went joyously home, and no one ever did anything to harm her again.
You may enjoy reading a "fractured fairy tale" version of this story in rhyme, How Little Red Riding Hood Came to Be Eaten, in our collection of Favorite Fairy Tales.
The story of Little Red Riding Hood
[en español]
by Leanne Guenther
Once upon a time, there was a little
girl who lived in a village near the forest.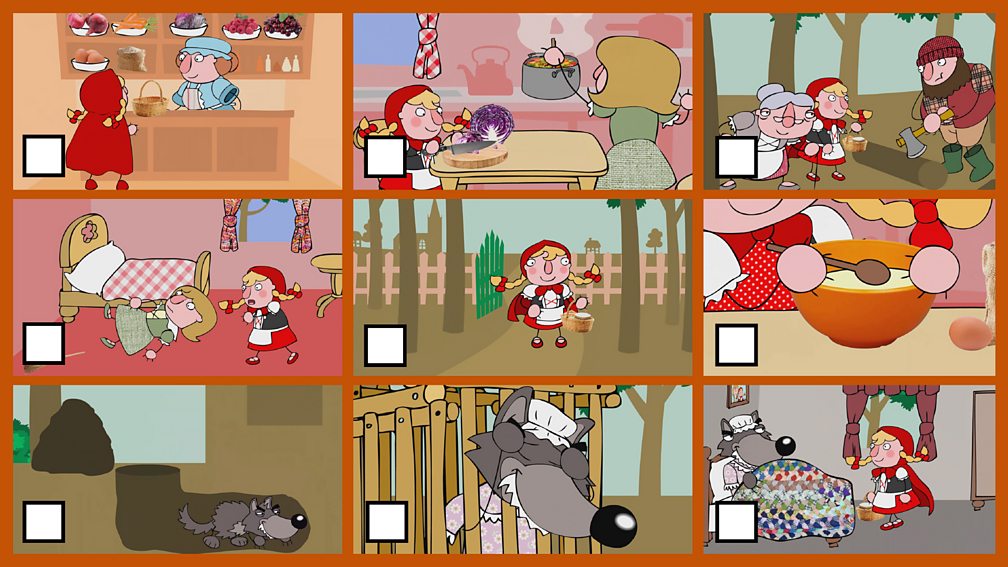 Whenever she went out, the little girl
wore a red riding cloak, so everyone in the village called her Little Red Riding Hood.
Whenever she went out, the little girl
wore a red riding cloak, so everyone in the village called her Little Red Riding Hood.
One morning, Little Red Riding Hood asked her mother if she could go to visit her grandmother as it had been awhile since they'd seen each other.
"That's a good idea," her mother said. So they packed a nice basket for Little Red Riding Hood to take to her grandmother.
When the basket was ready, the little girl put on her red cloak and kissed her mother goodbye.
"Remember, go straight to Grandma's house," her mother cautioned. "Don't dawdle along the way and please don't talk to strangers! The woods are dangerous."
"Don't worry, mommy," said Little Red Riding Hood, "I'll be careful."
But when Little Red Riding
Hood noticed some lovely flowers in the woods, she forgot her promise to
her mother. She picked a few, watched the butterflies flit about for
awhile, listened to the frogs croaking and then picked a few
more.
Little Red Riding Hood was enjoying the warm summer day so much, that she didn't notice a dark shadow approaching out of the forest behind her...
Suddenly, the wolf appeared beside her.
"What are you doing out here, little girl?" the wolf asked in a voice as friendly as he could muster.
"I'm on my way to see my Grandma who lives through the forest, near the brook," Little Red Riding Hood replied.
Then she realized how late she was and quickly excused herself, rushing down the path to her Grandma's house.
The wolf, in the meantime, took a shortcut...
The wolf, a little out of breath from running, arrived at Grandma's and knocked lightly at the door.
"Oh thank goodness dear! Come in,
come in! I was worried sick that something had happened to you in
the forest," said Grandma thinking that the knock was her
granddaughter.
The wolf let himself in. Poor Granny did not have time to say another word, before the wolf gobbled her up!
The wolf let out a satisfied burp, and then poked through Granny's wardrobe to find a nightgown that he liked. He added a frilly sleeping cap, and for good measure, dabbed some of Granny's perfume behind his pointy ears.
A few minutes later, Red Riding Hood knocked on the door. The wolf jumped into bed and pulled the covers over his nose. "Who is it?" he called in a cackly voice.
"It's me, Little Red Riding Hood."
"Oh how lovely! Do come in, my dear," croaked the wolf.
When Little Red Riding Hood entered the little cottage, she could scarcely recognize her Grandmother.
"Grandmother! Your voice sounds so odd. Is something the matter?" she asked.
"Oh, I just have touch of a cold,"
squeaked the wolf adding a cough at the end to prove the point.
"But Grandmother! What big ears you have," said Little Red Riding Hood as she edged closer to the bed.
"The better to hear you with, my dear," replied the wolf.
"But Grandmother! What big eyes you have," said Little Red Riding Hood.
"The better to see you with, my dear," replied the wolf.
"But Grandmother! What big teeth you have," said Little Red Riding Hood her voice quivering slightly.
"The better to eat you with, my dear," roared the wolf and he leapt out of the bed and began to chase the little girl.
Almost too late, Little Red Riding Hood realized that the person in the bed was not her Grandmother, but a hungry wolf.
She ran across the room and through the door, shouting, "Help! Wolf!" as loudly as she could.
A woodsman who was chopping logs nearby heard
her cry and ran towards the cottage as fast as he could.
He grabbed the wolf and made him spit out the poor Grandmother who was a bit frazzled by the whole experience, but still in one piece."Oh Grandma, I was so scared!" sobbed Little Red Riding Hood, "I'll never speak to strangers or dawdle in the forest again."
"There, there, child. You've learned an important lesson. Thank goodness you shouted loud enough for this kind woodsman to hear you!"
The woodsman knocked out the wolf and carried him deep into the forest where he wouldn't bother people any longer.
Little Red Riding Hood and her Grandmother had a nice lunch and a long chat.
Printable version of this page
Story Pages Templates:
- Close the template window after printing to return to this screen.
- Set page margins to zero if you have trouble fitting the template on one page (FILE, PAGE SETUP or FILE, PRINTER SETUP in most browsers).

Template Page 1 (color) or (B&W)
Template Page 2 (color) or (B&W)
Template Page 3 (color) or (B&W)
Template Page 4 (color) or (B&W)
Template Page 5 (color) or (B&W)
Template Page 6 (color) or (B&W)
Template Page 7 (color) or (B&W)
Template Page 8 (color) or (B&W)
Template Page 9 (color) or (B&W)
Template Page 10 (color) or (B&W)
The true story of Little Red Riding Hood
The true story of Little Red Riding Hood
© Tatyana Vorontsova
190 years ago, on October 18, 1812, two young scientists, the brothers Jacob and Wilhelm Grimm, put the final point in the book bestseller of German-language literature. The book was called “Children's and Household Tales”, and it was from it that the world became known
The book was called “Children's and Household Tales”, and it was from it that the world became known
“Once upon a time there was a little, sweet girl. And whoever looked at her, everyone liked her, but her grandmother loved her more than anyone and was ready to give her everything. So she once gave her a cap of red velvet, and because this cap suited her very well and she didn’t want to wear any other, they called her Little Red Riding Hood ... ”Who in childhood was not fascinated by this seemingly naive, artless text? Nevertheless, the story of Little Red Riding Hood is not so simple: it is tortuous and intricate, just as human consciousness is tortuous and intricate.
The first literary version of this old folk tale was published by Charles Perrault in 1697 in Paris - in the book "Tales of my mother Goose, or Stories and tales of bygone times with teachings", dedicated to the princess of the French royal house. In those days, the story of a girl who went to visit her grandmother and met a wolf on the road was told all over Europe - both in the homes of commoners and in the castles of the nobility. The tale was especially popular in the Tyrol and the foothills of the Alps, where it had been known at least since the 14th century. Actually, it was a lot of stories: in the north of Italy, the granddaughter brought fresh fish to her grandmother, in Switzerland - a head of young cheese, in the south of France - a pie and a pot of butter; in some cases, the wolf was the winner, in others, the girl ... Perrault took one of the options as a basis, dressed up the nameless girl in a “companion” cap of scarlet velvet and bestowed the name - Little Red Riding Hood. I must say that in France at the turn of the 17th-18th centuries, when social differences in clothing were strictly regulated, only aristocrats and middle-class women wore such headdresses. A simple village girl, who easily walked in a velvet cap of a defiant color, and even - contrary to her mother's orders - entered into a conversation with a stranger, obviously understood a lot about herself, which the harsh era of the Enlightenment did not encourage.
The tale was especially popular in the Tyrol and the foothills of the Alps, where it had been known at least since the 14th century. Actually, it was a lot of stories: in the north of Italy, the granddaughter brought fresh fish to her grandmother, in Switzerland - a head of young cheese, in the south of France - a pie and a pot of butter; in some cases, the wolf was the winner, in others, the girl ... Perrault took one of the options as a basis, dressed up the nameless girl in a “companion” cap of scarlet velvet and bestowed the name - Little Red Riding Hood. I must say that in France at the turn of the 17th-18th centuries, when social differences in clothing were strictly regulated, only aristocrats and middle-class women wore such headdresses. A simple village girl, who easily walked in a velvet cap of a defiant color, and even - contrary to her mother's orders - entered into a conversation with a stranger, obviously understood a lot about herself, which the harsh era of the Enlightenment did not encourage. In the finale, the wolf taught a cruel lesson to all the windy young ladies: he "attacked Little Red Riding Hood and swallowed her."
In the finale, the wolf taught a cruel lesson to all the windy young ladies: he "attacked Little Red Riding Hood and swallowed her."
The gallant author crowned the “cute trifle” (as he called his fairy tale) with a moral:
Little children, not without reason
(And especially girls, beauties and spoiled girls),
Encountering all kinds of men on the way,
No speeches
Otherwise, the wolf might eat them...
The popularity of Perrault's book was amazing, although the 69-year-old author himself, a prominent royal official and member of the French Academy, fearing ridicule, at first did not dare to put his own name on the collection, therefore for the first time, "Tales of Mother Goose" was published signed by the 11-year-old son of the writer - D'Armancourt.
But the “canonization” of the text did not end there. From the pages of a French book, Little Red Riding Hood returned to oral stories, and a hundred years later reappeared in a literary version - in German Kassel. This time, the philologists brothers Wilhelm and Jacob Grimm acted as authors, who saw in fairy tales by no means “trifles”. Grimms perceived folk tales as a necessary link in the unification of the fragmented German principalities-electors, who spoke different dialects, into a single national state. The goal of the Grimms was to collect and voice "living folk poetry", to preserve the authenticity of folk art. They believed that the “German pramith” was contained in fairy tales, and in their book “Children's and Household Tales” they selected only those stories that were popular in the territory of German settlement. Grimm's fairy tales were considered as pantries in which a single memory of the mythological ideas and beliefs of their ancestors was preserved, and they saw their task in revealing the “authenticity”, the true nationality of the plot. Based on the idea of the unity of the people, the Grimms did not distinguish between written and oral sources, as well as the belonging of authors to different social and cultural strata, believing that in any of the options there is both truth and artificiality.
This time, the philologists brothers Wilhelm and Jacob Grimm acted as authors, who saw in fairy tales by no means “trifles”. Grimms perceived folk tales as a necessary link in the unification of the fragmented German principalities-electors, who spoke different dialects, into a single national state. The goal of the Grimms was to collect and voice "living folk poetry", to preserve the authenticity of folk art. They believed that the “German pramith” was contained in fairy tales, and in their book “Children's and Household Tales” they selected only those stories that were popular in the territory of German settlement. Grimm's fairy tales were considered as pantries in which a single memory of the mythological ideas and beliefs of their ancestors was preserved, and they saw their task in revealing the “authenticity”, the true nationality of the plot. Based on the idea of the unity of the people, the Grimms did not distinguish between written and oral sources, as well as the belonging of authors to different social and cultural strata, believing that in any of the options there is both truth and artificiality. They presented their own version of Little Red Riding Hood, combining oral stories, the fairy tale of Charles Perrault, as well as the verse play “The Life and Death of Little Red Riding Hood”, written in 1800 by the German romantic writer Ludwig Tiek (it was Tiek who introduced the hunter who saves the girl and grandmother from the belly of a wolf).
They presented their own version of Little Red Riding Hood, combining oral stories, the fairy tale of Charles Perrault, as well as the verse play “The Life and Death of Little Red Riding Hood”, written in 1800 by the German romantic writer Ludwig Tiek (it was Tiek who introduced the hunter who saves the girl and grandmother from the belly of a wolf).
A feature of the fairy tale by the Brothers Grimm is the abundance of details, sometimes seeming nonsense, sometimes everyday life, sometimes just rudeness and cruelty. The girl's grandmother does not live in another village, but in the forest itself. Little Red Riding Hood brings her a piece of cake and a bottle of wine in her apron, and her mother sternly admonishes her: “Go modestly, as you should; don’t turn aside from the road, otherwise you’ll fall and break the bottle, then grandmother won’t get anything. And when you enter her room, do not forget to say hello to her, and not only to look back and forth in all corners first. The wolf reproachfully tells the girl that she is going, “as if she is in a hurry to go to school”, offers to “have fun in the forest”, and Little Red Riding Hood, succumbing to persuasion, enters the forest thicket and begins to collect flowers. Having eaten the grandmother, the wolf not only lays down in her bed, but first puts on a dress and cap. At the same time, he leaves the door wide open. Having swallowed the girl, the wolf snores so loudly throughout the forest that the hunter passing by the hut thinks if he needs to help the old woman. Seeing the wolf, the hunter takes the scissors and rips open the sleeping belly: “As soon as he made the first incision, he sees that the little red cap is visible inside. He quickly made a second incision, and a girl jumped out of there and screamed:
The wolf reproachfully tells the girl that she is going, “as if she is in a hurry to go to school”, offers to “have fun in the forest”, and Little Red Riding Hood, succumbing to persuasion, enters the forest thicket and begins to collect flowers. Having eaten the grandmother, the wolf not only lays down in her bed, but first puts on a dress and cap. At the same time, he leaves the door wide open. Having swallowed the girl, the wolf snores so loudly throughout the forest that the hunter passing by the hut thinks if he needs to help the old woman. Seeing the wolf, the hunter takes the scissors and rips open the sleeping belly: “As soon as he made the first incision, he sees that the little red cap is visible inside. He quickly made a second incision, and a girl jumped out of there and screamed:
— Oh, how scared I was! It was so dark in the wolf's belly!
Grandmother also got out after Little Red Riding Hood, barely alive - she could not catch her breath.” Then the wolf is punished: his belly is stuffed with large stones. Waking up, he wants to run away, but heavy stones are pulled down, and the wolf falls dead. Each of the winners receives his reward: the hunter takes home the skin taken from the wolf, the grandmother, after eating a cake and drinking wine, gets better, and Little Red Riding Hood learns a life lesson: “From now on, I will never turn off the highway alone without my mother’s permission” . Soon the girl meets another wolf in the forest, and this meeting turns out to be fatal for him: Little Red Riding Hood and Grandmother drown the stupid villain in the trough without anyone's help.
Waking up, he wants to run away, but heavy stones are pulled down, and the wolf falls dead. Each of the winners receives his reward: the hunter takes home the skin taken from the wolf, the grandmother, after eating a cake and drinking wine, gets better, and Little Red Riding Hood learns a life lesson: “From now on, I will never turn off the highway alone without my mother’s permission” . Soon the girl meets another wolf in the forest, and this meeting turns out to be fatal for him: Little Red Riding Hood and Grandmother drown the stupid villain in the trough without anyone's help.
The first publication of "Children's and Household Tales" did not arouse much enthusiasm. The Brothers Grimm's book was seen as a cross between a scientific document and children's fun, the publication was not bought up - readers demanded fabulous romantic short stories. However, after some time, either the authors successfully finalized the material, or the public got used to a strange mixture of archaic oral folk tradition and its literary fixation - the book began to diverge with a bang.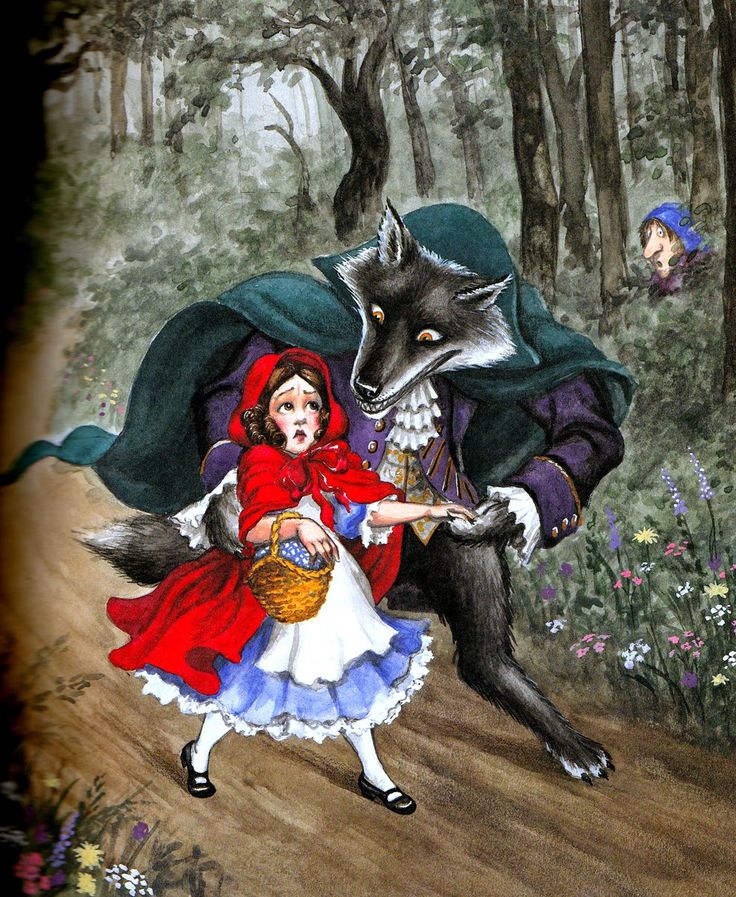 Numerous translations were also not long in coming...
Numerous translations were also not long in coming...
Since then, "Little Red Riding Hood" has become the most popular folk book fairy tale in Europe, and then in the world - always relevant and full of hidden meaning, which many tried to comprehend, sometimes crossing all sorts of boundaries in their conclusions.
So, since the fairy tales of the Brothers Grimm came out in the year of the victory over Napoleon, in 1812, and were collected at a time when the lands of the Rhine were under the French heel, some researchers saw the French “intruder” in the wolf, and the suffering German people in Little Red Riding Hood , and in the hunter - the expected disinterested liberator. And a century later, the ideologues of the Third Reich, who declared "Children's and Household Tales" by the Brothers Grimm a sacred book, wrote in all seriousness that Little Red Riding Hood embodies the German people, persecuted by the wolf of Jewry.
The Grimms themselves, deeply religious people, saw in Little Red Riding Hood a single symbol of rebirth - a descent into the darkness and transformation. A hundred years later, Christian researchers who developed this idea declared Little Red Riding Hood the personification of human passions: vanity, self-interest and hidden lust. In the wolf, these same passions are embodied clearly and definitely. Only freed from the wolf's belly, as if born again, the girl is transformed.
A hundred years later, Christian researchers who developed this idea declared Little Red Riding Hood the personification of human passions: vanity, self-interest and hidden lust. In the wolf, these same passions are embodied clearly and definitely. Only freed from the wolf's belly, as if born again, the girl is transformed.
Neo-mythologists, supporters of the so-called “wolf-solar theory”, who also considered themselves followers of the Grimms, argued that the fairy tale reflects the change of natural phenomena: the grandmother living in the forest in a house “under three large oaks” is mother nature, Little Red Riding Hood is the sun , the wolf is winter, and the hunter is the new year. Neo-pagans (there were some) considered the wolf to be the most positive character in the fairy tale. The red color of the girl's headdress seemed to them the embodiment of danger, and the grandmother, living in a dense forest, evoked associations with Baba Yaga and the goddess of death of the ancient Germans (by the way, pies and wine were a common sacrifice for the dead and other representatives of the underworld among all Indo-Europeans). So the wolf seemed to them to be something like an ancestor hero, who was trying to free the world from death and fell victim in an unequal struggle.
So the wolf seemed to them to be something like an ancestor hero, who was trying to free the world from death and fell victim in an unequal struggle.
Initially, in the oral tradition of the fairy tale about Little Red Riding Hood, the wolf was not just an animal, but a werewolf (this is where his ability to speak in a human voice and successful attempts to disguise himself as a grandmother come from). The Grimms, like Perrault, did not advertise it, but implied it. At the end of the 20th century, interest in mysticism provoked a number of relevant interpretations of Little Red Riding Hood, among which the most famous interpretation of the British "Oscar" Neil Jordan - he turned this story into a love thriller about werewolves "In the company of wolves".
People of the 19th century saw a pure image in Little Red Riding Hood. A fan of "Children's and Household Tales" Charles Dickens in his "Christmas Stories" shared naive childhood reflections: "I felt that if I could marry Little Red Riding Hood, I would know true happiness.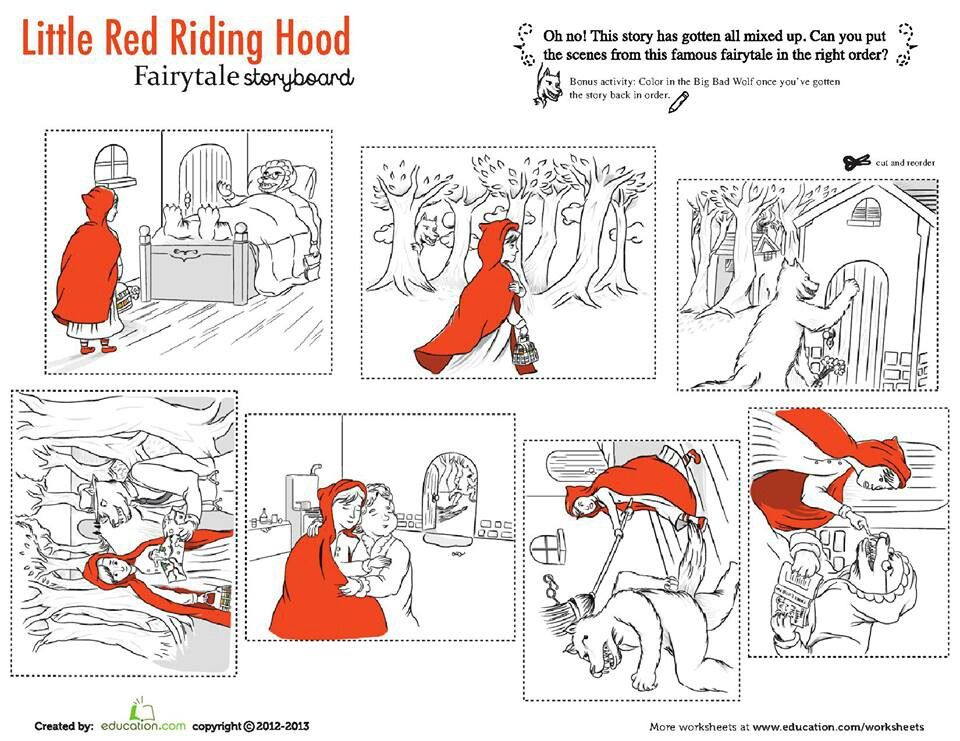 " And the Grimms themselves, who dreamed of returning to their national roots, generally believed that before the world was asexual, and “people produced children with just one look (as God acts only with a thought)” - only “then they needed kisses for this and, finally, hugs and carnal intercourse." “Teutonic religious neurotics” (so the brothers were dubbed by little-believing psychoanalysts of the 20th century) when preparing fairy tales for publication, they expelled from them all to any extent erotic scenes and expressions, because they believed that “old poetry” was “innocent”.
" And the Grimms themselves, who dreamed of returning to their national roots, generally believed that before the world was asexual, and “people produced children with just one look (as God acts only with a thought)” - only “then they needed kisses for this and, finally, hugs and carnal intercourse." “Teutonic religious neurotics” (so the brothers were dubbed by little-believing psychoanalysts of the 20th century) when preparing fairy tales for publication, they expelled from them all to any extent erotic scenes and expressions, because they believed that “old poetry” was “innocent”.
The 20th century made Little Red Riding Hood a brand and a diagnosis. So, in the 30s, supporters of Freud's student Erich Fromm declared that Little Red Riding Hood is a fully matured girl, and her headdress is a symbol of physiological maturity. The mother's warnings to stay on the road and beware of breaking the bottle are warnings against casual relationships and loss of virginity. The main characters of the tale are three generations of women. The wolf, embodying the masculine principle, is a “ruthless and treacherous animal”, and the hunter is a conventional image of Little Red Riding Hood's father (which is why he is not among the despised men). In general, the story tells about the triumph of the female half of humanity over the male and returns the reader to the world of matriarchy.
The wolf, embodying the masculine principle, is a “ruthless and treacherous animal”, and the hunter is a conventional image of Little Red Riding Hood's father (which is why he is not among the despised men). In general, the story tells about the triumph of the female half of humanity over the male and returns the reader to the world of matriarchy.
In the 1960s, the era of the sexual revolution and the rise of feminism, researchers began to talk about swallowing as rape, a symbolic description of uncontrollable sexual appetite. At the same time, the girl herself provokes the wolf to active actions: she wears a bright hat, talks to a stranger, has fun in the forest ... At the same time, the wolf turns out to be a transvestite and secretly envies the woman's ability to become pregnant. That is why he swallows his grandmother and granddaughter whole, making an attempt to put living beings in his stomach. At the end of the wolf, stones are killed - symbols of sterility, which is a mockery of the desire to play childbirth . ..
..
There were not so many of those who remembered that Little Red Riding Hood was a fairy tale for children. They timidly pointed to the educational aspect: an innocent child should beware of life's dangers and obey mother's orders. The initial “innocence” of the story was also indicated by the fact that the wolf did not die when the hunter cut open his stomach in order to free the girl and grandmother.
The story of the second wolf was forgotten in the 20th century, it is not mentioned in all modern editions of the Brothers Grimm's fairy tales. In essence, this is a sequel, a story about a completely different girl - more experienced, correct, who learned the lessons of the “previous series”. And Little Red Riding Hood, who has lost her innocent naivete, is not interesting to the world - even if it has comprehended everything and survived all possible revolutions ...
source: Everything for the teacher of literature
The Scariest Tale: The True Story of Little Red Riding Hood
In France, her name is La Chaperone Rouge, in Germany, Rotkäppchen, and in the Czech Republic, her funniest name is Červená Karkulka ("Chervena Karkulka"). Little Red Riding Hood is known all over the world, but few people know the story of this fairy tale.
Little Red Riding Hood is known all over the world, but few people know the story of this fairy tale.
The tale of Little Red Riding Hood was first heard in Europe in the 14th century. Like many fairy tales that later became children's, at first it was not at all childish, but terrible and nasty. For example, a wolf does not eat a grandmother, but prepares some vile food from her and feeds her granddaughter with it. And no rescue lumberjacks at the end!
Where did the hat come from
Charles Perrault was the first to remove horrors from the fairy tale in 1697. He also dressed Little Red Riding Hood in a red cap: before that, the fairy tale did not specify how the girl, deceived by the wolf, was dressed.
Perrault gave her not just a cap, but a chaperon - a headdress, which at that time was not worn in the cities for a long time, but it was still found in the villages. Thus, it was emphasized that Little Red Riding Hood is a village girl, “from the people”, and this story happened, most likely, a long time ago.
Uninvented wolf
Brothers Jakob and Wilhelm Grimm recorded the fairy tale in the usual form for us in 1812. Jacob Grimm, the eldest of the brothers, was a great lover of antiquities, ancient legends and myths, and for some time served as the personal librarian of Jerome Bonaparte, younger brother of Emperor Napoleon I.
Most likely, it was then that Jacob Grimm heard the story of the evil and cunning wolf, who attacked children and women in the French county of Gévaudan almost 50 years ago. From 1764 to 1767, the Gevaudan wolf, or, as it was more commonly called, the "Gevodan monster", attacked people more than 200 times, with almost 100 people killed.
Eyewitnesses spoke of a terrible beast that made the famous Hound of the Baskervilles look like a poodle. Incredibly huge and strong, the wolf was also distinguished by rare cunning. The King of France personally sent his best hunters to capture or kill this monster, but it always managed to escape. The local governor sent a detachment of 50 soldiers to Zhevodan, but even they could not find and kill the Zhevodan beast.
The local governor sent a detachment of 50 soldiers to Zhevodan, but even they could not find and kill the Zhevodan beast.
Residents locked themselves at home and did not go out alone. Many called the Zhevodan wolf a "werewolf": they say that he can, imitating a human voice, call travelers by name and lure the unwary into the forest or into the swamp.
Courageous children
Some still managed to escape - almost like Little Red Riding Hood. Once, seven peasant children were walking from the village of Villare when they were attacked by a Zhevodan beast. However, the children were not afraid: they had sticks with tied knives, and they were able to fight off the monster. The most courageous was 12-year-old Jacques Portfay, and as a reward for bravery, the King of France personally ordered the boy to be educated. When Jacques grew up, he became an artillery lieutenant in the French army.
On another occasion, a monster attacked a group of girls from the village of Pollac-en-Marjoride. One of the girls, Marie-Jean Vallee, grabbed a wooden stake and inflicted a serious wound on the beast, after which it ran away - so she escaped herself and saved her friends.
One of the girls, Marie-Jean Vallee, grabbed a wooden stake and inflicted a serious wound on the beast, after which it ran away - so she escaped herself and saved her friends.
A wolf or an extinct animal
Three years later the attacks stopped. But the mystery remained a mystery: was this monster a wolf? Eyewitnesses said that the beast “looks like a wolf, but not a wolf”: it was a huge predatory beast, with a mouth full of sharp teeth, but at the same time with a long thin tail and hooves instead of claws.
In addition, the “wolf” allegedly never howled like dogs or wolves howl, and his voice rather resembled human laughter. The skin of the "wolf" was not gray or black, but light brown, with dark spots. Finally, the “wolf” ran beautifully over rocks and swamps, and during the attack it often stood up on its hind legs, which real wolves never do.
At the end of the 19th century, scientists discovered the bones of ancient predators - mesonychia, such as Andrewsarchus or Synonyx. These animals were very large in size, with a long thin tail, a huge mouth with sharp teeth and hooves instead of claws.
These animals were very large in size, with a long thin tail, a huge mouth with sharp teeth and hooves instead of claws.
Descriptions of the "Gevaudan monster" surprisingly coincided with the conclusions of scientists in many details. For example, scientists believe that mesonychia lived in coastal or swampy areas. The "Zhevaudan Beast", according to the memoirs of contemporaries, also incredibly skillfully hid from hunters in the swamps. But mesonychia became extinct more than 30 million years ago. Where could such a beast appear in France in the 18th century?
A hundred years later, in Chauvet, not far from the county of Gévaudan, a previously unknown cave was discovered. More than 400 ancient rock paintings were found inside. The drawings depicted animals: horses, deer, the extinct woolly rhinoceros, as well as predators - lions, bears, wolves and a mysterious beast, which scientists called the "panther from Chauvet".
"Panther of Chauvet" Enormous in size, with a spotted skin, a thin long tail and a head like a wolf or a bear. This animal does not look like a panther at all, but at the same time it very well resembles the ancient mesonychia and the "Gevodan monster". So, just 30 thousand years ago, prehistoric hunters knew an animal that lived on Earth 30 million years ago? 30 thousand years is a very short time for biology.
This animal does not look like a panther at all, but at the same time it very well resembles the ancient mesonychia and the "Gevodan monster". So, just 30 thousand years ago, prehistoric hunters knew an animal that lived on Earth 30 million years ago? 30 thousand years is a very short time for biology.
It is not known whether individual specimens of ancient mesonychia could have survived in impenetrable swamps, but perhaps the “Gevodan monster” was one of the last representatives of a biological species considered extinct. Be that as it may, the story of the Gevaudan werewolf was preserved in the well-known fairy tale thanks to the Brothers Grimm.
This article was published in Luchik magazine, the best children's magazine in the country according to the results of the All-Russian Children's Media Competition. Issues of the journal are available for public access on the official website of the journal.
Subscribe to "Luchik", and the latest issue will be sent to your mailbox every month.