What are all the primary colors
Color Basics | Usability.gov
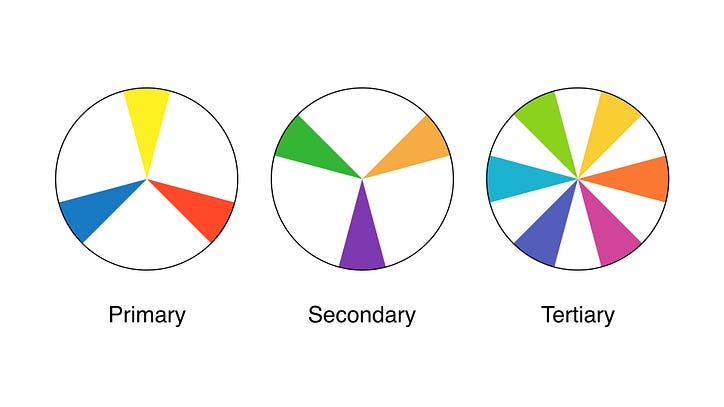
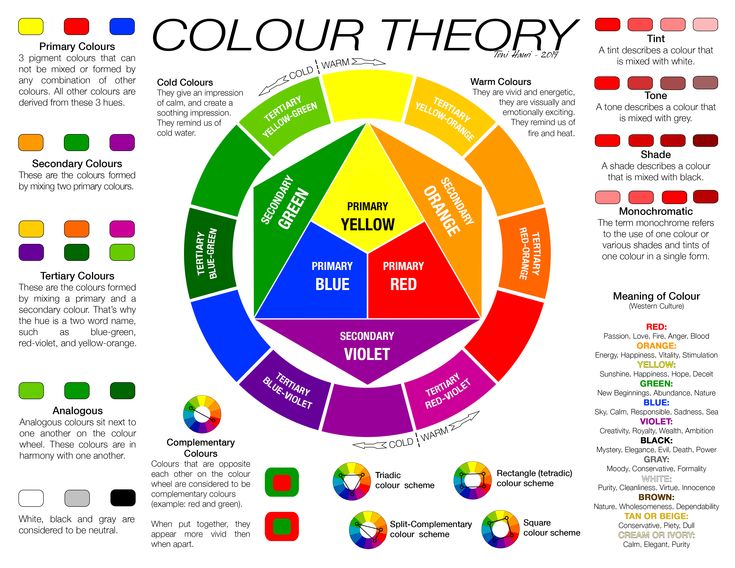
A color wheel is an illustrative model of color hues around a circle. It shows the relationships between the primary, secondary, and intermediate/ tertiary colors and helps demonstrate color temperature. Digital teams communicate exact colors through the use of hex codes.
Understanding the Color Wheel
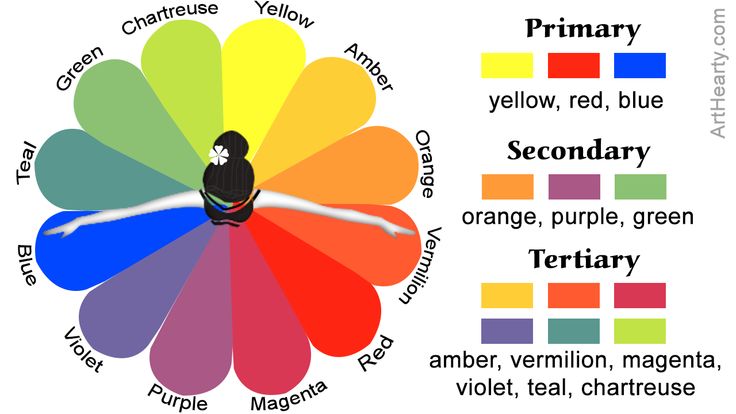
Many color wheels are shown using 12 colors. Using this color wheel as an example, it can be read as follows:
- Three Primary Colors (Ps): Red, Yellow, Blue
- Three Secondary Colors (S’): Orange, Green, Violet
- Six Tertiary Colors (Ts): Red-Orange, Yellow-Orange, Yellow-Green, Blue-Green, Blue-Violet, Red-Violet, which are formed by mixing a primary with a secondary
It’s important to note that some people add more intermediates, for 24 total named colors, and some color wheels show interior points and circles, which represent color mixtures.
Color Temperature
The colors on the red side of the wheel are warm; the green side of the wheel has the cooler colors. These color temperature designations are absolute. More subtle color temperature relationships are relative, meaning that each color on the warm side of the wheel can be known as cool, and colors on the cools side of the wheel can be known as warm depending on the relationship to their neighboring color. Colors from the same hue, for instance red, can also be warmer or cooler than one another.
Color temperatures affect us both psychologically and perceptually by helping us determine how objects appear positioned.
| Warm Colors | Cool Colors |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Neutrals
Neutral colors include black, white, gray, tans, and browns. They’re commonly combined with brighter accent colors but they can also be used on their own in designs. The meanings and impressions of neutral colors depend more so upon the colors around them.
Color Models: CMYK vs. RGB
There are two models for colors. They have different purposes and different attributes. They are as follows:
- CMYK Color Models: Stands for cyan, magenta, and yellow. It applies to painting and printing. The CMYK model is a subtractive model, meaning that colors are created through absorbing wavelengths of visible light.
 The wavelengths of light that don’t get absorbed are reflected, and that reflected light ends up being the color we see.
The wavelengths of light that don’t get absorbed are reflected, and that reflected light ends up being the color we see. - RGB Color Models: RGB stands for red, green, and blue. It applies to computers, televisions, and electronics. The RGB model is an additive model, meaning that colors are created through light waves that are added together in particular combinations in order to produce colors.
Hex Codes
To name colors in web design, teams use hexademal code. All hexadermal codes:
- Start with a hash mark (#)
- Consist of three pairs of characters sequenced together (totaling of six characters), with each pair controlling one of the primary additive colors (red, green, blue)
- Those six characters following the hash mark consist of ten numerals (0-9) and/ or six letters (a-f)
It is easy to identify patterns in the hex codes some colors; see SmashingMagazine’s great chart at the right for this.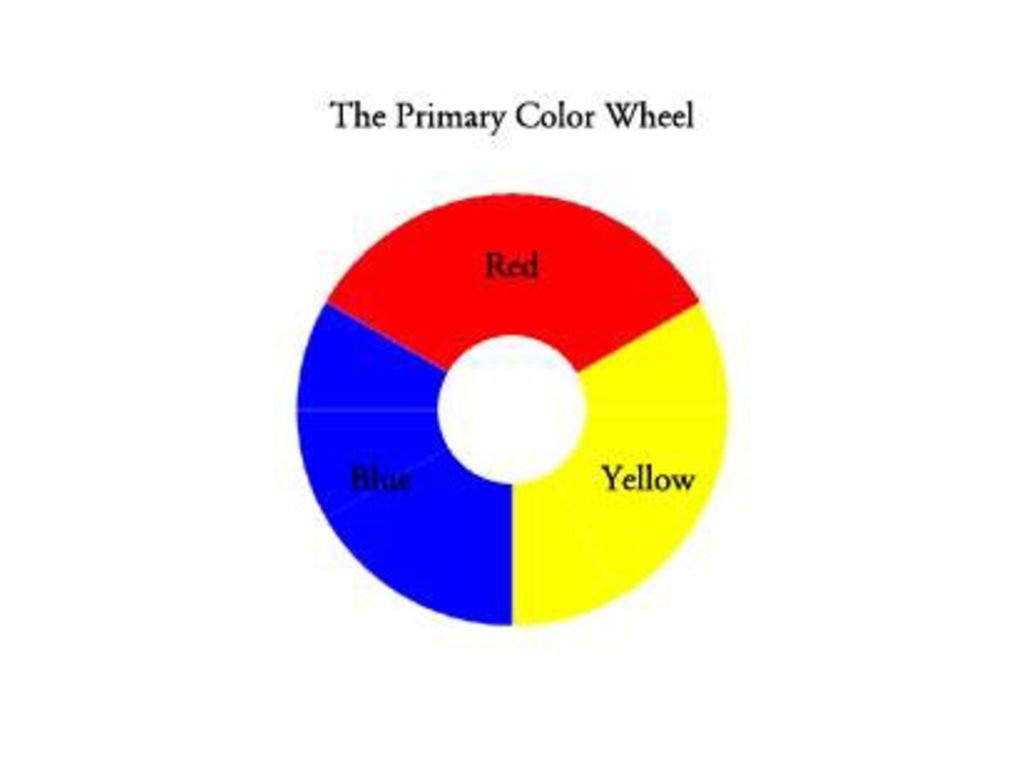 Some things to know include:
Some things to know include:
- 00 is a lack of primary
- ff is the primary at full strength
To find additive colors, start with black and change each pair to ff:
- #000000 is black (no primaries)
- #ff0000 is the brightest red
- #00ff00 is the brightest green
- #0000ff is the brightest blue
To find subtractive colors, start with white and change each pair to 00:
- #ffffff is white (all primaries
- #00ffff is the brightest cyan
- #ff00ff is the brightest magenta
- #ffff00 is the brightest yellow
It is also possible to abbreviate some hex numbers. For instances #fae expands to #ffaaee and #09b expands to #0099bb.
For instances #fae expands to #ffaaee and #09b expands to #0099bb.
Additional Resources
- Color Meaning
- Color Pallets
- Color Theory for Designers, Part 1: The Meaning of Color
- The Code Side of Color
- Color Theory 101: Deconstructing 7 Famous Brands' Color Palettes
- Color
- Color Meanings
- Color Wheel Pro: Color Meaning
Primary Colors - What Are the Primary Colors in Color Theory?
Most of us learned at school what the basic primary colors are, the main colors being red, yellow, and blue.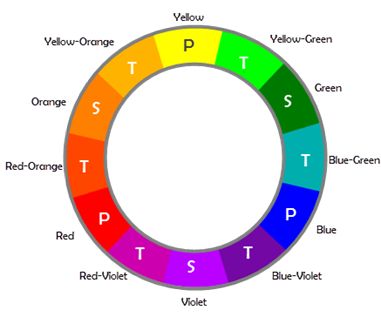 However, over the years, other color models have been discovered and the issue has become a little more complex. So, what are the primary colors and exactly how many primary colors are there?
However, over the years, other color models have been discovered and the issue has become a little more complex. So, what are the primary colors and exactly how many primary colors are there?
Table of Contents
- 1 What Are Primary Colors?
- 1.1 Additive Colors
- 1.2 Subtractive Colors
- 1.3 How Many Primary Colors Are There?
- 2 Color Psychology and Primary Colors
- 2.1 The Color Blue
- 2.2 The Color Green
- 2.3 The Color Yellow
- 2.4 The Color Red
- 3 How Can You Mix Primary Colors to Create New Colors?
- 3.1 Are Primary Colors Pure?
- 4 Frequently Asked Questions
- 4.1 How Many Primary Colors Are There?
- 4.2 What Are Additive Colors?
- 4.3 What Are Subtractive Colors?
- 4.4 Can You Mix All the Primary Colors?
What Are Primary Colors?
A primary color definition can be a bit tricky as it is not as simple as what you learned back in school. A basic explanation is that primary colors can be pigments or light, that when combined, create a myriad of other colors. The traditional color theory we all learned when painting, tells us that there are three main colors, red, yellow, and blue. However, when it comes to how many primary colors there are, it is a little more complex than this.
A basic explanation is that primary colors can be pigments or light, that when combined, create a myriad of other colors. The traditional color theory we all learned when painting, tells us that there are three main colors, red, yellow, and blue. However, when it comes to how many primary colors there are, it is a little more complex than this.
This is because the traditional color theory only involves the use of pigments in paint and does not take into consideration the way light blends color. So, there are other color models you should consider. These involve the RGB color model, which has red, green, and blue as your primary colors, and is used with things like television screens and computer images. The other is the CMYK model which includes cyan, magenta, yellow, as well as black, and is mainly utilized for printing.
As you can see a primary color definition is more than meets the eye. Speaking of, the eye is an amazing organ, and how it perceives color is due to where the color comes from. Some colors are sent directly to the eyes, while others reach the eyes through a reflection. When it comes to light and the RGB model, and how we see color, it involves color receptors in the retina, which are known as cone cells, and these are responsible for color vision and sensitivity.
Some colors are sent directly to the eyes, while others reach the eyes through a reflection. When it comes to light and the RGB model, and how we see color, it involves color receptors in the retina, which are known as cone cells, and these are responsible for color vision and sensitivity.
We have three types of cones, mainly green, red, and blue. This means we have trichromatic color vision. So, therein lies the major difference between the primary colors. Everything is about how colors enter the eye. There are two principal types of color mixing models called additive and subtractive colors.
Additive Colors
Additive colors were originally discovered by Sir Isaac Newton when he was experimenting using a prism and mirrors. He used the prism to refract white light, which split into different colors and when recombined, they formed white light. This was then used to develop the first visual representation of colors known as the color wheel. The experiments led to the theory that red, green, and blue are the primary colors that all other colors come from.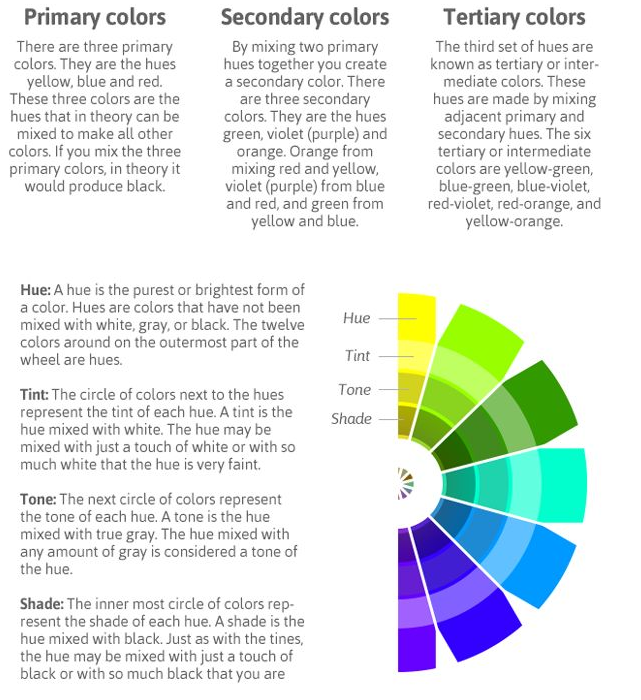
So, these colors are said to be the primary colors for the additive color model and are what happens when you look at a computer screen or television.
For example, if you combine green and blue light, you should come up with a cyan color. However, it might be more complicated than this, and some say that the yellow-green section of the spectrum responds better than the red when it comes to how the receptors in the eye respond. So, the range of colors can depend on the three additive primary colors, which could vary. However, we will remain with the traditional RGB primary colors, just to keep it simple.
Subtractive Colors
This color model is achieved when you are blending inks or paint pigments. These colors can be seen because they are reflected by the light that lands on them. For example, if you add yellow ink to a white piece of paper, the ink will absorb all the blue color wavelengths and leave the others, which you then observe as yellow.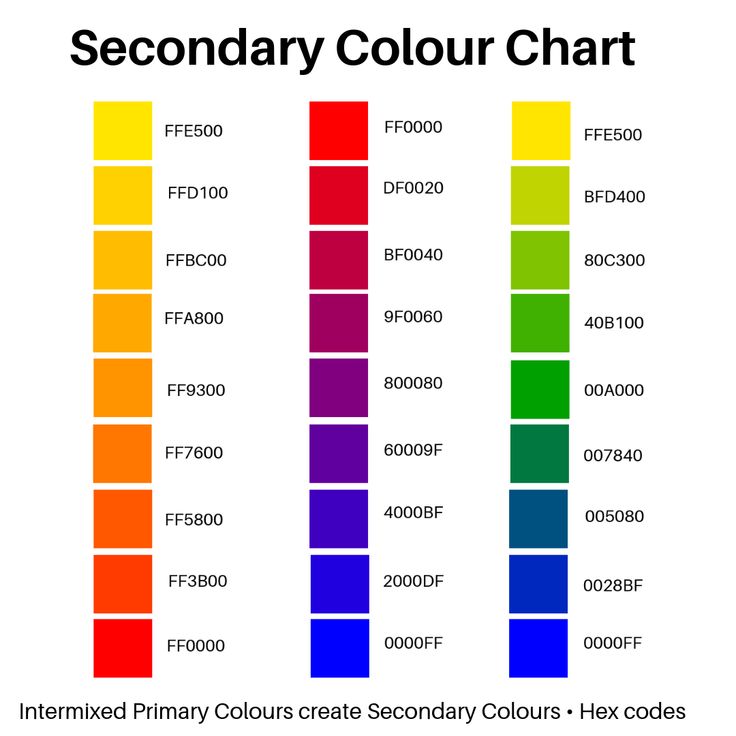 So, you begin with white and then subtract light at various wavelengths as the primary colors are added. The color gets darker as more colors are added, as light is reduced. This is different when compared to additive colors, which become brighter.
So, you begin with white and then subtract light at various wavelengths as the primary colors are added. The color gets darker as more colors are added, as light is reduced. This is different when compared to additive colors, which become brighter.
| Shade | Hex Code | CMYK Color Code (%) | RGB Color Code | Color |
| Red | #ff0000 | 0, 100, 100, 0 | 255, 0, 0 | |
| Yellow | #ffff00 | 0, 0, 100, 0 | 255, 255, 0 | |
| Blue | #0000ff | 100, 100, 0, 0 | 0, 0, 255 |
The main colors for paint pigments are red, yellow, and blue, and cannot be created by mixing other pigments. You also have subtractive primary colors for ink, which is used extensively in the printing industry.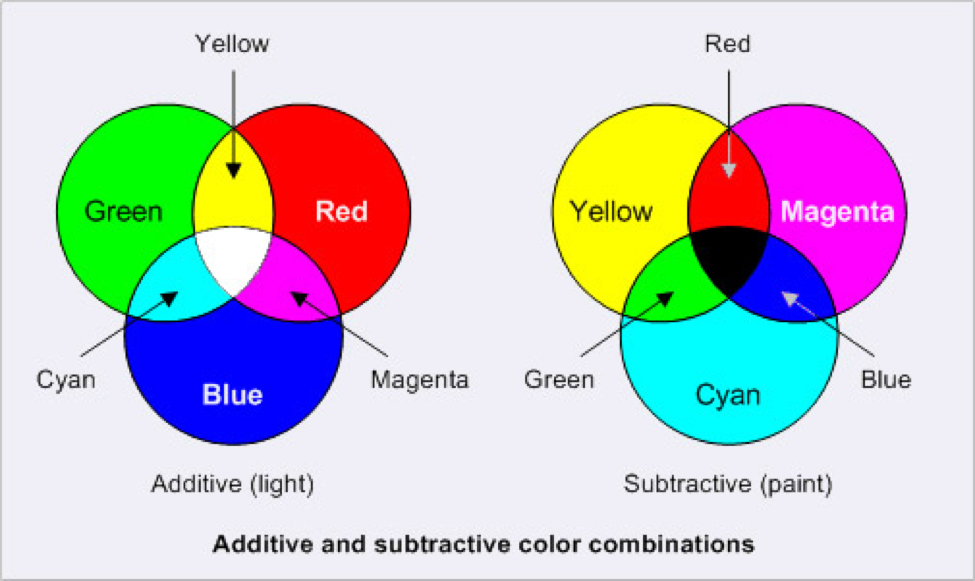 In this case, the primary colors used are cyan, magenta, yellow, and also the addition of black. You will notice that cyan and magenta are not the same as blue and red, some people use these synonymously.
In this case, the primary colors used are cyan, magenta, yellow, and also the addition of black. You will notice that cyan and magenta are not the same as blue and red, some people use these synonymously.
| Shade | Hex Code | CMYK Color Code (%) | RGB Color Code | Color |
| Cyan | #00ffff | 100, 0, 0, 0 | 0, 255, 255 | |
| Magenta | #ff00ff | 0, 100, 0, 0 | 255, 0, 255 | |
| Yellow | #ffff00 | 0, 0, 100, 0 | 255, 255, 0 | |
| Black | #000000 | 0, 0, 0, 100 | 0, 0, 0 |
Basic Facts for the RYB Color Model
There are a few essentials you can keep in mind when using this color model.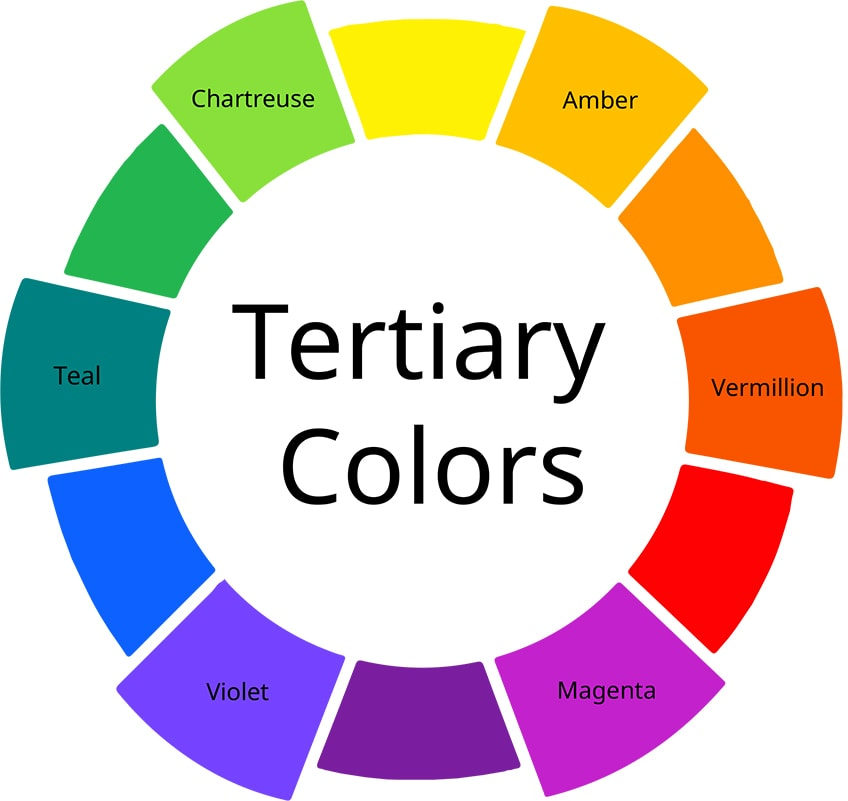 For example, this color model and its main colors are used for the mixing of paint pigments and include red, yellow, and blue as the primary colors. It cannot be used for designing websites, which does not have the same primary colors.
For example, this color model and its main colors are used for the mixing of paint pigments and include red, yellow, and blue as the primary colors. It cannot be used for designing websites, which does not have the same primary colors.
- You can blend the primary color to make more colors, for example, secondary colors like purple, green, and orange.
- However, adding all three primary colors in similar amounts will create a muddy or dark brown color.
- All the primary color paints are not the same. Different manufacturers add different ingredients, so there are various reds, yellows, and blue colors.
How Many Primary Colors Are There?
Now that we have gone through a bit of what primary colors are, you can see that it is more than simply the three colors red, blue, and yellow. The primary colors change from each color model. So, is red a primary color? Yes, it is, in the RGB and RYB color models. However, when it comes to the CMYK color model, it is a secondary color made by blending magenta and yellow.
However, when it comes to the CMYK color model, it is a secondary color made by blending magenta and yellow.
Blue is similar to red, as it is a primary color in both the RYB and RGB color models and a secondary color in the CMYK color model.
Cyan and magenta are blended to create a blue color. Yellow, on the other hand, is a primary color in the CMYK as well as the RYB color models, and secondary color in the RGB color model, where red and green are combined. Remember, that if you combine all the primary colors in the RGB color model, you will form white light. Green is a primary color in the RGB color model and secondary color in the CMYK and RYB color models. This is achieved by mixing yellow and cyan, and blue and yellow respectively.
Color Psychology and Primary Colors
When looking at the primary colors in psychology, there are four main colors blue, green, yellow, and red. All these colors represent the whole person from the body to the mind and emotions.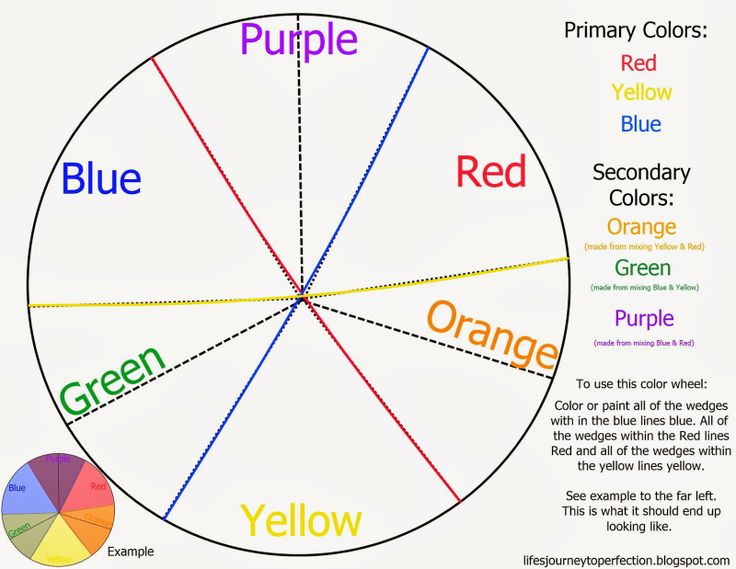 Let us now look closer at these primary colors.
Let us now look closer at these primary colors.
The Color Blue
When considering color psychology, blue is seen as something related to human intellect. Various shades of blue are all soothing, softer blues can calm the mind and so help improve concentration, while stronger shades of blue help to stimulate the mind. Blue is a color favored by many, but it is a favorite amongst men. The color is seen as trustworthy and confident.
However, blue can also have negative associations, for example, it can seem cold, distant, isolated, depressing, and predictable.
The Color Green
Green is another favorite color by many and is closely related to all things natural as well as associated with health, growth, prosperity, abundance, and balance. Green helps to connect all of the other primary colors and facilitates a certain balance or harmony. Green can be striking, but it does not overly intrude, which makes it quite a popular color. Green can also denote feelings of envy and can be related to stagnation, and boredom.
Green can also denote feelings of envy and can be related to stagnation, and boredom.
The Color Yellow
Bright, happy, and optimistic yellow, is a color that is associated with emotions. Yellow also inspires, energizes, can stimulate creativity, amuses, and provides warmth. However, it should be used carefully as it can also have adverse effects. For example, it can cause sadness and apprehension.
Yellow can also be seen as cowardly, egotistical, and deceiving.
The Color Red
Red has a long wavelength and is, therefore, considered a strong color that attracts attention, which is why it is used as a color for caution. For example, red traffic lights or other warning signs. The color is vibrant and easily seen and conveys a sense of urgency. Red is also associated with physical skills. Red is seen as warm, enthusiastic, and full of energy, strength, confidence, and passion. Negatively, it is associated with danger, anger, and aggression.
How Can You Mix Primary Colors to Create New Colors?
When you blend two primary paint colors, this creates secondary colors. Since you can get different paints and hues, and you might use different amounts, you can create different shades. For example, alizarin crimson or cadmium red medium will produce slightly different secondary colors.
When learning color theory, you will discover the color wheel, primary colors, secondary colors, intermediate, and tertiary colors. You also get warm and cool colors. Blues and greens are considered cool colors, while the reds, yellows, and orange colors are warm.
So, in the case of alizarin crimson, even though it is a red color, it is considered a cool red, which means it has more of a blue bias or undertone.
The cadmium red medium is a warm red, as it has more of a yellow bias. So, when mixing primary colors, this has to also be taken into consideration. When blending two warm colors, for example, cadmium red medium with cadmium yellow medium, it will produce a purer orange than if you mixed a warm red and cool yellow. Also, if you use, for example, the alizarin red, which is a cool red, and then blend it with the cadmium yellow medium, which is a warm yellow, you are including blue into the mixture. This means you have all three primary colors mixing, which can produce a muddy and less vibrant color than what you are expecting.
When blending two warm colors, for example, cadmium red medium with cadmium yellow medium, it will produce a purer orange than if you mixed a warm red and cool yellow. Also, if you use, for example, the alizarin red, which is a cool red, and then blend it with the cadmium yellow medium, which is a warm yellow, you are including blue into the mixture. This means you have all three primary colors mixing, which can produce a muddy and less vibrant color than what you are expecting.
Are Primary Colors Pure?
Most of us have been taught that you get pure colors, which cannot be created by mixing any other colors, which is part of the primary colors definition. However, this is not all true because you can make red by blending two colors, specifically, magenta, and yellow. Blue can also be created by blending cyan and magenta. So, you have more of a wider range of color capabilities with the CMYK color model.
Theoretically, there are the traditional primary colors that we rely on to understand colors, and they do form an important basis for color theory, but as you can see, it is not something that is absolute and there are variations.
This happens even more when working with paints because there are no “pure” paint colors. As we have mentioned when mixing colors, if you take two primary colors, you will not necessarily get the color you expect. This is because most paint colors contain more than one pigment, and each manufacturer has a different formula for their paints. For example, many of the yellow paints, have either a red or green undertone. Red colors have a yellow undertone or a blue bias, and many blue paints have a red or yellow undertone.
All of this will affect the color you want to mix, so if you want to make a green, it should be simple to mix blue and yellow. However, the yellow you use might have a reddish undertone. This will mean you are mixing red, yellow, and blue which will give you a muddy brownish-green color. The point is to always take into consideration the paint undertones before you mix colors, otherwise, you will simply be creating a muddy disaster.
Working with colors, whether it is with painting or creating a website, the process can be more complicated and challenging than you first realize.
This is why gaining a firm foundation in color theory and how colors work together is so important.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Many Primary Colors Are There?
This can be a trick question because most of us learned our primary colors and these add up to three, red, yellow, and blue. However, if you consider other color models, this widens the number a bit. For example, you also have the RGB and CMYK color models with different primary colors.
What Are Additive Colors?
The word additive explains it quite nicely, which means colors are added to make new colors. This is mostly used for light sources like web pages and television screens. The red, green, and blue light is blended in different ways to create the various hues. This deals with how the light is seen directly and is not reflected.
What Are Subtractive Colors?
Subtractive colors are used in the case of objects or real surfaces like a canvas or a piece of paper.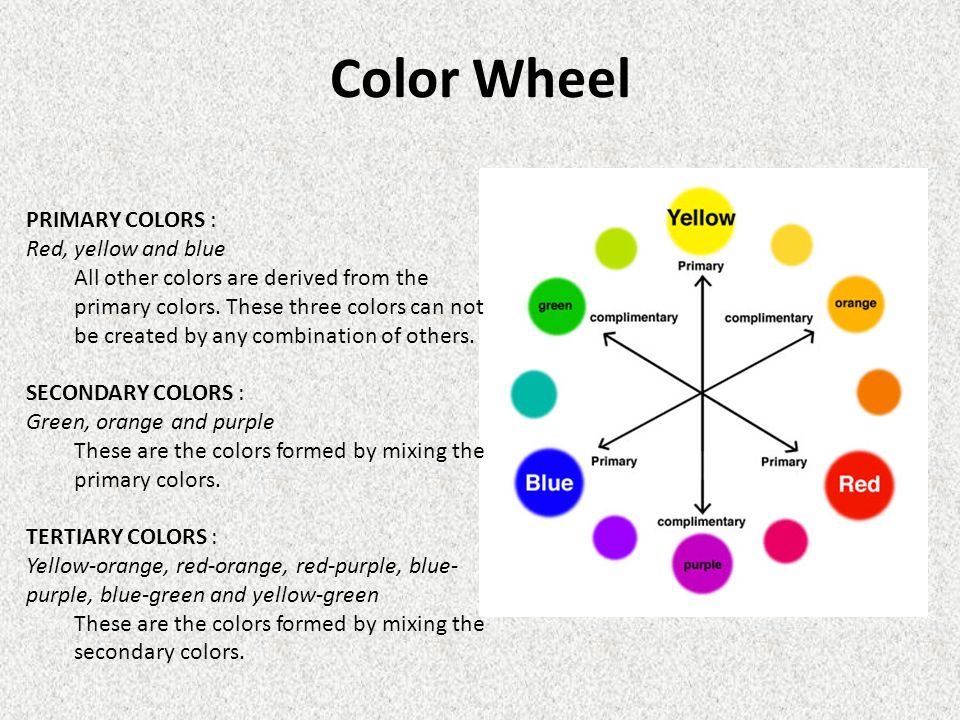 So, this means it is used for painting and things like printing. Subtractive simply means that certain color wavelengths are emitted, and you are left with the color you can visibly observe and deals with the reflection of light.
So, this means it is used for painting and things like printing. Subtractive simply means that certain color wavelengths are emitted, and you are left with the color you can visibly observe and deals with the reflection of light.
Can You Mix All the Primary Colors?
When painting, mixing all the primary colors will give you something close to a muddy brown color. This is why you should take note that many of the red, yellow, and blue paints in a tube might have an undertone or color bias. This will ultimately affect the color outcome.
Basic colors | LOOKCOLOR
Primary colors are the tones with which all other shades can be obtained.
This is RED YELLOW BLUE (for printing it is MAGENTA, YELLOW, CYAN, BLACK see below)
If you mix red, blue and yellow light waves together, you get white light. However, such a fusion will not work with paints. For artists, there is a separate mixing table that intersects with the combination of waves, but follows its own rules.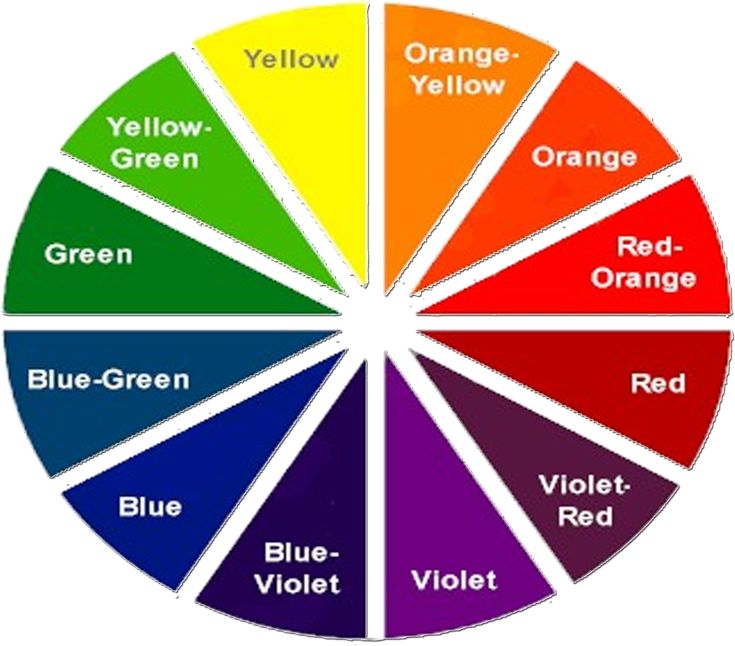
So in practice, when you combine yellow, red, blue paint, you get a shade of brown that does not exist in spectral light, but is our eye's response to an unbalanced reflection of waves. (see physics of color).
Yellow, red, blue - different in lightness, in which the brightness is at its peak. If you convert them to black and white, you will clearly see the contrast.
It is difficult to imagine a bright dark yellow tone, as well as a bright light red. Due to the brightness in different ranges of lightness, a huge range of intermediate saturated colors is created: orange, red-orange, light green, emerald green, blue-green, lilac, red-violet, violet, etc. These three colors form almost the entire palette, with the exception of black, white, grey. Taking them as the primary basis of color construction, it is worth imagining that the secondary colors are still less bright than their parents, and the shades formed from the second circle using black, white or shades produced from the primary circle are even duller.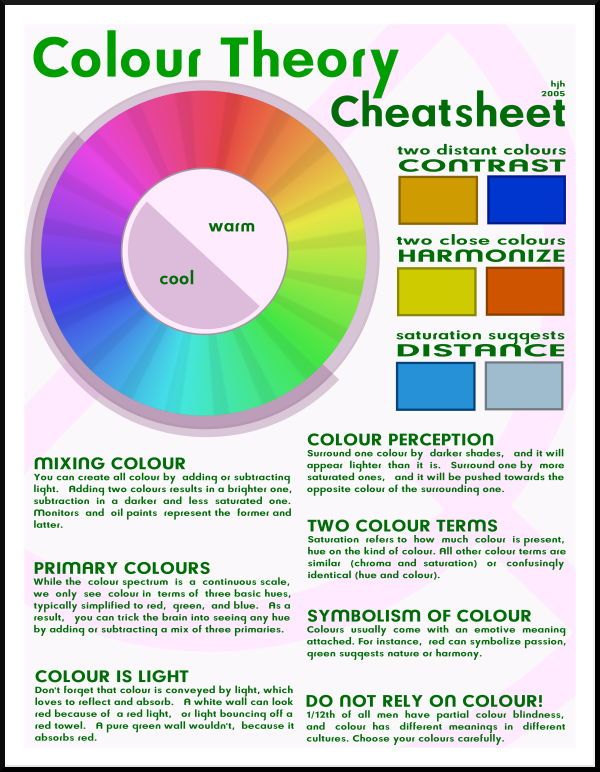
Building shades from primary colors
Pairs of "teams" of primary colors form the following paints of the second round:
_____ORANGE______PURPLE_______________GREEN____
YELLOW + RED = ORANGE (see how to get orange?)
RED + BLUE = PURPLE (see how to get purple?)
BLUE + YELLOW = GREEN (see how to get green06) 900
If you mix the secondary colors, i.e. orange, purple and green, with the primary ones (which are already present in the composition of the color), then their order will not change, they will also remain in the second circle, since we are currently changing the amount of content, not the quality :
__YELLOW ORANGE_____ RED ORANGE _____ RED VIOLET___
YELLOW + ORANGE = YELLOW ORANGE
RED + ORANGE = RED ORANGE
RED + VIOLET = RED VIOLET
__PURPLE BLUE___________BLUE GREEN___________LIME ___
BLUE + PURPLE = BLUE VIOLET
BLUE + GREEN = BLUE GREEN
YELLOW + GREEN = LIME
Adding primary tones to secondary tones, but which are not already present in it, lead to a mixture of all three primary colors. The result is brown. Such pairs are called complementary.
The result is brown. Such pairs are called complementary.
yellow + purple ( red + blue ) = brown
red + green ( yellow + Blue ) = brown
Blue + Orange ( red yellow ) = BROWN
Mixing complementary hues such as purple + yellow, red + green, blue + orange produces a medium dark reddish brown. If you mix not paint, but light rays, you should get the effect of gray light. But since the paint only reflects the wave, there will be no 100% replacement.
Primary ink colors for printing
It is very important to get the maximum tones from the minimum ink set for color printing. Today, there are 4 necessary colors to implement the entire spectrum, where red is replaced by rich pink. This color model is called CMYK.
MAGENTA, YELLOW, CYAN, BLACK
Where magenta is fuchsia, cyan is bright blue, and white is the tone of the printed material.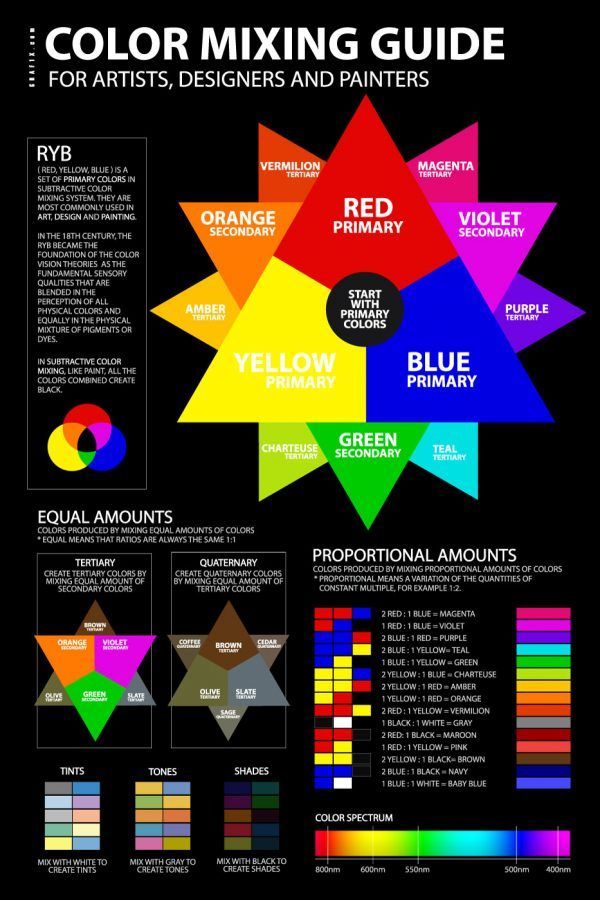
How to get other colors and their shades: theory and practice. Click on the icon.
Basic colors | it's... What are Primary Colors?
Additive color mixing. In Russian, the following names of colors used in the additive model are accepted: red, green, blue
Mixing colors according to the subtractive model. In Russian, the following names of colors used in the subtractive model are accepted: yellow, magenta, cyan
Primary colors are colors that can be mixed to get all other colors and shades.
|
Contents
|
History
The emergence of the concept of primary colors is associated with the need to reproduce colors for which there was no exact color equivalent in the artist's palette.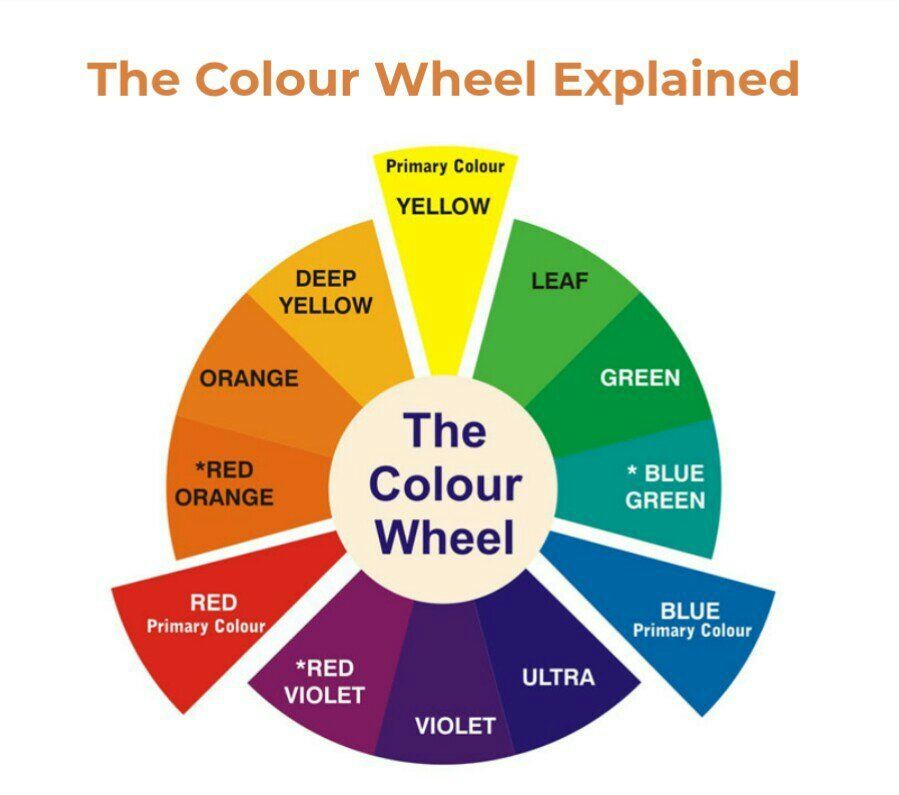 The development of color reproduction technology required minimizing the number of such colors, and therefore conceptually complementary methods for obtaining mixed colors were developed: mixing colored rays (from light sources that have a certain spectral composition), and mixing paints (reflecting light, and having their own characteristic reflection spectra) .
The development of color reproduction technology required minimizing the number of such colors, and therefore conceptually complementary methods for obtaining mixed colors were developed: mixing colored rays (from light sources that have a certain spectral composition), and mixing paints (reflecting light, and having their own characteristic reflection spectra) .
Various "primary colors" selections
Color mixing depends on the color model. There are additive and subtractive mixing models.
Additive model
Main article: Additive color mixing
In the additive mixing model, colors are obtained as ray blending. In the absence of rays, there is no color - black, the maximum mixing gives white. An example of an additive color model is RGB.
Subtractive color synthesis
Main article: CMYK
Method using light reflection and appropriate dyes. In the subtractive mixing model, colors are obtained as mixing paints.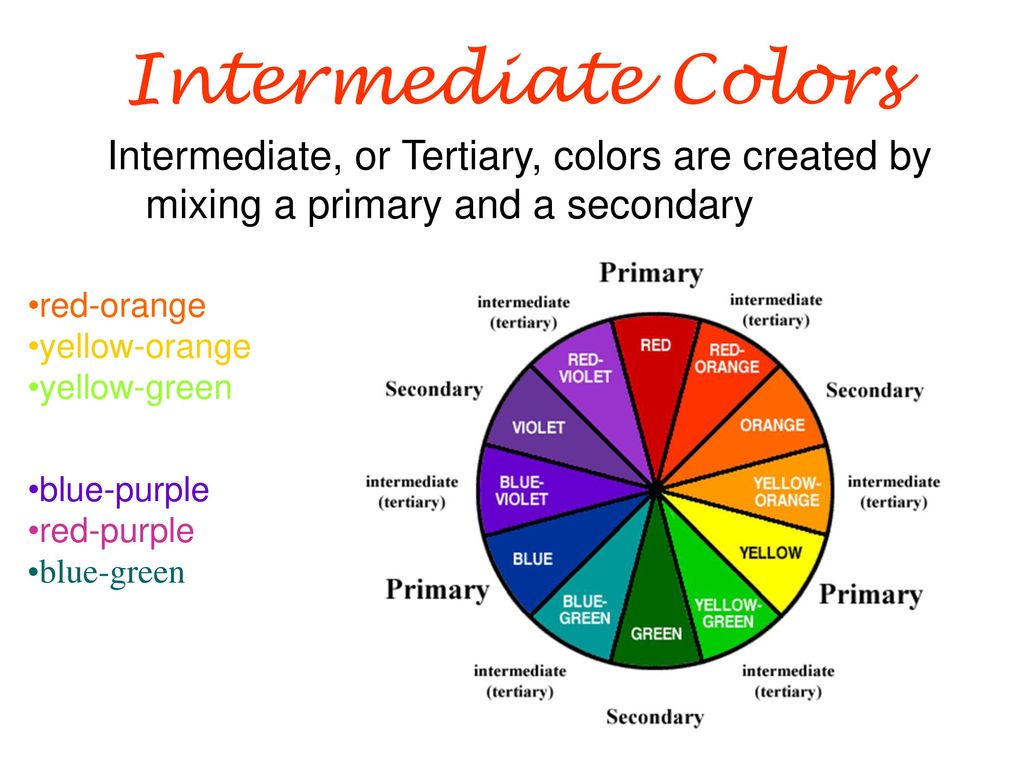 In the absence of paint, there is no color - white, the maximum mixing gives black. An example of a subtractive color model is CMYK.
In the absence of paint, there is no color - white, the maximum mixing gives black. An example of a subtractive color model is CMYK.
According to Johannes Itten, there are only 3 primary colors: red, yellow and blue. The remaining colors of the color wheel are formed by mixing these three in various proportions.
Biophysical background
Main article: Human vision
Main article: Psychology of color perception
Basic colors are not a property of light, their choice is determined by the properties of the human eye and the technical properties of color reproduction systems.
Four "pure" colors
Psychophysiological studies have led to the assumption of the existence of some "pure" and unique colors: [1] - red, yellow, green and blue, with red and green forming one color-contrasting axis, and yellow and blue forming another.
Technical options for the implementation of the model of the use of “Basic colors”
Emissive spectralyuminopors of red, green and blue, which determine the capabilities of the additive model of the color display based on ELT
Notes
- 9
- ↑
3 and perception.
Learn more