What does hands on learning mean
The Importance of Hands-On Learning in Child Education
Hands-on learning has long been touted by parents and educators as a key factor in raising children who develop a lifelong love of learning and who perform better academically. But what exactly do we mean when we say “hands-on learning,” and why is it so beneficial to students? Here, we explore both the concept and the benefits.
What is hands-on learning?
Hands-on learning is a form of education in which children learn by doing. Instead of listening to a teacher or instructor lecture about a given subject, the student engages with the subject matter to create something or solve a problem.
Free Downloadable Guide: Take a Closer Look at Friends' Central School
Though certain subjects come to mind more readily than others when talking about hands-on learning (for example, shop class), the truth is, a hands-on educational philosophy can be incorporated into nearly any subject matter. This philosophy provides students with engaging hands-on experiences that will further develop the learning process. A few examples might include:
- Solving problems as a part of math class
- Completing a lab experiment as a part of a science class
- Building circuits or working machines as a part of a tech class
- Recreating a historical document or artifact as a part of history class
- Writing a creative story, poem, or essay as a part of English class
The benefits of hands-on learning
Hands-on is by no means a “new” movement in the classroom. That being said, even today, many schools find it difficult to incorporate hands-on projects and principles into student work. This can be a particular challenge for public schools, which often have tight budgets and less freedom in developing curriculum.
And that’s a real shame, because hands-on learning brings so many benefits to students, including:
- It is a more engaging way to learn
- Leads to increased retention
- Offers practice in problem solving and critical thinking
- Often results in a physical creation
1.
 Hands-on is another way to learn.
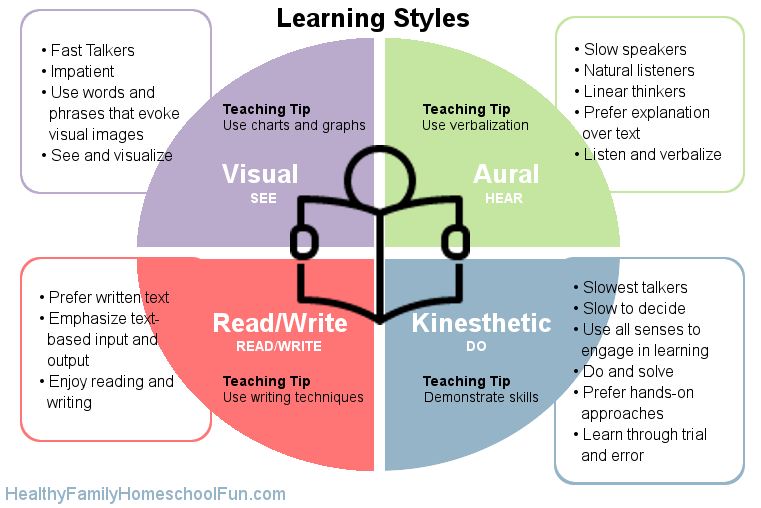
Hands-on is another way to learn.Hands-on learning allows for equal visibility of common learning styles in the classroom. Some children learn best by looking at visuals, some by listening to a parent or teacher speak, and some by reading and writing about a given topic. These are called visual, auditory, and reading/writing learning styles, respectively. But there is a fourth learning style that is easy to overlook: Kinesthetic learning, which is a fancy way of saying “learning by doing.”
There are a lot of theories about why hands-on learning is so effective. The reality is, there is no single reason why. But one hard-to-argue fact about hands-on learning is this: It is incredibly engaging.
When students are forced to do something, they are engaged in active learning. They’re practicing their critical thinking skills and they’re putting their knowledge to the test. Most importantly, this form of learning gives opportunities for students to actively
create knowledge, instead of passively consuming it.
In order to create, in order to do, students must be engaged in their education. And engagement has for years been linked to greater academic success like increased test scores and greater academic achievements.
2. Hands-on gives students practice.
Beyond simply leading to better engagement, hands-on learning allows students to practice the skills that they've already learned. As anyone who has ever learned a skill or learned information can attest to, the more practice you get, the better you will be at that skill, and the better you will be able to retain the information.
We can see this in action in many science classes around the country, which pair traditional study (lecture, discussion, reading) with active learning concepts in lab sessions. While students may learn about a concept in the classroom, it is by walking through an experiment in the laboratory that they are able to put that concept into action and gain practice in actually applying it. This process has been shown to lead to higher retention and a better understanding in the subject.
This process has been shown to lead to higher retention and a better understanding in the subject.
3. Hands-on gives students something “real.”
When it comes to education, one of the most difficult things for young children to understand is how what they are learning is important. They want to know: When will I use this in my life? Why does it matter?
Incorporating hands-on learning into the classroom or into the home is an easy way for parents and teachers to show their children exactly how what they are learning can be used in the real world.
Through hands-on learning, students will often actively create something, whether an essay, story, piece of art, construction project, or something else. This is something real. It is something that a student can look at and think: I was able to create this because of what I've learned and because of the skills that I've practiced.
Project-based learning can make this realization incredibly empowering because it shows students that they can have an impact on the world around them. It shows them that they can use their education to achieve something. And it’s a physical embodiment of what they’ve learned.
It shows them that they can use their education to achieve something. And it’s a physical embodiment of what they’ve learned.
4. Hands-on lets students be creative.
Creativity is a muscle. Just like other muscles, it needs to be regularly exercised or else it will become harder and harder to be creative. Hands-on learning gives your child one more opportunity to exercise their creative skills so that they don’t lose them.
It’s important to note that when people hear the word “creativity,” their minds often go immediately to subjects like art and music. While these are of course important classes for children, and should play a role in your child’s education, they’re not the only way that your child can be creative. Given enough practice, it’s possible for your child to put their creativity to use in classes as diverse as history, science, and even math.
You might be wondering how that could be. To answer simply: Creativity encourages children to develop a new way of thinking about something. This new way of exploring a concept or idea can lead to insights that may otherwise have been hidden. For example, your child may have learned to complete a math problem in a certain way. But that doesn't mean it’s the only way that the problem can be solved. A creative student may look at a problem and find a brand new way of completing it.
This new way of exploring a concept or idea can lead to insights that may otherwise have been hidden. For example, your child may have learned to complete a math problem in a certain way. But that doesn't mean it’s the only way that the problem can be solved. A creative student may look at a problem and find a brand new way of completing it.
What can parents do to encourage hands-on learning in their children?
When children are young and at home, parents have more control over how their children learn. At this stage of a child’s life, it’s important for parents to encourage hands-on activities that will challenge their child to learn through doing.
As a parent, there are various steps you can take to facilitate these yourself. You might, for example, encourage your child to create a diorama illustrating a critical scene from their summer reading assignments. If your child is an aspiring coder, there are many resources you can turn to online (or purchase from a store) to let them practice their skills. The possibilities really are endless.
The possibilities really are endless.
But when a child moves beyond the home—entering a nursery program, preschool, kindergarten, or grade school—parents who prioritize hands-on education will need to find a school that shares this priority. In addition to evaluating the school’s curriculum and asking questions during the admissions process, parents should also keep an eye out for schools that embrace Maker Education, which encourages learning through doing and offers many other benefits similar to hands-on education.
What are the Benefits of Hands on Learning?
hands on training and learningWhile educational approaches used to subscribe to a “one-size-fits-all” philosophy, observation, testing, and psychology have revealed, by degrees, a different picture over the last few decades. Different students learn different ways, and forcing all to adhere to a singular style of learning has the potential of limiting two-thirds – or more – of any given class.
At NewSchool, we incorporate hands-on learning and training techniques as an integral part of our teaching strategy in our academic programs. We know that not all students are the same, which is why we incorporate these progressive teaching methods in all of our classrooms. In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of hands-on learning for students, including a variety of learning styles and training techniques that are effective both in and out of the classroom – and how they can serve you in your future career.
We know that not all students are the same, which is why we incorporate these progressive teaching methods in all of our classrooms. In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of hands-on learning for students, including a variety of learning styles and training techniques that are effective both in and out of the classroom – and how they can serve you in your future career.
What Is The Best Way For A Student to Learn?
‘Best’ is a subjective term, but certain learning styles offer clear advantages over others, depending on the subject(s) of study. Below are several core learning styles commonly practiced in the classroom from grade school to college:
- Visual learning, often called “book” learning, has long been the prevailing method, compelling students to read, remember, and recite the information on a page in reports, tests, and quizzes. This method is most frequently used by teachers during early childhood for school-aged children, where information is traditionally taught using picture books, flashcards, and later, textbooks.

- Auditory learning, most easily observed in the lecture formats of certain college courses, relies upon the student to take in an instructor’s information through listening to them live, or via a pre-recorded session, requiring students to take notes accordingly throughout the process. This form of learning may or may not encourage discussion, depending on the preferences of a given professor.
- Kinesthetic learning is the third and most intriguing of the learning styles, mingling elements of both visual and auditory learning and compelling full participation from the student. Named after kinesiology, the study of human movement, it’s most commonly referred to as “hands-on” learning. This blended learning technique is one of the key drivers in trade school learning, as it allows students to become comfortable and familiar with the hands-on processes and skills of what will hopefully become their careers, rather than simply watching or reading about them.

Does Hands-On Learning Work For Everyone?
Barring severe shyness or anxiety, hands-on learning is uniquely positioned to support or elevate any type of learner. Everyone has their own specific needs when it comes to their personal learning style. Students that prefer to listen to their lesson can hear the instructor as they follow along, and those that do well with visuals can watch the instructor, duplicating his or her steps after they’re finished. Rather than a learning style alone, hands-on learning should be a functional part of every lesson plan, if only to familiarize students especially in the design degree and science studies with the models and materials they’ll use later in either professional, post-graduate employment or research positions.
Why Is Hands-On Learning So Powerful?
Hands-on learning (also known as experiential learning) is the biology lab that teaches a future scientist to be comfortable with dissection; the vehicle shop experience that helps a future mechanic understand the nuances of an engine with not just their eyes and ears but also with actual hands-on training. It gives students the opportunity to self-correct any educational missteps in the moment – with professional guidance at arm’s reach. While notes can be copied down incorrectly and the thread of learning can get buried under a teacher that talks too quickly or a poorly-written textbook, live examples of core concepts are registered in the brain as holistic experiences, giving the student’s mind more “anchors” to tie the memory to.
It gives students the opportunity to self-correct any educational missteps in the moment – with professional guidance at arm’s reach. While notes can be copied down incorrectly and the thread of learning can get buried under a teacher that talks too quickly or a poorly-written textbook, live examples of core concepts are registered in the brain as holistic experiences, giving the student’s mind more “anchors” to tie the memory to.
The sound two materials make when they’re joined together, the scent of a certain solvent, the vivid color of a particular plant leaf – these all become easy-access sensory “bookmarks” for bringing the memory to the surface when it needs to be reviewed. This works for every field of study as well, not just the sciences – that’s why so many condensed “how-to” courses use the format. People simply learn better when they’re allowed to roll up their sleeves and experience the subject matter in a simulation, rather than being distanced from it by a third-hand narrative experience or a dry passage of text.
How Does Hands-On Learning Help A Career?
While learning should ideally translate perfectly into practice, the reality is that it seldom does. Just as someone who may have only read a particular word in books might mispronounce it the first time they speak it aloud, self-focused learning methods may not reveal mistakes until the stakes are high. Particularly in fields where physical precision is important – manufacturing, architecture, medical studies, and so on – these innocent mistakes can become big problems if they aren’t identified and addressed beforehand. Hands-on learning helps instructors recognize and correct these mistakes while still in the learning process, dramatically reducing the chances of the same mistake cropping up after the training course is finished.
Hands-on learning also provides a student with the opportunity to safely make mistakes and learn organically through trial and error. Rather than experimenting when a job is on the line, they can experiment with new ideas and satisfy curiosity at their own natural pace without worrying about damaging an important project. This allows them to practice their critical thinking skills and utilize the knowledge they’ve accumulated during their training program. Humans naturally learn by making mistakes and determining how to either fix or avoid them, and the more times the cycle is repeated, the better a student becomes at meeting those challenges without hesitation. To put it another way, practice makes perfect!
This allows them to practice their critical thinking skills and utilize the knowledge they’ve accumulated during their training program. Humans naturally learn by making mistakes and determining how to either fix or avoid them, and the more times the cycle is repeated, the better a student becomes at meeting those challenges without hesitation. To put it another way, practice makes perfect!
Transferring Hands-On Learning From Classroom To Workplace
As most recent college graduates learn “the hard way,” life in the real world has very few things in common with life in the classroom. Real-world situations aren’t usually clear-cut or easily solved, a variety of different factors need to be considered and weighed, and sometimes real-world solutions – while they do work – aren’t very tidy. Hands-on learning can help lessen the imbalance between academia and employment by familiarizing students with the environments they’ll be confronted with.
An employer isn’t, for example, likely to hand a worker a document and give them a multiple-choice quiz on it a week later. Far more plausible is a sudden emergency situation that needs to be addressed, with little time to consider options and actions – therein lies the value of the hands-on experience. Such learning exercises can enable a virtual walk-through of actions and reactions, as hypothetical circumstances can be emulated and practiced by imposing time limits. Instructors may also wish to “surprise” students in the form of hands-on exercises, presenting them with unexpected problems and unique materials to work with.
Far more plausible is a sudden emergency situation that needs to be addressed, with little time to consider options and actions – therein lies the value of the hands-on experience. Such learning exercises can enable a virtual walk-through of actions and reactions, as hypothetical circumstances can be emulated and practiced by imposing time limits. Instructors may also wish to “surprise” students in the form of hands-on exercises, presenting them with unexpected problems and unique materials to work with.
Depending on the length of time spent in a hands-on environment and the complexities of the lessons, students may also be able to list certain experiences on their resume. For example, bullet points such as these could pique the interest of employers that might otherwise pass over a candidate without time “on the job”:
- Worked with (X) program/machine/tool/material several times a week.
- Built (X) in conjunction with a team of 5 students.
- Developed (X) from raw materials in accordance with the (X) method.
- Solved (X) problem using only (X) materials.
How Does Hands-On Learning Help Students?
Properly structured, hands-on learning encourages students to think outside of the proverbial box, coaxing them to experiment with and explore the problems, tools, and substances they’ll work with regularly in their chosen careers.
From an educator’s perspective, this learning style also offers a welcome respite from the rote repetition of “book learning” or lecturing. No teacher likes to think about it, lest their teaching confidence slip, but the fact of the matter is that adults do have a limited attention span, even when they’re earnestly trying to pay attention. The sound of an instructor’s voice may become a drone after an hour of class, or the words in a passage of text may blur together as eyes become tired or the thought of lunchtime intrudes. Legs and backs may get restless from sitting in place, and thoughts drift as students become a passive – rather than an active – participant in their classroom experience. Gossip and private conversations can become a distraction as students away from the front row seek alternate stimulation during class hours.
Gossip and private conversations can become a distraction as students away from the front row seek alternate stimulation during class hours.
Hands-on learning uproots this tired, traditional classroom instruction, allowing students to move, discuss, interact with, and truly engage with in the lesson. Rather than bored teammates simply waiting for their proverbial turn at bat, they are instead immersed in the actual functional points of the task, figuratively getting their hands dirty with the materials, techniques, and concepts being taught. Rather than a chore – listen, take notes, remember – it becomes that magical organic experience and students retain it the same way they would visiting a museum, or trying a new type of food. It’s interesting, and thus the subject matter becomes easier to recall and more enticing to explore.
No restless legs, no wandering thoughts, no dozing off during class – instead, they get to tackle challenges alongside classmates, delving into a “gamification” structure that encourages – or even directly endorses, depending on the instructor’s techniques – competition as each student attempts to be the first to create a result, or otherwise answer a challenge using their materials.
To receive the most benefits out of this valuable teaching method, students should arrive to each lesson ready to explore the projects and components in front of them. That means:
- Familiarizing themselves with any safety procedures beforehand
- Ensuring they have any necessary personal protective equipment (PPE) ready to use
- Arriving on time, so as not to miss preliminary show-and-tell steps
- Using hands-free recording devices so they can focus on doing rather than note-taking
- Never missing a class (barring emergencies) so that they always feel comfortable with the current expertise level being demonstrated
- Getting enough sleep and eating/drinking before class to keep the mind sharp
- Setting aside extra time before or after a class to work with an instructor on any problem areas
Hands-on learning is an incredibly powerful tool, but it won’t replace traditional learning entirely.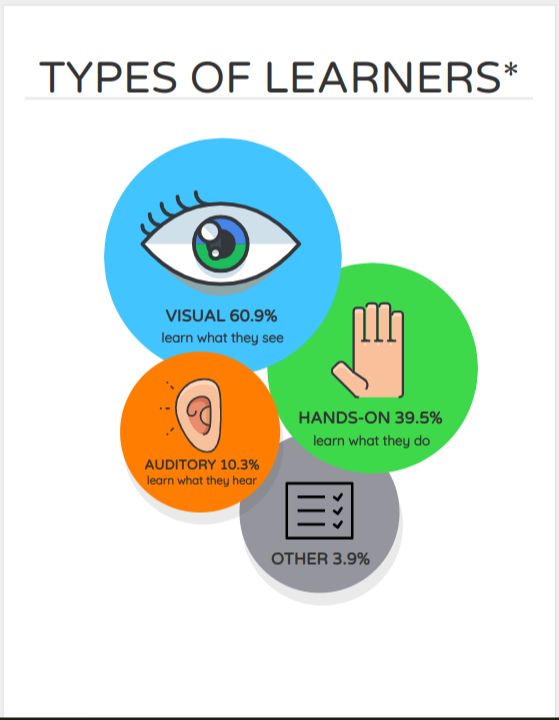 While it’s beneficial to get excited about hands-on sessions in your field of study, don’t neglect reviewing your notes, or collaborating with peers to ensure you understand important concepts. If you feel like you understand your hands-on session well but struggle with test and quiz concepts, be sure to confer with your instructor to bring your learning experience back into balance. Just as all students learn in different core methods, their ideal mix of the three learning methods will vary as well.
While it’s beneficial to get excited about hands-on sessions in your field of study, don’t neglect reviewing your notes, or collaborating with peers to ensure you understand important concepts. If you feel like you understand your hands-on session well but struggle with test and quiz concepts, be sure to confer with your instructor to bring your learning experience back into balance. Just as all students learn in different core methods, their ideal mix of the three learning methods will vary as well.
How Does Hands-On Learning Work In Groups?
Just as employees are directed to work in teams on important job projects, hands-on learning typically incorporates group work as well. To ensure the best experience for all students involved, each participant should be aware of his or her contributions and time spent with materials, stepping back to give others ample experience as well. While it’s normal and understandable to get into a groove while problem-solving a hands-on challenge, if you’re placed in a group, remember that your teammates are counting on you to support them as well.
Hands-on learning is a decidedly personal experience, but it should also be a communal one whenever possible – you’ll need to work well with others in an employment position, after all. Instead of allowing impatience or a competitive streak to spoil the experience, consciously spend time watching how others interact with the same problems you may already know how to solve.
- Did they use the materials in unexpected or unfamiliar ways while still solving the issue?
- Did they use more or less of a material than you would have done yourself?
- Did they tackle a certain step with more expertise than you’ve been able to? How?
- What did they struggle with while trying to solve the project or scenario?
Remember: if you allow your eagerness to get to the hands-on portion of learning eclipse your desire to learn, you could be missing important additional lessons from your classmates’ experiences with hands-on materials. You could even learn a new skill from them. Treat your classmates as part of the hands-on lesson – though not literally, of course. Ask them about their experiences with your mutual materials and tools, and don’t be afraid to ask them to demonstrate techniques they’re particularly skilled with to learn from them.
Treat your classmates as part of the hands-on lesson – though not literally, of course. Ask them about their experiences with your mutual materials and tools, and don’t be afraid to ask them to demonstrate techniques they’re particularly skilled with to learn from them.
Hands-on learning is a rewarding way for students to explore, retain, and experiment with all aspects of their chosen field of study, particularly at the collegiate/trade school level of career development and education. The potentials are essentially limitless, and the amount of preparation and confidence this method offers can’t be overstated. Even if a student struggles to pay attention to a spoken lecture or a lengthy text, they could find true academic breakthrough on the other side of a hands-on lesson. The most challenging career fields demand expertise, and one of the best ways to acquire it is to reach out and grab it – quite literally – with hands-on learning.
For more information on NewSchool’s hands-on learning philosophy, and opportunities for design scholarships contact our Enrollment Team!
In this article:benefits of hands on learning for students benefits of hands on learning in the classroom hands on learning style what are the benefits of hands on learning?The Latest News-chool
Find your place at NewSchool in 2023. APPLY NOW
APPLY NOW
Meaning, Definition, Suggestions . What is practical training
- Online translator
- Grammar
- Video lessons
- Textbooks
- Vocabulary
- Professionals
- English for tourists
- Abstracts
- Tests
- Dialogues
- English dictionaries
- Articles
- Biographies
- Feedback
- About project
Examples
Meaning of the word "PRACTICAL"
Pertaining to a field of practice (in 1 value).
See all meanings of PRACTICAL
Meaning of EDUCATION
See all meanings of EDUCATION thinking about your product.
Youth employment programs are most effective when they include both classroom learning and hands-on training with employment.
Experiential learning and project-based learning have led to the development of programs and spaces such as STEM and makerspaces.
Analysts recently reviewed 201 studies of the effectiveness of financial literacy courses and concluded that training had little to no effect.
Training takes place both theoretical and practical stages.
All employees of the department are specialists with higher specialized education, extensive practical work experience and trained by manufacturers.
The main advantages of this program are teaching basic professional skills, gaining practical experience and general education.
Based on the results of the interview, you will be offered training and practical training on the basis of our offices.
Many years of experience and a well-functioning team guarantee you effective, practice-oriented training.
They generally assume that learning is best done through a hands-on approach.
Irwin has spent most of his life studying and conserving wildlife, and had practical experience and training during this time at the Australian Zoo.
During the training contract, trainees must gain practical experience in at least three different areas of law.
This training works with both agricultural practices at the practical agricultural level and commercial concepts at the agribusiness level.
This could be any kind of hands-on activity, such as making cabinets—learning how to build a cabinet that doors fit properly.
Experiential learning was also strongly encouraged, and the training of new engineers became like an apprenticeship.
Practical information is now more readily available to farmers interested in cane rats, but training is still recommended.
The Dental Assistant will be trained to further develop their practical and theoretical skills relevant to the role of the Dental Radiologist.
Passing practical and theoretical training as a quartermaster sergeant of the regiment, the course included training in;.
It is almost impossible to find a job without completing your studies.
Training is conducted in combination with classroom training, practical hands-on application and live fire experience.
Education is interdisciplinary, integrating practical, artistic and conceptual elements.
These skills include evaluative attitude, practical reasoning, empathy, learning, and learning speed.
The connection between training and practical work is not close enough.
Computational design training is now practically essential in teaching drafting to future engineering, building and interior design professionals.
She developed a curriculum that was heavily based on both liberal arts and hands-on learning, with particular emphasis on workshops and studio art classes.
Hinton's practical guide to teaching VR can be found on his homepage.
This ultimately promotes growth and learning among students and teachers, not just in the classroom, but virtually all over the world.
Both formal training and mentoring provide the professional investigator with the knowledge and practice of investigative theory and practice.
In the learning process, theoretical studies are combined with practical ones.
We actively improve the skills of our staff through a variety of practical tasks and ongoing training.
This page provides the definition (meaning) of the phrase / expression "practical training", as well as synonyms, antonyms and sentences, if available in our database. We strive to make the English-Grammar.Biz explanatory dictionary, including the interpretation of the phrase / expression "practical training", as correct and informative as possible. If you have any suggestions or comments about the correctness of the definition of "practical training", please write to us in the "Feedback" section.
If you have any suggestions or comments about the correctness of the definition of "practical training", please write to us in the "Feedback" section.
Practical learning: how a school can lay the foundation for a future profession
Little practice, a lot of unnecessary subjects, and graduates do not know who they want to be - modern schools are often criticized for this. We tell you how this can be changed and why schoolchildren need internships
How do school graduates see their future careers?
The educational path "school - university" has long become almost the gold standard. Most parents are sure that it is impossible to succeed without a university diploma, and therefore children most often do not start building a career until they graduate from a bachelor's degree, and even better, they become masters. But not all young people are suitable for such a long training. Increasingly, high school students are thinking about starting a career earlier or even starting their own business, for example, after graduating from college or technical school.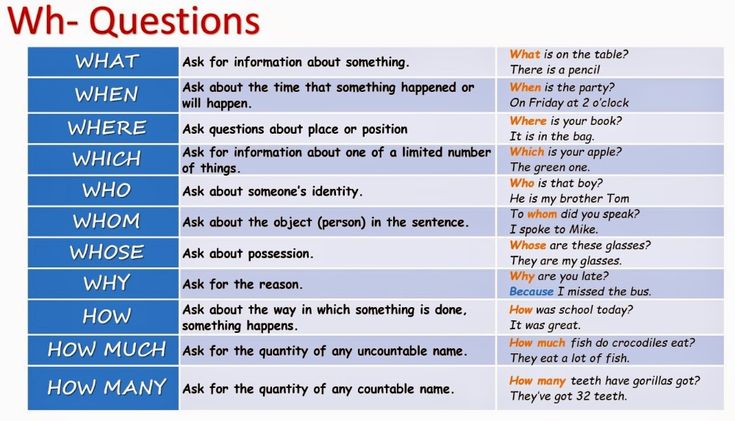
The trend towards a quick entry into the profession is also reflected in the change in the programs of secondary vocational education. For example, in the 2022/23 academic year, some Russian colleges and technical schools are starting to work according to a program that reduces the number of teaching hours, while redistributing time in favor of practice.
Why do we need a practice-oriented approach in education?
The answer to the demand for an earlier entry into the profession and the need to act in an ever-changing world is a practice-oriented approach. It allows you to form a professional picture of the world at school. Both such schools and separate classes are already appearing in our country.
Evgenia Anikina, project manager for the creation of an innovative school in Skolkovo:
“Even at school, it is important to prepare children for the fact that they will have to live in a constantly changing world, and the speed of these changes is only increasing every year. The traditional classroom system does not fully prepare for this, since the learning process in it is built linearly, where knowledge is transferred from teacher to student. However, the successful process of mastering knowledge should be flexible and inextricably linked with the application of this knowledge in practice, moreover, modern children should be able to independently "extract" the knowledge they need in the learning process. In recent years, we have seen an increase in the number of self-employed, young entrepreneurs, a growing demand from young people for alternative education and practice-oriented training. In such a model, through experiment and experience, a set of professional competencies and flexible skills necessary for a successful person in the modern world is formed. And it is this educational model that will be most in demand in the future.”
The traditional classroom system does not fully prepare for this, since the learning process in it is built linearly, where knowledge is transferred from teacher to student. However, the successful process of mastering knowledge should be flexible and inextricably linked with the application of this knowledge in practice, moreover, modern children should be able to independently "extract" the knowledge they need in the learning process. In recent years, we have seen an increase in the number of self-employed, young entrepreneurs, a growing demand from young people for alternative education and practice-oriented training. In such a model, through experiment and experience, a set of professional competencies and flexible skills necessary for a successful person in the modern world is formed. And it is this educational model that will be most in demand in the future.”
The benefit of this approach is that it gives children much more opportunities to gain practical insight into various professions and helps them understand what the child wants to be in the future. It is practice and project work that make it possible to move from the traditional scheme - "the teacher gives knowledge, the children memorize it" - to the scheme when the child learns the world himself, tries himself in various fields, and teachers and experts act more like mentors.
It is practice and project work that make it possible to move from the traditional scheme - "the teacher gives knowledge, the children memorize it" - to the scheme when the child learns the world himself, tries himself in various fields, and teachers and experts act more like mentors.
It's not just children who benefit from the practice-oriented approach. It is important both for future employers and for the state as a whole. It is business, that is, potential employers, who are interested in young people consciously choosing a profession and having basic skills with which it will be easier for them to start their professional path.
Features of practice-oriented educational systems
Practice-oriented educational institutions and individual classes have a number of distinctive features.
Participation of industrial partners
Participation of industrial partners helps to connect knowledge and practice. Companies cooperating with schools, manufacturing enterprises and research centers will be able to fully participate in the educational process, conduct practical classes and internships. Thanks to this, students will not only learn the theory from textbooks, but also gain real experience in various professions.
Thanks to this, students will not only learn the theory from textbooks, but also gain real experience in various professions.
Involved teachers
The task of practice-oriented schools is to create an environment for students in which they can experiment, try themselves in different directions, and form their own educational trajectory. To do this, educators must also be willing to test different approaches to learning, to continually learn and relearn throughout their lives.
Conscious career choice
According to EdTech research by MAXIMUM EDUCATION, 42% of 11th graders do not know who they are going to work in the future and where they want to go. The cooperation of schools with enterprises and companies will help schoolchildren decide which areas they like and which activities they have a penchant for.
Andrey Komarov, investor, co-chair of the Vocational Training and Professional Qualifications Committee of the RSPP:
“School has a strong influence on a child's choice of future profession. In most cases, the only goal of graduation, which parents see, is the subsequent admission to a university. After graduating from it and starting a professional career, after 3-4 years the young man realizes that he made the wrong choice, he is not interested in the profession, and the chosen field of activity does not suit him.
In most cases, the only goal of graduation, which parents see, is the subsequent admission to a university. After graduating from it and starting a professional career, after 3-4 years the young man realizes that he made the wrong choice, he is not interested in the profession, and the chosen field of activity does not suit him.
The practice-oriented model of education makes it possible to break this traditional chain for our country. Thanks to the involvement of industrial partners in the educational process, the child tries himself in different areas, gains applied skills and can make a clear choice of his future profession, consciously determine the further trajectory of his development.”
Variability of educational and professional trajectories
Practice-oriented schools will take into account the needs of the labor market, as industrial partners help to update the content of education. At the same time, topics and internship modules can be easily adapted without the need to rewrite the curriculum. Such educational models are very flexible, and this is perhaps the most important trend of our time.
Such educational models are very flexible, and this is perhaps the most important trend of our time.
Educational systems with a focus on practice
The global trend towards practice-oriented learning is gaining momentum both in Russia and abroad.
Innovative practice-oriented school in Skolkovo
Will be operational in 2023
Skolkovo is a modern scientific and technological complex where offices of the largest corporations, educational institutions and research centers are concentrated. On September 1, 2023, a new practice-oriented school will open in Skolkovo, designed for 825 children (grades 1-11). Later, it is planned to create a kindergarten and a college, which, together with the school, will be integrated into a single full-cycle educational ecosystem.
The project of the future school in Skolkovo. (Photo: bigskolkovo. career)
career)
The general education school being created in Skolkovo is focused on modern applied professions. Education in it will go in four main areas: creative industries, artificial intelligence and IT, biotech and space.
The new practice-oriented school will focus on the portfolio of projects that students develop, and not just on academic results. Entrepreneurial thinking will be at the forefront of them. Schoolchildren will be taught to manage a team and projects, to make decisions quickly.
The integration of the school into the Skolkovo ecosystem will allow maximum involvement of industrial partners in the educational process, which will allow students to gain specific professional competencies through practice and in the future choose a profession and even a place of work, based not on the dreams and stories of their parents, but on their own experience.
Evgenia Anikina:
“We want to create an environment in which children will be given the opportunity to try their hand at practical work under the guidance of educators and business experts, get acquainted with professions and choose what is right for them. The school is preparing to open next year, but for now we are creating a team of like-minded people: managers, teachers who share our approach and believe in its success. Of course, the leader plays a key role in this. Therefore, we have already announced an open competition to fill the vacancy of the school principal.”
The school is preparing to open next year, but for now we are creating a team of like-minded people: managers, teachers who share our approach and believe in its success. Of course, the leader plays a key role in this. Therefore, we have already announced an open competition to fill the vacancy of the school principal.”
IBM P-Tech Schools, 28 countries
Launched in 2011
In just over 10 years, IBM has opened 300 educational institutions where students can receive a high school diploma and an associate's degree in 6 years instead of 14 years in the regular US education system (12 years of high school plus a two-year college graduate program).
Pupils simultaneously complete the standard secondary school program and study in-depth subjects in their specialty. The profile disciplines depend on the specific institution: for example, some schools train graphic designers, others train engineers.
In addition to theoretical training, for 6-8 weeks during the entire period of study, students work, gaining practical experience in their chosen field. P-Tech partners with Volkswagen, American Airlines and over 600 other companies. Students can even train at NASA, learning to program satellites, analyze data from their sensors, and take space images.
P-Tech partners with Volkswagen, American Airlines and over 600 other companies. Students can even train at NASA, learning to program satellites, analyze data from their sensors, and take space images.
Students watch a rocket they helped prepare for launch with NASA staff. (Photo: ptech.org)
After graduation, students receive positions in the organizations where they did their internship. For example, in 2019, IBM began hiring the first specialists who studied at P-Tech.
The first P-Tech school appeared in the USA, and now such institutions are open in 28 countries - Great Britain, Canada, Italy, Morocco, Poland and others. Citizens of other states can also enter there, the conditions depend on the chosen country.
The need to link education with the real sector of the economy has been discussed for several years at the level of the state, business and educational institutions.