What level should 2nd graders be reading at
How to Overcome the 2nd Grade Reading Stumble
Learning to read involves a long journey, beginning with the ABCs and ending with (we hope) a lifelong love and interest in books. But many children experience a few bumps along the road as they develop into skilled readers, and often a problem arises in 2nd grade reading, when children are faced with more challenging material.
Some kids have trouble now because (1) they are still having decoding difficulties, (2) they have weak reading fluency (speed), or (3) the text is just too difficult. Here's what you need to know about each issue:
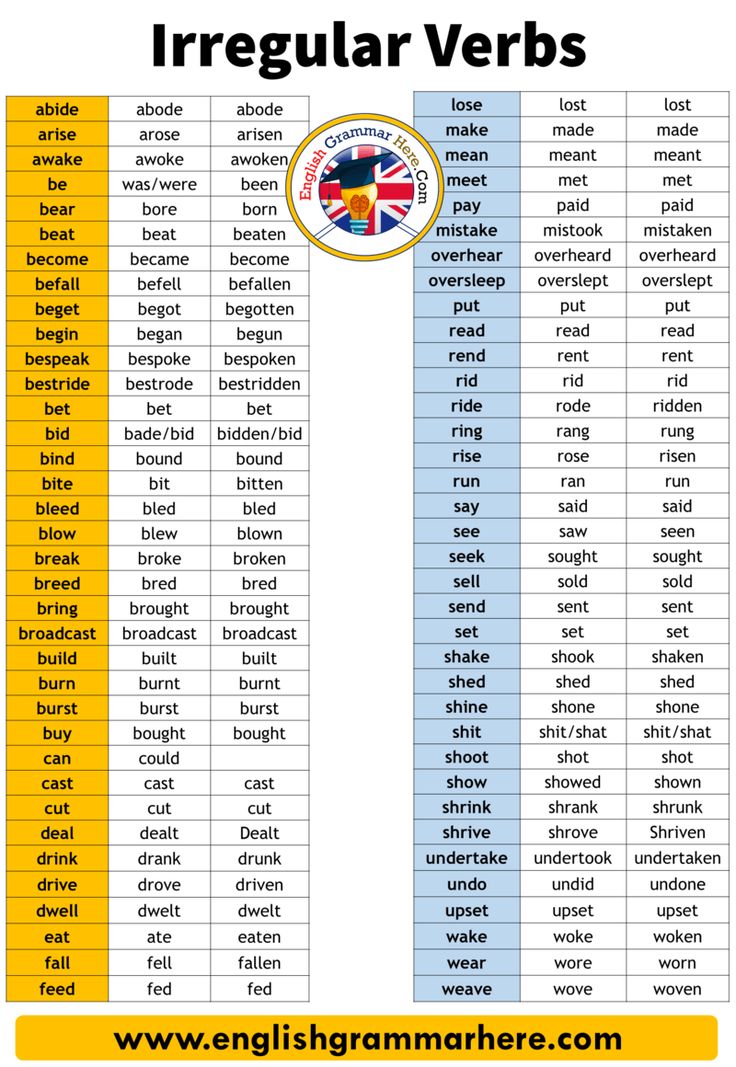
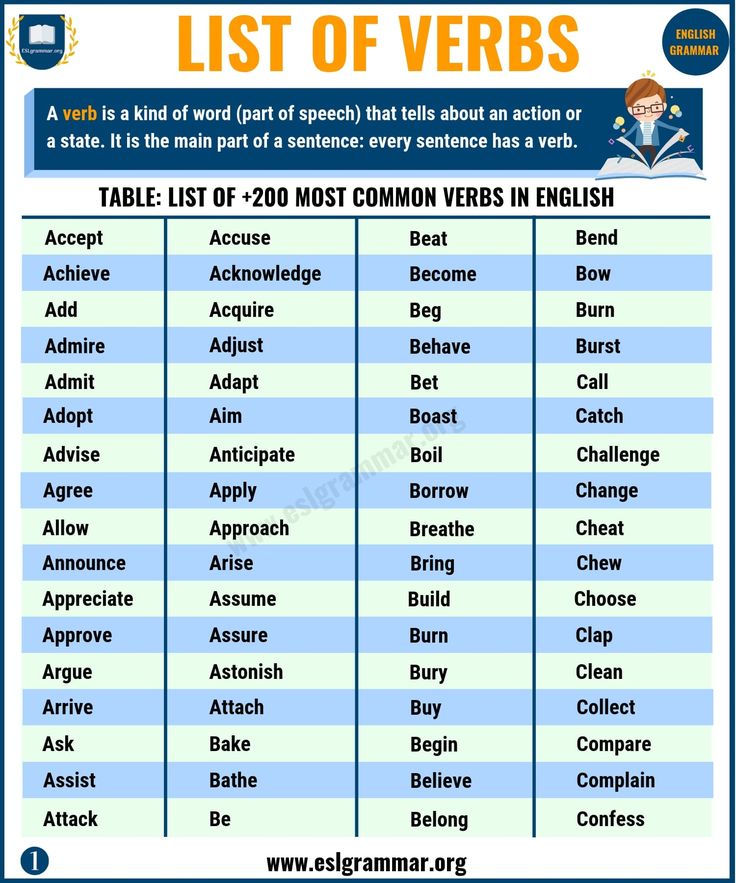
1. Weak Decoding. In 1st grade, some children do well by memorizing most words by sight rather than sounding them out. This strategy begins to break down in 2nd grade reading when the number of words increases and there is less repetition, making it more difficult to learn words by sight. One of the quickest ways to determine if your child is over-relying on reading words by sight is the Nonsense Word Test below.
These words are made up, but can be sounded out with early phonics skills. If he can sound them out, then decoding isn't the issue. If he uses one or two letters of the word to guess another word, decoding issues exist. More phonics work, including learning basic phonics skills and reading lots of simple phonics books, will help. A few great examples for the 2nd grade level are Pete the Cat Phonics Box Set, Pokemon Phonics Boxed Set, and Disney Learning: Toy Story Phonics Box which incorproates well-loved characters to make your child's learning journey a fun one!
Nonsense Word Test
Tell your child that these words are made-up words, and ask him to read them to you.
1. lat (rhymes with "cat")
2. rud (rhymes with "mud")
3. chab (rhymes with "grab")
4. stot (rhymes with "hot")
5. mabe (rhymes with "babe")
6. glay (rhymes with "play")
7. weam (rhymes with "team")
8. jern (rhymes with "fern")
9. froom (rhymes with "broom")
10. prouch (rhymes with "couch")
prouch (rhymes with "couch")
2. Weak Fluency. In order to understand what we read, we have to read at a speed appropriate for making meaning from the text (comprehension). In 2nd grade reading, your child should be reading 50 to 60 words a minute at the beginning of the school year and 90 words per minute by the end of the year. To test this, give your child a story from her reading list that she has not read, but will pique her interest. If it's below the speed levels noted above, then fluency is a problem. Make sure she has lots of experiences reading simple books. (One Scholastic Parents fan discovered that having her boys read the Elephant & Piggie Series aloud helped her boys improve reading fluency.) Repeated readings of stories she's already read in class will help, by providing the multiple exposures and decoding opportunities she needs.
MORE: How the Elephant & Piggie Series Helped My Kids Become Fluent Readers
3. Text Difficulty. Your child needs lots of reading practice in stories that are not too hard. That is, he should be able to recognize over 90 percent of the words in his 2nd-grade reading books without your help. If you need to assist your child more frequently, then the story is too tough for him. Stories at this level — his frustration level — do not advance his reading skills. They make comprehension difficult because he is stopping so frequently to figure out words. These constant stops break the flow of reading and don't allow him to focus on the meaning of the story. Give Scholastic Success With Grade 2: Reading Comprehension a try to better determine his level of reading difficulty and practice common skills he's learning in school.
Your child needs lots of reading practice in stories that are not too hard. That is, he should be able to recognize over 90 percent of the words in his 2nd-grade reading books without your help. If you need to assist your child more frequently, then the story is too tough for him. Stories at this level — his frustration level — do not advance his reading skills. They make comprehension difficult because he is stopping so frequently to figure out words. These constant stops break the flow of reading and don't allow him to focus on the meaning of the story. Give Scholastic Success With Grade 2: Reading Comprehension a try to better determine his level of reading difficulty and practice common skills he's learning in school.
©Ridofranz/iStockphoto
Raise a reader by getting the best book recommendations, reading tips, and discounts delivered straight to your inbox.
PLEASE ENTER A VALID EMAIL ADDRESS.
PLEASE SELECT A NEWSLETTER OPTION.
Preschool View Sample
Elementary School View Sample
Privacy Policy
<div><h3>Thanks for signing up! Look out for a confirmation email from us.</h3><h4>Want to connect now? Find us on social media!</h4><h3><a adhocenable="false" href="https://www.facebook.com/scholasticparents/" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/facebook. svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://www.instagram.com/scholasticparents/" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/instagram.svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://twitter.com/scholparents" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/twitter.svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://www.pinterest.com/scholparents/" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/pinterest.svg"></a></h3></div>
svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://www.instagram.com/scholasticparents/" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/instagram.svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://twitter.com/scholparents" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/twitter.svg"></a> <a adhocenable="false" href="https://www.pinterest.com/scholparents/" target="_blank"><img src="/content/dam/parents/icons/pinterest.svg"></a></h3></div>
2nd Grade / Fountas and Pinnell Reading Level Chart
-
Reading Levels
Grade Levels
A
K
B
K
1
C
K
1
D
1
E
1
F
1
G
1
H
1
2
I
1
2
J
2
K
2
L
2
3
M
2
3
N
3
O
3
4
P
3
4
Q
4
R
4
S
4
5
T
5
U
5
V
5
W
5
Reading technique.
 Norms 1-4 class.
Norms 1-4 class. Since many parents stubbornly refuse to understand what is the point of testing reading technique in elementary school (grades 1-4), I give up and publish reading norms. At the same time, I ask you to carefully read not only the quantitative norm of words per minute, but also my explanations both in the table and below it.
Reading Speed Standards Grade 1-4
→ Number of words may vary slightly depending on curriculum. Increased rates are given in parentheses. nine0014 → Grade 1: no mark given, student “passed” or “failed”. In the first half of the year, the reading technique may not be carried out.
| Grade | at the end of the first half of the year | at the end of the second half of the year |
| 1 class | at least 10 - 15 (20 - 25) wpm | 2 -> less than 15 (25) wpm by 3 -> 15-19 (25-34) words by 4 -> 20-24 (35-40) words by 5 -> from 25 (41) words |
| 2 cl. | by 2 -> less than 25 (40) words per minute by 3 -> 25-29 (40-48) words by 4 -> 30-34 (49-54) words by 5 -> from 35 ( 55) words | 2 -> less than 40 (50) words per minute 3 -> 40-44 (50-58) words 4 words -> 45-49(59-64) words by 5 -> from 50 (65) words |
| 3 cl. | by 2 -> less than 40 (55) words per minute by 3 -> 40-49 (55-64) words by 4 -> 50-59 (65-69) words by 5 -> from 60 (70) ) words | by 2 -> less than 65 (70) words per minute by 3 -> 65-69 (70-79) words by 4 -> 70-74 (80-84) words by 5 -> from 75 (85) ) words |
| 4 class | by 2 -> less than 65 (85) words per minute by 3 -> 65-74 (85-99) words by 4 -> 75-84 (100-114) words by 5 -> from 85 (115) ) words | by 2 -> less than 70 (100) words per minute by 3 -> 70-88 (100-115) words by 4 -> 89-94 (116-124) words by 5 -> from 95 (125) words |
Other reading parameters 1-4 class
| Grade | at the end of the first half of the year | at the end of the second half of the year |
| 1 class | Conscious, correct reading, simple words are read as a word. Words with a complex syllabic structure can be read syllable by syllable. Words with a complex syllabic structure can be read syllable by syllable. | |
| 2 cl. | nine0020 Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. Compliance with logical stresses. Words of a complex syllabic structure can be read syllable by syllable. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of logical stresses, pauses and intonations. Syllabic reading is undesirable. | |
| 3 cl. | Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the student expresses understanding of the meaning of what is being read. nine0025 | Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the student expresses understanding of the meaning of what is being read. |
| 4 cl. | Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the student expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is read, and his attitude to the content of what is read. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the student expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is read, and his attitude to the content of what is read. | Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the student expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is read, and his attitude to the content of what is read. nine0025 |
Criteria when setting an assessment for reading technique:
- Reading by syllables or word completely,
- Availability of errors when reading,
- number of words per minute,
- expression,
- awareness.
can be clicked to enlarge
As you can see, the number of words read is not decisive.
That is, parents need to understand that such a concept as reading speed is only one of the criteria for determining the level of reading technology . way of reading is checked : the child reads by syllables or the word is read by him smoothly, in its entirety. It is mandatory to check reading comprehension , in other words, whether the student understands what he has read or not. To do this, after reading, a question can be asked about the text, most often “What did you just read about?” and requires a simple answer (a detailed retelling is not needed 😉)
way of reading is checked : the child reads by syllables or the word is read by him smoothly, in its entirety. It is mandatory to check reading comprehension , in other words, whether the student understands what he has read or not. To do this, after reading, a question can be asked about the text, most often “What did you just read about?” and requires a simple answer (a detailed retelling is not needed 😉)
The expressiveness of reading, the presence of errors and / or stammers are also taken into account. Sometimes there is a return to re-reading the previous word, this indicates a lack of awareness and is considered a mistake.
It should also be taken into account that the standards for the speed (rate) of reading may differ depending on the educational institution, the requirements for a student of a gymnasium will be higher, for a student of a correctional class - lower.
The frequency of checking reading technique in elementary school is usually 2 times a year: the end of the first half of the year and the end of the second half of the year. However, in some schools the reading level is checked at the end of each quarter or trimester. nine0005
However, in some schools the reading level is checked at the end of each quarter or trimester. nine0005
And again! I warn, I exhort - and all the same, the "lion's" part of the students and parents steps on the rake, from which I try to warn.
Understand, memorize, write down and repeat:
No need to speed read! That is, only five words per minute is not good, of course. Some reading speed is needed.
BUT: she, speed, appears as if by itself. The task of the child is simply to read without errors, without stammering or straying, not to swallow the endings and try to observe intonation. nine0005
Of course, we are guided by word standards. And yet, do not set the child to "run ahead of the locomotive." Repeat to him a hundred times: you just read and that's it. Everything!
If you have been reading every day for a year, if your child does not become discouraged when he sees the text, he will pass the reading technique.
The number of words read is not decisive.
Well… I warned you. Conclusions are up to you, dear parents!
Reading standards for grade 2: GEF in primary school, how many words should be read
Parenting
FSES for reading in elementary school
Federal State Educational Standards (FSES) are not rigid. We know that all children are different. Some are ahead of their peers in development, others are lagging behind. The latter is not a reason for panic, but a signal to find approaches to the child and help him improve his knowledge and skills.
When studying with a child, parents can easily bring him closer to the reading standards for grade 2
- Photo
- Getty
In no case should parents put pressure on their child, forcing him to bring his performance closer to the standards. Compliance with average indicators is not a sign of high or low intelligence development. Although the ability to read quickly is necessary to master the complex program of a comprehensive school.
Compliance with average indicators is not a sign of high or low intelligence development. Although the ability to read quickly is necessary to master the complex program of a comprehensive school.
How many words per minute should a second grader read
For comparison, here are the average reading indicators created for the elementary school level:
- Grade 1 1st semester – 25-30 words in 60 seconds;
- Grade 1 2nd semester – 30-40;
- Grade 2 1st semester – 40-50;
- 2nd grade 2nd semester – 50-60;
- Grade 3 1st semester – 60-70;
- Grade 3 2nd half – 70-80;
- 4th grade 1st semester – 80-90;
- 4th grade 2nd semester – 100-120.
In high schools, teachers and students strive for higher performance.
Reasons for slow reading
It is not worth sounding the alarm because your beloved child has not reached the average level of reading norms. There is no need to scold the child either. Parents should understand the causes of the lag and eliminate them. Perhaps a second grader reads slowly because of:
Parents should understand the causes of the lag and eliminate them. Perhaps a second grader reads slowly because of:
- Difficult or uninteresting literature. Each student has their own interests and characteristics. It is important to consider them when compiling a list of literary works to read.
- Regressions. This phenomenon is easy to identify by observing how a second grader reads. If his eyes go back to the beginning of a word or sentence and he often says what he read in his head, there is a regression. It can be the result of habit or inattention. nine0300
- Bad memory. Special exercises will help to correct the situation.
- Poor development of the articulatory apparatus. You can fix it with exercise.
- Weak vocabulary. In this case, it is necessary to identify unfamiliar concepts that come across in the text and explain them.
These are the most common causes, but not all.
If a second grader reads slowly, it is not difficult to correct the situation.