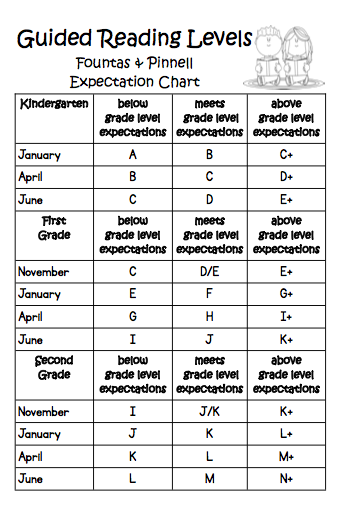
1St grade reading skills
How To Help 1st Grader Read Fluently
When our children are first learning to read, we want them to be successful. As a parent, you are likely to try to find out how to help 1st grader read better. By first grade, kids are learning to read full-length books and are able to read longer, more complex sentences.
This means that your child is reading at a more challenging level and might be struggling. Their reading fluency is likely a factor in how well they are understanding a text.
What should a 1st grader be able to read?
By 1st grade your child should have at least the following variety of reading skills:
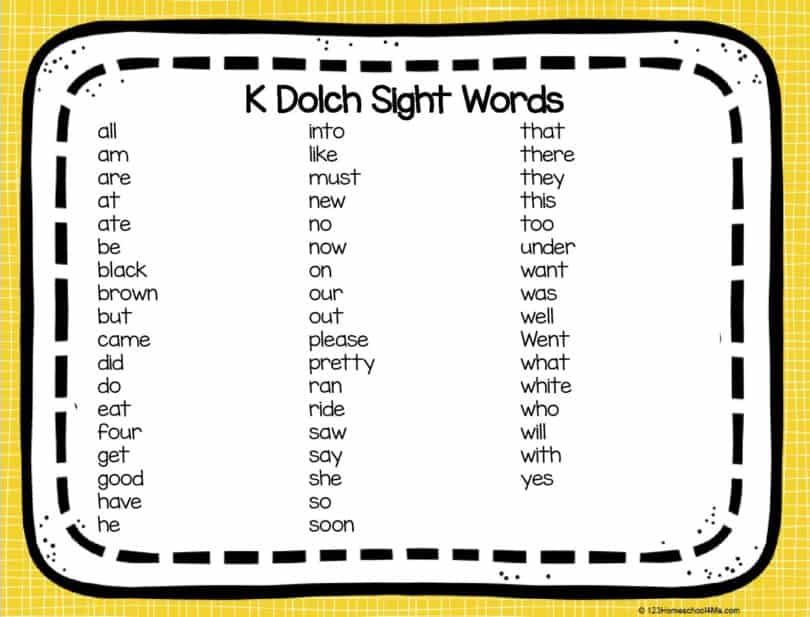
- They should be able to recognize about 150 sight words or high-frequency words.
- They are able to distinguish between fiction and nonfiction texts.
- They should be able to recognize the parts of a sentence such as the first word, capitalization, and punctuation.
- They are able to understand how a final “e” will change the sound of the vowels within a word.
- They are able to answer questions and recall details from a reading.
- They are able to read fluently meaning with speed, accuracy, and prosody.
Your first grader should be able to begin reading the first few levels of graded reader books. A graded reader book is a book that is set at a certain reading level. These books are often used in schools to help measure student progress.
What is fluency in reading?
Reading fluency is the ability to “read how you speak”. This means that your child is reading at a conversational pace with appropriate expression. Reading fluency is important because it is directly related to reading comprehension. The more fluent a reader is the better they understand the text.
Fluency in reading relies on speed, accuracy, and prosody. These factors make for a fluent reader and help your 1st grader not only to recognize words but to actually understand and comprehend text.
- Speed – Fluent readers read at a speed that is accurate for their grade level which is 60 words per minute for 1st graders.

- Accuracy – Fluent readers are able to recognize words quickly and have the skills to sound out and decode words they are unfamiliar with.
- Prosody – Fluent readers use expression and intonation to bring meaning into their readings. This is not just recognizing words, but also recognizing that expression also plays a part in understanding.
How can I help my 1st grader with reading fluency?
There are a variety of things you can do at home to help your 1st grader read more fluently:
- Model reading – Children learn best when they have a model showing them the skills they are meant to be learning. Reading to your child regularly provides a model of fluent reading for them.
- Echo Reading – As you and your child read a text, read one sentence then have them read the same sentence out loud. This form of repeated reading helps them see you model fluency then lets them practice it.
- Reader’s theatre – Turn a book into a script and have
your kids bring the story to life.
 This will help them practice their expression and intonation when they read.
This will help them practice their expression and intonation when they read. - Practice sight words – The more words your child recognizes, the more fluent they will become. Use word games and flashcards to help them learn sight words to help them read less choppy.
- Extensive reading – The best way to help your 1st grader to read fluently is to get them to read a lot! Provide lots of books of their choice at home and get them to enjoy reading so that they practice often.
- Utilize reading apps – Most kids play with technology already such as tablets and smartphones. Why not incorporate reading into this game time by downloading some reading apps?
Which reading app is helpful for improving fluency?
Readability is an app that helps improve fluency for emerging readers. The app is a great way to increase fluency for your 1st grader because it uses A.I. technology and speech-recognition to recognize errors your child might be making when reading out loud.
Readability provides a large library of original content that your child can read and is constantly being updated with new stories. The app works like a private tutor by actually listening to your child read out loud and recognizing their errors. It then provides feedback to help them improve. It can also read the material to your child as they follow along.
These forms of repeated reading can help your 1st grader practice their fluency wherever and whenever they want. Try Readability for free!
1st grade reading Reading | GreatSchools.org
Whether your first grader is still stumbling over beginning texts or sailing through books independently, there are key reading skills your child should learn this year.
Those tricky vowels
Your first grader certainly doesn’t need to know this, but there are 18 vowel phonemes — or distinct sounds — in the English language. Why is this important? Because phonemic awareness is an important indicator of how well a child will read within the first two years of school.
This year, your child will be learning how to distinguish between what’s known as long and short vowel sounds in one-syllable words — an essential concept. (Here’s a way to explain the difference between long and short vowels: when a vowel sounds like its name, it’s a long sound: ape, feet. Short vowels don’t sound like their letter: cat, dot.) Kids will become intimately familiar with that trickiest of vowels, the silent e — and how adding an e to the end of a word can transform a short vowel into a long one. Tip: play the silent e game with your child: What happens if you put an e on hop? It turns into hope!
Related 1st grade reading worksheet: Vowel sounds a and e
Breaking the code
First graders learn to recognize the most basic sounds and sound blends (phonemes) they find in one-syllable words. In class, they will be asked to separate — or segment — letters (e.g. h/a/t) or common consonant blends (e. g. st in stop, pl in plate, tr in tree), so they really hear how individual sounds come together to make a word. They also need to learn some common combinations of two consonants that make one sound (e.g. sh in shape, th in this, wh in what). First graders will also leap into the world of decoding two-syllable words (e.g. ap/ple, mon/key) and learn that each syllable contains at least one vowel.
g. st in stop, pl in plate, tr in tree), so they really hear how individual sounds come together to make a word. They also need to learn some common combinations of two consonants that make one sound (e.g. sh in shape, th in this, wh in what). First graders will also leap into the world of decoding two-syllable words (e.g. ap/ple, mon/key) and learn that each syllable contains at least one vowel.
Advertisement
Related: Watch our Milestone video Does your 1st grader sound out words like this?
Finally, first graders are learning how to read familiars words with new endings, such as run becoming running, bird becoming birds, and play becoming played.
Building vocabulary and word sense
“May I have a pomegranate, Mom?” First grade is often when parents start noticing that, wonder of wonders, their child’s vocabulary starts to flourish. Suddenly, multisyllabic words may be bursting forth from your young reader. It’s also the year of reading challenges: children are expected to become familiar with one of the common bugaboos of the English language: irregularly spelled words (e.g. school, people, thought). Some kids learn these words readily, but many struggle with sounding out common but unfamiliar spellings.
Suddenly, multisyllabic words may be bursting forth from your young reader. It’s also the year of reading challenges: children are expected to become familiar with one of the common bugaboos of the English language: irregularly spelled words (e.g. school, people, thought). Some kids learn these words readily, but many struggle with sounding out common but unfamiliar spellings.
First graders will also be expected to correct their own reading mistakes based on the context of the story. For example, your child might mispronounce porridge when reading Goldilocks and the Three Bears, then look at the bowl, remember the familiar fairy tale, and correct himself.
First graders practice language categorization, such as sorting words that are types of food, colors, or clothing, and learn to define words by one or more key attributes (e.g. a duck is a bird that swims, a tiger is a large cat with stripes). They’ll learn to use their own experience to understand shades of meaning among similar verbs (e. g. look, peek, glance, glare, scowl) and between adjectives that differ in intensity (e.g. large, huge, gigantic). Tip: ask your child to act out the difference between mean, fierce, and terrifying.
g. look, peek, glance, glare, scowl) and between adjectives that differ in intensity (e.g. large, huge, gigantic). Tip: ask your child to act out the difference between mean, fierce, and terrifying.
Your child’s teacher will also expect your child to use new words learned from conversations or reading, including employing frequently occurring conjunctions (e.g. and, or, so, because) in context. For example: “Let’s go to the park because I need to play!”
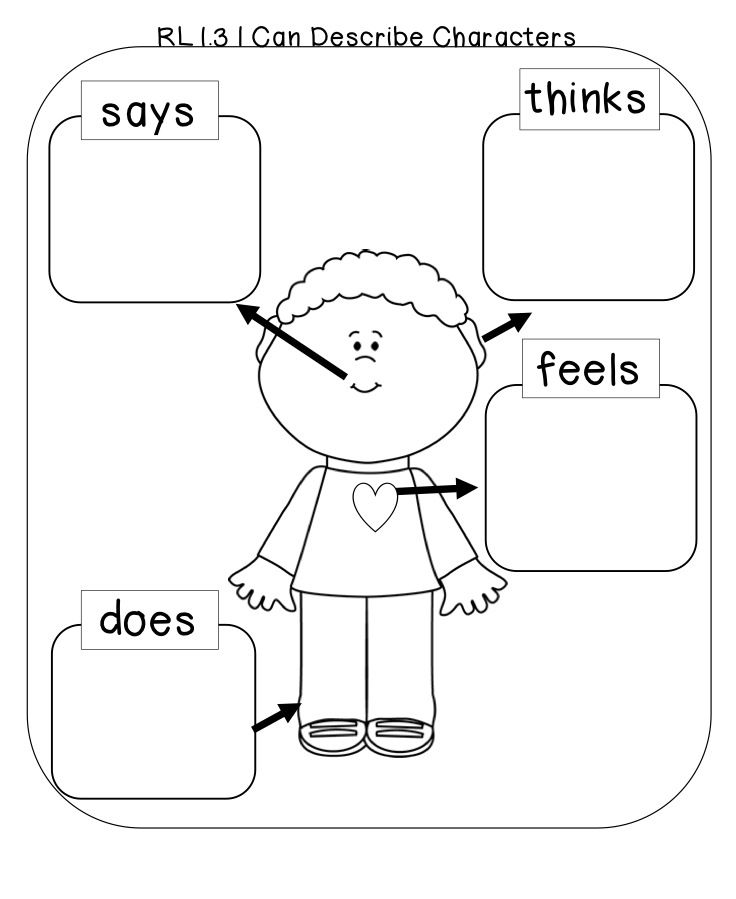
What makes a sentence?
First graders need to learn how to recognize the print features of a sentence.
- One: always capitalize the first letter of the first word in a sentence.
- Two: sentences always end with punctuation — a period for statements, a question mark for questions, and an exclamation point to convey excitement or urgency. (Bonus points for first graders who know the meaning of the exclamation point. It’s ahead of the curve!)
- Asking and answering questions about both the main point and key details in books and showing exactly where those answers show up in the text or illustrations.
- Figuring out a book’s one or two biggest ideas and using the text or images to show how the author conveys these ideas.

- Naming the reasons an author gives to support her points — and pointing those reasons out in the text or pictures.
Related 1st grade reading worksheets: Punctuation and Question words, question marks
Exploring fiction and nonfiction
By the end of first grade, your child should have a clear understanding that there are different kinds of books: ones that tell stories and ones that give information about things that are (or were) true. And, since reading stories, poems, and segments on George Washington’s early years are each challenging in their own way, your child should practice reading each type of text. Keep in mind this is still first grade, so subjects should remain grade-appropriate — and reading together and getting help along the way is expected.
And, since reading stories, poems, and segments on George Washington’s early years are each challenging in their own way, your child should practice reading each type of text. Keep in mind this is still first grade, so subjects should remain grade-appropriate — and reading together and getting help along the way is expected.
Related: See our list of history books for 1st graders.
Building your child’s knowledge bank
Kids learn by connecting new ideas and information from every book they read to what they already know. Think of it like using reading comprehension skills to build a knowledge bank: with every poem, story, or passage read, there’s a main point, a message, or a key fact (or two) that your child learns. The emphasis here is on thoughtfully relating these new bits of knowledge to your child’s life, experiences, and prior knowledge. Being able to remember storylines, recalling key details, and finding information — are positive signs that your child’s “banking” knowledge.
Related: Watch our Milestone video Does your 1st grader read to learn like this?
All about evidence
“Read like a detective, write like an investigative reporter” is how some experts say children should learn to read and write. For first graders, hunting for evidence means finding — and literally pointing to — answers to questions. To answer “What was Grandpa making for breakfast at the beginning of Cloudy with a Chance of Meatballs?” your child should flip through the pages and find the words — or the picture — to point out the answer.
Your child’s teacher will emphasize evidence in different ways this year, but the main skills your child should have include:
Related: Watch our Milestone video Does your 1st grader show understanding like this?
texts to test reading technique - NAUMENOK
It is advisable to test the formation of reading skills 3 times a year: at the beginning of the academic year, at the end of the first half of the year and at the end of the academic year. But sometimes the teacher prefers to check the reading technique at the end of each quarter.
The reading technique test includes not only reading speed, but also reading accuracy, comprehension and expressiveness. I wrote about this in more detail in article 9.0005 "How to test a child's reading technique."
- Special texts are selected to test the reading technique.
- The text should be understandable to the child, but be unfamiliar to him.
- Sentences should be short, without any complicating constructions or signs.

- It is better if the text for checking reading is without illustrations and dialogues so that children do not get distracted while reading.
- Text must be placed on one page.
- While reading the text, you can not interrupt the child, correct mistakes. After completing the reading, you need to return to those words that caused difficulty or were read incorrectly and ask the child to read them again. In the process of reading, a first grader can follow the text with his finger so as not to lose the line.
- To test reading comprehension, you need to ask a few questions about the text.
Reading technique norm in grade 1
1st half year
Reading should be smooth syllabic, conscious and correct, with clear pronunciation of syllables and words.
Reading speed - 25-30 words per minute.
2nd half year
The child reads whole words correctly, consciously. Words with a complex syllabic structure are read syllable by syllable.
Reading speed - 30-40 words per minute.
These texts can be used not only to test the child's reading skills, but also for retelling. How to teach a child to retell can be found in the article “Teaching a child to retell”.
Reading technique test texts in grade 1
Sparrow and swallows
Swallow made a nest. The sparrow saw the nest and occupied it. The swallow called her friends for help. Together, the swallows drove the sparrow out of the nest. (22 words)
Questions:
- What did the sparrow do?
- Who did the swallow call for help?
Ant
Ant found a big grain. He couldn't carry it alone. The ant called for help from his comrades. Together, the ants easily dragged the grain into the anthill. (22 words)
Questions:
- What did the ant find?
- Why did the ant call his friends for help?
Summer
Warm summer has come.
 Currants ripened in the garden. Masha and Tanya collect it in a bucket. Mom will make jam from it. In winter, in the cold, children will drink tea with jam. (29 words)
Currants ripened in the garden. Masha and Tanya collect it in a bucket. Mom will make jam from it. In winter, in the cold, children will drink tea with jam. (29 words) Questions:
- Which berry is ripe in the garden?
- What will mother do?
The fox and cancer
The fox suggested that the crayfish run a race. Cancer agreed. The fox ran, and the crayfish clung to the fox's tail. The fox ran to the place. The fox turned around, and the crayfish unhooked and said: "I've been waiting for you here for a long time." (32 words)
Questions:
- What did the fox offer to cancer?
- How did cancer outsmart the fox?
Cranes
Cranes live near swamps, forest lakes, meadows, river banks. Nests are built right on the ground. The crane circles over the nest, guarding it. At the end of summer, cranes gather in flocks and fly to warm countries.
 (33 words)
(33 words) Questions:
- Where do cranes build nests?
- When do cranes fly to warm countries?
Chicken
A little girl wrapped woolen threads around an egg. It turned out to be a ball. This ball she put on the stove in a basket. Three weeks have passed. Suddenly there was a squeak from the basket. The ball squeaked. The girl unrolled the ball. There was a little chicken there. (34 words)
Questions:
- How did the girl make the ball?
- What happened to the ball after three weeks?
Mushrooms
The guys went to the forest for mushrooms. Dima found a beautiful boletus under a birch. Tanya saw a small butter dish under a pine tree. Ilya saw a huge boletus in the grass. In the grove they collected full baskets of various mushrooms. The children returned home happy and happy. (38 words)
Questions:
- Who found the boletus?
- What mushroom grew under a pine tree?
- Where did the boletus hide?
Summer
Summer has come.
 In forest clearings, the grass is above the knees. Grasshoppers chirp. Strawberries turn red on the tubercles. Raspberries, lingonberries, wild roses, blueberries bloom. The chicks fly out of the nests. A little time will pass, and delicious wild berries will appear. Soon children will come here with baskets to pick berries. (39 words)
In forest clearings, the grass is above the knees. Grasshoppers chirp. Strawberries turn red on the tubercles. Raspberries, lingonberries, wild roses, blueberries bloom. The chicks fly out of the nests. A little time will pass, and delicious wild berries will appear. Soon children will come here with baskets to pick berries. (39 words) Questions:
- What is the grass in the meadows?
- Which berries bloom?
Hedgehog
The guys were walking through the forest. We found a hedgehog under a bush. He curled up in fear. The guys rolled the hedgehog into a hat and brought it home. They gave him milk. The hedgehog turned around and began to eat milk. And then the hedgehog ran back to his forest. (39 words) (according to E. Charushin)
Questions:
- Who did the guys find?
- What did the hedgehog do with fear?
- What did the guys give the hedgehog?
Bathing the cubs
A big bear and two merry cubs came out of the forest.
 The bear grabbed one cub with her teeth by the collar and let's dip into the river. The other cub got scared and ran into the forest. His mother caught up with him, slapped him, and then into the water. The cubs were happy. (40 words) (according to V. Bianchi)
The bear grabbed one cub with her teeth by the collar and let's dip into the river. The other cub got scared and ran into the forest. His mother caught up with him, slapped him, and then into the water. The cubs were happy. (40 words) (according to V. Bianchi) Questions:
- Who came out of the forest?
- What did the second bear do?
- Were the cubs satisfied with the bath?
Lynx
In a dark forest, near a forest path, a beast lay down. This is a lynx - a cat the size of a large dog. Her tail is short, her ears are tufted, her skin is spotted. The lynx lies on a thick bough and waits. She will rush from the tree to her prey. (40 words)
Questions:
- What is the tail of a lynx?
- Where did the lynx hide?
Spring
The sun warmed the earth. Ran the streams. The rooks have arrived. Birds hatch chicks.
 A hare jumps merrily through the forest. The fox went hunting and smells the prey. The she-wolf led the cubs into the clearing. The bear growls at the lair. Butterflies and bees fly over the flowers. Everyone is excited about spring. (41 words)
A hare jumps merrily through the forest. The fox went hunting and smells the prey. The she-wolf led the cubs into the clearing. The bear growls at the lair. Butterflies and bees fly over the flowers. Everyone is excited about spring. (41 words) Questions:
- What does the hare do?
- Where did the she-wolf lead the cubs?
- Where do butterflies and bees fly?
Woodpecker
What does the woodpecker do in the forest? He lives and works in the forest. A bird with a red cap on its head sits on a tall pine and knocks on the trunk with a strong beak. Why is he doing this? Woodpecker saves trees from harmful insects. Therefore, he is often called the forest doctor. (43 words)
Questions:
- What does a woodpecker have on his head?
- Why is a woodpecker called a forest doctor?
Meeting
Misha is walking along the alley of the old park.
 Suddenly, a small red animal runs out onto the path right at his feet. Squirrel! The squirrel has a fluffy tail. She looks with intelligent eyes. The squirrel is waiting for a treat. Misha hands her a nut. The animal is happy. And now her fluffy tail flashed on the tree. (44 words)
Suddenly, a small red animal runs out onto the path right at his feet. Squirrel! The squirrel has a fluffy tail. She looks with intelligent eyes. The squirrel is waiting for a treat. Misha hands her a nut. The animal is happy. And now her fluffy tail flashed on the tree. (44 words) Questions:
- Who was walking in the park?
- Who did Misha meet?
- What did the boy treat the squirrel to?
Brave men
The boys went to school. Suddenly a dog jumped out. She barked at the guys. The boys started to run. Only Borya remained standing still. The dog stopped barking and approached Borya. Borya stroked her. Then Borya calmly went to school, and the dog quietly followed him. (44 words)
Questions:
- Where were the guys going?
- What happened on the way?
- How did the boys behave?
- What did Borya do?
Sly fish
For a long time I sat with a fishing rod on the shore.
 Minnows do not peck at me. And grandfather is sitting under a bush and has already caught a bucket. I sat down in the shade. Immediately the minnows began to peck. It turns out that in a clean place the shadow of the fishing rod is visible. So the cunning fish did not go to the hook. (48 words) (According to E. Shim)
Minnows do not peck at me. And grandfather is sitting under a bush and has already caught a bucket. I sat down in the shade. Immediately the minnows began to peck. It turns out that in a clean place the shadow of the fishing rod is visible. So the cunning fish did not go to the hook. (48 words) (According to E. Shim) Questions :
- Where did grandfather fish?
- Why was he fishing?
- Why didn't the boy bite the fish at first?
Cockerel
A cockerel walks around the yard: a red comb on its head, a red beard under its nose. Petya's tail is a wheel, there are patterns on the tail, spurs on the legs. Petya found a grain. He calls a hen with chickens. They did not share the grain - they fought. Petya the cockerel reconciled them: he ate the grain himself, waved his wings, shouted at the top of his voice: “Ku-ka-re-ku!” (49words)
Questions:
- Where does the cockerel go?
- What did the cockerel find?
- Whom did he call?
- Why did the chickens fight?
Bats
Bats are very useful animals.
 They eat harmful insects. During the day, bats wrap their wide wings like cloaks and hang upside down in dark places. The night is coming. They fly out to hunt. Many harmful insects fly at night. Almost all birds sleep at this time. Therefore, the "work" of bats is especially important. (51 words) (According to Yu. Dmitriev)
They eat harmful insects. During the day, bats wrap their wide wings like cloaks and hang upside down in dark places. The night is coming. They fly out to hunt. Many harmful insects fly at night. Almost all birds sleep at this time. Therefore, the "work" of bats is especially important. (51 words) (According to Yu. Dmitriev) Questions:
- What are the benefits of bats?
- How do bats sleep?
- When do bats hunt?
Ducks
Vasya is sitting on the bank. He watches how the ducks swim in the pond: they hide their wide spouts in the water. Vasya does not know how to drive the ducks home. Vasya began to call the ducks: “Ooty-ooty-ducks! The noses are wide, the paws are webbed! Stop dragging worms, pinching grass - it's time for you to go home. Ducks Vasya obeyed, went ashore, go home. (52 words) (according to K. Ushinsky)
Questions:
- What did Vasya do on the beach?
- What kind of nose do ducks have?
- What did Vasya call the ducks?
- What did the ducks do?
Winter
Frost bound the earth.
 Rivers and lakes are frozen. Everywhere lies white fluffy snow. Children are happy with winter. It's nice to ski on fresh snow. Matvey and Lera are playing snowballs. Andrei and Sasha are making a snowman. Only animals have a hard time in the winter cold. Birds fly closer to housing. Guys, help our little friends in winter. Make bird feeders! (55 words)
Rivers and lakes are frozen. Everywhere lies white fluffy snow. Children are happy with winter. It's nice to ski on fresh snow. Matvey and Lera are playing snowballs. Andrei and Sasha are making a snowman. Only animals have a hard time in the winter cold. Birds fly closer to housing. Guys, help our little friends in winter. Make bird feeders! (55 words) Questions:
- Who is happy about winter?
- Who has it hard in winter?
- How can you help the birds?
Four butterflies
It was spring. The sun shone brightly. Flowers grew in the meadow. Four butterflies were flying above them: a red butterfly, a white butterfly, a yellow butterfly, and a green butterfly. Suddenly, a large black bird flew in. She saw butterflies and wanted to eat them. The butterflies got scared and sat on the flowers. A white butterfly sat on a chamomile. Red butterfly - on poppy. Yellow - on a dandelion, and green hid behind a leaf of a tree.
 A bird flew, flew, but did not see butterflies. (56 words)
A bird flew, flew, but did not see butterflies. (56 words) Questions:
- What butterflies were flying over the flowers?
- Why didn't the bird see butterflies?
If the child's reading technique is below the norm, then it is necessary to read a lot (which is very difficult with poor reading quality) and does not always bring results. It is better to use special techniques and exercises, because. The reasons for bad reading can be different.
Slow readers and children who are struggling to improve their reading speed can be helped by using syllabary reading or, much more effectively, by using an integrated approach that includes various professional techniques.
To do this, I suggest you use the books:
THE BIG BOOK OF SYLLING TABLES is
- a ready-made tool for training reading and speed reading skills;
- 200 syllabic tables of different levels of complexity;
- professional spreadsheet technique.
The most effective methods will allow each table to be used repeatedly several times, increasing the child's interest in reading.
Working with these syllabic tables the child will receive:
- improved reading skills;
- increased reading speed;
- improved diction;
- reading comprehension;
- development of thinking and attention;
- vocabulary expansion;
- increased self-confidence.
The child will stop stumbling over difficult words while reading. The reading process will become natural and painless.
You can easily print the pages you need. All pages of the book can be used separately.
THE BIG BOOK OF SAYLING CHARTS is suitable for those who are just taking their first steps in reading, and for those who want to significantly improve the quality of reading.
Syllabary charts help children develop speed reading skills. But it often happens that a child gets stuck at a reading speed of 10-20 words per minute. It is important to track this moment in time and start immediately performing the necessary exercises.
I have created a training that will help you overcome this barrier without much difficulty. It is convenient to use both at home and when working with the whole class. A variety of tasks will not let children get bored, and parents and teachers will not have to select the necessary material for a long time and torment children with an exhausting, incredibly difficult process at this stage - reading.
Download TRAINING "Speed Reading and Speech Development"
Together with the training you will receive a small book as a gift - 20 syllabic tables for practicing reading skills (they do not repeat the tables of a large book).
Reading texts grade 1 print with tasks
O.
 Naumova "Noisy texts for reading and retelling"
Naumova "Noisy texts for reading and retelling"
The skill of high-quality reading and writing depends on the state of visual perception and attention of the child.
The better the child recognizes visual images, the better he reads and writes more competently.
Working with noisy texts engages the child's brain as much as possible and greatly increases the productivity of classes. At the same time, there is a development of figurative thinking, attention, memory, the ability to understand what is read.
In the book you will find:
- Noisy texts with questions;
- Texts with questions for reading, retelling, checking reading technique;
- Method of working with noisy texts;
- High productivity options;
- Exercises for developing speech and reading comprehension.
As a result, the child:
- read speed increases;
- attention and memory develop;
- conscious reading skills are developed;
- develop self-control skills;
- speech develops;
- the number of writing errors decreases;
- the process of writing summaries and essays is facilitated;
- improvement of educational performance.

Suitable for individual and group lessons.
Easy to print and use.
The Noisy Texts book series consists of three parts.
Texts differ in the number of words, complexity and degree of noise.
It is desirable to work on all three levels of difficulty.
Level 1
Number of words in texts 25-55. A simple noisemaker.
Download
Level 2
Number of words in texts 35-75. Inclined skimmer.
Download
Level 3
Number of words in texts 45-95. Complicated noise.
Download
Also:
Come to
Bookshop for useful books!
Sincerely, Olga Naumova
Thank you for sharing this article on social networks!
standards for grades and quarters
Reading is a key skill that opens the gate to the land of knowledge for a child. Thanks to this skill, children learn about the phenomena and events of the world around them, get acquainted with the characters and actions of people, meet new problems and ideas. This skill helps them to broaden their horizons and ideas about the world, develops critical thinking and trains cognitive abilities - attention, imagination, memory. Reading is the foundation for further successful learning.
Thanks to this skill, children learn about the phenomena and events of the world around them, get acquainted with the characters and actions of people, meet new problems and ideas. This skill helps them to broaden their horizons and ideas about the world, develops critical thinking and trains cognitive abilities - attention, imagination, memory. Reading is the foundation for further successful learning.
To understand how well a child develops this skill, it helps to check the reading technique. Reading technique is a multifactorial test that characterizes the development of a skill from different angles. In reading technique, the following are evaluated:
- reading speed,
- reading method,
- reading awareness,
- correct reading,
- expressiveness of reading.
A difficult reading skill consists of both a technical and a semantic component and is aimed at achieving the main goal - understanding and assimilation of the information read.
Reading technique parameters
Let's consider all the components of reading technique in more detail.
- Reading speed - the number of words read in a certain period of time. Often, parents focus on the formation of fluent reading, while the child makes many mistakes, does not understand and does not remember what he read. It is not necessary to force only speed, slower conscious reading and a gradual increase in tempo are better than fast mechanical reading with errors and inaccuracies.
- Way of reading — syllabic reading or reading the whole word, smoothly. With the development of the skill, the child has a gradual transition from syllabic reading to smooth reading in whole words.
- The correctness of reading is characterized by the absence of errors and hesitation. Inattention, problems of diction lead to inaccurate reading, indistinct articulation and, as a result, to a distortion of meaning. Pay attention to the correct reading - this will be the key to competent writing.
- Reading awareness involves reading comprehension, awareness of the idea and meaning of the text, and in the future - this is the ability to catch the subtext, humor, irony, the attitude of the author. Interfering with reading comprehension can be low reading speed, distorted reproduction - guessing words, changing the shape of words, not reading endings.
- Reading expressiveness - the use of pauses, finding the right intonation, the correct placement of stresses. The expressiveness of reading is inextricably linked with awareness. When understanding what is read, it is easier for the child to observe the necessary pauses, select the correct intonation and place logical stresses.
Reading speed standards for primary school
GEF standards determine the desired reading speed for a child by a certain point in learning, help to understand whether the development of a skill is successful or whether additional attention is required. Standards - indicative values; it is important to take into account the individual psychophysiological characteristics of each child and evaluate the growth of his personal indicators.
Standards - indicative values; it is important to take into account the individual psychophysiological characteristics of each child and evaluate the growth of his personal indicators.
Grade 1 reading speed standards
Reading speed standards in grade 2
Reading speed standards in grade 3
Reading velocity
Reading speed, to which it is necessary schools, is reading at the speed of conversational speech, 110-120 words per minute. The human articulatory apparatus has adapted to this speed over time. And most importantly, the reading should be conscious, correct, expressive.
Other parameters of reading technique
Grade 1
At the end of the first half of the year. Reading is smooth syllabic, conscious and correct, with a clear pronunciation of syllables and words.
At the end of the second half of the year. Reading is conscious, correct, simple words are read as a word. Words with a complex syllabic structure can be read syllable by syllable.
Words with a complex syllabic structure can be read syllable by syllable.
Grade 2
At the end of the first half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. Compliance with logical stresses. Compound words can be read syllable by syllable.
At the end of the second half of the year. Reading meaningful, correct, in whole words. With observance of logical stresses, pauses and intonations. Syllabic reading is undesirable.
Grade 3
At the end of the first half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, with the help of which the child expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is being read.
At the end of the second half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the child expresses understanding of the meaning of what is being read.
4th grade
At the end of the first half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With the help of observed pauses and intonations, the child not only expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is being read, but is able to express his attitude to what he has read.
At the end of the second half of the year. Reading consciously, correctly, in whole words. With observance of pauses and intonations, through which the child expresses an understanding of the meaning of what is read, and his attitude to the content of what is read.
How can I test my child's reading skills on my own?
Have your child see how well they read already. Children usually love to know how many centimeters they have grown, and they may also be interested in knowing their progress in reading. Warn about the upcoming test and ask the child to read quickly.
The control of reading technique in sensitive children who, due to their temperament, can hardly tolerate various tests, can be carried out imperceptibly or in the form of a game. Do not create unnecessary excitement around the upcoming test, do not arrange a test in the form of an exam. If the child is worried, stutters, transfer control to another time.
Do not create unnecessary excitement around the upcoming test, do not arrange a test in the form of an exam. If the child is worried, stutters, transfer control to another time.
Verification process:
- Prepare a clock with a second hand or use the stopwatch on your phone, and choose the appropriate text.
- Ask the child to take a seat.
- Show him the text and ask him to read it aloud.
- Track the time from the moment your child starts reading. Not all children are able to immediately start reading on command, which leads to inaccurate results.
- Usually, one minute is noted for checking, but some experts recommend taking 2 minutes for monitoring, since not all children are equally quickly included in the work. Divide the result obtained in 2 minutes in half.
- When reading, do not correct or interrupt. It is better to discuss the mistakes made after the child has finished reading.
- Evaluate the speed, correctness, awareness and expressiveness of reading.

- Retest and compare results. Reading technique may differ depending on the child's fatigue, health status and mood.
Which text is suitable for verification?
Both fiction and non-fiction texts appropriate for the child's age are suitable for this purpose. The text should be unfamiliar, but understandable to the child, have educational and educational value. The texts of V. Bianchi, L. Tolstoy, N. Nosov, B. Zhitkov, K. Ushinsky, V. Dragunsky are suitable. The text for verification can be found in special manuals or in a textbook on the Russian language and literature.
You should find the text that is located on the spread of the book so that the child does not have to waste time turning pages. Choose text without an abundance of punctuation marks and distracting illustrations. It is not desirable that the passage contains common complex sentences and dialogues. The font must be large enough and legible. The text should not have a technical focus and contain terms incomprehensible to the child.
Test score
Speed score
Count how many words the child read in one minute. When counting words, pay attention:
- prepositions, conjunctions, particles of 1-2 letters are counted as one word;
- when wrapping, a word counts as 2 words;
- if the word is written with a hyphen, look at how many letters are on both sides of the hyphen: if there are more than three, we count it as 2 words, for example, "long, long", if less than three, for example, "somehow", - as one .
Compare the result with the recommended limits and the child's previous performance.
Comprehension score
Determine how well the child understood what they read. If the student reads slowly and has read only a couple of sentences, let him read the passage to the end. Ask your child a few questions about the text. Ask what or who he read about. Ask the child to identify the main idea of what they read and retell the text.
For a deeper check of the meaning of the reading and learning, use special teaching kits.
Correctness assessment
Pay attention to whether the child reads what is written correctly, whether he pronounces words clearly, whether there are hesitations and corrections, whether he alters words, whether he changes endings, whether he places stresses correctly. Discuss the mistakes with the student.
Evaluation of expressiveness
To assess the expressiveness of reading, the child is offered a familiar text. Listen to whether the child observes pauses and other punctuation marks, whether he changes intonation, whether he highlights the main idea.
Improving reading technique
Poor results in reading technique are not a reason to be upset, but only a signal that additional efforts need to be made to improve the skill. You can work with the child on your own or contact a specialist who will analyze the weak points and select the appropriate exercises. Conduct additional activities with the child in the mode of "sparing reading" without pressure. It is more important to observe the regularity and frequency of classes: 10-20 minutes daily.
Conduct additional activities with the child in the mode of "sparing reading" without pressure. It is more important to observe the regularity and frequency of classes: 10-20 minutes daily.
How can you motivate your child to read:
- Reward your efforts with stickers, stars.
- Mark progress visually - create a success board so your child can visually see their progress
- Conduct activities in the form of a game, such as "going to the library" or "reading to your favorite toys."
- Choose books and texts that are interesting for your child.
- Let the child read to the pets, they are grateful and accepting listeners. Reading to them, the child is not afraid to make a mistake, he relaxes and overcomes the fear of failure.
- Have a reading competition between peers and siblings.
To improve the speed of reading will help:
- Reading by syllabic tables.
- Multiple reading. Read the same text several times, increasing the pace.
 From the second time the child will be able to read faster.
From the second time the child will be able to read faster. - "Tug". An adult leads a finger along the line, setting the pace. The child tries to read at a given pace.
- Tops and roots. The child reads the words, covering the upper or lower half of the letters with a ruler.
- Reading in a book turned upside down.
- Lightning. Alternating reading at a comfortable pace with reading at the highest possible speed for 20 seconds on the command "Lightning!".
- "Sprint". Reading speed competition between classmates.
- Work on expanding the field of view according to Schulte tables.
- Reading with a window to eliminate "regression" - recurrent eye movements that lead to repeated reading.
For correct reading:
- Work on clear diction, do articulatory gymnastics.
- Read tongue twisters and tongue twisters.
- Invite the child to correct the deformed sentences: "The weather is good on the street.
 "
" - "Imaginary word". When reading, the wrong word is pronounced, the child must correct it.
Reading comprehension
- “Reading in a wave”. First, the child reads aloud, then retells what he read.
- Drawing up a plan for reading.
- The student reads to himself at a comfortable pace, tells what he understood and felt, what he thought about
- Discuss unfamiliar words and expressions.
- Invite the child to draw a picture of the passage they read.
- Ask them to tell you what they liked about the text, what they remember.
For expressive reading
- Role-playing, staging.
- Put on a "radio show".
- Expressive recitation of poems.
- Voice flexibility training. The ability to speak quieter-louder, higher-lower.
- Conducting reading indicating the tone or strength of the voice.
- Live Picture. One reads, the other reacts with facial expressions.

Learn more