At what age can children read
Reading Milestones (for Parents) - Nemours KidsHealth
Reviewed by: Cynthia M. Zettler-Greeley, PhD
Nemours BrightStart!
en español Hitos en la lectura
This is a general outline of the milestones on the road to reading success. Keep in mind that kids develop at different paces and spend varying amounts of time at each stage. If you have concerns, talk to your child's doctor, teacher, or the reading specialist at school. Getting help early is key for helping kids who struggle to read.
Parents and teachers can find resources for children as early as pre-kindergarten. Quality childcare centers, pre-kindergarten programs, and homes full of language and book reading can build an environment for reading milestones to happen.
Infancy (Up to Age 1)
Kids usually begin to:
- learn that gestures and sounds communicate meaning
- respond when spoken to
- direct their attention to a person or object
- understand 50 words or more
- reach for books and turn the pages with help
- respond to stories and pictures by vocalizing and patting the pictures
Toddlers (Ages 1–3)
Kids usually begin to:
- answer questions about and identify objects in books — such as "Where's the cow?" or "What does the cow say?"
- name familiar pictures
- use pointing to identify named objects
- pretend to read books
- finish sentences in books they know well
- scribble on paper
- know names of books and identify them by the picture on the cover
- turn pages of board books
- have a favorite book and request it to be read often
Early Preschool (Age 3)
Kids usually begin to:
- explore books independently
- listen to longer books that are read aloud
- retell a familiar story
- sing the alphabet song with prompting and cues
- make symbols that resemble writing
- recognize the first letter in their name
- learn that writing is different from drawing a picture
- imitate the action of reading a book aloud
Late Preschool (Age 4)
Kids usually begin to:
- recognize familiar signs and labels, especially on signs and containers
- recognize words that rhyme
- name some of the letters of the alphabet (a good goal to strive for is 15–18 uppercase letters)
- recognize the letters in their names
- write their names
- name beginning letters or sounds of words
- match some letters to their sounds
- develop awareness of syllables
- use familiar letters to try writing words
- understand that print is read from left to right, top to bottom
- retell stories that have been read to them
Kindergarten (Age 5)
Kids usually begin to:
- produce words that rhyme
- match some spoken and written words
- write some letters, numbers, and words
- recognize some familiar words in print
- predict what will happen next in a story
- identify initial, final, and medial (middle) sounds in short words
- identify and manipulate increasingly smaller sounds in speech
- understand concrete definitions of some words
- read simple words in isolation (the word with definition) and in context (using the word in a sentence)
- retell the main idea, identify details (who, what, when, where, why, how), and arrange story events in sequence
First and Second Grade (Ages 6–7)
Kids usually begin to:
- read familiar stories
- "sound out" or decode unfamiliar words
- use pictures and context to figure out unfamiliar words
- use some common punctuation and capitalization in writing
- self-correct when they make a mistake while reading aloud
- show comprehension of a story through drawings
- write by organizing details into a logical sequence with a beginning, middle, and end
Second and Third Grade (Ages 7–8)
Kids usually begin to:
- read longer books independently
- read aloud with proper emphasis and expression
- use context and pictures to help identify unfamiliar words
- understand the concept of paragraphs and begin to apply it in writing
- correctly use punctuation
- correctly spell many words
- write notes, like phone messages and email
- understand humor in text
- use new words, phrases, or figures of speech that they've heard
- revise their own writing to create and illustrate stories
Fourth Through Eighth Grade (Ages 9–13)
Kids usually begin to:
- explore and understand different kinds of texts, like biographies, poetry, and fiction
- understand and explore expository, narrative, and persuasive text
- read to extract specific information, such as from a science book
- understand relations between objects
- identify parts of speech and devices like similes and metaphors
- correctly identify major elements of stories, like time, place, plot, problem, and resolution
- read and write on a specific topic for fun, and understand what style is needed
- analyze texts for meaning
Reviewed by: Cynthia M. Zettler-Greeley, PhD
Date reviewed: May 2022
What is the best age to learn to read?
Loading
Family Tree | Education
What is the best age to learn to read?
(Image credit: Ozge Elif Kizil/Anadolu Agency via Getty Images)
By Melissa Hogenboom
2nd March 2022
In some countries, kids as young as four learn to read and write. In others, they don't start until seven. What's the best formula for lasting success? Melissa Hogenboom investigates.
I
I was seven years old when I started to learn to read, as is typical of the alternative Steiner school I attended. My own daughter attends a standard English school, and started at four, as is typical in most British schools.
Watching her memorise letters and sound out words, at an age when my idea of education was climbing trees and jumping through puddles, has made me wonder how our different experiences shape us. Is she getting a crucial head-start that will give her lifelong benefits? Or is she exposed to undue amounts of potential stress and pressure, at a time when she should be enjoying her freedom? Or am I simply worrying too much, and it doesn't matter at what age we start reading and writing?
Is she getting a crucial head-start that will give her lifelong benefits? Or is she exposed to undue amounts of potential stress and pressure, at a time when she should be enjoying her freedom? Or am I simply worrying too much, and it doesn't matter at what age we start reading and writing?
There's no doubt that language in all its richness – written, spoken, sung or read aloud – plays a crucial role in our early development. Babies already respond better to the language they were exposed to in the womb. Parents are encouraged to read to their children before they are even born, and when they are babies. Evidence shows that how much or how little we are talked to as children can have lasting effects on future educational achievement. Books are a particularly important aspect of that rich linguistic exposure, since written language often includes a wider and more nuanced and detailed vocabulary than everyday spoken language. This can in turn help children increase their range and depth of expression.
Since a child's early experience of language is considered so fundamental to their later success, it has become increasingly common for preschools to begin teaching children basic literacy skills even before formal education starts. When children begin school, literacy is invariably a major focus. This goal of ensuring that all children learn to read and write has become even more pressing as researchers warn that the pandemic has caused a widening achievement gap between wealthier and poorer families, increasing academic inequality.
There are many ways to enjoy reading. In this Namibian school, blind and visually impaired children learn the Braille script (Credit: Oleksandr Rupeta/NurPhoto/Getty Images)
Family Tree
In many countries, formal education starts at four. The thinking often goes that starting early gives children more time to learn and excel. The result, however, can be an "education arms race", with parents trying to give their child early advantages at school through private coaching and teaching, and some parents even paying for children as young as four to have additional private tutoring.
Compare that to the more play-based early education of several decades ago, and you can see a huge change in policy, based on very different ideas of what our children need in order to get ahead. In the US, this urgency sped up with policy changes such as the 2001 "no child left behind" act, which promoted standardised testing as a way to measure educational performance and progress. In the UK, children are tested in their second year of school (age 5-6) to check they are reaching the expected reading standard. Critics warn that early testing like this can put children off reading, while proponents say it helps to identify those who need additional support.
However, many studies show little benefit from an early overly-academic environment. One 2015 US report says that society's expectations of what children should achieve in kindergarten has changed, which is leading to "inappropriate classroom practices", such as reducing play-based learning.
The risk of "schoolification"
How children learn and the quality of the environment is hugely important. "Young children learning to read is one of the most important things primary education does. It's fundamental to children making progress in life," says Dominic Wyse, a professor of primary education at University College London, in the UK. He, alongside sociology professor Alice Bradbury, also at UCL, has published research proposing that the way we teach literacy really matters.
"Young children learning to read is one of the most important things primary education does. It's fundamental to children making progress in life," says Dominic Wyse, a professor of primary education at University College London, in the UK. He, alongside sociology professor Alice Bradbury, also at UCL, has published research proposing that the way we teach literacy really matters.
In a 2022 report, they state that English school system's intense focus on phonics – a method that involves matching the sound of a spoken word or letter, with individual written letters, through a process called "sounding out" – could be failing some children.
A reason for this, says Bradbury, is that the "schoolification of early years" has resulted in more formal learning earlier on. But the tests used to assess that early learning may have little to do with the skills actually needed to read and enjoy books or other meaningful texts.
For example, the tests may ask pupils to "sound out" and spell nonsense words, to prevent them from simply guessing, or recognising familiar words. Since nonsense words are not meaningful language, children may find the task difficult and puzzling. Bradbury found that the pressure to gain these decoding skills – and pass reading tests – also means that some three-year-olds are already being exposed to phonics.
Since nonsense words are not meaningful language, children may find the task difficult and puzzling. Bradbury found that the pressure to gain these decoding skills – and pass reading tests – also means that some three-year-olds are already being exposed to phonics.
"It doesn't end up being meaningful, it ends up being memorising rather than understanding context," says Bradbury. She also worries that the books used are not particularly engaging.
Language in all its richness – written, spoken, sung or read aloud – plays a crucial role in our early development (Credit: Xie Chen/VCG via Getty Images)
Neither Wyse nor Bradbury make the case for later learning per se, but rather highlight that we should rethink the way children are taught literacy. The priority, they say, should be to encourage an interest in and familiarity with words, using storybooks, songs and poems, all of which help the child pick up the sounds of words, as well as expanding their vocabulary.
This idea is backed up by studies that show that the academic benefits of preschool fade away later on. Children who attend intensive preschools do not have higher academic abilities in later grades than those who did not attend such preschools, several studies now show. Early education can however have a positive impact on social development – which in turn feeds into the likelihood of graduation from school and university as well as being associated with lower crime rates. In short, attending preschool can have positive effects on later achievement in life, but not necessary on academic skills.
Children who attend intensive preschools do not have higher academic abilities in later grades than those who did not attend such preschools, several studies now show. Early education can however have a positive impact on social development – which in turn feeds into the likelihood of graduation from school and university as well as being associated with lower crime rates. In short, attending preschool can have positive effects on later achievement in life, but not necessary on academic skills.
Too much academic pressure may even cause problems in the long run. A study published in January 2022 suggested that those who attended a state-funded preschool with a strong academic emphasis, showed lower academic achievements a few years later, compared to those who had not gained a place.
This chimes with research on the importance of play-based learning in the early years. Child-led play-based preschools have better outcomes than more academically focussed preschools, for example.
One 2002 study found that "children's later school success appears to have been enhanced by more active, child-initiated early learning experiences", and that overly formalised learning could have slowed progress. The study concluded that "pushing children too soon may actually backfire when children move into the later elementary school grade".
Similarly, another small study found that disadvantaged children in the US who were randomly assigned to a more play-based setting had lower behavioural issues and emotional impairments at age 23, compared to children who had been randomly assigned to a more "direct instruction" setting.
Preschool studies like these don't shed light on the impact of early literacy per se, and small studies in single locations must always be treated with care, but they suggest that how it is taught, matters. One reason why early education can result in positive social outcomes later in life may have nothing to do with the teaching at all, but with the fact that it provides childcare. This means parents can work uninterrupted and provide more income to the family home.
This means parents can work uninterrupted and provide more income to the family home.
Anna Cunningham, a senior lecturer in psychology at Nottingham Trent University who studies early literacy, argues that if a setting is too academically focused early on, it can cause the teachers to become stressed over tests and results, which can in turn affect the kids. "Of course it's not good to judge a five-year-old on their results," she says. Parental anxiety about how well their child is doing at school can also feed into this: according to a survey commissioned by an educational charity in the UK, school performance is one of parents' top concerns.
With the right support, children can learn to read in a wide range of settings, like this open-air school in Dhaka, Bangladesh (Credit: Anadolu Agency via Getty Images)
Later start, better outcomes?
Not everyone favours an early start. In many countries, including Germany, Iran and Japan, formal schooling starts at around six. In Finland, often hailed as the country with one of the best education system in the world, children begin school at seven.
In Finland, often hailed as the country with one of the best education system in the world, children begin school at seven.
Despite that apparent lag, Finnish students score higher in reading comprehension than students from the UK and the US at age 15. In line with that child-centred approach, the Finnish kindergarten years are filled with more play and no formal academic instruction.
Following this model, a 2009 University of Cambridge review proposed that the formal school age should be pushed back to six, giving children in the UK more time "to begin to develop the language and study skills essential to their later progress", as starting too early could "risk denting five-year-olds' confidence and causing long-term damage to their learning".
Research does back up this idea of starting later. One 2006 kindergarten study in the US showed there was improvement in test scores for children who delayed entry by one year.
Other research comparing early versus late readers, found that later readers catch up to comparable levels later on – even slightly surpassing the early readers in comprehension abilities. The study, explains lead author Sebastian Suggate, of the University of Regensburg in Germany, shows that learning later allows children to more efficiently match their knowledge of the world – their comprehension – to the words they learn. "It makes sense," he says. "Reading comprehension is language, they've got to unlock the ideas behind it."
The study, explains lead author Sebastian Suggate, of the University of Regensburg in Germany, shows that learning later allows children to more efficiently match their knowledge of the world – their comprehension – to the words they learn. "It makes sense," he says. "Reading comprehension is language, they've got to unlock the ideas behind it."
"Of course if you spend more time focusing on language earlier on, you are building a strong foundation of skills that takes years to develop. Reading can be picked up quickly but for language (vocabulary and comprehension) there's no cheap tricks. It's hard work," says Suggate. In other work looking at differing school entry ages, he found that learning to read early had no discernible benefits at age 15.
The question remains that if reading ability is not improved by learning early, then why start early? Individual variation in reading appetite and ability are one important aspect.
"Children are hugely different in terms of their foundational skills when they start school or start learning to read," explains Cunningham. In her study of Steiner-educated children, who only start formal education at about seven, she had to exclude 40% of the sample as the children could already read. "I think that's because they were ready for it," she says. She also found the older children were more ready "to learn the process to read in terms of their underlying language skills" because they had had three extra years of language exposure.
In her study of Steiner-educated children, who only start formal education at about seven, she had to exclude 40% of the sample as the children could already read. "I think that's because they were ready for it," she says. She also found the older children were more ready "to learn the process to read in terms of their underlying language skills" because they had had three extra years of language exposure.
World Book Day celebrates the joy of reading, and has become increasingly popular. Here, British Olympic Gold Medallist Greg Rutherford joins in (Credit: Matt Alexander/PA Wire)
Studies also show that reading ability is more closely linked to a child's vocabulary than to their age, and that spoken language skills are a high predictor of later literary skills. However, we know that many children who enter school are behind on their language skills, especially those from disadvantaged backgrounds. Some argue that formal teaching allows these children to access the support and skills that others may pick up informally at home. This line of thinking is espoused by UK educational authorities, who say that teaching reading early to those behind on their spoken language is "the only effective route to closing this [language ability] gap".
This line of thinking is espoused by UK educational authorities, who say that teaching reading early to those behind on their spoken language is "the only effective route to closing this [language ability] gap".
Others favour the opposite approach, of immersing children in an environment where they can enjoy and develop their language comprehension, which is after all central to reading success. This is exactly what a playful learning setting helps encourage. "The job of teaching is to assess where your children are and give them the most appropriate teaching related to their level of development," says Wyse. The 2009 Cambridge review echoed this and stated: "There is no evidence that a child who spends more time learning through lessons – as opposed to learning through play – will 'do better' in the long run."
Cunningham, whose daughter has also recently started learning to read, has a reassuringly generous view of the ideal reading age: "It doesn't matter whether you start to read at four or five or six as long as the method they are taught is a good, evidenced method. Children are so resilient they will find opportunities to play in any context."
Children are so resilient they will find opportunities to play in any context."
Our obsession with early literacy appears to be somewhat unfounded, then – there's no need, nor clear benefit of rushing it. On the other hand, if your child is starting early, or shows an independent interest in reading before their school offers it, that's fine too, as long as there is plenty of opportunity to down tools and have fun along the way.
* Melissa Hogenboom is the editor of BBC Reel. Her book, The Motherhood Complex, is out now. She is @melissasuzanneh on Twitter.
--
Join one million Future fans by liking us on Facebook, or follow us on Twitter or Instagram.
If you liked this story, sign up for the weekly bbc.com features newsletter, called "The Essential List".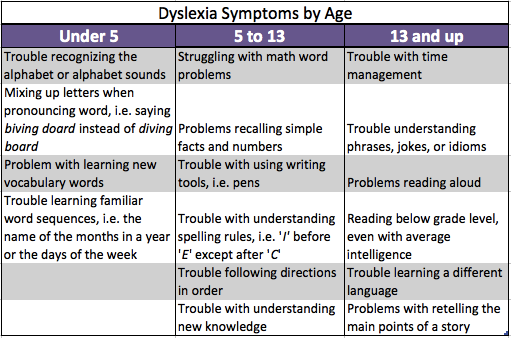 A handpicked selection of stories from BBC Future, Culture, Worklife, Travel and Reel delivered to your inbox every Friday.
A handpicked selection of stories from BBC Future, Culture, Worklife, Travel and Reel delivered to your inbox every Friday.
methods of teaching reading to the first grade
When to teach a child to read
There are early development studios where children are taught to read from the first years of life. However, pediatricians do not recommend rushing and advise starting learning to read no earlier than 4 years old, best of all - at 5–6. By this age, most children already distinguish sounds well, can correctly compose sentences and pronounce words. Therefore, most often parents think about how to teach their child to read, already on the eve of school.
Source: unsplash.com / @jonathanborba
How to know if your child is ready to learn to read
Before you start teaching your child to read, you need to make sure that the child is ready and wants to learn. To do this, try to answer the following questions:
To do this, try to answer the following questions:
- Does the child know the concepts of “right-left”, “big-small”, “inside-outside”?
- Can he generalize objects according to these characteristics?
- Can he distinguish between similar and dissimilar forms?
- Is he able to remember and execute at least three instructions?
- Does he form phrases correctly?
- Does he pronounce words clearly?
- Can he retell a story he heard or experienced?
- Can he formulate his feelings and impressions?
- Can you predict the ending of a simple story?
- Does he manage to participate in the dialogue?
- Can he listen without interrupting?
- Can he rhyme words?
- Do the letters attract his attention?
- Does the child have a desire to independently look at the book?
- Does he like being read aloud to him?
If you answered “yes” to these questions, your child is ready and will soon learn to read correctly.
Methods for teaching reading
Most of the methods involve learning while playing, so that the child is not bored and learns knowledge better.
<
Zaitsev's Cubes
For more than twenty years, these cubes have been introducing children to letters and teaching how to form words and syllables. They allow you to understand how vowels and consonants, deaf and voiced sounds differ. There are 52 cubes in total, each of which depicts warehouses (combinations of a consonant and a vowel). The cubes vary in color and size, the large ones depict hard warehouses, while the small ones are soft. During classes, parents are encouraged to pronounce or sing warehouses so that the child remembers them better.
K Zaitsev's ubikiSource: moya-lyalyas.ru
Vyacheslav Voskobovich's "towers" and "folds"
windows. You can put cubes in them to make syllables. And from several towers you can make a word.
Voskobovich's "towers"Source: catalog-chess.
 ru
ru Skladushki is a book with pictures, educational rhymes and songs. Parents sing them and in parallel show the warehouses in the pictures. The author of the methodology claims that a child of six years old can be taught to read in a month using "folds".
A page from V. Voskobovich's "folds"
Doman's cards
This method of teaching a child to read is based on memorizing whole words, from simple to more complex. First, the child masters the first 15 cards, which the parent shows him for 1-2 seconds and pronounces the words on them. Then the child tries to memorize phrases. This technique helps not only to learn more words, but also develops memory well in general.
Doman cardsSource: friendly-life.ru/kartochki-domana-dlya-samyh-malenkih
Maria Montessori's method of teaching reading
The essence of the Montessori method is that the child is first asked to feel the writing of a letter, and then pronounce it. For this, didactic materials are used - cardboard plates with pasted letters, the outline of which the child traces with his finger, naming the sound. After studying consonants and vowels, you can move on to words and phrases. The Montessori method not only helps to learn to read, but also develops fine motor skills, logic, and the ability to analyze.
For this, didactic materials are used - cardboard plates with pasted letters, the outline of which the child traces with his finger, naming the sound. After studying consonants and vowels, you can move on to words and phrases. The Montessori method not only helps to learn to read, but also develops fine motor skills, logic, and the ability to analyze.
Source: hendmeid.guru
Olga Soboleva's technique
The author of this technique believes that you need to start learning not from the abstract alphabet, but immediately in practice - by analyzing simple texts. The Soboleva program allows you to teach a child to read from the age of five - at this age, children are already able to keep their attention on a line of text. Different approaches are offered depending on how it is easier for a child to perceive the world - by eye, by ear or by touch. In addition to reading skills, the technique develops interest in creativity, imagination, attention and memory.
How to teach a child to read by syllables
Teaching a child to read by syllables should be done in stages. First, explain to him that sounds are vowels and consonants, deaf and voiced. Say them with the child - he must understand how they differ. Letters and sounds can be learned while walking: draw your child's attention to the letters on signs and announcements, and soon he will learn to recognize them.
When the child has mastered the letters and sounds, start teaching him to read simple words - "mom", "dad". Then move on to more complex ones - “grandmother”, “dog”, “apartment”. Show your child that syllables can be sung.
Syllabary for learning to read
Next, move on to word formation. You can cut cards with syllables and invite the child to make words out of them. When he gets comfortable, move on to reading short texts. It is better to start with two or three phrases, and a little later switch to texts of five to ten sentences.
To enroll in Foxford Online Elementary School, a child must have at least basic reading, numeracy and writing skills. To check the readiness of the child for school, we offer to pass a small test that does not require special preparation.
Source: freepik.com
Exercises for learning to read
There are many exercises on the Internet that help children learn to read, you can print them out and start learning right away. Start with exercises that teach you to recognize letters and tell correct spellings from incorrect spellings.
From O. Zhukova's manual “Learning to read. Simple Exercises.Source: mishka-knizhka.ru
When the child gets used to the letters, move on to the exercises for syllables. For example, like this:
Geometric hint exercise. For greater clarity, blocks with words can be cut out.
Such exercises not only teach reading, but also develop logical thinking well:
Gradually move on to exercises where you need not only to read correctly, but also write words:
One of the most difficult and entertaining exercises is fillords: you need to find and cross out the words on the field of letters.
Games for learning to read
With the help of cubes or cards with letters and syllables, you can play different educational games with your child. Let's take a few examples.
Garages
Take a word of 3-4 syllables and place the cards in random order on the floor. Explain to the child how these syllables are read. These will be garages. Give the child different toys and offer to send them to the garage as you wish: for example, the car goes to the TA garage, the bear goes to the RA garage, the ball rolls to the KE garage, and so on. Make sure your child is positioning the toys correctly. At the end of the game, invite the child to make a word from garage syllables. Perhaps not the first time, but he will get a "ROCKET". Gradually introduce new syllables into the game.
<
Store
Lay out images of various goods on the table - this is a store, and you are a seller. Give your child a stack of cards with syllables - they will function as money. The child needs to buy all the items in the store, but each item is only sold for the syllable it starts with. For example, fish can only be bought for the syllable "RY", milk - for the syllable "MO", and so on. Give your child a few extra cards to make the task more difficult. When he gets used to it, change the conditions of the game: for example, sell goods not for the first, but for the last syllables. The game is both simple and complex: it will allow the child to understand that words are not always spelled the way they are pronounced. After all, a cow cannot be bought for the syllable "KA", for example.
The child needs to buy all the items in the store, but each item is only sold for the syllable it starts with. For example, fish can only be bought for the syllable "RY", milk - for the syllable "MO", and so on. Give your child a few extra cards to make the task more difficult. When he gets used to it, change the conditions of the game: for example, sell goods not for the first, but for the last syllables. The game is both simple and complex: it will allow the child to understand that words are not always spelled the way they are pronounced. After all, a cow cannot be bought for the syllable "KA", for example.
Lotto
Game for several people. Give the children several cards with syllables. Take out the cubes with syllables one by one from the box and announce them. Whoever has a card with such a syllable - he takes it. The first person to complete all the cards wins. During the game, children will accurately remember the syllables that they had on their hands.
Summary
Finally, a few more tips on how to teach a child to read:
- It is better to start teaching children to read by memorizing letters.
 It is important that the child can recognize and name them without hesitation.
It is important that the child can recognize and name them without hesitation. - In the early stages, pronounce the consonants as they are read in words: not [em], [el], [de], but [m], [l], [d] - this way it will be easier for the child to find his bearings.
- Sculpt letters from plasticine, draw and color, buy an alphabet with voice acting - use all the channels of the child's perception.
- Gradually build letters into syllables and then into words. Play rearranging letters and syllables, let the child experiment.
- Teach your child rhymes about the letters of the alphabet, look at the primer, use cards with letters and pictures. Thanks to the illustrations, the child will be able to memorize the symbols faster.
- Distribute the load: fifteen minutes a day is better than an hour twice a week. Alternate entertaining and serious tasks.
- You can hang signs with their names on objects in the child's room - the child will quickly learn to recognize them in texts.

- Read aloud regularly to your child and gradually introduce them to independent reading. Every evening, offer to read at least a few lines from a well-known book on your own.
- Lead by example. For a child to want to learn to read, he must regularly see you with a book.
We hope that our recommendations will help you teach your preschooler to read. Even if your child is just learning to read, at Foxford Elementary School he will be able to improve his skills.
At what age should a child be able to read
The ability to read is one of the basic human social skills. Without it, it is impossible to receive and transmit information, therefore this skill should be developed in every person. Modern parents strive to teach their child to read as early as possible, so that by the time they start learning, they already have some knowledge base. So when should a child start doing this?
Content:
- A Few Important Details
When We Begin
Experts disagree about teaching children to read early, and neither do parents. Someone thinks that a child should get basic reading skills even before entering school: this will make it easier to adapt to the educational process. Others are sure that a teacher in the 1st grade should teach a child to read, since an unnecessarily early start to school is harmful for children: let them enjoy their childhood for now.
Someone thinks that a child should get basic reading skills even before entering school: this will make it easier to adapt to the educational process. Others are sure that a teacher in the 1st grade should teach a child to read, since an unnecessarily early start to school is harmful for children: let them enjoy their childhood for now.
Learning too early - why it is harmful
The development of a child's cognitive abilities follows certain patterns, certain stages, it is undesirable to change or accelerate it, and often it is completely impossible. Until the age of five, children think figuratively - in pictures, and it is difficult for them to perceive information in the form of letters, numbers or other signs. And even having understood the general principle of reading, little students read, but they cannot understand the essence of what is written.
Learning to read early can lead to health problems:
- excessive brain tension;
- abnormal blood flow to the cerebral hemispheres;
- eye strain.

Intensive classes can unbalance the development of different types of thinking in a child: the emphasis will be on the logical, and the figurative will be “abandoned”. Yes, the child will become better at remembering, speaking, analyzing, thinking logically, but the development of the right hemisphere will be slowed down, and it is responsible for no less important dreams, emotions, understanding of music and color. The emotional development of the baby will be somewhat retarded, and at an older age this may respond with serious problems in the form of:
- lack of ability to empathize with others;
- difficulties with correct understanding of one's emotions;
- inability to determine one's strengths and weaknesses;
- difficulties in understanding one's own and social values;
- isolation and uncertainty.
It is known that many geeks are developed from early childhood, but most often, growing up, they do not have happiness and are poorly adapted to the realities of the world around them. Therefore, it is more important to raise a socially adapted person from a child than to teach him to read too early.
Therefore, it is more important to raise a socially adapted person from a child than to teach him to read too early.
What the experts say
Psychologists, psychophysiologists and other experts recommend starting to teach a preschooler to read not earlier than he is 5 years old, but at the same time he must be ready to learn. They say about it:
A healthy five-year-old child usually has all of these skills. And at this age it is time to get acquainted with letters and sounds, then by the time of admission to grade 1, the child will master reading at a sufficient level.
Is it possible to instill a love for reading
It is not enough to teach a child to read - he still needs to instill a love for this occupation. View your favorite books and read them, study the illustrations, get acquainted with the adventures of the characters. It is important that older family members show the child that reading is an amazing learning opportunity, and not a hateful duty. It will be useful if the child saw people with books in his close circle, then, imitating them, he himself will want to plunge into the world of literature.
The first reading lessons should be conducted in the format of a game: in this way the material will be absorbed by the child easier and better, the child will not have time to lose concentration during the lesson, and avoid stressful experiences.
Choosing a teaching method
Today there are many methods to teach a child to read, it is important to choose the one that suits your child.
Perhaps the most popular method is classes in the classical alphabet (the alphabet itself can be developed by any author). The kid quickly remembers the letter, as it will now be associated with a certain picture. Later, you can move on to another well-known book - the primer and study reading by syllables from it.
The kid quickly remembers the letter, as it will now be associated with a certain picture. Later, you can move on to another well-known book - the primer and study reading by syllables from it.
Many techniques are based on the use of cubes or tablets. They are convenient and interesting, but are often criticized by school teachers. It is believed that such training misses a very important component - basic familiarity with the alphabet.
The most famous of these techniques:
- Zaitsev's cubes - the emphasis is on making syllables from individual letters and words from syllables, understanding vowels, unvoiced and voiced, hard and soft consonants.
- Chaplygin cubes - training not only allows you to compose syllables and words, but also develops fine motor skills, and this will have a beneficial effect on the overall development of the child;
- Glenn Doman's cards - learning is based on the use of visual memory: syllables and words are printed on cards, and the child memorizes their spelling;
- "Skladushki" by Voskobovich - 21 cards with syllables, from which you can build houses with whole words.

The Montessori method is another well-known teaching option. Toddlers first master the letter, then move on to getting to know the letters, and then learn to read the syllables.
Are there any downsides to learning to read at home? In addition, at home, parents usually miss such an important part of the lesson as the sound analysis of the word, and the child may also have difficulty breaking down words into syllables. It is not easy to correct this mistake later, therefore it is better to immediately entrust a professional teacher to teach the child to read and write. It can be either a private tutor or a teacher of preparatory courses before the first grade - such classes are held today in literally every school.
A few important details
If you decide to teach your child to read at home, it is important to follow a few rules. All studies should be built on the principle “From simple to complex”, that is, you first need to learn letters and sounds, then you can start to compose them into syllables and only then move on to whole words.