Basic math concept
4 Crucial Basic Math Concepts
Search my site:
Your child's success in learning Math depends on mastering these five crucial concepts. They are essential for building a strong foundation in Math. They help your child understand and make sense of numbers and problem-solving; they strengthen his or her number sense.
The good news is that it is very easy to help your child understand these concepts. The key is to practice a few minutes several times a day. Make it a family affair so your child does not feel overly stressed. Your child or children will remember the lessons better if they had fun with it.
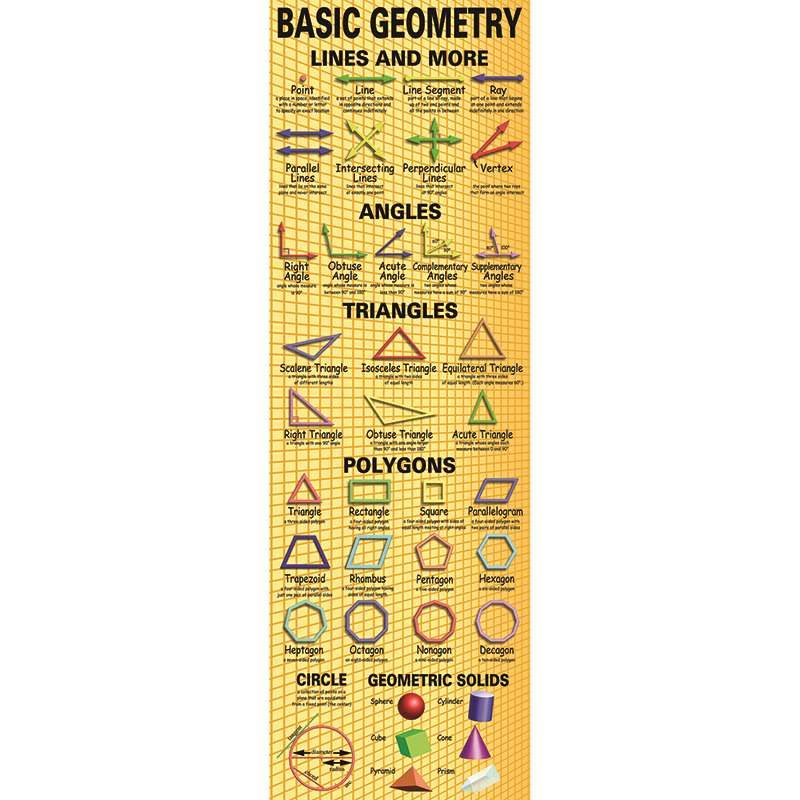
1. Understanding Numbers
The first concept your child must master is knowing how to read, write and understand numbers. Print out 2 sets of the number chart here. Use one set as a reference. Cut out the individual numbers from the second set.
Some ideas for you:
- read and write numbers
- recite a list of numbers forwards and backwards
- what number comes before or next
- arrange numbers in order (start with consecutive numbers)
- even and odd numbers
Print out this set of place numbers for older children.
2. More, Less or Equal
The next important concept in Math is to know how 2 numbers compare; whether one number is more, less or equal to another number.
Numbers represent quantity. Your child must first understand these types of questions.
- Amanda has 12 stickers. Benjamin has 9 stickers. Who has more stickers?
- Jack has 35 stamps. Alan has 19 stamps. Who has fewer stamps?
- Sam has 107 balloons. Jodie has 90 balloons. Who has more balloons? How many more?
- Charlie is 30-years-old. Mary is 17-years-old. Who is younger? How many years younger?
Followed by these types of questions:
- Rodney has $3 more than Janice. How much money does Rodney have if Janice has $26?
- I have 7 fewer pencils than books.
 How many books do I have if I have 20 pencils?
How many books do I have if I have 20 pencils? - John spent $11 less than Mark. How much did they spend altogether if Mark spent $15?
And these types of questions:
- 5 pencils cost the same as 2 books. Which is more expensive, the pen or the book?
- 6 apples cost the same as 10 oranges. What is the cost of 1 apple if 1 orange costs $0.60?
- Mary and James have the same amount of money. Mary spent half of her money. James spent one-third of his money. Who spent more money?
No matter how difficult the questions get, they can all be broken down into simple comparisons of more, less or equal.
3. Knowing Which Operation to Use
In Basic Maths there are actually only 4 operations your child needs to know: addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Here are some clues to help your child decide which of these to use. Print the following graphic for your child to use as a guide.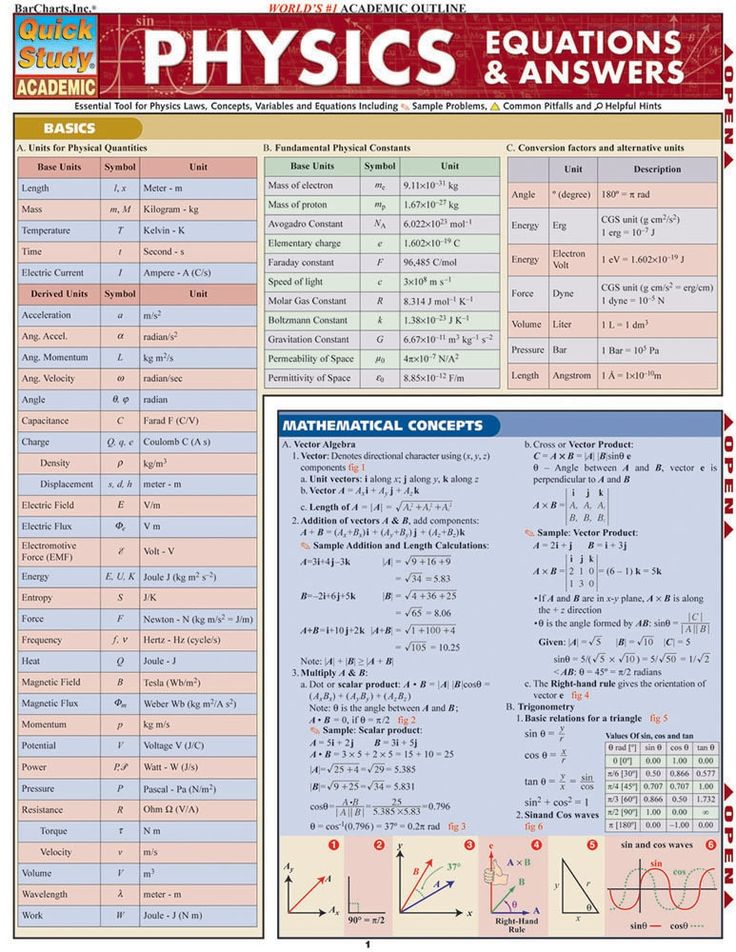
4. Different Ways to Get to the Answer
When it comes to Math, many children assume there is only one way or method to use to come up with the correct answer. If your child does not understand the teacher's method, he or she assumes that it is because he or she too stupid to understand.
You must help your child realize that there can be different ways of understanding a problem and different strategies can be used to find the answer. However, though the strategies may differ, the answer to the question must always be the same.
Play this family game: Write out simple word problems on cards. Read out a problem, then each person explains how he or she comes up with the answer.
Example
Mary has 9 sweets. She bought a few more sweets and now she has 13 sweets. How many sweets did Mary buy?
Some methods of solving:
- Say '9' then count '10, 11, 12, 13' on your fingers. Since you used 4 fingers to count, the answer is 4.
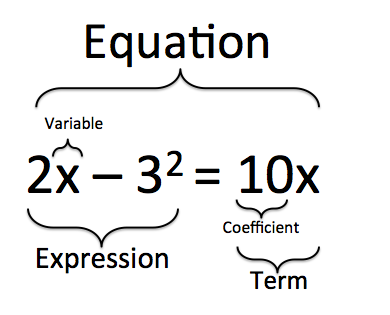
- Draw 9 circles in a row. Draw 13 circles in a second row below the first, making sure you line them up exactly. Compare the two rows and point out there are 4 extra circles in the second row. The answer is 4.
- Write the numbers 1 to 13 on a number line. Point out that after the number 9, there are 4 more numbers to reach the number 13. The answer is 4.
Play this game often and your child will become more flexible and logical in his or her thinking. He or she will automatically look for different ways to solve a hard problem. This will surely help in tackling complicated Math problems later on in school. Teach your child to ask "Is there another way of solving?" when he or she cannot understand one explanation.
This will help them realize that failure to understand does not mean they are cannot learn Math.
After your child has mastered this Math concept, introduce deliberate mistakes in your reasoning to see if your child can spot and correct them.
But do this only after your child has thoroughly understood the different strategies or you'll only end up confusing your child.
For older children, you can help them understand the properties of the different operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
Sometimes the order that these operations are used does not matter. Sometimes it does. Discuss the different strategies to find out when order matters, and when it doesn't.
Example
Max bought 3 boxes of pencils. Each box contains 12 pencils. He gave 5 pencils to his brother and 8 pencils to his sister. How many pencils does Max have left?
Methods of solving:
- To find the total number of pencils at first, you can multiple (3 x 12) or add (12 + 12 + 12).
- To find the number of pencils left, you can add first (5 + 8) and then subtract
(36 - 13). - Or you can subtract only (36 - 5 - 8).
I hope these strategies help your child excel in Maths. Share them with other parents whose children struggle with Maths.
Share them with other parents whose children struggle with Maths.
Basic Concepts in Mathematics | Sciencing
••• Rechenrahmen image by Yvonne Bogdanski from Fotolia.com
Updated April 24, 2017
By Erin Schreiner
Upon entering school, students begin to develop their basic math skills. Mathematics makes it possible for students to solve simple number based problems. Through the use of math, students can add up store purchases, determine necessary quantities of objects and calculate distances. While the discipline of math does become quite complex, there are some basic math skills that every student can and should learn during their math education program.
Number Sense
The first mathematics skill that students learn is basic number sense. Number sense is the order and value of numbers. Through the use of their number sense, students can recall that ten is more than five and that positive numbers indicate a greater value than their negative counterparts. Students commonly begin learning number sense skills in pre-school, and continue developing a more complex understanding of the concept throughout elementary school. Teachers introduce this skill to students by having them order digits and complete basic counting activities. They extend their knowledge by introducing the concept of the greater than and less than symbols and explaining what the use of each indicates.
Students commonly begin learning number sense skills in pre-school, and continue developing a more complex understanding of the concept throughout elementary school. Teachers introduce this skill to students by having them order digits and complete basic counting activities. They extend their knowledge by introducing the concept of the greater than and less than symbols and explaining what the use of each indicates.
Addition and Subtraction
The first mathematical operation that students learn is addition, followed closely by subtraction. Students begin studying these skills through the use of manipulatives, or physical tools that represent objects, as early as pre-school, and continue building their skills, adding and subtracting ever larger numbers through elementary school. When the skills are initially introduced, students perform rudimentary calculations using single digits. Later in their study, they practice applying these skills through the completion of story problems.
Multiplication and Division
After developing a complex understanding of addition and subtraction, students move on to studying multiplication and division. Depending on the student’s math achievement level, he may begin studying these operations as early as first grade. As with addition, students' study of these operations begins with single digit calculations. As they develop their multiplication and division skills, the problems become increasingly complex, involving larger numbers.
Decimals and Fractions
After students develop a strong understanding of number sense, they explore fractional numbers or numbers that lay between whole digits. Commonly this study begins in first grade with the exploration of basic fractions including ½ and ¼. After learning fractions, including how to add, subtract, divide and multiply non-whole numbers in fraction form, students study decimals. A strong understanding of fractions and decimals is vital, as students will use these non-whole numbers extensively as they continue their math study.
Related Articles
References
- NCTM: National Standards by Grade
- National Council for the Teachers of Mathematics: Math Skills
About the Author
Erin Schreiner is a freelance writer and teacher who holds a bachelor's degree from Bowling Green State University. She has been actively freelancing since 2008. Schreiner previously worked for a London-based freelance firm. Her work appears on eHow, Trails.com and RedEnvelope. She currently teaches writing to middle school students in Ohio and works on her writing craft regularly.
Photo Credits
Rechenrahmen image by Yvonne Bogdanski from Fotolia.com
| Catalog Book search Electronic applications Authorization Newsletter subscription Poems about us B wealth These difficulties have already turned into meanings. Feedback Send a message from the site Partners
|
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 24, 2013 N 2506-r approved the Concept for the Development of Mathematical Education in the Russian Federation. It is a system of views on the basic principles, goals, objectives and main directions for the development of mathematical education in the Russian Federation: Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation N 2506-r dated December 24, 2013 The Concept notes the role of mathematics in the modern world and in Russia. There are three groups of problems in the development of mathematics education:
The training received by the vast majority of students in the fields of mathematics and pedagogy does not contribute to either intellectual growth or the requirements of pedagogical activity in general education organizations. In the third section of the Concept, the objectives of the development of mathematical education in the Russian Federation are proclaimed:
The fourth section reflects the main directions of the development of mathematical education in basic and high school. In particular, it is said that mathematical education should:
Each student, regardless of location and living conditions, must be given the opportunity to achieve any level of training, taking into account his individual needs and abilities. The possibility of achieving the required level of mathematical education should be supported by the individualization of education, the use of e-learning and distance learning technologies. The possibility of achieving a high level of training should be ensured by the development of a system of specialized general educational organizations and specialized classes, a system of additional education for children in the field of mathematics, a system of mathematical competitions (olympiads, etc. At the same time, such new forms as receiving mathematical education in a distance form, interactive museums of mathematics, mathematical projects on Internet portals and social networks, professional mathematical Internet communities should develop. It is necessary to stimulate an individual approach and individual forms of work with lagging students, first of all, by attracting teachers with extensive experience. The implementation of this Concept will provide a new level of mathematical education, which will improve the teaching of other subjects and accelerate the development of not only mathematics, but also other sciences and technologies. This will allow Russia to achieve its strategic goal and take a leading position in world science, technology and economics. |
The Concept for the Development of Mathematical Education in the Russian Federation
1. Approve the attached Concept for the Development of Mathematics Education in the Russian Federation.
2. Within 3 months, the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation approves an action plan for the implementation of the Concept for the Development of Mathematical Education in the Russian Federation.
Chairman of the Government
of the Russian Federation
D. Medvedev
Note red.: the text of the order is published on the official Internet portal of legal information http://www.pravo.gov.ru, 27.12.2013.
The Concept for the Development of Mathematical Education in the Russian Federation
This Concept is a system of views on the basic principles, goals, objectives and main directions for the development of mathematical education in the Russian Federation.
I. The importance of mathematics in the modern world and in Russia
Mathematics occupies a special place in science, culture and public life, being one of the most important components of world scientific and technological progress. The study of mathematics plays a system-forming role in education, developing a person's cognitive abilities, including logical thinking, influencing the teaching of other disciplines. A high-quality mathematical education is necessary for everyone for his successful life in modern society. The success of our country in the 21st century, the efficiency of the use of natural resources, the development of the economy, the defense capability, the creation of modern technologies depend on the level of mathematical science, mathematical education and mathematical literacy of the entire population, on the effective use of modern mathematical methods. Without a high level of mathematical education, it is impossible to fulfill the task of creating an innovative economy, the implementation of long-term goals and objectives of the socio-economic development of the Russian Federation, and the modernization of 25 million high-performance jobs by 2020. Developed countries and countries that are currently making a technological breakthrough are investing significant resources in the development of mathematics and mathematical education.
The study of mathematics plays a system-forming role in education, developing a person's cognitive abilities, including logical thinking, influencing the teaching of other disciplines. A high-quality mathematical education is necessary for everyone for his successful life in modern society. The success of our country in the 21st century, the efficiency of the use of natural resources, the development of the economy, the defense capability, the creation of modern technologies depend on the level of mathematical science, mathematical education and mathematical literacy of the entire population, on the effective use of modern mathematical methods. Without a high level of mathematical education, it is impossible to fulfill the task of creating an innovative economy, the implementation of long-term goals and objectives of the socio-economic development of the Russian Federation, and the modernization of 25 million high-performance jobs by 2020. Developed countries and countries that are currently making a technological breakthrough are investing significant resources in the development of mathematics and mathematical education.
Russia has considerable experience in mathematics education and science, accumulated in 1950-1980. The accelerated development of mathematical education and science, providing a breakthrough in such capacious strategic areas as information technology, modeling in mechanical engineering, energy and economics, forecasting natural and man-made disasters, biomedicine, will help to improve the position and increase the prestige of Russia in the world. The system of mathematical education that has developed in Russia is a direct successor to the Soviet system. It is necessary to preserve its advantages and overcome serious shortcomings. Raising the level of mathematical education will make the life of Russians in modern society more fulfilling, and will provide the need for qualified specialists for science-intensive and high-tech production.
II. Problems of the development of mathematical education
In the process of social changes, the problems of the development of mathematical education and science have become more acute, which can be combined into the following main groups.
1. Problems of a motivational nature
Low educational motivation of schoolchildren and students is associated with public underestimation of the importance of mathematical education, overload of educational programs of general education, vocational education, as well as assessment and methodological materials with technical elements and outdated content, with the lack of curricula that meet the needs of students and the actual level of their training. All this leads to a discrepancy between the tasks of the intermediate and state final certification and the actual level of training of a significant part of students.
2. Content problems
The choice of the content of mathematical education at all levels of education continues to become outdated and remains formal and divorced from life, its continuity between levels of education is broken. The needs of future specialists in mathematical knowledge and methods are not sufficiently taken into account. The actual absence of differences in curricula, assessment and methodological materials, in the requirements of intermediate and state final certification for different groups of students leads to a low efficiency of the educational process, the substitution of training by "training" for an exam, ignoring the actual abilities and characteristics of students' preparation. Mathematical education in educational institutions of higher education is divorced from modern science and practice, its level is falling, which is due to the lack of a mechanism for timely updating the content of mathematical education, insufficient integration of Russian science into the world.
The actual absence of differences in curricula, assessment and methodological materials, in the requirements of intermediate and state final certification for different groups of students leads to a low efficiency of the educational process, the substitution of training by "training" for an exam, ignoring the actual abilities and characteristics of students' preparation. Mathematical education in educational institutions of higher education is divorced from modern science and practice, its level is falling, which is due to the lack of a mechanism for timely updating the content of mathematical education, insufficient integration of Russian science into the world.
3. Personnel problems
The Russian Federation lacks teachers and professors of higher educational institutions who can teach mathematics in a quality manner, taking into account, developing and shaping the educational and vital interests of various groups of students. The existing system of training, professional retraining and advanced training of pedagogical workers does not meet modern needs. Graduates of educational institutions of higher education with a pedagogical orientation, for the most part, do not meet the qualification requirements, professional standards, have little experience in teaching and experience in the application of pedagogical knowledge. The training received by the overwhelming majority of students in areas of mathematical and pedagogical specialties does not contribute to either intellectual growth or the requirements of pedagogical activity in general education organizations. Teachers of educational organizations of higher education, for the most part, are cut off both from modern areas of mathematical research, including applied ones, and from the applications of mathematics in scientific research and applied developments of their educational organization of higher education. The system of additional professional education for teachers is not effective enough and is often just formal in terms of improving mathematical education.
Graduates of educational institutions of higher education with a pedagogical orientation, for the most part, do not meet the qualification requirements, professional standards, have little experience in teaching and experience in the application of pedagogical knowledge. The training received by the overwhelming majority of students in areas of mathematical and pedagogical specialties does not contribute to either intellectual growth or the requirements of pedagogical activity in general education organizations. Teachers of educational organizations of higher education, for the most part, are cut off both from modern areas of mathematical research, including applied ones, and from the applications of mathematics in scientific research and applied developments of their educational organization of higher education. The system of additional professional education for teachers is not effective enough and is often just formal in terms of improving mathematical education.
III. Goals and objectives of the Concept
Goals and objectives of the Concept
The purpose of this Concept is to bring Russian mathematical education to a leading position in the world. Mathematics in Russia should become an advanced and attractive field of knowledge and activity, the acquisition of mathematical knowledge should be a conscious and internally motivated process.
The study and teaching of mathematics, on the one hand, ensure the readiness of students to apply mathematics in other areas, on the other hand, they have a system-forming function, significantly affect the intellectual readiness of schoolchildren and students for learning, as well as the content and teaching of other subjects.
The objectives of the development of mathematical education in the Russian Federation are: high achievements of science and practice;
ensuring that there are no gaps in basic knowledge for each student, forming among the participants of educational relations the attitude “there are no children incapable of mathematics”, ensuring confidence in an honest and adequate state final certification, providing teachers with diagnostic tools (including automated ones) and overcoming individual difficulties;
ensuring the availability of publicly available information resources necessary for the implementation of curricula of mathematical education, including in electronic format, tools for the activities of students and teachers, the use of modern technologies in the educational process;
Improving the quality of work of mathematics teachers (from pedagogical workers of general educational organizations to scientific and pedagogical workers of educational institutions of higher education), strengthening the mechanisms for their material and social support, providing them with the opportunity to refer to the best examples of Russian and world mathematical education, the achievements of pedagogical science and modern educational technologies, creation and implementation of their own pedagogical approaches and copyright programs;
support for leaders in mathematics education (organizations and individual teachers and scientists, as well as structures formed around leaders), identifying new active leaders;
providing highly motivated students with outstanding mathematical abilities with all the conditions for the development and application of these abilities;
popularization of mathematical knowledge and mathematical education.
IV. Main directions of implementation of the Concept
1. Preschool and primary general education
The system of curricula for mathematical education in preschool and primary education with the participation of the family must provide: child support) for pupils to master the forms of activity, primary mathematical concepts and images used in life;
in primary general education - a wide range of mathematical activity (classes) of students both in the classroom and in extracurricular activities (primarily solving logical and arithmetic problems, building algorithms in a visual and gaming environment), material, informational and personnel conditions for development students using mathematics.
2. Basic general and secondary general education
Mathematics education should:
provide each student with the opportunity to achieve the level of mathematical knowledge necessary for further successful life in society;
to provide each student with developing intellectual activity at an accessible level, using the beauty and fascination inherent in mathematics;
ensure the number of graduates necessary for the country, whose mathematical training is sufficient to continue their education in various areas and for practical activities, including teaching mathematics, mathematical research, work in the field of information technology, etc.
In basic general and secondary general education, training should be provided students in accordance with their requests for the level of training in the field of mathematical education.
Each student, regardless of location and living conditions, must be given the opportunity to achieve any level of training, taking into account his individual needs and abilities. The possibility of achieving the required level of mathematical education should be supported by the individualization of education, the use of e-learning and distance learning technologies. The possibility of achieving a high level of training should be ensured by the development of a system of specialized general education organizations and specialized classes, a system of additional education for children in the field of mathematics, a system of mathematical competitions (olympiads, etc.). Relevant programs can also be implemented by higher education organizations (including within the framework of existing and created specialized educational and scientific centers of universities, as well as network forms for the implementation of educational programs).
Achieving any of the levels of training should not prevent the individualization of education and close the possibility of continuing education at a higher level or changing the profile.
It is necessary to stimulate an individual approach and individual forms of work with lagging students, primarily involving teachers with extensive experience.
Improving the content of mathematics education should be ensured primarily through advanced training and additional professional education of teachers based on the leadership practices of mathematics education, formed in general education organizations.
3. Vocational education
The system of vocational education should provide the necessary level of mathematical training for the needs of mathematical science, economics, scientific and technological progress, security and medicine. To do this, it is necessary to develop modern programs, to include the main mathematical areas in the corresponding priority areas for the modernization and technological development of the Russian economy.
Mathematics, including information technology, students and their instructors should be involved in math research and projects. Teachers of mathematical faculties of classical universities need to conduct fundamental research recognized by the professional community, and their students should devote much more time than at present to solving creative educational and research problems. Teachers of mathematical departments of technical universities should conduct research in fundamental mathematics or in applied specialized areas, carry out work commissioned by organizations in which students also take part (similarly for economic and other educational organizations of higher education), teachers of mathematical departments of pedagogical universities should work with schoolchildren , participate in the development of certification materials, teaching aids for schoolchildren. Students (including those preparing to become teachers and educators in organizations engaged in educational activities) need to solve problems of elementary mathematics in their zone of proximal development, to a much greater extent than today, to practice at school, using this activity as a basis and motivating factor for obtaining psychological and pedagogical knowledge.
The interaction of the bodies exercising management in the field of education, educational organizations of higher education and general educational organizations should be focused on supporting the arrival of the best graduates of mathematical faculties of pedagogical educational organizations of higher education, graduates of specialized specialties of classical universities. It is necessary to provide the best graduates who studied under the programs of mathematical orientation of educational institutions of higher education and who have inclinations and abilities for pedagogical work with the opportunity to teach in an educational institution of higher education.
4. Additional professional education, training of scientific and pedagogical workers of educational organizations of higher education and scientific workers of scientific organizations, mathematics
Successful teachers should be provided with the possibility of their professional growth in the form of scientific and applied work, additional professional education , including internships in organizations - leaders in fundamental and applied research in the field of mathematics and mathematics education.
It is important to support world organizations in Russia that solve the problem of training researchers and teachers of the highest level, including the creation of world-class scientific and educational centers inviting scientists to conduct research and participate in the development of educational programs.
Higher education institutions and research centers should ensure the advanced level of fundamental and applied research in mathematics and its use in mathematics education. It is necessary to strengthen the integration of Russian mathematical research into world science, to ensure that the mathematical faculties of leading Russian universities achieve high positions in world rankings, as well as to increase the quality, quantity and citation of the works of Russian mathematicians, and the attractiveness of Russian mathematical education for the best foreign students and professors. The mobility of students, graduate students and young candidates of sciences should increase, cooperation between educational institutions of higher education and research institutes should be developed.
To solve the problems of this Concept, it is planned to finalize the system of labor assessment, taking into account the specifics of the activities and international practice of assessing the work of mathematics teachers, scientific and pedagogical workers of educational institutions of higher education and scientists of scientific organizations employed in the profile of mathematics.
Educational organizations of higher education and research centers should participate in the work on mathematical education and popularization of mathematical knowledge among the population of Russia.
5. Mathematical education and popularization of mathematics, additional education
For mathematical education and popularization of mathematics, it is planned to:
provide state support for the accessibility of mathematics for all age groups of the population;
creation of a public atmosphere of a positive attitude towards the achievements of mathematical science and work in this area, understanding the importance of mathematical education for the future of the country, the formation of pride in the achievements of Russian scientists;
providing continuous support and increasing the level of mathematical knowledge to meet the curiosity of a person, his general cultural needs, the acquisition of knowledge and skills used in everyday life and professional activities.
The system of additional education, including mathematical circles and competitions, is the most important part of the Russian tradition of mathematical education and should be provided with state support. At the same time, such new forms as obtaining mathematical education in a distance form, interactive museums of mathematics, mathematical projects on Internet portals and social networks, and professional mathematical Internet communities should be developed.
V. Implementation of the Concept
The implementation of this Concept will provide a new level of mathematical education, which will improve the teaching of other subjects and accelerate the development of not only mathematics, but also other sciences and technologies. This will allow Russia to achieve its strategic goal and take a leading position in world science, technology and economics.
The implementation of this Concept will contribute to the development and testing of mechanisms for the development of education applicable in other areas.


 It is said that “mathematics occupies a special place in science, culture and public life, being one of the most important components of world scientific and technological progress. The study of mathematics plays a system-forming role in education, developing a person's cognitive abilities, including logical thinking, influencing the teaching of other disciplines. A high-quality mathematical education is necessary for everyone for his successful life in modern society. Raising the level of mathematical education will make the life of Russians in modern society more fulfilling, and will provide the need for qualified specialists for science-intensive and high-tech production.”
It is said that “mathematics occupies a special place in science, culture and public life, being one of the most important components of world scientific and technological progress. The study of mathematics plays a system-forming role in education, developing a person's cognitive abilities, including logical thinking, influencing the teaching of other disciplines. A high-quality mathematical education is necessary for everyone for his successful life in modern society. Raising the level of mathematical education will make the life of Russians in modern society more fulfilling, and will provide the need for qualified specialists for science-intensive and high-tech production.”  All this leads to a discrepancy between the tasks of the intermediate and state final certification and the actual level of training of a significant part of students.
All this leads to a discrepancy between the tasks of the intermediate and state final certification and the actual level of training of a significant part of students. 
 ).
).