Basic shapes for kids
Teaching Basic Shapes to Kids In an Interesting Way
Table of Contents
| 1. | Introduction |
| 2. | Why is teaching shapes so important? |
| 3. | What are the different types of shapes for kids? |
| 4. | How to teach kids with the help of games and activities |
| 5. | Conclusion |
| 6. | About Cuemath |
| 7. | Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) |
| 8. | External References |
Introduction
Kids have dynamic learning capabilities that are enhanced by their observation skills. However, parents need to take tiny steps while teaching preschool kids. Basic shapes and colors impact children. They try to understand their surroundings by looking at the different objects around them. All kinds of objects and structures help kids in learning shapes. As a parent one should introduce different shapes for kids at an early age. There are various shapes activities for kindergarten that can help kids learn and understand basic shapes.
Shapes for Kids
Here is a downloadable PDF that lists out various shapes for kids. Teaching basic shapes for kids helps them understand their own observations. Different types of shapes for kids. Click on the download button to explore them.
Why is teaching shapes important?
Basic shapes for kids are being taught at every preschool today. It is important to understand the necessity of shaping activities for kindergarten kids. Few ways in which kids are impacted by basic shapes are:
- Visual Information
- Sign and symbols
- Alphabets and numbers
- Mathematical concepts
- Categorization and comparison
- Problem-solving
- Symmetry
- Kids Learn how to organize visual information
Children observe their surroundings very keenly and encounter different shapes every single day.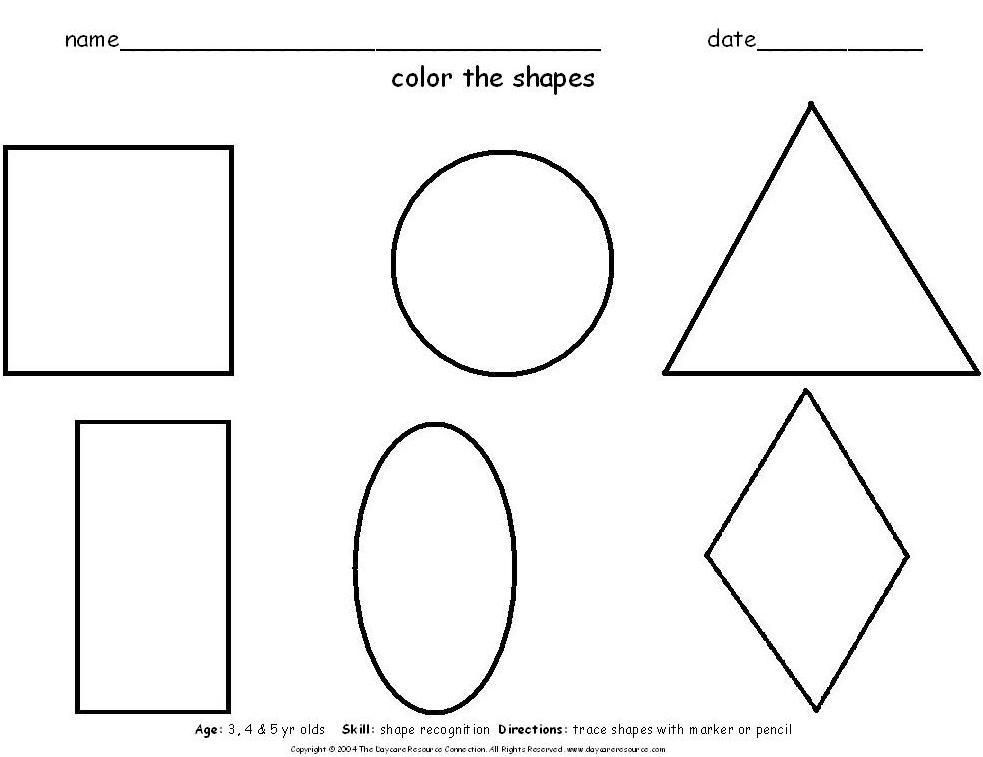 Teaching basic shapes for kids helps them understand their own observations. The visual information they gather comprises compound shapes that are formed by a combination of basic shapes. Shapes’ names for kids enable them to identify the basic shapes in compound shapes. For instance, when a child looks at a car it appears to be a rectangular box. However, children will learn to identify the compound shapes in a car once they learn basic shapes.
Teaching basic shapes for kids helps them understand their own observations. The visual information they gather comprises compound shapes that are formed by a combination of basic shapes. Shapes’ names for kids enable them to identify the basic shapes in compound shapes. For instance, when a child looks at a car it appears to be a rectangular box. However, children will learn to identify the compound shapes in a car once they learn basic shapes.
- Helps to teach signs and symbols
Symbols are very important for kids. But it will take some time for kids to get used to it. Kids take some time before they can actually name the shapes they see. However, this does not indicate that the kid is unable to comprehend basic shapes. Signs on the other hand impart certain information and details. Basic shapes for kids help them store information in their minds. Kids are usually 5 to 6 years old when they start following signs and symbols
.
- Help kids identify different alphabets and numbers
Toddlers may get confused among all the alphabets they see. As parents, it can be challenging to teach various letters and numbers. Kids tend to mix up similar-shaped letters like “b” and “d”. Patience is important while correcting these mistakes. Learning shapes for kids help them differentiate among the letters. Therefore all the preschools cover learning shapes for kids before moving into Alphabets and numbers.
- Basic mathematical concepts can be taught
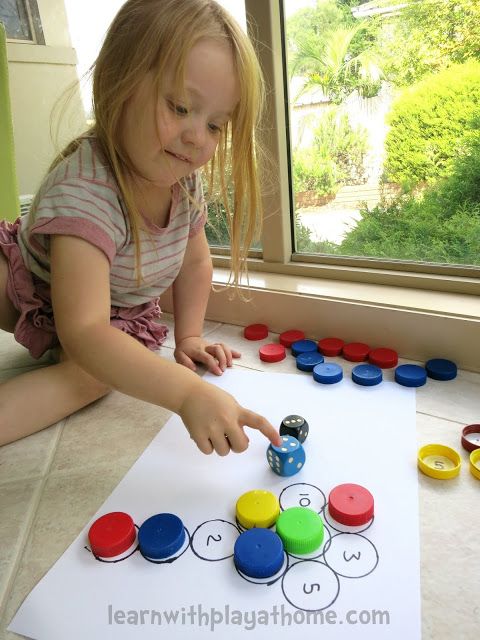
Once a child is comfortable identifying shapes for his /her own, they can start learning simple mathematical operations like addition and subtraction. It is always easier to teach addition than subtraction. Therefore we advise parents to start teaching addition and then venture into subtraction. Basic shapes for kids include balls, matchboxes, dice, etc. So you can pick the object of your choice and start teaching simple maths to your kids.
Basic shapes for kids include balls, matchboxes, dice, etc. So you can pick the object of your choice and start teaching simple maths to your kids.
- Categorization and comparison
Facial recognition and navigation skills are swiftly developed among kids who can categorize and compare various shapes. As kids learn to differentiate shapes, they understand facial features and their differences. It is also important to note that different shapes for kids imply different geographical locations or features. Have you noticed, in kids’ drawing- mountains and hills are always triangles and houses have a square or rectangle structure with a triangular roof? We do suggest you take a look and understand how kids observe and compare the shapes around them.
- Problem-solving
Brain development and thinking skills are really important for a kid in preschool or kindergarten. Shapes and colors are directly responsible for brain development. Kids analyze structures and start with 2-D mental mapping and then gradually, as the year progresses, they start 3-D mapping. These mental mapping of shapes plays a crucial role in the development of problem-solving abilities in children.
Shapes and colors are directly responsible for brain development. Kids analyze structures and start with 2-D mental mapping and then gradually, as the year progresses, they start 3-D mapping. These mental mapping of shapes plays a crucial role in the development of problem-solving abilities in children.
- Symmetry
Kids love to play around the parks or fields. This is important for the development of their motor skills. However, kids tend to lose their balance more often than adults. Growing up, we all had cuts and bruises on our knees Over the years these injuries started disappearing even when sports activities became more rigorous. This happens when kids are unable to understand the basic concept of balance and center of gravity. Now even though terms like the center of gravity feel fancy for kids, it is important to teach symmetry with the help of basic shapes for kids. This will help them understand how to position themselves and develop motor skills.
This will help them understand how to position themselves and develop motor skills.
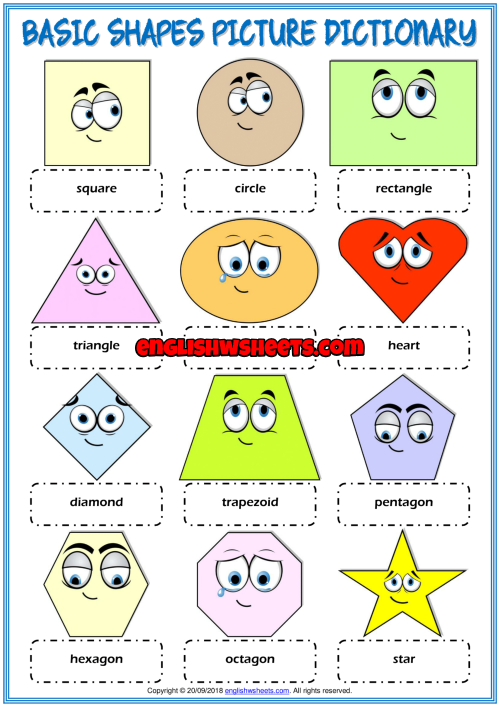
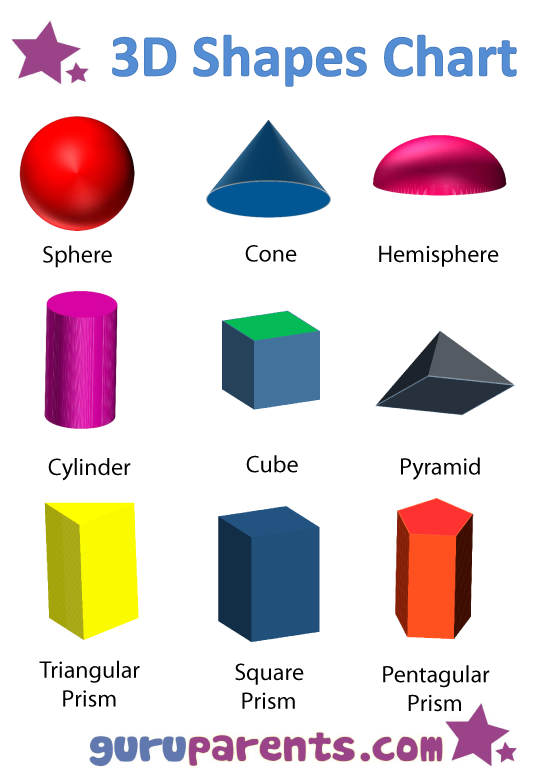
What are the different types of shapes for kids?
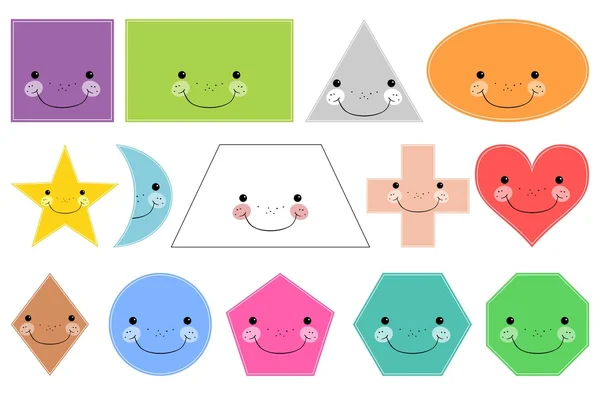
Different shapes for kids are available ranging from basic shapes to compound shapes. Basic shapes are simple shapes that can not be broken down into simpler shapes by general conventions, examples include square, circle, triangle, etc. Compound shapes can be split into simpler shapes, examples include Arrows, Starts, etc. Let us go through a few shapes to understand better.
|
Shape |
Image |
Number of Sides |
Example: |
|
Triangle |
3 Sides |
Mountains and Hills are Triangle in shape |
|
|
Square |
4 Sides |
Small houses or huts are square in shape |
|
|
Rectangle |
4 Sides |
Cars and buses are rectangle in shape |
|
|
Circle |
No Sides |
Wheels and Balls are circle in shape |
|
|
Arrow |
7 Sides |
Signs boards have an arrow shape |
|
|
Star |
10 Sides |
Starfish and star anise are star-shaped |
|
|
Diamond |
4 Sides |
Kites and crystals have diamond shape |
|
|
Heart |
No Sides |
Strawberries are heart-shaped. |
- Basic Shapes for kids
Shapes like squares, triangles, circles, and rectangles are taught first to kids. Once a child learns how to categorize and name these shapes, they are taught more complex shapes. However, it suggested that ample time is spent on basic shapes for kids. This is because all the shapes are taught at a later stage depending upon the concepts developed during learning basic shapes for kids. It may require a little while for kids to pick up the concept but we suggest parents be patient.
- Advanced Shapes for kids
Once a child is familiar with basic shapes he/she is ready to learn advanced shapes for kids. These shapes include arrows, stars, and hearts. Advanced shapes do not include 3-D structures in preschool as it may confuse them.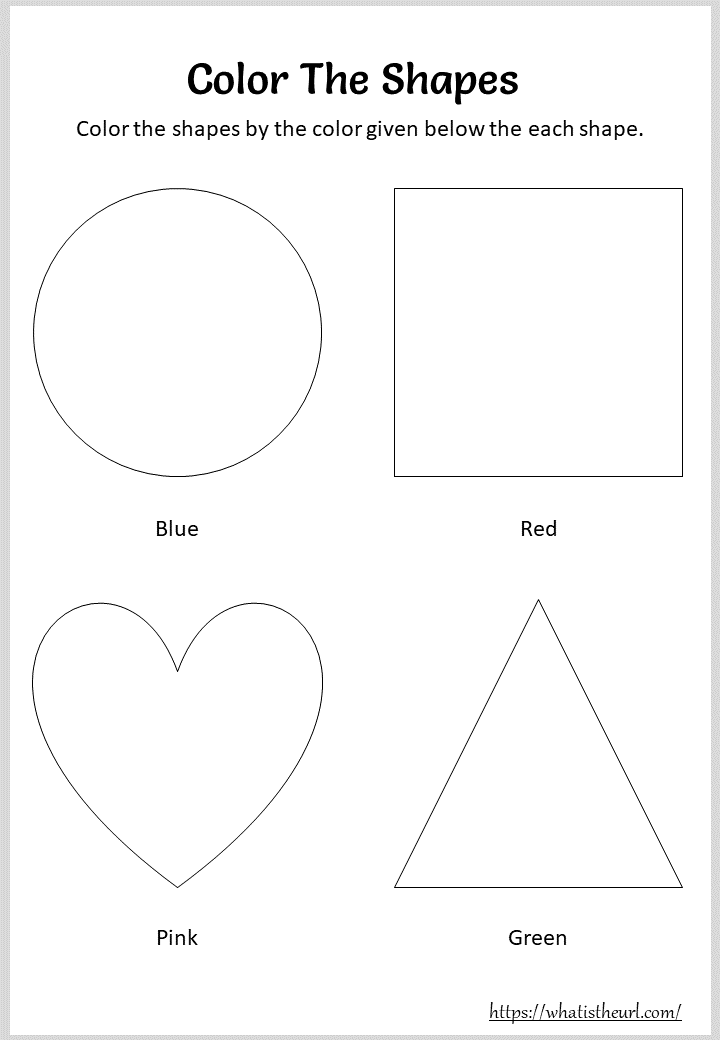 Kids with a clear conception of basic shapes will be able to ace this topic quickly.
Kids with a clear conception of basic shapes will be able to ace this topic quickly.
How to teach shapes to kids with the help of games and activities?
Till now, we saw how important basic shapes can be for a child's brain development. Teaching shapes can be cumbersome without activities as children find it difficult to comprehend something that can not be observed. Activities and games will help kids learn while having fun.
Now, we will look into a few activities and games to help your child play and learn.
- Flashcard shapes for kids
Flashcards are a really fun and interactive tool while teaching kids. They can be purchased in stores or prepared by hand. You can draw different shapes on cards made out of thick paper to prepare a set of flashcards. Use these cards to play with your child. Ask your kid to pick up a card and name the shape drawn on the card.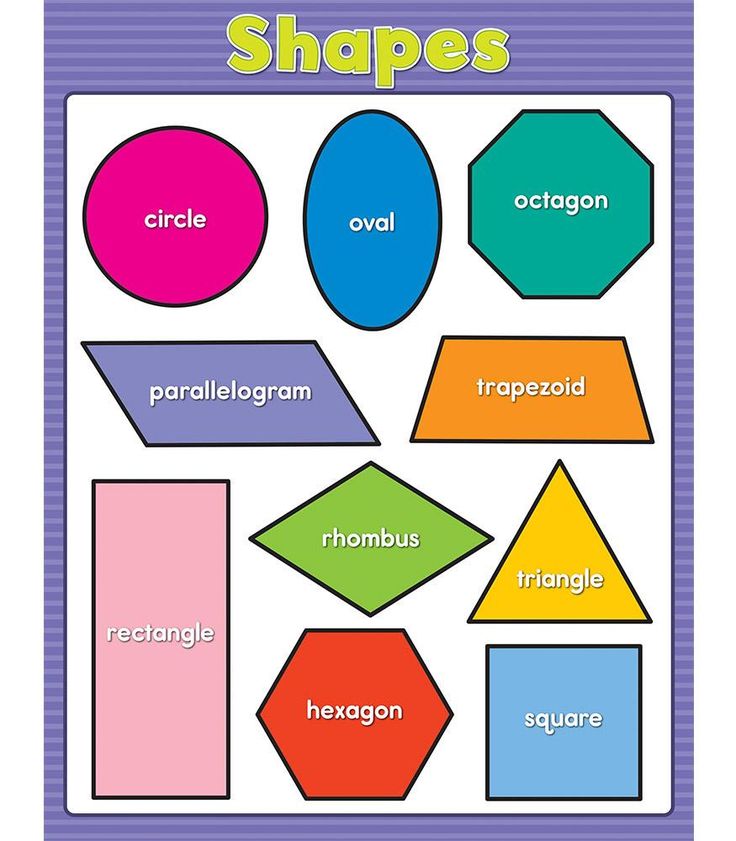 Maintain a scoreboard and let them beat their own high scores.
Maintain a scoreboard and let them beat their own high scores.
- Shapes for kids chart
Bright and colorful shape names for kid's charts are available in the market. To prepare them at home, you need to draw shapes and write down their names. Colorful shapes are easier to remember for kids. Ask your kids to look at the beautiful chart every day in the morning before going to preschool or kindergarten.
- Shapes hunt
Just like a treasure hunt, shapes hunting is fun and easy for preschoolers. Use a set of flashcards with different shapes on them. Ask your kid to pick up one card and identify the shape and once he or she has identified the shape, ask them to find an object of the same shape around the house. This will keep the kids engaged and help them relate basic shapes to their surroundings.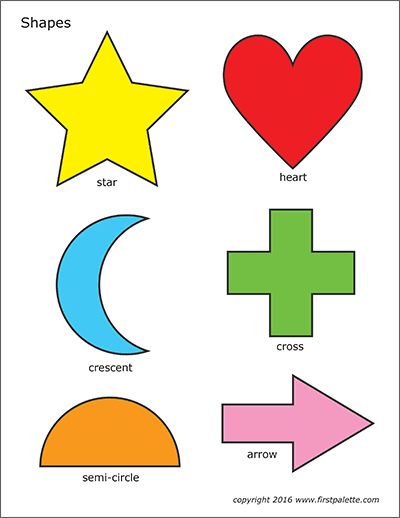
- Puzzle games
Two types of puzzles are available for kids to learn basic shapes. The first one contains pieces of brightly colored basic shapes for kids. These shapes need to be fitted onboard with hollows similar to the shapes. These boards with pieces of basic shape for kids are available in preschool supply shops and toy shops.
The second type is a conventional puzzle with bigger pieces. Once a child is proficient in basic shapes for kids they can try to join the pieces of a picture together.
We suggest you go for basic puzzles with pictures of fruits and flowers to keep the level easy for your child.
Conclusion
In the former section, we came across the various benefits of teaching basic shapes for kids. It is one of the most important topics covered in the kindergarten and preschool syllabus. Even though your child may be learning shapes for kids in school, it is suggested that parents help them out with shapes games for kids. This is because the identification of shapes and naming shapes are two different objectives. Kids tend to forget shape names.
Even though your child may be learning shapes for kids in school, it is suggested that parents help them out with shapes games for kids. This is because the identification of shapes and naming shapes are two different objectives. Kids tend to forget shape names.
Start teaching basic shapes to your child and try to relate them with the objects around you. This will help kids relate the concept of basic shapes with their surroundings. We suggest parents start with basic shapes and gradually move into advanced shapes. Spend more time on basic shapes for kids to build the foundation for advanced shapes.
About Cuemath
Cuemath, a student-friendly mathematics and coding platform, conducts regular Online Live Classes for academics and skill-development, and their Mental Math App, on both iOS and Android, is a one-stop solution for kids to develop multiple skills. Understand the Cuemath Fee structure and sign up for a free trial.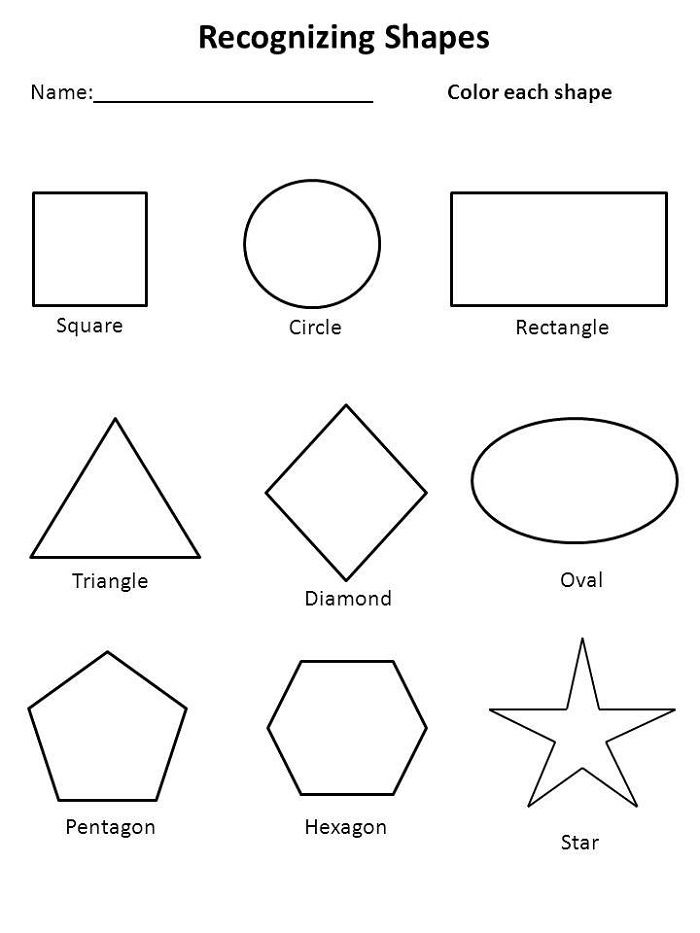
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between regular and irregular shapes?
- Regular Shapes are those which have equal sides as well as equal angles. Irregular Shapes are just the opposite,i.e, their angles and sides vary.
- Examples of Regular Shapes are Square, Circle, Equilateral Triangle, etc.
- Examples of Irregular Shapes are Rectangle, Heart, Right-angled triangle, etc.
- Cylinder - Circles
- Cuboid - Rectangles
- Cube - Squares
- Pyramid - Rectangles and Circles
- Tetrahedron - Triangles
- Geometric: These are simple shapes like rectangle, square, triangle, etc. which are geometric in nature.
 They form the basis of other types of shapes.
They form the basis of other types of shapes. - Organic: These shapes are curvier in nature and have a natural feel to them (for example, the shape made after the ink is spilled on a paper is of organic type). These are more soothing and relaxing to the eyes.
- Abstract: These shapes are complex in nature and are mostly used in graphics designing purposes. They are aesthetically beautiful but are not naturally found.
Why Teach Shapes? Why It Matters and Easy Learning Activities (Plus Printables!)
Why teach shapes? Learn why children need to learn shapes and the best activities to help. Plus printables!
Shapes are one of those things we work on with kids from a young age. We teach what a circle is, a triangle, a square. Colors, letters, numbers, shapes.
These are some of the first things we work on with children.
Colors are easy and fun to point out. Numbers and letters are building blocks for their entire future.
But why do we focus on shapes? Are they just easy?
There are actually some very concrete reasons for teaching toddlers and preschoolers shapes.
Here are 5 big reasons to teach preschoolers and toddlers shapes, plus some fun printables to color or use play-doh for sensory shape fun.
What's In This Post?
- Why Teach Shapes?
- Same or Different
- Categorization
- Problem Solving and Spatial Relations
- Math Skills
- Grab these printables for more shape practice!
- Letter Recognition
- Ways to Learn and Practice Shapes
- Just Talk
- Shape Hunts
- Shape Toys
- Coloring and Tracing
- Play-Doh Shapes
- Shape Sticks
- Shapes Everywhere
- I want the Freebies!
- Thank you!
- Bonus Shape Practice Printables
- Related
Why do we teach shapes to our children?
It isn’t just because it is easy. Shapes are building blocks for several bigger concepts that children will use throughout their schooling and lives.
Shapes are building blocks for several bigger concepts that children will use throughout their schooling and lives.
There are big reasons to start shape learning early. Here are some major concepts they work.
Same or DifferentBasic shapes like circles, triangles, and squares are distinctly different from each other. This makes them great for practicing same and different.
Same and different is the start of really recognizing distinctive traits objects can have. It is also the first level of categorizing.
Are these two objects the same or different? This is the start of basic observation skills.
CategorizationOnce the basic same or different concept is down, children can move into more complicated categorization.
What makes a circle different from a square? This is detailed recognition of traits objects have.
An important skill is being able to find a common characteristic among different items. A great way to practice this is to send your child on a shape hunt.
A great way to practice this is to send your child on a shape hunt.
How many circle objects can they find? How many squares? This shows them that shape is something that many different things can have in common.
Categorization is an important science skill.
Problem Solving and Spatial RelationsShapes are a great way to introduce problem-solving skills.
Take a shape sorter. Your child needs to determine which shape goes in which hole, and then they need to actually fit it in.
This works spatial relation skills as well. How do objects fit together? (As your children grow puzzles work the same sort of skill. How do you recognize what piece fits where?)
Anything that works problem-solving is helpful for children, and this sort of trait recognition is key for future science skills.
Math SkillsI feel math skills are an obvious area that gets worked when you teach your children shapes.
Geometry is in part the study of shapes. Having a basic understanding of them from a young age will make this math class a lot easier for kids.
Having a basic understanding of them from a young age will make this math class a lot easier for kids.
Understanding the characteristics of shapes involves a lot of counting. How many sides does a shape have? This easily folds in number practice when you play with your toddlers and preschoolers.
Pattern recognition comes into play as well. Every time you add a side you get a new shape, this is a pattern. Being able to physically see the difference between a shape with three sides and one with five helps with number sense, a key to all math success.
(Learn more about number sense and why it matters here.)
Grab these printables for more shape practice!
Letter Recognition
This is one of the biggest reasons to work on shapes early. Shapes help with letter recognition.
Think about letters, they are very similar to shapes. The letter V is a triangle missing a side, and the letter O is just a circle.
Understanding what shapes are and that they have meaning starts to build literacy. Practicing distinguishing between a square and a triangle help kids recognize between different letters.
The same is true for reading numerals. Having children draw shapes and working on the lines and angles needed to draw a triangle or rectangle helps them later in life when they are learning to write their letters.
Ways to Learn and Practice ShapesThere are lots of ways to practice shapes. One of my favorite things about this topic is that you can make it more and more challenging as your child learns more and more.
You start with circles, triangles, and squares. Then there are pentagons, hexagons, heptagons, octagons, and more. (This is a great lesson in prefixes too.)
Even with just 4 sides, there are a variety of shapes to work on. Square versus rectangle. Trapezoids, diamonds, parallelograms.
And don’t forget hearts, stars, crescents, and more. There is just so much depth to this simple subject.
There is just so much depth to this simple subject.
Here are some fun and easy ways to work on shapes with your children. Play is key with these.
Just TalkI think we try to make teaching our children too hard sometimes. The simplest way to work on shapes is just to talk about them.
My mother-in-law calls the toddler years the years of two names. Everything you share with your children has two names. For example, you don’t just hand your child a cup you hand them the blue cup. Or we play with the red ball.
Whatever it is, we can naturally add descriptors that are teaching our children. Use shapes the same way. You can read the square book or play with the triangle magnet. You don’t need big explanations, especially with very young toddlers.
Just start using the vocabulary.
Shape HuntsMy kids love going on scavenger hunts. It doesn’t matter what we are looking for, they adore it.
So send your kids on a shape hunt!
I have my children gather up anything that is triangle shaped, or circles. It is easier to focus on one shape at a time with toddlers. Preschoolers can look for more than one shape at a time, adding in sorting practice along with the shape practice.
It is easier to focus on one shape at a time with toddlers. Preschoolers can look for more than one shape at a time, adding in sorting practice along with the shape practice.
You don’t need anything special for this. Regular household items and kid toys come in all shapes. But if you want to make it more specific, try cutting shapes out of construction paper.
Low cost and easy cleanup.
Shape ToysShape sorters are a staple for a reason. You can find them in every price range. (In fact, Ali and Sammy’s favorite shape sorter came from Walgreens for about $5.)
These sorters practice shape recognition, problem-solving skills, and spatial relations, all in one little toy.
You can even make your own. Grab some blocks or other key shapes and trace them onto a shoebox or other box. Then cut the shapes out and let your children sort!
Coloring and TracingColoring books and shape workbooks are a wonderful way to work on shapes. Plus you get work on sitting still and focus skills.
Plus you get work on sitting still and focus skills.
Coloring is a childhood staple that is full of benefits. (Learn all about the benefits of coloring here!)
While your child is coloring, talk about the shapes on the page just as you would talk about the colors they are using. Tracing books provide additional writing practice that will come in handy when they are older.
Play-Doh Shapes
This is one of my favorite ways to work shapes. Sensory activities are stepping-stones for STEM skills in life, plus they help children really engage in what they are learning.
I created some shape printables for my children. You can laminate them and have your child fill the shapes in with Play-Doh. (Or slime, if you have a slime loving child.)
I don’t have a laminator, as much as I want one. So instead of that I purchased a few clear plastic sleeves used for binders and put the printables in those.
Easy to put together and easy to clean up. Head to the bottom of this post to learn how to get these for free to use with your children!
Head to the bottom of this post to learn how to get these for free to use with your children!
A great shape activity you can use as a busy bag activity is shape sticks!
Learn how to make them all here: Shape sticks for Preschool and Toddlers
The short version is to group sticks to make shapes and write the number of sticks needed on each group. So write 3 on three sticks for a triangle, etc. This is a great way to build independent play skills while practicing shapes!
Shapes EverywhereShapes are another one of those seemingly simple topics that have big implications for children. And adults.
Think of all the symbols and signs we can recognize just by the shape, even without words. Octagons are stop signs. An upside down triangle is a warning. Hearts mean love and stars are usually a good thing.
Shapes are such an important first step towards literacy and math skills. Things like shapes seem so simple and basic, yet they are teaching our children more than we can imagine.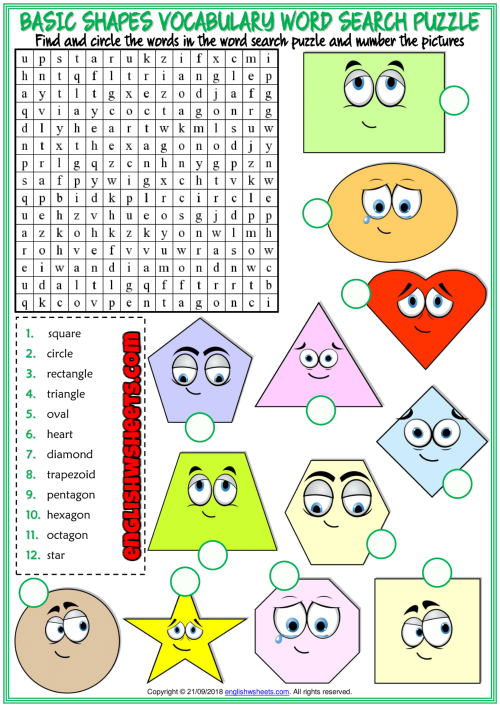
You can get these coloring pages and Play-Doh mats for your kids! These are available for download in my free printables section. You can gain access to all the free resources by signing up for the Team Cartwright mailing list. Once you sign up you will get an email with the printables password. This library contains all kinds of learning aids. The color by number pages, train learning activities, and my Lego coding worksheets. It also unlocks my twin tracking worksheets! Signing up also adds you to my email list, which you can, of course, unsubscribe from at any time.
I want the Freebies!
Sign me up to join the team! This gives me access to the free printables and adds me to the Team Cartwright mailing list.
Bonus Shape Practice Printables
Hands-on activities are amazing for learning about shapes. But worksheets can be helpful as well. These three free worksheets are great for shape practice.
But worksheets can be helpful as well. These three free worksheets are great for shape practice.
Your child can practice tracing the shapes and then draw them in with the dots. Finally, practice scissor skills while you cut and paste the pictures with the proper shape. Easy and fun! (And don’t forget to let them color their shapes too.)
Get the worksheets!
Find your next fun activity! Where would you like to start?
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Municipal budgetary preschool educational institution Kindergarten No. 16
Form of organization of education is a way of organizing education, which is carried out in a certain order and mode.
Forms differ:
- according to the number of participants;
- the nature of the interaction between them;
- ways of activity;
- venue.

Our kindergarten uses frontal, group, individual forms of organized education, development and training.
Individual form of organization of education allows individualization of education (content, methods, means), however, it requires a lot of nervous costs from the child; creates emotional discomfort; uneconomical training; limiting cooperation with other children.
Group form of organization of training (individual-collective). The group is divided into subgroups. The bases for a complete set: personal sympathy, common interests, but not on levels of development. At the same time, it is important for the teacher, first of all, to ensure the interaction of children in the process of development and learning.
Frontal form of organization of training . Work with the whole group, a clear schedule, a single content. At the same time, the content of learning in frontal classes can be activities: both cognitive and speech in nature, and artistically productive. The advantages of this form of education are a clear organizational structure, simple management, the possibility of interaction between children, the cost-effectiveness of education; The disadvantage is the difficulty in individualizing learning.
The advantages of this form of education are a clear organizational structure, simple management, the possibility of interaction between children, the cost-effectiveness of education; The disadvantage is the difficulty in individualizing learning.
The main form of organizing development and learning in our preschool educational institution is organized educational activities (OOE). Organized educational activities are organized and conducted by teachers in accordance with the main general educational program of the preschool educational institution and the recommendations of the Federal State Educational Standard. OOD are held with children of all age groups of the kindergarten. In the daily routine of each group, the time of the OOD is determined in accordance with the "Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the device, content and organization of the working hours of preschool educational organizations".
Organized educational activities are organized in all areas of educational work with children: familiarization with others, speech development, musical education, fine arts, design, the formation of elementary mathematical concepts, physical culture, etc.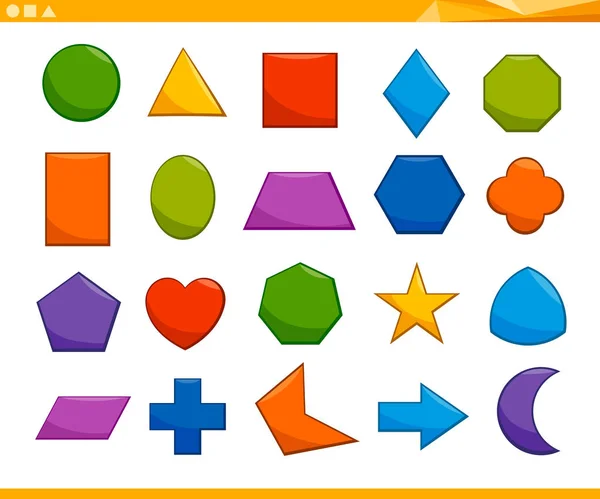
educational activities stand out three main parts.
First part - introducing children to the topic of the lesson, setting goals, explaining what children should do.
The second part of is the independent activity of children to fulfill the task of the teacher or the plan of the child himself.
The third part of - analysis of the performance of the task and its evaluation.
Requirements for organizing organized educational activities
Hygiene requirements:
- directly educational activities are carried out in a clean, ventilated, well-lit room;
- educator, constantly monitors the correct posture of the child;
- does not allow overwork of children in the classroom;
- provides for the alternation of various types of children's activities not only in different classes, but also throughout one lesson.
Didactic requirements:
- precise definition of the educational tasks of GCD, its place in the general system of educational activities;
- creative use of all didactic principles in unity when conducting GCD;
- determine the optimal content of GCD in accordance with the program and the level of training of children;
- choose the most rational methods and techniques of teaching, depending on the didactic goal of GCD;
- ensure the cognitive activity of children and the developmental nature of GCD, rationally correlate verbal, visual and practical methods with the purpose of the lesson;
- use didactic games for learning purposes (board-printed games, games with objects, plot-didactic and dramatization games, verbal and game techniques, didactic material;
- systematically monitor the quality of learning by children of cognitive material (knowledge, skills and abilities).
Organizational requirements
- have a well-thought-out plan for conducting GCD;
- clearly define the purpose and didactic tasks of GCD;
- competently select and rationally use various teaching aids, including TCO, ICT;
- to maintain the necessary discipline and organization of children during the GCD.
- conduct GCD in a playful way, because in the game, the child to a greater extent masters the ways of communication, masters human relations.
- GCD in a preschool educational institution should not be carried out according to school technologies, but should be organized as a planned GCD in the morning and evening in a playful way, in regime moments, in the play and creative activities of children.
- GCD should be carried out in a certain system, connected with the daily life of children (knowledge gained in the classroom is used in free activities.).
- When organizing the learning process, the integration of content is useful, which allows you to make the learning process meaningful, interesting for children and contributes to the effectiveness of development. To this end, integrated and comprehensive classes are conducted.
Home
Forms of education and upbringing of preschool children
The essence of education and upbringing of children of preschool age
Definition 1
Preschool age is the age period from 3 years before entering school (up to 7 years), during which there is a comprehensive development and formation of the child's personality.
In the period of preschool childhood, children actively develop analyzers, imagination, memory, speech, thinking, sensory knowledge of the world, the formation of a worldview and attitude to the surrounding reality.
The period of preschool childhood is a unique and important stage in the development of a child's personality. From what will be laid down in preschool age, it depends on how a person will grow up and become in the future.
That is why the processes of upbringing and education of preschool children are given such great importance. Despite the fact that training and education are implemented by different types of pedagogical activity, they are closely interconnected, and the effectiveness of the formation and development of a personality largely depends on their combined application. It is impossible to educate a worthy person, outside the process of education, just as it is impossible to get an educated person, outside the process of education. Only upbringing and education implemented in aggregate and unity are capable of forming an educated and educated member of society.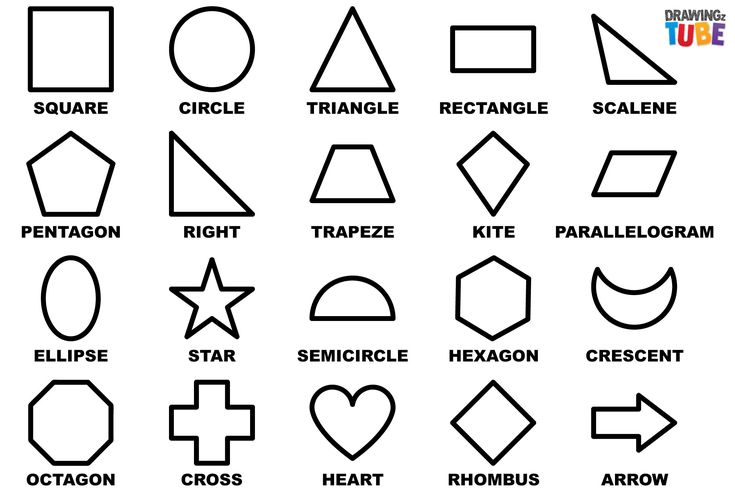
Education by its nature is carried out as a process of interpersonal communication between the educator and pupils. The learning process is the transfer of knowledge from the educator to the child within the framework of a specially organized training session. However, even during the educational process, the child receives not only educational influence, but also some knowledge. Just as during an organized training session, he receives not only knowledge, but also educational influence from the teacher.
Note 1
The effectiveness of education and training depends on the right methods and means, as well as on the form of organization of the pedagogical process.
Types of upbringing forms for preschool children
The form of upbringing, as part of the pedagogical process, depends on the goals, content and methods set, while at the same time determining their implementation in specific activities.
Proceeding from this, the forms of education largely depend on specific pedagogical situations, and therefore, they are very diverse, have a creative nature and are often individually unique.
Despite the uniqueness and individuality, it is customary to classify the forms of education of preschool children on a number of grounds.
Forms of education of preschoolers depending on the number of participants in the process:
- Individual - carried out in the form of conversations, individual lessons of one pupil with a teacher, etc.
- Group - represent the educational work of a teacher with a group of pupils, within the framework of a circle, a temporary group, etc.
- Mass - held in the form of holidays, rallies, processions, etc., in which several different age groups take part, the entire kindergarten or nearby preschool educational institutions.
Forms of education of preschool children depending on the main activity:
- forms of cognitive activity;
- forms of labor and socially useful activity;
- forms of aesthetic activity;
- physical culture and health-improving form of activity;
- value-oriented form of activity.
Forms of upbringing depending on the method of educational influence on the child (author NI Boldyrev):
Note 2
Thus, the forms of education of preschool children are subdivided depending on the method of educational influence, time and frequency, as well as on the number of participants.
Lesson as the main form of education for preschool children in preschool
Definition 2
Lesson is the main form of education for preschool children in preschool.
Classes in the kindergarten are organized in accordance with the Kindergarten Program and are conducted directly by the group teacher. Classes are held in all age groups of the preschool educational institution, the frequency of their conduct is set in accordance with the Federal State Educational Standard of DO and is prescribed in the daily routine of the group. Most classes are held in the morning.
Most classes are held in the morning.
At present, classes are held in kindergartens in the following areas:
- Acquaintance with the outside world.
- Development of speech.
- Musical education.
- Design.
- Fine arts.
- Formation of elementary mathematical representations.
- Physical culture.
Note 3
The teacher of the group draws up a schedule grid for the month, which shows how many and what classes will be held per week, their topic and purpose. The number of lessons depends on the age group.
Each lesson has three main parts:
-
First part – Introduction.
Content: introducing children to the topic of the upcoming lesson, defining the goals and objectives, explaining to the children the expected result.
-
The second part - Independent work of pupils.
Content: ten children perform tasks independently and with the help of an educator.
-
Third part – Analysis.
Content: the educator, together with the children, discuss the results obtained, give them an assessment. Reflection of the lesson.
Currently, kindergarten groups are staffed with children to the maximum. Sometimes the group is attended by 30-35 children. In this connection, the question arose of finding ways to improve the forms of education. The frontal form of the training session is increasingly showing shortcomings in conducting classes with a large number of children. The teacher is not physically able to "cover" all the children. Only a third of pupils work productively (the most active children of the group). Accordingly, the classes are formal and do not give the expected result. That is why more and more educators resort to dividing children into subgroups and the help of a junior educator. This form of organization of classes gives the necessary result in teaching children.