Basic sight words preschool
Dolch Word List
[Home] [Back] [Dolch Preschool] [Dolch Kindergarten] [Dolch Grade One] [Dolch Grade Two] [Dolch Grade Three]
© Contributed by Leanne Guenther
From 50-75% of all words used in school books, library books, newspapers, and magazines are in the Dolch Basic Sight Vocabulary of 220 words (preschool thru Grade 3). The Dolch word list is made up of "service words" (pronouns, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and verbs) which cannot be learned through the use of pictures.
In this section I've included a series of flashcards that can be printed and used to reinforce learning, the complete list of preschool words (see table) and some activity ideas for using the flashcards.
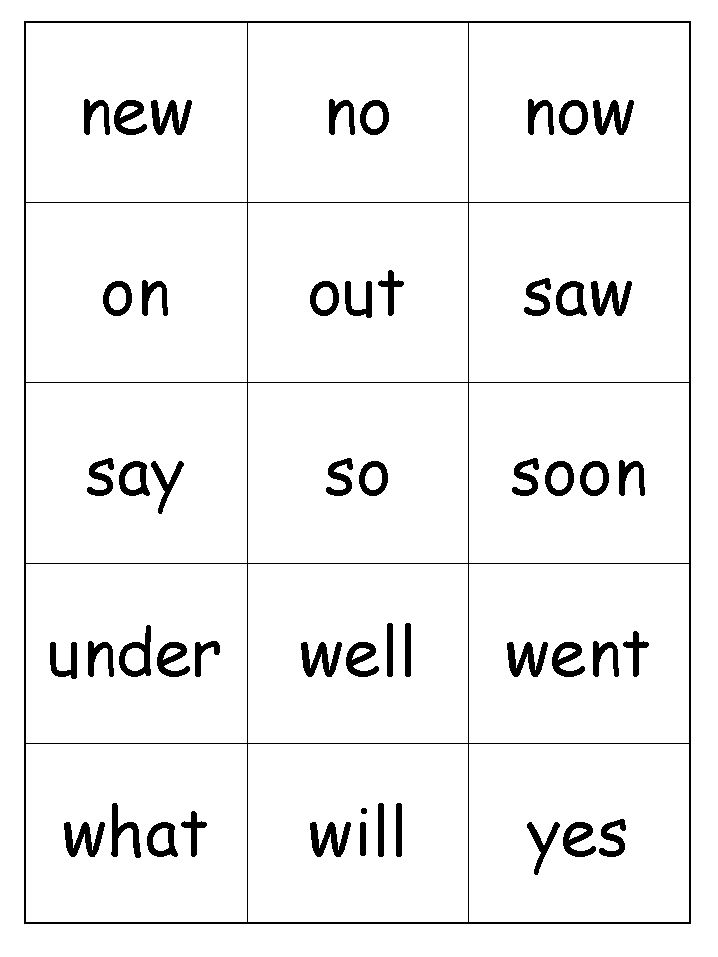
Set 1
Set 2
Set 3
Set 3 in color
Nouns 1
Nouns 2
Nouns 1 in color
Nouns 2 in color
Bingo Cards
Complete Preschool List
a |
and |
away |
big |
blue |
can |
come |
down |
find |
for |
funny |
go |
help |
here |
I |
in |
is |
it |
jump |
little |
look |
make |
me |
my |
not |
one |
play |
red |
run |
said |
see |
the |
three |
to |
two |
up |
we |
where |
yellow |
you |
Ideas for Using the Flashcards:
The flashcards can simply be held up, giving the child the opportunity to
read each one.
But if you're looking for a more engaging activity, try
combining the Dolch flashcards with the noun picture flashcards for a variety of
activities (I've listed some suggestions here from simplest to hardest)
- ACTIVITY ONE:
- have an adult arrange the flashcards to form a sentence.
- Read the sentence with/to the child
- Remove one of the dolch words from the sentence and put it back in the pile (you may want to make the pile smaller in the beginning to make the activity easier).
- Give the pile to the child and have them find the correct card to place back in the sentence.
- Re-read the sentence.
- ACTIVITY TWO:
- have an adult arrange the flashcards to form a sentence, leaving one card out.
- read the incomplete sentence with/to the child.
- present between 2 and 5 cards to the child (one of them should make the sentence complete)
- have the child chose which is the correct card
- re-read the sentence with the card chosen.
 Talk about whether it
makes sense or not.
Talk about whether it
makes sense or not.
- ACTIVITY THREE:
- provide the child with all or part of the pile of flashcards
- allow them to create their own sentences using the cards
- read the sentences with them and talk about what they've created.
- OPTIONAL: Have them glue their completed sentence to the bottom of a piece of construction paper and draw a picture of their sentence on the top. (author/illustrator of their own story).
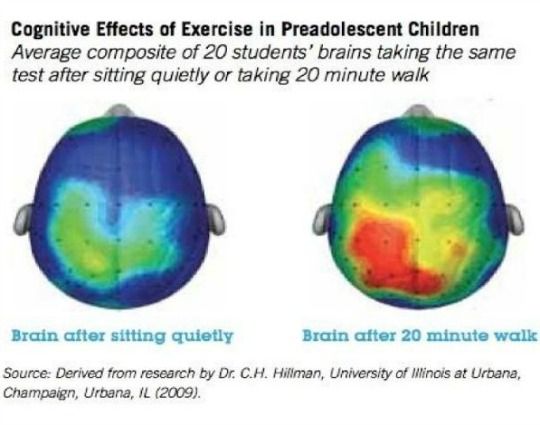
8 Easy Ways to Teach Sight Words to Preschoolers
Learning sight words is a critical skill for kids to learn how to read!
Teaching children how to learn sight words can be a challenge.
Why?
Because it all comes down to memorization. There is not a way to sound out these words. In case you are unfamiliar, sight words are words like that don’t follow the traditional rules of spelling or can’t be sounded out phonetically.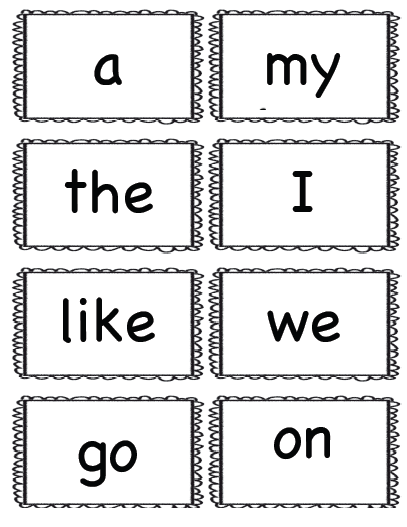 Some examples of sight words are who, does, and come.
Some examples of sight words are who, does, and come.
To give your preschooler a great jump start to reading, I have come up with 8 EASY ways that you can teach your preschooler sight words!
#1. Start With TWO Letter Sight Words
Does anyone have a toddler that says no to absolutely everything?
You’ll be hearing it all over again when you start teaching sight words because the word “no” is one of the easiest ones to recognize!
When you start out teaching a child sight words, it’s important to start small and build up to longer words. Starting with TWO letter words for them to memorize is going to be a lot easier than FOUR letter words.
Here are some two-letter sight words that you can start with: of, to, is, in, it, he, on, as, at, be, or, by, we, an, do, if, up, so, no, go
Once your little one has mastered the two-letter words, you can move onto three or more letter words!
While some of the words on this list can be sounded out and others can not, I think it’s easier to have your child just memorize the words so they can say it at a glance.
Here is a list of sight words for each age/grade level?
I use the above sight word checklist when I am deciding what new words to teach my daughter!
#2. Choose Sight Words In Your Child’s Favorite Books
I have a quiz for you.
How many sight words can you find in this sentence below from the book, Where the Wild Things Are?
“His mother called him “WILD THING!” and Max said “I’LL EAT YOU UP!” so he was sent to bed without eating anything.”
I found 12 sight words in that one sentence!
- (his, him, wild, and, said, eat, you, up, so, he, was, to)
Sight words are referred to as high-frequency words because some of them are the most common words in the English language!
When you are reading to a child, and they are starting to learn sight words, make sure to point out the words in their favorite books. They will be more interested in learning the sight words if it’s in a context they enjoy! We have a subscription to Highlights Magazine, and my daughter loves pointing out which words she recognizes.
They will be more interested in learning the sight words if it’s in a context they enjoy! We have a subscription to Highlights Magazine, and my daughter loves pointing out which words she recognizes.
Your kids will feel so proud when they can read a few words in their favorite stories. It will encourage them to want to learn more!
#3. Practice Daily
Just like teaching your kids the alphabet, numbers, and shapes, it takes repetition for them to understand the material!
At least a few minutes of work on sight words each day will help them immensely when it comes to memorizing sight words.
Here is what works best for my daughter:
I write the sight words that we have previously learned on a small dry erase board, which I limit to about 25 max.
Check Amazon's Price
We take some time and review those words plus add one or two new words depending on how well she does during the review.
Check out this short video of how I review the sight words with my daughter!
To ensure that she remembers the sight words we learned, I make sure to include ones that we learned in the past.
Tip#4: Make Reading Fun!
If I just focused on the above activity over and over again, I think I would struggle badly getting my kids to learn how to read.
It’s essential to come up with EXCITING ways to teach your kids how to read!
Here are FOUR ways to make learning sight words engaging!
Activity #1. Shaving Cream Sight Words
Shaving cream is such an amazing sensory activity! Your kids will be so excited to use shaving cream for a learning activity, it won’t even feel like they are learning!
I use men’s foaming shaving cream because I think it works the best! But other types can be used as well.
How to do this activity:
1. Spray foam shaving cream on an art tray.
2. Spread it out so the shaving cream is all over the tray!
3. Write a sight word that you are working on in the shaving cream and ask your child if they know what it is.
4. Repeat this process over and over again! Let your child erase the words so they get a chance to play in the shaving cream!
Activity #2. Do-A-Dot Painting Activity
Do-A-Dot painters are one of my MUST-HAVE supplies to have on hand at your house.
They are so much fun to play with and they are pretty much MESS FREE! Can’t beat that right?
Do-A-Dot markers can be used for so many fun and learning activities. This specific activity was great because it worked recognizing a specific sight word while getting to paint!
GRAB YOUR FREE Pre-K Sight Word Do-A-Dot WORKSHEETS HERE!
(Each grade level coming soon!)
Check Price - Amazon
Want to check out my other MUST-HAVE Supplies? Take a look at my list HERE!
Activity#3.
 Play Sight Word Games
Play Sight Word Games
My new thing is trying to turn games into a learning activity!
My kids love to play board games, so why not add a little bit of learning into the mix while getting to play?
How to do this activity:
1. Materials you need- Don’t Break the Ice Game, dot stickers, and a marker.
Check Amazon's Price
2. On white dot stickers, write some sight words that you are working on with your little one. I wrote one that my daughter already knew so she could play the game and be successful!
3. Explain to your kids that they have to tap lightly on the ice with the hammer instead of trying to hit it as hard as they can because a lot falls at once that way. Tell them they can play the regular way after you practice the sight words. 🙂
4. Ask them to find a specific word and tap on it with the hammer or they can tap on a word of their choice and tell you what it says!
5. After they say or find all the words, then you can play the normal way!
After they say or find all the words, then you can play the normal way!
Activity #4. FUN Worksheets
My daughter loves to color, so I created this Popsicle themed Color by Sight Word Worksheet for her to do.
Here are some excellent workbooks available on Amazon that have activities ready to go!
- 100 Write and Learn Sight Word Practice Pages
- Wipe Clean: Learning Sight Words
- The Best Sight Word Book Ever!
Don’t want to buy an entire workbook? I am constantly working on new FREE resources to make available for you.
Click here to grab your FREE Popsicle Color by Sight Word WORKSHEET!
Also, take a look at the other FREE RESOURCES that I have while you are there!
#5. Build Sentences with Sight Words
Building sentences using sight words is a GREAT way to show your child how the specific word is used in real life.
You can do this by verbally saying sentences or you can also do it in an interactive way.
We have a bunch of Thomas the Train, train tracks at home, so I thought it would be fun to work on sentence building with sight words with them!
How to do this activity:
1. Materials you need- Thomas the Train tracks, labels, and a marker.
View/ Check Amazons Price
2. On labels, write some sight words that make sense in a sentence that you kids know or you want them to learn!
3. Spread them all apart so they have to work on building the sentence so it makes sense. They will have to read each word then create the sentence!
#6. Add A New Word Each Day
Once your child can recognize words, you can start introducing at least one new sight word each day. In the beginning, you want to start slow.
Since sight words are based on memorization, that’s why learning one word a day is perfect for this age level.
While you should introduce one new word a day, remember to review past sight words that you practiced with them before. It’s crucial to go over these sight words so they won’t forget them.
Remember they are still preschoolers, repetition is key!
#7. Stay Positive!
You never want to rush the learning process.
Forcing preschoolers to sit and complete work when they are not ready may cause the child to think negatively about learning.
You want your child to be EXCITED to learn.
Don’t get frustrated if they don’t catch on right away or if it takes them a few days to master a word. It will happen with time, and they will feel successful if you encourage them!
There are times that my daughter can just not grasp on to a word.
For example, she had trouble memorizing the word “find. ” I asked her every day for TWO weeks about this word, and she still wasn’t getting it. I decided I was going to take a break and come back to it later. I introduced the word to her again after about a month, and now she has no problem with it!
” I asked her every day for TWO weeks about this word, and she still wasn’t getting it. I decided I was going to take a break and come back to it later. I introduced the word to her again after about a month, and now she has no problem with it!
As parents, we have to be patient with our children while they are learning.
We are supposed to be their biggest cheerleaders! Tell your child how proud you are when they learn a new word. They will feel your excitement and, in return, be more excited to keep on learning new material!
#8. Join An Online Learning Program
One great website that works on early reading skills is Kickstart Reading.
Kickstart Reading– This is such a fantastic reading program! I also have a promo code that you can use to get some money off of your subscription! You will receive a FOREVER plan for $39.00(normally $57.00). This is a program that focuses solely on reading, which I think is better than anything else out there. Your little ones will learn about phonetics, sight words, vowel sounds, digraphs and MORE!
This is a program that focuses solely on reading, which I think is better than anything else out there. Your little ones will learn about phonetics, sight words, vowel sounds, digraphs and MORE!
PROMO CODE: ABCDEE
Here is a short demonstration of just one of the segments included on Kickstart Reading. This is my 5-year-old daughter working on word blends.
Final Thoughts and Conclusion
Deciding when to start your preschooler’s journey into reading is a fun but challenging adventure!
It’s important to start slow, begin with two letter sight words, and stay positive with them! Try to mix up the activities that you do with them to learn sight words to keep them engaged and excited to learn!
I would love to help you on your journey to teaching your preschooler sight words. Whether you need some creative ideas or you need more helpful suggestions, please leave a comment below.
Whether you need some creative ideas or you need more helpful suggestions, please leave a comment below.
If you have any great ideas that you would like to share as well on what helped you teach sight words to a preschooler, please share them with us!
Preschool education in the modern perspective of perception — CEO Professional science
Abstract: the article discusses the content characteristics of the concept of "preschool education", presents a retrospective analysis of the relationship between preschool education, upbringing and training, describes modern conceptual and theoretical approaches on which the modern preschool education system
Abstract: In article discusses the substantive characteristics of the concept of preschool education, presents a retrospective analysis of the relationship of preschool education, education and training, describes the modern conceptual-theoretical approaches on which the modern system of education of children of preschool age
Keywords: pre-school education, education, education of preschool children, value of preschool age
Preschool education is a complex, multidimensional concept , which was considered in different directions as an autonomous system, a process result, etc. It is now generally recognized that the education of preschool children is the relationship and unity of education and upbringing, aimed at development - social and communicative, artistic and aesthetic, physical, speech, cognitive. The significance and value of any preschool educational organization, in this regard, is determined by how fully and effectively the versatile development of preschoolers is carried out, with optimal consideration of the very nature of childhood, its unique originality.
It is now generally recognized that the education of preschool children is the relationship and unity of education and upbringing, aimed at development - social and communicative, artistic and aesthetic, physical, speech, cognitive. The significance and value of any preschool educational organization, in this regard, is determined by how fully and effectively the versatile development of preschoolers is carried out, with optimal consideration of the very nature of childhood, its unique originality.
Preschool education aimed at the development of children should be built with a focus on the age values of preschoolers. This allows, firstly, to overcome the disagreements between the internal plan of the psyche of children and what is given as the content, means, forms of education of children; secondly, to determine the important forms of co-activity, co-creation, serving as a source of joint experiences, preserving the individuality of each subject of joint activity; thirdly, to design the educational process taking into account two types of children's activity: the child's own activity, completely determined by himself, his needs, desires, and the pedagogically determined activity of the child, stimulated by adults.
The nature of the manifestation of age values is largely related to the way of life of children. The child does not simply adapt to the present situation, but takes a certain internal position in relation to it. If we understand the process of education as a social situation of development, then age values are its basic foundations, on which the pedagogical interaction between an adult and a child unfolds.
The content basis of the concept of "values of preschool age" is the psychophysiological characteristics of children, which find practical reflection and their life meaning in the organization and implementation of the educational process, projective practical activities to create models of developing preschool education, as well as various manifestations of children's subculture - children's word creation, values, children's magic, etc.
Each age value of preschool childhood has its own significance in the development of the child's personal spheres, its own specifics of manifestation. Hence, their cumulative comprehension in educational work with children cannot bring an optimal developmental effect, it is also insignificant in terms of education as the end result of pedagogical activity. One of the ways to improve the efficiency of preschool education is to carry out the necessary research reflection of its organization in the aspect of scientific understanding of the role of each age value in the educational process of preschool organizations.
Hence, their cumulative comprehension in educational work with children cannot bring an optimal developmental effect, it is also insignificant in terms of education as the end result of pedagogical activity. One of the ways to improve the efficiency of preschool education is to carry out the necessary research reflection of its organization in the aspect of scientific understanding of the role of each age value in the educational process of preschool organizations.
An important age value of preschoolers is natural emotionality, emotions of preschoolers. Emotions color the whole life of a child: the process of cognition, attitudes towards the world around him, communication and interaction. Bright, rapidly growing emotional manifestations in time give special expressiveness to children's lives. Preschoolers are characterized by spontaneity, subservience to emotions and feelings. Zenkovsky V.V. wrote: "The power of moods, random, impatient, fast, puts the stamp of immediacy on all children's activity - in this sense, childhood can be called the golden time of emotional activity" [2].
And although psychological science provides answers to a number of fundamental questions for pedagogy (about the essence of emotions, age patterns of their development, about individual and typical in the emotional sphere), the lack of concepts that reveal the mechanisms of pedagogical control of the emotional sphere, the implementation of the educational process through the influence on the emotional the sphere of personality is the reason that in preschool educational organizations, they often do not find practical implementation of L.S. Vygotsky’s idea that one can not only think talentedly, but also feel and that only the unity of “affect and intellect” can provide a full-fledged, diverse children development. This is seen as an important perspective on the perception of the social significance of preschool organizations and the logic of their practical functioning.
An analysis of the historical aspects of preschool education up to the present time shows that the emotional life of children in many manifestations remains outside the framework of the pedagogical process. This is largely due to the fact that for many years in the education of preschoolers, important attention was paid to the formation of consciousness, the development of the cognitive sphere of children, methods of action (playing, practical, etc.), behavioral habits. To a large extent, it is also due to the weak scientific development of the theory of pedagogical control of emotions. An experimental study of the problem shows that children's emotions are perceived by teachers of preschool educational organizations as a secondary, background side of education. Practitioners do not have complete and holistic ideas about the directions, technologies for managing the emotional sphere of the child's personality, and there is no value attitude to this side of educational work. For persuasiveness, we will present the answers to some questions of the questionnaire, illustrating the legitimacy of the conclusions drawn. Questioning of 230 practitioners of preschool educational organizations showed that 59% — experience difficulties in planning work in the field of emotional development of children, managing the emotional sphere of preschoolers.
This is largely due to the fact that for many years in the education of preschoolers, important attention was paid to the formation of consciousness, the development of the cognitive sphere of children, methods of action (playing, practical, etc.), behavioral habits. To a large extent, it is also due to the weak scientific development of the theory of pedagogical control of emotions. An experimental study of the problem shows that children's emotions are perceived by teachers of preschool educational organizations as a secondary, background side of education. Practitioners do not have complete and holistic ideas about the directions, technologies for managing the emotional sphere of the child's personality, and there is no value attitude to this side of educational work. For persuasiveness, we will present the answers to some questions of the questionnaire, illustrating the legitimacy of the conclusions drawn. Questioning of 230 practitioners of preschool educational organizations showed that 59% — experience difficulties in planning work in the field of emotional development of children, managing the emotional sphere of preschoolers. Examples of answers: “We don’t plan such work on purpose”, “We fix the tasks in the field of emotional development in the plans when we describe surprise moments, work on the expressiveness of speech, staging theatrical games, etc.” 36% - identify emotional development with entertainment, leisure activities, as well as pedagogical simulation, including the use of surprise and competitive moments. Examples of answers: “It is necessary to develop the emotions of children through colorful exciting events: holidays, theatrical performances, etc.”, “For the development of emotions, it is necessary to use surprise moments, games”, “Emotional development of children is successfully carried out during team competitions”; 56% - associate emotional development with the emotional well-being of children in terms of the predominance of a calm, balanced, or joyful state; 62% found it difficult to identify the directions that are part of the process of emotional development of preschoolers. Typical answers were “I don't know”, “I'm not sure, so I won't answer this question”; 82% found it difficult to allocate funds, methods, forms of pedagogical work aimed at the emotional development of children.
Examples of answers: “We don’t plan such work on purpose”, “We fix the tasks in the field of emotional development in the plans when we describe surprise moments, work on the expressiveness of speech, staging theatrical games, etc.” 36% - identify emotional development with entertainment, leisure activities, as well as pedagogical simulation, including the use of surprise and competitive moments. Examples of answers: “It is necessary to develop the emotions of children through colorful exciting events: holidays, theatrical performances, etc.”, “For the development of emotions, it is necessary to use surprise moments, games”, “Emotional development of children is successfully carried out during team competitions”; 56% - associate emotional development with the emotional well-being of children in terms of the predominance of a calm, balanced, or joyful state; 62% found it difficult to identify the directions that are part of the process of emotional development of preschoolers. Typical answers were “I don't know”, “I'm not sure, so I won't answer this question”; 82% found it difficult to allocate funds, methods, forms of pedagogical work aimed at the emotional development of children.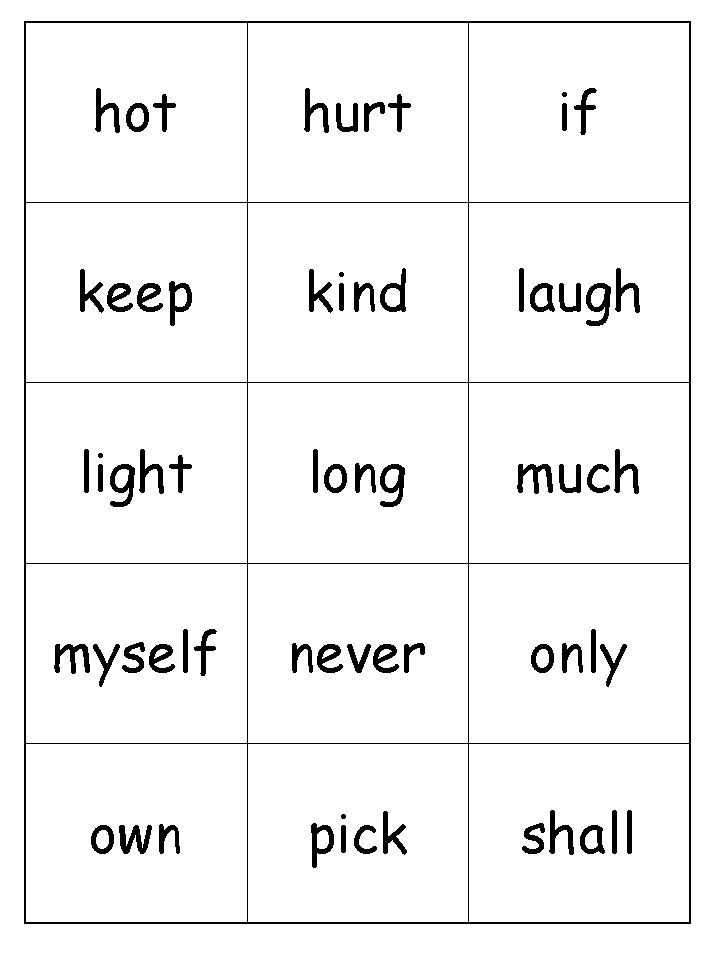 Examples of answers “The means of pedagogical work include works of art, didactic games. I find it difficult to single out the methods and forms of pedagogical work”, “I can’t single out special means, methods, forms of pedagogical work aimed at the emotional development of children.” The noted facts give grounds to say that the education of children with a focus on naturally given emotionality requires serious scientific analysis, including the improvement of the training of teachers in working with children in this direction.
Examples of answers “The means of pedagogical work include works of art, didactic games. I find it difficult to single out the methods and forms of pedagogical work”, “I can’t single out special means, methods, forms of pedagogical work aimed at the emotional development of children.” The noted facts give grounds to say that the education of children with a focus on naturally given emotionality requires serious scientific analysis, including the improvement of the training of teachers in working with children in this direction.
The implementation of an emotionally developing approach to the education of children involves timely and high-quality training of preschool workers. Such training should include the following areas: development of the ability to apply knowledge about the content, structure, methods of emotional development of preschoolers in the educational process of preschool organizations; development of the ability to professionally approach the choice and layout of methodological tools, methodological material, ensuring the success of the emotional development of children 3-7 years old in 4 directions: the development of emotional response, emotional expression, ideas about emotions and a dictionary of emotional vocabulary; enrichment with technologies of interaction with families in the direction of the emotional development of children aged 3-7 in order to ensure the unity of requirements for that side of the development of the child in the preschool organization and the family; development of the ability to identify levels of emotional development through the selection of diagnostic techniques and the conduct of a diagnostic examination of children.
Coordination of education with one of the main values of preschool age - the natural emotionality of children allows to achieve significant positive changes in the personal development of preschoolers, the nature of their self-realization in activities, and their attitude to the world around them as a whole. Orientation to the natural emotionality of children makes it possible to achieve qualitative changes in the functioning of preschool educational organizations, their target orientation and performance.
References
1. Vygotsky L.S., Pedagogical psychology. / Ed. V.V.Davydov. - M .: Pedagogy-Press, 1996. - 536 p.2. Zenkovsky, VV, Psychology of childhood. / V.V. Zenkovsky. - M.; Academy, 1996. - p. 40.
3. Ezhkova, N.S., Preschool education: scientific retrospective analysis and improvement prospects. /N.S.Ezhkova. //Pedagogy, 2015. - No. 7. - P.78-93.
4. Federal state educational standard for preschool education, approved by order of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation of October 17, 2013
Preschool education in Venezuela: history and current issues
Author : Romero De Pacheco Liliyan Alexandra
Heading : Pedagogy
Posted by in young scientist #9(113) May-1 2016
Publication date : 24. 04.2016 2016-04-24
04.2016 2016-04-24
Article viewed: 639 times
Download electronic version
Download Part 12 (pdf)
References:
Romero De Pacheco, Liliyan Alexandra. Pre-school education in Venezuela: history and contemporary problems / Lilian Alexandra Romero De Pacheco. - Text: direct // Young scientist. - 2016. - No. 9(113). - S. 1174-1176. — URL: https://moluch.ru/archive/113/29053/ (date of access: 31.10.2022).
The article considers and analyzes the system of preschool education in Venezuela. The features and directions of preschool education are highlighted. The main problems of the system of preschool education in Venezuela are determined. The characteristic of the main types of preschool institutions is given.
Keywords: pre-school education, education, study, kindergartens, nurseries, nursery-kindergartens.
Statement of the problem. Modernization of education in the countries of the world actualized the problem of early childhood, determined the need for scientific, theoretical and practical research of this age, contributing to the implementation of the ideas of early development in the work of preschool institutions. The development and scientific and methodological support of the development of the child during this period requires a thorough study of the content and organization of education for preschool children.
Research analysis. The existing problem encourages researchers to carry out a systematic analysis of preschool age (T. Ponimanskaya, Z. Plokhy and others), as well as to study the state and characteristics of preschool education in certain countries - Great Britain (L. Baeva and others), France (N. Sirotich and others), USA (L. Paramonova, K. Protasova, Maslov, N. Melnik and others), Japan (A. Nurutdinova and others), Germany (Z. Halo, I. Stashevskaya and others), Sweden (N. Karpenko and others), etc. Preschool education in each country forms its own special system, a component in the structure of which is the education and upbringing of young children [1].
Baeva and others), France (N. Sirotich and others), USA (L. Paramonova, K. Protasova, Maslov, N. Melnik and others), Japan (A. Nurutdinova and others), Germany (Z. Halo, I. Stashevskaya and others), Sweden (N. Karpenko and others), etc. Preschool education in each country forms its own special system, a component in the structure of which is the education and upbringing of young children [1].
To date, the specifics of preschool education in Venezuela have not been thoroughly studied, which determined the purpose of writing the article.
Purpose of the article. The purpose of this article is to study and analyze the system of preschool education in Venezuela, to determine the role of preschool childhood in the development of personality, as well as to analyze the current problems of preschool education.
Presentation of the main material. Preschool childhood is a period of intensive socialization of the individual, gaining life experience. A characteristic feature of this period is that during this period the overall development of the child is ensured. General development is due to changes in mental processes, their qualitative and structural transformations. The development achieved by a child at preschool age will serve as the basis for acquiring special knowledge, skills and abilities at the next age stage, the formation of stable personal qualities.
A characteristic feature of this period is that during this period the overall development of the child is ensured. General development is due to changes in mental processes, their qualitative and structural transformations. The development achieved by a child at preschool age will serve as the basis for acquiring special knowledge, skills and abilities at the next age stage, the formation of stable personal qualities.
One of the most pressing issues for Latin American countries is the development of public education. The need to solve this problem is dictated by the progress of science and technology, rapid social and political changes in the world.
The first schools in Venezuela were organized by missionaries in the 16th century, during the period of colonization by the Spaniards. The systematic development of public education began in 1821, after the liberation from the power of the Spaniards. In 1893, the first law on compulsory elementary education was passed. The organization of the first state preschool institutions belongs to 1920 year. The pre-school system for children aged 4–6 was introduced in Venezuela in 1956. According to statistics, in 1959 more than 20 thousand children were brought up in kindergartens, in 1967–33.8 thousand children [6, pp. 89–101].
The organization of the first state preschool institutions belongs to 1920 year. The pre-school system for children aged 4–6 was introduced in Venezuela in 1956. According to statistics, in 1959 more than 20 thousand children were brought up in kindergartens, in 1967–33.8 thousand children [6, pp. 89–101].
The basis of the modern system of public education is the Provisional Statute on Education, adopted on May 25, 1949 [15]. The legal framework, which serves as the basis for the education of preschool children, is contained in the “Constitution of the country”, the “Law on preschool education”, the “Law on the protection of minors” and the “Law on labor protection”. The general principles of preschool education (democratization, regionalization, creativity, flexibility and participation) are established by the current legislation in the field of planning, organization and functioning of the Venezuelan preschool system. In Venezuelan state documents, preschool education provides for formal and informal forms of education for children from birth to 6-7 years old, which can be carried out at home or in preschool educational institutions of various types and forms of ownership. As of 2015, there are 1,115 kindergartens in the country attended by 145.1 thousand children and employing 51 thousand teachers. Kindergarten services are used by 135,000 working mothers [15].
As of 2015, there are 1,115 kindergartens in the country attended by 145.1 thousand children and employing 51 thousand teachers. Kindergarten services are used by 135,000 working mothers [15].
The education of children in state-type kindergartens is free. In 1980, the "Restrictive Law on Education" came into force, confirming the principle of free education in all state educational institutions. However, not all children attend pre-school institutions (education in kindergartens is not compulsory). This is due to the difficult financial situation of many families, as well as the dispersion of the population in rural areas. However, if in the early 60s the annual increase in the number of students in state preschool institutions was 3.8%, in 1965, it reached 6.3%, then in 2015 - 32% [15].
There are also private (fee-paying) preschools in Venezuela. However, the share of the private sector in the system of preschool education is small, the number of such kindergartens does not exceed 2% of the total number of institutions for preschoolers. Foreigners mainly choose private institutions, because the level of education in them is still higher. Prices in paid kindergartens range from $300 to $800 per year. Until the age of 4, children can attend a nursery, after - a kindergarten. Many schools are combined with nursery gardens and you can distinguish in which group or class a child is studying by the color of the shirt. According to the unified Venezuelan law on education, which regulates the activities of educational institutions, children must wear the upper part of the clothing in a strictly matching color according to their stage position. So, children from 2 years old who go to a nursery wear yellow shirts. Kindergarten and elementary school (from 4 to 11 years old) - white shirt. Primary school education is compulsory for all children [13].
Foreigners mainly choose private institutions, because the level of education in them is still higher. Prices in paid kindergartens range from $300 to $800 per year. Until the age of 4, children can attend a nursery, after - a kindergarten. Many schools are combined with nursery gardens and you can distinguish in which group or class a child is studying by the color of the shirt. According to the unified Venezuelan law on education, which regulates the activities of educational institutions, children must wear the upper part of the clothing in a strictly matching color according to their stage position. So, children from 2 years old who go to a nursery wear yellow shirts. Kindergarten and elementary school (from 4 to 11 years old) - white shirt. Primary school education is compulsory for all children [13].
In Venezuela, as in other developing countries in Asia, Africa and Latin America, there is a growing perception that preschools are designed to prepare children for primary schooling. Even in the materials of the XIU Congress of OMEP (World Organization for Preschool Education), held in Caracas in 1974, it was emphasized that the practice of preschool education should be associated with the curriculum at school [9].
Even in the materials of the XIU Congress of OMEP (World Organization for Preschool Education), held in Caracas in 1974, it was emphasized that the practice of preschool education should be associated with the curriculum at school [9].
However, in Venezuela, as in a number of other Latin American countries, such educational standards are often absent, and the preparation of children for school comes down to teaching some particular knowledge or skills. Therefore, there is a special task of developing such programs. The main operating programs of preschool education are considered to be the following: formal (the main provisions are determined by the "Law on Preschool Education"), informal ("Family Program", "Child Care", etc.). Despite this, the peculiarity of the preschool system in Venezuela lies in the extreme variability of educational projects on which institutions work: international (“International Curriculum of Preschool Education” from 2 to 6 years, “Step by Step”, etc. ), national (state bills) and regional levels (which tailor national programs to the needs of a particular district). The development of a number of projects for preschool age indicates a special attention to this category of children [12].
), national (state bills) and regional levels (which tailor national programs to the needs of a particular district). The development of a number of projects for preschool age indicates a special attention to this category of children [12].
Preschool education in Venezuelan kindergartens is aimed at providing the child with the necessary knowledge, skills and abilities in play activities, as well as assistance in the development of individual abilities and inclinations, therefore, the mandatory content of education is not determined. In addition, the educational institution satisfies the needs of citizens of the corresponding territory in obtaining preschool education; creates safe and harmless conditions for the development, upbringing and education of children, working hours, conditions for physical development and health promotion in accordance with sanitary and hygienic requirements and ensures their observance; forms in children hygiene skills and the basics of a healthy lifestyle, the norms of safe behavior; contributes to the preservation and strengthening of health, mental, psychological and physical development of children; provides social and pedagogical patronage, interaction with the family; is a center for the dissemination of psychological, pedagogical and physiological knowledge about preschool children among parents; observes financial discipline, preserves the material and technical base; exercises other powers in accordance with the charter of the preschool educational institution
In Venezuela, public kindergartens have an average of 10–20 children per group. In one group, as a rule, an early childhood teacher, an educator, an assistant educator and a nanny work. It should be noted the good professional training of various preschool education specialists (early childhood teachers, nannies, educators, assistant educators) and their special attitude towards children, based on deep respect for the child's individuality. Teachers proceed from an understanding of the integrity of the development of the child, the relationship of all parties, and therefore the training is carried out comprehensively and has a thematic character. It is believed that the child's potential develops in favorable conditions, where the child's relationships with peers and adults play an important role.
In one group, as a rule, an early childhood teacher, an educator, an assistant educator and a nanny work. It should be noted the good professional training of various preschool education specialists (early childhood teachers, nannies, educators, assistant educators) and their special attitude towards children, based on deep respect for the child's individuality. Teachers proceed from an understanding of the integrity of the development of the child, the relationship of all parties, and therefore the training is carried out comprehensively and has a thematic character. It is believed that the child's potential develops in favorable conditions, where the child's relationships with peers and adults play an important role.
Teachers fully adhere to the wishes of the parents and do not make any decisions regarding the child without discussion with them. Parents have full information about the children's institution and the peculiarities of raising a child.
Thus, the system of pre-school education in Venezuela has developed less intensively over the years than the education system as a whole. This is due to many reasons: the attitude of the state and society to the education of preschoolers, the socio-economic situation in society, the traditions and culture of the Bolivarian Republic, climate, etc. [3]. However, today the main task of preschool education is clearly defined - socially organized support for the growth of each individual, his socio-cultural development.
This is due to many reasons: the attitude of the state and society to the education of preschoolers, the socio-economic situation in society, the traditions and culture of the Bolivarian Republic, climate, etc. [3]. However, today the main task of preschool education is clearly defined - socially organized support for the growth of each individual, his socio-cultural development.
Literature:
- Alferov Yu. S. Monitoring the development of education in the world // Pedagogy. - 2002. - No. 7.
- Belyaev V.P. Latin America: public education and problems of socio-economic development. - M., Nauka, 197I. — 228 p.
- Venezuela: Tendency of Economic and Socio-Political Development / ed. Yu. A. Zubritsky. - M., 1984. - 328 p.
- Galagan AI Financing education in developed foreign countries. - M., 2003.
- Dzhurinsky A. N. Development of education in the modern world. - M., 1999.
- History of preschool foreign pedagogy.
 Reader. Comp. N. B. Mchedlidze, A. A. Lebedenka, E. A. Grebenshchikova. - M., Enlightenment, 1974. - 464 p.
Reader. Comp. N. B. Mchedlidze, A. A. Lebedenka, E. A. Grebenshchikova. - M., Enlightenment, 1974. - 464 p. - Paramonova L. A., Protasova E. Yu. Preschool and primary education abroad: history and modernity. - M., 2001.
- Modern educational programs for preschool institutions / ed. T. I. Erofeeva. - M., 2000.
- Constitución de la Republica Bolivariana de Venezuela. Gaceta Oficial N° 5.453 Extraordinaria del 24 de Marzo del 2.000. Caracas. Venezuela.
- Leon, C. (1997) Factores protectores y desarrollo infantil integral. La ruta del papagayo. Año VI, Nº 25. Marzo 1997 pág. 4–5. CECODAP. Caracas. Venezuela.
- Gasso, A. (2004). La educación infantil. Ediciones Ceac: Barcelona.
- Preescolar Integral de Calidad (PIC) Linea Estratégica de la Educación Preescolar en Venezuela. Ministerio de Educación - Fundación Bernard van Leer. Caracas. 1997.
- Legislation [Electronic resource]. - Mode of access: www.
 loc.gov/law/help/guide/nations/venezuela.php.
loc.gov/law/help/guide/nations/venezuela.php. - Minvuz [Electronic resource]. - Mode of access: www.cnu.gov.ve.
- Politicas, programas y estrategias de la education Venezolana. — URL: http://www.oei.es/quipu/venezuela/Pol_Estrategias_Educ.pdfhttp://www.oei.es/quipu/venezuela/Pol_Estrategias_Educ.pdf
Basic terms (automatically generated) : preschool education, Venezuela, preschool age, child, preschool education, public education, elementary school, early childhood, garden, institution.
Keywords
preschool education, upbringing, nursery, studies, kindergartens, nursery-gardens. , nursery gardens
, nursery gardens preschool education, upbringing, study, kindergartens, nurseries, nursery-kindergartens.
Similar articles
Features
education children early ageearly age , kindergarten , child , educational work, early childhood , upbringing children , upbringing children , form of behavior, adult, parent.
Features
early development child . Advice point... Reduced enrollment of children pre-school education ; Pedagogical incompetence of parents in matters of education and development of children early age
Actual problems of modern
preschool education Undoubtedly, the period of pre-school education is an important step in the development of a child . It is in preschool age that children lay down all the main features of the personality, and the quality of his further physical and mental development is determined.
It is in preschool age that children lay down all the main features of the personality, and the quality of his further physical and mental development is determined.
Role
preschool education in life child | Article...Education is a very responsible process. It is doubly responsible when it comes to education preschool children and preschool education . Education as an influence on the formation of personal qualities actually comes from the first months of life children ...
Preschool pedagogy in the education system on a modern ...
Preschool Education , Child , Preschool Educational Institution , children age , preschool pedagogy. ..
..
Preschool education in Russia | Article in the collection...
Children Garden , Preschool Education , Children , Institution , Russia, Preschool 9000
Possibilities of implementing the ideas of Waldorf pedagogy...
Key words: Waldorf pedagogy, preschool age , pedagogical process, education preschoolers .
With regard to the preschool age Waldorf pedagogy is characterized by the recognition of the fact that childhood is a unique...
Short stay group "Mother and Child" as one of...
child Garden , Child , Parent, Early Age , Preschool Institution , Preschool 9000 .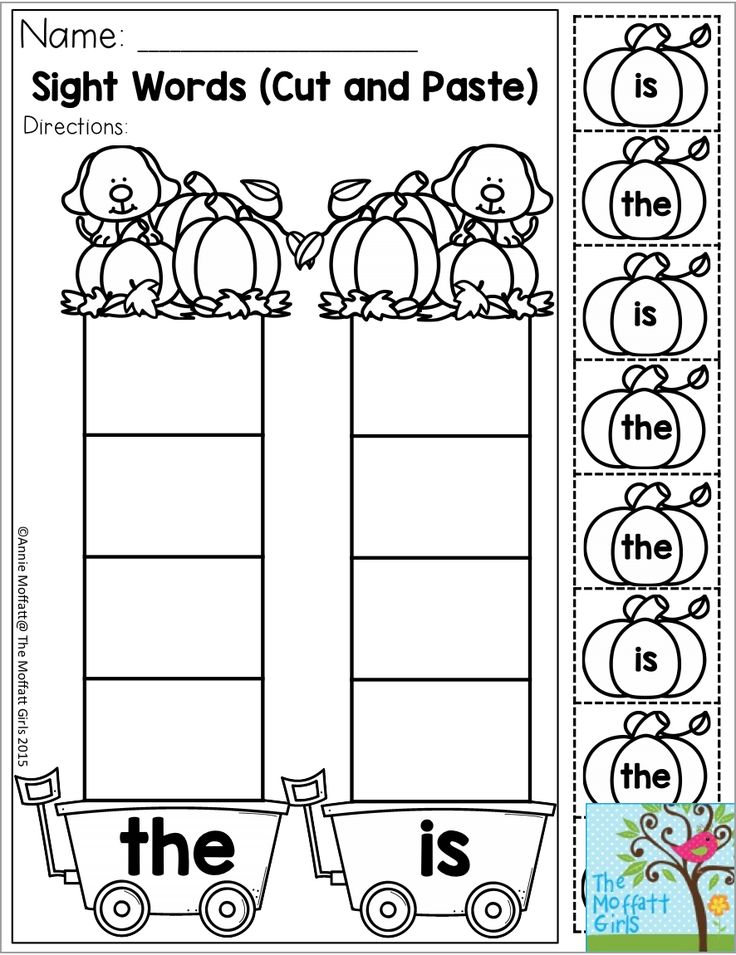
Scientific journal "Questions
preschool pedagogy"...Play technology in the environment education children preschool . Glukhikh I. A., Kazantseva E. V., Vasilyeva M. G., Islamova A. G.
Similar articles
Features
education children early ageearly age , kindergarten , child , educational work, early childhood , upbringing children , upbringing child , form of behavior, adult, parent.
Features
early development child . Advice point.. .
. Reduced enrollment of children pre-school education ; Pedagogical incompetence of parents in matters of upbringing and development of children early
Actual problems of modern
preschool educationUndoubtedly, the period of pre-school education is an important step in the development of a child . It is in preschool age that children lay down all the main features of the personality, and the quality of his further physical and mental development is determined.
The role of
preschool education in the life of children | Article... Education is a very responsible process. It is doubly responsible when it comes to education preschool children and preschool education . Education as an influence on the formation of personal qualities actually comes from the first months of life children ...
It is doubly responsible when it comes to education preschool children and preschool education . Education as an influence on the formation of personal qualities actually comes from the first months of life children ...
Preschool pedagogy in the education system on a modern ...
Preschool Education , Child , Preschool Educational Institution , children age , preschool pedagogy...
Preschool education in Russia | Article in the collection...
Children Garden , Preschool Education , Children , Institution , Russia, Preschool 9000
Possibilities of implementing the ideas of Waldorf pedagogy.



.png)