Concepts of print kindergarten
Concepts of Print in Preschool
posted by Vanessa Levin | filed under Literacy | affiliate disclosure
Developing concepts of print is an important part of the emergent literacy process. The best thing about teaching concepts of print to young children is that you don’t need any extra tools or supplies, you just need books!
What Are Concepts of Print?
The basic understandings of how books and print work are referred to as concepts of print.
These print concepts include:
- Letters and words hold meaning
- Print is what we read
- Illustrations correspond to the print
- We read from left to right
- We read from top to bottom
- Return sweep – when we get to the end of a line on a page we return to the next line and begin reading on the left again
- Books have a front, back, and an author
- Difference between a letter and a word
- Spaces between words
- Where to start reading
- One-to-One Correspondence – Print matches spoken words
- Punctuation
Why Are Print Concepts Important?
Before children can begin to read, they must understand how books and print work. Considered precursors to reading and writing, concepts of print are crucial for future reading success.
How Do Children Develop Concepts of Print?
Young children may begin to develop concepts of print at a very young age. How quickly young children learn concepts of print is directly related to how often they are read to.
The best way to teach young children about concepts of print is to invite them to explore books, writing, and drawing as often as possible.
10 Ways to Develop Concepts of Print
1. Point to the words in books as you read-aloud to develop one-to-one correspondence between spoken and written words.
2. Point out words, spaces, letters, lines of print, left to right, top to bottom, direction of print during your morning message.
3. Use environmental print to make references to words, spaces, letters and lines of print.
4. Have children suggest where the teacher should begin reading the words on the page of a big book.
5. Count the words in a line of print or clap for each word spoken aloud can help develop concept of a word.
How to Teach Concepts of Print
6. Use student name cards and classroom labels to help children recognize words that are most meaningful to them.
7. Use a variety of hands-on activities to develop an awareness of letters, e.g., play with letter cars, magnetic letters, plastic letters and alphabet games.
8. Display an alphabet chart at children’s eye level and refer to it daily.
9. Provide both upper and lowercase magnetic letters of the alphabet for children to use daily.
10. Invite each child to dictate a sentence. Write each child’s sentence on a sentence strip twice. Cut one sentence into individual words and encourage children to match words to the second sentence strip, specifically using “first word,” “last word.”
Teaching Trailblazers
Teaching concepts of print is important, but it’s only one small piece of the literacy puzzle. If you really want to bring your A game, the best place to learn current best teaching practices and get the support you need is in the Teaching Trailblazers. We have many printable lessons and on-demand video trainings to help you become the best teacher you can be! If you want to get on the waiting list for the Teaching Trailblazers, do it soon so you don’t miss the next open enrollment period!
If you really want to bring your A game, the best place to learn current best teaching practices and get the support you need is in the Teaching Trailblazers. We have many printable lessons and on-demand video trainings to help you become the best teacher you can be! If you want to get on the waiting list for the Teaching Trailblazers, do it soon so you don’t miss the next open enrollment period!
More Literacy Ideas
About Vanessa Levin
Welcome to Pre-K Pages! I'm Vanessa, a Pre-K teacher with more than 20 years of classroom experience.
You spend hours of your precious time each week creating amazing lesson plans with engaging themes and activities your kids will love.
You're a dedicated teacher who is committed to making learning FUN for your students while supporting their individual levels of growth and development.
I'm committed to helping teachers just like you teach better, save time, and live more by providing you with everything you need to create a fun and engaging learning environment, lesson plans, and activities for your little learners.
Are you ready to get started with teaching better, saving time, and living more? More than 75,000 teachers receive my exclusive teaching tips in their inbox each week, add your name to the list here!
Filed Under: Literacy Tagged With: Literacy, reading
Are you ready to teach smarter, save time, and get your life back?
Join 150,000+ teachers who receive my FREE weekly teaching tips; and I’ll send you a copy of my eBook 7 Circle Time Mistakes as a gift.
Privacy Policy
Concepts of Print Assessment | Reading Rockets
By: Reading Rockets
An informal assessment of the concepts of print, including what the assessment measures, when is should be assessed, examples of questions, and the age or grade at which the assessment should be mastered.
All assessments should be given one-on-one.
What it measures
If a student understands:
- That print has meaning
- That print can be used for different purposes
- The relationship between print and speech
- There is a difference between letters and words
- That words are separated by spaces
- There is a difference between words and sentences
- That there are (punctuation) marks that signal the end of a sentence
- That books have parts such as a front and back cover, title page, and spine
- That stories have a beginning, middle, and end
- That text is read from left to right and from top to bottom
When should it be assessed?
Assess concepts of print twice during kindergarten, at the start of school and at mid-year.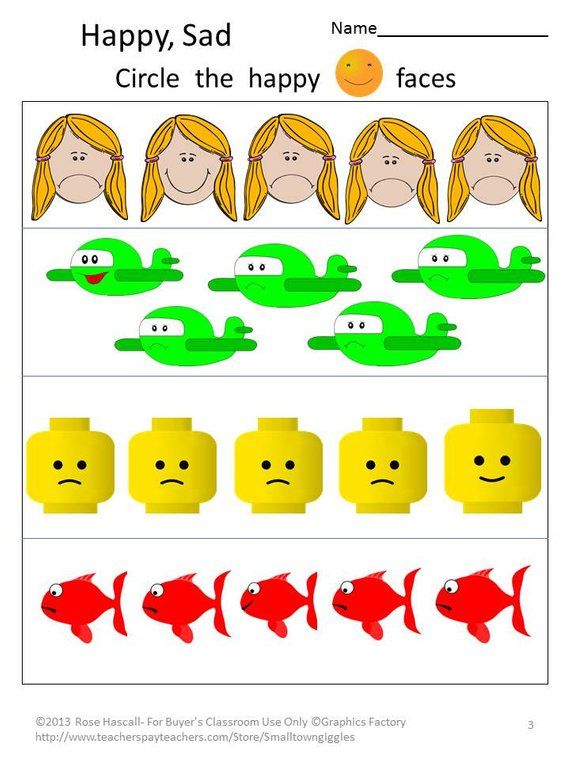 In addition, as you model story reading techniques to help guide instruction, identify students who need additional support, and determine if the pace of instruction should be increased, decreased, or remain the same.
In addition, as you model story reading techniques to help guide instruction, identify students who need additional support, and determine if the pace of instruction should be increased, decreased, or remain the same.
Examples of assessment questions
Give the student a book and ask the following questions:
- Can you show me:
- a letter?
- a word?
- a sentence?
- the end of a sentence (punctuation mark)?
- the front of the book?
- the back of the book?
- where I should start reading the story?
- a space?
- how I should hold the book?
- the title of the book?
- how many words are in this sentence?
Age or grade typically mastered
Some students enter kindergarten with an understanding of print concepts, but other will master it as the school year goes on.
See also this concepts of print assessment from Michigan's Mission: Literacy.
Reading Rockets (2004)
Reprints
You are welcome to print copies or republish materials for non-commercial use as long as credit is given to Reading Rockets and the author(s). For commercial use, please contact [email protected]
For commercial use, please contact [email protected]
Related Topics
Assessment and Evaluation
Early Literacy Development
Print Awareness
New and Popular
100 Children’s Authors and Illustrators Everyone Should Know
A New Model for Teaching High-Frequency Words
7 Great Ways to Encourage Your Child's Writing
All Kinds of Readers: A Guide to Creating Inclusive Literacy Celebrations for Kids with Learning and Attention Issues
Screening, Diagnosing, and Progress Monitoring for Fluency: The Details
Phonemic Activities for the Preschool or Elementary Classroom
Our Literacy Blogs
Teaching Students to Use Context
Kids and educational media
Meet Ali Kamanda and Jorge Redmond, authors of Black Boy, Black Boy: Celebrating the Power of You
Get Widget |
Subscribe
Development of the design and artistic concept of the Drakkar children's play complex
The modern development of the diversity of design and artistic trends, the dynamic growth of the range of technological possibilities in the field of architecture, the quality assurance of the integration of artistic disciplines with other scientific areas imposes on the designer a certain responsibility for the quality of the designed objects. The development of a children's playground is no exception. In this regard, it seems possible to consider the process of formation of one of the figurative and artistic ideas.
The development of a children's playground is no exception. In this regard, it seems possible to consider the process of formation of one of the figurative and artistic ideas.
In our opinion, first of all, it is necessary to touch on the aesthetic side of the issue - the subject of the artistic and semantic image, and only then solve the functional aspects [6, p. 203]. The initial thematic key and source of inspiration in this work was the culture of the early medieval Scandinavian sailors of the 8th-11th centuries - the Vikings. Over the past 20 years, many book, animation, game and film projects dedicated specifically to the Scandinavians have been released, which undoubtedly popularizes their centuries-old culture. Among the variety of projects, developments focused on children's age stand out noticeably. In our opinion, the most striking and impressive are cartoons and animated series: "Asterix and the Vikings" in 2006, the "How to Train Your Dragon" franchise and "Viking Wik". As well as books: Mauri Kunnas "Vikings are coming!", Andrew Langley "Dare to cross the Atlantic with the Vikings!" and a series of books written by English author Cressida Cowell, How to Train Your Dragon.
As well as books: Mauri Kunnas "Vikings are coming!", Andrew Langley "Dare to cross the Atlantic with the Vikings!" and a series of books written by English author Cressida Cowell, How to Train Your Dragon.
Rice. 1. Image of a drakkar [4]
As the sources show, in the cultural heritage of the Scandinavians, the most notable original object was the drakkar (Fig. 1) - a sailing and rowing deckless vessel that played a key role in military campaigns and in the colonization of new lands. In one of the sources, the following translation of the concept of “drakkar” is found: “Norwegian. Drakkar, from the Old Norse Drage - "dragon" and Kar - "ship" - this is how the wooden Viking ship is called today, long and narrow, with a high bow and stern. A. M. Stringholm specifies that Drakkars (dragons) got their name from stylized carved decorative elements in the form of a dragon's head on the bow and tail-like stern of the ship [7, p. 591–592]. According to Boyer Regis: "The maneuverable drakkar became the pride and national treasure of the descendants of the Vikings" [1, p. 78–79]. In our case, the bewitching plastic system of the Drakkar, which has an elegant intensity of artistic means expressing sacred ethno-cultural meanings, formed the basis of the artistic and plastic form type of the design concept of the Drakkar children's play complex.
78–79]. In our case, the bewitching plastic system of the Drakkar, which has an elegant intensity of artistic means expressing sacred ethno-cultural meanings, formed the basis of the artistic and plastic form type of the design concept of the Drakkar children's play complex.
On the basis of a comprehensive study of the cultural and historical prototype, analysis of existing and developed children's complexes that are close in the marked topics, it became possible to solve the design and artistic concept of the Drakkar children's play complex (Fig. 2). In the initial analytical operations with the subsequent reproduction of graphic variable sketches of the project, a very important regularity of the volume-spatial structure is dictated to us by a historical analogue - this is the organic development of the relationship between the main and secondary elements in the general nature of the composition, contrasting and nuanced combinations of such properties of the surface of volumes as texture, texture, color-graphic delights and design features of details.
Rice. 2. Color-graphic sketches of the Drakkar children's play complex [Developed by A. V. Pimenova, 2021]
It should be noted that the very process of performing multi-variant graphic sketches using a range of traditional (classical), mainly graphic art techniques, makes it possible to develop the designer's abilities and interest in his work with the greatest efficiency, to consolidate his professional knowledge, skills, and skills and to develop artistic experience. creative activity. The artistic and creative activity of a designer at the stages of searching for a design concept using graphic materials makes it possible to realize oneself, to embody one's ideas in the products of artistic and graphic activity, to develop reflective abilities that allow one to form the skills necessary for self-acquisition, deepening and application of one's knowledge on practice. At the same time, variable sketching opens up a wide field for overcoming stagnation moments, in other words, it stimulates the ability to find a solution to a new problem, helps to construct new methods of activity from known ones, and proves the mastery of the composition of mental operations.
As we can see, in the "found" graphic design and artistic image of the children's play complex, the basic figure is the stylized hull of the longship, the volumetric array of which rests on eight supporting pillars. Such stylized elements as a mast with a sail, round brightly decorated shields along each side, and bow parts of the “ship” located on both sides, decorated in the form of dragon heads, became a peculiar addition to the hull. It should be clarified that the shields in this play complex have two functions: firstly, they serve as a decorative element, and secondly, they are a fence to protect children from falling. Mental immersion in the atmosphere of the Middle Ages is enhanced by the expressive silhouettes of the Vikings, located under the base part of the complex.
The play equipment of the playground includes six elements: a ladder with a railing, a slide with a direct descent, a rope ladder, a sandbox, tic-tac-toe and an abacus. According to our plan, such a combination of elements allows you to combine mobile and less dynamic, more intellectual games in one complex. So, stairs and a slide provide physical activity for the child, and the sandbox, tic-tac-toe and abacus are more mental activity. The original, in our opinion, is the modification of the game element "tic-tac-toe", in which the classic "x" and "o" are replaced with similar symbols from the Scandinavian runes - "ᛞ" and "ᛟ", ancient letters, through which thoughts were expressed in writing and the concepts of people in a given geographical location of that time [7, p. 488].
So, stairs and a slide provide physical activity for the child, and the sandbox, tic-tac-toe and abacus are more mental activity. The original, in our opinion, is the modification of the game element "tic-tac-toe", in which the classic "x" and "o" are replaced with similar symbols from the Scandinavian runes - "ᛞ" and "ᛟ", ancient letters, through which thoughts were expressed in writing and the concepts of people in a given geographical location of that time [7, p. 488].
Trying to seriously approach the elaboration of the decorative details of the game complex, we did not forget that an important role in the functional and aesthetic solution of the elements of a three-dimensional composition is played by such an artistic tool as color. It is well known that color greatly affects the artistic expressiveness of design objects. According to the author of the design manual A. D. Grigoriev, a structure made of wood and metal should be attractive to the child, awaken his imagination and be in harmony with the surrounding landscape. Also, he notes, children do not see subtle differences between shades of color combinations, so bright and pure colors should be chosen for coloring elements of playgrounds. In this case, a certain measure should be followed, since very saturated colors in large quantities can have a negative effect; therefore, the general color of the playground elements is usually considered as a neutral background for bright color accents [2].
Also, he notes, children do not see subtle differences between shades of color combinations, so bright and pure colors should be chosen for coloring elements of playgrounds. In this case, a certain measure should be followed, since very saturated colors in large quantities can have a negative effect; therefore, the general color of the playground elements is usually considered as a neutral background for bright color accents [2].
Taking into account the above recommendations in the color scheme of the Drakkar gaming complex, we made a color close to the wood shade as the “general color”, and included bright color accents in the game and decorative elements. The choice of color combinations for the design project was influenced by the analysis of reconstructions and artistic interpretations of the cultural rudiments of the Vikings. The final color scheme of the playground is dominated by dark ocher, as well as yellow, red and blue, to a lesser extent there are white, green, gray colors.
As a rule, the final stages of the development of current design projects are developed and completed using the means of a graphic electronic environment. It should be noted that computer technologies, which are currently undergoing a period of intensive development, have enriched the possibilities of designers to a degree that was rarely achieved by means of other sciences. The great advantage of using the capabilities of computer technology in design engineering makes it possible to solve the problems of multivariate search for new forms of elements of a three-dimensional environment based on the laws of harmonization in a virtual environment, excluding time-consuming "manual" design methods, for example, prototyping or drawing. At the same time, in the process of design and artistic activity using graphic programs, the designer masters not only new knowledge and skills, but also develops mental abilities (analysis, synthesis, abstraction and concretization, comparison and opposition, integration and generalization, etc. ). .), as well as the ability to self-regulate intellectual activity.
). .), as well as the ability to self-regulate intellectual activity.
Thus, based on the analysis of the design documentation of existing analogues, a security zone was developed in the Adobe Illustrator graphics editor for the Drakkar children's play complex (Fig. 3). On views A; AT; D to the border of the marked zone, it is customary to set a distance of 150 cm, and from the side of the hill (view C) it is 250 cm, which takes into account the landing zone when the child rolls down the hill.
Based on building codes and regulations (SNiP), as well as sanitary rules and regulations (SanPiN), using computer graphics, the following were designed: a plan with geometric parameters (Fig. 4) and color-graphic scans of types A; FROM; AT; D (Fig. 5-6), indicating the levels, the scheme for laying the foundations and the positions of the parts. The main data of the gaming complex are summarized in Table 1.
Rice. 3. Safety zone. [Developed by A. V. Pimenova, 2021]
Rice. 4. Plan with geometric parameters. Units of measurement of parameters are indicated in centimeters [Developed by A. V. Pimenova, 2021]
4. Plan with geometric parameters. Units of measurement of parameters are indicated in centimeters [Developed by A. V. Pimenova, 2021]
Rice. Fig. 5. Scans of the Drakkar children's play complex, from left to right: view A, view C. Level units are indicated in centimeters [Developed by A. V. Pimenova, 2021]
Rice. Fig. 6. Scans of the Drakkar children's play complex, from left to right: view B, view D. Level units are indicated in centimeters [Developed by A. V. Pimenova, 2021]
Table 1
The main elements of the children's play complex "Drakkar"
| Position | Name | Qty |
| one | Decorative element Sail | 1 PC. |
| 2 | Pillar | 1 PC. |
| 3 | Decorative element Nose Drakkar | 2 pcs |
| four | Decorative element Shield blue-yellow | 2 pcs. |
| 5 | Decorative element Shield white-red | 2 pcs. |
| 6 | Board construction | 4 things. |
| eight | Wooden railing | 4 things. |
| 9 | straight slide | 1 PC. |
| ten | Pillar 10 x 10 x 340 cm | 4 things. |
| eleven | Staircase with handrails | 1 PC. |
| 12 | Pillar 10 x 10 x 260 cm | 4 things. |
| 13 | Decorative element Viking 1 | 1 PC. |
| fourteen | Decorative element Viking 2 | 1 PC. |
| fifteen | Decorative element Viking 3 | 1 PC. |
| 16 | Decorative element Viking 4 | 1 PC. |
| 17 | Tic-tac-toe | 1 PC. |
| eighteen | Sandbox 150 x 115 x 25 cm | 1 PC. |
| 19 | Pillar 7 x 7 x 80 cm | 5 pieces. |
| twenty | rope ladder | 1 PC. |
| 24 | abacus | 1 PC. |
According to anthropometric requirements, the geometric parameters of all elements of the children's play complex correspond to the approximate height of children from 7 to 12 years old. The structures of the playground are stabilized by supporting pillars, the depth of the sand-cement foundations of which ranges from 70 to 90 centimeters. It is recommended to give molded outlines to the forms of parts in order to avoid injuries. The steps of the stairs and the floor of the playing platform should be covered with anti-slip material. All protruding fasteners of structures must be hidden with smooth plugs. The main structure is supposed to be assembled from wood materials treated with safe, moisture-resistant, environmentally friendly septic tanks. Metal elements should be coated with non-toxic, frost-resistant paint. According to GOST R 52169-2012, the base of the playground should be equipped with shock-absorbing rubber tiles, since such a coating eliminates injuries to children, including the ingress of small particles into the eyes and respiratory organs, does not require regular restoration, and rubber tiles are also water-permeable, so children's shoes will not get wet, and in winter will prevent the formation of frost.
According to GOST R 52169-2012, the base of the playground should be equipped with shock-absorbing rubber tiles, since such a coating eliminates injuries to children, including the ingress of small particles into the eyes and respiratory organs, does not require regular restoration, and rubber tiles are also water-permeable, so children's shoes will not get wet, and in winter will prevent the formation of frost.
Thus, in the process of developing the design and artistic concept of the Drakkar children's play complex, it was found that an integrated approach and competent organization of the sequence of work stages (Fig. 7) portend (predict) the designer to master the basics of the theory and practice of design and artistic activity, to activate figuratively -associative abilities, the cultivation of a cultural and aesthetic attitude to the world around, the gradual approach to solving creative problems, the integration of computer technology with other disciplines of artistic training (drawing, painting, composition, design basics, etc. ), focused on solving design- artistic tasks.
), focused on solving design- artistic tasks.
Rice. 7. Stages of development of the design and artistic concept [5, p. 62].
Literature:
- Boyer Regis. Vikings: History and Civilization. Per from French. M. Yu. Nekrasov. - St. Petersburg: Eurasia, 2012. - 416 p.
- Grigoriev A.D. Designing. Children's playgrounds: textbook. allowance / A. D. Grigoriev. - Magnitogorsk: MaGU, 2012. - 234 p.
- Drakkar [Electronic resource]. - Access mode: wiki.wargaming.net/en/Navy:Drakkar
- Image of a drakkar [Electronic resource]. - Access mode: https://yandex.ru/images/search?pos=0&img_url=https %3A %2F %2Fpbs.twimg.com %2Fmedia %2FEvZTCKMXIAEGLef.jpg&text=drakkar-korabl-drakon-5726&lr=19&rpt=simage&source= Wiz
- Nekrasov R. V. Computer visual image in the composition of environmental design // Compositional thinking as a basis for professional training in the field of culture: All-Russia.
 scientific-practical. conf. Nov 21–22 2011: Sat. Art. Krasnoyar. State. Artistic Inst. - Krasnoyarsk: ID Class Plus, 2012. - P. 61-64.
scientific-practical. conf. Nov 21–22 2011: Sat. Art. Krasnoyar. State. Artistic Inst. - Krasnoyarsk: ID Class Plus, 2012. - P. 61-64. - Pimenova A.V. Fundamental factors in the design of a children's playground // Scientific research of young scientists: coll. Art. XIII International scientific and practical. conf. - Penza: MCNS "Science and Education", 2021. - P. 200–205.
- Strinngolm A.M. Viking Campaigns. / Per. with him. A. Shemyakina - M .: AST Publishing House LLC, 2003. - 736 p.
Basic terms (automatically generated) : children's play complex, decorative element, playground, play complex, Viking, design and art concept, element, rope ladder, design concept, design and art activity.
Authorities want to start an electronic dossier on Russians from kindergarten. While this is an experiment
Legislation Digitalization IT in the public sector
|
Share
The Ministry of Education wants to introduce digital profiles for schoolchildren and students in Russia. They will be created when parents apply to enroll their child in kindergarten or first grade. They will store all information about students, including their achievements in the process of obtaining education, up to graduation from the university.
They will be created when parents apply to enroll their child in kindergarten or first grade. They will store all information about students, including their achievements in the process of obtaining education, up to graduation from the university.
Schoolchildren will be "digitized"
An experiment will be held in Russia to assign each schoolchild and student their own digital profile. As it became known to CNews, the initiative belongs to the Ministry of Education.
The profile, which the ministry calls the "Digital Learner Profile" (DFL), is planned to be made mandatory for all students. The Ministry of Education has prepared the concept of the Central Federal District project (available to CNews), which states that the profile will be assigned to children when they enroll in kindergarten or first grade.
According to the text of the document, proposals for the introduction of the CFD in Russia were prepared on behalf of Deputy Prime Minister Dmitry Chernyshenko. He gave it on March 17, 2021
He gave it on March 17, 2021
The concept of the project was prepared by the Ministry of Education in April 2021 and sent to the Ministry of Digital Development for its further development. Representatives of the Mintsifra confirmed to CNews that the ministry is working on the CFD concept together with the Ministry of Education.
Russian children will go to the first grade not only with notebooks and textbooks, but also with a personal virtual profile
According to Kommersant, citing an unnamed source familiar with the details of the project, the Central Federal District will become part of an experiment to introduce a digital educational environment. It is held until December 31, 2022, as part of the Decree of the Russian Government dated December 7, 2020. According to the publication, Deputy Minister of Science and Higher Education Elena Druzhinina spoke about the need to introduce the CFD in Russia back in December 2020.
What is a “Digital Learner Profile”
According to the text of the concept of the project of the Ministry of Education, the CFD is a "single element of identification" of the student at all levels of education. It should include, first of all, “a register entry of up-to-date and verified information about a citizen, allowing him to be identified by the minimum available and necessary data as part of the educational process.”
It should include, first of all, “a register entry of up-to-date and verified information about a citizen, allowing him to be identified by the minimum available and necessary data as part of the educational process.”
By "levels" the authors of the project mean pre-school, primary general, basic general, secondary general, secondary vocational, additional, additional vocational and higher education. From this we can conclude that the CFA will be assigned to both students of general education schools and university students.
In addition, the profile must contain “a distributed data structure, including links to data stored in the relevant registers of executive authorities”, as well as “a mechanism and procedures for managing digital consents issued by a citizen to the processing of his personal data obtained from a digital profile , using the consent management service.
The authors of the project also plan to avoid the accumulation of large amounts of data about students in various government information systems. As an example, they cited the Unified Identification and Authentication System (ESIA), the National Data Management System (NSUD), the Interdepartmental Electronic Interaction System (SMEV), as well as federal and regional information systems in the field of education.
As an example, they cited the Unified Identification and Authentication System (ESIA), the National Data Management System (NSUD), the Interdepartmental Electronic Interaction System (SMEV), as well as federal and regional information systems in the field of education.
Alexey Pavlov, Rostelecom-Solar: Now there is a transformation of the established ideas about information security as a strictly internal function
Safety
To do this, the authors proposed to create a single distributed ledger. It will use de-identified digital profile identifiers.
Students will have a "digital portfolio"
In addition to the CFD, a “digital portfolio” will also be created for each Russian schoolchild as part of the experiment. This is a kind of database with all the achievements of students "in the process of mastering various educational programs for each level of education."
The portfolio can also include additional information about students, which is not related to the educational process. As stated in the text of the project concept, this is necessary "for the convenience of viewing by a citizen, teacher or educational organization, including the creation of a digital passport of the student's competencies." It was not known at the time of publication of the material what kind of information about a student or student that is not related to obtaining education can be supplemented by his portfolio.
As stated in the text of the project concept, this is necessary "for the convenience of viewing by a citizen, teacher or educational organization, including the creation of a digital passport of the student's competencies." It was not known at the time of publication of the material what kind of information about a student or student that is not related to obtaining education can be supplemented by his portfolio.
Special internet for schoolchildren
The Ministry of Education is working on several initiatives to digitally modernize the learning process for Russian schoolchildren. In particular, the head of department Sergey Kravtsov reported at the beginning of June 2021 about the ongoing work to create the so-called "white" Internet for schoolchildren.
Drones, robots and VR: what innovations are in demand in metallurgy
Industry innovation
“Today, the so-called white Internet for schoolchildren is being created, where there are social networks, there are instant messengers, there are all the tools that schoolchildren use today, but there is proven content and the values that we are talking about today,” the minister said.