Counting game for preschoolers
40 Counting Games And Number Activities For Preschoolers
The basic foundation of math is understanding numbers and quantities. One of the best ways to develop these understandings, or number sense, is through handling objects and counting them. We can listen to preschoolers recite numbers in order, but we want them to apply that to counting objects and understand that those numbers represent quantities of items. Counting games and activities encourage preschoolers to “play” with numbers and quantities and build math skills and number sense in natural ways. These ideas can help you build math and counting skills with preschoolers.
Counting Games and Activities
These 40 preschool math games include counting games and various number activities. They are perfect to help build counting skills and math skills in your preschoolers and kindergarten students.
1. Dog Bone Counting Game (Pre-K Pages) – This is a fun, hands-on counting game for students in your preschool, pre-k, or kindergarten classroom.
2. Farm Animal Counting Activity (Pre-K Pages) – What could be more fun than Counting Feet with farm animals?
3. Printable Counting Book (Pre-K Pages) – Identifying and naming numbers can be a difficult skill for young children in preschool and kindergarten.
4. Homemade Counting Board Game (Pre-K Pages) – This homemade game can help preschoolers develop math concepts while playing a game together.
5. Mouse Counts Game (Pre-K Pages) – Mouse Count inspired this activity that helps children practice counting to ten while also working on their fine motor skills – and it’s lots of fun too!
6. Fire Truck Counting Game (Pre-K Pages) – In this activity, children will explore fire trucks and firefighters with a counting game.
7. Penguin Counting Game (Pre-K Pages) – This Penguin Counting Game is the perfect addition to any winter theme, lots of fun for young children and great practice for counting, number sense, and one-to-one correspondence.
8. Ocean Theme Counting Activity (Pre-K Pages) – The best preschool activities allow children to be interactive and hands on while they explore new concepts. We’ve developed a fun, easy to prepare ocean theme counting activity to do just that.
9. Nursery Rhyme Number Game (Pre-K Pages) – This nursery rhyme activity relates to “Baa Baa Black Sheep” and encourage number recognition and counting, important math concepts.
10. Digital Counting Activities Using Google Slides (Teaching Mama) – This resource has digital counting activities, which is perfect for the preschool and kindergarten age.
11. Button Counting (Busy Toddler) – Grab a deck of cards for this fun button counting math activity.
12. Football Counting Game (Sunny Day Family) – With a die, football printable, and some yogurt Danimals it’s a fun counting game your preschoolers will love.
13. Snowman Hole Punch Counting (JDaniel4’s Mom) – Use your hole punch to create these snowmen and work in a fun counting activity to go along with it.
14. Ladybug Busy Bag (Preschool Inspirations) – Work on counting with your preschoolers with these adorable paper ladybugs.
15. Cookie Counting Game (Still Playing School) – Have your kids practice counting chocolate chips with these paper chocolate chip cookies.
16. Counting Snowballs (Fun-a-Day) – This easy counting cotton balls activity is a great math activity for your preschoolers.
17. Race to Fill the Cup (Mom Inspired Life) – Have fun filling a cup with these adorable erasers.
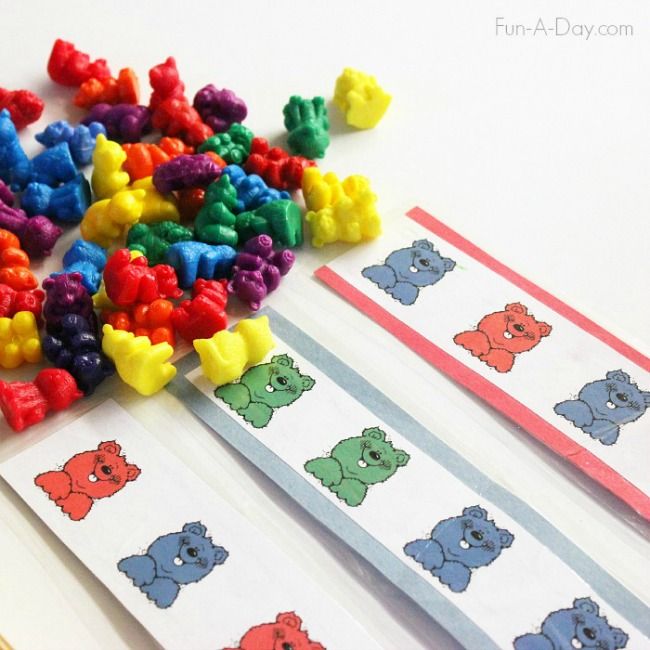
18. Count and Compare (Stir the Wonder) – Use these fun Farm Animal Rainbow Counters to inspire young children interested in animals or to go along with a farm theme!
19. Little Miss Muffet Path Game (Preschool Spot) – This fun activity is based on the nursery rhyme, Little Miss Muffet.
20. Tally Marks with Pencils (Munchkins and Moms) – Have fun practicing making tally marks with #2 pencils.
Counting Games and Number Activities For Preschoolers
More preschool math games to enjoy! These counting games and number activities will be definitely enjoyed by your preschoolers and build their math skills.
21. DIY Counting Boxes (Parenting Chaos) – Label containers with numbers and then have your preschooler fill each bucket with the labeled number of items.
22. Play Dough Numbers and Counting (Little Pinch of Perfect) – This activity is simple to set up and a great way to expose young kids to numbers and lets them visually see the difference in amounts. The activity can be adapted for different skill levels by making smaller or larger numbers.
23. Passing Car Count (Prekinders) – In this activity, we watched for red & blue cars as they passed by on the street. Children recorded the cars they saw by marking dots on their sheet with a corresponding color crayon.
24. Ways to Teach Counting (Prekinders) – Here are 15 ways to teach counting skills in Pre-K.
25. Ants on a Log Game (Teach Preschool) – DIY “ants on a log” counting game with the children then invite the children to draw their own ants on a log…
26. The Math Box (Teach Preschool) Create a simple math box and then watch as your preschoolers love filling it and practice their counting skills.
27. Counting and Addition Tray (Imagination Tree) – Set up an open-ended maths activity for kids using counting manipulatives, play dough and a dice, in a dip tray!
28. Simple Montessori Counting Activity (My Mundane and Miraculous Life) – This simple counting activity with rocks, your child can work on number recognition.
29. Things to Count With (Pre-K and K Sharing) – Repurpose what you have and count items with your preschooler!
30. How Many Blocks Long? (Brick by Brick) – This is a fun activity where your preschooler can see how many block longs they are and practice counting as they do it.
31. Make Groups of Numbers (Teach Me Mommy) – This simple counting activity is easy to setup, can be played with one or more children and it is fun too!
32. Count and Smash Activity (Stir the Wonder) – The great thing about play dough besides that it is just fun, is that it is also a great way to work on fine motor skills, work in some math skills, and get some sensory input and it can be used in many ways for hands-on learning!
33. Activities with Counting Blocks (Educators’ Spin on It) – These are 8 math and counting activities for your preschooler to enjoy.
Activities with Counting Blocks (Educators’ Spin on It) – These are 8 math and counting activities for your preschooler to enjoy.
34. Where the Wild Things Are Game (Mom Inspired Life) – While playing, children practice counting, learn one to one correspondence and even get some fine motor practice.
35. Listen and Spray Game (Fantastic Fun and Learning) – This activity is great for counting practice but also for fine motor practice.
36. Race to Lose a Tooth Game (Toddler Approved) – This fun dental theme inspired activity with marshmallows is a fun counting game for your preschoolers to enjoy.
37. Roll and Count (Buggy and Buddy) – Here’s a counting math game for kids perfect for practicing one-to-one correspondence. It’s super easy to make and lots of fun for the kids!
38. Count Forward and Back Game (Fantastic Fun and Learning)- This preschool math game would be perfect during St. Patrick’s day and March in your classroom.
39. Build a City Game (Learning 4 Kids) If your preschooler loves playing with Legos then they will love this math game.
40. Mystery Mitten Tactile Counting Game (Preschool Toolbox) – Gather some real mittens and come play a tactile mystery mitten counting game to encourage early math intuition with tactile support!
Also check out the free Winter Play Dough Counting Mats and our other thematic counting mats.
Follow my Counting Pinterest Board for more great ideas!
Homemade Counting Game - Pre-K Pages
posted by Editor | filed under Special | affiliate disclosure
Young children develop math concepts by playing and exploring. Using numbers and counting quantities will help children develop concepts through hands-on experiences. This homemade game can help preschoolers develop math concepts while playing a game together.
Building Concepts
This preschool math game reinforces several different math concepts:
- Subitizing – subitizing is recognizing quantities without counting; using a cube with dots develops these skills as children begin to recognize the number of dots rolled without counting all the dots
- One to One Correspondence – “one object, one number” – children can learn that, to get the correct quantity, they must assign one number per object, without skipping objects or counting them twice
- Number order – practicing counting a quantity helps reinforce the order of numbers
- Quantity – children learn that the quantity, the amount of objects, is the real meaning of a number (“four” means that many items)
In addition to number concepts, playing the game together reinforces taking turns, working together, and social interaction. Plus it’s just fun!
Plus it’s just fun!
Making the Counting Game
Gameboard
Making the gameboard is easy and uses items you probably already have on hand. For the board itself, I used a file folder. I have lots of these on-hand from discarded files; the folder is thick so it makes a sturdy base; and it folds easily for later storage. Use heavyweight paper or construction paper as an alternative.
Place circle stickers around the folder to make a gameboard track. (You can draw the track spaces or glue colored paper instead.) On some of the spaces, draw a square. Make your squares about every 3-4 spaces. At first, I only put a few squares on the game; I added more squares after we played the game once. You want several opportunities for children to count objects.
In the middle of the board, draw an area to place the counters. We were filling a “river” so I drew two lines to resemble the sides of a river. You could draw a square, circle, or other shape instead.
Other Game Supplies
- Game pieces – something for children to move around the board; I used game pieces from an old discarded game; other ideas are Lego bricks, plastic drink lids, small figures, or buttons
- Dot cubes – we used 2 cubes of different colors; you can get by with just one cube (see below for more information about this)
- Counters – something for children to count and add to the board; we used floral marbles; other ideas are animal counters, pompoms, small cars, or leaves
Note: I have 5-year-olds, so smaller \dot cubes and floral marbles were not an issue. For younger children, use large foam cubes and counters that are age-appropriate for them.
Playing the Counting Game
Each child can choose a game piece and place it on the board (any space).
The first child rolls the white cube. Note the quantity rolled. Help children identify the quantity, so they will begin to quickly recognize each configuration (subtizing!).
Invite the child to move that many spaces around the track. Help a child count one number for each space. Also, you may need to help a child understand that she starts counting on the next space, not the space her piece is already on.
If the child lands on a space with a square, she rolls the green numbered cube and places that many counters in the river. Count the number of objects together as she places them in the river.
Help children keep track of turns as they play. The game is finished when the river is full (all the counters are in the river).
Variations and Ideas
1. We used two dot cubes of different colors. This helped the children keep track of what to do. Land on a square and roll the green cube to count marbles. You could play this game with just one cube and use it for both moving around the board and counting marbles. However, that could cause some confusion during the game. (Whose turn is it? Do I move or count objects?)
2. We used a game piece for each child. You could use just one game piece and every child moves the same one around the board. Our kids liked having their own pieces to move around the board.
We used a game piece for each child. You could use just one game piece and every child moves the same one around the board. Our kids liked having their own pieces to move around the board.
3. You could make colored cards to move around the board and only use the cube to roll and count.
4. Make the game fit whatever theme you need. Use foam flowers to plant or pick for a spring theme, for example.
5. You can start the game with the objects on the board and count to remove them. For example, fill the river with floral marbles. When you roll the green cube, take off that many marbles and put in the basket.
I played this game for a long time with one girl. We filled up the river. She wanted to continue to play, so we kept going, taking the marbles off the river and putting them back in the basket.
Overall, play the game so children will have fun. They may think of different variations to this game, too. Look for ways to follow their ideas.
Concepts about numbers can easily be developed as children play with these ideas. Practicing counting with small objects and practicing counting spaces in moving on a gameboard are two ways for children to “play” with counting. This easy-to-make board game can help your children build important math concepts.
Practicing counting with small objects and practicing counting spaces in moving on a gameboard are two ways for children to “play” with counting. This easy-to-make board game can help your children build important math concepts.
BIO: Scott Wiley, an early childhood educator for over 25 years, is editor for Pre-K Pages. He blogs at Brick by Brick, exploring the connection between play and learning. His kids enjoy playing this trail game over and over. Connect with Scott on Twitter, Facebook, and Pinterest.
More Counting Game Ideas—
Fire Truck Counting Game
Gingerbread Man Counting Game
Mouse Counts: Counting Game
Dog Bone Counting Game
Follow my Counting Pinterest Board for more great ideas!
Filed Under: Special Tagged With: counting, games, math, subitizing
Are you ready to teach smarter, save time, and get your life back?
Join 150,000+ teachers who receive my FREE weekly teaching tips; and I’ll send you a copy of my eBook 7 Circle Time Mistakes as a gift.
Privacy Policy
Didactic game as a means of developing counting skills in senior preschool age
The Federal State Educational Standard for Preschool Education (FSES DO) involves a revision of the content, methods, forms and means of working with children. Provided that the pedagogical process is properly organized with the use of scientifically verified methods, as a rule, gaming methods that take into account the characteristics of children's perception, children can already at preschool age, without overload and stress, learn much of what they used to learn at school.
Much attention in the process of teaching preschool children the elements of mathematics is given to work on developing their counting skills, since these skills are the basis for further education at school.
Research by many scientists (J.A. Komensky, I.G. Pestalozzi, K.D. Ushinsky, F. Froebel, M. Montesori, L.V. Glagoleva, E.I. Tikheeva, F.I. Bleher, A.M. Leushina and others) it is proved that counting activity has a complex psychophysiological and psychological structure, which is ensured by the joint work of various analyzer systems, which are a functional system that is the basis for the formation and implementation of the counting function.
The formation and development of counting functions is closely connected with speech, which, being included in its structure, acts, on the one hand, as a means of expressing this complex system of knowledge, and on the other hand, as an organizer of counting activities.
Along with various methods and techniques, as well as the use of a variety of didactic materials, one of the effective means of developing counting skills in preschool children is a didactic game.
Didactic games are a kind of games with rules specially created by pedagogy for the purpose of teaching and educating children. They are aimed at solving specific problems of teaching children, but at the same time, they show the educational and developmental influence of gaming activities.
It is no coincidence that didactic games have taken a firm place among the methods of teaching and educating children. The main feature of didactic games is determined by their name: these are educational games. In the process of games, children learn to solve cognitive problems. Any didactic game aims to enrich the sensory experience of the child, to develop his mental abilities. A distinctive feature of didactic games is the ability to teach children through active and interesting activities for them.
In the process of games, children learn to solve cognitive problems. Any didactic game aims to enrich the sensory experience of the child, to develop his mental abilities. A distinctive feature of didactic games is the ability to teach children through active and interesting activities for them.
Basic requirements for planning didactic games: when choosing a game, the teacher must take into account both the content and the degree of complexity and novelty for children. Taking into account age-related capabilities requires a wider use of didactic games with toys and objects at a younger age for the development of sensory and mental abilities in children; at an older age, the importance of board-printed and word games increases. To avoid monotony, the plan indicates the changes that are made to various versions of the same game. Each didactic game should give exercises that are useful for the mental development of children and their upbringing. In a didactic game, there must be an exciting task, the solution of which requires mental effort, overcoming some difficulties.
Didactic game as an independent game activity is based on the awareness of this process. Independent play activity is carried out only if the children show interest in the game, its rules and actions, if these rules are learned by them.
Thanks to didactic games, it is possible to concentrate attention and attract the interest of even the most uncollected children. In the beginning, they are fascinated only by game actions, and then by what this or that game teaches. Gradually, children awaken interest in the very subject of education. When using didactic games, various objects and visual material are widely used, which contributes to the fact that educational activities take place in a fun, entertaining and accessible way.
While playing, children learn to solve cognitive problems. Any didactic game aims to enrich the sensory experience of the child, to develop his mental abilities. A distinctive feature of didactic games is the ability to teach children through active and interesting activities for them.
The game reveals the characteristics of the child's character, reveals the level of his development, so the game requires an individual approach to children. When choosing a task, the teacher should take into account the individual characteristics of each child.
In the process of playing, children develop the habit of concentrating, thinking independently, developing attention, striving for knowledge. Carried away, children do not notice that they are learning: they learn, remember new things, navigate in unusual situations, replenish the stock of ideas, concepts, develop imagination. Even the most passive of the children are included in the game with great desire, making every effort not to let down their playmates.
In the game, the child acquires new knowledge, skills and abilities. Games that contribute to the development of perception, attention, memory, thinking, the development of creative abilities are aimed at the mental development of a preschooler as a whole.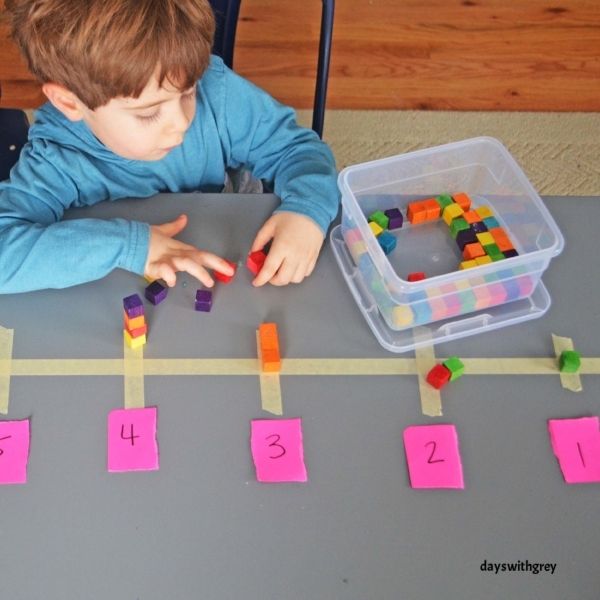
The game makes educational activities emotionally rich, brings a cheerful mood to the children's team, helps to perceive the situation related to mathematics aesthetically.
Teaching children to play and while playing to count and solve ensures the education of those necessary qualities that a child needs in the learning process, since in the game, unnoticed by themselves, children perform a large number of exercises, train in counting.
In order to develop counting skills in children of senior preschool age, it is possible to group didactic games aimed at developing counting skills in accordance with the sections:
- 1. Games for the formation of knowledge about the figure.
- 2. Games for the formation of the number and score.
- 3. Games for the formation of quantitative relations.
- 4. Games for the formation of counting operations.
- 5. Games with the solution of arithmetic problems.
During preschool age, the game goes through stages of its development. Due to its diversity, it really becomes a leading activity. The didactic game allows you to achieve the targets indicated by the Federal State Educational Standard for Education: the child is interested in the surrounding objects and other objects, and actively acts with them; masters the main cultural ways of activity; has a positive attitude towards the world; has a developed imagination; the child has a good command of oral speech; shows curiosity; prerequisites for learning activities are formed at the stage of completion of preschool education.
Due to its diversity, it really becomes a leading activity. The didactic game allows you to achieve the targets indicated by the Federal State Educational Standard for Education: the child is interested in the surrounding objects and other objects, and actively acts with them; masters the main cultural ways of activity; has a positive attitude towards the world; has a developed imagination; the child has a good command of oral speech; shows curiosity; prerequisites for learning activities are formed at the stage of completion of preschool education.
The place of the didactic game in the structure of the GCD on the formation of elementary mathematical concepts is determined by the age of the children, the purpose, purpose, content of the lesson. It can be used as a training task, an exercise aimed at performing a specific task of forming ideas, developing counting skills.
Games with counting sticks for the development and learning of children
Children, especially at preschool age, are very inquisitive. The task of adults is to help them cognize the world not only with the help of toys, natural phenomena, specific household items, but also with the help of abstract teaching aids, one of which are ordinary counting sticks.
The task of adults is to help them cognize the world not only with the help of toys, natural phenomena, specific household items, but also with the help of abstract teaching aids, one of which are ordinary counting sticks.
The use of counting sticks in the mathematical development of preschool children
It is a mistake to think that with the help of these improvised means you can teach a child to count, and nothing more. Their task in the capable hands of parents is to develop children's thinking, namely:
- They help to learn colors, add and study geometric shapes, design intricate castles, solve logical problems. Therefore, counting sticks can be an excellent teaching aid when organizing homework.
- With the help of this simple and multifunctional manual, you can study the order of numbers and their composition, the concepts of "shorter-longer", "more-less", "higher-lower".
- It is also worth listening to the opinion of psychologists who simply insist that, along with fine motor skills, games and activities with these counting elements help to develop in a preschooler:
- intelligence;
- independence;
- imagination and creative thinking;
- attention;
- interest in research and learning;
- activity;
- will to win;
- purposefulness;
- persistence;
- independence;
- ability to plan, control and evaluate own activities;
- concentration.

Ways to use the didactic aid in the fun of toddlers
It is very easy to involve a toddler in work with sticks. The main thing is to be interested! The most familiar and main activity for children from 2 to 6 years old is a game. It is in the form of a game that you need to conduct classes, coming up with an interesting plot and even distributing roles. Set the rules from the very beginning and let the little one understand the ultimate goal of the game. It can be anything, depending on what you need to teach in games with sticks. For example, fold a figure out of sticks or arrange them by color in separate boxes, lay out a name or count how many counting elements a house consists of. Thus, at home, counting sticks will become an excellent didactic game.
Important! Interest in the correct solution of the set task stimulates the child to active brain activity and overcoming difficulties in the work begun. The kid will especially try if someone else does the same work next to him - children love to compete and show the will to win.
Stick games for the little ones (9 months +)
When and how to organize didactic games with counting sticks at home? Experts emphasize: at an early age, when kids are just starting their journey to learning objects, counting sticks can be used as a game material, learn colors with their help, design figures of various sizes and shapes, and use them in non-standard drawing.
The starting age for familiarization with counting sticks is 9 months. The kid already knows how to grab objects with two fingers - forefinger and thumb, which means that it's time to develop fine motor skills of the hands. The following can be an excellent exercise for this:
- Take a small box or case, cut an oblong slit in them with a knife or scissors, and show the little one that you can put sticks into it one at a time. Toddlers will do an excellent job with the task, because at this age they really like to push objects through holes.
- We sculpt a hedgehog from dough and offer the little one, under the strict guidance of his mother, to stick sticks like needles.
 Such an action is still difficult for a baby, so mother's hand will become an extension of the child's hand.
Such an action is still difficult for a baby, so mother's hand will become an extension of the child's hand.
Important! Small children must not be left unsupervised when performing tasks with small parts. Indeed, in addition to the hole in the box, the child can, without hesitation, send one of the counting elements into his mouth.
What can be offered to a baby aged 1 to 1.5 years
1. Young children are already capable of learning concepts such as color, size, length. Therefore, armed with a didactic (training) manual, it's time to offer them such games with sticks :
- Name the color of all available sticks.
- Collect elements of a certain color.
- Find sticks with the same length (Kuizener sticks).
- Collect one stick of each color.
- Find the shortest and longest stick and name their colors (Kuizener sticks).
- Arrange the sticks in a row, alternating two colors, eg yellow and red.

- Choose any stick and ask the child to the left of it to lay out all the sticks that are shorter than the chosen one, and to the right - all those that are longer. You can make it easier to solve the puzzle by asking leading questions. For example, show two sticks and ask if they are different or the same. You can complicate the question of how they differ from each other (color, length) or what is their similarity.
2. At an early age, children begin to be interested in and learn about the properties of plasticine. Therefore plasticine modeling for children can be both an activity and a game with counting sticks. Sticks in this case are auxiliary material: to play the role of a stem for a flower, legs for a fungus or a trunk for a tree; serve as legs-handles for a plasticine man or a chimney for a house.
3. Similarly, you can organize non-standard drawing with sticks for kids. For example, laying out various objects (road, cars, houses, flowers, men and animals) on the floor or table, you can create whole pictures and toy cities. Such an activity will surely arouse the interest of an inquisitive kid, will develop imagination, will make you feel not only a member, but also the creator of an exciting game.
Such an activity will surely arouse the interest of an inquisitive kid, will develop imagination, will make you feel not only a member, but also the creator of an exciting game.
Didactic games from 2 to 4 years old
During this period, preschool children make a significant breakthrough in the field of self-knowledge and intelligence development. There is a formation of speech, contact with peers is easily established, the baby acts purposefully. He is interested in drawing, designing, which are increasingly based on children's imagination. It's time to channel these abilities in the right direction and deepen the knowledge about the purpose of counting sticks. Suitable for this will be the following games with sticks, which are widely used in kindergarten.
Where is less?
Place the counting sticks opposite each other in two rows, one of which will have one fewer number of counting sticks. The preschooler must show which row has fewer elements and which has more. They complicate the puzzle with the question: “What needs to be done so that the number of sticks becomes the same?”.
They complicate the puzzle with the question: “What needs to be done so that the number of sticks becomes the same?”.
Task with an asterisk: ask the child to independently lay out two rows with the same number of elements, and so that there are one or two less of them in one row.
Repeat drawing
You will need a sheet of paper with an image of an object understandable to the child (a house, sweets, butterflies, Christmas trees, etc.), made in two or three colors. The kid should lay out this drawing with chopsticks, repeating the colors on paper. At the end, ask the preschooler to name the colors with which he created his picture.
This exercise helps to learn colors, develop fine motor skills of children's fingers, as well as creative imagination.
Building and counting
An adult lays out some simple figure from the didactic material, for example, a triangle, and asks the student to repeat it. After the kid copes with the task, you need to voice the name of the figure and ask him how many elements were needed to build this triangle.
Next, you can build a square, a rhombus, a rectangle, as well as any other objects with the same conditions of the problem. For deeper knowledge, you can ask what geometric figure the roof of a house, a window, a truck body, etc., looks like.
The task with an asterisk is to ask an adult to divide a rectangle of 6 sticks into two equal squares using one. Or with one stick turn a square into two triangles.
The purpose of this game exercise is to develop spatial, logical and creative thinking in children.
Games for older preschoolers
Classes with children aged 5-7 involve more thorough preparation for their schooling. This will require not only perseverance, but also basic knowledge in the field of reading and mathematics, the ability to generalize, highlight, compare. Of course, you can not strain the child with any tasks, because everything you need will be taught at school in due time. But if a preschooler has an interest in learning, he should not be denied self-development. Using sticks for counting, you can invite him to perform the following exercises according to ready-made schemes. This is how games with counting sticks are played in kindergarten.
Complete the picture
It is necessary to show the child a diagram-drawing of half of an object depicted on paper. The task is to complete the picture symmetrically, using the same colors and proportions.
Draw numbers and letters
Use chopsticks to lay out the names of letters (if it comes easy, then simple words), as well as numbers within ten. With good success, you can do it at speed with one of your peers.
What numbers are made of
When a preschooler already knows what the numbers look like, you can offer him to lay out each one with the help of sticks of two colors, thereby giving the concept of the composition of the number. So, the number 5 can be laid out from two red and three green sticks or from one yellow and four red ones.
Count!
Easy option: use sticks to lay out an example (as an option, two sticks + three sticks). The child must be asked to count and give the correct answer by laying out the required number of elements after the equal sign. If the kid knows the numbers, then you can lay out the expression with their help.
The child must be asked to count and give the correct answer by laying out the required number of elements after the equal sign. If the kid knows the numbers, then you can lay out the expression with their help.
Psychologists recommend
- Parents themselves determine the age at which children should be involved in activities with a set of counting sticks. But experts still recommend not to load the baby's brain too early. It is optimal to start classes at about three years of age.
- At first, it is worth giving the baby to get acquainted with the didactic material - let him play, put figures, pyramids. So it will be easier for a small student to study the shape and color of the parts, to feel the material from which they are made. Only in this way will children be able to conclude that some sticks are shorter than others, to catch their color differences.
- The beginning of classes must be made playful - the child should not feel pressure from adults, otherwise in the future he will develop an aversion to mathematics.
Learn more