Counting games for kindergarteners
Kindergarten Math Games That Make Learning Fun from the Start
Looking for ways to make math fun for young learners? Check out these kindergarten math games! They teach all the basic math skills kindergartners need to master and are sure to engage every kid in the learning process.
(Just a heads up, WeAreTeachers may collect a share of sales from the links on this page. We only recommend items our team loves!)
ADVERTISEMENT
1. Conquer cardinality with penguin dominoes
Kindergarten math students work to master cardinality, understanding that written numerals correspond to the number of items pictured. These free printable penguin dominoes make the concept fun to practice.
Learn more: Playdough to Plato
2. Put together puzzles to gain number sense
Kindergarten math students learn to understand that numbers can be represented in a variety of ways. These free printable puzzles help them practice those skills.
Learn more: Tickled Pink in Primary
3. Play teen-number bingo
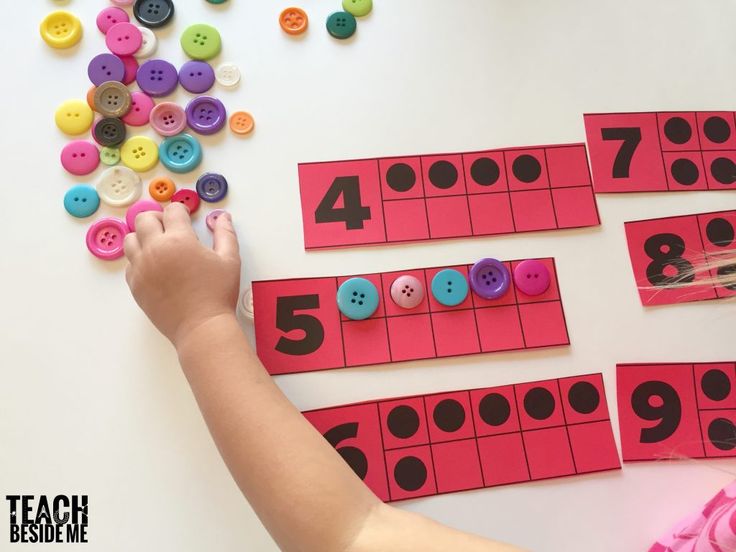
This free printable game helps little ones master their numbers from 11 to 20, both as numerals and represented on ten-frames.
Learn more: The Measured Mom
4. Stack cups and count to 100
Kids love stacking things, so they’ll get a kick out of kindergarten math games that make use of stackable cups. This one has them doing it with 100 cups while they count! Turn it into a competition by putting them in teams and timing them to see who can finish the task the fastest.
Learn more: Kindergarten Smorgasboard/100 Cups
5. Visit the skip-counting store
How fun is this? Grab some toys and label them with price tags in increments of 10 cents. Give kids a handful of plastic dimes, and have them count out the amount needed for each “purchase.”
Learn more: Creative Family Fun/Skip Counting Store
6. Have a rubber duck race
In this game, kids race to see who can be the first to get their rubber duckies to 10 (or any number you choose). They roll a die and lay out tiles to move their duck. The twist? To get to 10 at the end, they must roll the exact number they need—no going over! Kindergarten math games like this one are terrific for practicing counting on, basic addition, and making 10.
They roll a die and lay out tiles to move their duck. The twist? To get to 10 at the end, they must roll the exact number they need—no going over! Kindergarten math games like this one are terrific for practicing counting on, basic addition, and making 10.
Learn more: Happy Toddler Playtime
7. Practice counting on with cards and dice
Remove the face cards from a deck of playing cards and grab a pair of dice. The first player turns over a card and then rolls the dice. The number on the dice indicates how far they “count on” from the card. (For example, a player turns over a three and rolls a four. They say, “Three: four, five, six, seven.”) If the player gets it right, they keep the card, and the other player(s) get a turn.
Learn more: Creative Family Fun/Counting On
8. Skip-count with craft sticks
There are endless ways to use craft sticks in the classroom. For this game, number a series of colorful sticks by fives, as shown. Kids can practice by putting them in order first. Then, have a student draw a stick and count on by fives from that number to 100—if they draw 75, they then count 75, 80, 85, 90, 95, 100. If they get it right, they keep the stick, and the next player takes a turn.
Then, have a student draw a stick and count on by fives from that number to 100—if they draw 75, they then count 75, 80, 85, 90, 95, 100. If they get it right, they keep the stick, and the next player takes a turn.
Learn more: Simply Kinder
9. Match teen numbers
Once they’ve mastered the numbers 1 to 10, it’s time to understand how those numerals add up to make bigger numbers. These free printable cards show numerals and matching bundles of sticks that deconstruct each teen number into tens and ones.
Learn more: The Kindergarten Connection
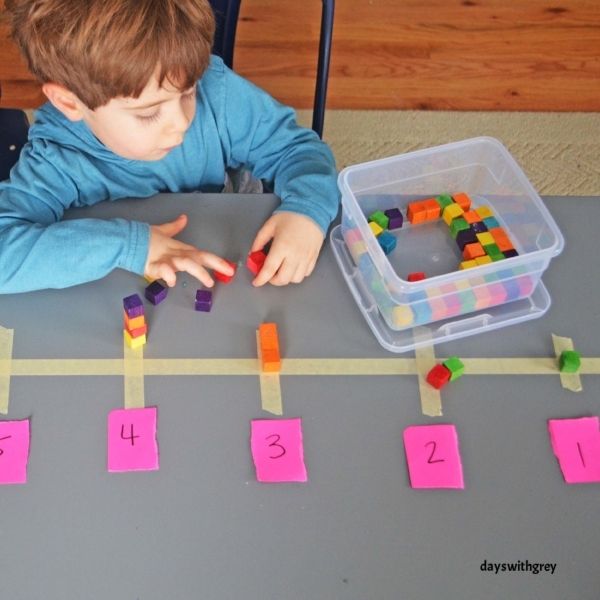
10. Compare numbers with dominoes
Kindergartners learn to compare numbers to determine which is larger and which smaller. Stacking math cubes based on the numbers on dominoes is a fun, hands-on way to compare the two numbers side by side, making it easier to see the difference.
Learn more: My Fabulous Class
11. Face off and compare numbers
You’ll need some small toys for this game, as well as polyhedral dice. Kids roll and place the number of items on their side. Then, they compare the two to see which is bigger.
Kids roll and place the number of items on their side. Then, they compare the two to see which is bigger.
Learn more: Natalie Lynn Kindergarten
12. Make 10 with two-sided chips
You’ll need counting chips that are a different color on each side for this activity. Kids shake up 10 chips in a cup and pour them out on the table. Then they see how many they have of each color and write that number bond to make 10.
Learn more: First Grade Fairytales
13. Throw snowballs to make 10
Make “snowballs” from paper (or any way you like), then place them in a bucket at one end of the room. Start kids out by having them toss snowballs into another bucket until they reach 10 (or any target number). Then, up the challenge by placing some snowballs in each bucket and have kids figure out how many more they need to toss in to make 10.
Learn more: Frugal Fun for Boys and Girls—Snowball Math Games
14. Use Uno cards to play addition war
In the card game War, players each flip an Uno card, and the one whose card is greatest takes them both. In this twist on one of our favorite kindergarten games, players each flip two cards. They then use counting blocks to represent the numbers and count on or add to find the sum. The largest sum wins the hand, and play continues.
In this twist on one of our favorite kindergarten games, players each flip two cards. They then use counting blocks to represent the numbers and count on or add to find the sum. The largest sum wins the hand, and play continues.
Learn more: Planning Playtime—Addition Game
15. Roll and add for fluency within 5
Kindergarten math students work to become fluent in adding and subtracting within 5. This free printable board game makes it fun!
Learn more: Liz’s Early Learning Spot
16. Get four in a row and learn place value
This customizable game helps teach the early place-value concept of tens plus ones. Get it for free at the link.
Learn more: Two Boys and a Dad
17. Bowl and subtract within 10
Set up a toy bowling pin set (or make one from plastic bottles or toilet-paper tubes). Kids bowl and see how many pins they knock down, subtracting that number from 10. Then they repeat, this time subtracting from the previous answer. First to get to zero wins!
First to get to zero wins!
Learn more: Planning Playtime—Subtraction Worksheets
18. Get off my boat!
So simple, so engaging, so fun! Use tape to outline a boat shape on the floor (or try this outside with sidewalk chalk). Let some kids board the “boat,” then make some get off. Use those numbers to write a subtraction number sentence and solve the equation!
Learn more: Kindergarten Smorgasboard—Get Off My Boat!
19. Drive and compare numbers to music
Prep for this game by using dot markers on paper plates as shown (visit the link below for more examples). Each kid takes a plate then uses it to “drive” around the room as you play music. When the music stops, they find a nearby partner and compare what they see on each other’s plates (e.g., “8 dots is more than 4 dots. 1 green dot is less than 4 green dots.” Then start the music up and repeat!
20. Build a weigh station
Use a hanger and plastic cups to build a super-simple weigh station. Kids will love dropping items into the cups to see which weighs more or less. Turn it into a game by having them try to guess which object weighs more first or how many of one item equals another.
Kids will love dropping items into the cups to see which weighs more or less. Turn it into a game by having them try to guess which object weighs more first or how many of one item equals another.
21. Battle it out in ribbon war
Looking for kindergarten math games that teach non-standard measurement? This idea is fun and easy. Cut colorful ribbons into a variety of lengths and place them in a bag. Each student pulls a ribbon from the bag. Then, put students in pairs and have them compare their ribbons to identify the longer one. The student with the longer ribbon keeps both, and the game continues.
22. Hold a shape scavenger hunt
Kindergarten math students are learning to recognize shapes in their environment and also to categorize and sort. This scavenger hunt does it all! Send them out to find objects in the room that match the shapes. Then count and compare to see how many you have in each category.
Learn more: Frugal Fun for Boys and Girls—Shape Scavenger Hunt
23.
 Hop along a shapes maze
Hop along a shapes mazeUse sidewalk chalk to lay out a shape maze on the playground or driveway. Choose a shape and hop from one to the next, or call out a different shape for every jump!
Learn more: Creative Family Fun—Shape Maze
24. Make a match to learn shapes
Grab these free printable memory cards at the link. Then play and learn the basic shapes.
Learn more: Life Over C’s
25. Guess the mystery shapes
Work on geometry terms like “sides” and “vertices” when you sort shapes using these attributes. Start by placing 3D shapes into paper bags and asking students questions like “The shape in this bag has 4 sides. What could it be?”
Learn more: Susan Jones Teaching
Love these kindergarten math games? You’ll also enjoy these 50 Kindergarten Math Word Problems of the Day!
Want more articles like this? Subscribe to our newsletters!
Counting Games for Kindergarteners Online
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q1: What are the activities to learn counting numbers?
Ans: To learn counting numbers, students can use pictures to count, they can also count on fingers or use counters to count.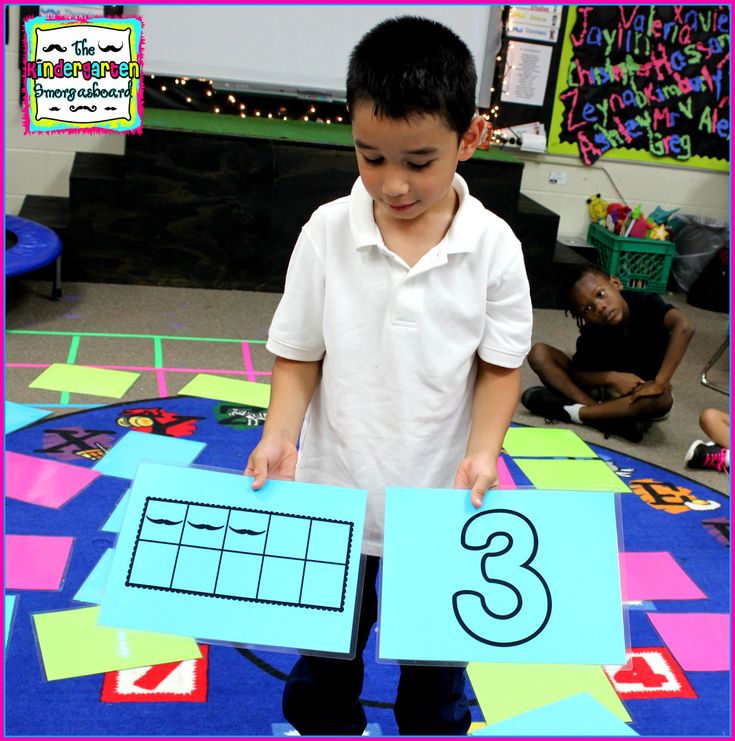 Kids can learn counting numbers by playing games or using fun drawing and coloring activities and worksheets Further, they can also count forward or backward to practice counting.
Kids can learn counting numbers by playing games or using fun drawing and coloring activities and worksheets Further, they can also count forward or backward to practice counting.
Q2: How do we introduce counting to kids?
Ans: We can introduce counting to kids by looking at the things and objects in our surroundings and asking them "how many objects are there"? Kids learn to count by using their fingers. They may also use counters to count all the objects. Once they can easily count things up to 5, they can be gradually taught to count larger quantities using other counting techniques.
Q3: Till what number a child should be able to count in kindergarten?
Ans: A kindergartener should be able to count till 20 using various tools such as fingers on the hand, pictures, counters and objects.
Basic math and number concepts learnt in prekindergarten or kindergarten classroom lays the foundation for understanding higher math concepts. Counting is an essential foundation skill which kids begin learning through preschool activities.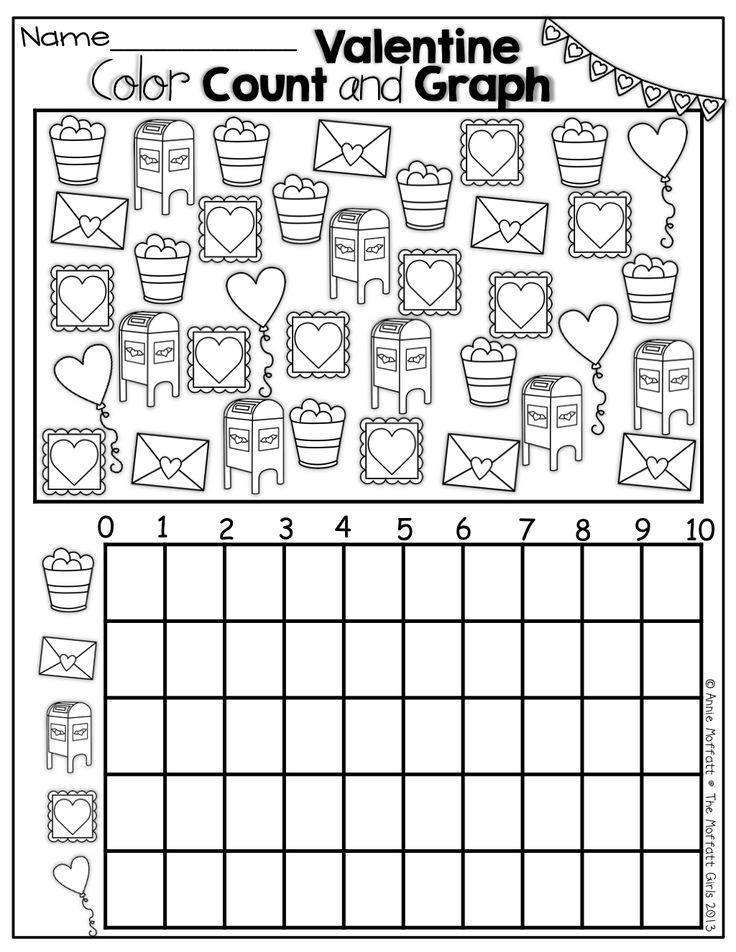 By the start of the first day of kindergarten, the kids are expected to count from 1 to 10 (basic rote memorization) and recognize some numerals. In kindergarten, the kids are expected to count to 100, count group of objects up to 20 and create complex patterns.
By the start of the first day of kindergarten, the kids are expected to count from 1 to 10 (basic rote memorization) and recognize some numerals. In kindergarten, the kids are expected to count to 100, count group of objects up to 20 and create complex patterns.
Kindergarten math involves variety of skills that includes:
1: Numeral Identification which involves identification or recognition of all 10 numerals from 0 to 9. The kindergarten curriculum expects kids to learn number names for numbers from 0 to 20.
2: Counting which involves learning counting strategies like count out loud, touch and count, move and count, line up and count, and count on.
3: Pattern recognition and creation which starts with recognizing pattern in the objects and extend to observing patterns in the number system.
4: Classifying and sorting which develops logical reasoning skills and divergent thinking in kids.
- Numeral Identification and counting sequence: In kindergarten, the kids learn to count to 100 by ones and tens.
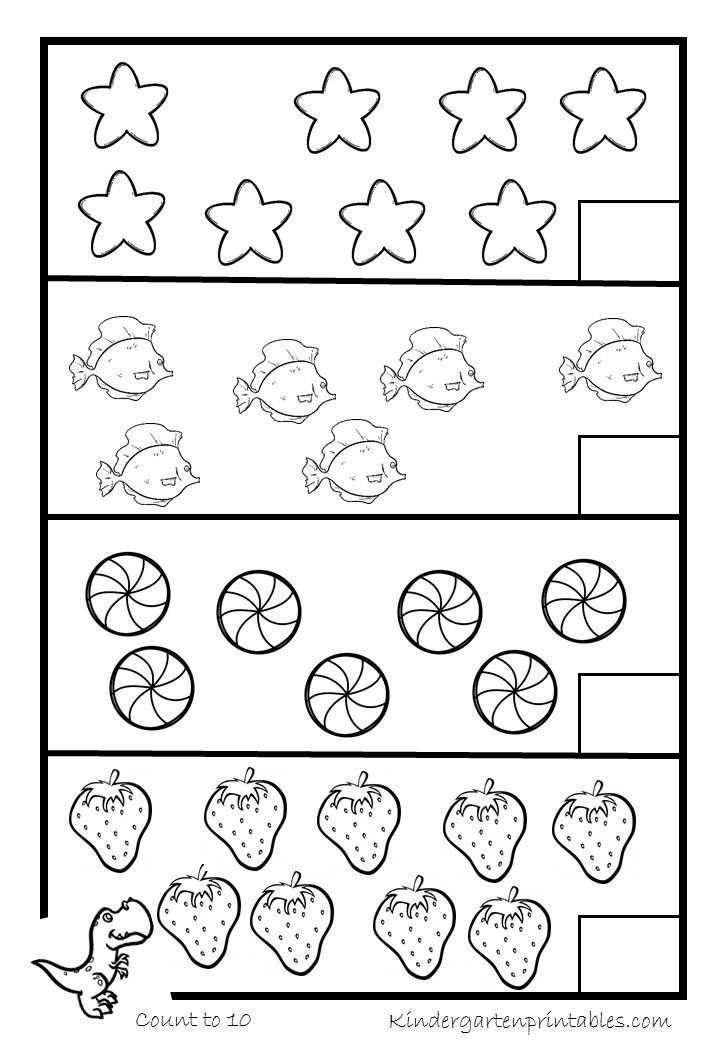 They learn forward rote counting by ones from any number less than 100. When counting by tens, they are expected to count only by decades like 10, 20, 30, …. etc. The kids practice kindergarten worksheets to develop fluency with number sequence.
They learn forward rote counting by ones from any number less than 100. When counting by tens, they are expected to count only by decades like 10, 20, 30, …. etc. The kids practice kindergarten worksheets to develop fluency with number sequence.
The kids learn to write numbers 0-20 in words. They also learn to represent a number by pictures or objects. For example, the kids can represent number 8 by 8 pictures or 8 tiles.
- Count to tell the number of objects in a set: The kids develop an understanding of numbers. They understand the relationship between the numbers and the quantities. They first learn one-to-one correspondence with numbers and objects. They connect one number with each object. They begin by counting objects in small sets.
The kids also understand the order irrelevance while counting. They understand that the number of objects in a set remains the same irrespective of the arrangement or the order in which the objects are counted.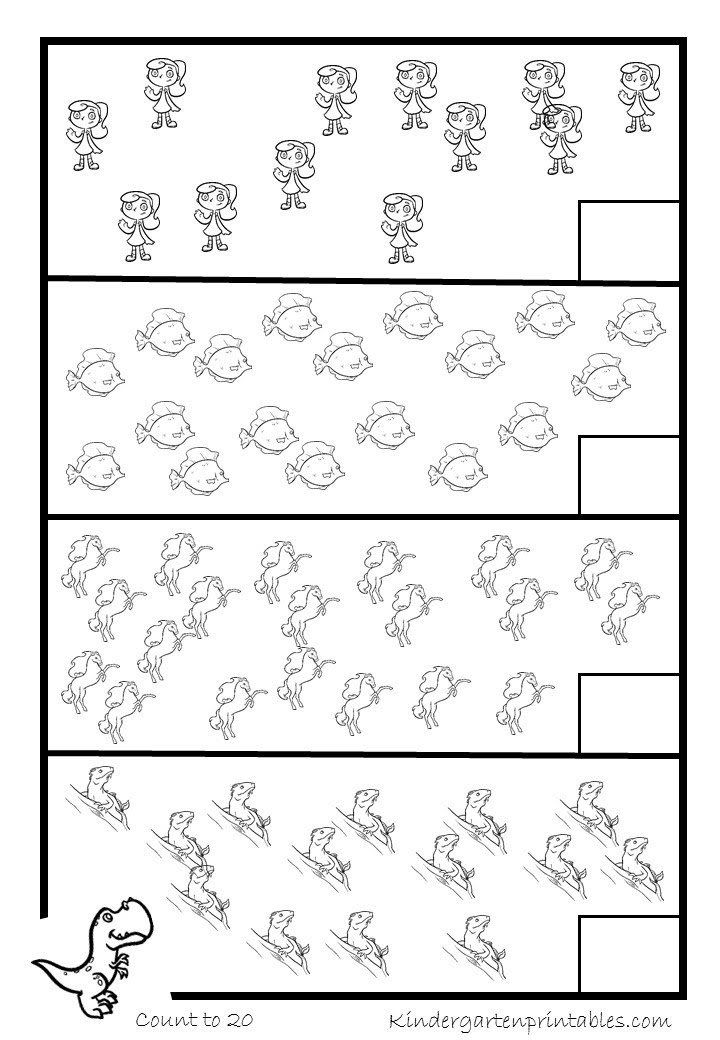 Also, they understand that each successive number is one quantity larger. The kids practice various counting worksheets to strengthen their skills.
Also, they understand that each successive number is one quantity larger. The kids practice various counting worksheets to strengthen their skills.
Counting strategies:
- Count out Loud: Counting out loud in everyday routine with kids can be fun way to develop fluency in counting. There are so many counting games that can be played in everyday routine. For example, asking kids to count the steps aloud while walking can develop fluency in counting. The games like counting crows sitting on a tree or counting coins can improve their counting skills.
- Touch and count: When asked to count a group of objects, the kids touch each object and say 1 each time. They may touch the objects randomly at first. With proper instructions, the kids learn to math counts in sequence. They touch each object and count 1, 2, 3,…..
- Count and Move: Another strategy to teach counting is to move the objects being counted to another place. This strategy eliminates the chances of double counting any object.
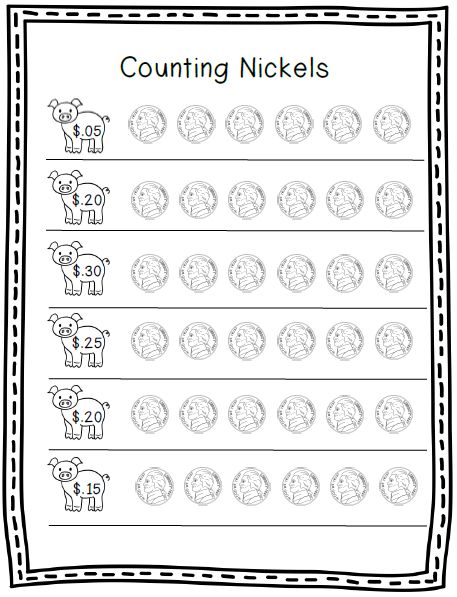
- Line up and count: In this strategy, the objects are lined up and the kids are asked to say the counting sequence while touching the objects from left to right or right to left.
- Counting on: This strategy enables the kids to count new objects without recounting the already counted objects. For example, give kids four coins and ask him/her to count them. Now, give him/her two more coins. By using counting on strategy, the kid will start counting coins from five, six, instead of counting coins from 1.
- Pattern Recognition & Creation: Understanding patterns is an important everyday math concept. The kids start learning and recognizing patterns at an infant stage. There are many toddler games based on pattern recognition. Understanding this form an important part of the early childhood education. The first type of patterns introduced at pre school are AB patterns. These are the patterns that involve two objects lined up in an alternating manner.
 For example, car bike car bike and so on. Gradually, the understanding of the math patterns grows among kids. They develop their skill from recognizing AB pattern to understanding ABC pattern and much more. The skills are further enhanced by practicing various pattern worksheets.
For example, car bike car bike and so on. Gradually, the understanding of the math patterns grows among kids. They develop their skill from recognizing AB pattern to understanding ABC pattern and much more. The skills are further enhanced by practicing various pattern worksheets.
This understanding enables kids to recognize the recurring math patterns in counting. When counting, they notice the recurring pattern of the digits from 0 to 9. This makes it easier for them to learn the long counting sequence up to billions and trillions.
- Sorting and Classifying to compare numbers: Sorting and classifying forms a part of preschool activities or kindergarten worksheets. These activities or worksheets develop logical reasoning skills which in turns develop comparing skills in the kids. While comparing two different sets of objects, for example, apple and oranges, the kids can be made to put all the apples in one group and all the oranges in another group. They may then be asked to arrange all the apples in one line and oranges in another line.
 Sorting and arranging objects in a line makes comparison easier. Sorting and comparing different objects in groups are some of the activities which form the base for understanding higher mathematical concepts. The kids develop skills to compare numbers presented to them in different ways. They compare number of objects in different sets to identify which set has fewer or lesser objects.
Sorting and arranging objects in a line makes comparison easier. Sorting and comparing different objects in groups are some of the activities which form the base for understanding higher mathematical concepts. The kids develop skills to compare numbers presented to them in different ways. They compare number of objects in different sets to identify which set has fewer or lesser objects.
Strategies for comparing numbers:
- Matching numbers
- Counting strategies
- Equal strategies
Manipulatives For Learning Counting
Learning Math concepts become fun when manipulatives are incorporated in the learning. The abstract concepts like counting and numbers are easier to understand through manipulatives. For example, the kids often get distracted when counting to 20 or higher numbers. This problem can be solved by coin counter. Giving 20 coin counters to kids for counting, he/she will likely use on-to-one correspondence and count all 20 counters without getting distracted.
These counters also proves beneficial in teaching sorting and pattern recognization to kids. For example, verbally telling patterns to the kids might confuse them. However, showing the pattern through coin counter makes it easier for them to understand and they are able to continue the same pattern.
Learning counting in a fun way
Counting the beans: Developing fluency in counting to 10.
Take 10 plastic cups and label them 1-10. Give a bowl filled with marbles to the kids and ask them to put marbles in each cup. The number of marbles in each cup should be same as the number labelled on them.
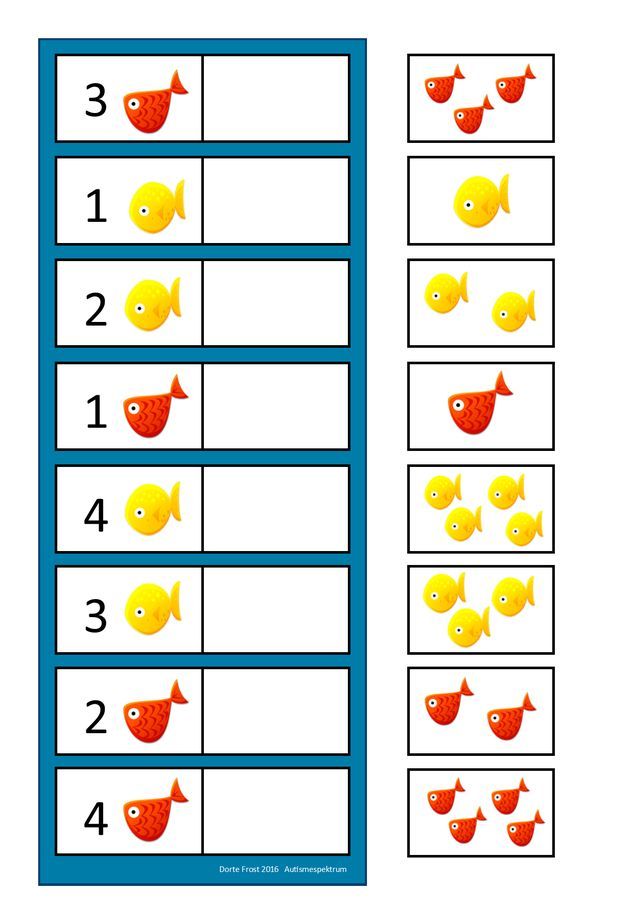
Memory matchup- Fish counts: This activity aims to develop number sense and skills to count to 10.
The game will have 20 cards. Of which 10 cards will have numerals from 1 – 10 and the other 10 cards will have pictures of fish from 1 – 10. The game is played by mixing up the cards and laying them in rows face down. The player 1 turn over any two cards, if the cards match, that is, the fish counts and the number on the cards are the same. He/She keeps the cards. If they do not match, they are turned back over. The players need to remember what was on each card and the place where they are. The game gets over when all the cards are matched. The player with the maximum number of match cards won the game.
He/She keeps the cards. If they do not match, they are turned back over. The players need to remember what was on each card and the place where they are. The game gets over when all the cards are matched. The player with the maximum number of match cards won the game.
Try SplashLearn for Free
Games with counting sticks for the development and education of children
Children, especially at preschool age, are very inquisitive. The task of adults is to help them cognize the world not only with the help of toys, natural phenomena, specific household items, but also with the help of abstract teaching aids, one of which are ordinary counting sticks.
The use of counting sticks in the mathematical development of preschool children
It is a mistake to think that with the help of these improvised means you can teach a child to count, and nothing more. Their task in the capable hands of parents is to develop children's thinking, namely:
- They help learn colors, add and study geometric shapes, construct intricate castles, and solve logic problems.
 Therefore, counting sticks can be an excellent teaching aid when organizing homework.
Therefore, counting sticks can be an excellent teaching aid when organizing homework. - With this simple and multifunctional manual, you can study the order of numbers and their composition, the concepts of "shorter-longer", "greater-less", "higher-lower".
- It is also worth listening to the opinion of psychologists who simply insist that, along with fine motor skills, games and activities with these counting elements help to develop in a preschooler:
- intelligence;
- independence;
- imagination and creative thinking;
- attention;
- interest in research and learning;
- activity;
- the will to win;
- purposefulness;
- persistence;
- independence;
- ability to plan, control and evaluate own activities;
- concentration.
Ways to use the didactic aid in the fun of toddlers
It is very easy to involve a toddler in work with sticks. The main thing is to be interested! The most familiar and main activity for children from 2 to 6 years old is a game. It is in the form of a game that you need to conduct classes, coming up with an interesting plot and even distributing roles. Set the rules from the very beginning and let the little one understand the ultimate goal of the game. It can be anything, depending on what you need to teach in games with sticks. For example, fold a figure out of sticks or arrange them by color in separate boxes, lay out a name or count how many counting elements a house consists of. Thus, at home, counting sticks will become an excellent didactic game.
The main thing is to be interested! The most familiar and main activity for children from 2 to 6 years old is a game. It is in the form of a game that you need to conduct classes, coming up with an interesting plot and even distributing roles. Set the rules from the very beginning and let the little one understand the ultimate goal of the game. It can be anything, depending on what you need to teach in games with sticks. For example, fold a figure out of sticks or arrange them by color in separate boxes, lay out a name or count how many counting elements a house consists of. Thus, at home, counting sticks will become an excellent didactic game.
Important! Interest in the correct solution of the set task stimulates the child to active brain activity and overcoming difficulties in the work begun. The kid will especially try if someone else does the same work next to him - children love to compete and show the will to win.
Stick games for the little ones (9 months +)
When and how to organize didactic games with counting sticks at home? Experts emphasize: at an early age, when kids are just starting their journey to learning objects, counting sticks can be used as a game material, learn colors with their help, design figures of various sizes and shapes, and use them in non-standard drawing.
Starting age for counting sticks is 9 months. The kid already knows how to grab objects with two fingers - forefinger and thumb, which means that it's time to develop fine motor skills of the hands. The following can be an excellent exercise for this:
- Take a small box or case, cut an oblong slot in them with a knife or scissors, and show the little one that you can put sticks into it one at a time. Toddlers will do an excellent job with the task, because at this age they really like to push objects through holes.
- We sculpt a hedgehog from dough and offer the little one, under the strict guidance of mother, to stick sticks like needles. Such an action is still difficult for a baby, so mother's hand will become an extension of the child's hand.
Important! Small children must not be left unsupervised when performing tasks with small parts. Indeed, in addition to the hole in the box, the child can, without hesitation, send one of the counting elements into his mouth.
What can be offered to a baby aged 1 to 1.5 years
1. Young children are already capable of learning concepts such as color, size, length. Therefore, armed with a didactic (training) manual, it's time to offer them such games with sticks :
- Name the color of all available sticks.
- Collect elements of a certain color.
- Find sticks with the same length (Kuizener sticks).
- Collect one stick of each color.
- Find the shortest and longest stick and name their colors (Kuizener sticks).
- Arrange the sticks in a row, alternating two colors, eg yellow and red.
- Choose any stick and ask the child to the left of it to lay out all the sticks that are shorter than the selected one, and to the right - all those that are longer. You can make it easier to solve the puzzle by asking leading questions. For example, show two sticks and ask if they are different or the same. You can complicate the question of how they differ from each other (color, length) or what is their similarity.

2. At an early age, children begin to be interested in and learn about the properties of plasticine. Therefore plasticine modeling for children can be both an activity and a game with counting sticks. Sticks in this case are auxiliary material: to play the role of a stem for a flower, legs for a fungus or a trunk for a tree; serve as legs-handles for a plasticine man or a chimney for a house.
3. Similarly, you can organize non-standard drawing with sticks for kids. For example, laying out various objects (road, cars, houses, flowers, men and animals) on the floor or table, you can create whole pictures and toy cities. Such an activity will surely arouse the interest of an inquisitive kid, will develop imagination, will make you feel not only a member, but also the creator of an exciting game.
Didactic games from 2 to 4 years old
During this period, preschool children make a significant breakthrough in the field of self-knowledge and intelligence development. There is a formation of speech, contact with peers is easily established, the baby acts purposefully. He is interested in drawing, designing, which are increasingly based on children's imagination. It's time to channel these abilities in the right direction and deepen the knowledge about the purpose of counting sticks. Suitable for this will be the following games with sticks, which are widely used in kindergarten.
There is a formation of speech, contact with peers is easily established, the baby acts purposefully. He is interested in drawing, designing, which are increasingly based on children's imagination. It's time to channel these abilities in the right direction and deepen the knowledge about the purpose of counting sticks. Suitable for this will be the following games with sticks, which are widely used in kindergarten.
Where is less?
Place the counting sticks opposite each other in two rows, one of which will have one fewer number of counting sticks. The preschooler must show which row has fewer elements and which has more. They complicate the puzzle with the question: “What needs to be done so that the number of sticks becomes the same?”.
Task with an asterisk: ask the child to independently lay out two rows with the same number of elements, and so that there are one or two less of them in one row.
Repeat drawing
You will need a sheet of paper with an image of an object understandable to the child (a house, sweets, butterflies, Christmas trees, etc.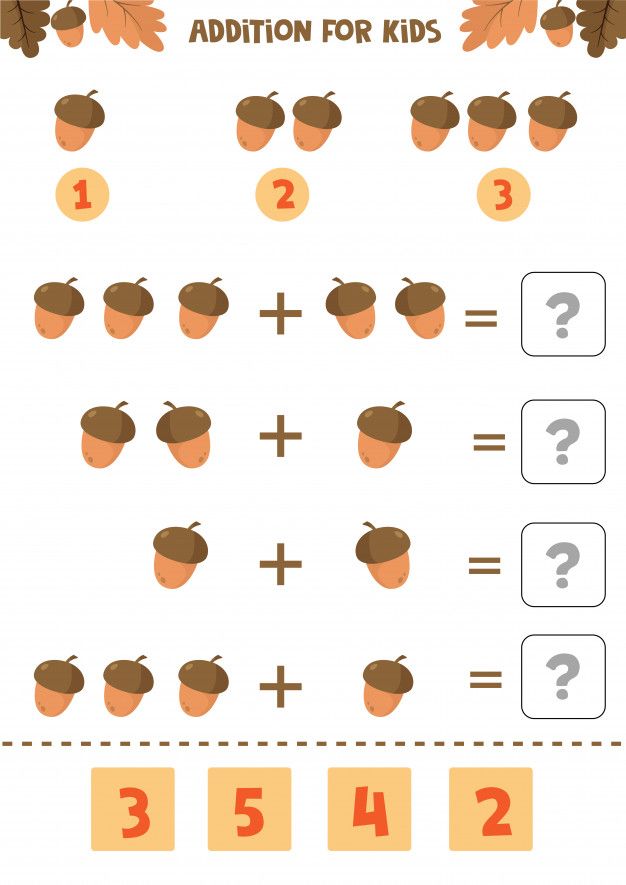 ), made in two or three colors. The kid should lay out this drawing with chopsticks, repeating the colors on paper. At the end, ask the preschooler to name the colors with which he created his picture.
), made in two or three colors. The kid should lay out this drawing with chopsticks, repeating the colors on paper. At the end, ask the preschooler to name the colors with which he created his picture.
This exercise helps to learn colors, develop fine motor skills of children's fingers, as well as creative imagination.
Building and counting
An adult lays out some simple figure from the didactic material, for example, a triangle, and asks the student to repeat it. After the kid copes with the task, you need to voice the name of the figure and ask him how many elements were needed to build this triangle.
Next, you can build a square, a rhombus, a rectangle, as well as any other objects with the same conditions of the problem. For deeper knowledge, you can ask what geometric figure the roof of a house, a window, a truck body, etc., looks like.
The task with an asterisk is to ask an adult to divide a rectangle of 6 sticks into two equal squares using one.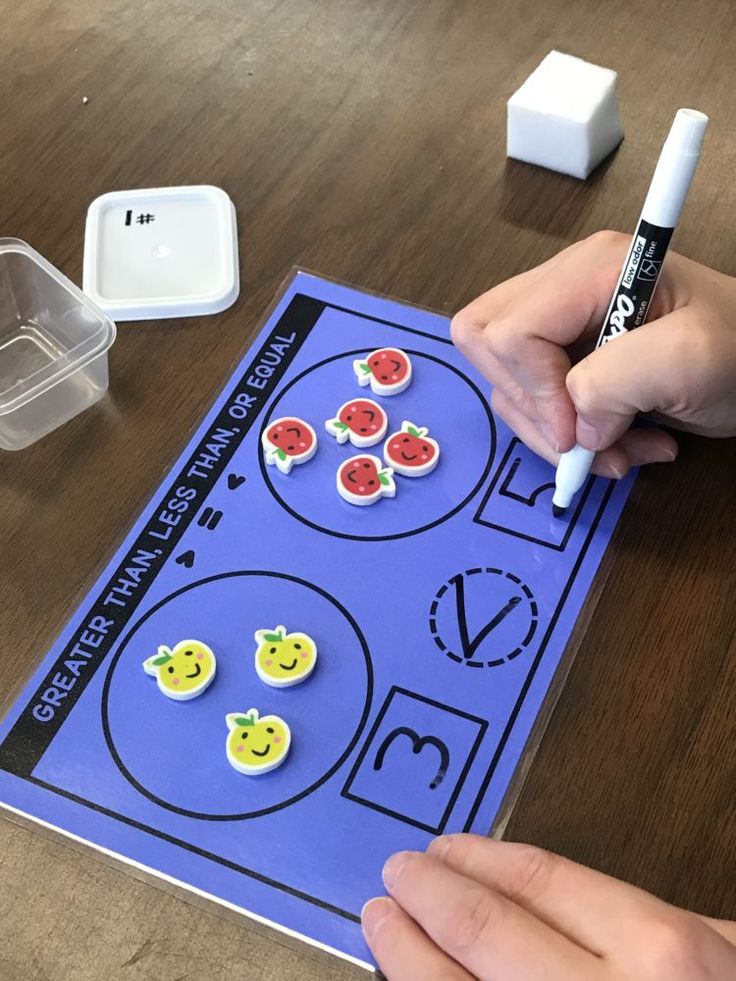 Or with one stick turn a square into two triangles.
Or with one stick turn a square into two triangles.
The purpose of this game exercise is to develop spatial, logical and creative thinking in children.
Games for older preschoolers
Classes with children aged 5-7 involve more thorough preparation for their schooling. This will require not only perseverance, but also basic knowledge in the field of reading and mathematics, the ability to generalize, highlight, compare. Of course, you can not strain the child with any tasks, because everything you need will be taught at school in due time. But if a preschooler has an interest in learning, he should not be denied self-development. Using sticks for counting, you can invite him to perform the following exercises according to ready-made schemes. This is how games with counting sticks are played in kindergarten.
Complete the picture
It is necessary to show the child a diagram-drawing of half of an object depicted on paper. The task is to complete the picture symmetrically, using the same colors and proportions.
Draw numbers and letters
Use chopsticks to lay out the names of letters (if it comes easy, then simple words), as well as numbers within ten. With good success, you can do it at speed with one of your peers.
What numbers are made of
When a preschooler already knows what the numbers look like, you can offer him to lay out each one with the help of sticks of two colors, thereby giving the concept of the composition of the number. So, the number 5 can be laid out from two red and three green sticks or from one yellow and four red ones.
Count!
Easy option: use sticks to lay out an example (as an option, two sticks + three sticks). The child must be asked to count and give the correct answer by laying out the required number of elements after the equal sign. If the kid knows the numbers, then you can lay out the expression with their help.
Psychologists recommend
- Parents themselves determine the age at which children should be involved in activities with a set of counting sticks.
 But experts still recommend not to load the baby's brain too early. It is optimal to start classes at about three years of age.
But experts still recommend not to load the baby's brain too early. It is optimal to start classes at about three years of age. - At first, it is worth giving the baby to get acquainted with the didactic material - let him play, put figures, pyramids. So it will be easier for a small student to study the shape and color of the parts, to feel the material from which they are made. Only in this way will children be able to conclude that some sticks are shorter than others, to catch their color differences.
- The beginning of classes must be made playful - the child should not feel pressure from adults, otherwise in the future he will develop an aversion to mathematics. The kid must come to all the conclusions and answers himself - it is independent thinking that will make his knowledge strong and durable. So say experts in the field of pedagogy.
Science has proven that the development of a child's speech and mental activity directly depends on the fine motor skills of the hands.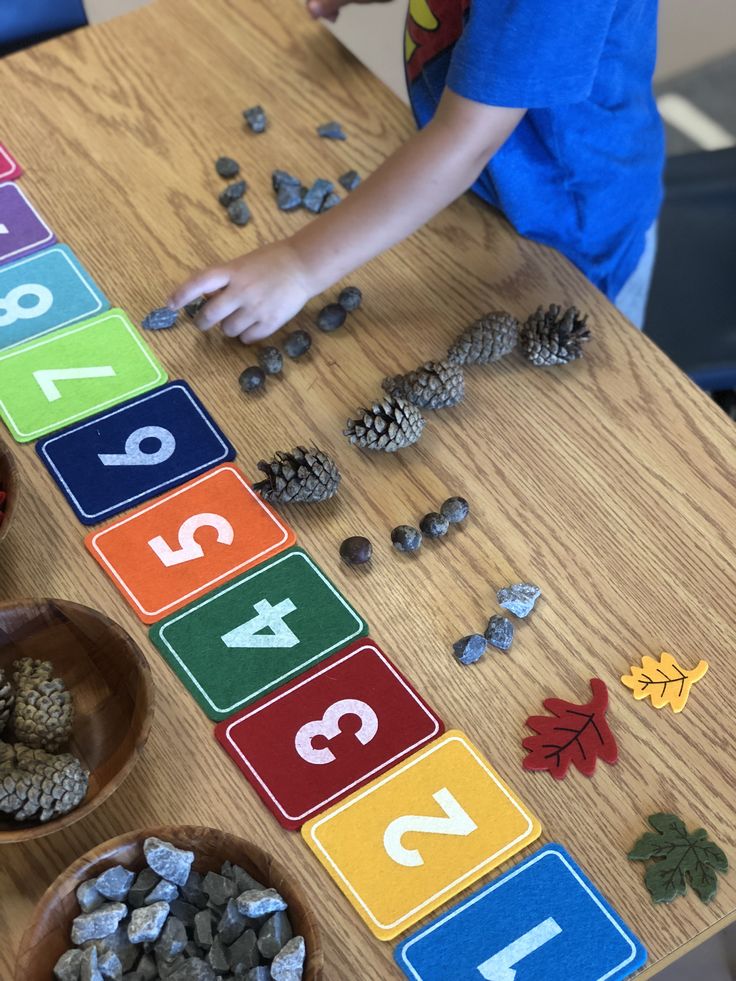 With the training of fingers, the hand of the future student is preparing for writing. Therefore, it is extremely important to help him in this with the help of educational games, which include games with counting sticks. They are a simple and at the same time a universal tool for developing hands and stimulating intellectual abilities at the same time.
With the training of fingers, the hand of the future student is preparing for writing. Therefore, it is extremely important to help him in this with the help of educational games, which include games with counting sticks. They are a simple and at the same time a universal tool for developing hands and stimulating intellectual abilities at the same time.
Counting sticks are easy to use. To show concern for the development of the mental abilities of a preschooler, parents do not need to reinvent the wheel. After all, everything ingenious is simple.
Didactic games with counting sticks | Card file (younger group):
COUNTING STICKS FOR CHILD DEVELOPMENT
Children, especially at preschool age, are very inquisitive. The task of adults is to help them cognize the world not only with the help of toys, natural phenomena, specific household items, but also with the help of abstract teaching aids, one of which are ordinary counting sticks.
THE USE OF COUNTING STICKS IN THE MATHEMATICAL DEVELOPMENT OF PRESCHOOL CHILDREN
It is a mistake to think that with the help of these improvised means you can teach a child to count, and nothing more.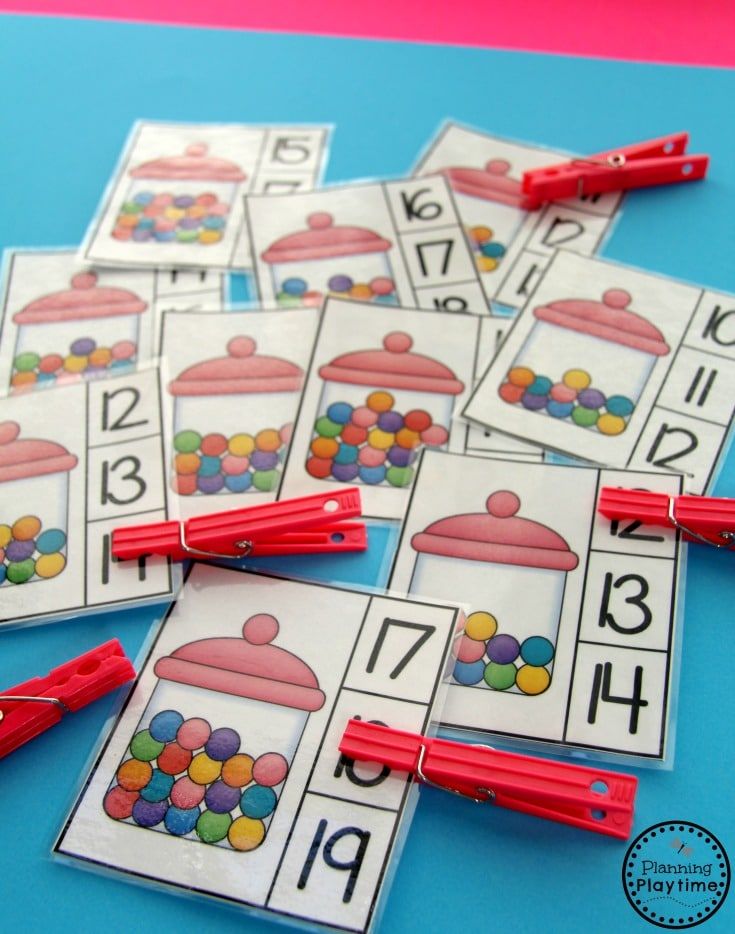 Their task in the skillful hands of parents, and then educators, is to develop children's thinking, namely: they help to learn colors, add and study geometric shapes, design intricate castles, and solve logical problems. Therefore, counting sticks can be an excellent teaching tool for organizing homework, and then didactic games in kindergarten.
Their task in the skillful hands of parents, and then educators, is to develop children's thinking, namely: they help to learn colors, add and study geometric shapes, design intricate castles, and solve logical problems. Therefore, counting sticks can be an excellent teaching tool for organizing homework, and then didactic games in kindergarten.
With this simple and multifunctional manual, you can study the order of numbers and their composition, the concepts of "shorter-longer", "more-less", "higher-lower".
It is also worth listening to the opinion of psychologists who simply insist that, along with fine motor skills, games and activities with these counting elements help to develop a preschooler:
- intelligence;
- independence;
- imagination and creative thinking;
- attention;
- interest in research and learning;
- activity;
- the will to win;
- purposefulness;
- persistence;
- ability to plan, control and evaluate own activities;
- concentration.

OPTIONS FOR USE OF THE DIDACTIC TOOL IN CHILDREN'S FUN
It is very easy to involve a child in work with sticks. The main thing is to be interested! The most familiar and main activity for children from 2 to 6 years old is a game. It is in the form of a game that you need to conduct classes, coming up with an interesting plot and even distributing roles. Set the rules from the very beginning and let the child understand the ultimate goal of the game. It can be anything, depending on what you need to teach in games with sticks. For example, fold a figure out of sticks or arrange them by color in separate boxes, lay out a name or count how many counting elements a house consists of. Thus, at home, counting sticks will become an excellent didactic game.
Important! Interest in the correct solution of the task at hand stimulates the child to active brain activity and overcoming difficulties in the work begun. The child will especially try if someone else does the same work next to him - children love to compete and show the will to win.
DIDACTIC GAMES FROM 2 TO 4 YEARS
During this period, preschoolers make a significant breakthrough in the field of self-knowledge and intelligence development. There is a formation of speech, contact with peers is easily established, the child acts purposefully. He is interested in drawing, designing, which are increasingly based on children's imagination. It's time to channel these abilities in the right direction and deepen the knowledge about the purpose of counting sticks. Suitable for this will be the following games with sticks, which are widely used in kindergarten.
WHERE IS LESS?
Place the counting sticks opposite each other in two rows, one of which will have one fewer number of counting sticks. The preschooler must show which row has fewer elements and which has more. They complicate the puzzle with the question: “What needs to be done so that the number of sticks becomes the same?”.
Task with an asterisk: ask the child to independently lay out two rows with the same number of elements, and so that there are one or two less of them in one row.
REPEAT PICTURE
You will need a sheet of paper with an image of some object understandable to the child (house, sweets, butterflies, Christmas trees, etc.), made in two or three colors. The kid should lay out this drawing with chopsticks, repeating the colors on paper. At the end, ask the preschooler to name the colors with which he created his picture.
ORAL ACCOUNT. ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION
Significant increase in intellectual potential
Trouble-free teaching of exact disciplines
Increases the speed and quality of perception of information
The ability to quickly count in the mind adds self-confidence
Skills of mental arithmetic - for life
The percentage of people who perfectly count in the mind is higher among managers than among their subordinates
Such an exercise helps to learn colors, develop fine motor skills of children's fingers, as well as creative imagination.
BUILDING AND COUNTING
The teacher lays out some simple figure from the didactic material, for example, a triangle and asks the child to repeat. After the kid copes with the task, you need to voice the name of the figure and ask him how many elements were needed to build this triangle.
After the kid copes with the task, you need to voice the name of the figure and ask him how many elements were needed to build this triangle.
Next, you can build a square, a rectangle, as well as any other objects with the same conditions of the problem. For deeper knowledge, you can ask what geometric figure the roof of a house, a window, a truck body, etc., looks like.
The task with an asterisk will be the teacher's request to divide a rectangle of 6 sticks into two equal squares using one. Or with one stick turn a square into two triangles.
The purpose of this game exercise is to develop spatial, logical and creative thinking in children.
WHEN TO START
Parents themselves determine the age at which children should be involved in activities with a set of counting sticks. But experts still recommend not to load the baby's brain too early. It is optimal to start classes at about three years of age.
First, let the child get acquainted with the didactic material - let him play, put figures, pyramids.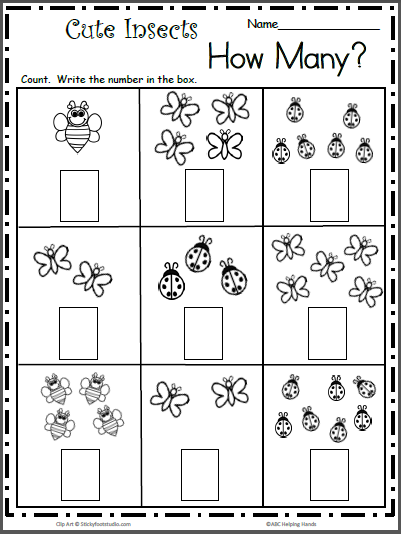 So it will be easier for the pupil to study the shape and color of the parts, to feel the material from which they are made. Only in this way will children be able to conclude that some sticks are shorter than others, to catch their color differences.
So it will be easier for the pupil to study the shape and color of the parts, to feel the material from which they are made. Only in this way will children be able to conclude that some sticks are shorter than others, to catch their color differences.
The beginning of “classes” must be made playful - the child must not feel pressure from adults, otherwise he will develop an aversion to mathematics in the future. The kid must come to all the conclusions and answers himself - it is independent thinking that will make his knowledge strong and durable. So say experts in the field of pedagogy.
Science has proven that the development of a child's speech and mental activity directly depends on the fine motor skills of the hands. With the training of fingers, the hand of the future student is preparing for writing. Therefore, it is extremely important to help him in this with the help of educational games, which include games with counting sticks. They are a simple and at the same time a universal tool for developing hands and stimulating intellectual abilities at the same time.