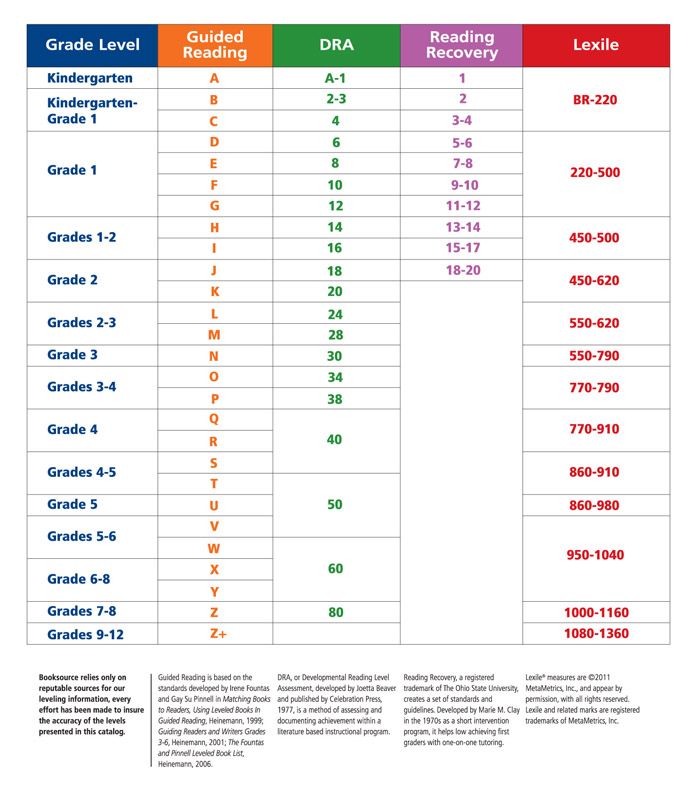
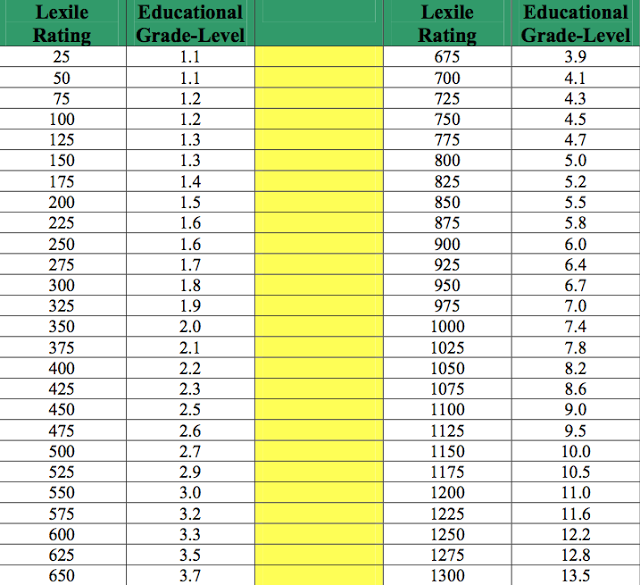
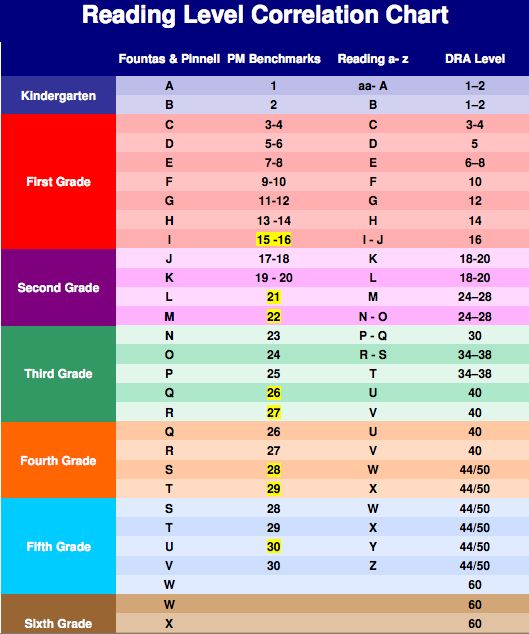
Determining lexile levels
What is Lexile measure? | EdWords
What is Lexile
® Measure?The Lexile® Framework for Reading is a scientific approach to measuring reading ability and the text complexity of reading materials. The Lexile scale is like a thermometer, except rather than measuring temperature, it measures a text’s complexity and a reader’s skill level.
When these two measures match, a targeted reading experience occurs. Students who read at the right levels experience more reading achievement and growth. Renaissance partners with the creators of the Lexile Framework, MetaMetrics®, Inc., to bring Lexile measures into Renaissance Accelerated Reader 360® and Renaissance Star Reading®.
How can Lexile measures guide students to appropriate books and articles?
The Lexile Framework assesses both sides of reading development: the reader and the material being read. When a student chooses texts 100L below to 50L above his or her reported Lexile reader measure, a targeted reading experience can occur. The Lexile reader measure describes an individual’s reading ability. The Lexile text measure describes the semantic and syntactic features of a book, article, or text. Both Lexile reader measures and Lexile text measures are reported on the Lexile scale and are represented by a number followed by the letter “L” (i.e., 1000L).
Lexile measures are quantitative measures that provide insights into the difficulty of the words in a book or article. It is, however, only one of three components associated with text complexity. The other two are qualitative measures (i.e., content, themes, and maturity level) and reader/task considerations. Lexile measures do NOT measure age appropriateness, the book quality, the book’s theme, or other characteristics of the book. For example, The Grapes of Wrath is a rather simple read, but it may have a theme that is inappropriate for a certain age group.
All books with Accelerated Reader 360 quizzes include an ATOS level, a Lexile measure, and an interest level (i.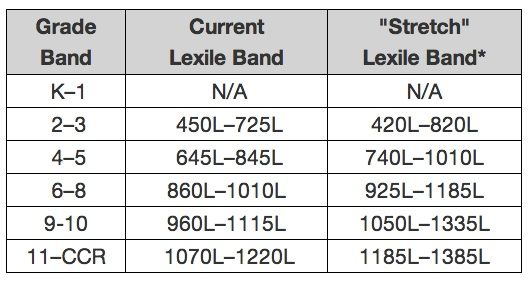 e., lower grades [K–3], middle grades [4–8], middle grades plus [6–8], and upper grades [9–12]. Teachers, librarians, and parents may want to consider all three components when matching students with books.
e., lower grades [K–3], middle grades [4–8], middle grades plus [6–8], and upper grades [9–12]. Teachers, librarians, and parents may want to consider all three components when matching students with books.
ATOS and Lexile measures are both valid, reliable measures of text complexity that provide a basis for matching students to reading materials. As with all readability formulas, the resulting value is an estimate of the text’s understandability.
How is a Lexile measure obtained?
To obtain a Lexile measure for a book or article, text is split into 125-word slices. Each slice is compared to the nearly 600-million word Lexile corpus, which is taken from a variety of sources and genres, and the words in each sentence are counted. The lengths of sentences and the difficulty of the vocabulary are examined. These calculations are put into the Lexile equation. Then, each slice’s resulting Lexile measure is applied to the Rasch psychometric model to determine the Lexile measure for the entire text.
Select your school
Searching for schools in ZIP code ---
Loading schools…
Don't see your school?
Lexile and Quantile Measures
Lexile Measures in Nevada
The Lexile Framework® for Reading, commonly referred to as the Lexile Framework, has been linked with the Smarter Balanced summative assessment in English Language Arts for grades 3-8. In addition, the Lexile Framework been linked to the SAT and ACT. With Lexile measures, educators and parents can spur and support student learning.
What Is a Lexile Measure?
There are two kinds of Lexile measures: Lexile reader measures and Lexile text measures. Lexile reader measures describe how strong a student’s reading is. Lexile text measures describe how difficult, or complex, a text like a book or magazine article is. Lexile measures are expressed as numbers followed by an “L” (for example, 850L), and range from below 0L for beginning readers and text to above 1600L for advanced readers and text. Comparing a student’s Lexile measure with the Lexile measure of what they are reading helps gauge the “fit” between a student’s ability and the difficulty of text.
Comparing a student’s Lexile measure with the Lexile measure of what they are reading helps gauge the “fit” between a student’s ability and the difficulty of text.
Access communications resources including the Lexile parent guide, educator guide, librarian guide, Lexile map, Lexile infographic and video at Lexile Educator Resources and Lexile Parent Resources.
- Lexile Educator Resources
- Lexile Parent Resources
Lexile Tools
- The Lexile Hub
The new Hub platform provides access to all of the free Lexile tools that support student learning and growth in reading
- Lexile Find a Book
Search among over half a million books using the Find a Book book browser that:
- Offers previews of challenging words and their definitions for each book.
- Identifies the Lexile level and vocabulary by chapter for over 1,600 popular books.
- Creates and manages personal book lists that can be shared.
- Searches by a student’s Lexile measure or range, grade level or interests.
- Lexile Analyzer
Paste or type in text of 1,000 words or less to discover:
- The Lexile range for the text.
- Early Reading Indicator information for texts 650L and below.
- Lists of similar books.
- Challenging words highlighted in the text along with their definitions, parts of speech, example sentences.
- Toggle to Spanish to paste or type text in Spanish and get a Lexile range.
- Lexile Word Lists
Create your own customized lists of consequential words from a collection of 40 million words based on general and academic domain 1-12 vocabulary. Lists can be downloaded and printed.
- Lexile Career Database
Identify the Lexile level associated with the reading demands of a particular career in this new tool.
- Lexile Grade Level Charts
See how a large sample of students in grades K1-12 who were administered tests that reported Lexile measures performed based on this 2010-2016 research.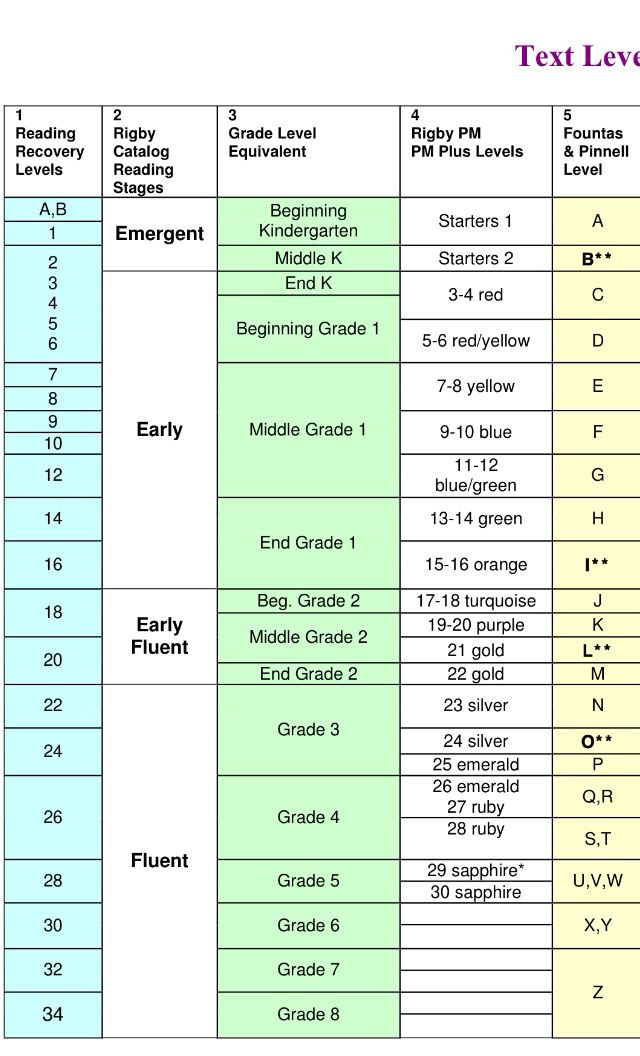 Interactive charts are provided for descriptive purposes only and are not intended to be interpreted as state performance standards.
Interactive charts are provided for descriptive purposes only and are not intended to be interpreted as state performance standards.
- Lexile Growth Planner
Chart a student’s reading growth across different annual state assessments and forecast future growth. With the Growth Planners, you can:
- Forecast college and career readiness with Lexile measures.
- Compare individual student results to national student performance.
- Explore career options along with expected reading demands.
- View national, state and regional career information.
- Access resources to support growth in reading.
- Lexile Measures Manager
Determine a student's optimal reading measure when two assessments have resulted in significantly differing Lexile measures.
Resources
- Educator Guide
- Lexile Librarian Guide
- Spanish Lexile Measures for Reading
- Lexile Map
- Compare Lexile Measures With Grade Levels
- Lexile Parent Guide
2.
 Vocabulary and other levels of language
Vocabulary and other levels of language The language as a whole is hierarchical "system of systems" , located not in the same plane, but as if built on top of each other according to the types of units that are available in this system.
Main types units - phoneme, morpheme, word, sentence . They correspond to four main levels (tiers) distinguished in the language system: phonological, morphological, lexical and syntactic .
All levels located within the level model language system from below up. Any unit of language is related to units lower level in its design and with higher-level units according to its function .
In the hierarchy of languages levels lexical level relies on morphological and precedes by syntactic . In accordance with this, morphemes, units underlying, morphological level, are means of word formation, and words - means of registration sentences, higher-level units.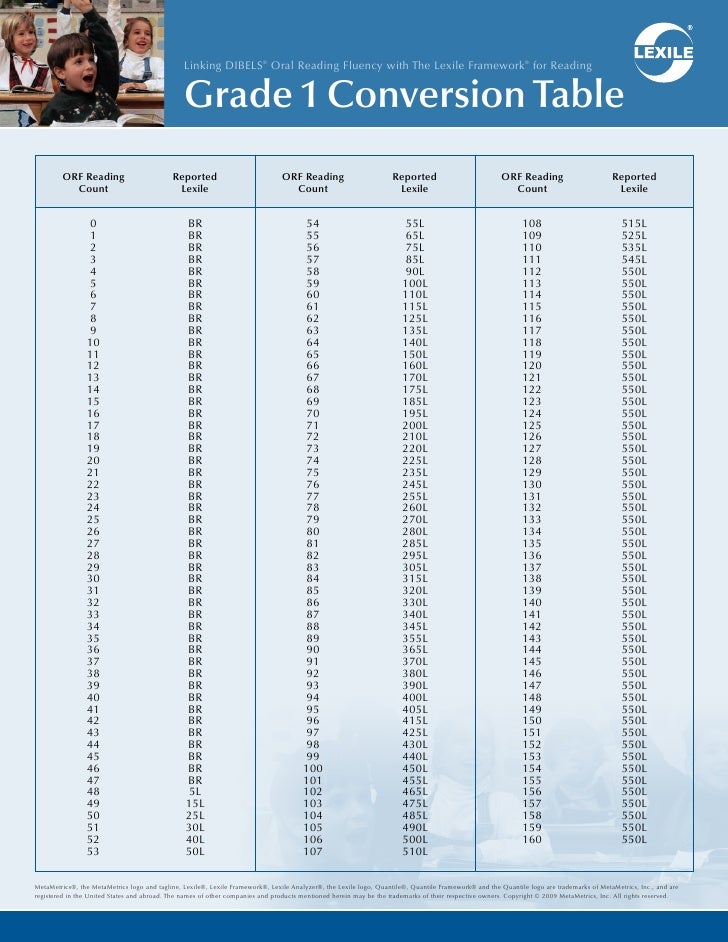
Word fulfills the entirety of its functions only in sentence, just like a morpheme, only within the word. From here arises the possibility of at least tripartite approach to the word: 1) as a unit lexical level;
2) from the side morphology - as a complex of morphemes;
3) side syntax - as an integral part suggestions.
N-r, communion cracked (over-tres-well-t-th)
1) as a unit lexical system has the main value "s small, shallow crack" , and also portable - "rattling, trembling" (about the sound of the voice), etc.
2) in plan morphologically this word is characterized by belonging to a part of speech ( p. or app name ) and lexical-semantic category ( relative ), and also as a derivative word formed prefix way from "cracked".
3) syntax a word can be characterized only in sentence, cf: Cracked the bell struck once (definition) and Right the bottom corner of the board was cracked (predicate).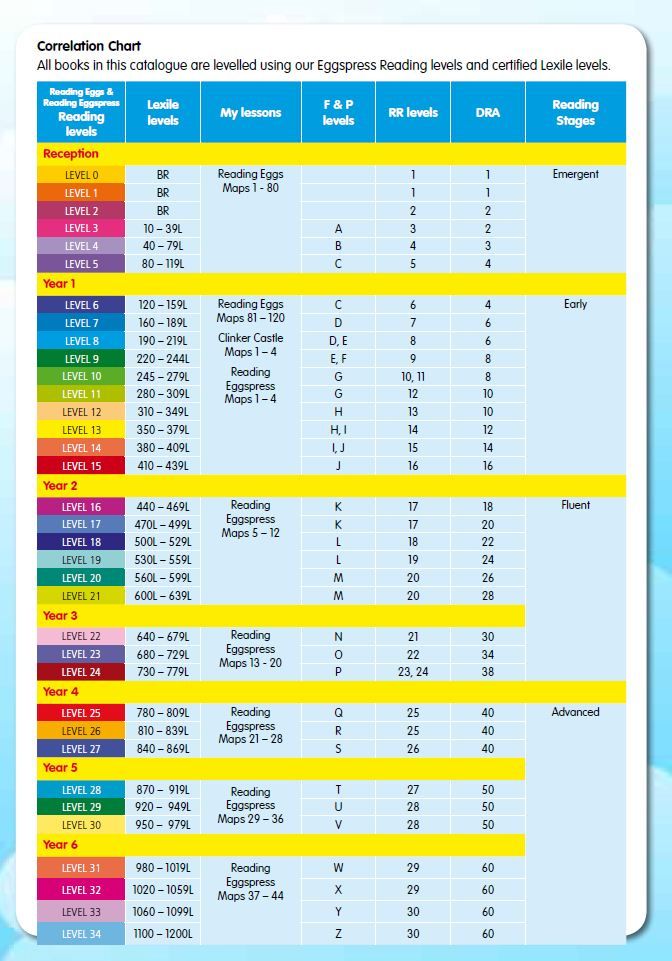
Staying united a real object, a word in each of of these sections of linguistics is a special subject of study, but rarely possible isolation within same language level.
Various vocabularies fix a different number of words (Written by S.I. Ozhegov - 57,000, 1997 - 80,000; sl. D.N. Ushakov - more than 80,000). Already these figures speak of one of the most significant vocabulary features compared to other areas of the language: with limited the number of phonemes, a foreseeable number inflectional affixes language has huge number of items objects and phenomena of real reality.
First in the vocabulary turn reflects the changes that occur in the life of society, i.e. vocabulary has permeability .
in the language all the time new words are included; some long ago existing words begin to apply to indicate new items and phenomena ( nr, foreman ), individual words are being phased out from the language, etc.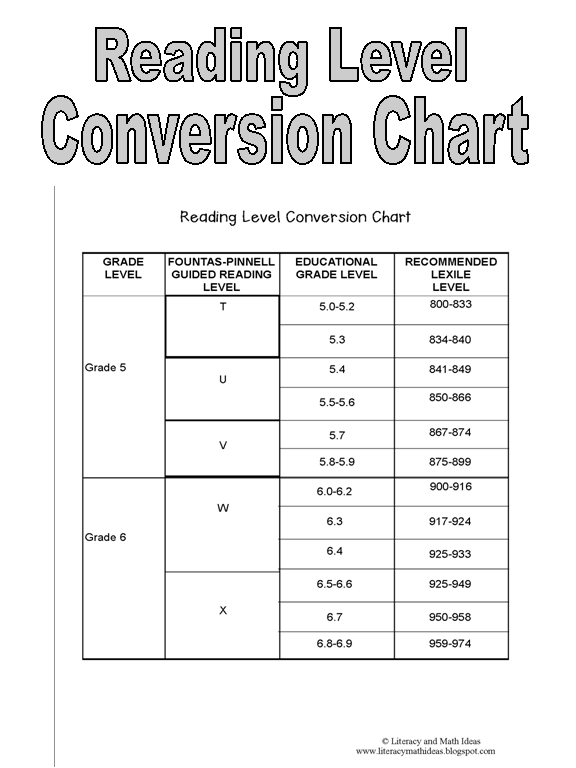 ( Solicitor ).
( Solicitor ).
All this causes mobility vocabulary (we can't answer the question how much is in the language in this or that moment of words)
Vocabulary is characterized not only mobility, but also known uncertainty, "blurring" of its borders : not all new words, for example, found in colloquial speech are the real treasure literary language. However, not always it is possible to say with certainty which of these neoplasms are already "included in literary language", and which ones remain outside of it.
Another feature vocabulary: it is in the vocabulary that are reflected in first line contacts between various peoples and in the vocabulary is concentrated that is common to many different languages. These are the so-called international words , most often based on Greek and Latin roots and included in the whole a number of languages, such as revolution, socialism, radio, photography, etc.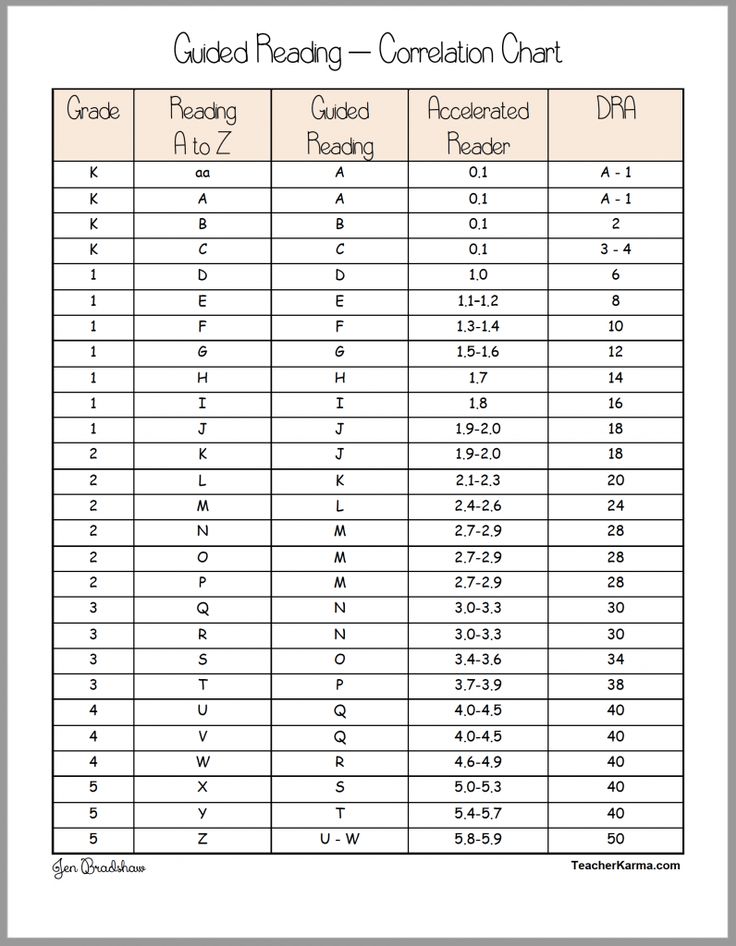
So the vocabulary characterized by:
-
multiplicity its constituent units,
-
variability composition
-
permeability structures
-
"blur" borders.
All these features due to the fact that it is in the vocabulary find the most direct and immediate reflection of the phenomenon of the environment reality, which in the lexical value fixes the results collective experience of people, results knowledge of the world.
European Language Proficiency Levels
(A1) - Beginner
(A2) - Lower Intermediate
(B1) - Intermediate
(B2) - Upper Intermediate
(C1) - Advanced
(C2) - Professional
There are two main recognized English language proficiency scales: International and European. The proposed table gives a description of each of the levels and shows the correspondence between the levels according to the International and European classification.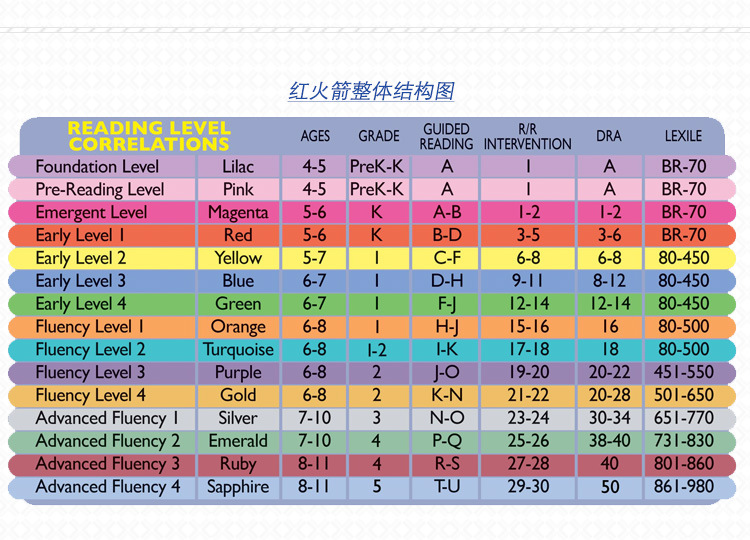
A2
Prescribing level
Below average
(Pre-Intermediate)
You can tell about your family, your family, their family , season…). You understand the texts of advertisements, announcements at the airport, store, inscriptions on products, postcards, you know how to write personal and business letters. Read and retell not very difficult texts.
B1
Threshold level
Average
(Intermediate)
You can understand what is being discussed in most radio and television and television programs about current events. You know how to express your own opinion, justify your views, retell the content of what you read or see, conduct personal and business correspondence of medium complexity, read adapted literature in a foreign language.
B2
Threshold advanced level
higher than the average
(UPPER -intermediate) 9000
You have owns the conversational language in various situations (from the comments) language.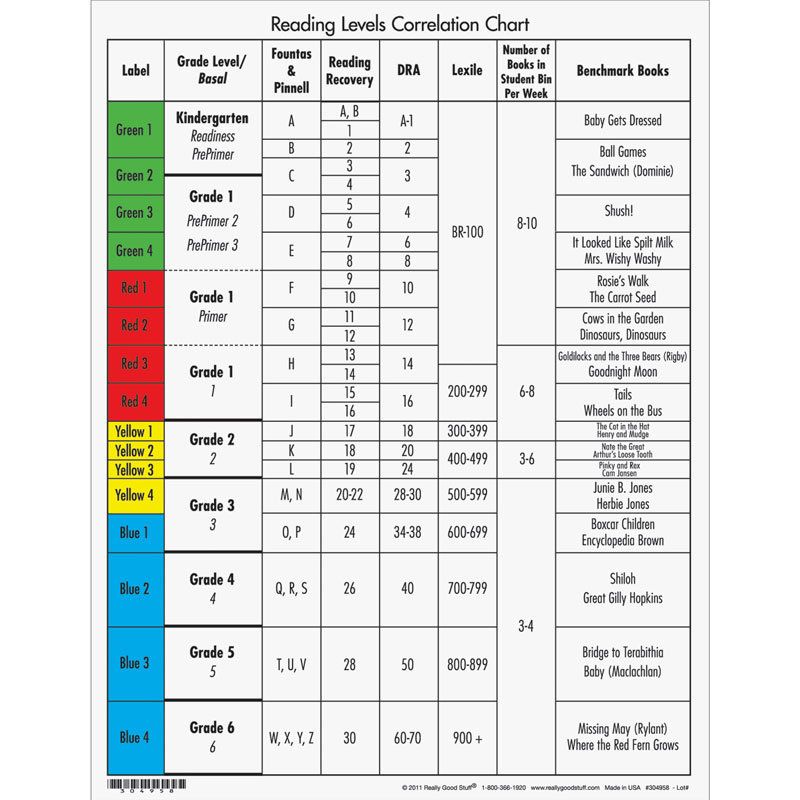 You can speak almost clearly and in detail on a wide range of issues, explain your point of view on an important issue, giving arguments for and against. You read non-adapted literature in a foreign language, you know how to retell the content of complex texts.
You can speak almost clearly and in detail on a wide range of issues, explain your point of view on an important issue, giving arguments for and against. You read non-adapted literature in a foreign language, you know how to retell the content of complex texts.
C1
The level of professional ownership
Advanced (Advanced)
You understand the variable detailed texts and you can identify the implications contained in them. in the choice of words to express their thoughts. Your speech is distinguished by a variety of language means and the accuracy of their use in situations of everyday, educational or professional communication. You can write clear, logical, detailed messages on complex topics.
C2
Providing level
Professional
(Proficiency)
You can freely understand any kind of oral information, you can freely understand any oral information. present it in the form of a clearly reasoned coherent message. You can express your thoughts fluently and clearly, even on complex issues, while conveying the subtlest shades of meaning.
present it in the form of a clearly reasoned coherent message. You can express your thoughts fluently and clearly, even on complex issues, while conveying the subtlest shades of meaning.
More information about the European scale can be found on the website of the Council of Europe at (in English): http://www.coe.int/t/dg4/linguistic/Cadre1_en.asp
(A1) – initial
According to the generally accepted method of teaching foreign languages, 4 types of speech activity develop at each level: Speaking, Reading, Listening and Writing. Chief among these is speaking, and it is to the goal of speaking fluently and correctly that all other learning is subordinated. Level A1 is the basics of a foreign language. Here they are introduced to the alphabet and the peculiarities of the pronunciation of sounds that have no analogues in our native language. They learn to understand foreign speech and speak within the framework of the studied vocabulary on certain topics.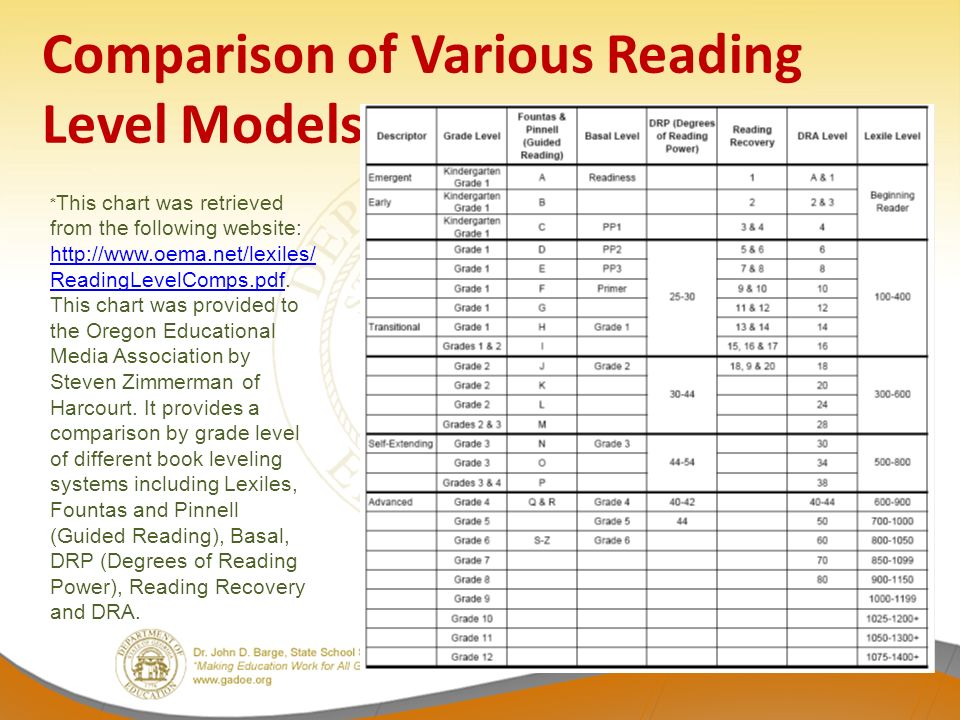
(A2) - below average
Level A 2 is a kind of "key moment" in the life of a foreign language learner. It is at this level that all the basic grammar is laid down that is necessary to keep a conversation on a certain topic, expressing one's opinion or requirement in a familiar context. You can forget about the expression “I understand, but I can’t say”. Of course, it is important how conscientiously you worked throughout this level of language learning, as well as what knowledge you had at the start.
(B1) - intermediate
B1 - this is the so-called "average" level of language proficiency, but in fact it is already quite a decent level, allowing you to speak a foreign language quite fluently, discuss many professional and everyday topics, understand hearing almost everything said in a foreign language at a normal pace. Students understand what is being discussed in most radio and television programs, they know how to express their own opinion, justify their views, retell the content of what they have read or seen, conduct personal and business correspondence of medium complexity, read literature in a foreign language.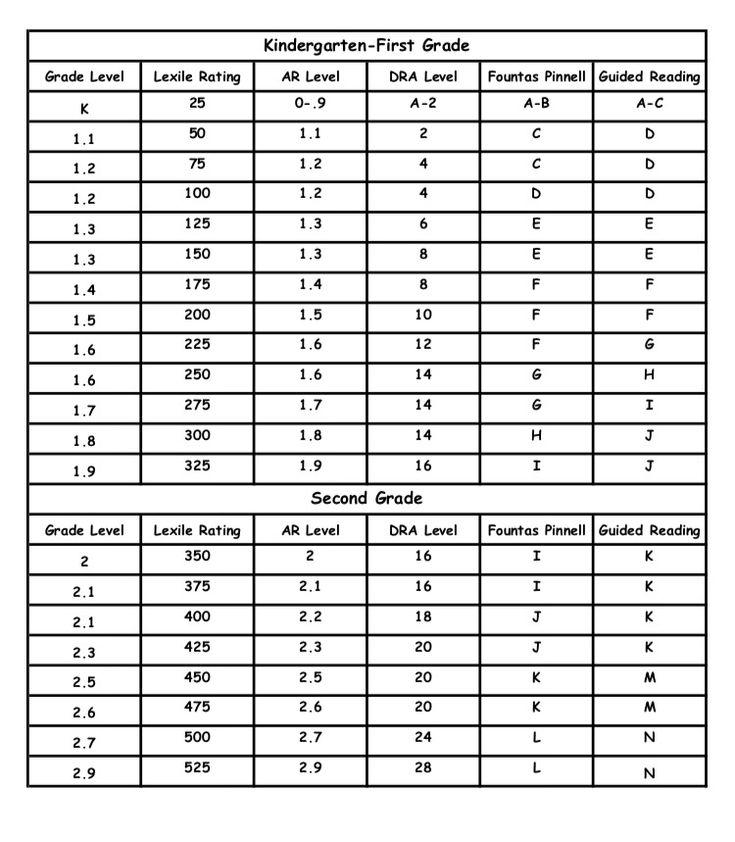 This level of language proficiency allows you to take entrance exams to Russian universities and preparatory courses abroad.
This level of language proficiency allows you to take entrance exams to Russian universities and preparatory courses abroad.
(B2) - above average
B2 is not just an average level of foreign language proficiency, it is already a serious level of knowledge sufficient for foreign language communication in almost all areas of communication. Knowledge at level B2 is enough to live and communicate in a country where the studied language is considered the main one. Knowledge at this level is consolidated, systematized and expanded by more complex cases of using grammatical structures. At this stage of learning in each of the main activities (Speaking, Reading, Listening, Writing) in more detail.
(C1) - advanced
This is a serious level of knowledge of a foreign language, because it is the level C1 that graduates of the philological faculties of higher educational institutions of our country should master. That is, for the most part, people who teach a foreign language as a foreign language speak it at an advanced level.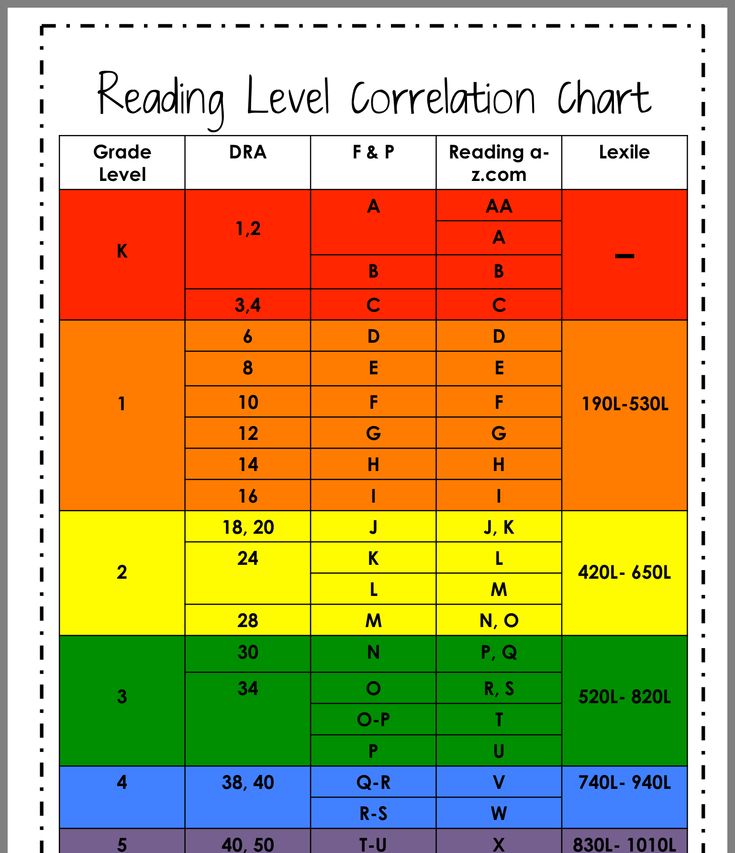 At this level, a person already spontaneously (that is, without prior preparation) and relatively freely can verbally express his opinion on any topic, including narrowly focused ones. At the same time, he does not have difficulties using complex grammatical constructions and with a large number of synonyms that are used to reinforce his point of view with examples and so on. At this level of learning, the ability to speak about everything will develop, even if you do not know much about the topic of conversation, the main thing is not what you say, but how you say it.
At this level, a person already spontaneously (that is, without prior preparation) and relatively freely can verbally express his opinion on any topic, including narrowly focused ones. At the same time, he does not have difficulties using complex grammatical constructions and with a large number of synonyms that are used to reinforce his point of view with examples and so on. At this level of learning, the ability to speak about everything will develop, even if you do not know much about the topic of conversation, the main thing is not what you say, but how you say it.
(C2) - professional level of proficiency
This is the highest level of foreign language proficiency New grammar material at this stage of training, students will not meet, since all the grammar was passed at the previous levels. Grammar is repeated and consolidated on the basis of thematic articles with a large content of specific vocabulary. As for vocabulary , it will be replenished due to specific vocabulary, jargon, terms.