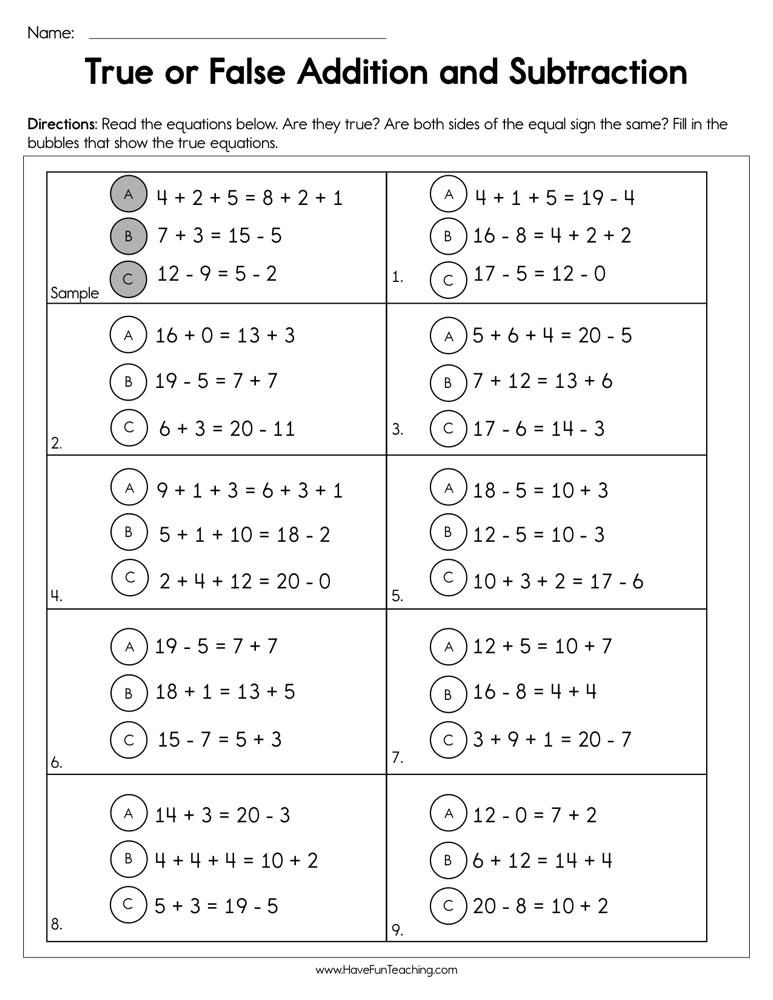
First grade adding and subtracting
Relationship between Addition & Subtraction
- Teaching Resources
- 1st Grade
Determining the relationship between addition and subtraction is a first grade, Common COre math skills: 1.OA.3. Below we show two videos that demonstrate this standard. Then, we provide a breakdown of the specific steps in the videos to help you teach your class.
Prior Learnings
Your students should be familiar with the Kindergarten skill of understanding the number pairs that equal 10 and knowing all decompositions (e.g. 5=4+1, 5=2+3) of numbers below 10. This skill builds a foundation for strategy development, the understanding of place values, and properties of operations (K.OA.3-4). Your students should also understand that ten 1’s plus more 1’s are considered “teens” (K.NBT.1).
Future Learnings
Understanding how to perform addition and subtraction within 20 will enable your students to perform similar skills up to 100, eventually extending those skills to work with larger numbers and solve two-step word problems (2. OA.1). They will also be able to apply this skill with problems in a variety of contexts involving length, picture graphs and bar graphs (2.NBT.5).
Common Core Standard: 1.OA.3 - Applying properties of operations as strategies to add and subtract
Students who understand this principle can:
- Represent addition and subtraction problems in various ways.
- Understand and describe addition and subtraction properties and strategies.
- Demonstrate or explain their thinking.
2 Videos to Help You Teach Common Core Standard: 1.OA.3
Below we provide and breakdown two videos to help you teach your students this standard.
Video 1: Adding and Subtracting Strategies
The video, narrated by the number 1 in a tie, starts by visualizing addition by counting yellow and blue rubber duckies. There are three blue ducks and seven yellow ducks, so 3 + 7 = 10 ducks. It then switches the order of the blue and yellow ducks and shows that the answer (10) is still the same.
There are three blue ducks and seven yellow ducks, so 3 + 7 = 10 ducks. It then switches the order of the blue and yellow ducks and shows that the answer (10) is still the same.
Only in addition, there is the Commutative Property: The order of numbers can be switched as many times as you want and the answer remains the same.
The video then presents a series of practice math problems for your students to practice what they just learned. However, there is a mix of addition and subtraction.
- If 8 + 2 = 10, then __ + 8 = 10.
a. So, 2 + 8 = 10 - If 9 - 4 = 5, then 9 - 5 = __
a. Subtraction does not work like addition, but the two are similar.
b. Uses a “math mountain” to demonstrate this idea.
i. At the top is the total, at the bottom are “partners” or “addends.”
ii. You can add the partners to get the total, and subtract the total from one of the partners to find the other partner.
c. So, 9 - 5 = 4 :) - If 2 + 6 + 4 = 12 is the same as 10 + __ = 12
a.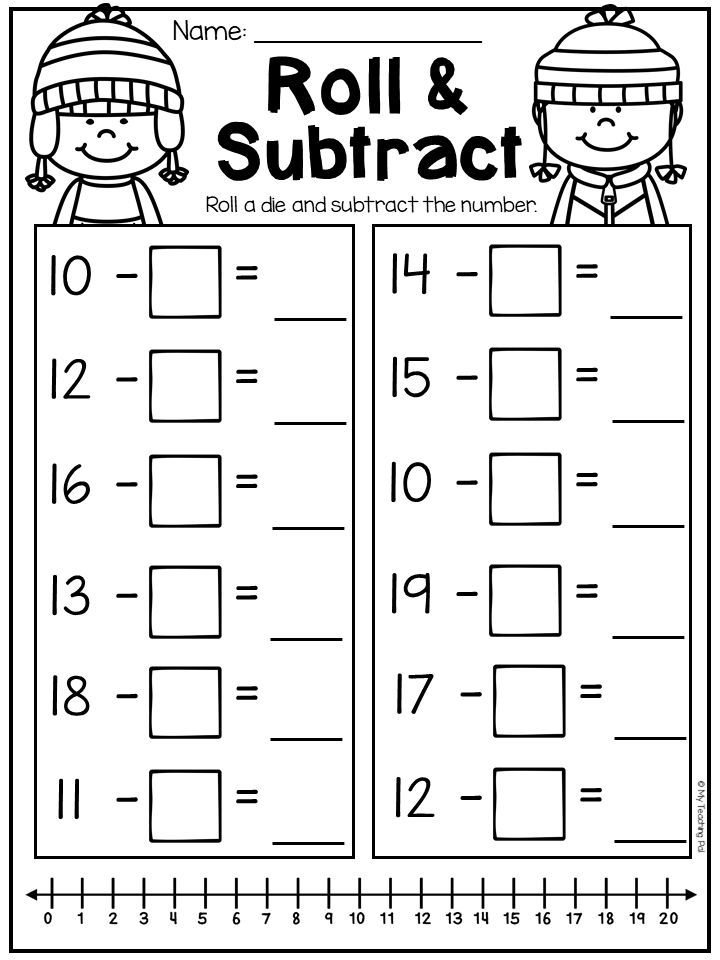 Making groups of doubles or tens is helpful in situations like this.
Making groups of doubles or tens is helpful in situations like this.
b. Adding 6 and 4 makes 10.
c. So, 10 + 2 = 12
Video 2: Adding and Subtracting Cupcakes
The video follows Jen as she tries to bake the proper number of cupcakes for herself and her friends. Knowing that 7 friends were coming, she baked 7 cupcakes, then she baked one more for herself. Boddle asks how many cupcakes she baked in total.
- First, 7 cupcakes are counted.
- Next, the 1 cupcake is added to the 7, ending with 8.
a. 7 + 1 = 8
The situation is flipped, and Jen bakes one cupcake first and then 7 for her friends.
- So now, 1 + 7 = 8. She still baked 8 cupcakes.
- 7 + 1 and 1 + 7 are the same in addition.
Later, Jen eats her cupcake before her friends arrive because she is hungry. The video asks how many cupcakes she has left.
- There were 8 cupcakes, but Jen ate one.
- 8 - 1 = 7.
The situation is reversed; this time all her friends eat their cupcakes, but she does not eat hers.
- So now, 8 - 7 = 1
During the lesson, your students have made a Fact Family. A Fact Family is made of only 3 numbers: 8, 7, and 1. In the lesson, two addition and two subtraction equations are made.
Want more practice?
Give your students additional standards-aligned practice with Boddle Learning. Boddle includes questions related to Comparing and Measuring Lengths plus rewarding coins and games for your students to keep them engaged. Click here to sign up for Boddle Learning and create your first assignment today.
*Information on standards is gathered from The New Mexico Public Education Department's New Mexico Instructional Scope for Mathematics and the Common Core website.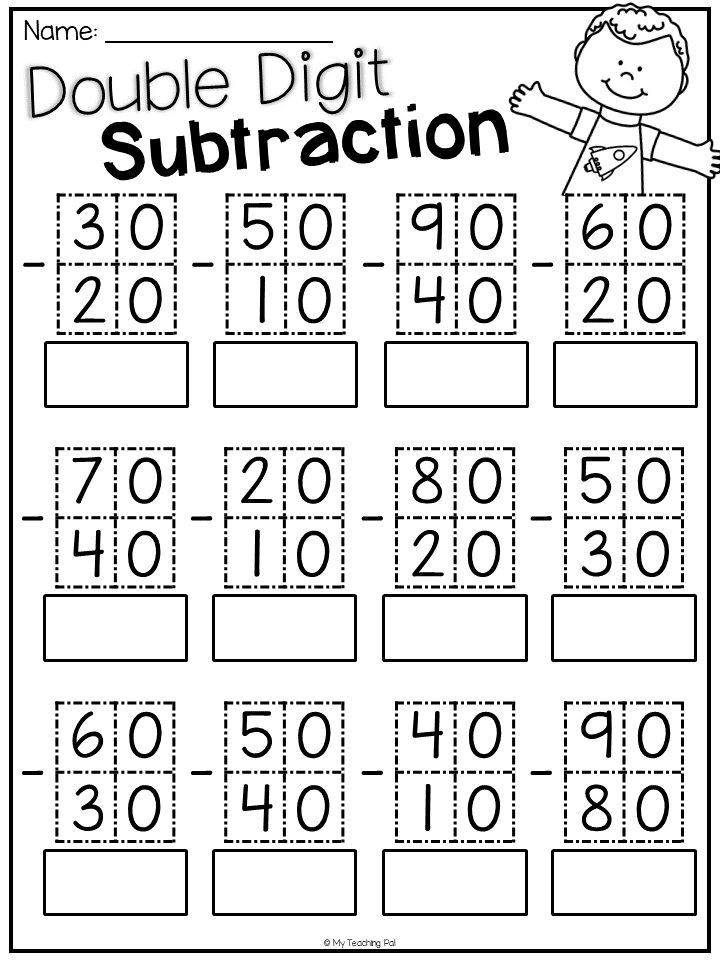
1st Grade Math Games | First Grade Math Skills
How it works
Learn how ST Math can make a difference for your students.
Nationwide Results
ST Math has repeatable results at scale.
Play select games from the ST Math first grade curriculum. Concepts include place value, addition, subtraction, number line, shapes, and more.
Tens and Ones with Spaceships
Count and represent numbers to 20 using place value.
- Decompose numbers into groups of tens and ones by using visual models.
- Levels begin with representing sets of spaceships ≤10 on a ten frame, then move to representing ≤20 spaceships by creating a set of 10 and 1’s.
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
- Level 4
- Level 5
- Level 6
Push Box Addition and Subtraction
Develop strategies for solving addition and subtraction problems.
- Use problem solving strategies to find missing values in visual addition and subtraction situations where blocks are added or subtracted.
- Determine if a situation requires addition or subtraction, or a combination of both.
- Levels begin with finding sums or differences given a visual model, then move to determining which value (a missing addend or subtrahend) is needed.
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
- Level 4
- Level 5
- Level 6
- Level 7
- Level 8
Numbers on a Number Line
Estimate and plot numbers on number lines to 20.
- Build the concept of numbers as equidistant points on a line by plotting and estimating numbers to 20.
- Levels start by using number lines to 10 ticked and labeled with all the numbers, then progress to showing only benchmark numbers.
- Apply concepts of numbers on a number line to estimate numbers to 20.
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
- Level 4
- Level 5
- Level 6
- Level 7
Composite Shapes
Create a composite shape by arranging the given shapes.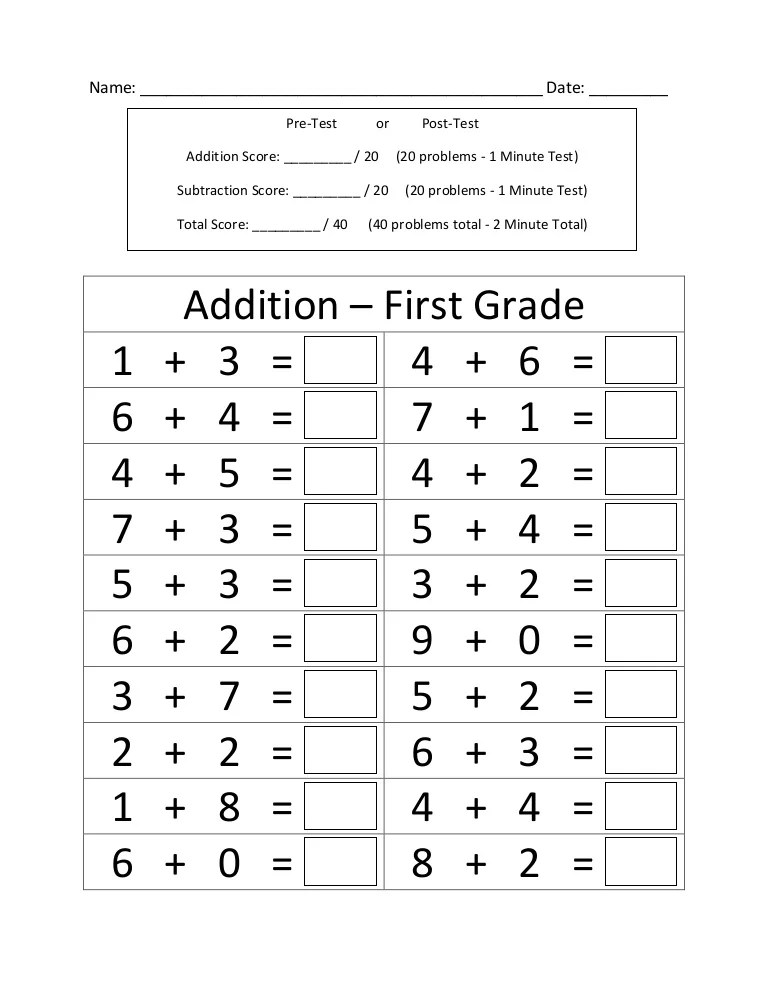
- Compose a given 2-dimensional shape by using smaller shapes.
- Levels begin by simple matching of shapes, then move to more complex problems that require close attention to specific attributes of given shapes.
- Develop spatial strategies for reasoning about angles and sides to compose a larger shape.
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
- Level 4
Making Tens and Ones with Ten Frames
Decompose quantities less than 20 into tens and one using visual models and equations.
- Represent numbers 11-19 as a set of 10 and 1’s using ten frame models
- Solve missing addend equations.
- Levels start with finding the missing addend for numbers less than 10 with ten frames, then progress to representing numbers 11-19 using equations in the form 10+ _ (ones).
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
- Level 4
- Level 5
- Level 6
- Level 7
- Level 8
Tug Boats Equal Groups
Create equal groups of tug boats using addition and subtraction strategies.
- Develop addition and subtraction strategies for creating equal groups.
- Levels begin with visual models, then progress to working with numbers to create equivalent sets.
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
- Level 4
- Level 5
- Level 6
- Level 7
- Level 8
Hands-on Math Activities Pair these activities with specific ST Math games. Read Now »
Visual Addition and Subtraction Explanation of ST Math games that visually model addition and subtraction. Read Now »
Scary Feet Storybook Free math storybook to read together featuring dinosaurs. Read Now »
Educators, ready to learn about the full ST Math experience?
Mathematics Grade 1 Addition and subtraction of the form □+1, □-1 | Lesson plan in mathematics (grade 1) on the topic:
Mathematics grade 1
Addition and subtraction of the form □+1, □-1
Purpose: in the course of practical work and observations, develop the ability to add and subtract the number 1.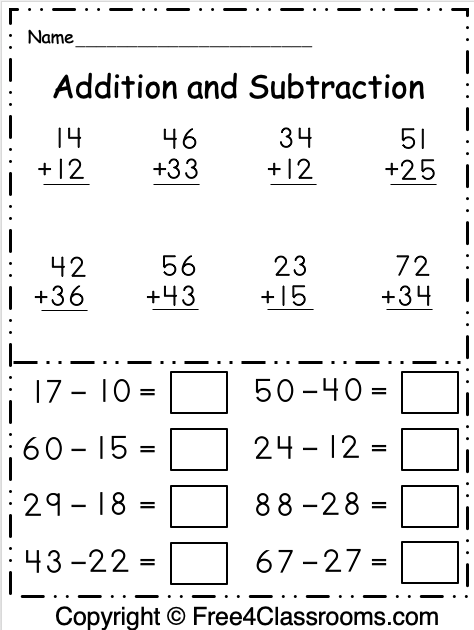
Expected results: students will learn to perform addition and subtraction of the form □+ 1, □ - 1; simulate the actions of addition and subtraction using objects (cut material), drawings, a numerical segment; establish analogies and causal relationships, draw conclusions; assess yourself, the boundaries of your knowledge and ignorance; work in pairs and evaluate a friend.
Course of the lesson
- Organizational moment
- Updating knowledge
Oral counting
Pupils at the blackboard compare numbers.
2 □ 5 2 □ 8 7 □ 5 5 □ 6
6 □ 9 9 □ 10 8 □ 1
game “Who is faster”
- On the board there are two mixed sets of 1 to 10. Two students according to the command of the command teachers put the numbers first in descending order, then in ascending order.)
- Show with a number fan:
- number following 4, 7;
- the number before 3, 1;
- neighbors of numbers 4, 10;
- previous number for numbers 5, 8.

III. Self-determination for activity
Game "Where is my place?"
(Seven students go to the blackboard, each receives a card with a number from 1 to 7 (cards are distributed randomly). Children should quickly line up in order of numbers at the blackboard.)
-Did the guys line up correctly?
-First, second, third step forward. How many guys are here? (3)
-Add 1 to this number. Which student will step forward? (Fourth)
-To 3 they added 1 and got 4. And if we add 1 to 4, the student with which card will take a step forward? (5.)
(The cases 5+1,6+1 are considered by analogy.)
-Conclude: what number do we get if we add 1 to the number? (If we add 1 to the number, we get the next number.)
(Several students repeat the conclusion one after another, each time giving an example. Next, the teacher invites the seventh student to put a card on the table and sit down.)
- How many students were there? (7)
How many students sat down in their seats? (1. )
)
-How many students are left? (6)
- How do I write this down? (7 - 1 = 6.)
(The cases 6 - 1.5 - 1.4 - 1 etc. are considered similarly)
-Who guessed what we will learn in the lesson? (Add and subtract the number 1.)
That's right, today we will remember how to add and subtract the number 1, find out how this can be done using a numerical segment.
IV. Work on the topic of the lesson
Work on the textbook
-Open the textbook on p. 80. See if we have correctly determined what we will do in the lesson.
-Who already knows how to add and subtract the number 1?
- Read the textbook sentence about how to add the number 1.
- Who can complete the following sentence? (To subtract from the number 1, you need to call the previous number.)
- Look at the tables and figure below. What sport do frogs do? (Jumping into the water.)
- How many frogs are there? (10.)
- How many frogs are already in the water? (1.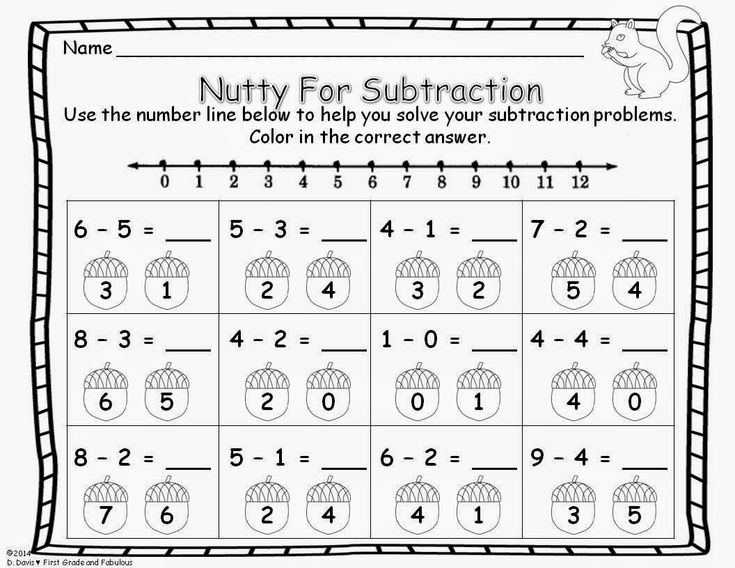 )
)
There is 1 frog in the water, and 1 more has already jumped off the bridge. How many frogs will be in the water now? (2)
How to write it down? (1 + 1= 2.)
-Write your answer in the table.
(Then students explain in a chain how many frogs are already in the pool, how many have jumped, how many frogs will now be in the water, and fill in the first table.)
-How many frogs were on the tower? (10.)
-How many frogs jumped? (1.)
-How many are left? (9.)
- How to write it down? (10-1=9.)
(Then students explain in a chain how many frogs are on the tower, how many jumped, how many frogs are left, and fill in the second table.)
-How can you read these records? What do the authors of the textbook say about this?
-Make a conclusion. How to add or subtract the number 1? (To add 1, you need to say the next number. To subtract from the number 1, you need to say the previous number.)
V. Physical education
In the morning the butterfly woke up,
Smiled, stretched.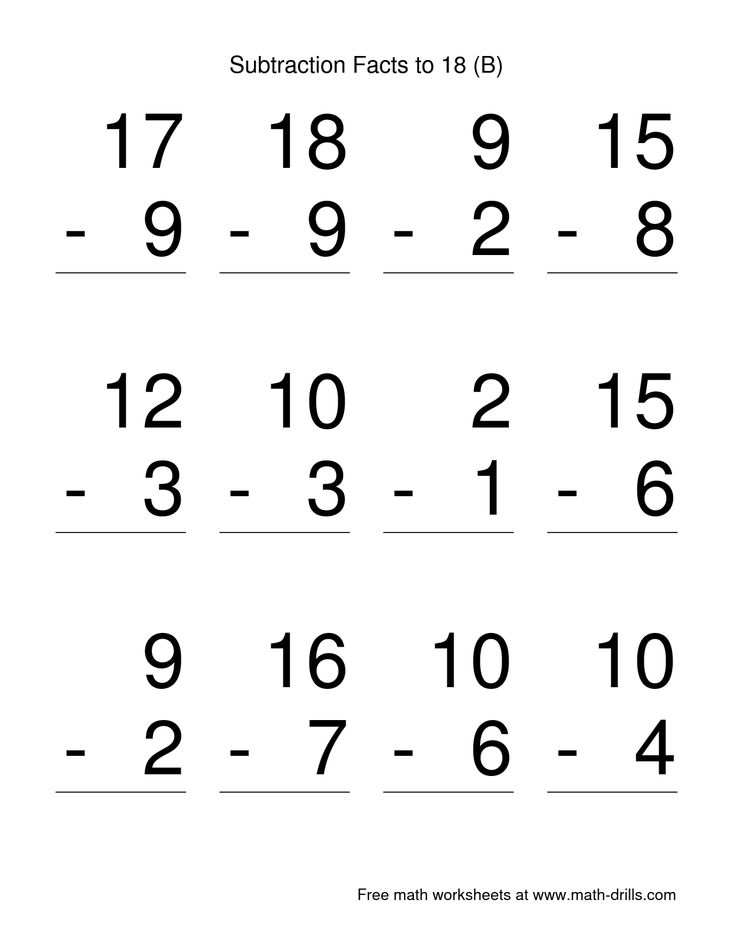
Once - she washed herself with dew,
Two - gracefully circled,
Three - bent down and sat down,
Four - flew away.
VI. Consolidation of the studied material
1) Work with the electronic supplement to the textbook "Mathematics" by M.I. Moreau.
Theme "Numbers from 1 to 10". Addition and subtraction. Add and subtract 1.
2) Work according to the textbook
No. 1 (p. 80).
- Consider the number series along which the squirrel and the hare go.
- What action does the hare perform? (Adds the number 1.)
- Which way is he going and why? (To the right. When we add, it becomes more. The more to the right, the more numbers.)
-What action does the squirrel perform? (Subtracts the number 1.)
- Which way is the squirrel going and why? (To the left. When we subtract, it becomes smaller. The further to the left, the smaller the numbers.)
-The squirrel and the hare do not just walk along the number row, they solve examples.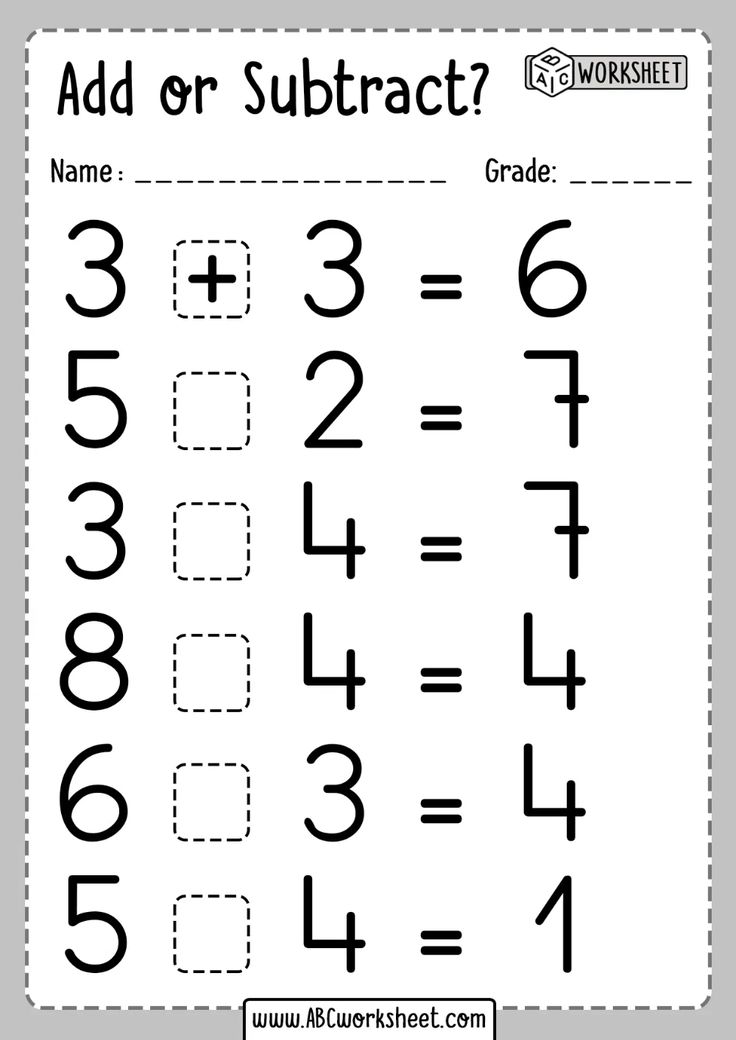 Let's solve the example 1 + 1 = 2 together with the bunny.
Let's solve the example 1 + 1 = 2 together with the bunny.
-From what division did the hare start moving? (From the number 1.)
-Which way is the hare going? How did you know? (To the right, he has a + sign on the plate.)
- How many steps will the hare take to the right? (1.)
- At what division did the hare stop? (On the number 2.)
(The following example is analyzed by analogy.)
- Let's solve the example 9-1 = 8 together with the squirrel.
- From what division did the squirrel start moving? (From the number 9.)
-Which way is the squirrel going? How did you know? (To the left, she has a sign on the sign -)
- How many steps does the squirrel take to the left? (1.)
- At what division did the squirrel stop? (On the number 8.)
(The following example is analyzed by analogy.)
3) Practical work
The teacher distributes cards with numbers from 0 to 10 to the children, they build a number series.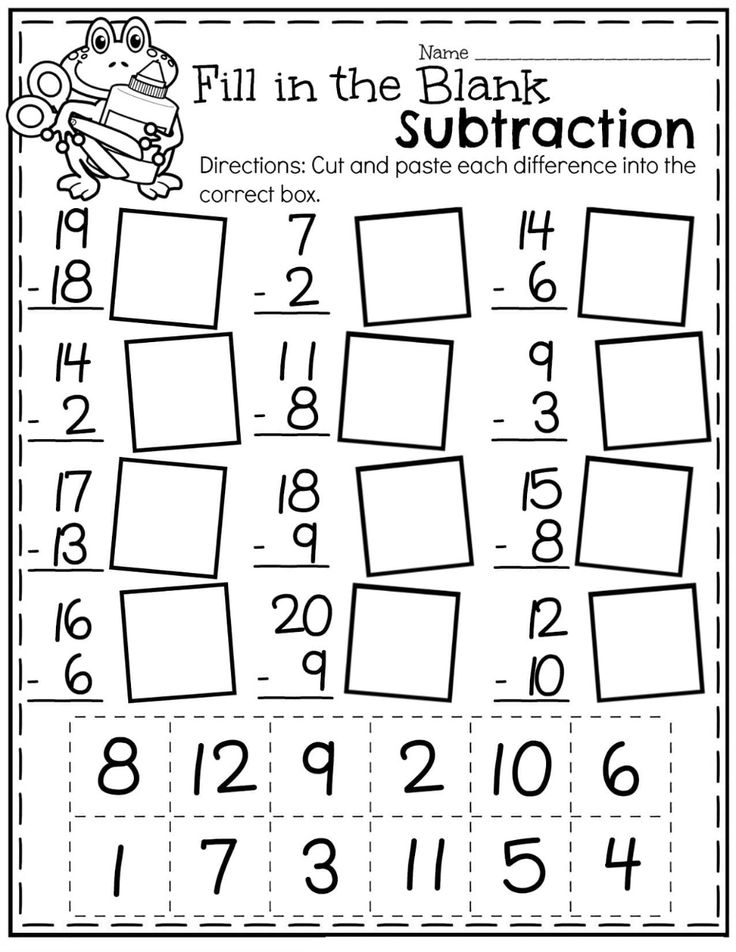 Work is being done with students who have not learned well enough to solve examples using a number series. The teacher calls an example for addition and subtraction with the number 1 and asks questions: from which division will you start the movement? Which direction will you go? How many steps will you take? At what date did you stop? What is the answer in the example?
Work is being done with students who have not learned well enough to solve examples using a number series. The teacher calls an example for addition and subtraction with the number 1 and asks questions: from which division will you start the movement? Which direction will you go? How many steps will you take? At what date did you stop? What is the answer in the example?
4) Work according to the textbook
No. 2 (p. 81).
- Look at the pictures. Make up expressions for them and explain what they mean.
No. 3 (p. 81).
(Work in pairs. Students correlate the number, pattern and number of dots on dominoes.)
5) Work in a notebook with a printed base
Open the notebook to p. 29.
- Tell us what you see in the first picture. (There were 3 sparrows, 1 more sparrow flew to them.)
-What equality can be made? (3 + 1 = 4.)
-Make an equation yourself according to the second picture. (Check.)
(Independent completion of the next task.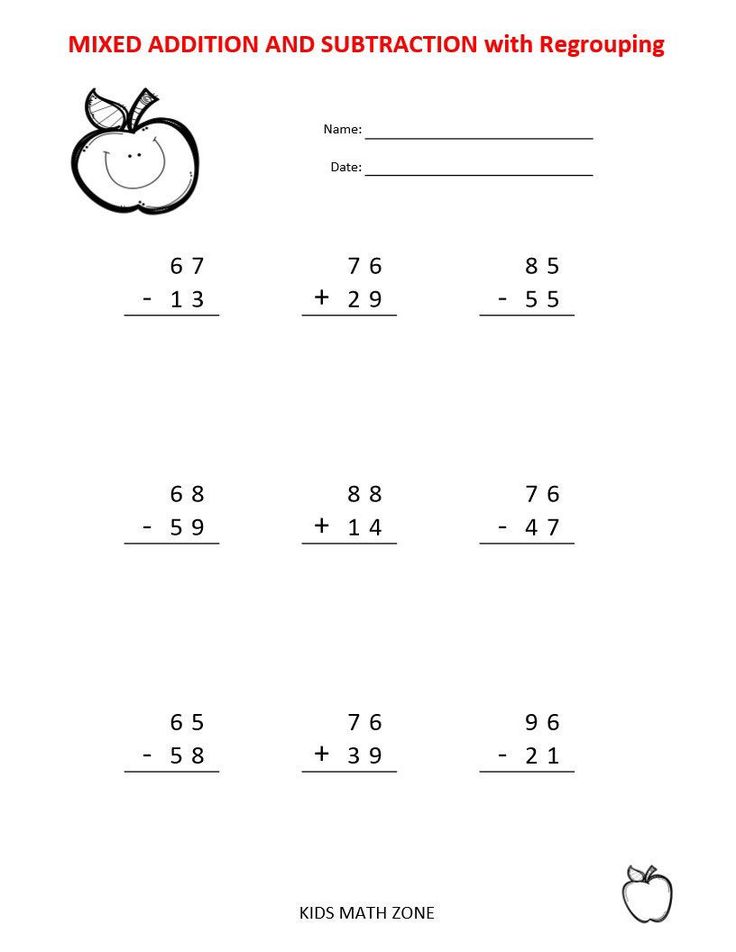 Check. Students in unison read the composition of each number.)
Check. Students in unison read the composition of each number.)
-Read the following task. Calculate.
-What pattern did you find in the first column? (The first number becomes less by 1, subtract 1 everywhere. The answer decreases by 1.)
-Name the pattern in the second column. (The first number increases by 1, we add 1 everywhere. The answer becomes more by 1.)
What is interesting about the third column? (Both the first and second numbers decrease by 1. The answer is 0 everywhere.)
VII.Reflection
("Check yourself" (textbook, p. 81). Work in pairs. You can use KIM (mathematical dictation No. 2 on topic “Addition and subtraction of the form +1, -1).)
VIII. Summing up the lesson
What did you remember in this lesson? (To add 1, you need to name the next number. To subtract from the number 1, you need to name the previous number.)
Examples for addition and subtraction within 10 and 20 (math simulator for grade 1)
- Category: Elementary School
The very first examples that a child gets to know even before school is addition and subtraction. It is not so difficult to count the animals in the picture and, crossing out the extra ones, count the rest. Or shift the counting sticks, and then count them. But for a child it is somewhat more difficult to operate with bare numbers. That is why it takes practice and more practice. Do not stop studying with your child in the summer, because over the summer the school curriculum simply disappears from a small head and it takes a long time to catch up on lost knowledge.
It is not so difficult to count the animals in the picture and, crossing out the extra ones, count the rest. Or shift the counting sticks, and then count them. But for a child it is somewhat more difficult to operate with bare numbers. That is why it takes practice and more practice. Do not stop studying with your child in the summer, because over the summer the school curriculum simply disappears from a small head and it takes a long time to catch up on lost knowledge.
If your child is a first-grader or just going to the first grade, start by repeating the composition of the number by house. And now we can take examples. In fact, addition and subtraction within ten is the first practical application by a child of knowing the composition of a number.
Click on the pictures and open the simulator in maximum magnification, then you can download the image to your computer and print it in good quality.
It is possible to cut A4 in half and get 2 worksheets if you want to reduce the load on the child, or let them decide one column a day if you decide to work out in the summer.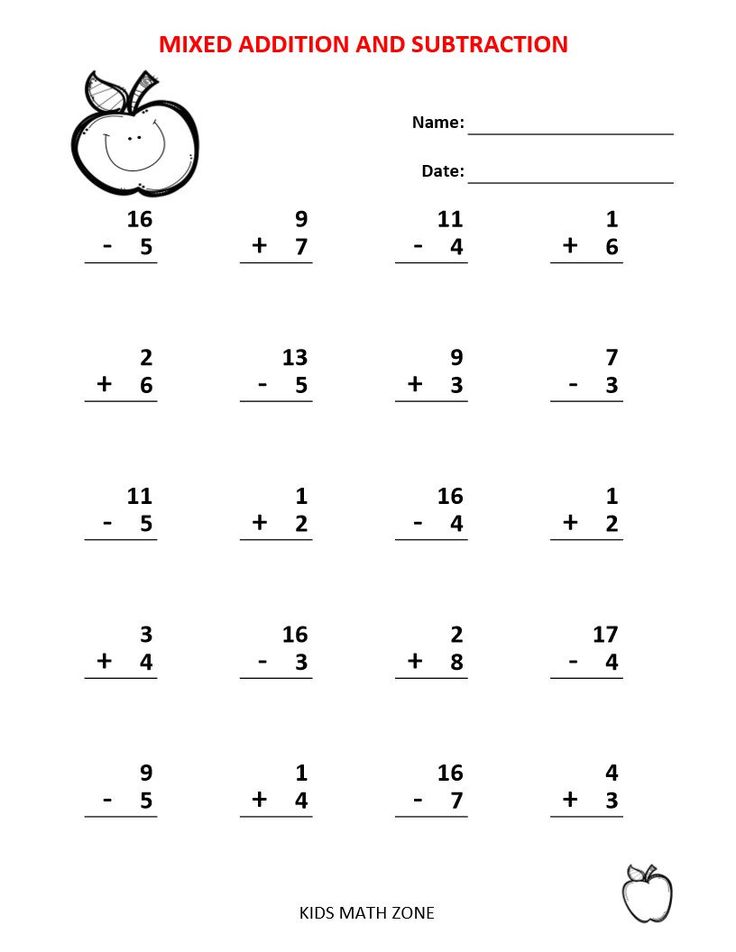
Solving the column, celebrating successes: cloud - not very well solved, smiley - good, sun - great!
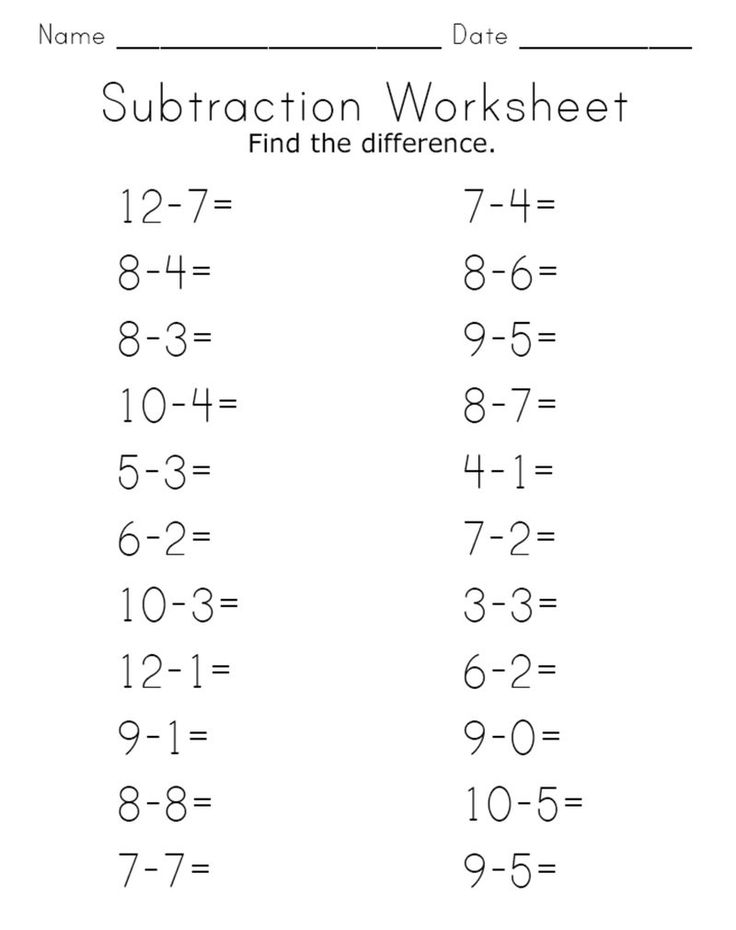
Addition and subtraction within 10
And now scatter!
Examples for addition and subtraction within 20
By the time the child starts studying this topic of mathematics, he should know very well, by heart, the composition of the numbers of the first ten. If the child has not mastered the composition of numbers, it will be difficult for him in further calculations. Therefore, constantly return to the topic of the composition of numbers within 10 until the first grader masters it to automatism. Also, a first grader should know what the decimal (bit) composition of numbers means. In math class, the teacher says that 10 is, in other words, 1 ten, so the number 12 consists of 1 ten and 2 units. In addition, units are added to units. It is on the knowledge of the decimal composition of numbers that the methods of addition and subtraction within 20 9 are based0226 without jumping through ten .