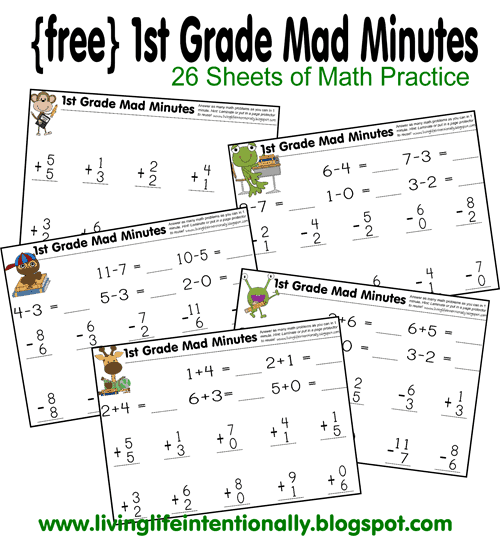
Helping kids learn to read
Tips to Help Children Learn to Read
Written by Dayva Segal
In this Article
- Read Out Loud to Your Children
- Other Tips to Help Your Children Learn to Read
- What to Do if Your Child Is Having Trouble With Reading
Reading is an important skill that children will use daily for the rest of their lives. While many children learn to read at school, parents can enhance the experience by offering support at home. This support can begin as soon as your child is born.
Read Out Loud to Your Children
Experts agree that reading out loud to your children is the best way to help them learn to read. Start when your child is a newborn baby and continue throughout childhood. As a baby, your child is primed to learn the skills that will help them learn to read as they get older.
To make reading out loud as effective as possible, make sure to:
- Read age-appropriate books. Babies, for example, enjoy board books that they can touch and play with.
Older children may enjoy "big books" that help them to see differences in words and letters.
- Use silly voices and voice effects. This helps your children to engage with the story and feel excited about reading time.
- Point to words as you read so your child can follow along. Doing this helps solidify the idea that words are where the story comes from.
- Talk about the pictures. Ask your child to name what they see in the pictures and talk about what the images show as it relates to the story.
- Relate the story to life. Show your child how things in the book relate to things that happen in real life.
- Answer questions. If your child asks a question, stop and answer it. That will keep them engaged and interested.
- Read more difficult books. Once your child learns to read, keep reading out loud to them. You can read books that are above their reading level to encourage further improvement in their reading level.

Other Tips to Help Your Children Learn to Read
Besides reading out loud to your children, there are other things you can do to encourage literacy.
- Listen to your child read out loud. Once they learn to read, encourage them to read to you. This helps them build confidence in reading. The goal with reading aloud is for your child to understand the story. So if they need help pronouncing a word, tell them how it's said instead of making them sound it out — that way, they don't lose their place or the meaning of the sentence. If your child accidentally uses a word that doesn't make sense, have them go back and reread the sentence.
- Praise your child's reading. As your child learns reading, offering praise helps them gain confidence.
- Make reading time part of your daily routine. Daily reading time creates a routine that lets your child know reading is part of everyday life. Many families choose bedtime as their preferred reading time.

- Leave books in your kid's bedroom. That way, they can look at them and enjoy them whenever they want.
- Let your child complete sentences. If your child learns the words in their favorite books, let them finish the sentences or "read" the whole book out loud.
- Read books your child likes. This helps them to engage with reading time and enjoy it more.
- Remember, anyone can teach reading. Some parents think that only teachers can teach reading to children. But parents can, too. Reading is an essential life skill.
- Be patient. If your child shows no interest in a book, don't force it. If your child tries to write a word and gets a letter wrong, they still deserve praise. Patience and praise are more helpful for a child's learning to read than getting frustrated or yelling.
- Talk to your children. Exposing your child to new words and language can help their literacy skills.
 Talking to your baby a lot, for example, can help them become better readers later on.
Talking to your baby a lot, for example, can help them become better readers later on. - Encourage writing. Writing is part of literacy. Provide writing tools like crayons, pencils, and markers. Encourage your child to write, even if it's just scribbling. One idea is to write your child a letter and ask them to write one back.
- Have your child tell you a story and write it down. Ask your child to tell you a simple story. Write it down and then read it back to them while pointing at the words.
- Teach your child phonics. There are countless products available that help children learn the sounds that are associated with letters. This helps them to sound out words as they are learning to read. You can also just use paper and a pencil to help them learn this skill. Research shows that when children don't know phonics, they struggle more with reading.
- Avoid "leveled" reading programs.
 Some people believe that children who get frustrated by reading difficult material will get turned off by reading. But experts say that children learn more when they're exposed to more challenging reading material. Easy-level books often train children to rely on word memorization because they often use the same words over and over. They also train children to rely more on pictures. That can lead to slower reading development. It's best if children are exposed to a variety of challenges in their reading materials.
Some people believe that children who get frustrated by reading difficult material will get turned off by reading. But experts say that children learn more when they're exposed to more challenging reading material. Easy-level books often train children to rely on word memorization because they often use the same words over and over. They also train children to rely more on pictures. That can lead to slower reading development. It's best if children are exposed to a variety of challenges in their reading materials. - Talk to teachers. Ask your child's teachers about their reading program and how they teach literacy. Look for them to include phonics, reading out loud in class, vocabulary, and writing practice.
What to Do if Your Child Is Having Trouble With Reading
If your child's reading is not progressing, you should work with their school to get testing done. That way, you can find out if your child has a learning difficulty or difference, or if it's simply that the reading program in their class doesn't work for them. If your child does get diagnosed with a learning difference, like dyslexia, they're entitled to receive extra services from their school for free.
If your child does get diagnosed with a learning difference, like dyslexia, they're entitled to receive extra services from their school for free.
You can also hire a tutor to help your child improve their reading. Free tutoring may be available for students from low-income families.
At home, provide ongoing emotional support to keep your child from getting discouraged.
Teaching children to read isn’t easy. How do kids actually learn to read?
A student in a Mississippi elementary school reads a book in class. Research shows young children need explicit, systematic phonics instruction to learn how to read fluently. Credit: Terrell Clark for The Hechinger ReportTeaching kids to read isn’t easy; educators often feel strongly about what they think is the “right” way to teach this essential skill. Though teachers’ approaches may differ, the research is pretty clear on how best to help kids learn to read. Here’s what parents should look for in their children’s classroom.
How do kids actually learn how to read?
Research shows kids learn to read when they are able to identify letters or combinations of letters and connect those letters to sounds. There’s more to it, of course, like attaching meaning to words and phrases, but phonemic awareness (understanding sounds in spoken words) and an understanding of phonics (knowing that letters in print correspond to sounds) are the most basic first steps to becoming a reader.
If children can’t master phonics, they are more likely to struggle to read. That’s why researchers say explicit, systematic instruction in phonics is important: Teachers must lead students step by step through a specific sequence of letters and sounds. Kids who learn how to decode words can then apply that skill to more challenging words and ultimately read with fluency. Some kids may not need much help with phonics, especially as they get older, but experts say phonics instruction can be essential for young children and struggling readers “We don’t know how much phonics each kid needs,” said Anders Rasmussen, principal of Wood Road Elementary School in Ballston Spa, New York, who recently led the transformation of his schools’ reading program to a research-based, structured approach. “But we know no kid is hurt by getting too much of it.”
“But we know no kid is hurt by getting too much of it.”
How should your child’s school teach reading?
Timothy Shanahan, a professor emeritus at the University of Illinois at Chicago and an expert on reading instruction, said phonics are important in kindergarten through second grade and phonemic awareness should be explicitly taught in kindergarten and first grade. This view has been underscored by experts in recent years as the debate over reading instruction has intensified. But teaching kids how to read should include more than phonics, said Shanahan. They should also be exposed to oral reading, reading comprehension and writing.
The wars over how to teach reading are back. Here’s the four things you need to know.
Wiley Blevins, an author and expert on phonics, said a good test parents can use to determine whether a child is receiving research-based reading instruction is to ask their child’s teacher how reading is taught.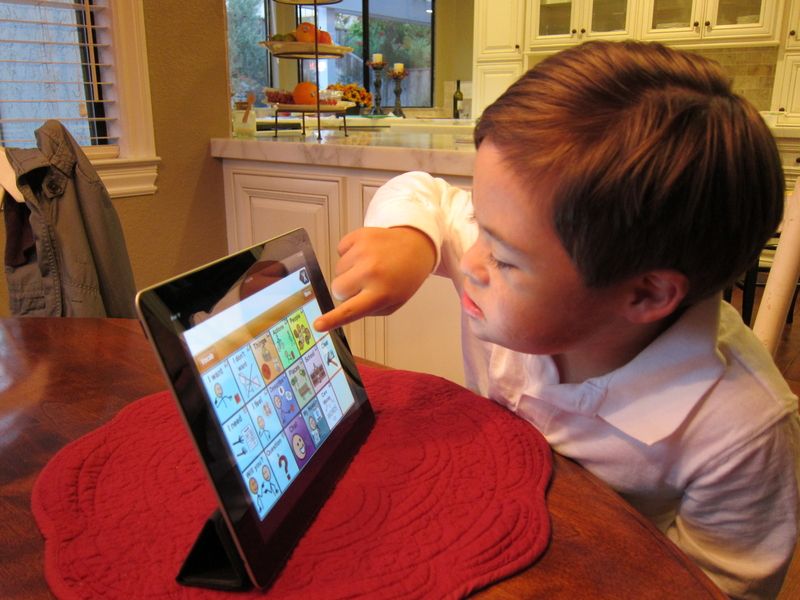 “They should be able to tell you something more than ‘by reading lots of books’ and ‘developing a love of reading.’ ” Blevins said. Along with time dedicated to teaching phonics, Blevins said children should participate in read-alouds with their teacher to build vocabulary and content knowledge. “These read-alouds must involve interactive conversations to engage students in thinking about the content and using the vocabulary,” he said. “Too often, when time is limited, the daily read-alouds are the first thing left out of the reading time. We undervalue its impact on reading growth and must change that.”
“They should be able to tell you something more than ‘by reading lots of books’ and ‘developing a love of reading.’ ” Blevins said. Along with time dedicated to teaching phonics, Blevins said children should participate in read-alouds with their teacher to build vocabulary and content knowledge. “These read-alouds must involve interactive conversations to engage students in thinking about the content and using the vocabulary,” he said. “Too often, when time is limited, the daily read-alouds are the first thing left out of the reading time. We undervalue its impact on reading growth and must change that.”
Rasmussen’s school uses a structured approach: Children receive lessons in phonemic awareness, phonics, pre-writing and writing, vocabulary and repeated readings. Research shows this type of “systematic and intensive” approach in several aspects of literacy can turn children who struggle to read into average or above-average readers.
What should schools avoid when teaching reading?
Educators and experts say kids should be encouraged to sound out words, instead of guessing. “We really want to make sure that no kid is guessing,” Rasmussen said. “You really want … your own kid sounding out words and blending words from the earliest level on.” That means children are not told to guess an unfamiliar word by looking at a picture in the book, for example. As children encounter more challenging texts in later grades, avoiding reliance on visual cues also supports fluent reading. “When they get to ninth grade and they have to read “Of Mice and Men,” there are no picture cues,” Rasmussen said.
“We really want to make sure that no kid is guessing,” Rasmussen said. “You really want … your own kid sounding out words and blending words from the earliest level on.” That means children are not told to guess an unfamiliar word by looking at a picture in the book, for example. As children encounter more challenging texts in later grades, avoiding reliance on visual cues also supports fluent reading. “When they get to ninth grade and they have to read “Of Mice and Men,” there are no picture cues,” Rasmussen said.
Related: Teacher Voice: We need phonics, along with other supports, for reading
Blevins and Shanahan caution against organizing books by different reading levels and keeping students at one level until they read with enough fluency to move up to the next level. Although many people may think keeping students at one level will help prevent them from getting frustrated and discouraged by difficult texts, research shows that students actually learn more when they are challenged by reading materials.
Blevins said reliance on “leveled books” can contribute to “a bad habit in readers.” Because students can’t sound out many of the words, they rely on memorizing repeated words and sentence patterns, or on using picture clues to guess words. Rasmussen said making kids stick with one reading level — and, especially, consistently giving some kids texts that are below grade level, rather than giving them supports to bring them to grade level — can also lead to larger gaps in reading ability.
How do I know if a reading curriculum is effective?
Some reading curricula cover more aspects of literacy than others. While almost all programs have some research-based components, the structure of a program can make a big difference, said Rasmussen. Watching children read is the best way to tell if they are receiving proper instruction — explicit, systematic instruction in phonics to establish a foundation for reading, coupled with the use of grade-level texts, offered to all kids.
Parents who are curious about what’s included in the curriculum in their child’s classroom can find sources online, like a chart included in an article by Readingrockets.org which summarizes the various aspects of literacy, including phonics, writing and comprehension strategies, in some of the most popular reading curricula.
Blevins also suggested some questions parents can ask their child’s teacher:
- What is your phonics scope and sequence?
“If research-based, the curriculum must have a clearly defined phonics scope and sequence that serves as the spine of the instruction.” Blevins said.
- Do you have decodable readers (short books with words composed of the letters and sounds students are learning) to practice phonics?
“If no decodable or phonics readers are used, students are unlikely to get the amount of practice and application to get to mastery so they can then transfer these skills to all reading and writing experiences,” Blevins said. “If teachers say they are using leveled books, ask how many words can students sound out based on the phonics skills (teachers) have taught … Can these words be fully sounded out based on the phonics skills you taught or are children only using pieces of the word? They should be fully sounding out the words — not using just the first or first and last letters and guessing at the rest.”
“If teachers say they are using leveled books, ask how many words can students sound out based on the phonics skills (teachers) have taught … Can these words be fully sounded out based on the phonics skills you taught or are children only using pieces of the word? They should be fully sounding out the words — not using just the first or first and last letters and guessing at the rest.”
- What are you doing to build students’ vocabulary and background knowledge? How frequent is this instruction? How much time is spent each day doing this?
“It should be a lot,” Blevins said, “and much of it happens during read-alouds, especially informational texts, and science and social studies lessons.”
- Is the research used to support your reading curriculum just about the actual materials, or does it draw from a larger body of research on how children learn to read? How does it connect to the science of reading?
Teachers should be able to answer these questions, said Blevins.
What should I do if my child isn’t progressing in reading?
When a child isn’t progressing, Blevins said, the key is to find out why. “Is it a learning challenge or is your child a curriculum casualty? This is a tough one.” Blevins suggested that parents of kindergarteners and first graders ask their child’s school to test the child’s phonemic awareness, phonics and fluency.
Parents of older children should ask for a test of vocabulary. “These tests will locate some underlying issues as to why your child is struggling reading and understanding what they read,” Blevins said. “Once underlying issues are found, they can be systematically addressed.”
“We don’t know how much phonics each kid needs. But we know no kid is hurt by getting too much of it.”
Anders Rasmussen, principal of Wood Road Elementary School in Ballston Spa, New York
Rasmussen recommended parents work with their school if they are concerned about their children’s progress. By sitting and reading with their children, parents can see the kind of literacy instruction the kids are receiving. If children are trying to guess based on pictures, parents can talk to teachers about increasing phonics instruction.
By sitting and reading with their children, parents can see the kind of literacy instruction the kids are receiving. If children are trying to guess based on pictures, parents can talk to teachers about increasing phonics instruction.
“Teachers aren’t there doing necessarily bad things or disadvantaging kids purposefully or willfully,” Rasmussen said. “You have many great reading teachers using some effective strategies and some ineffective strategies.”
What can parents do at home to help their children learn to read?
Parents want to help their kids learn how to read but don’t want to push them to the point where they hate reading. “Parents at home can fall into the trap of thinking this is about drilling their kid,” said Cindy Jiban, a former educator and current principal academic lead at NWEA, a research-based non-profit focused on assessments and professional learning opportunities. “This is unfortunate,” Jiban said. “It sets up a parent-child interaction that makes it, ‘Ugh, there’s this thing that’s not fun. ’” Instead, Jiban advises making decoding playful. Here are some ideas:
’” Instead, Jiban advises making decoding playful. Here are some ideas:
- Challenge kids to find everything in the house that starts with a specific sound.
- Stretch out one word in a sentence. Ask your child to “pass the salt” but say the individual sounds in the word “salt” instead of the word itself.
- Ask your child to figure out what every family member’s name would be if it started with a “b” sound.
- Sing that annoying “Banana fana fo fanna song.” Jiban said that kind of playful activity can actually help a kid think about the sounds that correspond with letters even if they’re not looking at a letter right in front of them.
- Read your child’s favorite book over and over again. For books that children know well, Jiban suggests that children use their finger to follow along as each word is read. Parents can do the same, or come up with another strategy to help kids follow which words they’re reading on a page.
Giving a child diverse experiences that seem to have nothing to do with reading can also help a child’s reading ability. By having a variety of experiences, Rasmussen said, children will be able to apply their own knowledge to better comprehend texts about various topics.
By having a variety of experiences, Rasmussen said, children will be able to apply their own knowledge to better comprehend texts about various topics.
This story about teaching children to read was produced by The Hechinger Report, a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education. Sign up for Hechinger’s newsletter.
The Hechinger Report provides in-depth, fact-based, unbiased reporting on education that is free to all readers. But that doesn't mean it's free to produce. Our work keeps educators and the public informed about pressing issues at schools and on campuses throughout the country. We tell the whole story, even when the details are inconvenient. Help us keep doing that.
Join us today.
How to teach a child to read: techniques from an experienced teacher
At what age should you start teaching a child to read
Speech therapist Naya Speranskaya believes that the optimal age at which you can gradually start learning to read is 5. 5 years.
5 years.
“But still, the starting point for the first steps in this matter should be not a specific age, but the child himself. There are children who are ready to master the skill as early as 3-4 years old, and there are those who "mature" closer to grade 1. Once I worked with a boy who could not read at 6.5 years old. He knew letters, individual syllables, but he could not read. As soon as we began to study, it became clear that he was absolutely ready for reading, in two months he began to read perfectly in syllables, ”said Speranskaya.
How to teach a child to read quickly and correctly
The first thing you need to teach your baby is the ability to correlate letters and sounds. “In no case should a child be taught the names of letters, as in the alphabet: “em”, “be”, “ve”. Otherwise, training is doomed to failure. The preschooler will try to apply new knowledge in practice. Instead of reading [mom], he will read [me-a-me-a]. You are tormented by retraining, ”the speech therapist warned.
Therefore, it is important to immediately give the child not the names of the letters, but the sounds they represent. Not [be], but [b], not [em], but [m]. If the consonant is softened by a vowel, then this should be reflected in the pronunciation: [t '], [m'], [v '], etc.
To help your child remember the graphic symbols of letters, make a letter with him from plasticine, lay it out with buttons, draw with your finger on a saucer with flour or semolina. Color the letters with pencils, draw with water markers on the side of the bathroom.
“At first it will seem to the child that all the letters are similar to each other. These actions will help you learn to distinguish between them faster, ”said the speech therapist.
As soon as the baby remembers the letters and sounds, you can move on to memorizing syllables.
close
100%
How to teach your child to join letters into syllables
“Connecting letters into syllables is like learning the multiplication table. You just need to remember these combinations of letters, ”the speech therapist explained.
You just need to remember these combinations of letters, ”the speech therapist explained.
Naya Speranskaya noted that most of the manuals offer to teach children to read exactly by syllables. When choosing, two nuances should be taken into account:
1. Books should have little text and a lot of pictures.
2. Words in them should not be divided into syllables using large spaces, hyphens, long vertical lines.
“All this creates visual difficulties in reading. It is difficult for a child to perceive such a word as something whole, it is difficult to “collect” it from different pieces. It is best if there are no extra spaces or other separating characters in the word, and syllables are highlighted with arcs directly below the word, ”the speech therapist explained.
According to Speranskaya, cubes with letters are also suitable for studying syllables - playing with them, the child will quickly remember the combinations.
Another way to gently help your child learn letters and syllables is to print them in large print on paper and hang them all over the apartment.
“Hang them on the fridge, on the board in the nursery, on the wall in the bathroom. When such leaflets are hung throughout the apartment, you can inadvertently return to them many times a day. Do you wash your hands? Read what is written next to the sink. Is the child waiting for you to give him lunch? Ask him to name which syllables are hanging on the refrigerator. Do a little, but as often as possible. Step by step, the child will learn the syllables, and then slowly begin to read,” the specialist said.
Speranskaya is sure that in this way the child will learn to read much faster than after daily classes, when parents seat the child at the table with the words: “Now we will study reading ...”
“If it is really difficult for you to give up such activities, then pay attention that the nervous system of preschoolers is not yet ripe for long and monotonous lessons. Children spend enormous efforts on the analysis of graphic symbols. Learning to read for them is like learning a very complex cipher. Therefore, it is necessary to observe clear timing in such classes. At 5.5 years old, children are able to hold attention for no more than 10 minutes, at 6.5 years old - 15 minutes. That's how long one lesson should last. And there should be no more than one such “lessons” a day, unless, of course, you want the child to lose motivation for learning even before school,” the speech therapist explained.
Therefore, it is necessary to observe clear timing in such classes. At 5.5 years old, children are able to hold attention for no more than 10 minutes, at 6.5 years old - 15 minutes. That's how long one lesson should last. And there should be no more than one such “lessons” a day, unless, of course, you want the child to lose motivation for learning even before school,” the speech therapist explained.
How to properly explain to a child how to divide words into syllables
When teaching a child to divide words into syllables, use a pencil. Mark syllables with a pencil using arcs.
close
100%
“Take the word dinosaur. It can be divided into three syllables: "di", "but", "zavr". The child will read the first syllables without difficulty, but it will be difficult for him to master the third. The kid cannot look at three or four letters at once. Therefore, I propose to teach to read not entirely by syllables, but by the so-called syllables. This is when we learn to read combinations of consonants and vowels, and we read the consonants separately. For example, we will read the word "dinosaur" like this: "di" "but" "for" "in" "p" The last two letters are read separately from "for". If you immediately teach a child to read by syllables, he will quickly master complex words and move on to fluent reading, ”the speech therapist is sure.
For example, we will read the word "dinosaur" like this: "di" "but" "for" "in" "p" The last two letters are read separately from "for". If you immediately teach a child to read by syllables, he will quickly master complex words and move on to fluent reading, ”the speech therapist is sure.
In a text, syllables can be labeled in much the same way as syllables. Vowel + consonant with the help of an arc, and a separate consonant with the help of a dot.
Naya Speranskaya gave parents a recommendation to memorize syllables/syllable fusions for as long as possible, and move on to texts only when the child suggests it himself.
“If a preschooler is not eager to read, then there is no need to put pressure on him. Automate syllables. Take your time. Learning should take place gradually, from simple to complex. The reading technique develops over time, ”added Speranskaya.
Another important clarification from the speech therapist: when the child begins to read words and then sentences, parents need to clarify the meaning of what they read.
“The child reads the word “mom”, after that you ask the question: “what does it mean that you just read it”,” the speech therapist shared, “It is necessary that the child not only reads well, but also feels the meaning of what he read. Unfortunately, it is not uncommon to meet children who “spell” entire texts, but are not able to explain what they are about.”
Naya Speranskaya recommended the following manuals for home schooling:
1. A book to start learning to read - a set of Bezrukov O. A. Kalenkova O. N. "Lessons of Russian literacy", publishing house "Russian Rech"
2. Posters for teaching reading and letter of V. G. Dmitriev, publishing house "AST"
3. "Come on, letter, respond!" Kolesnikova E.V., workbook
4. Books from the series "We read ourselves" by the publishing house "Vakosha"
How to teach a child to read: important rules and effective methods
October 26LikbezEducation
Teaching a preschooler to read without losing interest in books is real. Lifehacker has selected the best ways for responsible parents.
Lifehacker has selected the best ways for responsible parents.
Share
0How to understand that it's time to teach your child to read
There are several signs of psychological readiness.
- The child speaks fluently in sentences and understands the meaning of what is said.
- The child understands directions: left-right, up-down. For learning to read, it is important that the baby can follow the text from left to right and from top to bottom.
- The child distinguishes sounds (what speech therapists call developed phonemic hearing). Simply put, the baby will easily understand by ear where the house and the bow are, and where the tom and the hatch are.
- Your child pronounces all the sounds and has no speech problems.
Natalya Zharikova
Speech therapist teacher with 33 years of experience
A child with speech therapy problems does not hear and does not distinguish similar sounds. From here come errors with speech, and subsequently with reading, and even more often with writing. It is very difficult for a parent to identify violations on their own, so usually a teacher or a speech therapist can point this out to them.
From here come errors with speech, and subsequently with reading, and even more often with writing. It is very difficult for a parent to identify violations on their own, so usually a teacher or a speech therapist can point this out to them.
How to teach your child to read
Be patient and follow these simple guidelines.
Set an example
In a family where there is a culture and tradition of reading, children themselves will reach for books. Read not because it is necessary and useful, but because it is a pleasure for you.
Read together and discuss
Read aloud to the child and then look at the pictures together, encouraging them to interact with the book: “Who is that drawn? Can you show me the cat's ears? And who is that standing next to her?” Older children can be asked more difficult questions: “Why did he do this? What do you think will happen next?"
Don't learn the letters as they are called in the alphabet
Instead, help your child remember the sound the letter makes. For example, you show the letter "m" and say: "This is the letter m (not em )". If a child remembers the alphabetic names of letters ( em , es, ef and so on), it will be quite difficult for him to learn to read. Then, when he sees the word ra-ma in the book, he will try to pronounce er-a-um-a .
For example, you show the letter "m" and say: "This is the letter m (not em )". If a child remembers the alphabetic names of letters ( em , es, ef and so on), it will be quite difficult for him to learn to read. Then, when he sees the word ra-ma in the book, he will try to pronounce er-a-um-a .
Go from easy to hard
Once the child has memorized a few letters (from 2 to 5) and the sounds they represent, move on to syllables. Let the words consisting of repeating syllables be the first: ma-ma, pa-pa, uncle, nanny . In this case, it is not necessary to break the syllable into separate sounds. Do not say: "These are the letters m and a , and together they read ma ". Immediately learn that the syllable is pronounced like ma , otherwise the baby may start to read letter by letter. After mastering simple combinations, move on to more complex ones: ko‑t, zhu‑k, house .
Help to understand the meaning of what is read
Do this when the child begins to slowly but surely reproduce words and whole sentences in syllables. For example, the kid read: "Mom washed the frame." Stop and ask: “What did you just read about?”. If he finds it difficult to answer, let him read the sentence again. And you ask more specific questions: “Who washed the frame? What did mom wash?
Show that letters are everywhere
Play a game. Let the child find the letters that surround him on the street and at home. These are the names of stores, and memos on information stands, and advertising on billboards, and even traffic light messages: it happens that the inscription “Go” lights up on green, and “Wait so many seconds” on red.
Play
And play again. Stack blocks with letters and syllables, make up words, ask your child to read you some kind of sign or inscription on the packaging in the store.
Natalya Zharikova
There are many exercises for memorizing letters. For example, circle the desired letter among a number of others, circle the correctly written among the incorrect ones, color or shade. You can also ask the child to tell what the letter looks like.
For example, circle the desired letter among a number of others, circle the correctly written among the incorrect ones, color or shade. You can also ask the child to tell what the letter looks like.
Use every opportunity to train
Whether you are waiting in line at the clinic or driving somewhere, take out a book with pictures and short stories to them and invite your child to read together.
Build on your success
Repeat familiar texts, look for familiar characters in new stories. Runaway Bunny is found both in "Teremka" and "Kolobok".
Do not force
This is perhaps the most important. Don't take away a child's childhood. Learning should not go through violence and tears.
What techniques to use to teach your child to read
Here are six popular, affordable and effective techniques. Choose one or try several and choose the one that interests your child the most.
1. ABCs and primers
Frame: This is all mine / YouTube Traditional, but the longest way. The difference between these books is that the alphabet fixes each letter with a mnemonic picture: on the page with B a drum will be drawn, and next to Yu - spinning top. The alphabet helps to remember letters and often interesting rhymes, but will not teach you how to read.
The primer consistently teaches the child to combine sounds into syllables, and syllables into words. This process is not easy and requires perseverance.
There are quite a lot of author's primers now. According to the books of Nadezhda Betenkova, Vseslav Goretsky, Dmitry Fonin, Natalya Pavlova, children can study both with their parents before school and in the first grade.
Parents agree that one of the most understandable methods for teaching preschoolers is Nadezhda Zhukova's primer. The author simply explains the most difficult thing for a child: how to turn letters into syllables, how to read ma-ma rather than start calling individual letters me-a-me-a .
2. Zaitsev's Cubes
Shot: Little Socrates / YouTubeIf a child consistently learns letters and syllables while learning from the primer, then in 52 Zaitsev's Cubes he is given access to everything at once: a single letter or combinations of consonant and vowel, consonant and hard or soft sign.
The child effortlessly learns the differences between voiceless and voiced sounds, because the cubes with voiceless consonants are filled with wood, and the cubes with voiced consonants are filled with metal.
The cubes also differ in size. The large ones depict hard warehouses, the small ones - soft ones. The author of the technique explains this by the fact that when we pronounce to (hard warehouse), the mouth opens wide, or (soft warehouse) - lips in a half smile.
The set includes tables with warehouses that the parent sings (yes, he doesn’t speak, but sings).
The child quickly masters warehouse reading with the help of cubes. But there are also disadvantages: he may begin to swallow endings and face difficulties already at school when parsing a word by composition.
3. “Skladushki” and “Teremki” by Vyacheslav Voskobovich
Frame: Play and Toy Club / YouTubeIn “Skladushki” Vyacheslav Voskobovich reworked Zaitsev’s idea: 21 cards show all the warehouses of the Russian language with nice thematic pictures. Included is a CD with songs, the texts of which go under each picture.
Folders are great for kids who like looking at pictures. Each of them is an occasion to discuss with the child where the kitten is, what the puppy is doing, where the beetle flew.
It is possible to teach a child with these cards from the age of three. At the same time, it should be noted that the author of the methodology himself does not consider it necessary to force early development.
Voskobovich's "Teremki" consist of 12 wooden cubes with consonants and 12 cardboard cubes with vowels. First, the child gets acquainted with the alphabet and tries with the help of parents to come up with words that begin with each of the letters.
Then it's time to study the syllables. In the tower with the letter M is inserted into A - and the first syllable is ma . From several towers you can lay out words. Learning is based on play. So, when replacing the vowel , the house will turn into smoke .
You can start playing tower blocks from the age of two. At the same time, parents will not be left alone with the cubes: the kit includes a manual with a detailed description of the methodology and game options.
4. Chaplygin's dynamic cubes
Shot: Both a boy and a girl! Children's channel - We are twins / YouTube Evgeny Chaplygin's manual includes 10 cubes and 10 moving blocks. Each dynamic block consists of a pair - a consonant and a vowel. The task of the child is to twist the cubes and find a pair.
Each dynamic block consists of a pair - a consonant and a vowel. The task of the child is to twist the cubes and find a pair.
At the initial stage, as with any other method of learning to read in warehouses, the child makes the simplest words from repeating syllables: ma-ma, pa-pa, ba-ba . The involved motor skills help to quickly remember the shape of the letters, and the search for already familiar syllables turns into an exciting game. The cubes are accompanied by a manual describing the methodology and words that can be composed.
The optimal age for classes is 4-5 years. You can start earlier, but only in the game format.
5. Doman's cards
Frame: My little star / YouTube American doctor Glenn Doman suggests teaching children not individual letters or even syllables, but whole words. Parents name and show the child the words on the cards for 1-2 seconds. In this case, the baby is not required to repeat what he heard.
In this case, the baby is not required to repeat what he heard.
Classes start with 15 cards with the simplest concepts like female and male . Gradually, the number of words increases, those already learned leave the set, and the child begins to study phrases: for example, color + object, size + object.
How can one understand that a child has understood and memorized the visual image of a word, if the author of the methodology recommends starting classes from birth? Glenn Doman in "The Harmonious Development of the Child" strongly emphasizes that it is not necessary to arrange tests and checks for the child: kids do not like this and lose interest in classes.
It's better to remember 50 cards out of 100 than 10 out of 10.
Glenn Doman
But given that parents can't help but check, he advises the child to play the game if they are willing and ready. For example, you can put a few cards and ask to bring one or point to it.
Today, psychologists, neurophysiologists and pediatricians agree that the Doman method is aimed not at teaching reading, but at mechanical memorization of visual images of words. The child turns out to be an object of learning and is almost deprived of the opportunity to learn something on his own.
The child turns out to be an object of learning and is almost deprived of the opportunity to learn something on his own.
It is also worth adding: in order to proceed to the stage of reading according to Doman, parents need to prepare cards with all (!) words that are found in a particular book.
6. Montessori method
Photo: Kolpakova Daria / ShutterstockMontessori reading comes from the opposite: first we write and only then we read. Letters are the same pictures, so you first need to learn how to draw them and only then engage in pronunciation and reading. Children begin by tracing and shading the letters, and through this, they memorize their outline. When several vowels and consonants have been studied, they move on to the first simple words.
Much attention is paid to the tactile component, so children can literally touch the alphabet cut out of rough or velvety paper.
The value of the methodology lies in learning through play. So, you can put a rough letter and a plate of semolina in front of the child and offer to first circle the sign with your finger, and then repeat this on the semolina.
So, you can put a rough letter and a plate of semolina in front of the child and offer to first circle the sign with your finger, and then repeat this on the semolina.
The challenge for parents is purchasing or stocking up a significant amount of handouts. But you can try to make cards with your own hands from cardboard and sandpaper.
What's the result
On the Internet and on posters advertising "educators", you will be offered ultra-modern methods of teaching your child to read at three, two or even from birth. But let's be realistic: a happy mother is needed a year, not developmental classes.
The authors of the methods as one insist that the most natural learning process for a child is through play, and not through classes in which the parent plays the role of a strict controller. Your main assistant in learning is the curiosity of the child himself.