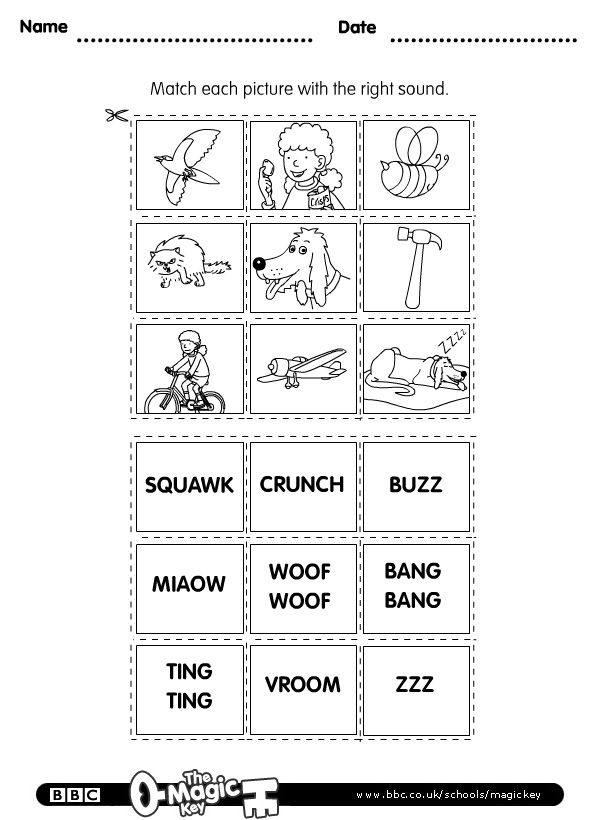
High frequency words games for kindergarten
7 Awesome and Fun High-Frequency Word Games for Kindergarten
High-frequency word games for kindergarten have always been a favorite of mine! I try to use them in my classroom to support learning whenever possible. After learning the difference between sight words vs. high-frequency words, I knew I needed to provide my students with repeated exposure and practice. Playing high-frequency word games for kindergarten can help students turn high-frequency words into sight words.
Benefits of High-Frequency Word Games for Kindergarten
Why use games for high-frequency words in the classroom? High-frequency word games for kindergarten help students learn while having fun. Simply saying the word game adds instant excitement. Sight word practice games also provide an opportunity to reinforce learning. In addition, when playing games, students may have the opportunity to practice teamwork and problem-solving.
What Are Some High-Frequency Word Games for Kindergarten?
Many games you already have will work great in the classroom. However, if you don’t have any games lying around, you can often find old board games to transform at yard sales, garage sales, or Goodwill. Add high-frequency words to the cards or pieces, and you have created high-frequency word games for kindergarten. These 7 games are also perfect for hands-on sight word activities and sight word literacy centers.
Jenga
Jenga is a well-loved game. Turn this game into a high-frequency word game by writing a high-frequency word on each block. Then, when students pull out a block, they must read the word aloud before placing it on top of the tower.
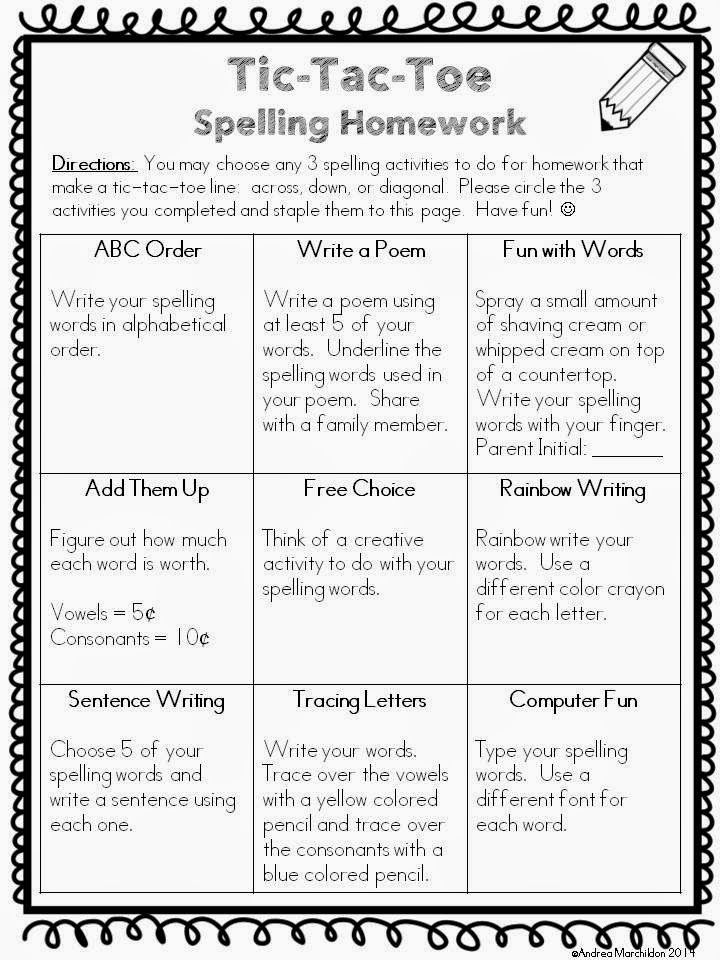
Tic-Tac-Toe
When playing Tic-Tac-Toe, players typically mark X or O. Instead, have students choose a sight word to write on their turns. The first to get three in a row with their sight word wins.
Hangman
Hangman is already a word game. Instead of picking any word, pick a high-frequency word to play with. Players will take turns guessing letters to spell the high-frequency word before an entire person is drawn. You can also play this game digitally and project it on an interactive whiteboard. Build a House and Food Builder are examples of digital sight word games.
You can also play this game digitally and project it on an interactive whiteboard. Build a House and Food Builder are examples of digital sight word games.
Movement Games
Games and movement are a great combo. Movement Games: Pre-Primer Words and Movement Game: Primer Words allow students to exercise and read simultaneously. Use the programmed boards or enter your own sight words.
Board Games
Candy Land and Connect 4 are just a few examples of board games that can become high-frequency word games. Write words on the Candy Land cards and have students read them before moving to the color. Use yard sale stickers to add sight words to the Connect 4 chips. Read the words before making a play.
Zap
Popsicle sticks and a cup are all that are needed to play Zap. First, write a sight word on each stick. Next, write ZAP on several sticks. Finally, place all of the sticks into the cup. Students take turns pulling out sticks and reading the sight word. If they pull a Zap! they return all of their sticks to the cup.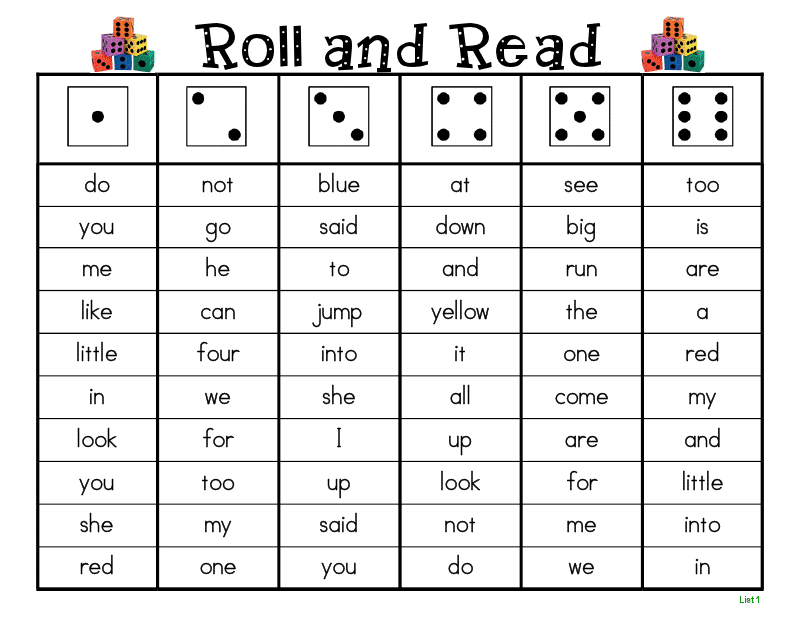
Memory
Choose the high-frequency words you wish to play with. Write each word on 2 cards. Flip the cards over. To play, students take turns flipping over 2 cards to try and make a match.
When Can I Use High-Frequency Word Games for Kindergarten?
High-frequency word games for Kindergarten can be used in the classroom at various times during the school day. After they have been introduced, they would be a great way to ease into school and start the day! These fun sight word practice games would also be a great way to practice and review during your phonics block. They would also work well during word work, guided reading, or sight word literacy centers. Since your students feel like they are playing and not learning, they may even want to play them during free-choice.
Research shows it can take 17 exposures to learn a new word. Therefore, high-frequency word activities for kindergarten, such as high-frequency word games for kindergarten, will provide exposure and help students turn high-frequency words into sight words.
Check out these other sites to learn more about high-frequency word games for kindergarten:
- 10 Fun Activities for High-Frequency Words
- 20 Sight Word Games, Activities, and Reading Ideas
- 25 Super Sun Sight Word Games
What are some of your favorite high-frequency word games to play with your students?
13 Highly Effective And Fun Sight Word Games To Help Your Kids Learn
What Are Sight Words?
What’s the most common word in the English language? It’s the. Imagine pausing every time you ran across this word in a book, on a poster, or in a magazine. Even the simplest texts would become grueling to read.
Common words in the English language (like the) are often grouped together in the early stages of reading — these are what we mean when we speak about sight words. Sight words aren’t easy to sound out or decode, especially for young readers who are just learning the rules to sound out words, so we memorize them (or, in other words, recognize them by sight).
These words occur so frequently that readers, including very young readers, need to know them instantly. And once your child learns basic sight words, they won’t need to spend a lot of time trying to decipher these high-frequency words.
Sight words are dually helpful in this way: they help your child instantly recognize familiar words and help them bypass trying to sound them out because, phonetically, they often don’t make much sense!
Why, for instance, doesn’t the word was rhyme with has? Why doesn’t have rhyme with gave? The first of each is phonetically irregular, despite the fact that they’re some of the most common words in the English language.
As adults who learned to read many years ago, we don’t think twice about why we pronounce sight words the way we do. We also don’t consider why was and has or have and gave don’t rhyme.
Our reading of these words happens automatically, and that’s what helps us read fluently. But early readers who are learning the rules of the English language need a little help.
But early readers who are learning the rules of the English language need a little help.
That’s where sight word games come in. We’ve compiled a list of fun activities that you can do with your young reader to help them learn sight words. And these activities are great for both you and your child.
For you, a majority of the activities require minimal supplies and prep time, which is great for a busy parent. For your child, the games are lots of fun, so they can learn without even realizing it.
But before we get to these fun activities, let’s be clear on the specific sight words your child will need to be familiar with.
What Words Should You Use For Sight Word Games?
Decades ago, an educator named Edward Dolch developed a list, used widely by teachers, of the words most frequently used in children’s books. He identified 220 “service words” and 95 nouns. The words are broken down by levels: pre-primer, primer, first grade, second grade, and third grade.
Some of the 315 words that comprise the two lists are very easy for kids to learn: a, I, it. Others offer more of a challenge. For instance, the pre-primer list includes you, said, and where.
Others offer more of a challenge. For instance, the pre-primer list includes you, said, and where.
Here is a list of the 45 sight words we include in our Beginning Reader and Growing Reader pathways:
And, a, the, on, is, to, I, was, you, your, yes, no, do, they, with, that, are, said, girl, boy, were, this, look, like, want, has, of, what, see, go, play, here, very, good, his, her, there, where, have, walk, talk, know, blue, green, little.
Are Sight Words Just High-Frequency Words?
The short answer: not quite. But it’s a little more complicated.
While the terms sight words and high-frequency words are often used interchangeably, there are some key differences.
High-frequency words, as the name suggests, are the most commonly found words in our written language. For example, like, the, it, etc., are all high-frequency words. And some of them follow standard phonetic patterns while others don’t.
On the other hand, though sight words may frequently occur in text, what sets them apart is that they do not fit standard phonetic patterns or the applicable phonetic rules are more advanced. Therefore, they often need to be memorized.
Therefore, they often need to be memorized.
In essence, many high-frequency words can become sight words once a learner reads them instantly without trying to decode them.
One of the best ways to help kids get to this stage of word recognition is to continue exposing them to sight words. This is where games come into play!
13 Fun Sight Word Games To Help Your Child Learn
Parents wear many hats — companion, guidance counselor, teacher, and so on — and all of them are crucial. But one of the most enjoyable parts of being a parent is cutting up with your child and having a little bit of fun.
The good news? Your child can learn and have fun at the same time while playing these games!
We know how invested you are in your child’s future. We want to help you set them up with the best tools for success in the easiest, most enjoyable way possible. So here are some sight word games that will get their brain working and their belly laughing!
1) Sight Word Twister
This is a version of the popular game Twister. If you want to try this game, choose between six or twelve words to work with at a time.
If you want to try this game, choose between six or twelve words to work with at a time.
That number will depend on your child’s comfort level with sight words, their attention span, and the amount of time on your hands! Feel free to start small and work your way up with additional rounds.
Write each sight word you chose on a blank index card. Then, clear a space on a wooden or linoleum floor and tape each word so that they are all just a little bit apart from each other (make sure your little one can still reach!). Now the fun begins.
Tell your child to find one of the words — have, for instance — and place an elbow on the word. Then they must put their knee on a second word and their nose on a third. You can go on to a fourth, fifth, or sixth word, or you can stop at three.
Your child isn’t the only one who has to twist and turn. In our experience, children want you to play along with them and be just as silly about the shapes you make with your body!
Plus, giving your child the chance to choose the word you have to touch helps them practice reading their sight words. Being the “game boss” will give them another opportunity to learn!
Being the “game boss” will give them another opportunity to learn!
Your child may have a blast with this game and insist they want to keep going, but it’s best to limit your play to two or three rounds per player. That will help keep them from getting bored with the game (and give their brain a chance to rest!).
2) Pick The Word
If you want to try this game with your child, write your six sight words on index cards — one word per card. On a separate sheet of paper, list the six words twice — one list for you, one for your child.
Next, place the index cards with the words facing down. You can take the first turn. After picking a word from your list, flip four of the cards so the words are showing. If you uncover the word you’re seeking, you can cross that word off your list.
At the end of your turn, flip the cards back over, mix them up, and give your child a turn at flipping four of the cards.
If on your first turn you did not find the word you wanted, you have to hunt for the same word on your next turn. If you found the word you wanted, pick a second word from the list.
If you found the word you wanted, pick a second word from the list.
The first player to cross off four words wins. To make the game more challenging, you can turn over three cards per turn instead of four, or you can aim to find all six words instead of just four of the words.
3) Word Match Up
On a sheet of paper, write your six sight words three times. Your child’s job is to draw a line that connects each word to the two identical words on the sheet.
After drawing a line that connects the first three words, it’s time to connect the next three matching words.
This game may sound pretty easy, but here’s the hitch: your child cannot cross any line already on the page. The page gets pretty crowded with lines, so this is not an easy accomplishment. They may end up with some kooky, loopy lines — and that’s the goal!
Try it yourself. The more you stumble and struggle, the more your child will enjoy the game!
4) Word Toss
If you’d like to give this game a go, write each sight word on its own Post-it® and then stick the words on the floor. You can also stick them to a wall or a door.
You can also stick them to a wall or a door.
Get a soft toy, like a small stuffed animal, and stand a few feet away from the words. Choose a word and say it aloud. Your child must toss the toy so that it hits the right word.
Your turn next. Your child picks a word for you to hit. The game is more fun if you miss, so don’t worry about having poor aim. You can play to see who reaches a set number of points or who has the most points after five or six rounds.
5) Sight Word Bingo
Selecting from the Dolch lists, you can make custom Bingo cards that use sight words. It makes the perfect, classic sight word game for your child!
We’re sure you know how Bingo works, but just in case, we’ll give you a refresher. Set up one regular bingo board each for you and your child. If more people are playing, you might have teams or make sure you have one card for each player.
Tell your child to pick 24 words. The same words will go on both boards, but in different places on each board. Then write the words on index cards. Turn the cards over and mix them up.
Then write the words on index cards. Turn the cards over and mix them up.
Players will take turns picking cards — reading the words and finding each word on their card. When they find a word, they will cover it with a token or a penny. The first person to get five words in a row wins. Bingo!
6) Sight Word Go Fish
Introducing your child to this game will be easier if they have prior experience with Go Fish. If they don’t, that’s OK, too! It’s easy to learn and a blast to play.
If you’d like to give this game a go, use index cards or cut pieces of paper for playing cards. You can write matching pairs of whichever sight words you want your child to focus on. It’s important that there are at least two cards for each word — the point of Go Fish is to match them!
We recommend starting with 20 cards (ten sets of words) and giving each player five cards in their hand. You can decrease the number for younger children and increase the number (or difficulty) of words as your child gets more comfortable playing.
Tip: For younger kids, you might let your child lay the words on the floor and hide them from you by using a book as a shield rather than them holding the cards in their hand, as that can be challenging.
Your child will read out the word they want to match. If the word is an, for example, and you have the other an card in your hand, then you have to hand it over. If you don’t have the matching card, then you tell them to “Go fish!” from the pile of extra cards.
If your child is a little older and experienced with some sight words already, feel free to sprinkle in words they already know.
The familiarity will help their confidence as they work with their new words. We all like the feeling of knowing how to do something correctly — reinforcing their knowledge positively (like through a game!) will help keep them encouraged to learn more.
7) Sight Word Scavenger Hunt
This option is super versatile — it can be played indoors or outdoors!
We all love a good, old-fashioned scavenger hunt. Instead of hunting pastel eggs filled with candy, though, this game has your child hunting their sight words.
Instead of hunting pastel eggs filled with candy, though, this game has your child hunting their sight words.
If you want to try this game with your child, write the sight words you want to use on a stack of index cards and number them 1-10. It may also be beneficial to write the words on a separate sheet of paper for your child to reference so they know the selection.
Then make a list of clues for those same words on a separate piece of paper. For example, one clue might be, “I __ a cookie” (have) or, “What word rhymes with buzz?” (was).
Next, simply hide the cards in places familiar to your child. You can use the backyard, a favorite park, or your whole house if it’s an extra rainy or cold day. They’ll use the clues to figure out which words to search for.
Tip: make sure you remember where you put the cards! You’ll need to keep in mind the different locations while you write out your sheet of clues. The numbers on the cards should coincide with the clues. Have fun with some wacky rhymes and hints that will get your child laughing!
The clue list can also be made optional. If you’re working in a small space, your child can always just try to find however many words you hid. If they know to look for 10 cards, then they can just run wild through the room (hopefully not upturning furniture!) searching for them.
If you’re working in a small space, your child can always just try to find however many words you hid. If they know to look for 10 cards, then they can just run wild through the room (hopefully not upturning furniture!) searching for them.
8) Sight Word Tower
This is an easy, fun sight word game for your child to try that we guarantee they’ll love — because it involves things crashing and making a mess (but one that’s easy to clean up, we promise!).
While trying this game, you’ll need a stack of paper or plastic cups that you don’t mind writing on with a marker. Near the rim of each cup, write a single sight word you want your child to focus on (that way all the cups are the same).
Then your child simply picks up the cup, reads off the sight word, and tries to create a “tower” or “castle” out of all their sight word cups! Here’s the rub — you can only have three cups on the floor! All others must build on top of those three and cannot be inside each other.
The trick is to make sure the cups don’t fall over — if they do, you have to start again! They win once they stack all the cups (and read all the sight words!).
9) Volleyball
This sight word game is easy and simple as well. All you need is an inflatable beach ball that you can write on with a permanent marker.
For each “sliver” of the beach ball, you’ll simply write down a sight word. Then you and your child will toss the ball back and forth. If you want to simulate a proper volleyball game, then you can do this over a net propped up in a yard.
When you catch the volleyball with your hands, you have to read aloud the two words your thumbs touch. For example, your left thumb may touch the word “blue” while your right thumb touches the word “our.” Once you read the words, toss the ball back to the other player.
You don’t have to write in-between the lines on the ball, either. To make it wilder (and challenging!), you can write words all over the ball. That way the words your child “catches” are even more unpredictable.
10) Sight Word Path
All you need for this fun game is masking tape (or painter’s tape), index cards, and a marker.
First, write one sight word on each index card. Then, arrange your cards face up on the floor to make a “path.” This path doesn’t have to be straight. It can have as many twists and turns as you’d like (i.e., over the chairs, under the table, etc.).
When placing the cards, make sure they are close enough to each other that your child can step from one card to the next. Important tip: Don’t forget to tape them down with your masking tape to prevent slips or falls. Safety first!
Your child will need to stand at the beginning of the “path” you’ve created and read the word on the first card out loud to start the game. Then, when they’ve read it correctly, they step onto that card.
The goal is to read the next word, and the next, and so forth until they reach the end of the path. If you’re playing with multiple children, each child can start once the player before them has gotten to the end of the course.
Once your child is comfortable with this game, encourage them to read and walk more quickly.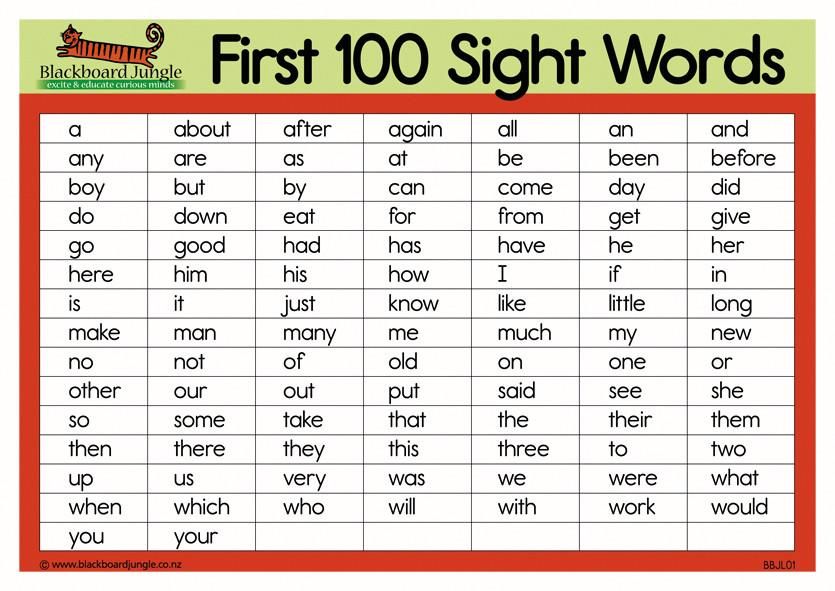 If they are just starting to learn sight words, you can first introduce them to easy terms and increase the difficulty as they go along.
If they are just starting to learn sight words, you can first introduce them to easy terms and increase the difficulty as they go along.
This activity helps kids read sight words quickly and gain confidence through repetition. They’ll also be burning a lot of energy in the process!
11) Hangman
Hangman is a popular game that can also be great to help children learn sight words. To begin, grab some index cards, a marker, and some sheets of paper.
Write one sight word on each index card. Then, use your marker to draw a Hangman “scaffold” on a sheet of paper. (You can also use a chalkboard and chalk for this activity if those are available.)
Next, place the sheet of paper in front of your child, and put the index cards face down next to it. To play, have your child draw a card from the stack and read it aloud. Give them five to 10 seconds to do so.
If your child mispronounces the word on their card, show them how to add the first body piece to the hangman structure (e. g., the head). That index card will then return to the bottom of the stack for them to try again later.
g., the head). That index card will then return to the bottom of the stack for them to try again later.
(Remember to help them pronounce this word before returning it to the stack so that they’ll be better prepared next time.)
If they pronounce the word correctly (yay!), move that card to a “correct” pile. Then, continue playing until all the Hangman body pieces have been added — head, torso, arms, and legs.
Once the game is over, have your child count all the cards from their correct pile and tally this as their score. If you’re playing with more than one person, the one with the most cards is the winner! Note: Each child will need their own sheet of paper with the Hangman structure.
If you’re playing with very young children just starting to learn sight words, you can take two turns to draw each body piece (e.g., for legs, you can draw from the waist to knees, then the knees to the feet). This will give them more chances to get words right before the game ends.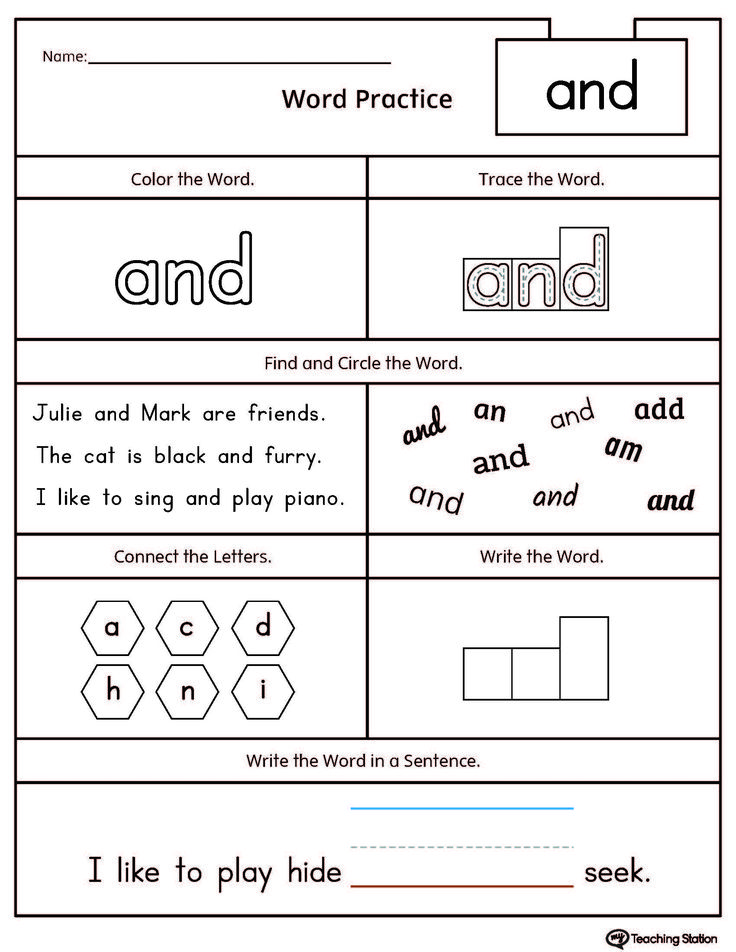
If your child or children are more familiar with sight words, begin the game with the head and torso already drawn, giving them fewer chances to make mistakes.
Also, since any mispronounced words get returned to the stack of cards, your child will be exposed to them again, giving them more opportunities to get the pronunciation correct.
12) Sight Word Discovery
Most kids love discovering interesting items in their homes or backyards. Sight Word Discovery takes this natural love for exploring and mixes it with learning.
You’ll need a few items to get started — index cards, a marker, a large plastic tub, a lot of sand, and craft sticks and rocks (these are optional).
First, write a sight word on each index card. Then, fill the large plastic tub with sand. While filling it up, randomly put the index cards into the tub. You can add some sticks and rocks to the mix as well.
For this game, your child will need to act as a paleontologist who’s on the hunt for sight words (no fossil-finding today!).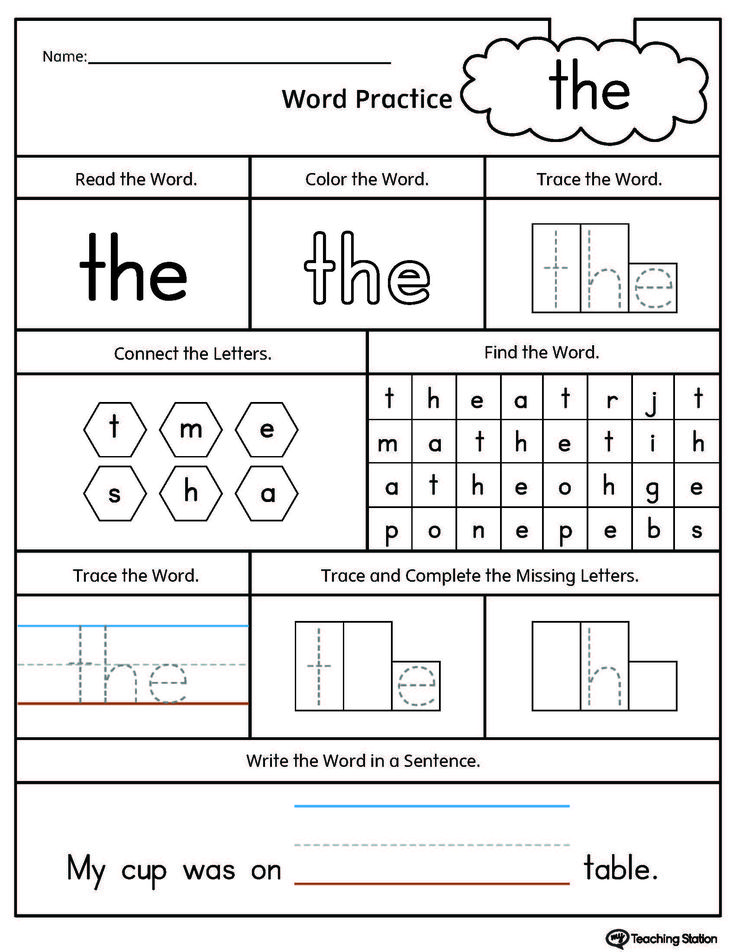 Every time your child finds a new card, have them read it aloud.
Every time your child finds a new card, have them read it aloud.
Wow! Look what I found! It’s “the!”
Sometimes parents find it difficult to encourage their children to participate in learning activities or games. But, since children often love playing with sand or dirt, you don’t have to worry about that here!
13) Sight Words On Playdough
Hands-on learning activities are a great way to help children grasp many concepts. That’s because they’re very interactive, allow for creativity, and help to make abstract concepts real.
All you need to get started with this game is playdough, magnetic letters (or letter cutouts from cardboard paper), index cards, and a marker.
The goal is to encourage your child to construct sight words using the magnetic letters. They will then place these letters upright on the playdough.
To play, place a stack of index cards in front of them, face down. Each index card will have a sight word. When your child draws a card, they’ll need to read it aloud and then construct the word on the playdough.
For example, if your child draws the word like, they’ll need to read it, find the word’s letters, and place them upright on the playdough.
To make things a little more interesting, give your child a timer and ask, “How many words can you construct in five minutes?”
This is a great hands-on learning activity to help kids build their own sight words. And playing with multiple children can add some friendly competition.
What About Reading?
Here at HOMER, we’re big advocates of early childhood reading.
Not only do books expose your child to sight words (and high-frequency words), but they also help improve their vocabulary, strengthen their concentration, and expose children to the world around them.
In addition to playing the above sight word games, you can also continue to read regularly to your child to familiarize them with sight words.
Here are a few activity books you can also check out:
- Learn to Read: Sight Words Storybook (For three to five-year-olds)
- Sight Words Word Search Book for Kids (For four to eight-year-olds)
- 100 Sight Words Kindergarten Workbook (For four to six-year-olds)
- Sight Words Activity Book (For five to nine-year-olds)
- Sight Words and Spelling Workbook (For six to eight-year-olds)
Sight Word Games Are Fun And Functional
Games like these are easy to play, require very little equipment, and are highly effective. The more you play these or similar games, the faster your child will learn lots of sight words, which will make them stronger, more confident readers.
The more you play these or similar games, the faster your child will learn lots of sight words, which will make them stronger, more confident readers.
We hope you found some interesting options in this list that you’ll try with your child. Remember, sight word games are all about having fun and learning at the same time! Your child will work up their stamina the more they play these sight word games.
And as always, we’re here to offer a helping hand any time you need it. If you find yourself struggling to fit in practice time for your child’s sight words, you can leave them in our hands with the HOMER Learn & Grow app!
Author
Word games and exercises for children in kindergarten, Card file of word games in kindergarten
Playing activities of a preschooler > Games for children round, what is oval?
Game progress: The teacher asks the child to name as many round and oval objects as possible. The child starts the game.
The child starts the game.
If he cannot name, the teacher starts: “I remembered that an apple is round and a testicle is oval. Now you go on. Remember what shape is a plum, and what is a gooseberry? That's right, the plum is oval, and the gooseberry is round. (Helps the child name objects and compare them in shape: ring-fish, hedgehog-ball, cherry-cherry leaf, watermelon-melon, acorn-raspberry, tomato-eggplant, sunflower-seed, zucchini-apple) .
In case of difficulty, the teacher shows the child a set of pictures and together they arrange them into two groups.
“Flies - does not fly”
Game progress: The teacher invites children to quickly name objects when he says the word “flies”, and then name other objects when he says the word “does not fly”.
The teacher says: “Flies”.
Children call: “Crow, plane, butterfly, mosquito, fly, rocket, dove”, etc. Then the teacher says: “Does not fly”. Children call: “Bicycle, chamomile, cup, dog, pencil, kitten”, etc. The game continues: the words “flies”, “does not fly” are called by one of the children, and the teacher names the objects together with the children. The game can be played while walking.
Children call: “Bicycle, chamomile, cup, dog, pencil, kitten”, etc. The game continues: the words “flies”, “does not fly” are called by one of the children, and the teacher names the objects together with the children. The game can be played while walking.
"Edible - inedible"
The game is played by analogy with the previous one.
"Alive-non-living"
Game progress: First, we explain that we call all living objects "WHO", and inanimate objects "WHAT". Here are some examples.
Then we play questions and answers. You can use picture books.
What is growing? Who is growing?
Who flies? What flies?
Who swims? What is floating?
Who is the biggest? What is the biggest?
Etc.
“What happens below and what happens above?”
Game progress: The teacher invites the children to think and name something that happens only upstairs.
If the children find it difficult, he prompts: “Let's look up, above us is the sky. Does it happen below? No, it always happens only at the top. And what else happens only at the top? Where are the clouds? (stars, moon) . Now think about what happens only below? Look at the ground. Where does the grass grow? Where does she go?” (plants, ponds, earth, sand, stones, etc.) .
Does it happen below? No, it always happens only at the top. And what else happens only at the top? Where are the clouds? (stars, moon) . Now think about what happens only below? Look at the ground. Where does the grass grow? Where does she go?” (plants, ponds, earth, sand, stones, etc.) .
After that, the children independently enumerate the objects of nature that exist only above and those that exist only below.
"What can be sweet?"
Game progress:
The teacher offers the children: Listen carefully, I will name something that is sweet. And if I make a mistake, then I must be stopped, I must say: “Stop!”
The teacher says: "Sugar, marshmallows, raspberries, strawberries, lemons."
The children listen attentively and stop him on the word where he "wrong". Then the children themselves name what is sweet.
“Answer quickly”
Game progress: The teacher, holding the ball in his hands, becomes a circle with the children and explains the rules of the game: “Now I will name some color and throw it to one of you ball. The one who catches the ball must name an object of the same color. Then he himself calls any other color and throws the ball to the next one. He also catches the ball, names the object, then his color, etc.”
The one who catches the ball must name an object of the same color. Then he himself calls any other color and throws the ball to the next one. He also catches the ball, names the object, then his color, etc.”
For example, “Green,” says teacher (makes a short pause, giving the children the opportunity to remember green objects) and throws the ball to Vitya.
"Grass", - Vitya answers and, having said: "Yellow", throws the ball to the next one.
The same color can be repeated several times, as there are many objects of the same color.
The main feature for classification can be not only the color, but also the quality of the object.
The beginner says, for example: "Wooden", and throws the ball.
“Table,” answers the child who caught the ball and offers his word: “Stone”.
"Home" - the next player answers and says: "Iron", etc.
The next time the form is taken as the main feature. The teacher says the word "round" and throws the ball to any player.
"Sun" - he answers and calls another shape, for example "square", throwing the ball to the next player.
Thoth names a square object (window, handkerchief, book) and suggests some form. The same shape can be repeated several times, since many objects have the same shape. When repeating, the game can be made more difficult by offering to name not one, but two or more objects.
“How are they similar?”
Game progress: The teacher invites the children to look around and find two objects that are somewhat similar to each other.
He says: “I will call: the sun-chicken. How do you think they are similar to each other? Yes, that's right, they are similar in color to each other. And here are two more items: a glass and a window. How are they similar to each other? And now each of you will name your two similar objects.
Games to eliminate the fourth "extra" word
“Be careful!”
Game progress: The teacher says to the children: I will name four words, one word does not fit here. You must listen carefully and name the "extra" word. For example: matryoshka, tumbler, cup, doll; table, sofa, flower, chair; chamomile, hare, dandelion, cornflower; horse, bus, tram, trolleybus; wolf, crow, dog, fox; sparrow, crow, dove, chicken; apple, tree, carrot, cucumber.
You must listen carefully and name the "extra" word. For example: matryoshka, tumbler, cup, doll; table, sofa, flower, chair; chamomile, hare, dandelion, cornflower; horse, bus, tram, trolleybus; wolf, crow, dog, fox; sparrow, crow, dove, chicken; apple, tree, carrot, cucumber.
After each highlighted "extra" word, the teacher asks the child to explain why this word does not fit into this group of words, i.e., to explain the principle of grouping.
“Listen carefully!”
Game progress: The teacher says to the child: “I will name the words, and you will say which word does not fit: cat, fox, horse, cow; tractor, car, rocket, bus; pear, turnip, beet, carrot; book, pencil case, ball, notebook; water, thermometer, medicine, cotton wool.
In case of difficulty, he slowly repeats a certain set of words and helps the child to highlight the unsuitable for some reason.
Find out!
Game progress: What berries do you know? Now I will name the words, if among them you hear the word for a berry, then clap your hands.
Presentation words - cabbage, strawberry, apple, pear, currant, raspberry, carrot, strawberry, potato, dill, blueberry, lingonberry, plum, cranberry, apricot, marrow, orange.
"Now I'm going to name the words, if you hear a word related to berries, clap once, if it's about fruits, clap twice."
(Words can be used the same, you can come up with others.)
As a basis for systematization, there can be a theme - tools, furniture, clothes, flowers, etc.
Tell me, what are the similarities in taste? color? size?
- lemon and pear
- raspberry and strawberry
- apple and plum
- currant and gooseberry
What is the difference in taste? color? size?
Divided into groups
Game progress: "What groups do you think these words can be divided into? Sasha, Kolya, Lena, Olya, Igor, Natasha.
What groups can be made from these words: dove, sparrow, carp, titmouse , pike, bullfinch, zander".
“Pick up the words”
Game progress:
- Match as many words as possible that can be attributed to the wild animals group (pets, fish, flowers, weather phenomena, seasons, tools and etc.) .
- Another version of the same task.
Use arrows to connect words that match the meaning:
ball | furniture
poplar | flower
cabinet | insects
plate | wood
coat | clothing
ant | crockery
pike | toy
rose | fish
“Similarities and differences”
Game progress: Invite the child to indicate the similarities and differences of the following pairs of words:
Book - notebook | Day - night
Horse - cow | Tree - bush
Telephone - radio | Tomato - cucumber
Airplane - rocket | Table - chair
"Find the opposite object"
Game progress: Calling any object (for example, sugar) , you need to name as many others as possible that are opposite to this one. It is necessary to find opposite objects according to the function "edible - inedible", "useful - harmful", etc., on the basis of (size, shape, condition) , etc.
It is necessary to find opposite objects according to the function "edible - inedible", "useful - harmful", etc., on the basis of (size, shape, condition) , etc.
"Search for an analogy"
Game progress: A word is called, for example, a briefcase. It is necessary to come up with as many "analogues" as possible, i.e. other items similar to it in various essential features (bag, sack, backpack, etc.) Game progress: Invite the child to name a group of objects in one word. We call many specific objects with one word. For example, birch, pine, oak, etc. we call trees.
Invite the child to name in one word:
- a table, a chair, a cupboard are...
- a dog, a cat, a cow are...
- a cup, a saucer, a plate are...
- cornflower, chamomile, tulip - this.
"Find a common word"
Game progress: This task contains words that are united by a common meaning. It is necessary to try to convey this general meaning in one word.
What is the common word for the following words:
- Faith, Hope, Love, Elena
- a, b, c, c, n
- table, sofa, armchair, chair
- Monday, Sunday, Wednesday, Thursday
- January, March, July, September.
The generalizing word can be "spring months", or it can be "months of the year", etc.
A more complex version of the exercise contains only two words for which it is necessary to find a common concept.
Find out what the following words have in common:
a) bread and butter (food)
b) nose and eyes (parts of the face, sensory organs)
c) apple and strawberries (fruits)
d) clock and thermometer 900 devices)
d) Kit and lion (animals)
e) Echo and mirror (reflection)
“Words-twin”
Course of the game: This exercise is associated with this a phenomenon of the Russian language, like homonymy, that is, when words have different meanings, but are the same in spelling.
Which word means the same as the words:
1) a spring and something that opens the door;
2) the girl's hair and a grass cutter;
3) a branch of grapes and a drawing tool.
Think of words that are the same in sound but different in meaning.
Additional tasks for the exercise:
4) a crying vegetable and a weapon for shooting arrows (burning vegetable and small arms) ;
5) part of a gun and part of a tree;
6) things to paint on and greenery on the branches;
7) a construction site hoist and a mechanism that must be opened to allow water to flow.
"What is needed"
Game progress: The car runs on gasoline or other fuel; tram, trolleybus or electric train are powered by electricity. All this together can be attributed to the group "transport".
Seeing an unfamiliar car (e.g. truck crane) , they ask: what is it? Why?
Similar exercises are performed with other concepts: tools, utensils, plants, animals, furniture, etc.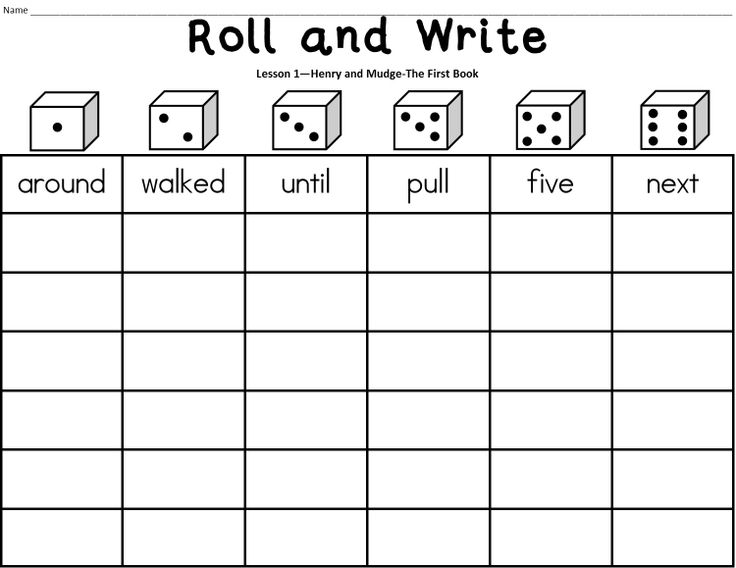
"Why?"
Game progress: Now I will tell you words, and you will answer me, which is more, which is less, which is longer, which is shorter.
- Pencil or pencil? Which one is shorter? Why?
- Cat or whale? Which one is more? Why?
- Boa constrictor or worm? Which one is longer? Why?
- Tail or ponytail? Which one is shorter? Why?"
The teacher can come up with his own questions, focusing on the above.
"Choose the main thing"
Game progress: An adult says to the children: Now I will read a series of words. From these words you will have to choose only two, denoting the main features of the main word, i.e., without which this object cannot exist.
Other words are also related to the main word, but they are not main.0003
For example, a garden... What do you think, which of these words are the main ones: plants, gardener, dog, fence, earth, i.e. something without which a garden cannot exist? Can there be a garden without plants? Why?. .. Without a gardener... a dog... a fence... land?.. Why?
.. Without a gardener... a dog... a fence... land?.. Why?
Each of the proposed words is analyzed in detail. The main thing is that children understand why this or that word is the main, essential feature of this concept.
Sample tasks:
a) Boots (laces, sole, heel, zipper, shaft)
b) River (shore, fish, angler, mud, water)
c) City (car, building, crowd, street, bike)
d) Barn (hayloft, horses, roof, livestock, walls)
e) Cube (corners, drawing, side, stone, wood)
f) Division (class, dividend, pencil, divider, paper)
g) Game (cards, players, fines, penalties, rules)
h) Reading (eyes, book, picture, printing, word)
and) War (plane, guns, battles, rifles, soldiers)
“Dungeon”
games: The host thinks of a word or tells the conditions of some completely unusual situation, and the players (children or adults) must guess the word or explain the situation by asking questions that can be answered with one of five answers: "yes"; "No"; "Yes and no"; "there is no information about it"; "it's not significant.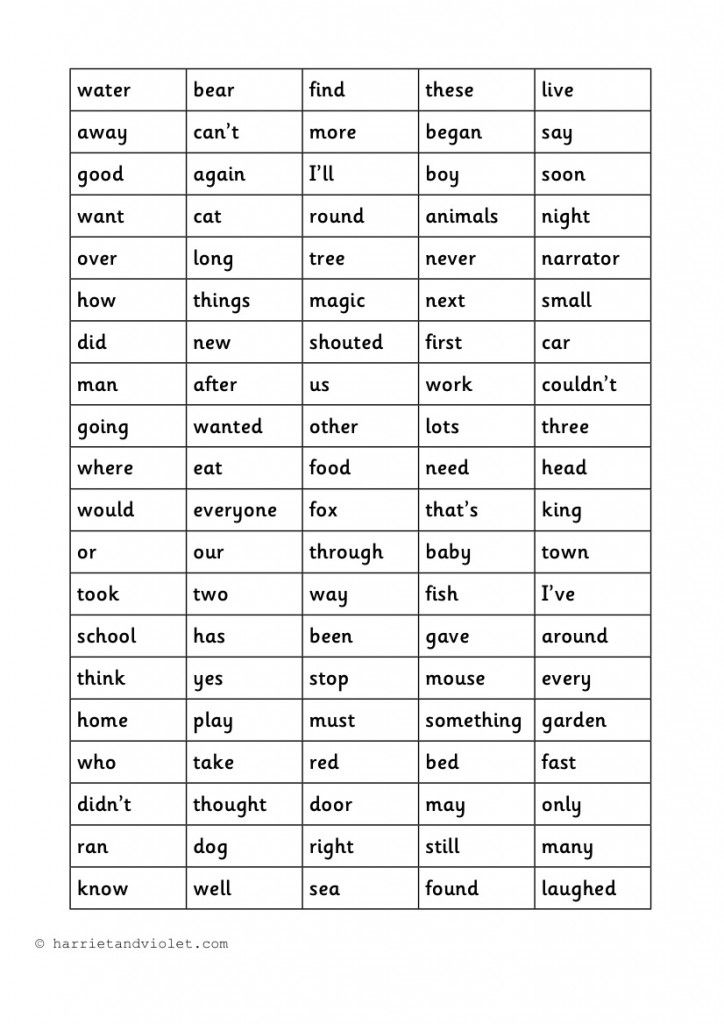 "
"
For example: "I thought of a plant in the middle zone. In ten questions, determine the plant that I thought of."
Themes for "danetok" and possible continuation of the game.
What vegetable did I have in mind?
- Is it a root vegetable? (Carrot, beet, radish)
- Is it a leafy vegetable? (Cabbage, lettuce)
- Is it a fruit vegetable? (Tomatoes, cucumbers)
What name did I think of?
- Is it a male name?
- Does the name begin with a vowel?
- Is there such a name in our group?
What piece of clothing did I have in mind?
- Is this outerwear?
- Are these men's clothes?
What fairy tale did I have in mind?
- Is this a Russian fairy tale?
What historical figure did I have in mind?
- Is this a man?
What must I do in the morning?
What color do I have in mind?
What property of ice cream, light bulb, watermelon, pencil did I guess?
What country did I have in mind?
What kind of writer, storyteller, poet, scientist did I have in mind?
What famous battle did I have in mind?
"Black box"
Game progress: Children are shown a "black box" or just a bag, briefcase and are asked to guess what is there in 10 questions? Etc.
- Is there a man-made object? Is there something soft? Is there something metallic? Etc.
List the items
Game progress: One leader is selected from the group of children. He leaves the room for 2 minutes. At this time, 7 objects are placed on the table in the room and the situation is thought about. For example, children think of the situation "I'm going for a walk", then 7 items of clothing should lie on the table.
The driver is invited, the situation is told to him and he is allowed to inspect the table for 1-2 minutes. Then he turns his back to the table and faces the group of children and starts listing the things on the table. After each correct answer, the group says "Correct!", after the wrong - "Wrong!". If the driver has not listed all the items, the group says which items he forgot.
"Opposite"
Game progress: The leader calls the group of children a word. The task is to name a word denoting the opposite object.
For example, the facilitator says the word "cup". Children can name the following items: "board" (the cup is convex, and the board is straight) , "sun" (the cup is made by a person, and the sun is part of nature) , "water" (water is a filler, and a cup is a shape) , etc.
Each child takes turns offering their answer and making sure to explain why they chose that particular subject.
“Come up with a riddle”
Game progress: A leader is selected from a group of children. His task is to come up with a riddle. The group must solve this riddle. Then another child comes up with a riddle, and so on. Children of 6 years old love to come up with riddles, the game is lively.
“Who is whom (than) will be?
Game progress: The good thing about the game is that you can play with the company or together with your child anywhere. Ask each other questions, make sure that the baby answers the question correctly.
Who will the egg be? (may be a chick, a crocodile, a turtle, a snake.)
- a chicken - a rooster;
- a boy - a man;
- calf - cow or bull - paper - book;
- snow - water;
- water - ice;
- seed - flower;
- flour - pancakes;
etc.
Reverse game: "Who was who?".
- horse - foal
- flower - seed
"Third extra"
Game progress: Adult says three words - owl, crow, fox. The child should quickly analyze these three words in his mind and determine that all three words refer to wildlife, however, an owl and a crow are birds, and a fox is not. Therefore, the fox is superfluous here.
More examples for younger preschoolers:
- milk, juice, bread - all three words mean edible. But they drink milk and juice, but eat bread;
- car, horse, tram;
- hat, scarf, boots;
- rose, birch, tree.
For children aged 5-7 the tasks become more difficult:
- rain, snow, river;
- doctor, tourist, driver;
- shadow, sun, planet;
- frost, blizzard, January;
- stone, clay, glass;
- door, carpet, window;
- sea, river, pool.
“What happens?”
Game progress: First, the adult asks questions, and the child answers. Then you need to give the child the opportunity to express themselves.
Examples:
- What is high? (tree, pole, man, house) . Here it is appropriate to ask which is higher - a tree or a house; person or pole.
- What is long? (short)
- What is wide (narrow) ?
- What is round (square) ?
A variety of concepts can be included in the game: what is fluffy, soft, hard, sharp, cold, white, black, etc.
“What is outside, what is inside?”
Game progress: The adult names a couple of objects, and the child says what can be outside and what can be inside. House - closet; book - cabinet; purse; wallet-money; pan - porridge; aquarium - fish; booth - dog; nora - fox.
Then switch roles - let the child think of pairs of words.
Who is this?
Game progress:
Option 1: We ask questions: who treats the sick? Who teaches children at school? Who is preparing dinner? Who is working on the tractor? Who delivers letters and newspapers? Who sews the dress?
Option 2: Questions: what does the janitor do? What does the doctor do? What does an electrician do? What does the teacher do? What does the driver do? What does a painter do? What does a hairdresser do?
3rd option: We come up with riddles.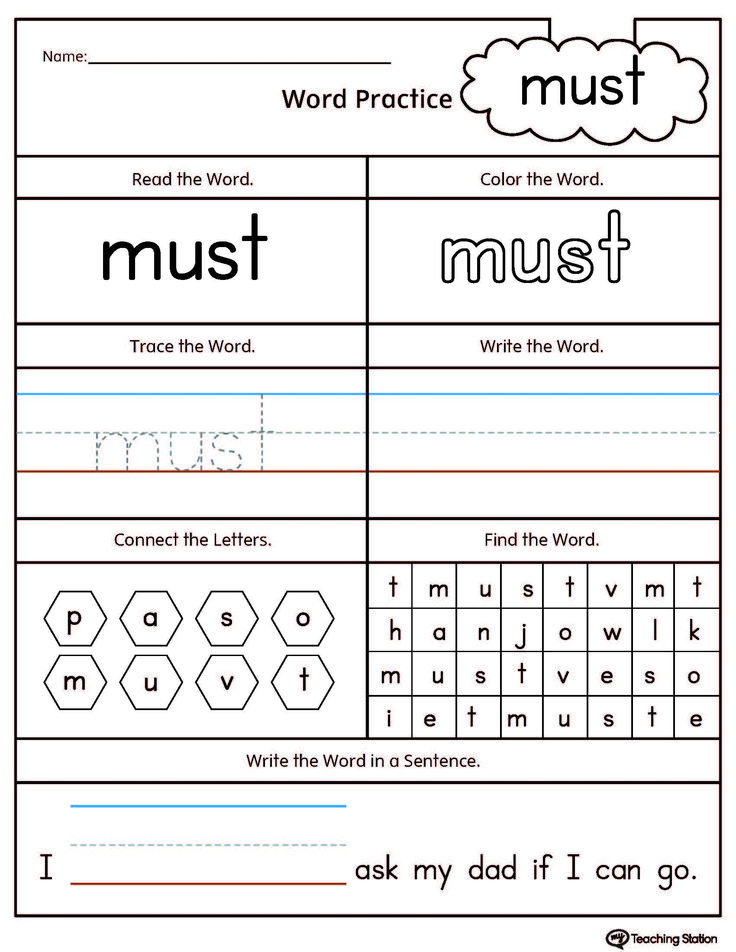 For example: this person works on the street, he has a broom, a shovel.
For example: this person works on the street, he has a broom, a shovel.
4th option: "Who needs what?" What does the postman need? What does a hairdresser need? And vice versa: who needs scissors? Who needs a needle?
"Guess the object by its parts"
Game progress: Children name the parts of the object. The first person to guess what it is about gets one point. This option is good because you can play together with your child anywhere. For example, on the way to kindergarten, while waiting in line to see a doctor, etc.
Examples:
Four legs, backrest, seat.
Numbers, arrows.
Letters, pictures, sheets.
Trunk, branches, leaves.
Root, stem, leaves, petals.
Screen, buttons, electric cord, remote control.
Spout, handle, lid, electric cord.
Paws, tail, collar.
Paws, tail, trunk.
Does everything seem too simple at first glance? But in fact, not all children can describe objects.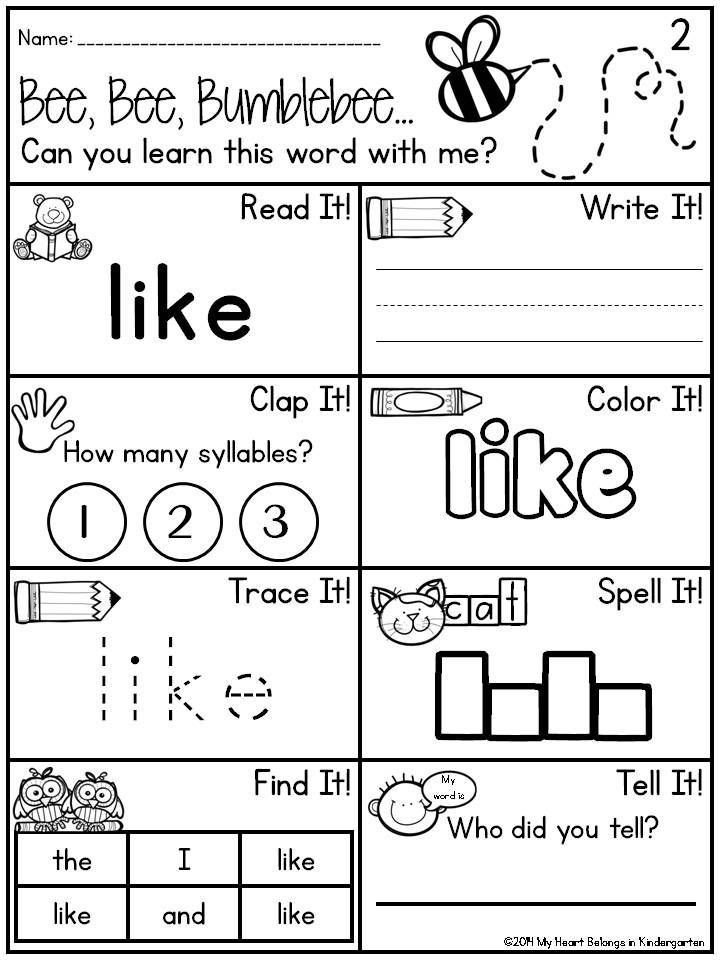 Try it!
Try it!
"Guess the item from the description"
Game progress: Game conditions are the same as in the previous one. But the task here is more difficult. It is necessary not only to find the correct definitions of objects, but also to correctly coordinate adjectives and nouns by gender, as well as to know such concepts as furniture, vegetables, fruits, insects, domestic and wild animals, etc.
Wild animal, lives in the forest , big, shaggy, likes honey.
Wild animal, sly, red, with a fluffy tail.
Insect, with colorful wings, similar to a flower.
Transport, large, heavy, with wings and tail.
Vegetable, red, round, put in salads and soups.
Sweet, small, in a beautiful paper.
“Think and choose!”
Game progress: Now I will read you a proverb, and you try to find a suitable phrase for it that reflects the general meaning of the proverb, for example:
Measure seven times, and cut once
a) If you cut it wrong yourself, then do not blame the scissors
b) Before you do it, you need to think carefully
c) The seller measured seven meters of fabric and cut it off
The right choice here is "Before you do, you need to think carefully"
Example tasks:
1. Better less is better.
Better less is better.
a) One good book is more useful to read than seven bad ones.
b) One delicious cake is worth ten bad ones.
c) What matters is not quantity, but quality.
2. If you hurry, you will make people laugh.
a) The clown makes people laugh.
b) To do a job better, you need to think about it well.
c) Haste can lead to ridiculous results.
3. Strike while the iron is hot.
a) A blacksmith forges hot iron.
b) If there are favorable opportunities for business, you should immediately use them.
c) A blacksmith who works slowly often gets more done than one who is in a hurry.
4. There is nothing to blame on the mirror, if the face is crooked.
a) You should not blame the cause of failures on circumstances, if the problem is in yourself.
b) A good quality mirror does not depend on the frame, but on the glass itself.
c) The mirror hangs crooked.
5. The hut is not red in the corners, but red in the pies.
The hut is not red in the corners, but red in the pies.
a) You can't eat pies alone, you have to eat rye bread too.
6) A case is judged by its results.
c) One tasty cake is worth ten bad ones.
6. Done the job - walk boldly.
a) If you did a good job, you can rest.
b) The boy went for a walk.
7. Skilful hands do not know boredom.
a) Petr Ivanovich never gets bored.
b) A master of his craft loves and knows how to work.
8. Don't get into your sleigh.
a) If you don't know the job, don't take it on.
b) In winter they ride on a sleigh, and in summer on a cart.
c) Ride only on your own sleigh.
9. All that glitters is not gold.
a) The copper bracelet shone like gold.
b) Outward brilliance is not always combined with good quality.
c) What seems good to us is not always good.
Gaming activity:
| | | | | in preschool
Word games for preschool children | Card index for the development of speech (senior group) on the topic:
Word games
for children
older preschoolers
What kind of subject?
Purpose: to learn to name an object and describe it.
Stroke.
The child takes out an object, a toy, from a wonderful bag, calls it (this is a ball). At first, the teacher describes the toy: “It is round, blue, with a yellow stripe, etc.”
Guess the toy
Purpose: to form in children the ability to find an object, focusing on its main features, description.
Stroke.
3-4 familiar toys are put on display. The teacher reports: he will outline the toy, and the task of the players is to listen and name this object.
Note: 1-2 features are indicated first. If children find it difficult 3-4.
Who will see and name more
Purpose: to learn to designate parts and signs of the appearance of a toy with a word and action.
Stroke.
Educator: Olya doll is our guest. Olya loves to be praised, pay attention to her clothes. We will give the doll pleasure, describe her dress, shoes, socks.
Magpie
Purpose: to correlate the verb with the action it denotes and with the subject who performed this action.
Material: needles, glasses, soap, bell, brush, iron. Brush, broom, toy - bird Magpie.
Stroke.
Educator: While you were at home, a magpie flew into the kindergarten and collected various things in her bag. Let's see what she took
(The teacher lays out the objects)
Next, a dialogue occurs between the children and the magpie:
Children:
Magpie, magpie
Give us the soap
Magpie:
I won't give it, I won't give it back
I'll take your soap
I'll give my shirt to wash.
Children:
Magpie, magpie
Give us the needle!
Magpie:
I won't give it, I won't give it back.
I'll take a needle
I'll sew a shirt for my shirt.
Children:
Magpie, magpie,
Give us glasses
Magpie:
I won't give, I won't give.
I myself have no glasses,
I can't read a shirt of verses.
Children:
Magpie, magpie.
Give us a call.
Magpie:
I won't give it, I won't give it back.
I'll take the bell.
I'll give you a shirt - call me, my son.
Educator:
You, forty, do not hurry
You ask the children.
They will all understand you.
Everything you need will be served.
Teacher:
What do you want to do, magpie? (Clean, iron, paint...)
Educator:
Children, what does a magpie need for this?
(Children call and bring all the items)
Magpie thanks and flies away.
“Name as many objects as you can”
Purpose: to exercise children in the clear pronunciation of words.
Stroke.
The teacher invites the children to look around themselves and name as many objects that surround them as possible (name only those that are in their field of vision)
The teacher makes sure that the children pronounce the words correctly and clearly, do not repeat. When the kids can no longer name anything themselves, the teacher can ask them leading questions: “What is hanging on the wall?” etc.
Olya's helpers
Purpose: to form a plural form. Numbers of verbs.
Material: Olya doll.
Stroke.
- Olya doll came to us with her assistants. I'll show them to you, and you can guess who these assistants are and what they help Olya to do.
The doll is walking on the table. The teacher points to her feet.
- What is it? (These are legs)
- They are Olya's helpers. What are they doing? (They walk, jump, dance, etc.)
Then they point to other parts of the body and ask similar questions, the children answer (take hands, draw ...; teeth chew, bite, gnaw ...; eyes look, blink ...)
"Colorful chest"
Purpose: to teach children, when agreeing neuter (feminine) nouns with a pronoun, to focus on the end of the word.
Material: box, subject pictures according to the number of children.
Stroke.
Educator:
I put the pictures
In a colorful chest.
Come on, Ira, take a look,
Take out the picture, name it.
Children take out a picture and say what it shows.
"Tell me which one?"
Purpose: To teach children to distinguish the signs of an object.
Stroke.
The teacher (or child) takes out objects from the box, names them, and the children point out any sign of this object.
If the children find it difficult, the teacher helps: “This is a cube. What is he?
"Magic Cube"
Game material: cubes with pictures on each side.
Rules of the game. The child rolls the dice. Then he must depict what is drawn on the upper face and pronounce the corresponding sound.
Stroke.
The child, together with the teacher, says: “Twist, turn, lie down on the side”, and rolls the die. On the top face - for example, an airplane. The teacher asks: "What is it?" and asks to imitate the rumble of an airplane.
Other faces of the die are played in the same way
“Unusual song”
Rules of the game. The child sings vowel sounds to the motive of any melody familiar to him.
Stroke.
Educator. One day, beetles, butterflies and grasshoppers argued who would sing a song best of all. Big, fat beetles came out first. They sang importantly: O-O-O. (Children sing a melody to the sound O). Then the butterflies fluttered out. They sang a song loudly and cheerfully. (Children perform the same melody, but to the sound A). Grasshopper musicians were the last to come out, they played violins - E-I-I. (Children sing the same melody to the sound I). Then everyone came out into the clearing and began to chant with words. And immediately all the beetles, butterflies, grasshoppers realized that our girls and boys sing best of all.
"Echo"
Rules of the game. The teacher loudly pronounces any vowel sound, and the child repeats it, but quietly.
Stroke.
The teacher says loudly: A-A-A. the echo child quietly answers: ahhh. And so on. You can also use a combination of vowel sounds: ay, wah, ea, etc.
"Gardener and flowers"
Purpose: to consolidate children's knowledge about flowers (wild berries, fruits, etc. )
)
Move.
Five or six players sit on chairs arranged in a circle. This is flowers. They all have a name (you can have the players choose a flower picture; you can’t show it to the host). The leading gardener says: “I haven’t seen a wonderful white flower with a yellow eye that looks like a small sun for so long, I haven’t seen a chamomile.” Chamomile stands up and takes a step forward. Chamomile, bowing to the gardener, says: “Thank you, dear gardener. I'm glad you wanted to take a look at me." Chamomile sits on another chair. The game continues until the gardener has listed all the flowers.
The content of this game can be easily changed: "Gardener and fruit trees", "Forest man and wild berries", "Animal trainer and his animals", etc.
“Who will name more actions”
Purpose: to actively use verbs in speech, forming various verb forms.
Material. Pictures: clothes, plane, doll, dog, sun, rain, snow.
Stroke.
Neumeyka comes and brings pictures. The task of children is to pick up words that denote actions related to objects or phenomena depicted in the pictures.
The task of children is to pick up words that denote actions related to objects or phenomena depicted in the pictures.
For example:
- What can you say about the plane? (flies, buzzes, rises)
- What can be done with clothes? (wash, iron, sew up)
- What can you say about the rain? (walks, drips, pours, drizzles, knocks on the roof)
Etc.
"Kids and Wolf"
Purpose. End the story at its beginning.
Material. Flannelgraph and attributes for the fairy tale "Goat with kids", bunny
Hod.
The teacher tells the beginning of the tale, demonstrating the figures of the characters.
- Listen to what happened next: The goat went back to the forest. The goats were left alone at home. Suddenly there was a knock on the door again. The kids got scared and hid. And it was a small one /show/… (Children agree: bunny)
Educator: bunny says….
Children: don't be afraid of me, it's me, a little bunny.
Educator: The goats treated him….
Children: carrots, cabbages…
Educator: then they became…
Etc.
Wake up the cat
Target. Activate the name of animal cubs in the speech of children.
Material. Animal costume elements (hat)
Move.
One of the children gets the role of a cat. He sits down, closing his eyes (as if sleeping), on a chair in the center of the circle, and the rest, choosing the role of any animal cub at will, form a circle. The one whom the teacher points out with a gesture gives a voice (makes an onomatopoeia corresponding to the character).
The task of the cat: name who woke him up (cockerel, frog, etc.). If the character is named correctly, the performers switch places and the game continues.
Veterok
Purpose. Development of phonemic hearing.
Stroke.
Children stand in a circle. The teacher makes different sounds. If you hear a sound such as y, raise your arms and circle slowly.
Sounds are pronounced y, and, a, o, y, and, y, a. Children, having heard the sound y, make the appropriate movements
"Pinocchio-traveler"
Purpose. Focus on the meaning of verbs.
Material. Pinocchio doll.
Stroke.
Pinocchio is a traveller. He travels to many kindergartens. He will tell about his travels, and you will guess which rooms of the kindergarten or on the street he visited.
- I went into the room where the children roll up their sleeves, soap their hands, and dry themselves.
- They yawn, rest, sleep ...
- They dance, sing, whirl ...
Pinocchio was in kindergarten when the children:
- come, say hello ... (When does this happen?)
- have lunch, thank you ...
- getting dressed, saying goodbye...
- making a snowman, sledging
"Hide and Seek"
Purpose. Formation of the morphological aspect of speech. Bring children to the understanding of prepositions and adverbs that have a spatial meaning (in, on, behind, under, near, between, next to, left, right)
Material. Small toys.
Stroke.
The teacher hides the toys made in advance in different places of the group room, and then, having gathered the children around him. He informs them: “I was informed that uninvited guests settled in our group. The tracker who was watching them writes that someone hid in the upper right drawer of the desk. Who will go looking? Fine. Found? Well done! And someone hid in the corner of the toys, behind the closet (Search). Someone under the doll's bed; someone on the table; that stands to my right"
T.O. the children look for all the uninvited guests, hide them in a box and agree that they will play hide and seek again with their help.
"The postman brought a postcard"
Purpose. To teach children to form verb forms in the present tense (draws, dances, runs, jumps, laps, waters, meows, barks, strokes, drums, etc.)
Material. Postcards depicting people and animals performing various activities.
Stroke.
The game is played with a small subgroup.
Someone knocks on the door.
Educator: Guys, the postman brought us postcards. Now we will consider them together. Who is on this postcard? That's right, Mishka. What is he doing? Yes, drumming. This postcard is addressed to Olya. Olya, remember your postcard. This postcard is addressed to Pasha. Who is pictured here? What does he do? And, you, Petya, remember your postcard.
T.O. 4-5 pieces are considered. And those to whom they are addressed must correctly name the actions of the character and remember the image.
Teacher: Now I will check if you remember your postcards? Snowmen are dancing. Whose postcard is this? Etc.
"Finish the sentence"
Purpose: use of complex sentences)
· Mom put the bread... where? (to the breadbasket)
· Brother poured sugar... where? (to the sugar bowl)
· Grandmother made a delicious salad and put it... where? (to the salad bowl)
· Dad brought sweets and put them ... where? (in candy bowl)
Marina didn't go to school today because. .. (fell ill)
We turned on the heaters because... (it got cold)
I don't want to sleep because... (it's still early)
· We will go to the forest tomorrow if... (weather is fine)
· Mother went to the market to... (buy groceries)
· The cat climbed a tree to... (to save the dogs) )
"Mode of the day"
8-10 plot or schematic pictures about the daily routine. Offer to consider, and then arrange in a certain sequence and explain.
"Who wants a treat?"
Purpose: the use of difficult forms of nouns
The teacher says that there are gifts for animals in the basket, but is afraid to confuse someone with what. Asks for help. Pictures depicting a bear, birds - geese, chickens, swans, horses, wolves, foxes, lynxes, monkeys, kangaroos, giraffes, elephants are offered. Who wants honey? Who is the grain for? Who needs meat? Who wants fruit?
"Name three words"
Purpose: vocabulary activation
Children line up. Each participant is asked a question in turn. It is necessary, taking three steps forward, to give three words-answers with each step, without slowing down the pace of walking.
· What can I buy? (dress, suit, trousers)
· What can be cooked? What can be read? What can you draw? What can fly? What can float? What (who) can jump? Etc.
"Who wants to be what?"
Purpose: the use of difficult forms of the verb
Children are offered plot pictures depicting labor actions. What are the boys doing? (The boys want to make a model airplane) What do they want to be? (They want to become pilots). Children are invited to come up with a sentence with the word want or want.
"Zoo"
Purpose: development of coherent speech.
Children sit in a circle, each receiving a picture without showing them to each other. Everyone should describe their animal, without naming it, according to the following plan:
1. Appearance;
2. What does he eat.
The "game clock" is used for the game. Turn the arrow first. Whom she points to, he begins the story. Then, by rotating the arrows, it is determined who should guess the described animal.
"Compare items"
Purpose: development of observation, specification of the vocabulary due to the names
details and parts of objects, their qualities).
In the game, you can use both things and toys that are the same in name, but differ in some features or details, as well as paired subject pictures. For example, two buckets, two aprons, two shirts, two spoons, etc.
An adult reports that a package has been sent to the kindergarten. What is this? Gets things. "Now we will consider them carefully. I will talk about one thing, and one of you - about another. We will tell in turn."
For example:
| Adult: "I have a smart apron." | Child: "I have a work apron. |