Learn about verbs
Learning Verbs - E2 English Blog
What are verbs?
Verbs are doing words. They describe actions or states. Verbs tell us about what things do or what they are like. Some examples of verbs are: run, walk, work, eat, think.
Along with nouns, verbs are the building blocks of English. If we have a noun and a verb we can make a simple sentence, for example: Lisa runs.
Most verbs describe actions but some describe states. These are called state verbs or stative verbs. Some examples are: like, know, feel, belong, cost and be.
What are the most common verbs in English?
Very common verbs, verbs that we use a lot, are sometimes called hot verbs, because they never get a chance to cool down. Some hot verbs are: be, do, have, go, see, give, take, make, put, say and get. These verbs are used as main verbs in sentences as well as to form
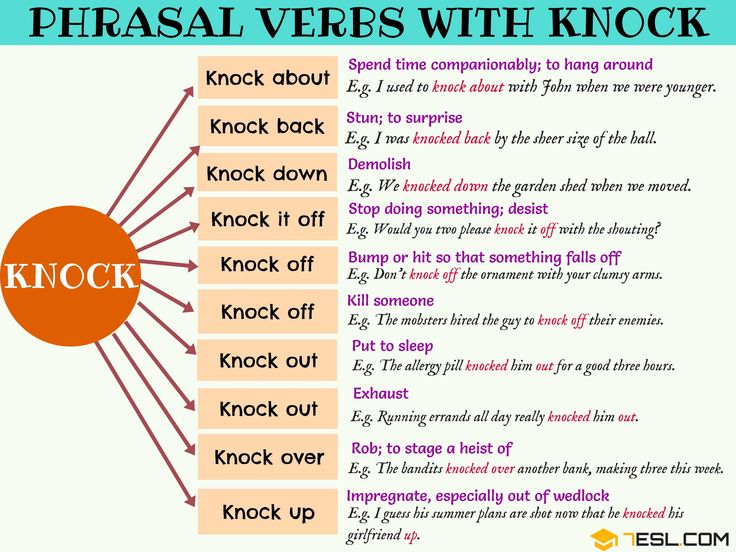
phrasal verbs and to act as auxiliary verbs. Phrasal verbs, sometimes called multi-word verbs, are verbs made up of two or three words which often have many different meanings. We will look at phrasal verbs in another blog post.
What are auxiliary verbs?
Auxiliary verbs are simply verbs that help the main verb in a sentence. We can call them “helping verbs”. We use them to make questions and negative sentences as well as to form some tenses. If we want to make “Lisa runs.” negative, we can change it to “Lisa doesn’t run.” by using a form of the helping verb “do”. We also use a form of “do” to make a question such as “Does Lisa run?” The helping verb “have” and “be” are used to form some of the different tenses in English.
What are regular verbs?
Most verbs in English are regular. This means that they all follow the same pattern in the way that they change into the three main forms which are used to construct the various tenses. However, most of the most commonly used verbs, the hottest verbs are irregular. You have probably learned about irregular verbs before. They are the ones where we have to learn three forms and repeat them. Some examples are eating, ate, eaten and give, gave, given. There is not really any other way to learn how they behave other than repeating the words like a parrot. Regular verbs simply add “ed” for the second and third forms of the verb (walk, walked, walked).
Some examples are eating, ate, eaten and give, gave, given. There is not really any other way to learn how they behave other than repeating the words like a parrot. Regular verbs simply add “ed” for the second and third forms of the verb (walk, walked, walked).
What are irregular verbs?
When you learn the three forms of an irregular verb, for example, take, took, taken– you are learning the infinitive form, the past simple form and the past participle. These names seem a bit difficult at the beginning but it is helpful to know what they are called because it will help you in learning the more advanced tenses and grammatical structures.
The most irregular verb in English is “be”. This is the case in many languages. “Be” is the only verb which has an infinitive form different from the first person singular form of the present simple tense. When we talk about a form of “be”, we mean “am”, “are” and “is” and in the past tense, “was” and “were”.
Verb tenses
When we use verbs in English, we change the form of the verb depending on the tense. The tense is a combination of time (past, present, future) and aspect (simple, continuous, perfect). There are twelve basic tenses in English as listed below with the regular verb “to walk”:
The tense is a combination of time (past, present, future) and aspect (simple, continuous, perfect). There are twelve basic tenses in English as listed below with the regular verb “to walk”:
- Present simple: I walk.
- Present continuous: I am walking.
- Present perfect: I have walked.
- Present perfect continuous: I have been walking
- Past simple: I walked.
- Past continuous: I was walking.
- Past perfect: I had walked.
- Past perfect continuous: I had been walking
- Future simple: I will walk.
- Future continuous: I will be walking.
- Future perfect: I will have walked.
- Future perfect continuous: I will have been walking
You can see how the auxiliary verbs “be”, “have” and “will” are used to help form continuous, perfect and future tenses.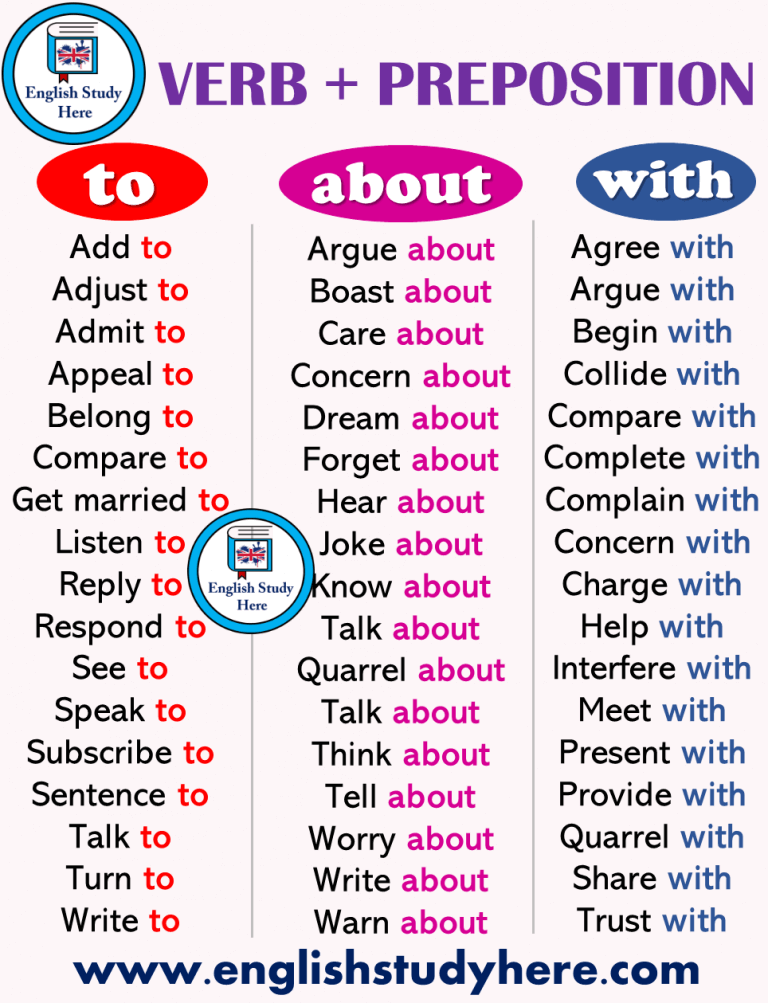 It might look very complicated. However, the way the different tenses are formed is actually quite logical and regular and it will become clear as you study each one how and when we use them.
It might look very complicated. However, the way the different tenses are formed is actually quite logical and regular and it will become clear as you study each one how and when we use them.
Learning English verbs is easier than you thought!
Believe it or not, English verbs are actually much simpler than many other languages because we don’t change the ending of the verb in every case, according to the number and person of the subject, as many languages do. This is one of the reasons that English has become an international language. Please remember that English lessons tend to focus on the more difficult aspects of the language. Most elements of English are straightforward and easy to pick up so don’t need to be taught.
How to Learn Verbs
What is the best way to learn verbs?Good question. Verbs and nouns are the most important words in English, the building blocks that contain most of the meaning. It is quite easy to learn most nouns by putting labels on objects or looking at picture dictionaries. You can point to something, or a picture of something and repeat the name of the thing and keep testing yourself until you know it. Verbs are not so easy, They are actions. You can’t see them. You can’t pin them down and put a label on them like a noun. They move and change and are tricky to define.
You can point to something, or a picture of something and repeat the name of the thing and keep testing yourself until you know it. Verbs are not so easy, They are actions. You can’t see them. You can’t pin them down and put a label on them like a noun. They move and change and are tricky to define.
A word family is a group of words that share a common root so deal with the same specific area of meaning but function as a different type of word or “part of speech”, for example, nouns, verbs, adjectives and adverbs.
When learning verbs it can be helpful to learn them as part of a word family. Everyone learns and remembers new information differently so do what works best for you. Some people like to keep a vocabulary notebook with words grouped in lists while others use drawings or “mind maps” to help them make connections in their thinking. There is no right or wrong way.
Let’s look at an example of a word family. Students study. “Student” is a noun. “Study” is a verb, It can also be a noun, meaning a room in someone’s house to study in. The adjective “studious” and the adverb “studiously” belong to the same word family. Learning new vocabulary in a word family is efficient and effective. It gives you several pathways to remember the words.
Students study. “Student” is a noun. “Study” is a verb, It can also be a noun, meaning a room in someone’s house to study in. The adjective “studious” and the adverb “studiously” belong to the same word family. Learning new vocabulary in a word family is efficient and effective. It gives you several pathways to remember the words.
Most verbs are regular and we don’t need to learn the pattern of endings that they use in past tenses because we simply add “-ed” to the base verb. Irregular verbs need to be memorized. There are not a lot of irregular verbs but they are very common verbs that we use every day. By definition, irregular verbs don’t follow a consistent pattern like regular verbs so we have to learn the patterns in order to use them correctly. Most English language-learners do this with the help of a simple list or chart which gives the three forms of the verb, for example, “eat, ate, eaten” or “take, took, taken”. Sometimes there is repetition within the three forms, for example, “come, came, come” or “bring, brought, brought”.
Sometimes there is repetition within the three forms, for example, “come, came, come” or “bring, brought, brought”.
When you first learn English, you need to learn these three forms of a verb by reciting them with a rhythm and by testing yourself until you know them all “off by heart”. We call this “rote learning” or learning “parrot-fashion”. It might feel childish, like learning your multiplication tables but it really is the only way to get these irregular verb forms locked in your head until they are a natural feature of your English.
The three forms of an irregular verb that you learn by reciting these groups of three words are called the infinitive, the past simple and the past participle. You really need to know all three of them for all irregular verbs to be able to communicate effectively, as they are the verbs that we use most often. Soon they become second nature. Learning irregular verbs is the first step. Once you know them, you can form all of the tenses for any verb in English.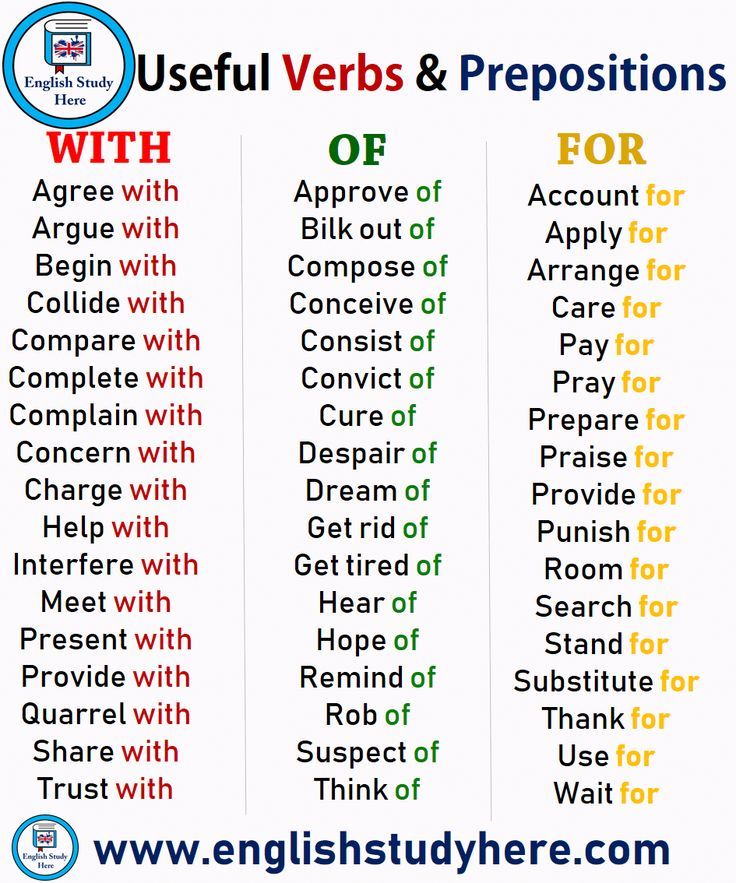
Begin with the past simple. Most of the time we talk about the past so we use past tenses or narrative (story-telling) tenses. These include past simple, past continuous, past perfect (less common) and present perfect.
A native-speaker doesn’t need to learn the jargon because they simply copy what they hear their parents and older children and adults say. They master grammar by imitation and trial and error. Adult learners, however, usually find it helpful to understand at least basic grammar so that they can work out what errors they are making and how they can improve.
Put very simply,
- We add “-ed” to the base form of regular verbs to form the past simple tense.
- We also add “-ed” to the base form of regular verbs to form the past participle.
- We add “-ing” to the base form of regular verbs to form the present participle.
Past participles (walked, ate) are used with has, have and had to make “perfect” tenses.
Present participles (walking) are used with forms of be to make “continuous” tenses.
Some examples:
- Past simple: I walked (to the shop)
- Past continuous: I was walking (when my phone rang)
- Past perfect: I had walked (for an hour before I realised I was lost)
- Present simple: I walk (every day)
- Present continuous: I am walking (right now)
Present perfect: I have walked (for an hour now)
There is a lot to learn but these simple example sentences will get you started.
Peter Ward
English Verbs - Learn English for Free
What are verbs in English grammar? Verbs are words that describe an action, state of being or occurrence. Learn English verbs usage and find out verbs types, examples and common mistakes. Learn English the most effective way and reach your language goals faster: take private English lessons or online English group classes from the comfort of your own home!
English verbs by category
Here are how-to guides for every type of word you'll find when you learn English verbs.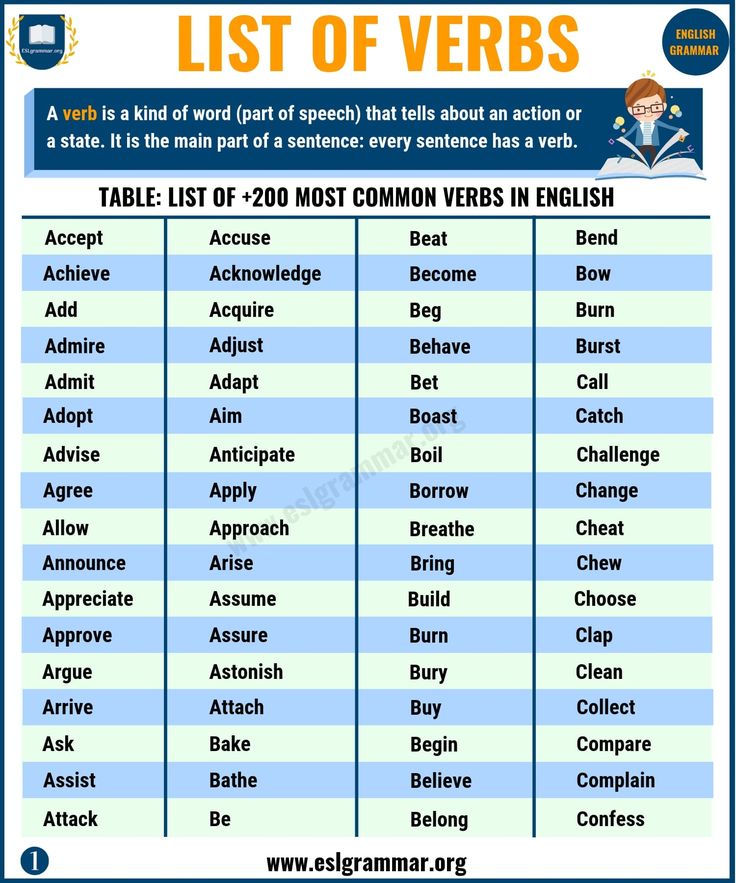 Check out the dedicated categories:
Check out the dedicated categories:
Gerunds act as nouns but are formed with present participle verb forms.
Infinitives are the basic forms of verbs which include 'to.'
Phrasal verbs are verb phrases which include a verb and an adverb or preposition.
Modal verbs are a type of auxiliary verb that give additional information about the main verb.
In active voice, the subject of a sentence performs the action of the verb. In passive voice, it is acted on by the verb.
Conditionals describe the probability of one thing happening in relation to another.
Participle verb forms include '-ed' or '-ing' and function in various ways.
Stative verbs describe states of being rather than actions.
Auxiliary verbs help main verbs and may form questions or negatives.
Subjunctive mood is used to express a wish or to talk about improbable situations.
Sign up to get access to a full range of English verbs exercises
Improve your English with exercises and materials about verbs.
Sign up now
Free resources about English Verbs
English
1/26/2021
Article by Neha D.
English
9/13/2020
Article by Larry Jones
English
8/9/2020
Article by Larry Jones
English
6/21/2020
English
6/21/2020
Article by Nadiia Mykhalevych
English
6/6/2020
Article by Larry Jones
Videos
More videos
Test your English vocabulary
How many words do you know? Get an estimate in minutes with this simple test.
Test my Vocab
English topics
Speaking practice
Develop fluency with everyday conversation topics
Master business English
Increase scores on IELTS, TOEFL and more
Expand your vocabulary
Learn practical words for everyday use and specialized topics
Learn English in small groups
Practice and improve in structured classes with 4-5 other students
Join group classesImprove faster with 1-on-1 lessons
Ready to speak English? Check out our tutors and start with a native English speaker.
Preply in the press
Top publications love to feature Preply’s approach to language learning
Bernat
Aug 3, 2022
Alex is very friendly and professional. He adapts the classes based on the level, the topics of interest and on the type of class. In my case, we are doing 1 hour of speaking per week and after few classes I feel more fluent. I do recommend him! ;)
Jose Javier
Aug 3, 2022
Katie is an amazing teacher!! We contacted her to prepare us for a job interview and she gave us good materials to prepare it. She was so kind and even gave us a couple of lessons before the interview day. We are very grateful to her!
Andrea
Aug 3, 2022
I highly recommend Sana because she is a very good teacher. Lessons are always interesting and tailored to my needs. She is friendly, patient and she makes me feel comfortable even if I make mistakes
Deborah
Aug 3, 2022
My son (14 years old) absolutely enjoys the lessons with David who is an amazing teacher - my son understands him well, David is very patient, focuses on the goals of the student, and talks about interesting subjects. We definitely recommend him!
We definitely recommend him!
Daniel
Aug 3, 2022
Tina is an excellent teacher. She always suggests an interesting topic for our conversations and at the same time focuses on various useful grammar issues. Her lessons are for me thought-provoking and motivating.
Preply uses cookies according to the settings of your browser. Detailed information can be found in the Cookies Policy
How to determine the perfect and imperfect form of the verb?
Let's learn how to write without errors and make interesting stories
Start learning
187.9K
Harry Potter's girlfriend used the time-wheel to be in two places at the same time. Different types of verbs will help to describe the actions of Miss Granger. There are only two of them: perfect and imperfect. Let's talk about them in more detail.
Basic Definitions
First, let's remember what a verb is.
The verb is a part of speech that designates an action or state as a process and expresses this meaning using the categories of aspect, voice, mood, tense and person.
Verbs answer questions: what to do? what to do? what have you been doing? What did you do? what do they do? what will do?
Examples of verbs:
The form in Russian is a constant grammatical feature of verbs, which is possessed by conjugated verbs, infinitives, gerunds and participles. It shows how some action of the verb proceeds in time:
-
completed and one-time (read, passed)
-
unfinished and repeatable (lives, does).
What types of verbs are there in Russian:
Now we will learn what a perfect and imperfect form of a verb is and give examples of perfect and imperfect verbs.
Demo lesson in Russian
Take the test at the introductory lesson and find out what topics separate you from the "five" in Russian.
Perfective verbs
Perfective verbs in indefinite form answer the question: what to do?
Perfective verbs have two tense forms:
In any tense form they call:
-
an action that is limited by some limit;
-
result, completion of an action or a separate stage.
Examples of perfective verbs:
-
what did you do? sat down - past tense, the action is completed and was done once, that is, it was not repeated;
-
what will they do? they will talk - the future simple tense, the action will be done and will not be repeated.

-
what to do? close, pay, perform;
-
what to do? identify, answer, simplify.
Perfective verbs can also denote actions that have already begun or are about to begin: I spoke, I will speak.
Imperfect verbs
Imperfect verbs in the indefinite form answer the question: what to do?
Imperfective verbs have three tenses:
They denote:
In any tense, they denote a repeated or ongoing action, without indicating whether the action has been completed.
Examples of imperfective verbs:
-
what did you do? jumped - past tense, the action could be repeated several times and it is not known whether the result was achieved;
-
what are they doing? they are watching - the present tense, the action continues and it is not known how long the action has been going on and how long it will continue;
-
what shall I do? I will dance - the future is a difficult time, the action can be repeated and there are no signs that it will be completed.

-
what to do? talk, paint, run;
-
what to do? drag, go.
Imperfective verbs can also denote actions that have begun, are beginning or will begin: I looked, I look, I will light.
Now we know what questions are answered by perfective and imperfective verbs. And here is a cheat sheet to fix and learn the difference of two types:
Free English lessons with a native speaker
Practice 15 minutes a day. Learn English grammar and vocabulary. Make language a part of life.
Formation of verb types
Perfective verbs can be formed from imperfective verbs in different ways.
Ways of education:
-
Adding a prefix: read - read, sit - sit up.
-
Dropping suffixes: give - give, save - save.
-
Replacement of suffixes: decide - decide, jump - jump.
-
Replacement of suffixes and alternation of letters in the root: forgive - forgive, wither - wither.
When forming imperfective verbs, the alternation of consonants and vowels is possible at the root: be late - be late, state - state, protect - protect.
Learn Russian at the Skysmart online school with attentive teachers and interesting examples from modern texts.
Determine the form of the verb
If you are in doubt how to understand what kind of verb you have: perfect or imperfect, use these methods:
| How to determine the aspect of a verb |
|---|
|
Now you can easily tell your classmates how to determine the form of a verb in Russian.
Examples of pairs of perfective and imperfective verbs
Aspective pair are verbs that have a perfective and imperfective form.
Some Russian verbs have the same lexical meaning, but differ in the grammatical meaning of the form. For example: what to do? decide what to do? decide.
Such aspectual pairs differ in the way of word formation:
-
Through the suffix: quit - throw, meet - meet, offend - offend, reach - achieve, decide - decide.
-
Through the prefix: cook - cook, call - name, work - process, speak - talk, read - finish reading.
The aspectual pairs of verbs may differ:
-
Emphasized.
fall asleep - fall asleep, cut - cut.

-
Roots.
what to do? catch - what to do? to catch;
put - put;
to invest - to invest;
to take - to take;
search - find.
The aspect of the verb may depend on the context of the sentence. For example:
-
She is now (what is she doing?) sleeping with a friend. — Present tense, imperfective form.
-
Tomorrow (what will she do?) she is staying with a friend. — Future tense, perfect form.
Such verbs are called two-part verbs, they include: telegraph, take possession, spend the night, injure, marry, execute, promise, use, attack and others. Two aspect verbs can denote both a complete action and an action in length.
Table of perfect and imperfect verbs
| | imperfective | Perfect look |
|---|---|---|
| Infinitive | What to do? play | What to do? play |
| Past tense | What did you do? played | What did you do? played |
| Present | What am I doing? playing | - |
| Future tense | What will I do? will play | What will I do? play |
Russian cheat sheets for parents
All Russian language rules at hand
Verb: definition, features, tables, rules
Verbs in Russian are not comparable to any other part of speech. They inform the reader or listener about the action in relation to the subject. It has long been noticed that verbs give the language liveliness, capacity, and arouse interest on the part of the reader. No wonder the word "verb" in Russian also means "talk".
They inform the reader or listener about the action in relation to the subject. It has long been noticed that verbs give the language liveliness, capacity, and arouse interest on the part of the reader. No wonder the word "verb" in Russian also means "talk".
But verbs are not as simple as they seem at first glance. They must be able to use. Compare two passages:
« Aleksey was doing repairs at his dacha. The repair was difficult. He needs good materials "and" Aleksey was repairing the dacha. The repair is difficult, so Alexey ordered good materials .”
In the second case, the verb seems to enliven the text. A picture of Alexei's actions immediately appears before my eyes. If you use the turnover “did repairs”, there will be no such picture. The word does not affect anything in the imagination.
Content
Initial form of the verb
Acquaintance with any part of speech begins with the presentation of its initial form. In the initial form, verbs are called the infinitive. If the part of speech has the suffix "t", we have an infinitive.
In the initial form, verbs are called the infinitive. If the part of speech has the suffix "t", we have an infinitive.
True, sometimes verbs are disguised and instead of "t" they have "ti". This happens if the root of the verb ends in a consonant. Such words include, for example, the lexeme "carry".
As for the ordinary infinitive, there are a lot of them:
- Jump;
- Run;
- Fly.
Infinitives are convenient in terms of solving specific problems. In these words, it is impossible to determine a single verbal feature, except for aspect and conjugation.
Perfect and imperfect form of the verb
Surely, you have already heard that there is a perfect and imperfect form of the verb. A complicated name that can be a little confusing. Some students believe that the names of the perfect and imperfect form of the verb come from the word "perfection" and try to find some nuances indicating that this particular verb can be supplemented with something, and until then it is imperfect.
This is not true. In fact, the words perfective and imperfective come from the adjective "perfect" and report the type of action. In the first case, we mean such an action that can lead to a specific result. In the second case, the action takes place, but there is no specific result. Moreover, it is impossible to achieve it.
If you remember this feature, it will not be difficult to figure out what kinds of verbs there are:
- Imperfect kind. Answers the question "what to do?" and speaks of some action, the completion of which does not imply the appearance of a specific result. For example, "draw". Agree, if you just “draw”, the result can be anything, or it may not be at all.
- Perfect look. Answers the question "what to do?" and talks about some action that can be completed with a specific result.
 For example, "draw". If a person does not just draw, but wants to draw a specific picture, we have a perfective verb.
For example, "draw". If a person does not just draw, but wants to draw a specific picture, we have a perfective verb.
However, the types of verbs can be remembered with the help of one more trick. The perfect form of the verb answers the question "what to do?". Pay attention to the letter "c". It is present both in the word "make" and in the word "perfect" form of the verb.
If we take into account the peculiarity of the Russian language, the types of verbs will no longer be a problem.
Additional features
Sometimes perfective and imperfective verbs do not have their mirror pair. Pay attention to the word " belongs to ." The lexeme answers the question “what to do?”, but it is impossible to imagine a pair about which one could say that this is the perfect aspect of the verb . You can not belong to someone and complete this action with a specific result.
You can not belong to someone and complete this action with a specific result.
The opposite situation also happens. For example, the word " find yourself " is, without a doubt, the perfect form of the verb. But you can not imagine his pair in an imperfect form.
Learning to distinguish verbs
What are the perfect and imperfective verbs sorted out a little. Consider the signs of a particular part of speech, regardless of whether the perfect form of the verb is in front of us or the imperfect form of the verb.
Features of the verb :
- Person . The verb can be in the first, second or third person. But sometimes the face is undetectable. For example, "take off". This is the perfect form of the verb indefinite person.
- Number . It can be singular and plural. For example, "I'm learning.
 " Before us is a sentence consisting of the pronoun "I" and the word "I teach." This is the imperfect form of the verb in the singular in the first person. If we say “we learned”, then the word “learned” is a plural perfective verb. Sometimes the number is impossible to determine. For example, in the infinitive.
" Before us is a sentence consisting of the pronoun "I" and the word "I teach." This is the imperfect form of the verb in the singular in the first person. If we say “we learned”, then the word “learned” is a plural perfective verb. Sometimes the number is impossible to determine. For example, in the infinitive. - Time . Past, present or future tense. Sometimes it is impossible to determine the tense of the verb. This is what happens with the infinitive. For example, you can “fly up” both in the past and in the future. In the first case, the narrator recalls past events, while in the second he dreams of future ones. The word "fly up" itself is a perfective verb, and only from the context you can find out what time it is.
- Inclination . Including the infinitive, there are four mood forms in Russian. You will meet them below.
- View . There are only two types. Now you know how to determine the form of the verb perfect or imperfect, you also know how to determine.

- Genus . These are very important features of the verb. It is best to determine the gender of verbs in the past tense. For example, "have you already read the book". Obviously referring to a man. If you say “you are reading a book” or “you should read a book”, it is impossible to determine the gender.
- Deposit . A terrible word means only the relation of the verb to a specific object. If "I eat porridge", this is a valid pledge. The subject is acting. The passive pledge will be if you say "porridge is eaten by mouth." The action is performed on an object.
- The conjugation of verbs is similar to the declension of nouns in person and number. Imperfective and perfective verbs are conjugated exclusively in the present and future tenses.
- Returnable . The presence or absence of "sya" in the word.
Mood
The reader already knows what a perfect and imperfect form of a verb is, how to determine - too. Consider an equally interesting thing - inclination. To do this, let's turn to the table, which will tell you some of the secrets of the Russian language.
Consider an equally interesting thing - inclination. To do this, let's turn to the table, which will tell you some of the secrets of the Russian language.
Do not confuse the indicative mood with the present tense. These verb forms describe an action that will actually take place.
Consider, for example, such a form of the verb as "saw". This word informs the reader that the action actually took place. The person really saw something and reports it. But if you add a particle “would” to this word, the word immediately acquires a different lexical meaning.
Let us now take the word " would see ", this will be a perfect verb, subjunctive. Such inclinations report actions that can only be under certain conditions. In oral or written speech, usually such conditions are immediately listed. For example, " if I were an eagle, I would see every grain of sand on the beach from a huge height ". The subjunctive without listing the conditions hardly makes sense.
The subjunctive without listing the conditions hardly makes sense.
We have already found out what kinds of verbs there are in Russian. Let's get acquainted now with the imperative mood. How does the verb change in this case? The very word "imperative" already contains the answer to this question. The verb appears before us in the form of an order, a request, a command in a different form.
Imperative verbs of which the reader may see examples in the table may sound rude, but this is not necessarily the case. After all, a request is also a command. Let's compare two sentences.
Compare “ draw quickly or you will be punished ” with “please draw and then you will receive an award ”.
One and the same word takes on a completely different, even directly opposite, meaning depending on the context.
Conjugations
Although, we already know how to determine the perfect or imperfect form of a verb, but this is clearly not enough for a true master of Russian literature. We must also learn to correctly distinguish verb conjugations in Russian.
If you do not know the conjugation and speak illiterately, others may not understand your thought or understand it incorrectly. It is for this reason that most often there are misunderstandings between people.
To avoid this, let's learn how to conjugate. There are two conjugations in total:
- The first conjugation of the verb. Let's put the part of speech in the third person plural. For example, "disdain". Here the ending is "yut". This is what the first conjugation looks like. This is also true for verbs with the ending "ut".
- The second conjugation of the verb. Let's repeat the steps of the first paragraph. The reader will see the second conjugation if the verb ending is "at" or "yat".
Learn more