Lexile and guided reading levels
Leveling Chart | Scholastic Guided Reading Program for the Classroom
Use the grid below to shop by Guided Reading, Developmental Reading Assessment (DRA), and Lexile® Levels. This chart includes Lexile level recommendations and may also be used as a general leveling guide.
Click on links to shop the Teacher Store!
| Grade | Scholastic Guided Reading Level | DRA Level | Lexile® Levels |
|---|
| Grade | Scholastic Guided Reading Level | DRA Level | Lexile® Levels | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kindergarten |
| Beginning Reader | |||||||||||||||||||
| 1 |
|
| 190L-530L | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2 |
|
| 420L-650L | ||||||||||||||||||
| 3 |
|
| 520L-820L | ||||||||||||||||||
| 4 |
|
| 740L-940L | ||||||||||||||||||
| 5 |
|
| 830L-1010L | ||||||||||||||||||
| 6 |
|
| 925L–1070L |
Back to Top
Booksource Reading Level Correlation Chart
Despite global supply chain issues, Booksource is making sure customers get their book orders. Click to learn more.
Reading Level Chart
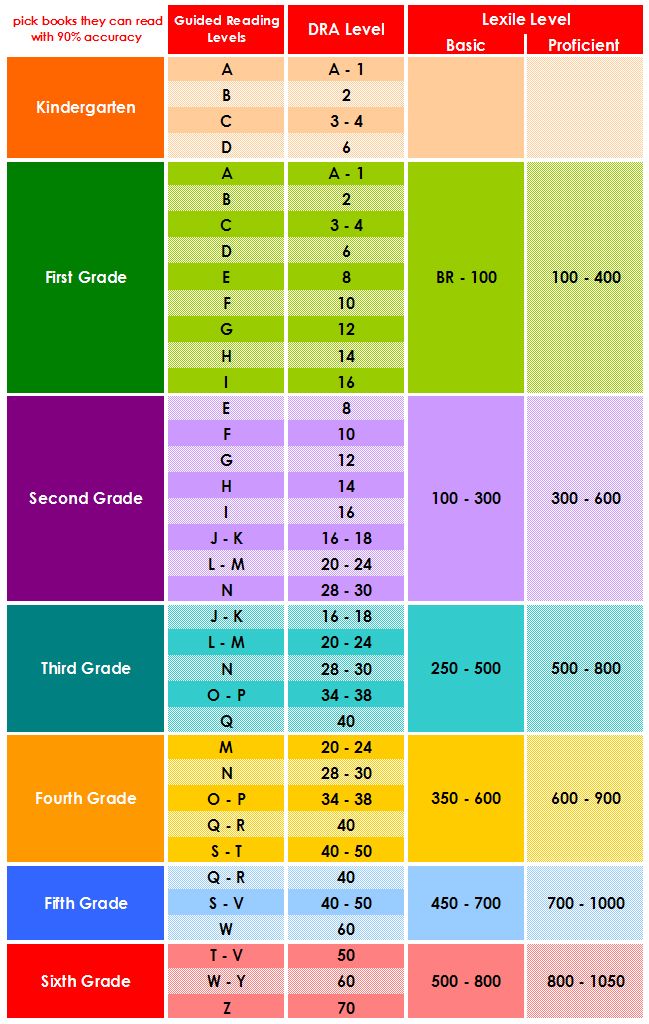
Booksource knows that reading levels can serve as a helpful tool for educators. Use this Reading Level Chart to better understand how the common leveling systems correlate to one another and match students to texts that can be read with success. To start shopping for books by reading level, click on your desired Grade, Guided Reading or Lexile Level below.
Print PDF
To shop for books, tap on your desired Grade, Guided Reading or Lexile Level below. View more information by swiping left and right.|
Grade |
Guided |
Lexile |
DRA |
Reading |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Asset 5 Booksource relies only on reputable sources for our leveling information. |
|||||
|
Asset 5 Guided Reading is based on standards developed by Irene Fountas and Gay Su Pinnell. When leveling a title, Fountas & Pinnell consider factors such as text difficulty, vocabulary and developmental appropriateness. For example, a level P book is appropriate for grade three students in terms of both content and complexity. When necessary, Booksource relies on publisher guided reading levels. Every effort is made to ensure that reading levels designated by publishers are comparable to Fountas & Pinnell reading levels. |
|||||
|
Asset 5 Lexile levels are determined through quantitative evaluation of sentence length and difficulty. |
|||||
|
Asset 5 Developmental Reading Level Assessment, better known as DRA, was developed by Joetta Beaver and published by Celebration Press, 1977. DRA is a method of assessing and documenting achievement within a literature-based instructional program. |
|||||
|
Asset 5 Developed by Marie M. Clay in the 1970s as a short intervention program, Reading Recovery helps low achieving first-graders reach grade level standards through one-on-one tutoring. |
|||||
|
Emergent Asset 5Books for emergent readers tell simple stories, with one to two lines per page. They follow patterns and use repeated vocabulary. Emergent readers “read” from picture cues, and from hearing the story read aloud. Concepts are familiar. Emergent readers are developing an understanding of the alphabet and will recognize beginning letters and some sight words. They can attend to short read alouds featuring familiar narratives and concepts. Emergent readers may “pretend” read, as they recount a familiar story or rely heavily on picture cues. |
Kindergarten |
A |
BR |
A-1 |
1 |
|
B |
2-3 |
2 |
|||
|
C |
4 |
3-4 |
|||
|
D |
6 |
5-6 |
|||
|
Early Asset 5Books for early readers contain more pages and longer sentences. Early readers start to read simple stories and can sound out new words with one or two syllables. They will recognize and read some high-frequency words and begin self-monitoring for some comprehension. They predict words based on beginning sounds and picture cues. |
Grade 1 |
E |
190L-530L |
8 |
7-8 |
|
F |
10 |
9-10 |
|||
|
G |
12 |
11-12 |
|||
|
H |
14 |
13-14 |
|||
|
I |
16 |
15-17 |
|||
|
J |
18 |
18-20 |
|||
|
Transitional Asset 5Books for transitional readers include a larger core of frequently-used words, new vocabulary and longer words that require chunking. Transitional readers have developed several reading strategies for decoding and monitoring comprehension. They read longer, more complex texts, including narratives and informational texts, with fluency and phrasing. Their rate of reading has increased, and they are transitioning from reading to decode to reading to comprehend and learn. |
Grade 2 |
K |
420L-650L |
20 |
18-20 |
|
L |
24 |
||||
|
M |
28 |
||||
|
Grade 3 |
N |
520L-820L |
30 |
||
|
O |
34 |
||||
|
P |
38 |
||||
|
Fluent Asset 5Books for fluent readers come from different genres and sources. Fluent readers read fluently with phrasing, inflection and expression. They read independently and silently. They will read for longer durations and maintain comprehension of the text over several days or weeks. They set purposes for reading, and react to text. Fluent readers understand that reading will build knowledge, and influence ideas and attitudes. |
Grade 4 |
Q |
740L-940L |
40 |
|
|
R |
|||||
|
S |
|||||
|
Grade 5 |
T |
830L-1010L |
50 |
||
|
U |
|||||
|
V |
|||||
|
Grade 6 |
W |
925L-1070L |
60 |
||
|
X |
|||||
|
Y |
|||||
|
Proficient Asset 5Proficient readers continue to read for a variety of purposes, including learning or enjoyment. Proficient readers read across a wide variety of materials and for multiple purposes. They make adjustments to their reading style based on the text and their purpose. They read regularly, for enjoyment and knowledge, and synthesize information from reading. Due to mature content, the Z+ titles should be reserved for high school and adult readers. Reader discretion is advised. |
Grade 7 |
Z |
970L-1120L |
70 |
|
|
Grade 8 |
Z |
1010L-1185L |
80 |
||
|
Grade 9-12 |
Z (+) |
1050L-1385L |
|||
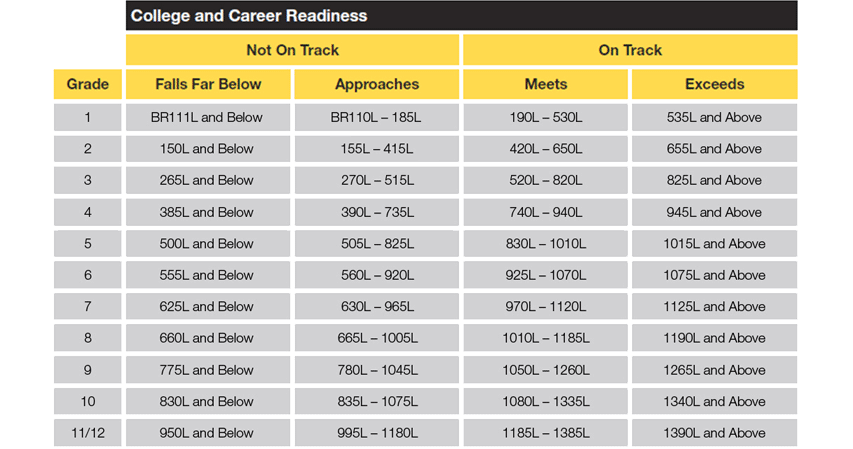
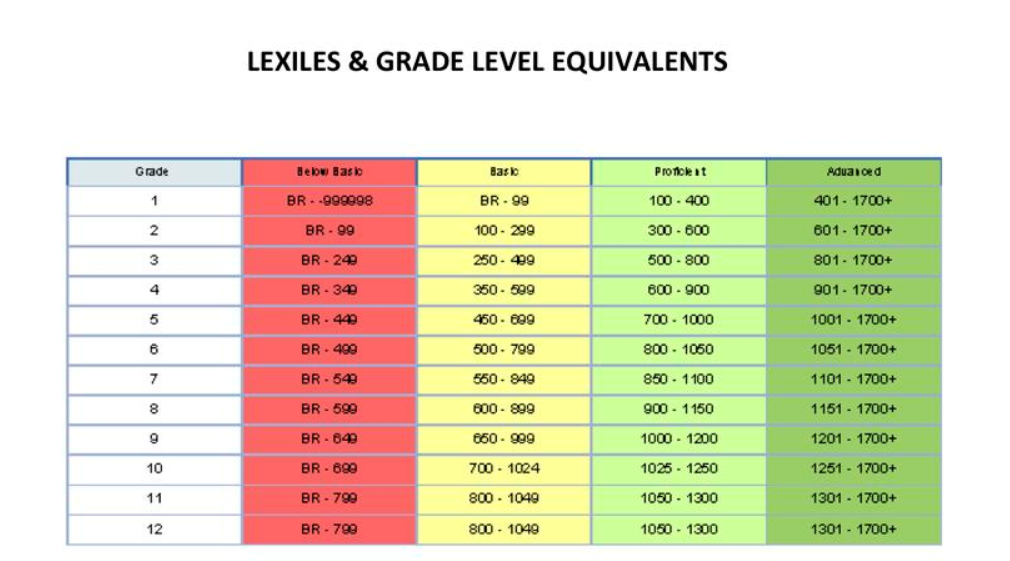
Lexile - a scale for improving reading
Today we will talk about the Lexile method.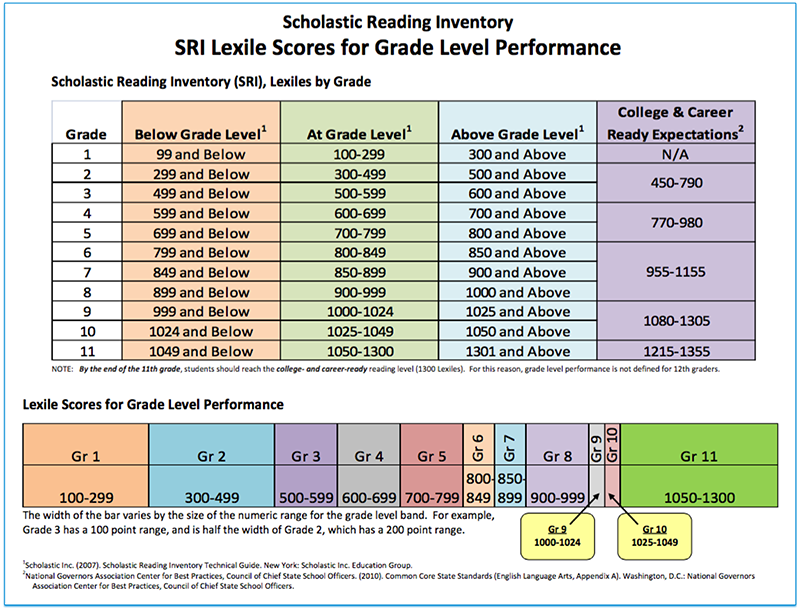 Reading is one of the central language skills with which you can develop others. When reading a text, students see the correct grammatical constructions in context and can then use them as a model for writing and speaking. Regular reading stimulates imagination and creative thinking. As a result, writing and speech become more informative and original.
Reading is one of the central language skills with which you can develop others. When reading a text, students see the correct grammatical constructions in context and can then use them as a model for writing and speaking. Regular reading stimulates imagination and creative thinking. As a result, writing and speech become more informative and original.
There are many approaches and techniques for developing reading skills. nine0003
What is it?
A popular method for measuring reading ability. It allows you to determine both the level of the reader and the complexity of the text. Lexile was not created for competition and the rating designation is just a handy tool to help you choose texts that are suitable for the student from a great variety.
The Lexile Reading Score measures a student's ability to read on the Lexile scale. The Lexile text measure indicates the level of complexity of the text on the Lexile scale. The Lexile measure ranges from a minimum of 0L to a maximum of 2000L. There are certain norms of indicators depending on the class: for example, for the first class, indicators from 25 to 325 units are considered the norm, and for the ninth from 1100L to 1125L. nine0003
There are certain norms of indicators depending on the class: for example, for the first class, indicators from 25 to 325 units are considered the norm, and for the ninth from 1100L to 1125L. nine0003
Here is the complete table of values. Despite this, there is not always a direct relationship between the Lexile score and a particular class. In any class there are students of different levels and with different sets of skills, so it is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of the students.
How to use for teaching
The Lexile tool is useful in that it allows you to predict how difficult a text a student will be able to understand. For example, if the Lexile reading score is 1000L, the reader will understand approximately 75% of the text with a Lexile level of 1000L. Here you will find books with different indicators and for different classes. Let's say you need to find materials for the seventh grade with an indicator of 700L, enter the data in the appropriate cells and get the result.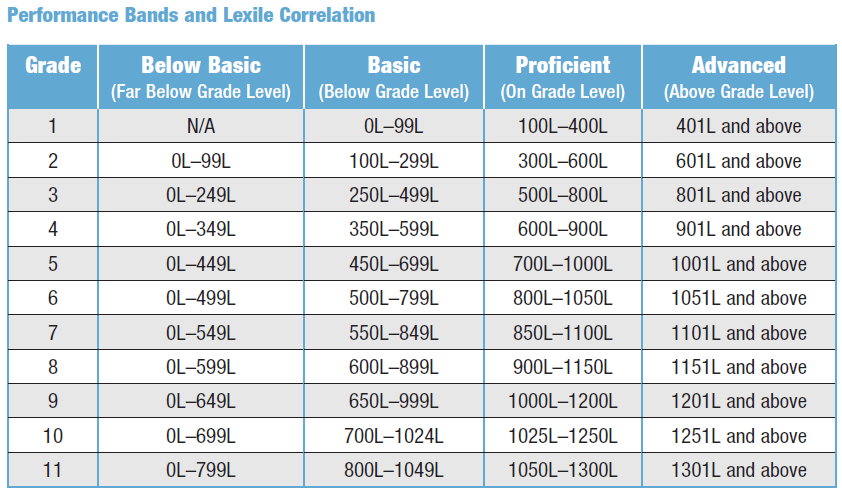 You also need to select the complexity of the text: easy, medium or difficult, and there is even an option to select books that are suitable for your interests. nine0003
You also need to select the complexity of the text: easy, medium or difficult, and there is even an option to select books that are suitable for your interests. nine0003
But remember not to focus on the exact number. If the measure is Lexile 700L, then note the range of approximately 100L below and 50L above the measured value.
Why Lexile is useful
The Lexile scale shows the student's progress in reading. Using this scale, you can find out whether the reading skills of a particular student have developed over a certain period of time. For example, in the sixth grade, a student receives some score on the Lexile scale, if next year his score is higher than the previous one, then reading skills are developing. If the increase in points is insignificant or even absent, it is an occasion to focus on reading, to think about how you can diversify the methods for training reading and how to help your student achieve better results. nine0003
At the same time, it is important to remember that deviations from the norm are quite possible. Lexile is a student level prediction, and like any prediction, it's not always 100% accurate. The complexity of the text is only one of the indicators, some topics may be completely uninteresting to teenagers, and because of this they are not involved in reading, so reading comprehension will decrease. At the same time, you need to select topics that your teenagers already know something about, so it will be much easier for them to understand the text presented. nine0003
Lexile is a student level prediction, and like any prediction, it's not always 100% accurate. The complexity of the text is only one of the indicators, some topics may be completely uninteresting to teenagers, and because of this they are not involved in reading, so reading comprehension will decrease. At the same time, you need to select topics that your teenagers already know something about, so it will be much easier for them to understand the text presented. nine0003
Why it is important to find material with information already known to students, we wrote in the article: How to work on the development of background knowledge in adolescents
So, using Lexile, you can predict whether the text will suit your students. When the student understands most of what he read, he feels more confident, calmer, begins to be more interested in the text. As a result, the student is likely to become interested in reading in general, which means he will read more and better.
This is our goal: to awaken students' interest in reading and help them develop a valuable language skill.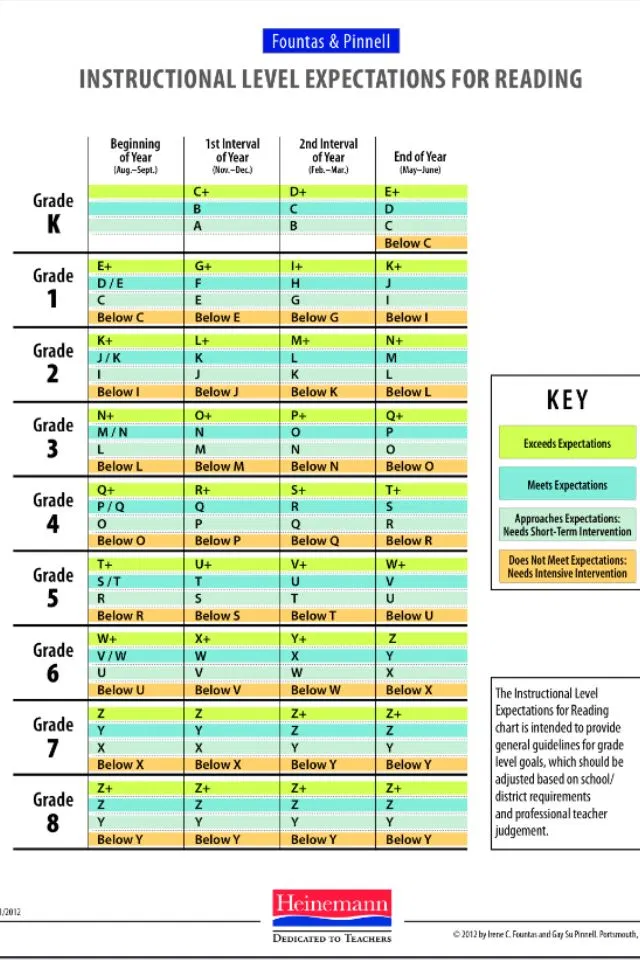 nine0003
nine0003
How do you know your level of reading comprehension?
Understanding. There are many ways to evaluate understanding. One easy way to assess understanding is to ask students to retell what they have read and/or ask a couple of questions and rate their responses using our retelling rubric. Maximize the time using the same passage that you used to assess fluency.
Accordingly, what is the level of understanding? Reading comprehension is the ability to process read information and understand its meaning. Three levels of understanding literal level, logical level and critical/evaluative level .
What are the 5 basic reading skills? Effective curricula and materials emphasize the five essential components of effective reading instruction: phonemic awareness, phonetics, fluency, vocabulary, and comprehension.
Also, how can I check my reading skills?
The most common example of fluency assessment is ask the student to read the passage aloud for one minute .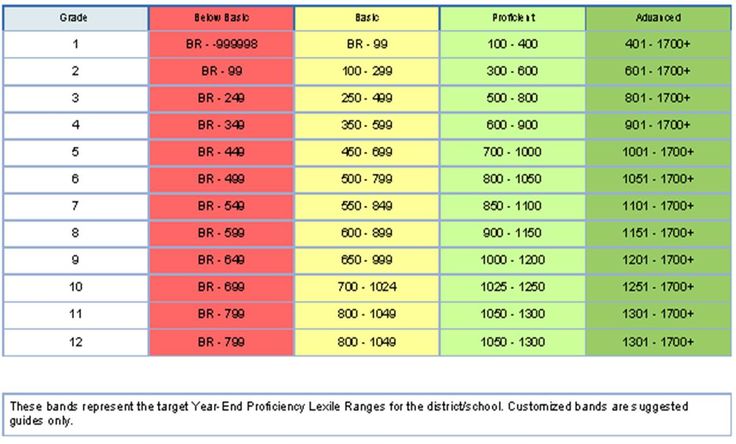 Missed or mispronounced words are not counted. The number of correctly read words is counted, and this sum equals the student's oral reading speed.
Missed or mispronounced words are not counted. The number of correctly read words is counted, and this sum equals the student's oral reading speed.
How can I check my child's reading comprehension?
One way to get around this and still get a sense of her understanding is to read silently but together . Read the same material, stopping periodically. It can be after a paragraph, passage, or chapter. Then ask her questions about what you both read. nine0003
What are the 5 levels of understanding? There are six levels: literal, inferential, evaluative, critical, evaluative, and essential. For each level, you come up with questions and then, WHAT IS MOST IMPORTANT, well-designed and well-explained answers.
What are the 4 levels of understanding?
- 4 levels of reading comprehension.
- Level 1: Right here - the answer is in front of you.
- Level 2: Think and Seek - the answer is in front of you, but you need it.
 look for it. nine0068
look for it. nine0068 - Level 3: “The author and you - the answer is not in front of you, use it. …
- Level 4: "In your Head - the answer is not in the book - it's yours.
What are the 3 levels of reading? A handy guide to three reading levels: literal, inferential, and evaluative. Information and resources about reading in text, between the lines and beyond.
What are the Big Five in reading?
The main components of reading, often referred to as the "Big Five", include: phonetics, phonological awareness, fluency, vocabulary and comprehension . These 5 must be taught together, systematically and explicitly, in order to properly sow the seeds for gradual growth towards lifelong literacy.
What are the 3 main components of fluency? Fluency is a key factor in independent and successful reading and consists of three components: accuracy, speed and prosody (expression) .
What are the 6 basic reading skills? nine0003
- Explanation.
 Transcription is a vital step in the reading process. …
Transcription is a vital step in the reading process. … - Fluency. To read fluently, children must instantly recognize words, including words they cannot pronounce. …
- Dictionary. …
- Sentence construction and connectivity. …
- Reasoning and background knowledge. … №
- Working memory and attention.
What are the 4 types of reading assessment? Result - Provides a summary score of the reader's performance in relation to the established performance levels. nine0037
- Screening scores. …
- Diagnostic evaluations. …
- Progress monitoring assessments.
How do teachers assess the level of reading?
The three most common assessment tools are Lexile Measures, DRA (Reading Development Assessment) levels, and Guided Reading Levels. Each of these tools vary in complexity and administration, but each is designed to help educators and parents gain insight into a child's reading skills.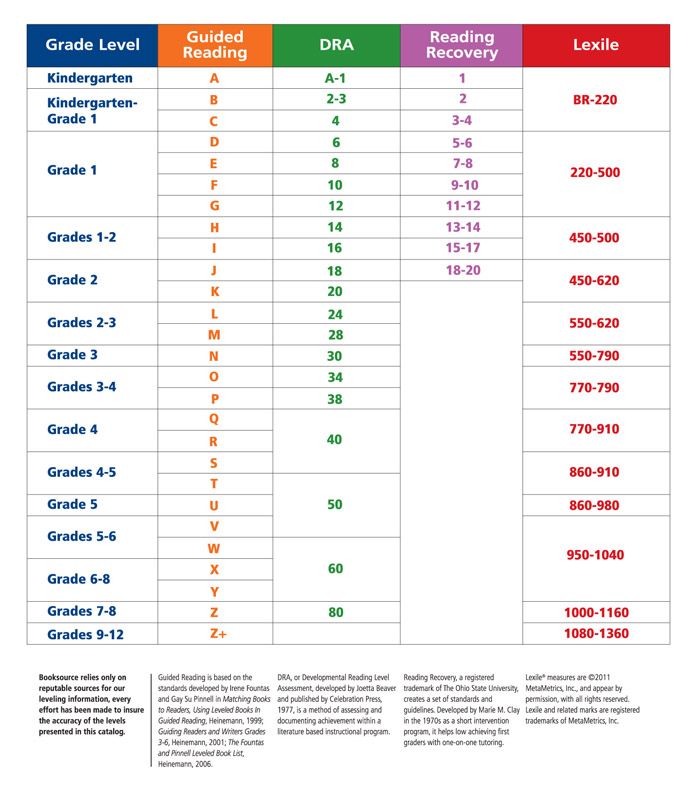 nine0003
nine0003
What is extensive reading skill?
Intensive Reading engages students in reading texts for enjoyment and general reading skills . It can be compared to intensive reading, that is, reading in detail with specific learning goals and objectives. The teacher reads a short story to the students, but does not set them any tasks other than reading and listening.
See also
At what level should my 6 year old read? The typical six year old child is usually either at kindergarten or first grade (depending on birthday and district mandates). Reading skills at age six can vary greatly - some children read well, others work on verbal instruction and early literacy skills.
What should a 7 year old read? Reading Milestones for Children 6 to 7 Years Old
- Retell familiar stories.
- Write simple stories using pictures and words. nine0067 Read their own letter back (even if it has spelling errors)
- Write a letter for each sound they hear in the word.
- When writing, put spaces between words.
What level should a five year old read?
A 5-year-old child should also be able to sight-read a few words. . Children typically learn common words like "come", "some", "many", "from", "where", "were", etc. before learning less common words like build, beautiful, group , think, etc.
What are the levels of reading? Before we can improve our reading skills, we need a deep understanding of the levels of reading. There are four levels of reading .
...
4 levels of reading
- Elementary reading. …
- Control reading. …
- Analytical reading. …
- Syntopic reading.
What does reading at level 5 mean?
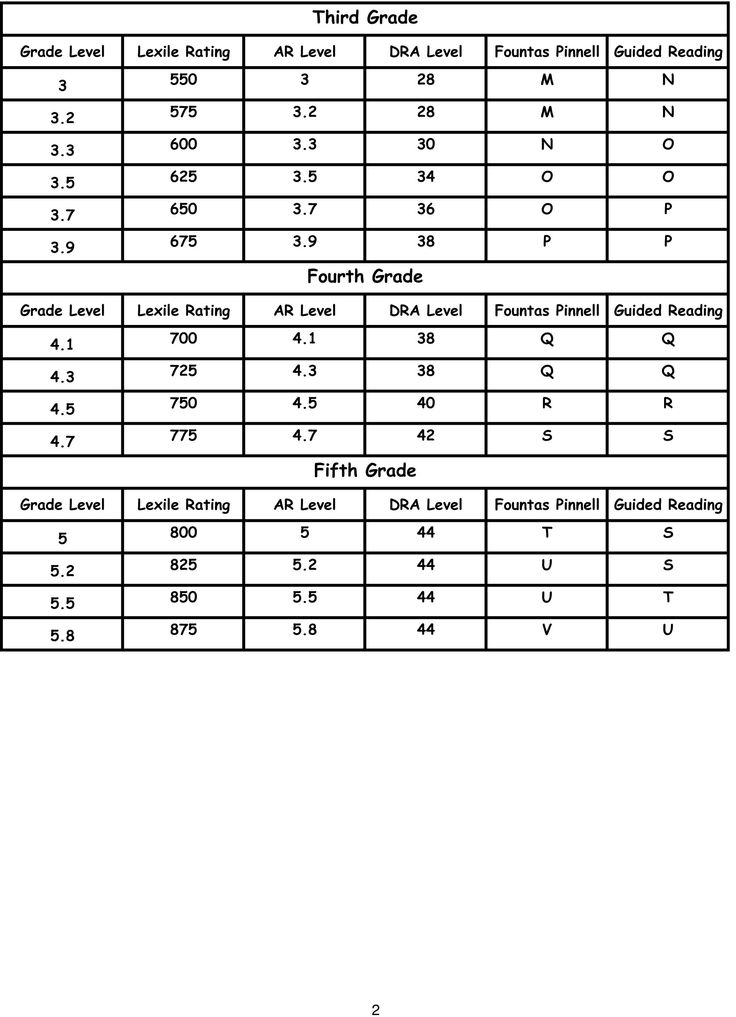
At level 5, children are given an understanding section at the end of each book called Gleaning Meaning. This helps children capture the "big idea", a critical aspect of reading . Main Features of Books .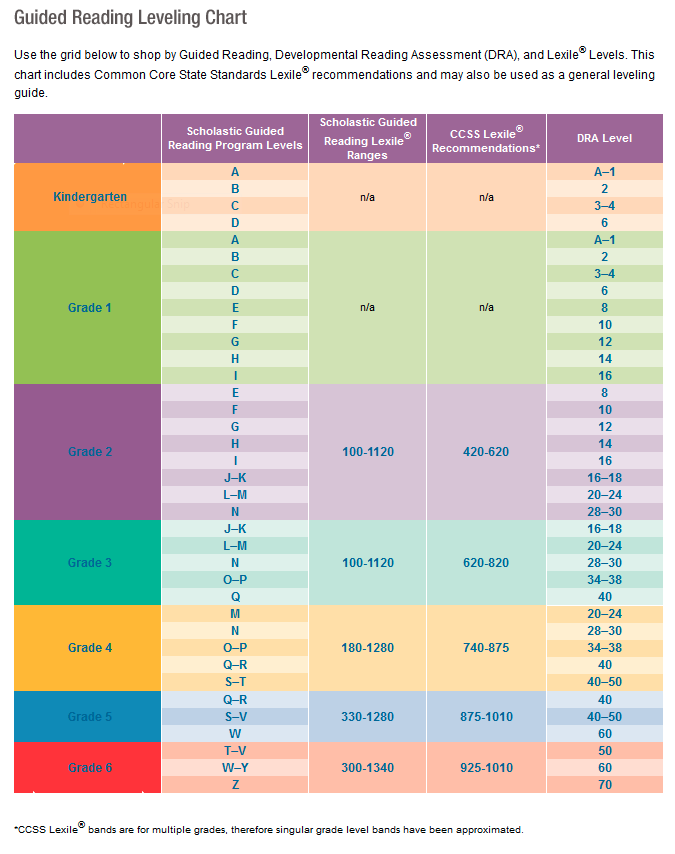

 Each reading level system is designed independently, using various metrics to determine grade level targets. Every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of the levels presented.
Each reading level system is designed independently, using various metrics to determine grade level targets. Every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of the levels presented. Theme and developmental appropriateness are not considered. Lexile measures are from @2011 Metametrics, Inc., and appear by permission with all rights reserved. Lexile and related marks are registered trademarks of MetaMetrics, Inc.
Theme and developmental appropriateness are not considered. Lexile measures are from @2011 Metametrics, Inc., and appear by permission with all rights reserved. Lexile and related marks are registered trademarks of MetaMetrics, Inc.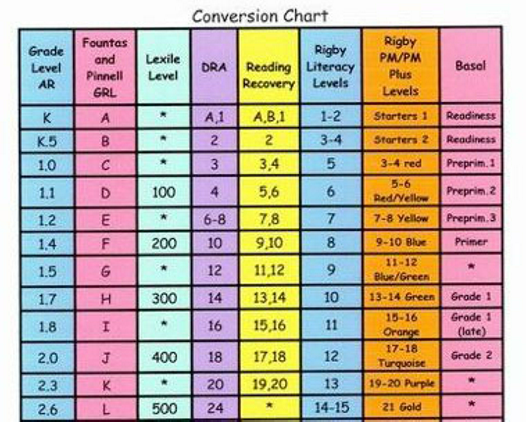 Reading Recovery is a registered trademark of The Ohio State University.
Reading Recovery is a registered trademark of The Ohio State University.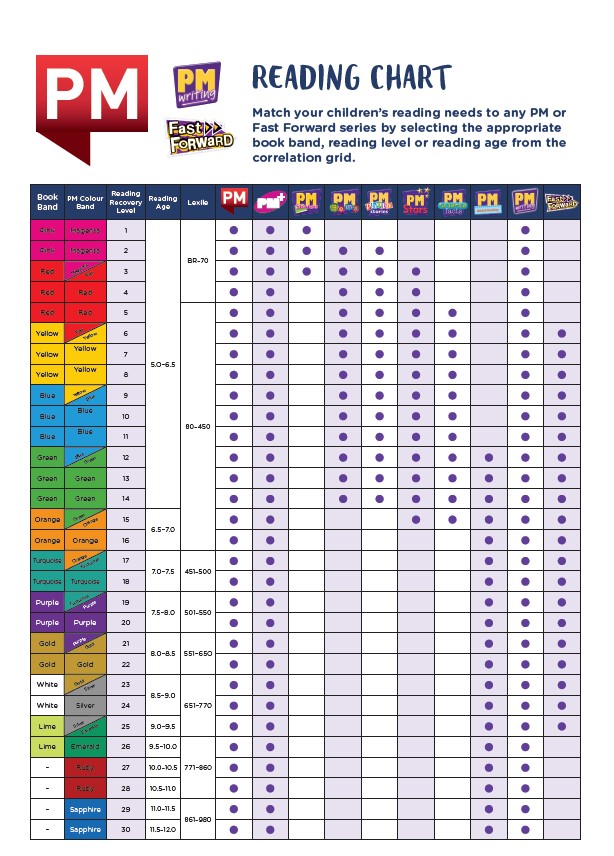 There is more variety in sentence structure. They include high-frequency words and picture cues to provide support while introducing early readers to new vocabulary. Concepts are familiar.
There is more variety in sentence structure. They include high-frequency words and picture cues to provide support while introducing early readers to new vocabulary. Concepts are familiar.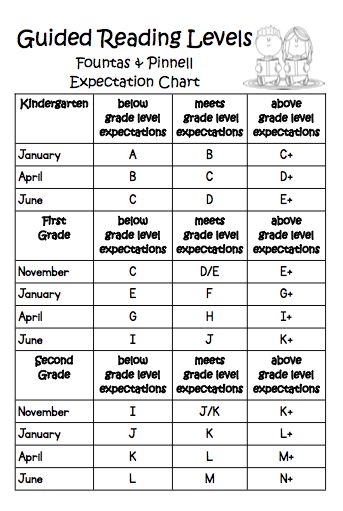 These books include text features and are on varied topics and from multiple genres. Transitional books can be short chapter books or more complex picture books. Concepts are less familiar and the text encourages readers to make connections.
These books include text features and are on varied topics and from multiple genres. Transitional books can be short chapter books or more complex picture books. Concepts are less familiar and the text encourages readers to make connections.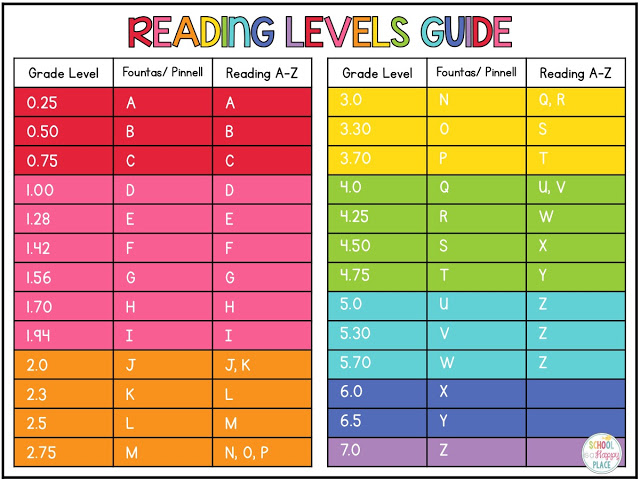 The text is longer and more complex and requires sustained understanding over a few days or weeks of reading. Text features are used to gain and infer meaning. Fluent readers read for purposes such as enjoyment or for learning. Many concepts are new, as fluent readers read to gain new ideas and explore new perspectives.
The text is longer and more complex and requires sustained understanding over a few days or weeks of reading. Text features are used to gain and infer meaning. Fluent readers read for purposes such as enjoyment or for learning. Many concepts are new, as fluent readers read to gain new ideas and explore new perspectives. Books are specific to subject matter, such as the sciences or the humanities. Text is in different styles and lengths and includes different genres, contents and authors to meet a range of self-set purposes for reading.
Books are specific to subject matter, such as the sciences or the humanities. Text is in different styles and lengths and includes different genres, contents and authors to meet a range of self-set purposes for reading.